

Articles
What Is A Conduit
Modified: October 20, 2024
Discover what a conduit is and how it functions. Explore insightful articles about the uses, types, and installation of conduits in various industries.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
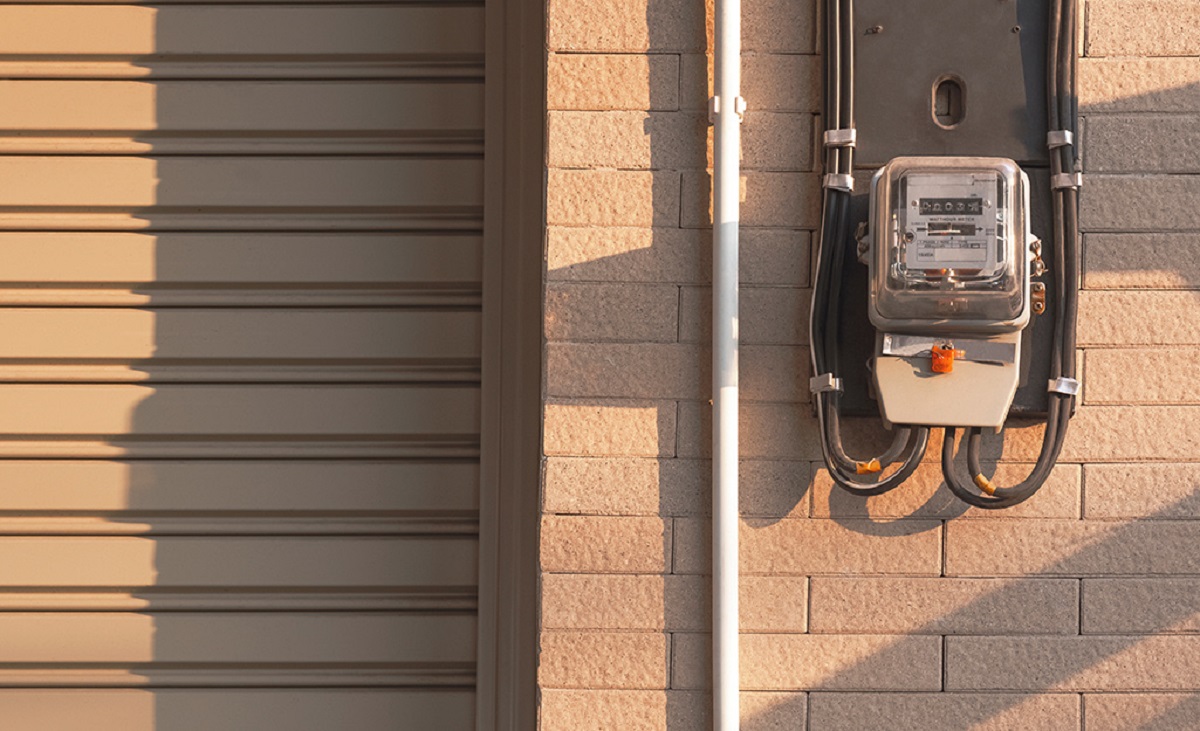
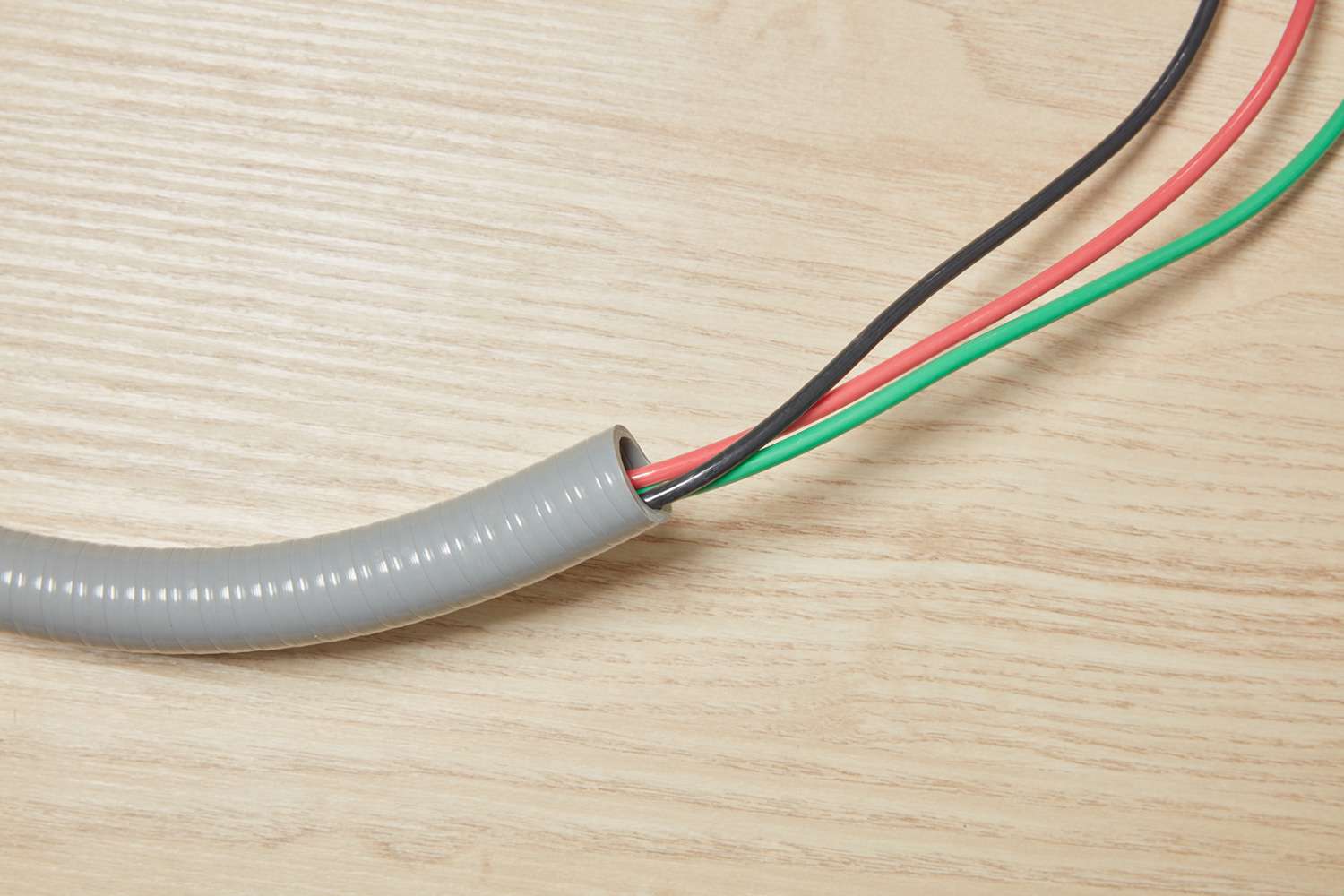
A conduit is an essential component in various construction and electrical systems. It provides a protective pathway for electrical wires, cables, and other types of wiring to ensure their safety and longevity. In simpler terms, a conduit acts as a protective sleeve that shields the wires from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
Conduits are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They not only safeguard electrical wiring but also offer flexibility and ease of maintenance. From underground installations to surface-mounted applications, conduits play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of electrical systems.
This article will provide an in-depth understanding of conduits, including their definition, types, uses, installation techniques, and advantages. Whether you are a homeowner, a professional electrician, or someone with a curiosity for the inner workings of electrical systems, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to comprehend and appreciate the importance of conduits.
Key Takeaways:
- Conduits are essential for protecting electrical wiring from environmental factors, organizing cables, and ensuring safety. Understanding their types, uses, and advantages is crucial for homeowners and professionals alike.
- While conduits offer significant protection and organization benefits, they come with costs, installation complexities, and potential limitations. Proper planning, adherence to local building codes, and regular maintenance are key to maximizing their effectiveness.
Read more: What Is An EMT Conduit
Definition of a Conduit
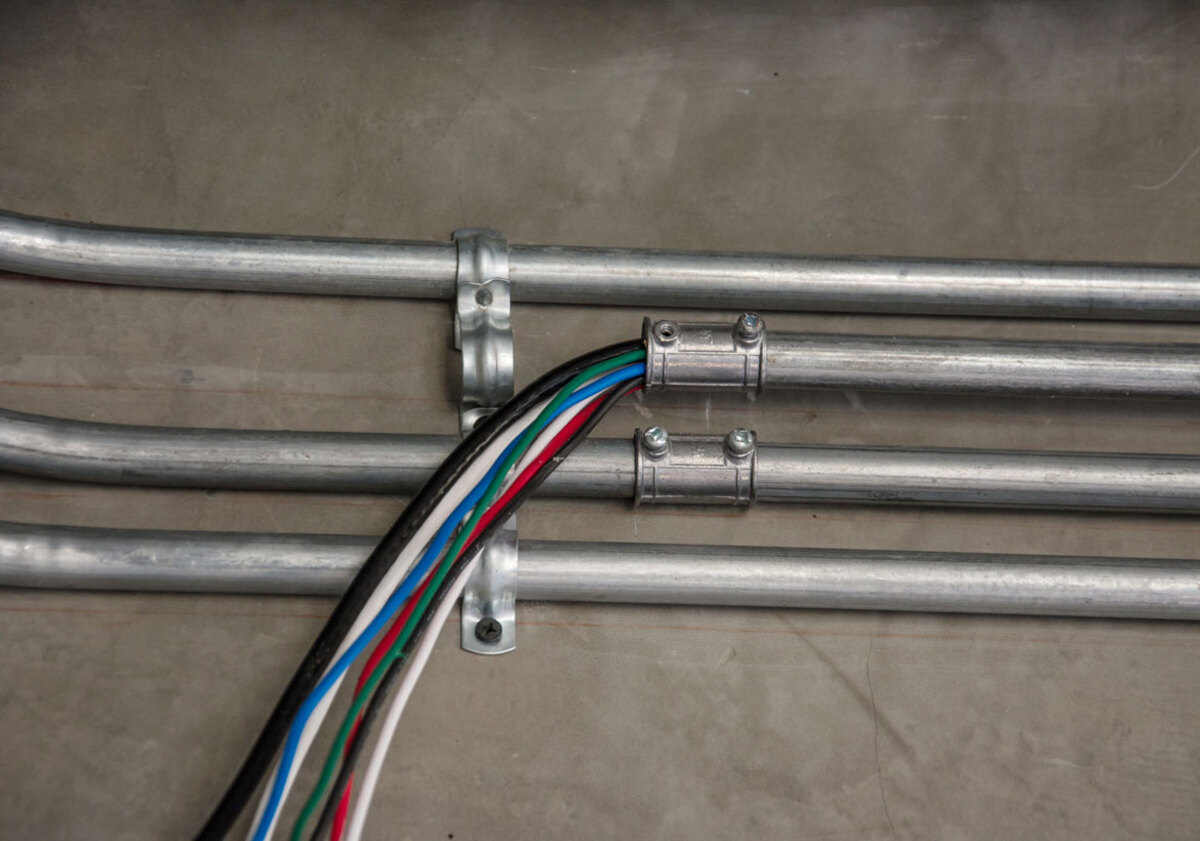
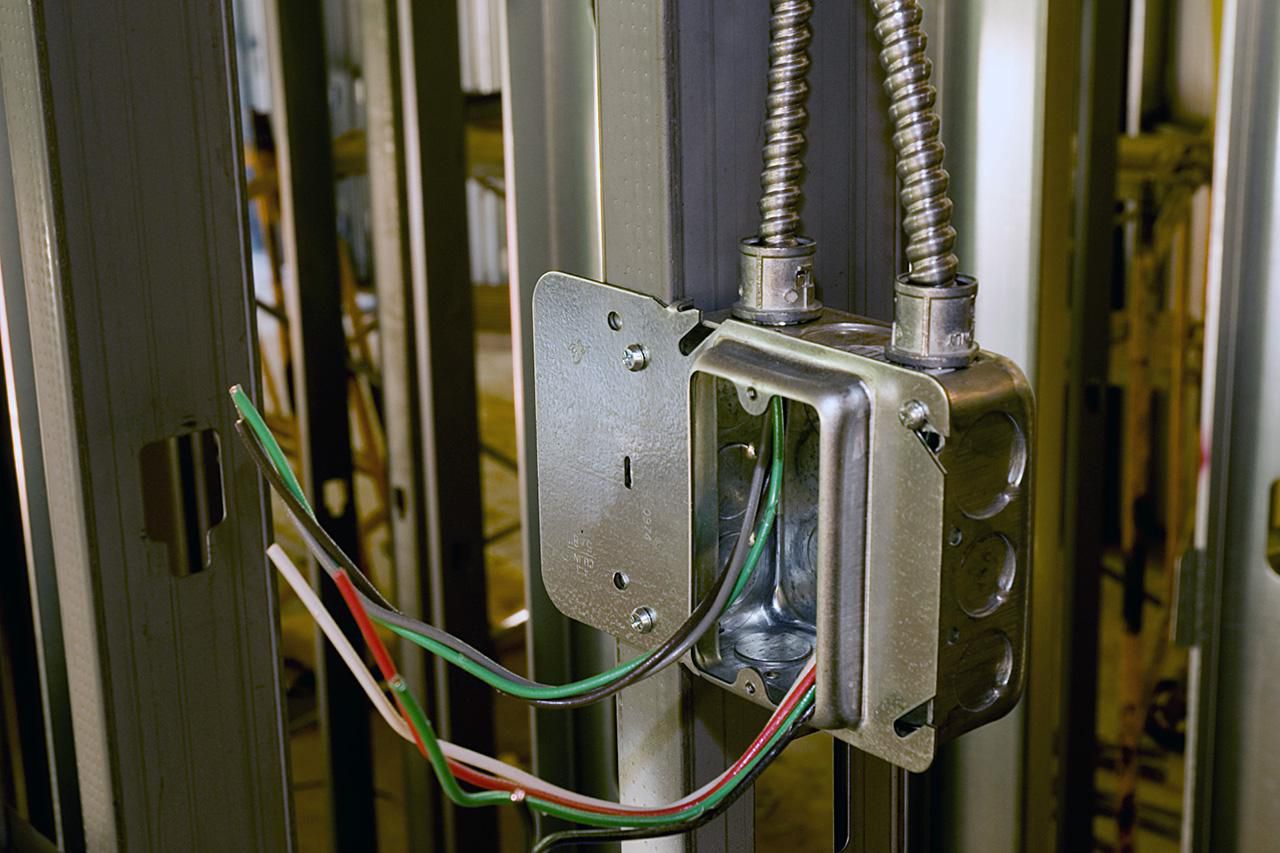
A conduit, in the context of construction and electrical systems, refers to a tube or pipe that is designed to protect and enclose electrical wiring. It provides a secure pathway for the wires, ensuring their safety and preventing any damage that could occur due to exposure to various elements.
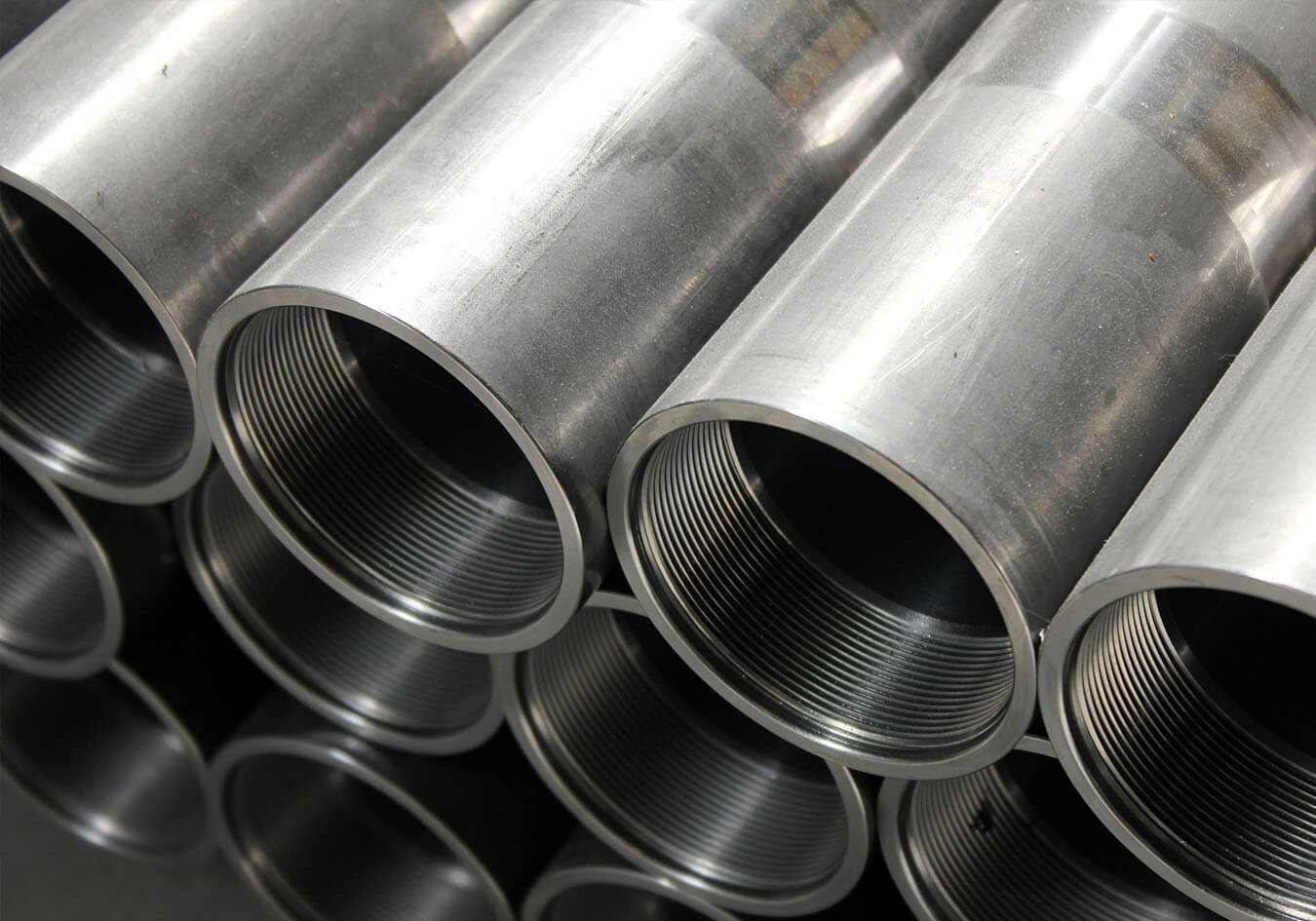
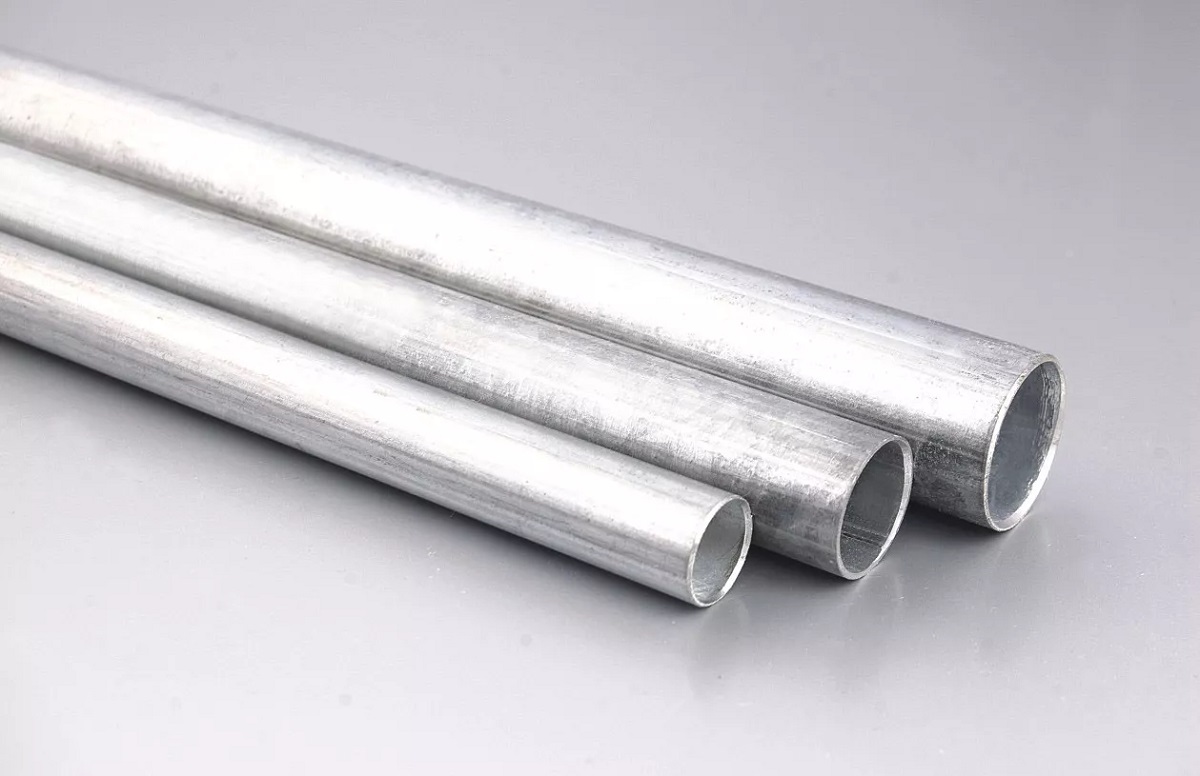
Conduits are typically made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, or non-metallic materials like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). They come in various sizes and types, depending on the specific application and the environment in which they will be installed.
The primary function of a conduit is to safeguard electrical wiring from moisture, dirt, dust, impact, and other external factors that could potentially cause damage or compromise the integrity of the wires. By enclosing the wiring within the conduit, it minimizes the risk of electrical hazards and ensures the longevity and reliability of the electrical system.
In addition to protection, conduits also facilitate the easy routing and organization of electrical wiring. They allow for the neat arrangement of cables and wires, preventing tangling and reducing the chances of accidental damage during installation or maintenance.
Overall, a conduit is an essential component in electrical systems, providing safety, organization, and durability to the wiring infrastructure. Whether it’s residential, commercial, or industrial applications, the use of conduits is crucial in ensuring the efficiency and safe operation of electrical systems.
Types of Conduits
There are several types of conduits available, each designed to meet specific requirements and installation conditions. The choice of conduit type depends on factors such as the location, environment, wiring materials, and the level of protection needed. Here are some of the common types of conduits:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): RMC is a heavy-duty conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It provides excellent protection against physical damage and can withstand harsh environments. RMC is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where durability is crucial.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is a lightweight conduit made of steel or aluminum. It is easy to bend and install, making it ideal for residential and commercial applications. EMT is often used for surface-mounted electrical installations due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
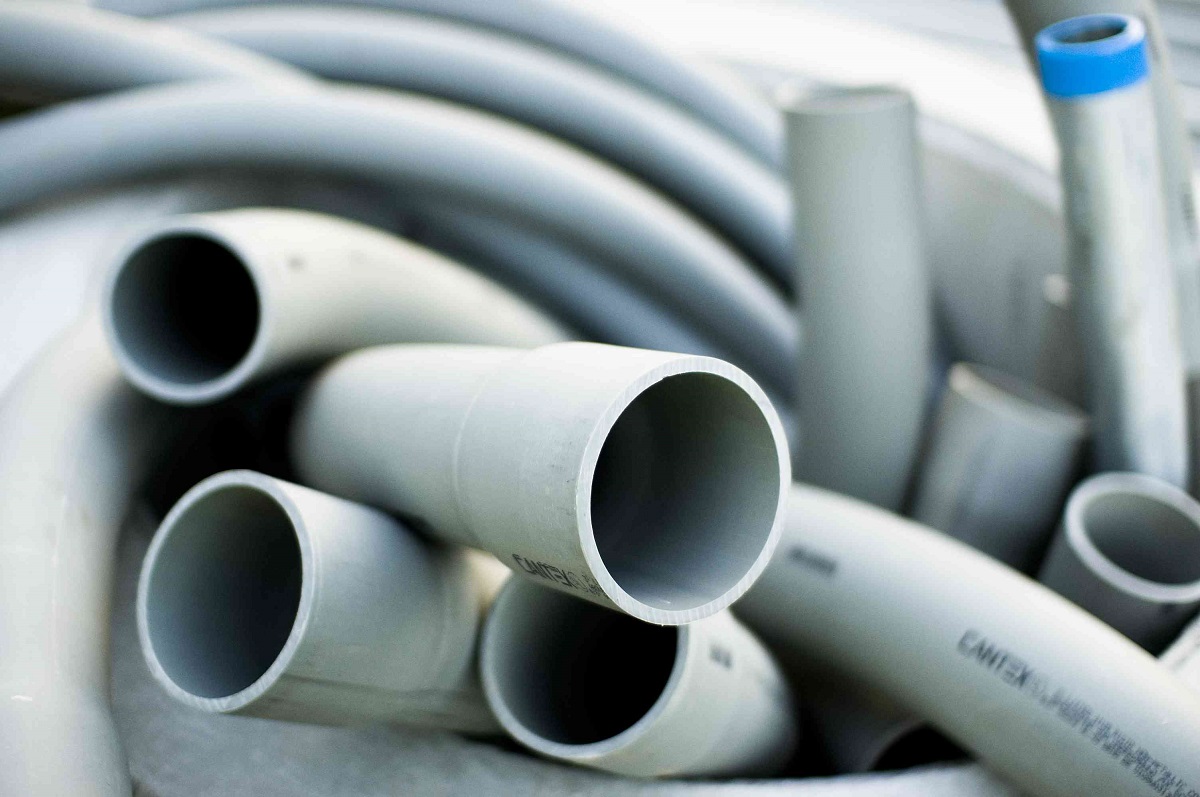
- Rigid Non-Metallic Conduit (RNC): RNC, also known as PVC conduit, is a non-metallic conduit made of PVC material. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective. RNC is widely used in residential applications and areas where moisture exposure is minimal.
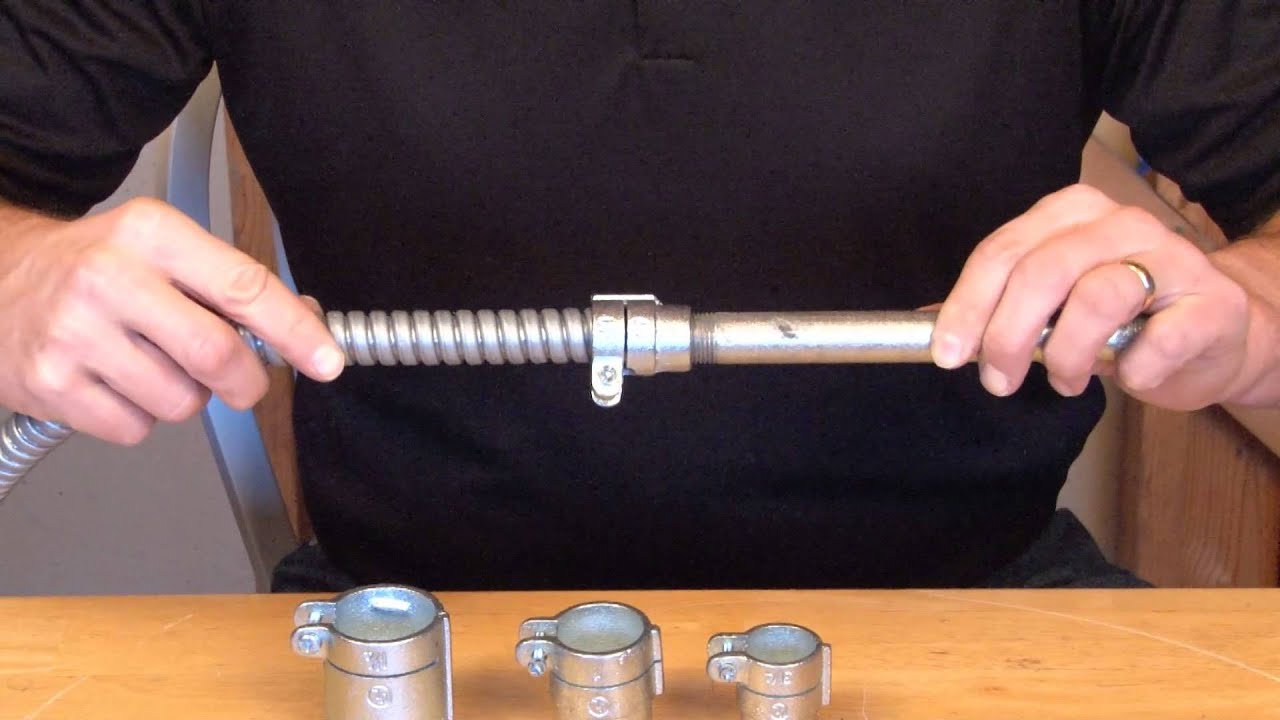
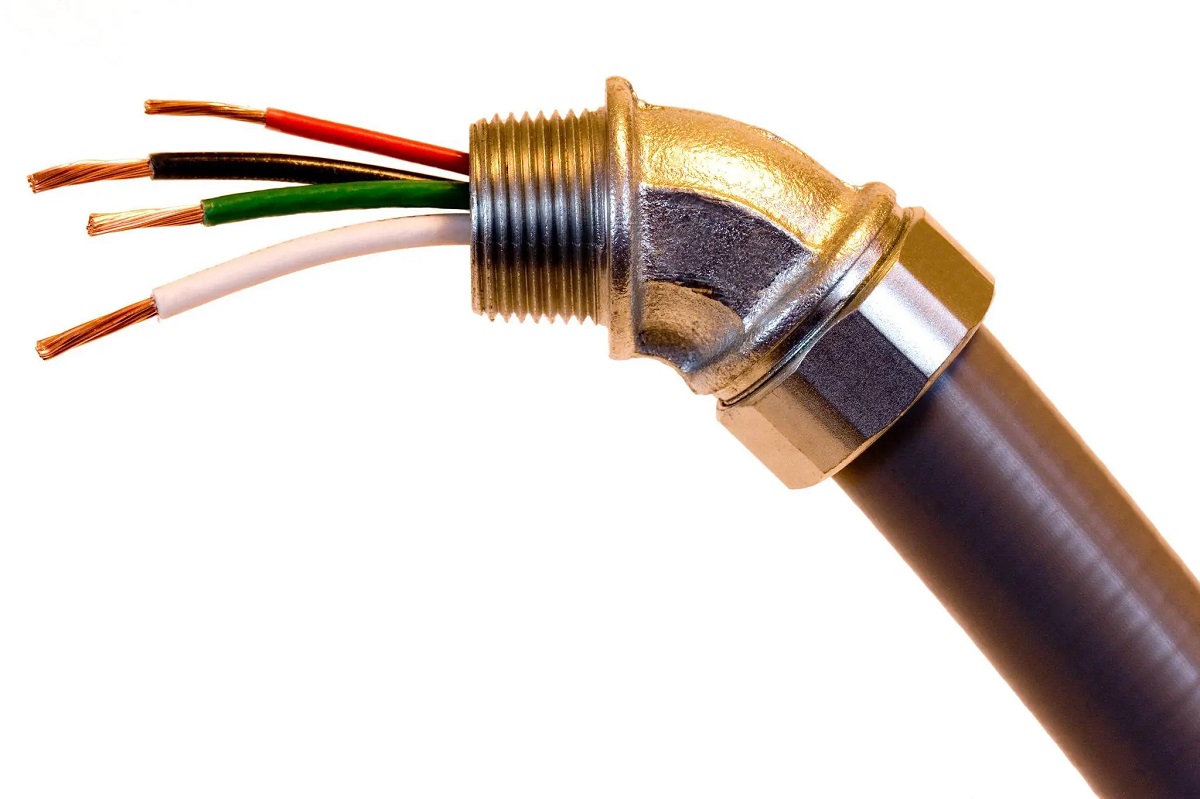
- Flexible Metallic Conduit (FMC): FMC is a flexible conduit made of steel or aluminum, with a spiral-wound or interlocked design. It provides flexibility for routing wiring in tight spaces and is commonly used in short-run surface installations.
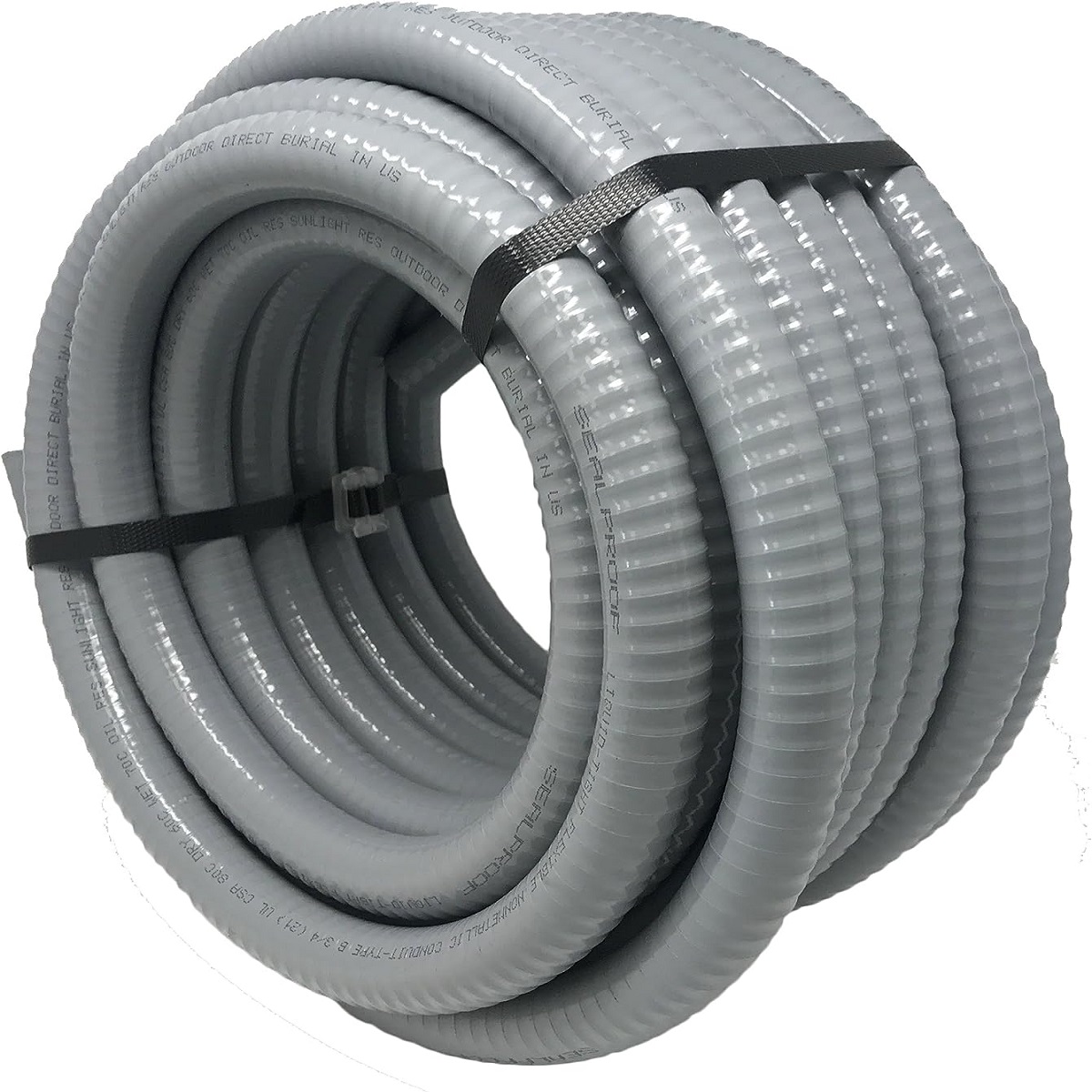
- Liquid-Tight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC): LFMC is a flexible conduit with a waterproof outer covering, making it suitable for outdoor and damp locations. It is often used in areas where the wiring needs protection from water or moisture.
- Plenum Rated Conduit: Plenum rated conduits are designed to meet safety standards for installations in plenum spaces, such as air ducts. They are made of flame-retardant materials to prevent the spread of fire and toxic fumes in case of a fire emergency.
Each type of conduit has its advantages and is suitable for specific applications. It is important to choose the appropriate conduit based on factors such as the installation environment, wiring materials, and local building codes to ensure the optimal safety and performance of the electrical system.
Uses and Applications of Conduits
Conduits have a wide range of uses and applications across various industries and settings. They are an integral part of electrical systems, providing protection and organization to the wiring infrastructure. Here are some common uses and applications of conduits:
- Residential Wiring: In residential buildings, conduits are used to route and protect electrical wiring, ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system. They are commonly installed in walls, floors, and ceilings to hide and secure the wiring.
- Commercial Buildings: Conduits play a crucial role in commercial buildings, such as offices, retail spaces, and hospitals. They provide a safe and organized pathway for electrical wiring, allowing for efficient power distribution and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Industrial Installations: In industrial settings, where electrical systems are subjected to harsh conditions and heavy machinery, conduits offer robust protection for wiring. They help safeguard against physical damage, moisture, and other environmental factors, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of machinery and equipment.
- Data and Communication Networks: Conduits are also used to house data and communication cables, such as Ethernet cables and fiber optics. They provide a secure pathway for these cables, protecting them from interference and maintaining the integrity of the network infrastructure.
- Outdoor Installations: Conduits designed for outdoor use, such as weatherproof and UV-resistant types, are widely used in outdoor lighting systems, underground installations, and outdoor electrical setups. They protect the wires from exposure to moisture, sunlight, and other weather elements.
- Public Infrastructure: Conduits are used in the construction of public infrastructure such as bridges, tunnels, and highways. They help ensure the safe and efficient routing of electrical and communication cables that power street lights, traffic signals, and other infrastructure components.
- Data Centers: In data centers, where the accumulation of cables is extensive, conduits are essential for proper cable management. They help maintain an organized and easily accessible network infrastructure, simplifying maintenance and troubleshooting tasks.
Overall, conduits have diverse applications in residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. They provide essential protection, organization, and durability for electrical wiring and communication systems, ensuring the efficient and safe operation of these systems.
A conduit is a pipe or tube used to protect and route electrical wiring. When installing a conduit, make sure to use the appropriate size and material for the specific application to ensure safety and compliance with building codes.
Installation and Maintenance of Conduits
The proper installation and maintenance of conduits are crucial to ensure their effectiveness in protecting electrical wiring. Here are some key considerations when it comes to installing and maintaining conduits:
Installation:
- Plan the installation: Before beginning the installation, assess the routing requirements and determine the appropriate conduit type, size, and fittings needed for the specific application.
- Follow local regulations and codes: Ensure that the installation adheres to local building codes and regulations. This includes the correct placement, spacing, and securing of conduits.
- Prepare the work area: Clear the area of obstructions and ensure that the installation site is clean and free from any debris that could potentially cause damage to the conduit or wiring.
- Measure and cut the conduits: Mark the conduit lengths according to the planned routing and use appropriate tools to cut them to the required size.
- Maintain proper spacing and support: Install the conduits at the recommended spacing and use appropriate clamps, straps, or hangers to support them, ensuring they are securely fastened and properly aligned.
- Make secure connections: Use connectors, couplings, or fittings that are suitable for the conduit type and ensure that all connections are securely tightened to prevent any movement or separation.
- Test and inspect: After installation, test the conduits and ensure that they are free from any obstructions or damage that could hinder the passage of wiring. Regularly inspect the conduits for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage and address any issues promptly.
Maintenance:
- Regular inspections: Conduct routine inspections to check for any signs of wear, damage, or deterioration in the conduits. Focus on areas where the conduits are exposed to moisture, extreme temperatures, or physical stress.
- Clear obstructions: Remove any debris or foreign objects that may have accumulated within the conduits to maintain a clear pathway for the wires.
- Repair or replace damaged conduits: If any conduits are found to be damaged or compromised, take immediate action to repair or replace them to ensure continued protection for the wiring.
- Check for proper grounding: Verify that the conduits are properly grounded to minimize the risk of electrical shocks and ensure the overall safety of the electrical system.
- Conduct preventive maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule to address potential issues before they escalate. This may involve cleaning, lubricating, and tightening fittings, as well as testing the conduits for continuity and insulation integrity.
- Document maintenance activities: Keep a detailed record of all maintenance activities performed on the conduits, including inspections, repairs, and replacements. This documentation can aid in future troubleshooting and ensure a comprehensive maintenance history.
By following proper installation techniques and implementing regular maintenance practices, the lifespan and effectiveness of conduits can be maximized, ensuring the long-term protection and functionality of the electrical wiring they enclose.
Read more: What Is Electrical Conduit
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Conduits
Conduits offer several advantages when it comes to the protection and organization of electrical wiring. However, they also have some limitations. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages can help you make informed decisions regarding the use of conduits. Here are the main advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Protection: Conduits provide a robust and reliable means of protecting electrical wiring from physical damage, moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. This helps to prevent electrical hazards and extends the lifespan of the wiring.
- Organization: Conduits enable the neat and organized arrangement of electrical wiring. This makes it easier to trace, maintain, and troubleshoot the wiring, saving time and effort during installation and maintenance processes.
- Flexibility: With different types of conduits available, such as flexible metallic conduits, routing wiring becomes feasible, even in tight spaces or areas that require frequent adjustments. The flexibility of conduits allows for adaptability during installations.
- Fire Resistance: Certain types of conduits are designed to be fire-resistant, helping to prevent the spread of fire and smoke. This adds an additional layer of safety in installations where fire hazards are a concern.
- Code Compliance: By using conduits, you can ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations, promoting safety and avoiding any potential legal issues.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Conduits can add to the overall cost of electrical installations, particularly in large-scale projects. The cost of materials and labor associated with conduit installation should be considered in the project budget.
- Complex Installation: Installing conduits requires careful planning, measuring, cutting, and fitting. The installation process can be complex, especially when dealing with complicated routing or intricate configurations.
- Space Limitations: In some cases, conduit installation may require additional space, especially when installing in-wall or in-ceiling applications. This can be a limitation in situations where space is already at a premium.
- Expansion Limitations: Once conduit systems are installed, making changes or expanding the wiring infrastructure can be challenging. This can lead to additional costs and disruptions in the future.
- Higher Skill Requirement: Proper installation of conduits requires a certain level of expertise and knowledge. It may be necessary to hire or consult with experienced professionals to ensure the installation is done correctly.
While conduits offer significant advantages in terms of protection, organization, and safety, it is important to consider the associated costs, installation complexities, and potential limitations. Assessing the specific requirements of each project and evaluating the benefits and drawbacks can help determine whether utilizing conduits is the right choice.
Conclusion
Conduits play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, organization, and durability of electrical wiring systems. They provide a protective pathway for wires, shielding them from environmental factors and potential physical damage. Understanding the definition, types, uses, installation techniques, and advantages and disadvantages of conduits is essential for anyone involved in construction, electrical work, or even homeowners looking to enhance the safety of their electrical systems.
By using conduits, you can effectively protect electrical wiring from moisture, dust, and other contaminants, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards. The organization and neat arrangement of wires within conduits make maintenance and troubleshooting more efficient and convenient. Additionally, certain types of conduits offer fire resistance, adding an extra layer of safety to installations.
While conduits offer significant benefits, it is important to be aware of the associated costs, installation complexities, and potential limitations. Proper planning, adherence to local building codes, and regular maintenance can help mitigate these challenges and ensure the optimal performance of conduits over time.
Whether you are a homeowner looking to enhance the safety of your electrical system, a professional electrician working on a construction project, or someone with a general interest in electrical infrastructure, understanding the role and importance of conduits is essential. By utilizing conduits in your electrical installations, you can ensure the longevity, reliability, and safety of your electrical wiring system.
So, the next time you embark on a construction or electrical project, consider the benefits that conduits bring to the table. They are more than just protective sleeves; they are the backbone of an efficient and secure electrical system.
Curious about upgrading your electrical setups? Dive into our latest review on the best options for metal conduit next year. With detailed insights into durability, efficiency, and safety features, you're sure to find the perfect match for any installation needs. Whether you're a seasoned electrician or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the options available helps you make informed decisions for all your wiring tasks. Don't miss out on our comprehensive guide to finding the best solutions for your home or workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Conduit
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A Conduit”