

Articles
What Is Conduit Used For
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn all about the different uses of conduit in this informative article. Find out how conduit can be used in electrical systems, plumbing installations, and more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
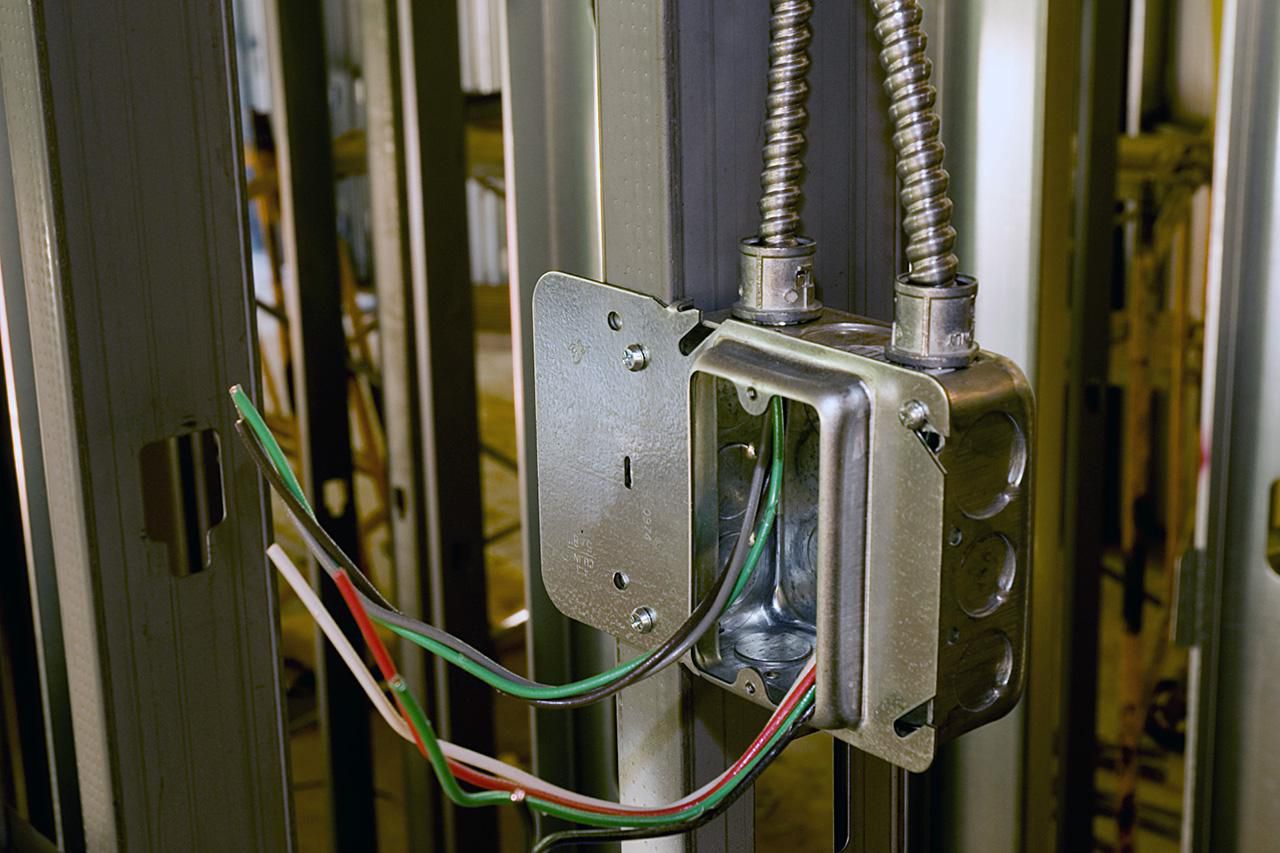
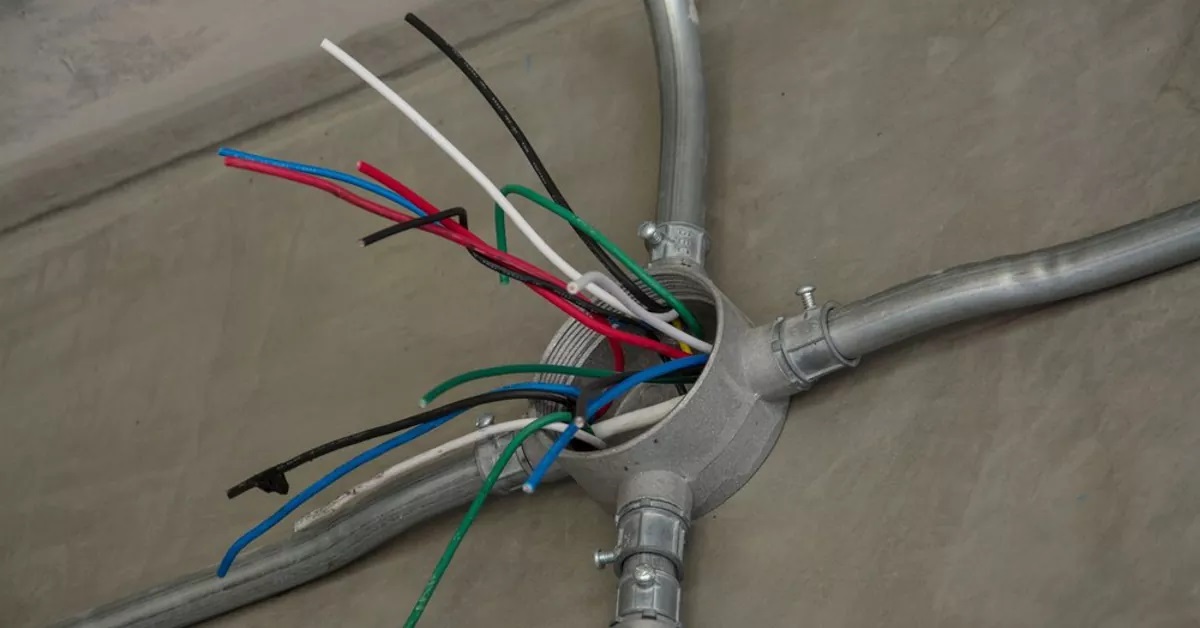
Conduit is a crucial component in various industries, particularly in electrical installations. It provides protection and organization for electrical wires, cables, and other conductors, ensuring their safe and efficient operation. Whether it’s in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, conduit plays a vital role in safeguarding electrical systems.
Conduit, in simple terms, is a specialized pipe or tube that is used to enclose and protect electrical wiring. It acts as a conduit, as the name suggests, guiding electrical conductors from one point to another. But beyond its basic function of serving as a pathway for wires, conduit offers several other benefits that make it an essential part of any electrical system.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of conduit and explore its different types, applications, materials, installation techniques, and maintenance considerations. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what conduit is and its significance in various industries.
Key Takeaways:
- Conduit serves as a protective pathway for electrical wiring, offering benefits such as protection, organization, compliance with codes, noise reduction, and environmental safeguarding. It plays a vital role in ensuring safe and reliable electrical systems.
- The selection of appropriate conduit material is crucial, considering factors such as application, level of protection, flexibility, wire capacity, ease of installation, cost, compliance, and maintenance requirements. Proper installation and maintenance practices are essential for the optimal performance of the conduit system.
Read more: What Is Red Conduit Used For
Definition of Conduit
Conduit, in the context of electrical installations, is a protective channel or pathway that is used to house and safeguard electrical wiring and cables. It is designed to provide a barrier between the conductors and the outside environment, protecting them from physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and other potential hazards.
Conduits come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, allowing for flexibility and customization based on specific installation requirements. They can be rigid or flexible, depending on the type of conduit chosen.
The primary purpose of conduit is to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. By enclosing the wiring, it prevents accidental contact with live wires and reduces the risk of electrical fires and short circuits. Additionally, conduit offers protection against mechanical damage, such as impacts or crushing, which can occur in high-traffic areas or during construction and renovation projects.
Moreover, conduit facilitates the easy organization and management of wiring systems. It allows for neat and orderly installation by providing a clear path for cables and wires to follow. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance tasks by providing easy access to individual wires or cables.
Overall, the use of conduit ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations, enhancing safety and promoting good electrical practices in various industries.
Types of Conduit
Conduit comes in a variety of types, each suitable for specific applications and installation requirements. Here are the main types of conduit commonly used in electrical installations:
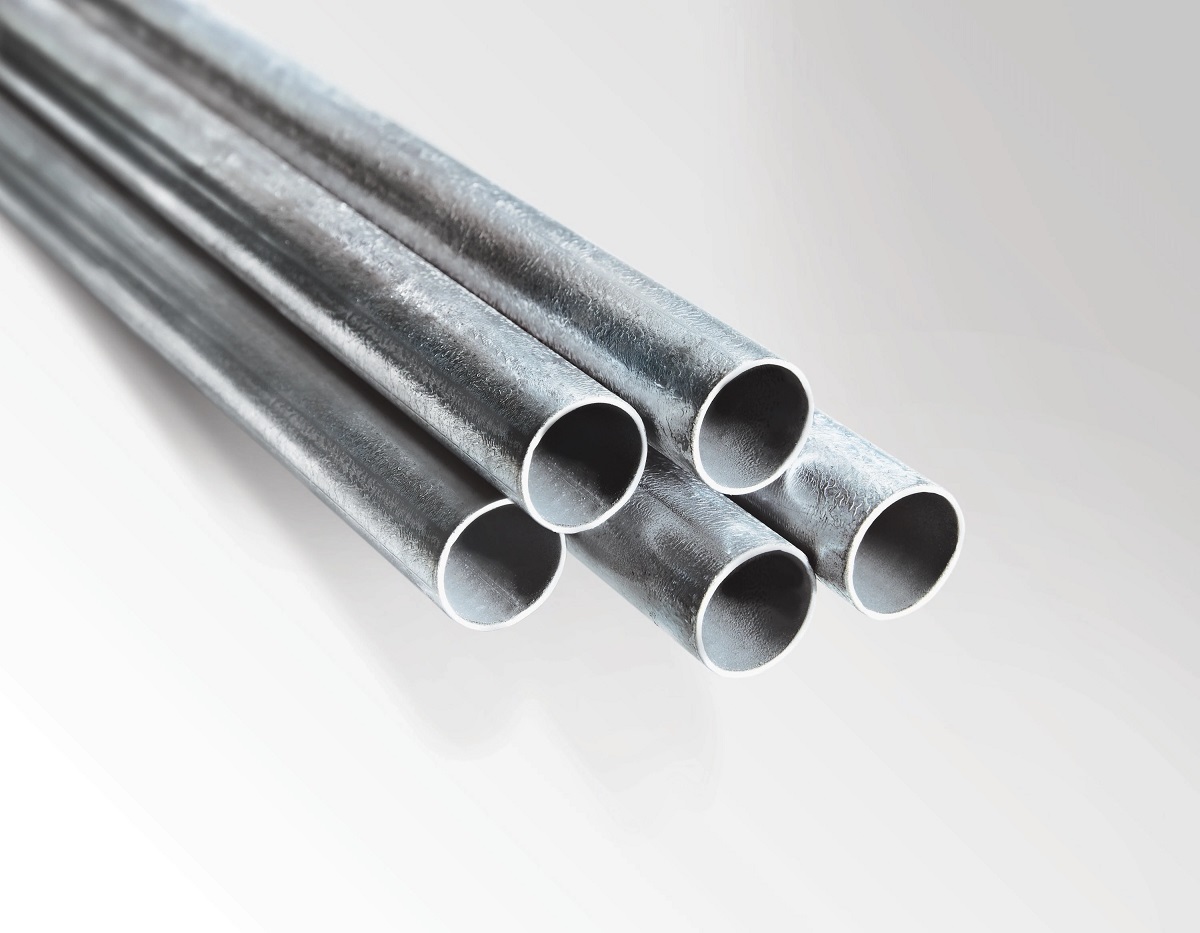
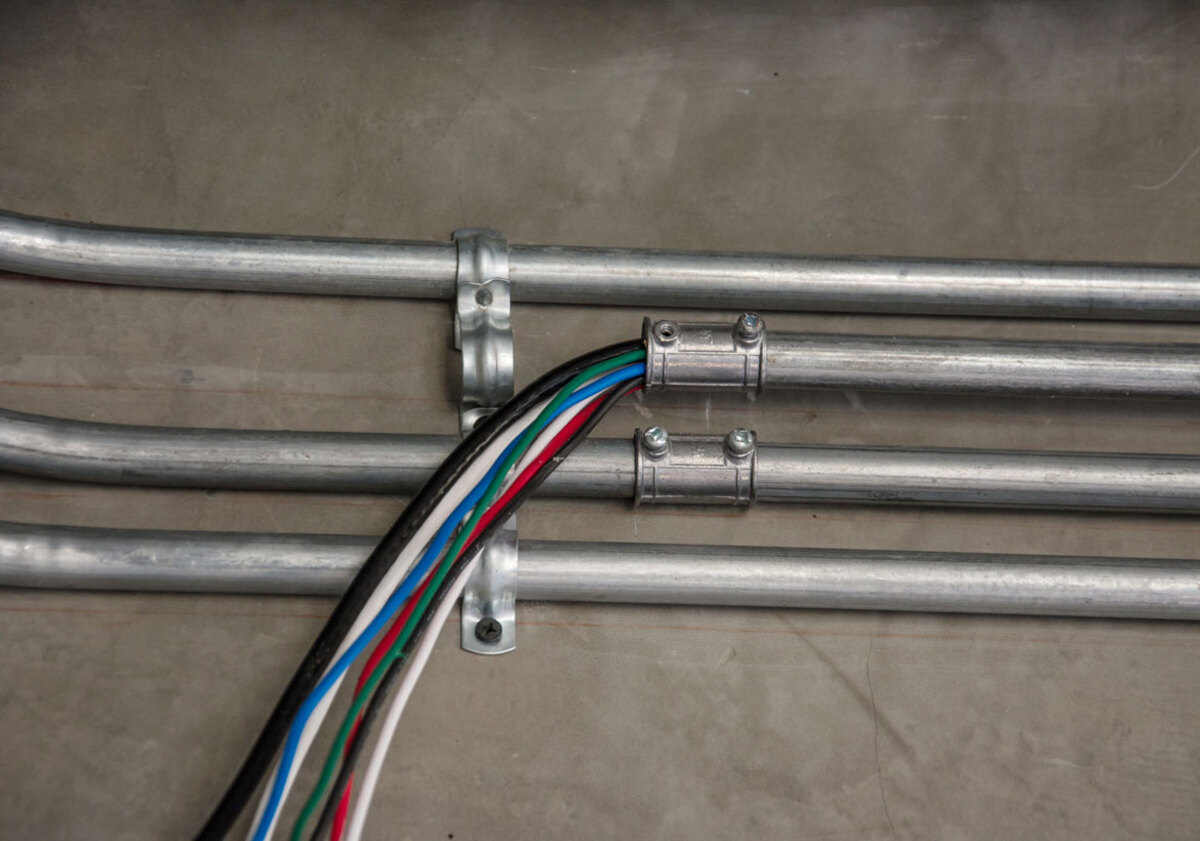
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): This type of conduit is made of galvanized steel or aluminum, offering excellent durability and protection. RMC is rigid and provides the highest level of physical protection for electrical wiring. It is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where there is a higher risk of mechanical damage or exposure to hazardous environments.
- Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC): Similar to RMC, IMC is also made of galvanized steel. However, it is lighter and easier to work with, making it a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor installations. IMC provides good strength and protection against physical damage, making it suitable for commercial and residential applications.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is a lightweight and flexible conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is commonly used in residential and commercial installations due to its ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. EMT is best suited for environments where the risk of physical damage is low.
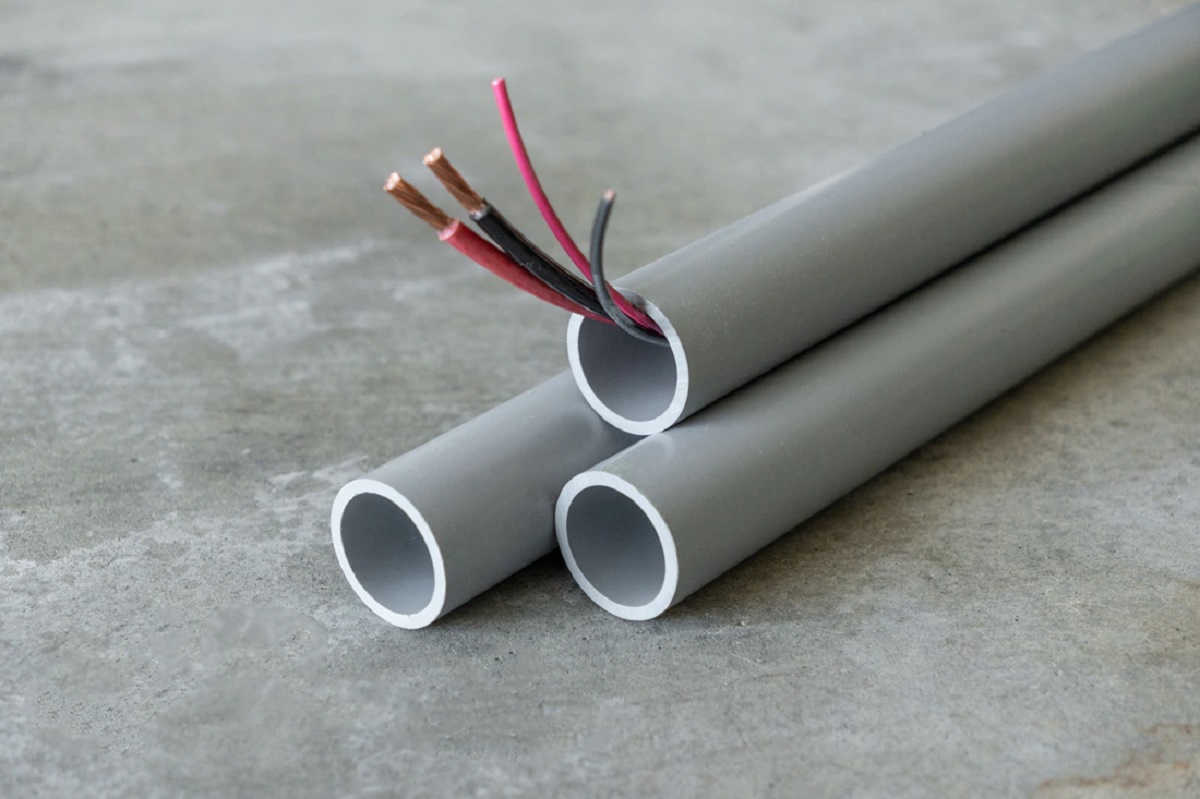
- Rigid Non-Metallic Conduit (RNC): Also known as PVC conduit, RNC is made of a non-metallic material, usually PVC (polyvinyl chloride). It is lightweight, easy to cut, and resistant to corrosion. RNC is commonly used in residential applications and areas where moisture or corrosive substances are present.
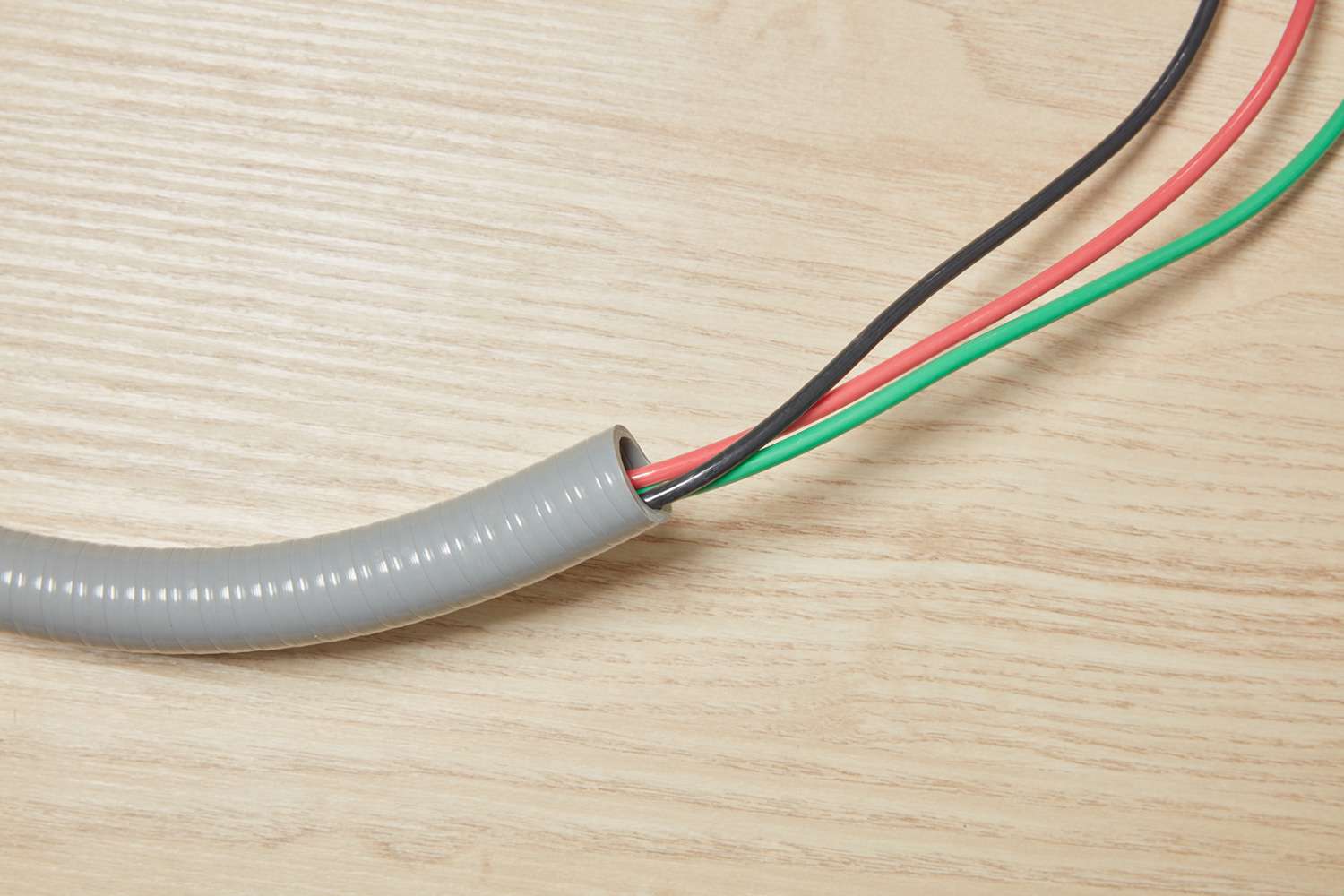
- Flexible Metallic Conduit (FMC): FMC, also known as “Greenfield,” consists of a coiled metal strip with a plastic coating. It provides flexibility, making it ideal for installations that require bends and turns. FMC is commonly used for short runs or where vibrations or movement are expected.
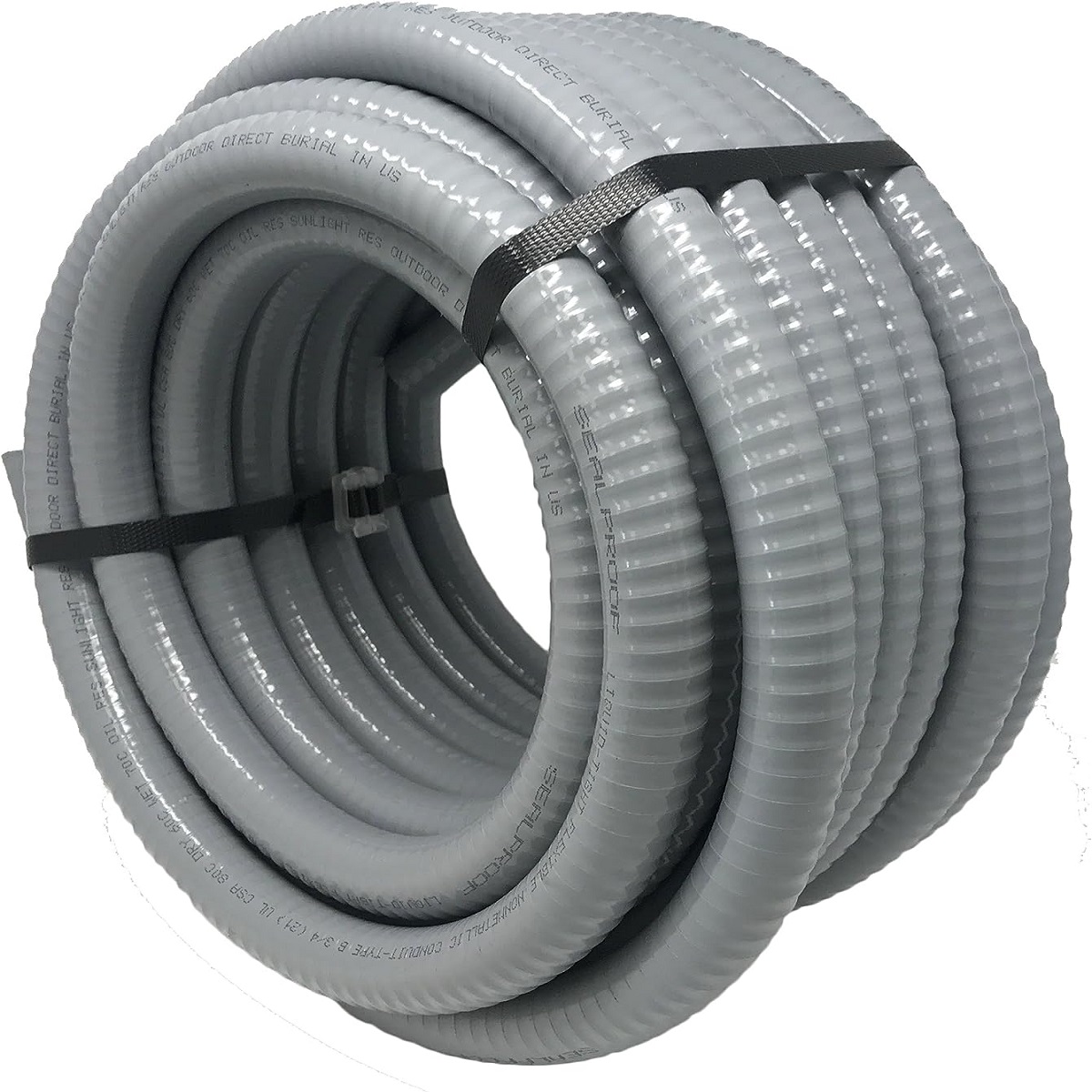
- Flexible Non-Metallic Conduit (FNMC): FNMC, or “Liquidtight,” is a flexible conduit made of a non-metallic material such as PVC or thermoplastic rubber. It is resistant to moisture, oils, and chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor or wet locations.
When selecting the appropriate conduit type for an electrical installation, factors such as the environment, wiring requirements, and code regulations should be considered to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Electrical Applications of Conduit
Conduit is widely used in electrical installations across various industries due to its numerous benefits and protective capabilities. Here are some common applications of conduit in electrical systems:
- Residential Electrical Wiring: In residential settings, conduit is used to protect and organize electrical wiring throughout the house. It is commonly employed in areas such as basements, attics, and crawl spaces, where the risk of damage or exposure to moisture is higher.
- Commercial and Industrial Buildings: Conduit plays a vital role in commercial and industrial settings to safeguard electrical systems in buildings, factories, warehouses, and other facilities. It is used to protect wiring in installation areas that may be subject to mechanical stress, such as manufacturing plants or construction sites.
- Data and Communication Cabling: Conduit is also utilized for routing and protecting data and communication cables, such as Ethernet, fiber optic, and coaxial cables. By using conduit, these cables are shielded from external interference, ensuring uninterrupted and reliable data transmission.
- Outdoor Electrical Installations: Outdoor electrical installations, such as overhead power lines, street lighting, and underground wiring, require conduit to protect wires from weather elements, moisture, and potential damage caused by accidental contact or environmental factors.
- Industrial Control Systems: In industrial control systems, conduit is essential for protecting the wiring and cables used for control mechanisms, sensors, and instrumentation. This ensures the proper functioning and safety of automated processes and machinery in manufacturing plants and industrial facilities.
- Electrical Panel and Service Entrance: Conduit is used to route conductors from the main electrical panel to various circuits within a building. It provides a protective pathway for the main service cables, helping to prevent damage and facilitating easy access during maintenance or repairs.
By employing conduit in these electrical applications, the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits, electrical fires, and electrocution, is significantly reduced. Conduit offers a reliable and efficient means of protecting and organizing electrical wiring, enhancing the overall safety and performance of electrical systems in diverse environments.
Purpose of Conduit
The primary purpose of conduit in electrical installations is to provide protection and organization for electrical wiring and cables. Let’s explore the key purposes of using conduit:
- Protection: One of the main functions of conduit is to protect electrical conductors from various potential hazards. This includes physical damage from impact, crushing, or abrasion, as well as exposure to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. By enclosing the wiring within conduit, the conductors are shielded from these external factors, reducing the risk of electrical malfunctions, short circuits, and electrical fires. Conduit also prevents accidental contact with live wires, minimizing the chances of electric shocks or electrocution.
- Organization: Conduit enables the neat and systematic organization of electrical wiring systems. By providing a clear and designated pathway for cables and wires, conduit helps to maintain a tidy and easily accessible installation. This organization facilitates troubleshooting, maintenance, and future expansions or modifications, as individual wires can be easily identified and accessed without disruption to the entire system.
- Compliance: The use of conduit ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations. Conduit installation standards are specified by national and international electrical codes, which outline the requirements for safety and performance in different types of installations. By adhering to these regulations, electrical systems can be installed and maintained properly, providing a higher level of safety and reducing potential liabilities.
- Noise and EMI Reduction: In certain applications, conduit can help reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and control noise caused by electrical signals. Metal conduits, such as RMC and IMC, can act as a shield, preventing the spread of electromagnetic fields and limiting interference with nearby sensitive equipment or electrical systems.
- Environmental Protection: Conduit provides a barrier against environmental factors that can potentially damage electrical wiring. It protects wires and cables from exposure to moisture, dust, dirt, corrosive substances, and other contaminants. This is particularly important in outdoor or harsh environments where the risk of damage is higher, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical system.
Overall, the purpose of conduit is to enhance the safety, organization, and performance of electrical systems. By providing a protective pathway for wiring and cables, conduit ensures the reliable and efficient operation of electrical installations in various industries and environments.
Conduit is used to protect and route electrical wiring in buildings. It provides a safe and organized way to run wires, protecting them from damage and making it easier to make repairs or upgrades in the future.
Read more: What Is Blue Conduit Used For
Benefits of Using Conduit
The use of conduit in electrical installations offers numerous benefits that contribute to the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the system. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using conduit:
- Protection: Conduit provides a physical barrier that protects electrical wires and cables from potential damage, including impacts, crushing, abrasion, moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. This protection minimizes the risk of electrical malfunctions, short circuits, and electrical fires, ensuring the safety of individuals and the integrity of the electrical system.
- Organization and Accessibility: By organizing electrical wiring and cables within conduit, the installation becomes neat and orderly, facilitating ease of access for troubleshooting and maintenance. Conduit enables efficient identification, repair, and replacement of individual wires or cables, reducing downtime and minimizing disruption to the overall system.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Conduit is available in various types and sizes, offering flexibility and adaptability to different installation requirements. This versatility allows for easy customization and modification of electrical systems, accommodating changes in equipment, layout, or future expansions without the need for extensive modifications or rewiring.
- Compliance with Codes and Regulations: The use of conduit ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations established by local authorities. By adhering to these standards, electrical installations meet the necessary safety and performance requirements, reducing the risk of accidents, liabilities, and potential legal issues.
- Noise and EMI Control: Metal conduit, such as RMC and IMC, can help control electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce noise caused by electrical signals. This benefit is particularly valuable in applications where sensitive equipment or systems are located nearby, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the chances of signal interference.
- Longevity and Durability: Conduit, especially those made of durable materials such as galvanized steel or PVC, offers long-lasting protection for electrical wiring. It is resistant to corrosion, UV rays, and other environmental factors, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical system.
- Aesthetics: Conduit installation provides a visually appealing and professional appearance to electrical systems. By concealing and carefully routing the wiring, conduit creates a clean and organized look, enhancing the overall aesthetics of the installation, particularly in commercial or public-facing environments.
These benefits make conduit an essential component in electrical systems, contributing to the overall safety, efficiency, and performance of the installation. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, the use of conduit ensures a reliable and well-protected electrical infrastructure.
Common Materials Used for Conduit
Conduit comes in various materials, each offering specific characteristics and suitability for different applications. Let’s explore some of the common materials used for conduit:
- Galvanized Steel: One of the most common materials for conduit is galvanized steel. It offers excellent durability, strength, and protection against corrosion. Galvanized steel conduit, such as Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) and Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where mechanical protection is essential.
- Aluminum: Aluminum conduit is lightweight and highly corrosion-resistant. It is commonly used in outdoor installations where weight reduction or resistance to environmental elements is important. Aluminum conduit is favored for its ease of installation and lower cost compared to other materials.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC conduit, also known as Rigid Non-Metallic Conduit (RNC), is a popular choice for both residential and commercial applications. It is lightweight, easy to work with, and resistant to corrosion and moisture. PVC conduit is highly flexible and can be easily cut and connected using PVC fittings.
- Flexible Metal: Flexible metal conduit (FMC) is made of coiled metal strips that are coated with a plastic or rubber layer. It offers excellent flexibility, making it suitable for installations that require frequent bends or movement. FMC is commonly used in shorter runs or in areas where vibrations or motion are expected.
- Flexible Non-Metallic: Flexible non-metallic conduit (FNMC), also known as Liquidtight conduit, is made of a non-metallic material such as PVC or thermoplastic rubber. It is resistant to moisture, oils, and chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor or wet locations. FNMC provides flexibility and is often used in applications where the conduit needs to be waterproof or resistant to various environmental conditions.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is made of thin-walled steel or aluminum, offering both strength and flexibility. It is commonly used in residential and commercial installations due to its ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. EMT is lightweight and easy to bend, making it suitable for areas where wiring needs to navigate tight spaces or obstacles.
The choice of conduit material depends on various factors such as the installation environment, level of mechanical protection required, flexibility needs, and budget considerations. It is important to select the appropriate material to ensure the longevity, performance, and safety of the electrical system.
Installation and Maintenance of Conduit
The proper installation and maintenance of conduit are crucial for ensuring the longevity, safety, and functionality of electrical systems. Here are some key considerations for installing and maintaining conduit:
Installation:
- Planning and Preparation: Before installation, carefully plan the conduit layout, taking into account the location, routing, and spacing requirements. Ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.
- Material Selection: Select the appropriate type and material of conduit based on the specific installation requirements. Consider factors such as environmental conditions, mechanical protection needs, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Routing and Supports: Determine the best pathway for the conduit, minimizing bends and sharp turns. Use appropriate supports, such as straps or clips, to secure the conduit and prevent sagging or tension. Avoid stretching or crushing the conduit during installation.
- Conduit Joints and Connectors: Use proper connectors, couplings, and fittings to join conduit sections together. Ensure secure and tightly sealed connections to maintain the integrity of the conduit system.
- Grounding and Bonding: Follow grounding and bonding guidelines to ensure electrical safety. Properly connect the conduit system to grounding electrodes and other conductive surfaces.
- Proper Wiring Techniques: Employ correct wiring techniques, such as securing wires within the conduit, using appropriate wire pulling lubricants, and maintaining the required wire fill ratios. This helps prevent wire damage during installation and facilitates future maintenance or troubleshooting.
Maintenance:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct routine visual inspections to check for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear on the conduit. Inspect the fittings, connectors, and supports to ensure proper functioning and tightness.
- Repair or Replacement: Promptly repair or replace any damaged conduit, fittings, or connectors to prevent further deterioration or compromised safety. Replace conduit if it shows signs of severe corrosion, cracks, or deformation.
- Cleanliness: Keep the conduit system clean and free from debris, dust, or moisture that may accumulate over time. Ensure that conduits are not obstructed by other equipment or objects.
- Protection: Take steps to protect the conduit from physical damage, such as impacts, crushing, or accidental contact. Mark conduit locations to ensure they are not disturbed during construction or maintenance activities.
- Environmental Considerations: Consider the impact of environmental factors, such as temperature changes, moisture, or corrosive substances, on the conduit system. Take proper measures to mitigate any potential damage caused by these factors.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate records of the conduit installation, including diagrams, wiring information, and any modifications or repairs made over time. This information becomes valuable for future maintenance or troubleshooting needs.
By following proper installation techniques and implementing regular maintenance practices, the conduit system can function optimally, ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system it houses. When in doubt, consult with a qualified electrician or electrical contractor to ensure proper installation and maintenance procedures are followed.
Key Considerations for Choosing Conduit
When selecting conduit for an electrical installation, several key factors should be taken into consideration. The right choice of conduit will depend on the specific requirements of the project. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind:
- Application and Environment: Evaluate the application and environment where the conduit will be installed. Consider factors such as indoor or outdoor use, exposure to moisture, corrosive substances, extreme temperatures, and potential physical hazards. This will help determine the appropriate material and type of conduit that can withstand the specific conditions.
- Level of Protection: Assess the level of protection required for the electrical wiring and cables. Consider potential risks such as impact, crushing, vibration, chemicals, and moisture. Choose a conduit that offers the necessary level of physical protection to ensure the safety and integrity of the electrical system.
- Flexibility and Bend Radius: Evaluate the flexibility requirements of the installation, considering any bends or turns that the conduit may need to make. Determine if flexibility is needed for routing wires around obstacles or navigating tight spaces. Depending on the requirements, choose either rigid conduit or flexible conduit accordingly.
- Wire Capacity: Determine the number and size of wires that will be installed within the conduit. Ensure that the chosen conduit has sufficient capacity to accommodate the wires comfortably, without exceeding the maximum fill ratio defined by electrical codes.
- Ease of Installation: Consider the ease of installation and the associated labor requirements. Some conduit types, such as PVC or flexible conduit, are generally easier and quicker to install compared to rigid metal conduit. Evaluate the installation method, such as cutting, joining, and fastening, to determine the most efficient option for the project.
- Cost Considerations: Evaluate the budget for the project and consider the cost of the conduit material and associated fittings and accessories. While costs shouldn’t be the sole determining factor, it is important to find a balance between performance, durability, and affordability to meet project requirements.
- Compliance with Codes and Standards: Ensure that the chosen conduit complies with relevant electrical codes and standards. Familiarize yourself with local regulations and installation requirements to select conduit that meets the necessary safety and performance criteria.
- Maintenance Requirements: Assess the potential maintenance needs of the conduit. Some materials, such as PVC, require minimal maintenance, while others, like metal conduits, may require regular inspections for corrosion or damage. Consider the long-term maintenance efforts and associated costs when choosing the conduit material.
Ultimately, the decision of which conduit to choose will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the electrical installation. It is advisable to consult with electrical professionals or contractors to ensure the appropriate conduit is selected for a safe and successful project.
Read more: What Type Of Conduit To Use Outside
Conclusion
Conduit plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, functionality, and longevity of electrical systems in various industries. By serving as a protective pathway for electrical wiring and cables, conduit offers numerous benefits that make it an indispensable component in electrical installations.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of conduit and its different types, including rigid metal conduit, intermediate metal conduit, electrical metallic tubing, rigid non-metallic conduit, flexible metallic conduit, and flexible non-metallic conduit.
We have also discussed the electrical applications of conduit in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. From protecting wiring in buildings to routing communication cables and facilitating outdoor installations, conduit serves as the backbone for safe and reliable electrical systems.
The purpose of conduit extends beyond protection. It provides organization, compliance with codes and regulations, noise reduction, and protection against environmental factors. These benefits ensure the integrity, accessibility, and efficiency of electrical systems.
The selection of appropriate conduit material is a critical decision. Factors such as application and environment, level of protection, flexibility, wire capacity, ease of installation, cost, compliance, and maintenance requirements must be carefully considered to meet project-specific needs.
Furthermore, proper installation and maintenance practices are essential for the optimal performance of the conduit system. Adequate planning, routing, grounding, and connections, along with regular inspections and repairs, contribute to the longevity and safety of the electrical installation.
In conclusion, conduit plays a vital role in electrical installations, offering protection, organization, and compliance. By understanding the different conduit types, applications, materials, installation techniques, and maintenance considerations, professionals can ensure the effective and safe operation of electrical systems. Whether it’s in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, the use of conduit remains a fundamental and indispensable aspect of electrical infrastructure.
Curious about stepping up your home improvement skills? If our rundown on conduit uses has sparked your interest, you won't want to miss our hands-on guide on fitting conduit within walls. Perfect for those ready to tackle a bit more hands-on work, this guide walks you through every step needed for secure and efficient conduit installation. Ready to get your hands dirty and make that project a reality? Head over to our detailed tutorial and get all the tips and tricks you'll need.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Conduit Used For
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Conduit Used For”