Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Become A CAD Technician
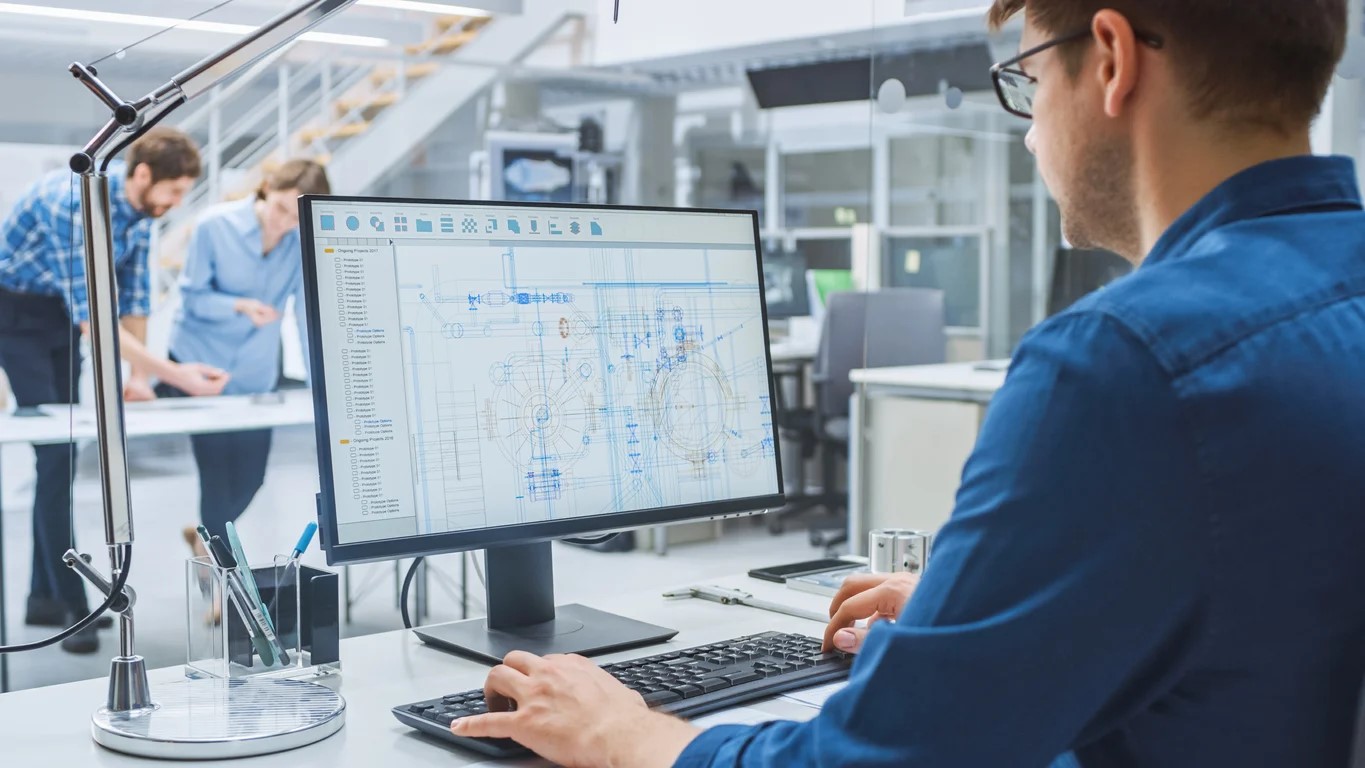


Architecture & Design
How To Become A CAD Technician
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to become a CAD technician in the field of architecture and design. Gain the skills needed to excel in this in-demand profession.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of CAD technicians! If you have a passion for design, a keen eye for detail, and a knack for problem-solving, then a career as a CAD technician may be the perfect fit for you. In this article, we will explore what it takes to become a CAD technician, including the necessary qualifications, skills, and training programs.
CAD, short for Computer-Aided Design, is a technology that has revolutionized the field of architecture, engineering, and construction. By using specialized software, CAD technicians create detailed technical drawings, blueprints, and 3D models of buildings, products, or mechanical components. These digital models serve as the foundation for the construction or manufacturing process.
As a CAD technician, you are responsible for translating design concepts into precise and accurate digital representations. You will work closely with architects, engineers, and other professionals to ensure that the final product meets the client’s requirements and complies with industry standards.
Being a CAD technician requires a unique combination of technical skills, creativity, and attention to detail. You must be proficient in CAD software, have a thorough understanding of engineering drawings, and possess strong problem-solving abilities. Additionally, effective communication and collaboration skills are essential, as you will often work as part of a team.
The demand for CAD technicians is steadily increasing, as industries continue to rely on digital design tools to streamline their processes and improve efficiency. Whether you aspire to work in architecture, manufacturing, or product design, this field offers a wide range of career opportunities.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the educational requirements, skills, and steps you can take to become a CAD technician. Whether you are just starting your career or looking to transition into the field, this guide will provide you with the information you need to succeed.
Key Takeaways:
- Becoming a CAD technician involves obtaining a high school diploma, pursuing technical training, gaining practical experience, and considering professional certification. Continuous learning and networking are essential for success in this dynamic field.
- Specializing in a specific industry or CAD software, building a portfolio, and seeking mentorship are crucial steps for aspiring CAD technicians. Embracing opportunities for growth and staying updated with industry trends are key to a rewarding career.
Read more: How To Become A BIM Technician
What is a CAD Technician?
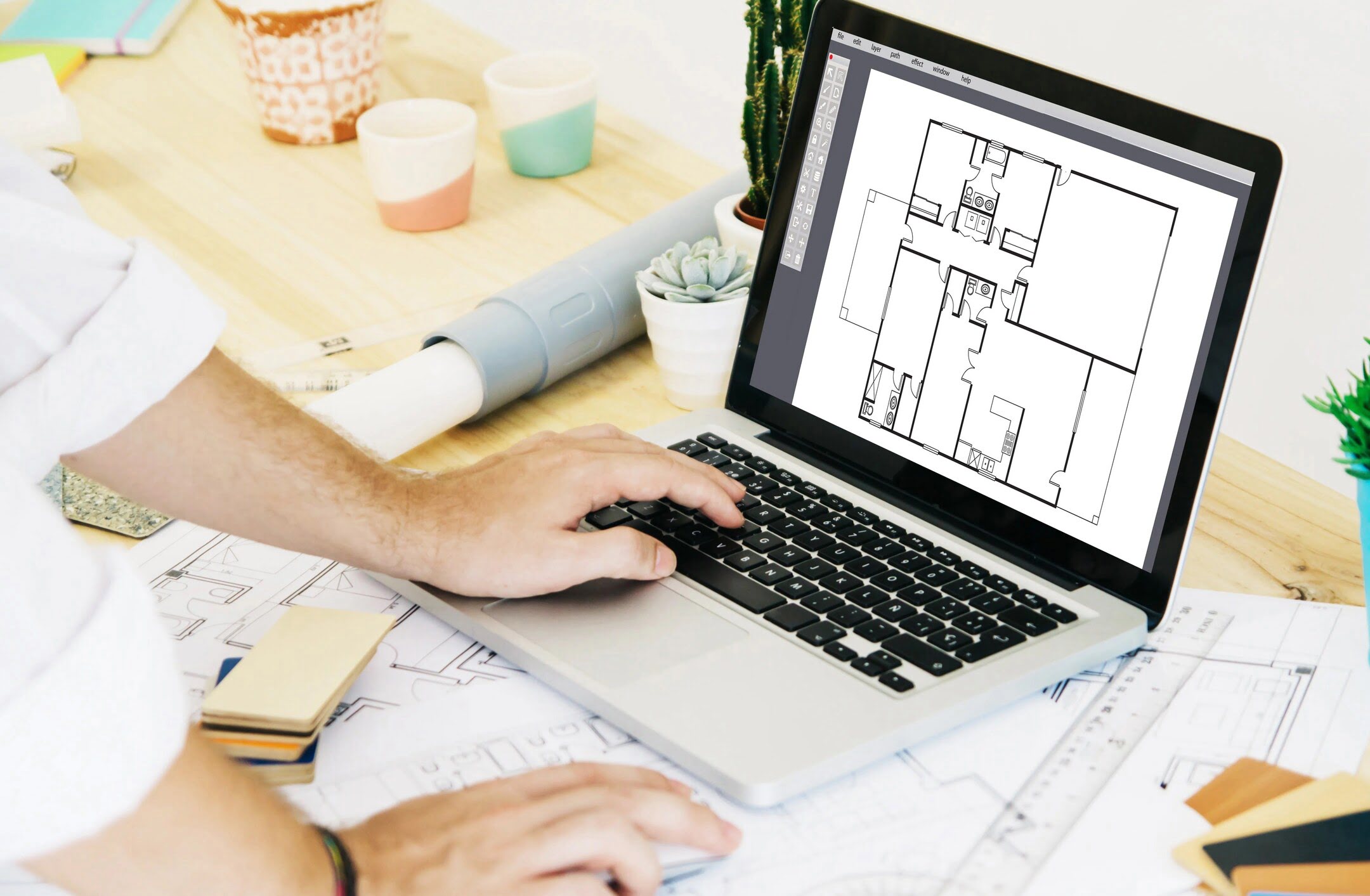
A CAD technician, also known as a drafter or CAD operator, is a skilled professional who uses computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed technical drawings and 3D models. These digital representations are essential in the design, development, and manufacturing processes in various industries, including architecture, engineering, construction, and product design.
The primary role of a CAD technician is to transform conceptual designs, ideas, or sketches into precise and accurate digital models. They work closely with architects, engineers, and designers to translate their visions into tangible plans and blueprints. This includes creating detailed drawings of building structures, mechanical components, electrical circuits, or product designs.
CAD technicians utilize specialized software programs to design, analyze, and modify 2D and 3D models. They are responsible for ensuring that the designs comply with industry standards, regulations, and client specifications. They may also need to consider factors such as material properties, structural integrity, and manufacturing processes while creating the digital models.
One of the key advantages of CAD technology is the ability to view and manipulate the designs in a virtual environment before they are turned into physical objects. CAD technicians can test the functionality and feasibility of their designs, identify potential issues, and make necessary modifications to optimize the final product.
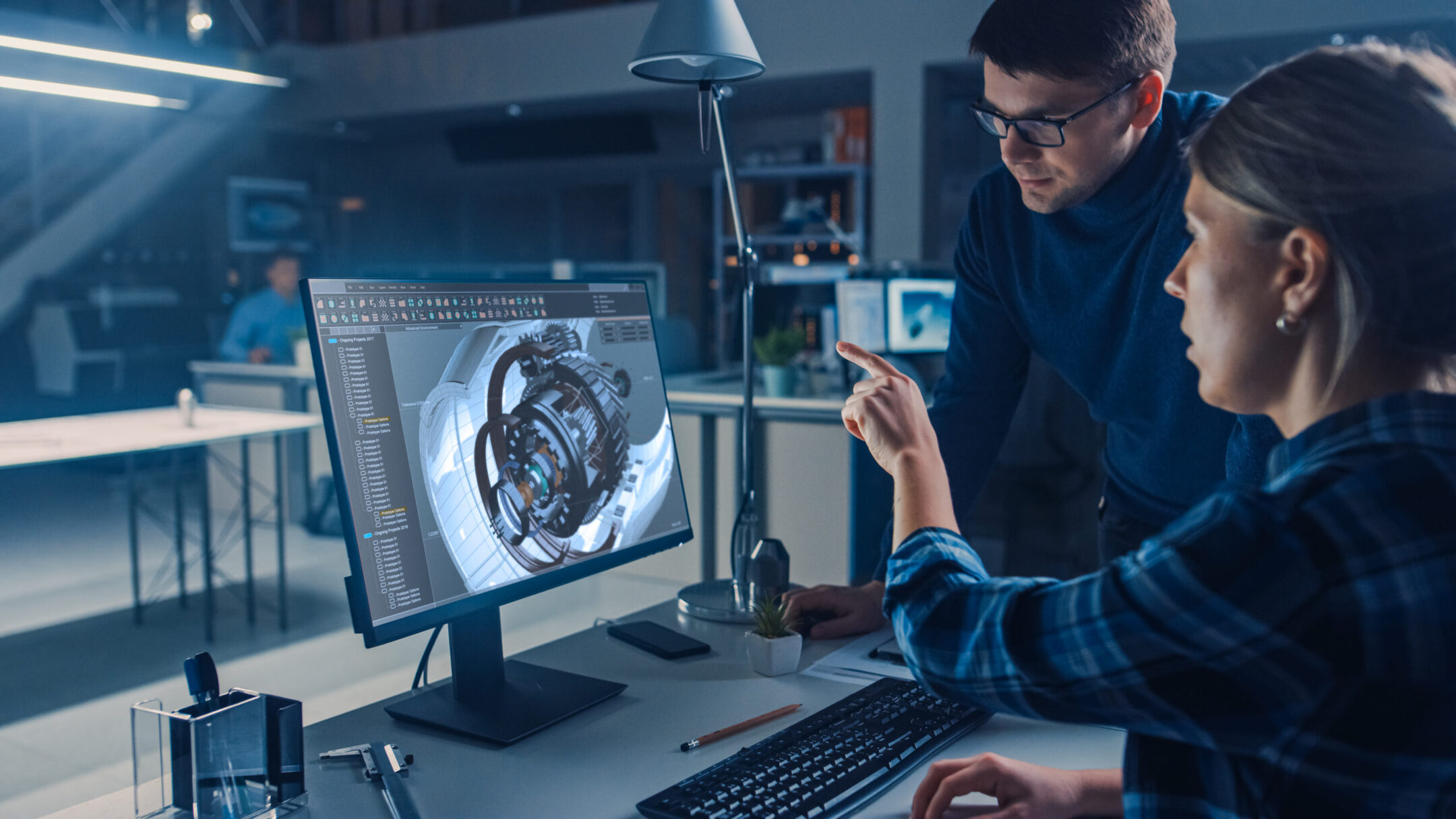
In addition to creating technical drawings, CAD technicians may also be involved in tasks such as creating material lists, generating cost estimates, and collaborating with other professionals involved in the design and construction process. Effective communication and collaboration skills are crucial for CAD technicians to work effectively as part of a multidisciplinary team.
Overall, CAD technicians play a vital role in bridging the gap between design concepts and tangible outcomes. By harnessing the power of CAD software, they contribute to the efficient and accurate creation of structures, products, and systems that meet the needs of clients and consumers.
In the next sections, we will explore the educational requirements, skills, and training programs that can help you embark on a successful career as a CAD technician.
Educational Requirements
To become a CAD technician, it is essential to have a solid educational foundation. While there is no specific degree requirement for entry-level positions, most employers prefer candidates with formal education and training in CAD technology and drafting. Here are the common educational paths for aspiring CAD technicians:
- High School Diploma or Equivalent: The first step to becoming a CAD technician is to obtain a high school diploma or an equivalent qualification. This educational milestone is necessary to expand your knowledge in core subjects such as mathematics, computer science, and technical drawing.
- Associate’s Degree or Technical Training: Although not always mandatory, obtaining an associate’s degree or completing a technical training program in CAD can give you an edge in the job market. These programs typically cover subjects such as drafting principles, CAD software proficiency, technical drawing techniques, and industry standards. Some community colleges and vocational schools offer specialized CAD programs that can be completed in as little as two years.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Engineering or Architecture: While not mandatory, a bachelor’s degree in engineering or architecture can provide a deeper understanding of the design principles, construction methods, and industry practices. This level of education may open up more advanced and specialized job opportunities within the field.
In addition to formal education, continuous learning and staying up-to-date with the latest CAD software and industry trends are crucial for CAD technicians. Many professionals pursue online courses, attend workshops, and participate in professional development programs to enhance their skills.
It is important to note that while education is essential, practical experience and hands-on skills are equally valuable. Many employers value relevant experience and portfolio projects that showcase your ability to apply CAD skills in real-world scenarios.
In the following sections, we will explore the key skills required to excel as a CAD technician and the specific CAD software proficiency you should aim to achieve. These skills, coupled with a strong educational foundation, will help you stand out in the competitive job market and build a successful career in CAD technology.
Skills and Qualifications
As a CAD technician, possessing a diverse set of skills and qualifications is essential to thrive in this field. Here are some of the key skills and qualifications that can help you excel as a CAD technician:
- Technical Drawing Skills: Proficiency in technical drawing is the foundation of a CAD technician’s role. This includes knowledge of geometric construction, orthographic projections, sectional views, dimensioning, and annotations. Being able to interpret and create accurate technical drawings is crucial for creating precise and detailed CAD models.
- CAD Software Proficiency: A CAD technician must be well-versed in the use of CAD software. This includes mastering popular CAD software applications such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Revit, or CATIA. Having a strong understanding of the software’s functionalities, tools, and features will enable you to create complex designs, optimize workflows, and ensure accuracy in your work.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: CAD technicians often encounter design challenges and technical issues that require problem-solving skills. Being able to analyze problems, develop creative solutions, and make informed decisions is crucial in this role. You should have a strong ability to think critically, troubleshoot issues, and adapt to changing design requirements.
- Attention to Detail: CAD technicians are responsible for creating precise and accurate digital models. Paying attention to detail is essential to ensure that the designs are error-free and comply with specific requirements. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and other specifications to guarantee the quality and reliability of the final product.
- Communication and Collaboration Skills: Effective communication and collaboration skills are vital as CAD technicians often work as part of a team. Clear and concise communication with colleagues, clients, and other stakeholders is crucial for understanding project requirements, addressing feedback, and ensuring project success. Additionally, being able to collaborate with other professionals such as architects, engineers, or project managers is essential for successful project completion.
In addition to these skills, having a strong attention to detail, being highly organized, and having a passion for learning and staying updated with the latest CAD technologies and industry trends are valuable qualifications for a CAD technician.
Continuous improvement of these skills and qualifications can be achieved through practice, hands-on experience, professional development courses, and networking within the CAD community. By honing these skills and qualifications, you will be well-prepared to embark on a successful career as a CAD technician.
CAD Software Proficiency
As a CAD technician, having proficiency in CAD software is crucial to successfully perform your job duties. CAD software allows you to create, modify, and analyze detailed 2D and 3D models, bringing your design concepts to life. Here are some essential points to consider regarding CAD software proficiency:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is one of the most popular CAD software applications used by professionals in various industries. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for creating precise 2D and 3D drawings, annotations, and documentation. Proficiency in AutoCAD is highly valued in the job market and is often a requirement for many CAD technician positions.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a powerful 3D CAD software commonly used for mechanical design and engineering. It offers a wide range of advanced features for creating complex parts, assemblies, and simulations. Proficiency in SolidWorks can open up opportunities in industries such as manufacturing, product design, and engineering.
- Revit: Revit is a Building Information Modeling (BIM) software widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. It allows you to create intelligent 3D models of buildings, incorporating design, construction, and documentation information. Proficiency in Revit is essential for CAD technicians working on architectural and construction projects.
- CATIA: CATIA is a CAD software widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and industrial design industries. It is known for its robust capabilities in designing complex surfaces, assemblies, and parts. Proficiency in CATIA can open up career opportunities in industries that require advanced geometric modeling and engineering analysis.
- Other CAD Software: Additionally, there are numerous other CAD software applications available, each with its own set of features and specializations. These include Fusion 360, Inventor, SketchUp, and more. Familiarity with multiple CAD software platforms can enhance your versatility as a CAD technician and make you more adaptable to different project requirements.
Proficiency in CAD software is typically developed through a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, and self-learning. Many educational programs and training courses provide instruction on specific CAD software applications, allowing you to gain practical experience and develop your skills.
Furthermore, staying updated with the latest versions of CAD software and keeping abreast of new tools and features is crucial. Software providers often offer certifications or training programs to enhance your expertise in their specific CAD software. Obtaining these certifications can demonstrate your proficiency to employers and strengthen your resume.
Ultimately, having a strong command of CAD software is essential for a CAD technician to efficiently create accurate and detailed digital models. Continuously honing your CAD software proficiency will enhance your productivity, improve your employability, and ensure success in your career as a CAD technician.
Read more: How To Become A Plumbing Technician
Understanding Engineering Drawings
As a CAD technician, one of your primary responsibilities is to create technical drawings that accurately represent design concepts. To achieve this, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of engineering drawings. Engineering drawings serve as a common language for engineers, architects, and other professionals involved in the design and construction process. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to understanding engineering drawings:
- Different Types of Engineering Drawings: Engineering drawings can take various forms, depending on the purpose and scope of the project. Common types include assembly drawings, detail drawings, schematic diagrams, and isometric drawings. Each type has its specific purpose and provides detailed information for different aspects of the design.
- Technical Standards and Conventions: Engineering drawings adhere to specific technical standards and conventions to ensure consistency and clarity. These standards include dimensioning practices, symbols, line types, and notation systems. Familiarize yourself with industry standards, such as ANSI/ASME Y14.5 or ISO 128, to create drawings that are universally understood and easily interpreted by others.
- Reading and Interpreting Drawings: The ability to read and interpret engineering drawings is crucial as a CAD technician. You must be able to understand the different views, such as plan views, elevations, sections, and isometric perspectives. Additionally, you should be able to interpret dimensions, tolerances, and annotations to accurately create the digital models.
- Scale and Proportion: Engineering drawings often include scales to accurately represent the size and proportions of objects. Understanding scale is essential for creating drawings that accurately reflect the real-world dimensions. It is important to know how to calculate scale ratios and accurately represent objects in relation to the reference dimensions.
- Materials and Symbols: Engineering drawings may include symbols and notations to indicate specific materials, finishes, or manufacturing processes. Familiarize yourself with commonly used symbols such as weld symbols, surface finish symbols, and fastener notations. Understanding these symbols ensures that your digital models accurately represent the intended specifications.
Developing a strong understanding of engineering drawings requires practice and experience. Study sample drawings, reference books, and online resources to familiarize yourself with the different components and conventions. Additionally, working closely with engineers, architects, or senior CAD technicians can provide invaluable insight into interpreting and creating accurate drawings.
By mastering the skills of understanding engineering drawings, you will be equipped to create precise and accurate digital models that convey the design intent effectively. This expertise will enable you to collaborate seamlessly with other professionals and contribute to the successful execution of various design projects.
Technical Drawing Skills
As a CAD technician, possessing strong technical drawing skills is essential to effectively create and interpret detailed designs. Technical drawing skills provide the foundation for accurately communicating design concepts and specifications. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to technical drawing skills:
- Geometry and Construction: Technical drawing requires a solid understanding of geometric principles and construction techniques. You should be familiar with concepts such as points, lines, angles, and curves. Mastery of construction methods, including bisecting angles, perpendicular and parallel lines, and tangent constructions, is crucial for creating accurate drawings.
- Orthographic Projection: Orthographic projection is the method used to represent three-dimensional objects in two dimensions. It involves accurately projecting different views of an object onto a 2D plane, such as top, front, and side views. Proficiency in creating accurate orthographic projections is essential for CAD technicians to ensure precise representation of the design.
- Sectional Views: Sectional views are used to represent the internal structure of objects by cutting them along specific planes. Being able to interpret and create sectional views is important, as it provides valuable insight into the internal components and dimensions of a design. Understanding different types of sectional views, such as full sections, half sections, and revolved sections, is crucial for accurately representing the design.
- Dimensioning: Dimensioning is the process of indicating the size and location of features of a design on a technical drawing. Proficiency in dimensioning ensures that the digital models accurately represent the intended specifications. It involves using proper dimensioning techniques, including linear dimensions, angular dimensions, and tolerances.
- Annotations and Symbols: Annotations and symbols are used to provide additional information and clarify specific features on a technical drawing. Understanding common symbols and annotations, such as surface finishes, fasteners, or welding symbols, is important for creating accurate and comprehensive drawings. Clear and concise annotations ensure that the intended specifications are communicated effectively.
Developing technical drawing skills takes practice and experience. Familiarize yourself with drafting tools, such as compasses, rulers, protractors, and drafting software, to effectively create accurate drawings. Study reference materials, textbooks, and online resources to expand your knowledge and refine your technical drawing skills.
Additionally, working on real-world projects under the guidance of experienced professionals can provide valuable hands-on experience and help you develop a keen eye for detail. Continuously practicing and challenging yourself to explore more complex drawing tasks will enhance your technical drawing skills over time.
By honing your technical drawing skills, you will be equipped to create precise and accurate digital models that effectively capture the design intent. These skills will enable you to create detailed and comprehensive drawings that facilitate successful collaboration with architects, engineers, and other professionals in the design and construction process.
Problem-Solving Abilities
As a CAD technician, strong problem-solving abilities are essential to navigate the challenges that arise in the design and drafting process. Problem-solving skills allow you to tackle complex design issues, make informed decisions, and ensure the successful completion of projects. Here are some key considerations when it comes to problem-solving abilities:
- Analytical Thinking: Problem-solving starts with the ability to analyze and understand the problem at hand. CAD technicians must be adept at breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable components. This involves critically assessing the design requirements, identifying potential issues or conflicts, and developing strategies to address them effectively.
- Critical Thinking: CAD technicians must be skilled in critical thinking, which involves evaluating different options and making informed decisions. This includes considering factors such as feasibility, efficiency, cost implications, and design constraints. By analyzing the pros and cons of various solutions, CAD technicians can choose the most appropriate approach to solve the problem at hand.
- Creativity: Problem-solving often requires thinking outside the box and coming up with innovative solutions. CAD technicians should possess a creative mindset to explore different design possibilities and overcome constraints. By approaching problems with creativity, CAD technicians can find unique solutions that optimize the design and improve efficiency.
- Adaptability: Design projects can present unforeseen challenges and changes. CAD technicians must be adaptable and flexible in their problem-solving approach. This involves being open to new ideas, adjusting strategies and plans as needed, and finding alternative solutions when obstacles arise. Adaptability allows CAD technicians to navigate unexpected issues and keep the project on track.
- Attention to Detail: Problem-solving requires attention to detail to ensure accurate analysis and evaluation. CAD technicians should have a keen eye for detecting errors, inconsistencies, and potential issues within the design. By paying close attention to detail, they can identify problems early on and prevent costly mistakes in the final product.
Developing problem-solving abilities takes practice and experience. Engaging in projects that challenge your problem-solving skills, collaborating with other professionals, and seeking feedback from mentors can all contribute to your growth as a CAD technician.
Additionally, staying current with advancements in CAD technology and industry practices will enable you to approach problems with up-to-date knowledge and tools. Continuous learning and professional development programs can expand your problem-solving toolkit and enhance your abilities in the field.
By honing your problem-solving abilities, you will become a valuable asset to design teams, enabling you to efficiently overcome challenges, provide innovative solutions, and contribute to the successful completion of design projects.
Communication and Collaboration Skills
Effective communication and collaboration skills are essential for CAD technicians, as they often work closely with architects, engineers, and other professionals in the design and construction process. Strong communication and collaboration abilities facilitate effective project coordination, ensure clarity in design intent, and contribute to successful project outcomes. Here are key points to consider when it comes to communication and collaboration skills:
- Clear and Concise Communication: CAD technicians must be able to communicate their ideas, concerns, and project updates clearly and concisely. This includes verbal and written communication, as well as the ability to present design concepts and technical information effectively. Clear communication ensures that all team members have a shared understanding of the project goals and requirements.
- Active Listening: CAD technicians should be skilled in active listening, actively engaging with team members to understand their perspectives and concerns. By actively listening, CAD technicians can gather valuable feedback, clarify design requirements, and address any potential misunderstandings promptly. Active listening also fosters a collaborative and inclusive working environment.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaboration is key in the design and construction industry, and CAD technicians must excel in working as part of a team. CAD technicians need to collaborate with architects, engineers, project managers, and other stakeholders. This involves coordinating efforts, sharing information, and collectively working towards project objectives. Strong teamwork skills contribute to a cohesive and efficient project workflow.
- Presentation and Visualization: CAD technicians should be able to effectively present their designs and ideas to clients, team members, and other stakeholders using visual aids and presentations. The ability to communicate design intent through compelling visuals helps others understand the concepts and provides a platform for meaningful discussions and feedback.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: CAD technicians must be flexible and adaptable in their communication and collaboration approach. They need to be able to adjust to different communication styles, work within diverse teams, and adapt to changing project requirements. Being open to feedback, accepting alternative viewpoints, and being willing to compromise when necessary contribute to effective collaboration.
Developing communication and collaboration skills includes practices such as active participation in team projects, seeking feedback from colleagues, and developing an awareness of different communication styles and preferences. Actively seeking opportunities to collaborate with others and engaging in effective communication exchanges will enhance these skills over time.
Additionally, staying up-to-date with advancements in communication technologies, such as project management software and collaborative platforms, enables efficient sharing of information and effective team collaboration.
By honing your communication and collaboration skills, you will foster positive working relationships, facilitate effective project coordination, and contribute to the successful execution of design projects as a CAD technician.
Tip: Gain a strong understanding of CAD software and industry standards by pursuing a relevant degree or certification. Practice regularly to improve your skills and stay updated on the latest software advancements.
Read more: How To Become A HVAC Technician
Career Outlook and Opportunities
The field of CAD technology offers promising career prospects for individuals with the right skills and qualifications. As industries continue to adopt digital design tools and processes, the demand for skilled CAD technicians is expected to grow. Here is an overview of the career outlook and opportunities in CAD technology:
- Growing Industries: CAD technicians are in demand in various industries, including architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, and product design. These industries rely on CAD technology to streamline their design processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. With the increasing emphasis on sustainability and advanced manufacturing techniques, the need for CAD technicians is expected to grow.
- Technology Advancements: CAD technology continues to advance rapidly, introducing new features such as 3D modeling, BIM, simulation, and virtual reality integration. CAD technicians who stay updated with the latest software and tools will be in high demand in the market. Keeping up with technological advancements and continuously improving your skills will open doors to new career opportunities.
- Specialization Opportunities: Within the field of CAD technology, there are opportunities to specialize in specific industries or areas of expertise. By developing specialized skills in areas such as architectural drafting, mechanical design, electrical design, or civil engineering, you can differentiate yourself and pursue specialized career paths.
- Advancement Potential: With experience and additional training, CAD technicians can advance in their careers and take on more senior roles. This may include roles such as CAD manager, design engineer, project manager, or even transitioning into roles in product development or engineering management. Continuous skill development and professional growth contribute to long-term career success.
- Freelancing and Consulting: Many CAD technicians choose to work as freelancers or consultants, offering their services to multiple clients or companies. This provides flexibility in terms of work hours, project variety, and the ability to work remotely. Freelancing can be an excellent option for those seeking independence and diverse experiences.
To capitalize on the career opportunities in CAD technology, it is crucial to develop and maintain relevant skills and qualifications. This includes staying updated with the latest CAD software, continuously improving technical drawing skills, and keeping abreast of industry trends and best practices.
Building a strong professional network, staying engaged with industry associations, and actively seeking professional development opportunities are also key to success in this field. Attending conferences, participating in workshops, and obtaining industry certifications can enhance your credibility and open doors to new career prospects.
Overall, the career outlook for CAD technicians is promising, with opportunities for growth, specialization, and advancement. By staying proactive and adaptable, you can position yourself for a rewarding and successful career in the dynamic field of CAD technology.
Training and Certification Programs
When pursuing a career as a CAD technician, obtaining formal training and certifications can significantly enhance your skills, knowledge, and employability. The following are key training and certification programs to consider:
- Community College and Technical School Programs: Many community colleges and technical schools offer CAD programs that provide comprehensive training in drafting and CAD software. These programs typically offer associate degrees or certificates and cover topics such as technical drawing, CAD software proficiency, and industry standards. Choosing an accredited program ensures that you receive quality education and increases your chances of finding employment after graduation.
- Vendor-Specific Training: CAD software vendors often offer training programs and certifications for their specific software. For example, Autodesk offers the Autodesk Certified Professional certification for AutoCAD, Revit, and other CAD software. These certifications validate your proficiency and expertise in using specific software platforms, adding credibility to your resume and enhancing your job prospects.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Online learning platforms offer a wide range of CAD courses and tutorials that allow you to learn at your own pace. Websites such as Udemy, Coursera, and LinkedIn Learning provide comprehensive CAD courses taught by industry professionals. These online courses cover various CAD software applications, technical drawing techniques, and specialized topics, allowing you to acquire new skills from the comfort of your own home.
- Industry Associations and Professional Organizations: Industry associations and professional organizations, such as the American Design Drafting Association (ADDA) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), offer professional development resources, conferences, and certifications. These memberships provide access to industry insights, networking opportunities, and continuing education programs specific to CAD technicians.
- Apprenticeships and Internships: Apprenticeships and internships are valuable opportunities to gain practical experience and learn from experienced CAD technicians. Many companies offer these programs to provide hands-on training and mentorship. Participating in an apprenticeship or internship can help you develop industry-specific skills, build a professional network, and potentially secure full-time employment in the field.
When choosing a training program or certification, consider your career goals, budget, and learning preferences. It is essential to select a program that aligns with your specific interests and the industry in which you want to specialize. Remember that gaining practical experience through projects, internships, or freelance work alongside your training can further strengthen your skills and make you stand out as a competent CAD technician.
Investing in training and certification programs showcases your commitment to professional growth and demonstrates your expertise to potential employers. Continuously expanding your knowledge and skills through these programs will keep you up-to-date with the latest industry practices and help you succeed in your career as a CAD technician.
Steps to Becoming a CAD Technician
If you aspire to become a CAD technician, there are several steps you can take to achieve your career goals. The following are important steps to consider:
- Step 1: Obtain a High School Diploma or Equivalent: A high school diploma or equivalent qualification is typically the minimum educational requirement for becoming a CAD technician. Focus on courses that develop your mathematics, computer science, and technical drawing skills. These foundational subjects will provide a strong basis for your future studies and career in CAD technology.
- Step 2: Pursue Technical Training or an Associate Degree in CAD: While not always mandatory, obtaining technical training or an associate degree in CAD can significantly enhance your skills and employability. Look for community colleges or technical schools that offer CAD programs. These programs typically cover subjects such as technical drawing, CAD software proficiency, and industry standards. Consider choosing a program accredited by a recognized accrediting body for quality assurance.
- Step 3: Gain Experience through Internships or Entry-Level Positions: Practical experience is invaluable for CAD technicians. Look for internships or entry-level positions in CAD departments or design firms to get hands-on experience in the field. These opportunities allow you to apply your knowledge, develop your skills, and work alongside professionals who can provide mentorship and guidance.
- Step 4: Develop Specialization or Advanced Skills: Consider specializing in a specific industry or CAD software to set yourself apart from the competition. Focus on developing advanced skills in areas such as architectural drafting, mechanical design, or electrical design. This specialization can lead to more specialized job opportunities and career growth.
- Step 5: Consider Professional Certification: Professional certifications in specific CAD software platforms, such as AutoCAD or SolidWorks, can boost your credentials and showcase your proficiency to employers. Research the available certifications for the software you are proficient in and pursue the ones that align with your career goals. These certifications validate your skills and knowledge, making you a more competitive candidate in the job market.
Continuing education and staying updated with the latest advancements in CAD technology are also crucial for your professional development. Attend workshops, conferences, and online courses to expand your knowledge and sharpen your skills in response to evolving industry requirements.
Building a strong professional network is essential in the CAD industry. Join industry associations, participate in CAD-related forums, and engage in networking events to connect with other professionals, gain insights, and explore potential job opportunities.
Remember, becoming a CAD technician is a journey that requires dedication, continuous learning, and practical experience. By following these steps and being proactive in your career development, you can pave the way for a successful and fulfilling career in CAD technology.
Step 1: Obtain a High School Diploma or Equivalent
The first step in becoming a CAD technician is to obtain a high school diploma or an equivalent qualification. A high school education provides the foundational knowledge and skills necessary to excel in the field of CAD technology. Here are some key considerations for this initial step:
Focus on Math and Science: High school coursework in math and science subjects is essential for a career in CAD technology. Courses such as algebra, geometry, trigonometry, and physics provide a solid foundation for understanding the mathematical principles and concepts utilized in CAD software and technical drawings. These subjects develop your analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities, which are vital skills for CAD technicians.
Technical Drawing: If your high school offers technical drawing or drafting courses, take advantage of these opportunities. Technical drawing courses can familiarize you with the basics of drafting conventions, construction techniques, and concepts such as orthographic projection and dimensioning. These skills will serve as a valuable starting point for your CAD career.
Computer Science: Developing a basic understanding of computers and computer science principles is important for CAD technicians. Courses in computer science, computer-aided design, or computer programming can introduce you to the fundamentals of software applications and programming languages commonly used in CAD technology. These courses will provide a solid foundation for your future studies and career in CAD.
Extracurricular Activities: Consider participating in extracurricular activities that emphasize creativity, problem-solving, and technical skills. Joining clubs or competitions related to mathematics, engineering, or design can provide hands-on experience and further develop your understanding of these fields. Additionally, engaging in activities such as robotics, model-making, or computer programming can enhance your practical skills and demonstrate your dedication to pursuing a career in a technical field.
Continued Learning: High school is just the beginning of your educational journey. Even after securing a high school diploma, it is important to continue learning and stay updated with advancements in CAD technology and industry practices. Consider enrolling in online courses, attending workshops, or exploring self-study materials to expand your knowledge and skills in CAD software and technical drawing.
By obtaining a high school diploma or equivalent qualification, you lay the foundation for your future studies and career as a CAD technician. The knowledge and skills gained during this stage provide a solid base upon which you can build your expertise in CAD software, technical drawing, and problem-solving. Taking full advantage of the resources available to you in high school sets you on the path toward a successful career in CAD technology.
Read more: How Much Does A CAD Technician Earn
Step 2: Pursue Technical Training or Associate Degree in CAD
After obtaining a high school diploma or equivalent qualification, the next step in becoming a CAD technician is to pursue technical training or an associate degree in CAD. These programs provide in-depth instruction and hands-on experience in CAD software, technical drawing, and industry-specific practices. Here are key points to consider for this step:
Research CAD Programs: Start by researching community colleges, vocational schools, and technical institutes that offer CAD programs. Look for programs that align with your career goals and offer a comprehensive curriculum covering topics such as technical drawing, CAD software proficiency, and industry standards.
Program Accreditation: When selecting a CAD program, ensure that it is accredited by a recognized accrediting body or association. Accreditation ensures that the program meets specific educational standards and provides quality instruction. Graduating from an accredited program enhances your credentials and increases your employability.
Curriculum: Review the curriculum of the CAD program you are interested in. The curriculum should include courses that cover fundamental technical drawing principles, CAD software proficiency, 3D modeling, and design principles specific to your area of interest. Look for programs that offer a balance between theoretical knowledge and hands-on practical experience.
Faculty: Learn about the faculty members of the CAD program. Look for instructors with industry experience and expertise in CAD software applications. Knowledgeable and experienced instructors can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and guidance throughout your educational journey.
Internship Opportunities: Explore whether the CAD program offers opportunities for internships or cooperative education experiences. Internships provide real-world exposure and hands-on experience, giving you the chance to apply your knowledge and skills in a professional setting. These opportunities can help you build your portfolio and network with industry professionals.
Online Learning: If attending a physical campus is not feasible, consider online learning options. Many reputable institutions offer online CAD programs that provide flexibility in terms of scheduling and location. Online programs provide access to instructional materials, virtual labs, and interactive exercises to develop your CAD skills remotely.
Continued Learning: Even after completing your technical training or associate degree, continue seeking opportunities to expand your knowledge and skills in CAD technology. Stay updated with advancements in CAD software, industry best practices, and emerging trends. Attend workshops, webinars, and professional development courses to stay current in this constantly evolving field.
Completing technical training or an associate degree program in CAD will provide you with a solid educational foundation and practical experience. It will equip you with the necessary skills to create accurate technical drawings, navigate CAD software proficiently, and understand industry-specific standards. Your formal education in CAD technology sets the stage for your future as a skilled and competent CAD technician.
Step 3: Gain Experience through Internships or Entry-Level Positions
Gaining practical experience is crucial for developing your skills and building a successful career as a CAD technician. Step 3 involves seeking opportunities to gain experience through internships or entry-level positions in the field. Here are some key considerations for this step:
Internships: Internships provide valuable hands-on experience in a professional setting. Look for internships offered by architectural firms, engineering companies, manufacturing companies, or design agencies. During your internship, you will have the opportunity to work alongside experienced CAD technicians, learning from their expertise and applying your skills to real-world projects. Internships also allow you to build a professional network and gain exposure to industry practices.
Entry-Level Positions: Entry-level positions such as CAD technician assistant or junior CAD designer can provide valuable practical experience. These positions often involve supporting senior CAD technicians or engineers with drafting tasks, revisions, and project coordination. Apply for entry-level positions in industries such as architecture, engineering, construction, or manufacturing. Even if these positions are temporary or contract-based, they lay the foundation for future career growth.
Networking: Networking plays a crucial role in finding internship or entry-level job opportunities. Connect with professionals in the CAD industry by attending industry events, joining professional organizations, and utilizing online platforms such as LinkedIn. Engage in conversations, seek advice, and express your enthusiasm for learning and gaining experience. Networking can help you learn about hidden job opportunities and make connections that can lead to valuable mentorship and career growth.
Portfolio Development: As you gain practical experience through internships or entry-level positions, start building a portfolio of your work. Include examples of technical drawings, CAD models, and any projects you have contributed to. Having a portfolio showcases your skills and serves as a visual representation of your capabilities. Continuously update and refine your portfolio with each new project or achievement.
Professionalism and Work Ethic: Approach your internships or entry-level positions with professionalism and a strong work ethic. Be punctual, reliable, and willing to learn. Demonstrate your commitment to producing quality work and meeting deadlines. These characteristics will make a lasting impression and potentially open doors for future opportunities.
Continued Learning: The learning process does not stop with internships or entry-level positions. Continuously seek opportunities to expand your knowledge and skills in CAD technology. Stay updated with advancements in CAD software, learn new design techniques, and develop expertise in specialized areas. Pursue professional development courses, certifications, or online tutorials to enhance your skill set.
Gaining experience through internships or entry-level positions is a practical way to apply your knowledge, develop your skills, and expand your professional network. Embrace these opportunities to learn from experienced professionals, gain exposure to real-world projects, and solidify your understanding of CAD technology. With each experience, you will grow as a CAD technician and pave the way for future career success.
Step 4: Develop Specialization or Advanced Skills
Step 4 in becoming a CAD technician involves developing specialization or advanced skills in a specific area of CAD technology. By honing your expertise in a particular industry or CAD software, you can differentiate yourself in the job market and open up more specialized career opportunities. Here are important considerations for this step:
Identify Areas of Interest: Reflect on your interests and career goals to determine which area of CAD technology you would like to specialize in. Consider industries such as architecture, mechanical engineering, electrical design, or civil engineering. Research the latest trends and developments in these areas to understand which specialization aligns best with your passion and career aspirations.
Specialized CAD Software: Familiarize yourself with CAD software applications that are widely used in your chosen specialization. For example, if you want to specialize in architectural design, you may focus on software such as AutoCAD or Revit. Specializing in mechanical engineering may require expertise in software like SolidWorks or CATIA. Understanding industry-specific software will make you a valuable asset in your chosen field.
Continuing Education: Seek out advanced courses, workshops, or professional development programs that provide specialized training in your chosen CAD specialization. These programs can expand your knowledge and skills in areas such as advanced modeling techniques, project management, or industry-specific design standards. Engaging in lifelong learning allows you to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements in your specialized field.
Collaborate with Industry Professionals: Connect with professionals in your chosen specialization through networking events, industry associations, or online forums. Engaging with experts in your field of interest can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and guidance. Collaborating with industry professionals offers opportunities to learn from their experiences and gain a deeper understanding of the CAD practices and requirements specific to your specialization.
Build a Specialized Portfolio: Showcase your specialized skills and projects by developing a focused portfolio. Include examples of CAD models, technical drawings, or projects that demonstrate your expertise in your chosen field. A specialized portfolio will attract the attention of potential employers or clients who are seeking CAD technicians with expertise in your particular area of specialization.
Pursue Certifications: Explore professional certifications that are relevant to your specialization. These certifications validate your expertise and enhance your professional credibility. Vendor-specific certifications, industry-recognized certifications, or certifications offered by professional organizations can boost your credentials and make you stand out among other candidates in your specialized field.
By developing a specialization or advanced skills, you position yourself as a sought-after professional in your chosen area of CAD technology. Specialization enhances your marketability and increases your chances of securing positions that align with your specific interests and expertise. Continually strive to expand your knowledge and skills to stay at the forefront of your specialized field and maximize your career opportunities as a CAD technician.
Step 5: Consider Professional Certification
Step 5 in becoming a CAD technician involves considering professional certification to validate your skills and enhance your credentials in the field. A professional certification demonstrates your proficiency in CAD software applications and industry-specific standards, making you a competitive candidate for job opportunities. Here are important points to consider for this step:
Research Available Certifications: Begin by researching the available certifications relevant to your chosen CAD software or specialization. Identify reputable certification programs from software vendors, industry associations, or professional organizations. Examples of widely recognized certifications include Autodesk Certified Professional (ACP) for AutoCAD, SolidWorks Certification, or certifications offered by organizations like the American Design Drafting Association (ADDA) or the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
Evaluation of Requirements: Review the requirements of each certification program to determine if they align with your skills and qualifications. Consider factors such as prerequisites, examination formats, costs, and maintenance requirements. Evaluate which certifications will enhance your career prospects and are relevant to the specific CAD software applications or industries you are interested in.
Preparation and Study: Once you have chosen a certification program, allocate dedicated time to prepare for the certification exam. Familiarize yourself with the exam content and focus your studying on the specific areas outlined in the certification syllabus. Utilize study guides, practice exams, and online resources to reinforce your knowledge and identify areas that may need further improvement.
Participation in Training Programs: Consider participating in training programs or courses offered by the certification provider. These programs are designed to prepare individuals for the certification exam by covering the required topics in-depth. Training programs may be available in various formats, including online courses, workshops, or boot camps. Participation in these programs can enhance your understanding of the certification material and increase your chances of success on the exam.
Scheduling and Examination: Once you feel adequately prepared, schedule the certification examination. Be mindful of any deadlines or eligibility requirements imposed by the certification program. Prioritize ample time for studying and revision before the examination date. Remember to review the examination format and requirements to ensure a smooth testing experience.
Maintaining Certification: After successfully earning your certification, be aware of any maintenance requirements to keep the certification valid. Many certifications require ongoing professional development or renewal examinations to ensure competency and keep up with evolving industry standards. Stay engaged in continuing education opportunities to stay current with the latest advancements in CAD technology and fulfill any maintenance requirements.
Professional certification adds credibility to your resume and demonstrates your commitment to career advancement and proficiency in CAD technology. It increases your marketability to potential employers and provides validation of your skills and knowledge. Certification can not only make you a more competitive candidate in the job market but also opens doors for career progression and networking opportunities.
Consider professional certification as a valuable investment in your CAD technician career, as it serves as a testament to your expertise and dedication to excellence in the field. Continually seek opportunities for professional development and staying up-to-date with evolving industry standards to maintain and expand upon your certified status as a CAD technician.
Read more: How To Become An Air Conditioning Technician
Conclusion
Congratulations on reaching the end of this guide on becoming a successful CAD technician. We have explored the necessary steps and considerations to embark on this rewarding career path. As a CAD technician, you will leverage your skills in computer-aided design, technical drawing, problem-solving, and communication to contribute to the creation of precise and accurate digital models that shape the world around us.
By obtaining a high school diploma or equivalent, pursuing technical training or an associate degree, gaining practical experience, developing specialization or advanced skills, and considering professional certification, you will be well on your way to becoming a competent and in-demand CAD technician. Remember that the journey does not stop here – continuous learning, staying updated with the latest CAD technologies, and networking with industry professionals are essential elements of a successful career in this rapidly evolving field.
As a CAD technician, you will find yourself contributing to diverse industries such as architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, and product design. Your ability to bring design concepts to life through precise technical drawings and accurate digital models will make you an integral part of the design and development process. Your attention to detail, problem-solving abilities, and strong communication skills will ensure that projects are executed to meet client requirements and industry standards.
Embrace opportunities to specialize in specific industries or CAD software applications, as this will set you apart from others and open doors to more advanced and specialized career opportunities. Consider pursuing professional certifications to validate your expertise and boost your professional credibility.
Remember, as you embark on your career as a CAD technician, each experience and project is an opportunity for growth and skill development. Strive for excellence, be adaptable, and continue expanding your knowledge. Build a strong professional network, seek mentorship, and stay engaged with industry trends.
The journey to becoming a CAD technician is both challenging and fulfilling. Your passion for design, attention to detail, and problem-solving skills will enable you to shape the future of various industries. So, take the first step, acquire the necessary skills and education, and embrace the exciting world of CAD technology. Your creativity and expertise will contribute to the innovative and transformative projects of tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Become A CAD Technician
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “How To Become A CAD Technician”