Home>Articles>Understanding Electrical Cords: How To Identify A Hot Wire


Articles
Understanding Electrical Cords: How To Identify A Hot Wire
Modified: October 20, 2024
"Discover articles that answer the question – on an electrical cord, which one is the hot wire? Gain insights and knowledge on electrical safety and wiring practices."
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical cords play a crucial role in our daily lives, powering various devices and appliances that make our lives more convenient. However, understanding the inner workings of electrical cords and knowing which wire is the hot wire is important for both safety and proper functioning of electrical equipment.
In this article, we will explore the basics of electrical cords, discuss how to identify the hot wire, and highlight some key safety precautions to keep in mind when handling electrical cords. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of electrical cords and be equipped with the knowledge to ensure safe and efficient electrical usage.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the components of electrical cords, including conductors, insulation, and sheathing, is crucial for safe and efficient electrical usage. Proper handling and maintenance are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring longevity.
- Identifying the hot wire in electrical cords can be done through color coding or using a multimeter. When in doubt, seeking guidance from a licensed electrician is the best way to ensure accurate identification and safe installation.
Understanding Electrical Cords
Electrical cords are made up of several components that work together to deliver electricity safely and efficiently. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
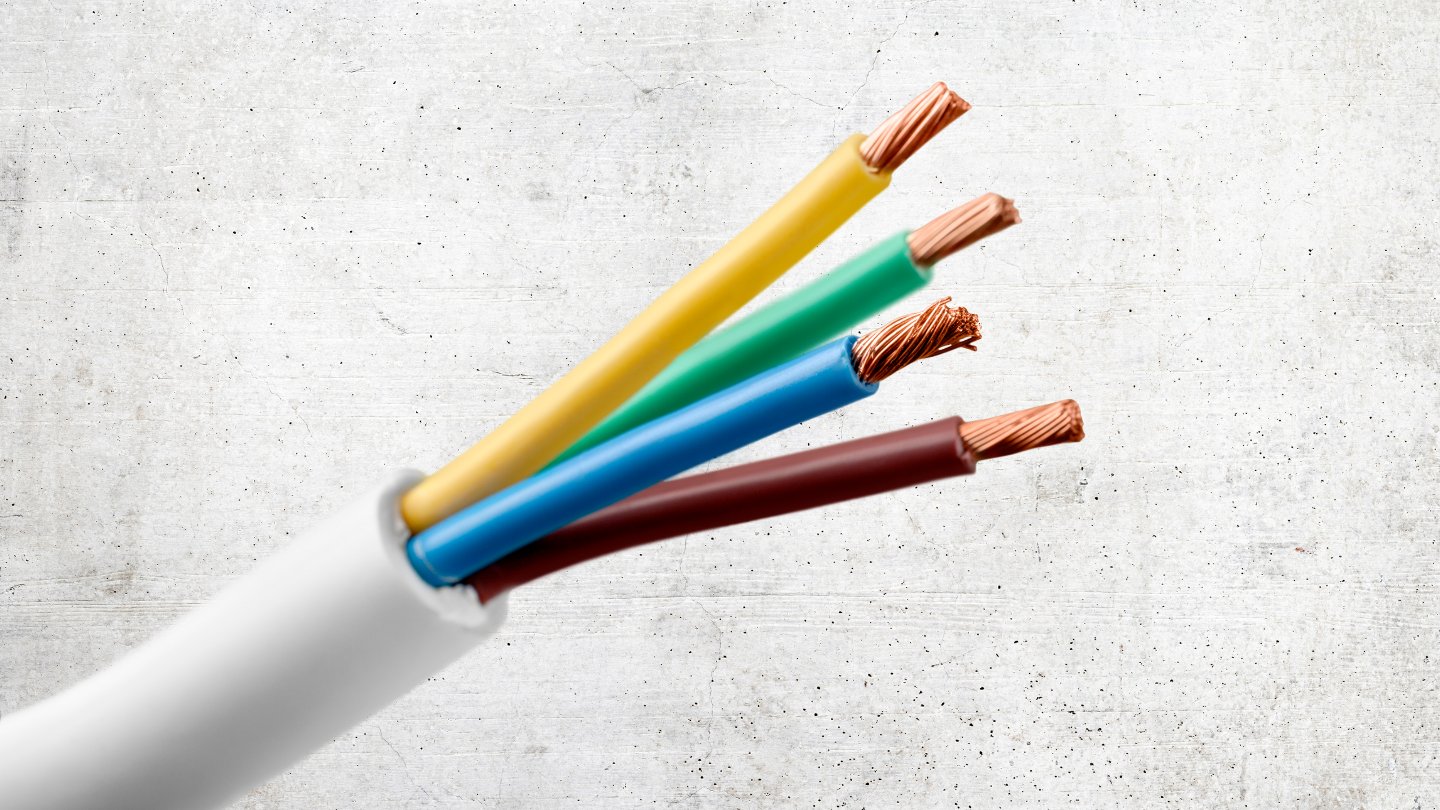
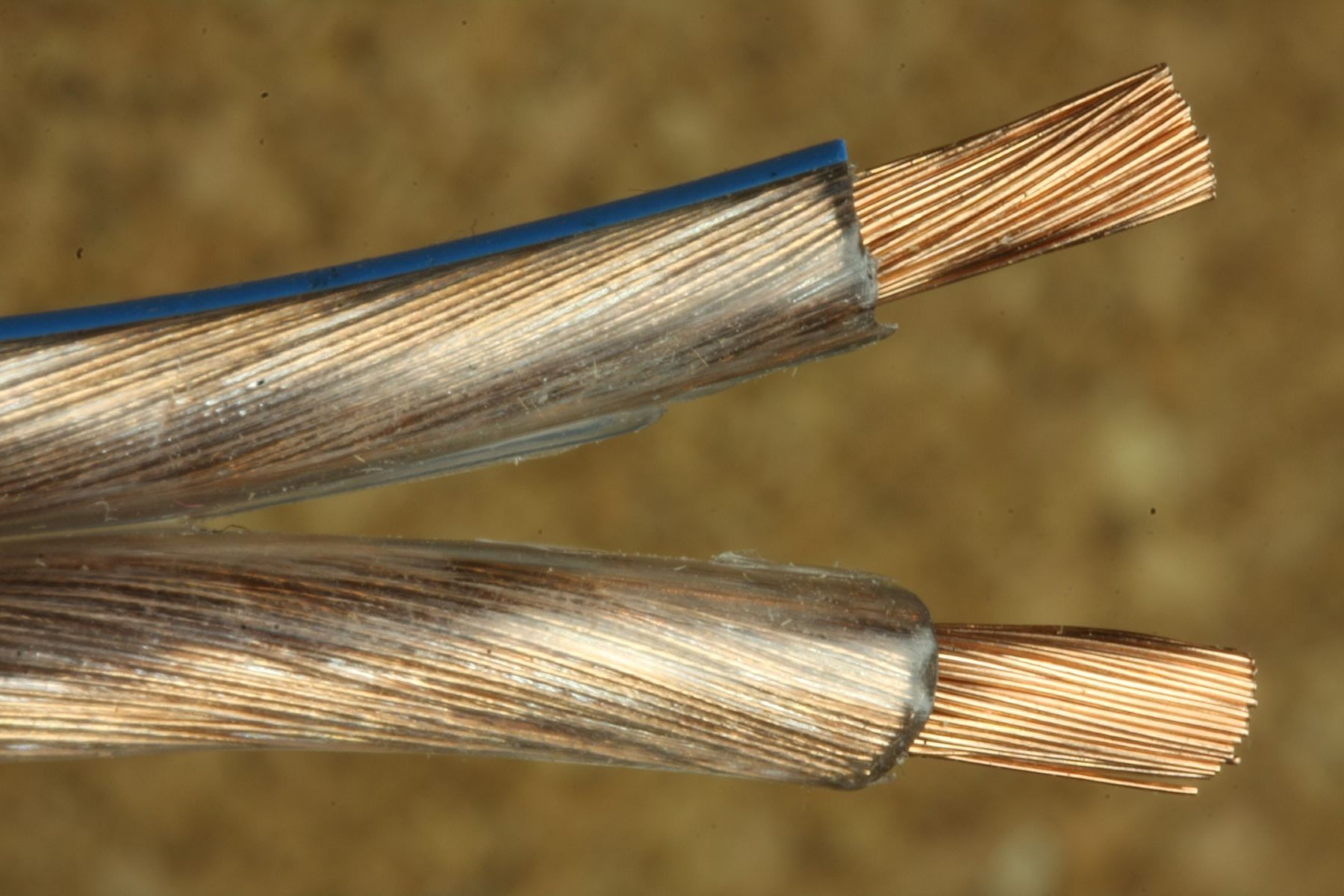
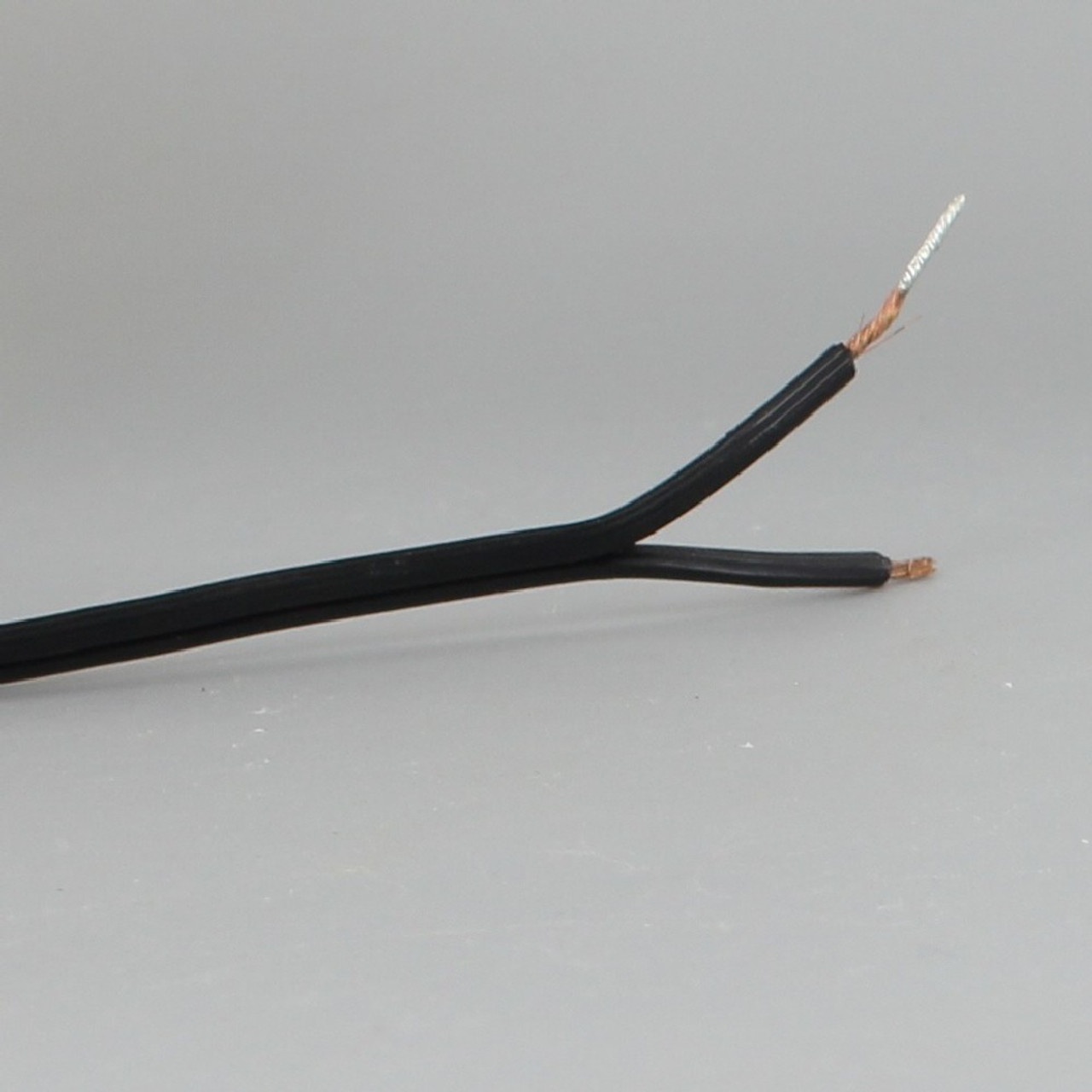
- Conductors: Electrical cords consist of two conductors: the hot wire and the neutral wire. The hot wire carries the current from the power source to the device, while the neutral wire carries the current back to the power source.
- Insulation: The conductors of electrical cords are insulated to prevent electrical shocks and protect against damage. The insulation is typically made of durable materials like rubber or PVC.
- Sheathing: The conductors and insulation are enclosed in a protective sheath, which provides further insulation and safeguards the conductors from physical damage.
- Plug and Receptacle: At the ends of the electrical cord, you will find a plug and a receptacle. The plug is inserted into the power source, while the receptacle is where the device connects to the cord.
Electrical cords come in various lengths and gauges. The gauge refers to the thickness of the wire, with a lower gauge indicating a thicker wire capable of carrying a higher amount of current. It is important to select the appropriate gauge for the intended use to prevent overheating and electrical hazards.
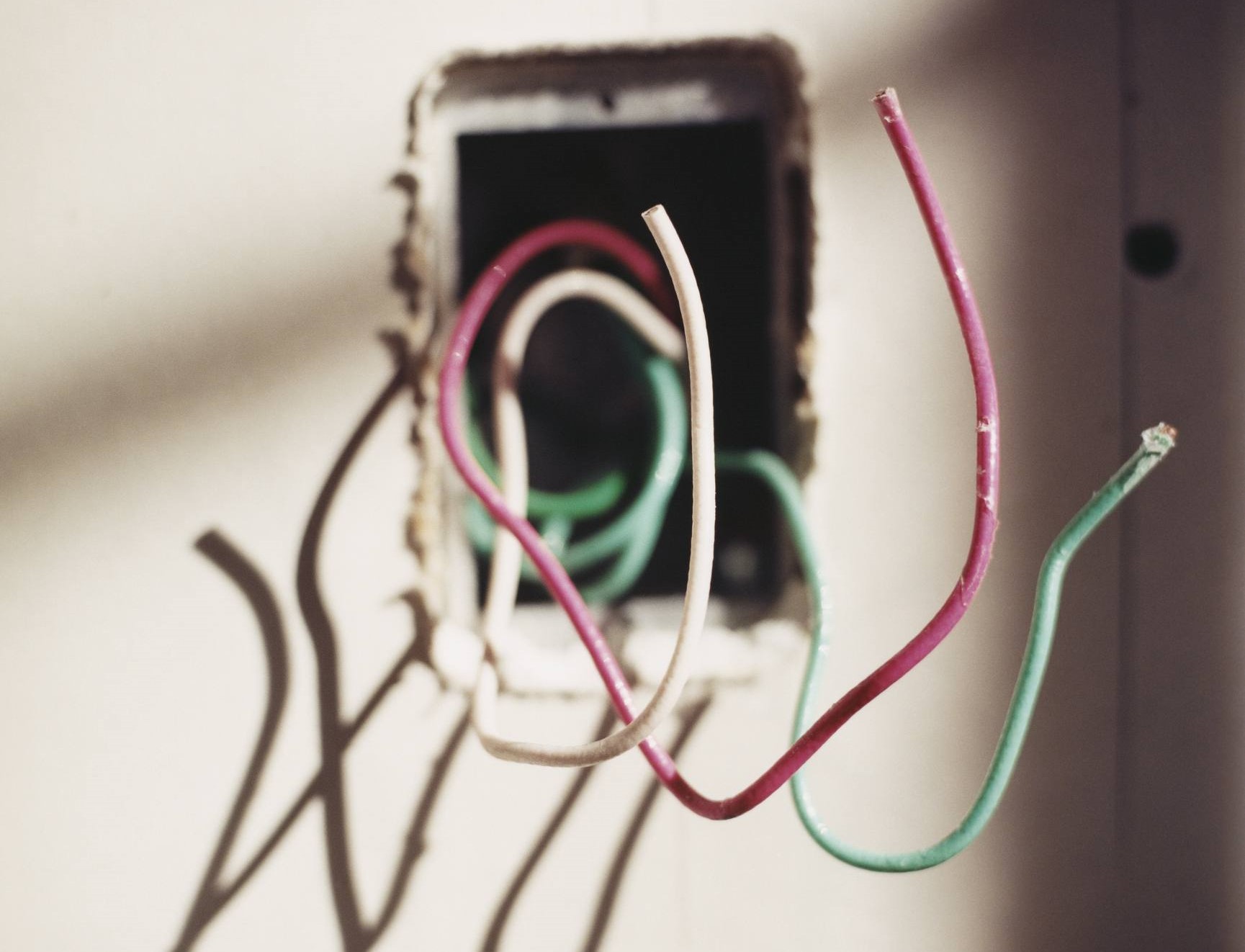
The color coding of electrical cords can also provide valuable information. In many countries, the hot wire is typically colored black or red, while the neutral wire is colored white or light blue. However, it is essential to note that these color codes may vary, so always refer to local electrical standards and guidelines.
Now that we have a basic understanding of electrical cords, let’s delve into how to identify the hot wire.
Identifying the Hot Wire
Identifying the hot wire in an electrical cord is crucial for proper installation and safe usage. Here are some methods to help you determine which wire is the hot wire:
- Check for color coding: As mentioned earlier, electrical cords often have color-coded wires. The hot wire is typically black or red, while the neutral wire is white or light blue. However, it’s important to verify these color codes as they may vary in different locations or for different applications.
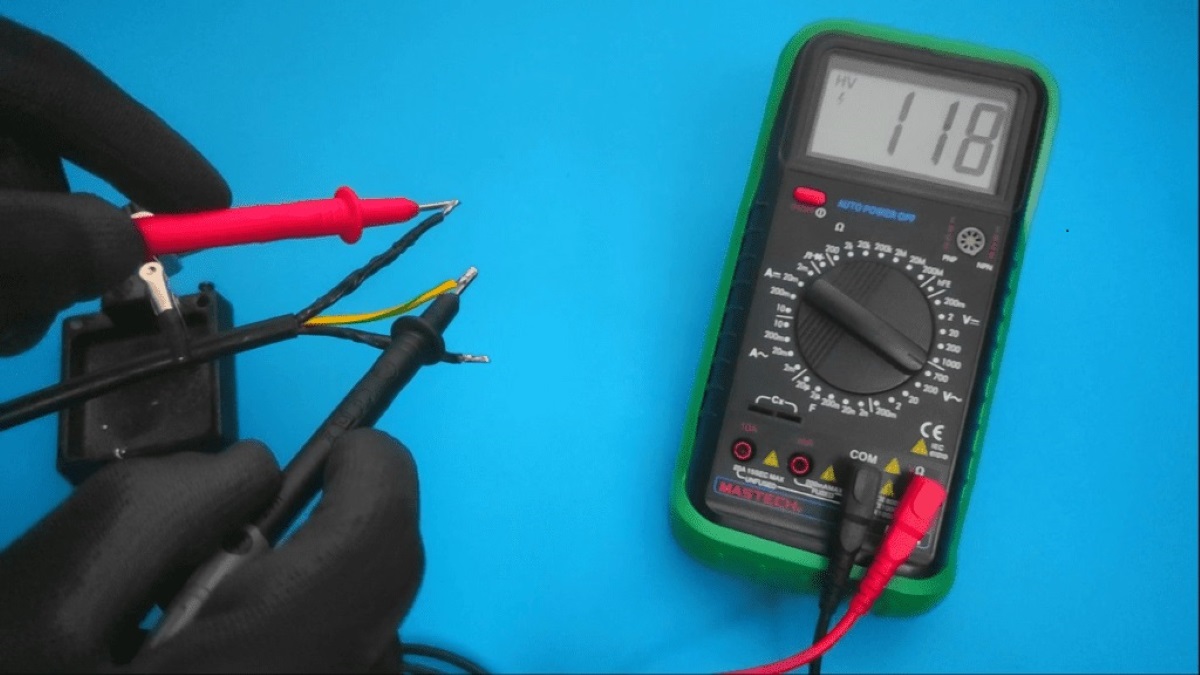
- Use a multimeter: A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure various electrical properties, including voltage. By setting the multimeter to the voltage mode, you can test each wire in the cord. The wire that shows a higher voltage reading relative to the other wire is likely the hot wire. Ensure proper safety precautions and follow the multimeter’s instructions while performing this test.
- Consult an electrician: If you are unsure or uncomfortable with identifying the hot wire, it is always a good idea to seek guidance from a licensed electrician. They have the expertise and experience to accurately identify the hot wire and ensure proper electrical connections.
Remember, misidentifying the hot wire can lead to electrical shocks, damage to devices, or even electrical fires. It is crucial to take the necessary precautions and seek professional help when needed.
Additionally, when working with electrical cords, it’s important to consider safety precautions to minimize risks.
The hot wire in an electrical cord is typically the one with smooth insulation, while the neutral wire has ribbed or grooved insulation. Always use caution when working with electrical cords to avoid injury.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical cords requires following proper safety precautions to prevent accidents and ensure personal safety. Here are some essential safety tips to keep in mind:
- Disconnect power: Before handling electrical cords or making any connections, ensure that the power source is turned off and unplugged. This will prevent any potential electrical shocks.
- Inspect the cord: Regularly inspect the electrical cord for any signs of damage such as frayed wires, worn-out insulation, or loose connections. If you notice any issues, replace the cord immediately to avoid electrical hazards.
- Avoid overload: Do not overload electrical cords by plugging in too many devices or appliances into a single outlet. Overloading can lead to overheating, which may result in electrical fires or damage to the devices.
- Proper storage: When not in use, store electrical cords in a safe and dry area, away from potential hazards that could damage the cord or cause tripping hazards.
- Handle with care: Avoid pulling or tugging on the cord when unplugging it from a power source. Gently grip the plug and pull it straight out to avoid damaging the cord or the plug.
- Keep away from water: Water and electricity do not mix. Keep electrical cords away from wet areas or liquids to prevent electrical shocks or short circuits.
- Use proper extension cords: If you need to extend the reach of an electrical cord, use an appropriate extension cord with the correct gauge and length for the intended purpose.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for both the electrical cord and the devices or appliances you are using. This includes information on voltage compatibility, maximum load capacity, and proper usage guidelines.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of electrical accidents and ensure a safe working environment when using electrical cords.
Conclusion
Having a clear understanding of electrical cords and knowing how to identify the hot wire is essential for safe and efficient usage of electrical devices and appliances. By understanding the components of electrical cords, such as conductors, insulation, and sheathing, you can better grasp the importance of proper handling and maintenance.
Identifying the hot wire can be done through various methods, including color coding and the use of a multimeter. However, when in doubt, it is always best to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician to ensure accurate identification and proper installation.
Remember, safety should always be a top priority when working with electrical cords. Following safety precautions such as disconnecting power before handling cords, inspecting cords for damage, avoiding overloads, and handling cords with care can help prevent accidents and protect both individuals and property.
By incorporating these safety measures and applying the knowledge gained from this article, you can confidently and responsibly handle electrical cords and enjoy safe electrical usage in your everyday life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Understanding Electrical Cords: How To Identify A Hot Wire
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “Understanding Electrical Cords: How To Identify A Hot Wire”