Home>Articles>Our Helpful Guide To Understanding Electrical Cables And Wires


Articles
Our Helpful Guide To Understanding Electrical Cables And Wires
Modified: January 6, 2024
Looking for informative articles on understanding electrical cables and wires? Our helpful guide provides all the insights you need to know about this essential topic.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our helpful guide to understanding electrical cables and wires. Whether you are a homeowner, electrician, or simply someone interested in learning more about electrical systems, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of the different types of cables and wires used in electrical installations.
Electrical cables and wires play a critical role in delivering electricity from a power source to various electrical devices and appliances. They are essential components of any electrical system, ensuring the safe and efficient transmission of power.
In this guide, we will explore the various types of electrical cables and wires, the importance of understanding electrical conductors, the role of insulation and jacketing materials, the different sizes and gauges available, color coding and markings, as well as safety precautions to consider when working with these components.
Whether you are embarking on a DIY project or looking to gain a better understanding of electrical systems, having a solid foundation in electrical cables and wires is essential. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions about electrical installations, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the safety of yourself and those around you.
So, let’s dive in and explore the world of electrical cables and wires!
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the different types of electrical cables and wires, the role of insulation and jacketing materials, and the importance of proper safety precautions is crucial for safe and successful electrical installations and maintenance.
- Prioritizing safety, following proper guidelines, and seeking assistance from qualified electricians when in doubt are essential for minimizing risks and ensuring a reliable electrical system when working with electrical cables and wires.
Read more: What Is Red In Electrical Wire
Types of Electrical Cables and Wires
Electrical cables and wires come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Understanding the different types will help you choose the right cable or wire for your specific needs. Here are some common types:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated copper wires twisted together to minimize electromagnetic interference. They are commonly used in Ethernet networking and telephone applications.
- Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cables have a central conductor surrounded by insulation, a metallic shield, and an outer sheath. They are widely used in television and internet applications.
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals through thin glass or plastic fibers. They offer high bandwidth, low signal loss, and are used in telecommunications and high-speed internet connections.
- Shielded Cable: Shielded cables have additional layers of shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference. They are commonly used in industrial settings and areas with high levels of electrical noise.
- Armored Cable: Armored cables have a protective metal or plastic sheath for added mechanical protection. They are often used in outdoor and underground installations.
- Ribbon Cable: Ribbon cables consist of multiple parallel conductors placed side by side, often used for internal computer connections, such as connecting a hard drive to a motherboard.
- Direct Burial Cable: Designed for underground installations, direct burial cables have waterproof insulation and protection against soil corrosion. They are commonly used in outdoor lighting and irrigation systems.
- Marine Cable: Marine cables are designed to withstand harsh marine environments, with resistance against moisture, oil, and UV radiation. They are used in boats, ships, and offshore installations.
These are just a few examples of the many types of electrical cables and wires available. It’s important to choose the right type based on your specific application requirements to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Understanding Electrical Conductors
Electrical conductors are the materials that allow the flow of electric current. They are the vital component of electrical cables and wires, as they are responsible for transmitting electricity from the power source to the connected devices or appliances.
The most common material used for electrical conductors is copper due to its excellent conductivity properties. Copper wires are widely used in various electrical applications. Copper offers low resistance to the flow of electrical current, ensuring efficient transmission and minimal power loss.
Another material commonly used for electrical conductors is aluminum. While aluminum has a slightly lower conductivity than copper, it is a cost-effective alternative. Aluminum conductors are often used in larger cables and overhead power lines.
When choosing electrical conductors, it’s important to consider factors such as the conductivity, ampacity (current-carrying capacity), flexibility, and environmental conditions. This will ensure that the conductors can handle the required electrical load safely and efficiently.
Keep in mind that the size of the conductor, known as the gauge, also plays a significant role. The gauge determines the conductor’s capacity to carry current. Smaller gauge conductors have larger diameters and can carry more current, while larger gauge conductors have smaller diameters and can carry less current.
It’s important to select the appropriate gauge of conductor based on the electrical load and the distance it needs to travel. Using an undersized conductor can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential electrical hazards, while an oversized conductor can be wasteful and unnecessary.
In applications where high temperatures or extreme environments are prevalent, special types of conductors may be required. For example, heat-resistant conductors are designed to withstand high temperatures without losing their conductivity properties. They are commonly used in ovens, heaters, and other high-temperature appliances.
Understanding electrical conductors is crucial in ensuring proper installation, optimizing electrical system performance, and preventing electrical hazards. If you are unsure about the type or size of conductor to use in a specific application, it’s always wise to consult with a qualified electrician or refer to the appropriate electrical codes and standards.
Insulation and Jacketing Materials
Insulation and jacketing materials play a crucial role in electrical cables and wires by providing protection and insulation against electrical current and external factors. They help prevent electrical leakage, short circuits, and damage to the conductors.
Various materials are used for insulation and jacketing, each with different properties suited for specific applications. Here are some commonly used insulation and jacketing materials:
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC is one of the most widely used materials for both insulation and jacketing. It is cost-effective, flexible, and provides excellent insulation properties. PVC cables are commonly used in residential and commercial electrical installations.
- Polyethylene (PE): PE is another popular material used for insulation. It offers good resistance to moisture, abrasion, and chemicals. PE cables are often used in outdoor and underground installations.
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): XLPE is a thermosetting material known for its excellent thermal stability and high resistance to heat. It is commonly used in high-voltage applications, such as power distribution lines and electrical substations.
- Rubber: Rubber is a flexible and durable insulation material that provides excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. It is commonly used in portable tools, extension cords, and industrial applications.
- Silicone: Silicone is a high-temperature insulation material known for its exceptional heat resistance and flexibility. It is commonly used in high-temperature applications, such as ovens, furnaces, and automotive wiring.
- Nylon: Nylon is a strong and durable material used for jacketing purposes. It offers excellent resistance to moisture, abrasion, and chemicals. Nylon jackets are commonly used in high-stress applications, such as industrial machinery and heavy-duty equipment.
Choosing the appropriate insulation and jacketing materials is essential to ensure the longevity, safety, and performance of electrical cables and wires. Factors to consider when selecting materials include the environment, temperature, moisture levels, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
It’s also important to adhere to the relevant electrical codes and standards when selecting and installing insulation and jacketing materials. Consulting with a qualified electrician or referring to the appropriate guidelines can help ensure compliance and safe electrical installations.
Different Sizes and Gauges of Cables and Wires
In electrical cables and wires, size matters. The size, often referred to as the gauge or AWG (American Wire Gauge), plays a crucial role in determining the current-carrying capacity and the electrical resistance of the wire.
The gauge of a wire is inversely proportional to its size. In other words, the smaller the gauge number, the larger the wire diameter. The larger the wire diameter, the more current it can safely carry. This is because a larger wire offers less electrical resistance, allowing for a smoother flow of electricity.
The most commonly used gauges for residential and commercial electrical wiring are 14, 12, and 10 AWG. These gauges are suitable for general-purpose applications, such as lighting, outlets, and small appliances. The larger the gauge number, the smaller the wire diameter and the lesser the current-carrying capacity.
In situations where higher currents are present, such as in heavy-duty appliances, power tools, or HVAC systems, thicker wires with lower gauge numbers are required. For example, 8 AWG or 6 AWG wires may be used to handle higher current loads.
It’s important to choose the appropriate wire size based on the electrical load and the distance the wire needs to travel. Using an undersized wire can result in overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards. On the other hand, using an oversized wire can be wasteful and unnecessary.
When working with cables and wires, it’s also important to consider their sizes. The size refers to the overall dimensions of the cable, including the conductors and insulation. Larger cables are often used for high-current applications, such as main power feeders or industrial installations, where more current-carrying capacity is required.
Consulting with a qualified electrician or referring to electrical codes and standards will help you determine the appropriate wire sizes and gauges for your specific application. Taking into account factors such as the electrical load, distance, ambient temperature, and allowable voltage drop will ensure the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system.
When working with electrical cables and wires, always make sure to use the right gauge for the current load to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
Read more: What Is SOOW Electrical Wire
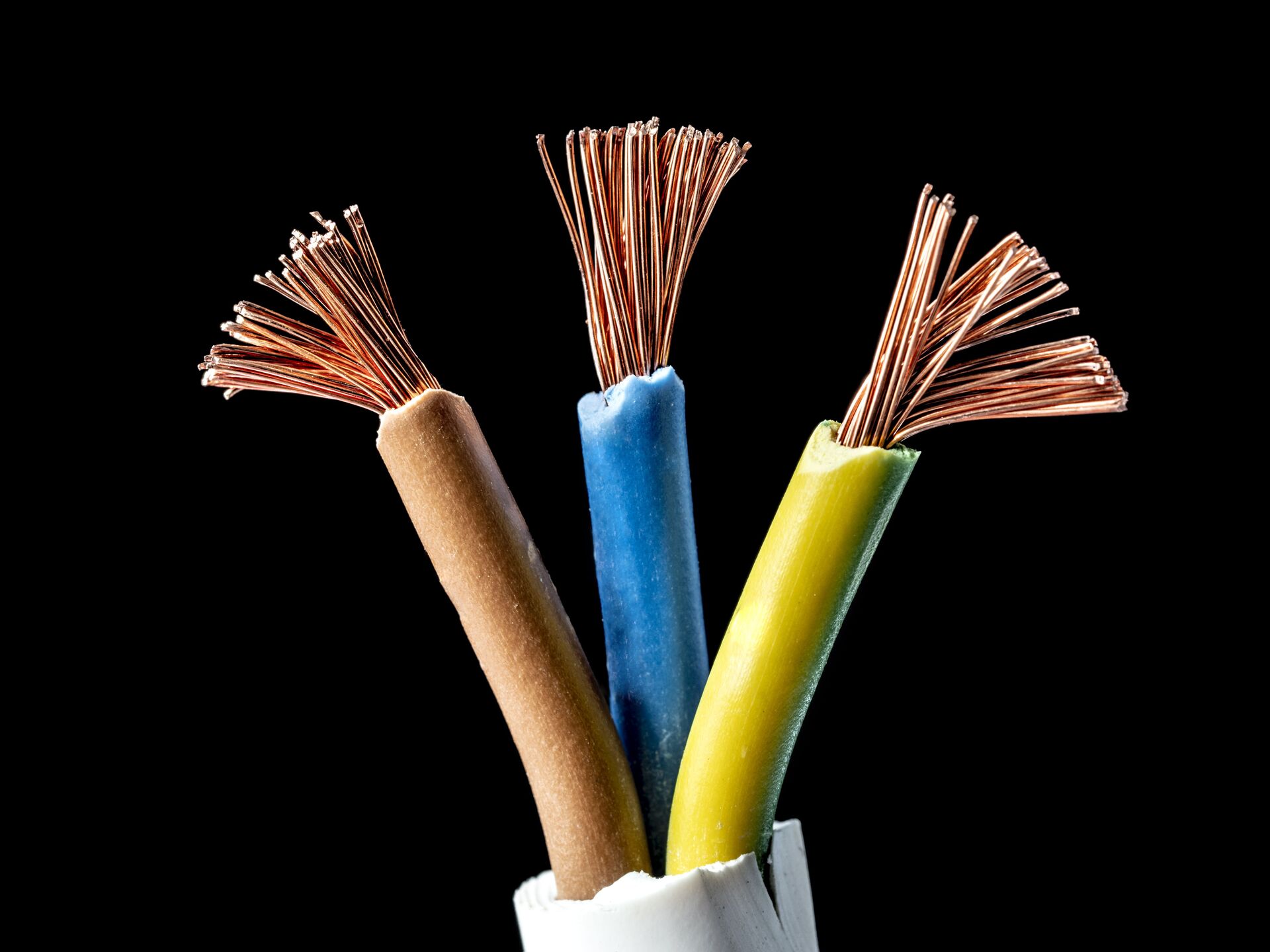
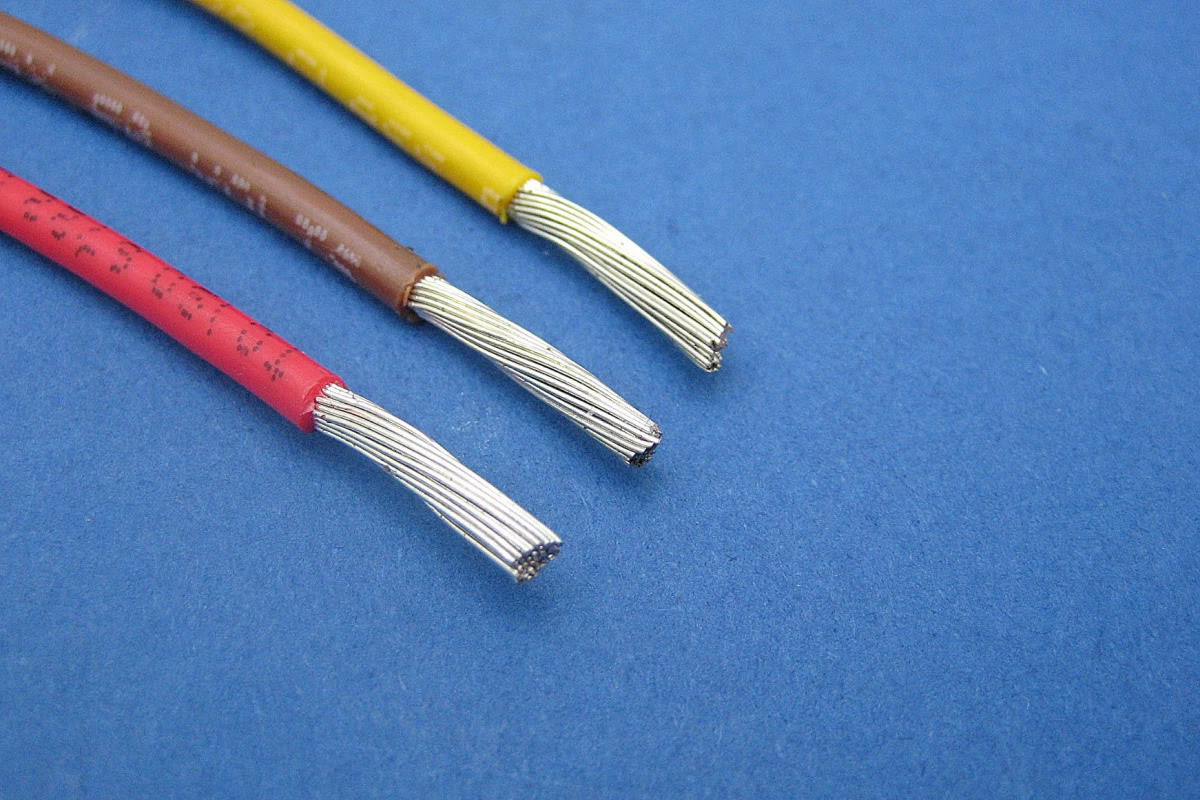
Color Coding and Markings
Color coding and markings on electrical cables and wires serve important purposes, providing crucial information about their intended use, voltage rating, and other specifications. Understanding these color codes and markings is essential for proper identification and safe installation.
Here are some commonly used color codes and markings:
- Color Coding of Insulation: In many countries, electrical wires are color-coded to indicate their function or purpose. For example, in the United States, black wires are typically used for hot or live wires, white or gray wires for neutral wires, and green or bare wires for ground wires. However, it’s important to note that color coding can vary depending on local regulations and standards.
- Stripes and Tracers: In addition to solid colors, cables and wires may have stripes or tracers along their length. These markings provide additional information about the wire, such as its voltage rating or special properties.
- Printed Markings: Some cables and wires have printed markings directly on the insulation. These markings usually include important information such as the manufacturer’s name, cable type, gauge or size, voltage rating, and sometimes temperature ratings or special certifications.
- Subtle Differences in Colors: In certain cases, subtle differences in color or shade may indicate variations in the wire’s properties. For example, a light blue wire may indicate a low-voltage wire, while a dark blue wire may indicate a higher voltage rating.
- International Standards: Different countries may have their own specific color coding standards. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the applicable standards and guidelines in your region to ensure proper identification and usage.
Color coding and markings on cables and wires help electricians and installers easily identify wires, making it safer and more efficient to work with electrical systems. They also aid in troubleshooting, maintenance, and repair tasks.
It’s essential to always verify the color coding and markings on the cables and wires before installation or any electrical work. Any deviation from the expected color coding should be thoroughly investigated and confirmed to avoid any potential hazards or issues.
If you are unsure about the color coding or markings of a specific wire, consult with a qualified electrician or refer to the appropriate electrical codes and standards in your area.
Working with Electrical Cables and Wires
Working with electrical cables and wires requires knowledge, skill, and adherence to safety practices to ensure proper installation and minimize the risks associated with electrical work. Here are some important considerations when working with cables and wires:
- Preparation and Planning: Before starting any electrical project, it’s crucial to thoroughly plan and prepare. Familiarize yourself with the project requirements, gather the necessary tools and materials, and ensure that the power supply is turned off to prevent accidental shock.
- Proper Handling: Handle cables and wires with care to avoid damaging the insulation or conductors. Avoid pulling, twisting, or bending them beyond their recommended limits. Any damaged cables or wires should be replaced to ensure safety and optimal performance.
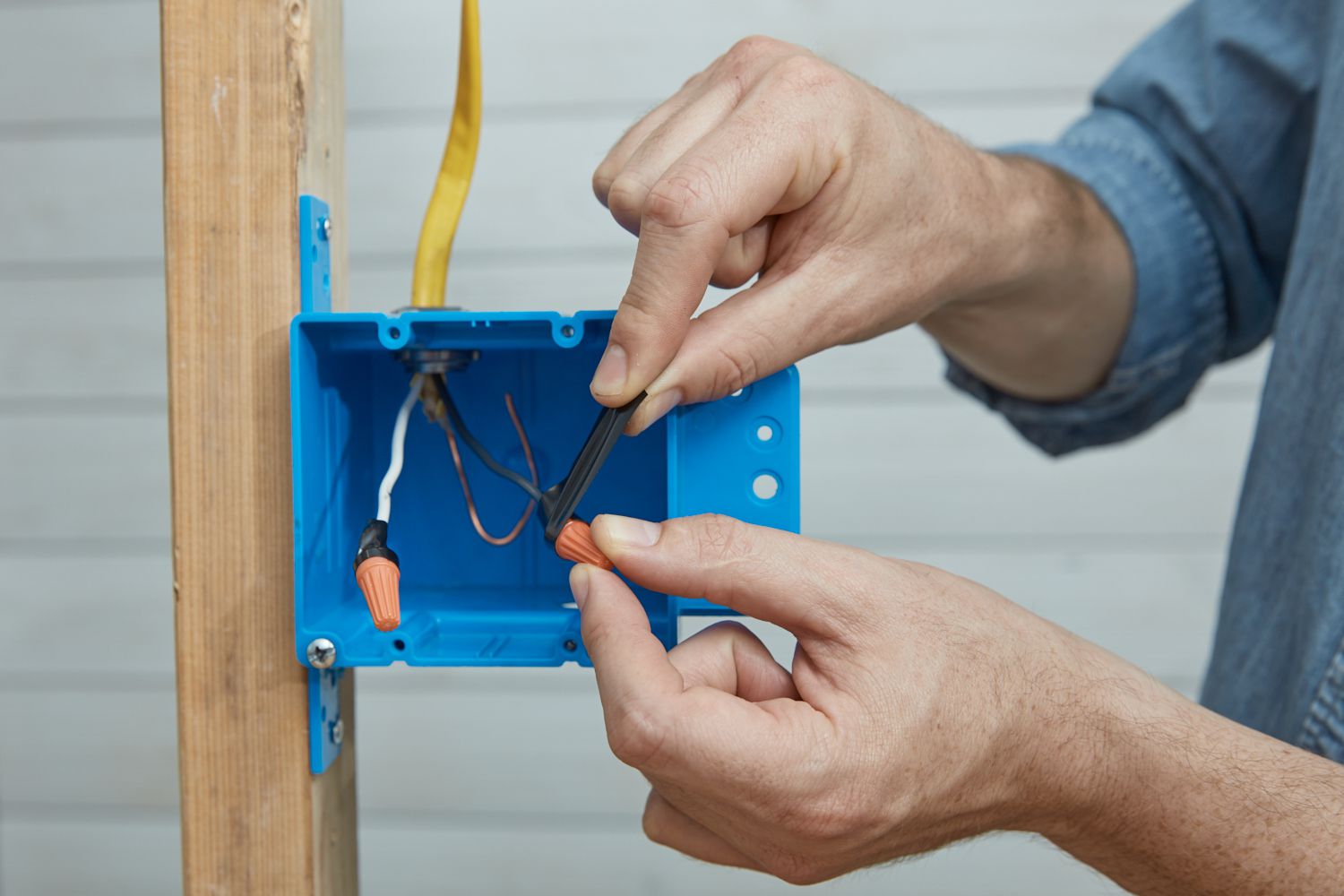
- Stripping the Insulation: When connecting wires, it may be necessary to strip a portion of the insulation to expose the bare conductors. Use a wire stripper or a sharp knife, being careful not to cut into the conductor. Remove only the necessary amount of insulation to make a secure connection.
- Creating Secure Connections: Properly connecting wires is essential for electrical continuity and safety. Use appropriate connectors, such as wire nuts, terminal blocks, or crimp connectors, and follow manufacturer instructions for proper installation. Ensure that connections are secure, tight, and free from any loose strands or exposed conductors.
- Safeguarding Against Short Circuits: Take precautions to avoid short circuits, which can be caused by the unintentional contact between live wires or between live wires and ground. Use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to insulate exposed conductors and prevent accidental short circuits.
- Testing and Inspection: After completing the installation or repair, it’s crucial to test the electrical circuits using a voltage tester or a multimeter to ensure that power is flowing correctly. Inspect the connections, cables, and wires for any signs of damage or overheating. Make any necessary adjustments or repairs before restoring power.
Always prioritize safety when working with electrical cables and wires. It’s important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from electrical hazards. Additionally, ensure that your work area is well-lit and properly grounded.
If you are unsure about any aspect of working with electrical cables and wires or if the project involves complex wiring or high-voltage systems, it’s recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge and experience to handle the job safely and efficiently.
By following proper guidelines, being diligent, and paying attention to safety at all times, you can successfully work with electrical cables and wires while minimizing risks and ensuring a reliable electrical system.
Safety Precautions
Working with electricity can be hazardous if not approached with caution. To ensure the safety of yourself and others, it’s essential to follow proper safety precautions when working with electrical cables and wires. Here are some important safety measures to keep in mind:
- Turn Off Power: Before starting any electrical work, always turn off the power supply to the circuit you will be working on. This can be done by switching off the circuit breaker or removing the corresponding fuse. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the power is off before proceeding.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE to protect yourself from electrical hazards. This includes insulated gloves, safety glasses, and, if necessary, flame-resistant clothing. PPE helps minimize the risk of electric shock, burns, and other injuries.
- Inspect Cables and Wires: Before working with cables and wires, carefully inspect them for any signs of damage, such as frayed insulation or exposed conductors. Damaged cables and wires should be replaced before proceeding. Additionally, check for any heat or burning smells near electrical connections, as this may indicate a problem or overheating.
- Avoid Water Contact: Never work on electrical circuits or devices with wet hands or in wet conditions. Water is a conductor of electricity and increases the risk of electric shock. Keep work areas dry and use appropriate insulation techniques to protect against moisture ingress.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not overload electrical circuits by connecting devices or appliances that draw more current than the circuit can safely handle. Overloading increases the risk of overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage. When in doubt, consult a qualified electrician to determine the appropriate electrical load for a circuit.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Grounding is a vital safety measure in electrical systems. Ensure that your electrical devices, appliances, and circuits are properly grounded. Faulty grounding can lead to electrical shock and other hazards. Consult with an electrician or refer to electrical codes and standards to ensure proper grounding practices.
- Work in Well-Ventilated Areas: When working on electrical projects, ensure that the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of potentially hazardous gases or fumes. This is especially important when working with soldering irons or other tools that generate heat or produce fumes.
- Properly Dispose of Waste: Dispose of electrical waste, such as old cables, wires, and components, in accordance with local regulations. Improper disposal can lead to environmental pollution and may pose health and safety risks.
Remember, electrical work can be complex and dangerous. If you are unsure about any aspect of the work or lack the necessary knowledge and skills, it’s always best to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician. They have the expertise to handle electrical installations, repairs, and maintenance safely and effectively.
By taking these safety precautions and being diligent when working with electrical cables and wires, you can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system.
Common Electrical Cable and Wire FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about electrical cables and wires:
- What is the difference between a cable and a wire?
- What is the purpose of insulation on electrical cables and wires?
- Do I need to follow specific regulations for color coding electrical cables and wires?
- What does the gauge of a wire indicate?
- How can I determine the appropriate wire size for my electrical project?
- Can I use different gauge wires together in an electrical circuit?
- Can I splice electrical cables and wires?
- What safety precautions should I take when working with electrical cables and wires?
A cable consists of multiple wires that are bound together, often with insulation and a protective jacket. A wire, on the other hand, is a single conductor used for transmitting electrical current.
The insulation on electrical cables and wires serves to protect against electrical shock, prevent short circuits, and minimize the risk of damage to the conductors. It also helps to maintain the integrity of the electrical current.
Yes, color coding regulations for electrical cables and wires may vary depending on your country or region. It’s crucial to be familiar with the applicable codes and standards to ensure proper identification and compliance.
The gauge of a wire indicates its size and current-carrying capacity. Smaller gauge numbers correspond to thicker wires capable of carrying higher currents, while larger gauge numbers correspond to thinner wires with lower current-carrying capacity.
The appropriate wire size for your project depends on factors such as the electrical load, distance, and voltage drop allowances. Consult with a qualified electrician, refer to electrical codes and standards, or use wire size calculators to determine the right size wire for your specific application.
It is not recommended to use different gauge wires together in a circuit, as the thinner wire may overheat and pose a safety risk. It’s crucial to use wires of the same gauge for a circuit, especially when connecting them.
Splicing electrical cables and wires is permissible in certain situations if done correctly using approved methods and materials. However, it is generally best to consult with a qualified electrician to ensure proper splicing techniques and compliance with electrical codes.
When working with electrical cables and wires, always follow safety precautions such as turning off the power supply, wearing appropriate PPE, inspecting cables and wires for damage, and avoiding contact with water. Refer to the safety precautions section in this guide for more details.
These are just a few common questions about electrical cables and wires. If you have any other specific inquiries or concerns, it’s always best to consult with a qualified electrician or refer to the appropriate codes and guidelines in your area.
Read more: How To Cap An Electrical Wire
Conclusion
Understanding electrical cables and wires is essential for anyone looking to work with electricity, whether as a homeowner, DIY enthusiast, or professional electrician. By having knowledge of the different types of cables and wires, understanding electrical conductors, knowing about insulation and jacketing materials, being familiar with wire gauges and color coding, and following proper safety precautions, you can ensure safe and successful electrical installations.
From twisted pair cables to coaxial cables, from PVC insulation to XLPE insulation, each component plays a crucial role in the efficient and reliable transmission of electrical current. By selecting the right cables and wires for your specific application, you can optimize performance, prevent hazards, and adhere to electrical codes and standards.
When working with electrical cables and wires, always prioritize safety. Turn off the power supply, use appropriate PPE, inspect cables and wires for damage, and follow proper installation techniques. Awareness of potential hazards and strict adherence to safety precautions can prevent accidents, electrical shocks, and fires.
Whether you are a homeowner undertaking a small DIY project or a professional electrician working on a complex electrical system, having a solid understanding of electrical cables and wires is crucial. It empowers you to make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical installations.
Remember, if you ever have doubts or concerns about working with electrical cables and wires, it is best to consult with a qualified electrician. They have the expertise and experience to guide you and ensure that the work is done correctly and safely.
By applying the knowledge gained from this guide, you can navigate the world of electrical cables and wires with confidence, ensuring a successful and secure electrical system.
Frequently Asked Questions about Our Helpful Guide To Understanding Electrical Cables And Wires
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Our Helpful Guide To Understanding Electrical Cables And Wires”