Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is 3D CAD


Architecture & Design
What Is 3D CAD
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn what 3D CAD is and how it revolutionizes architecture design. Explore the benefits and applications of 3D CAD technology in this comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the world of design and architecture, the use of 3D computer-aided design (CAD) has revolutionized the way projects are conceptualized, developed, and brought to life. 3D CAD has transformed traditional design methods, allowing designers and engineers to create and manipulate digital models of objects and structures in a three-dimensional space.
With 3D CAD, designers can create detailed and accurate representations of their ideas, enabling them to better communicate their vision and make informed decisions throughout the design process. This technology has become an essential tool in fields such as industrial design, architecture, engineering, product development, and more.
In this article, we will explore the world of 3D CAD, diving into its definition, history, importance in design, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and the future trends in this rapidly evolving field.
So, whether you’re a seasoned design professional, a student studying architecture or engineering, or simply curious about the wonders of design technology, let’s embark on a journey to discover the fascinating world of 3D CAD.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D CAD has revolutionized design by enhancing visualization, enabling faster design iterations, and promoting collaboration. Despite potential drawbacks, its transformative impact and future potential make it an essential tool for designers and engineers.
- The future of 3D CAD holds exciting possibilities, including integration with AI, VR/AR, cloud technologies, generative design, and additive manufacturing. These advancements will empower designers to push the boundaries of creativity and create sustainable, customized, and optimized designs.
Read more: What Is CAD In 3D Printing
Definition of 3D CAD
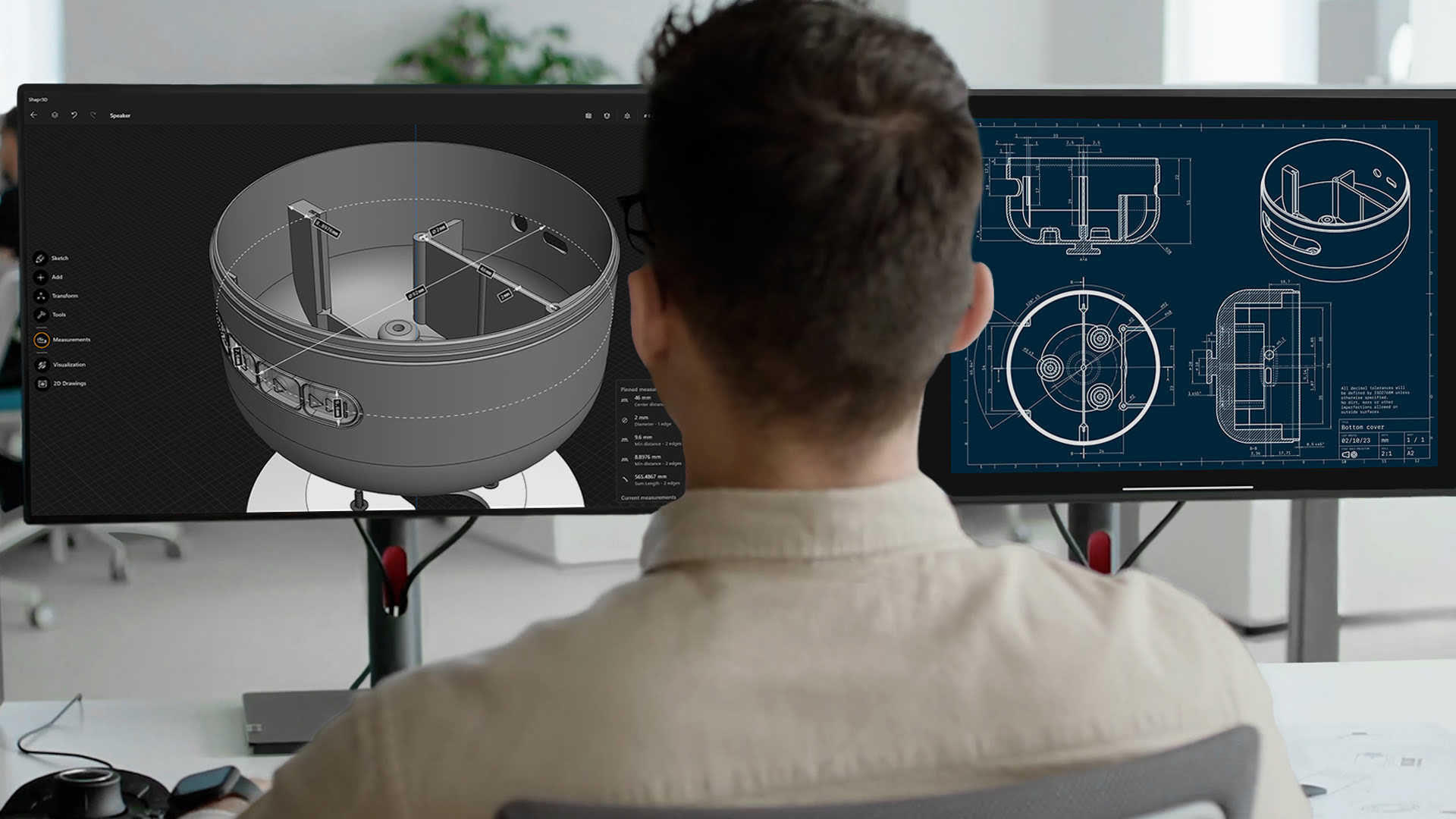
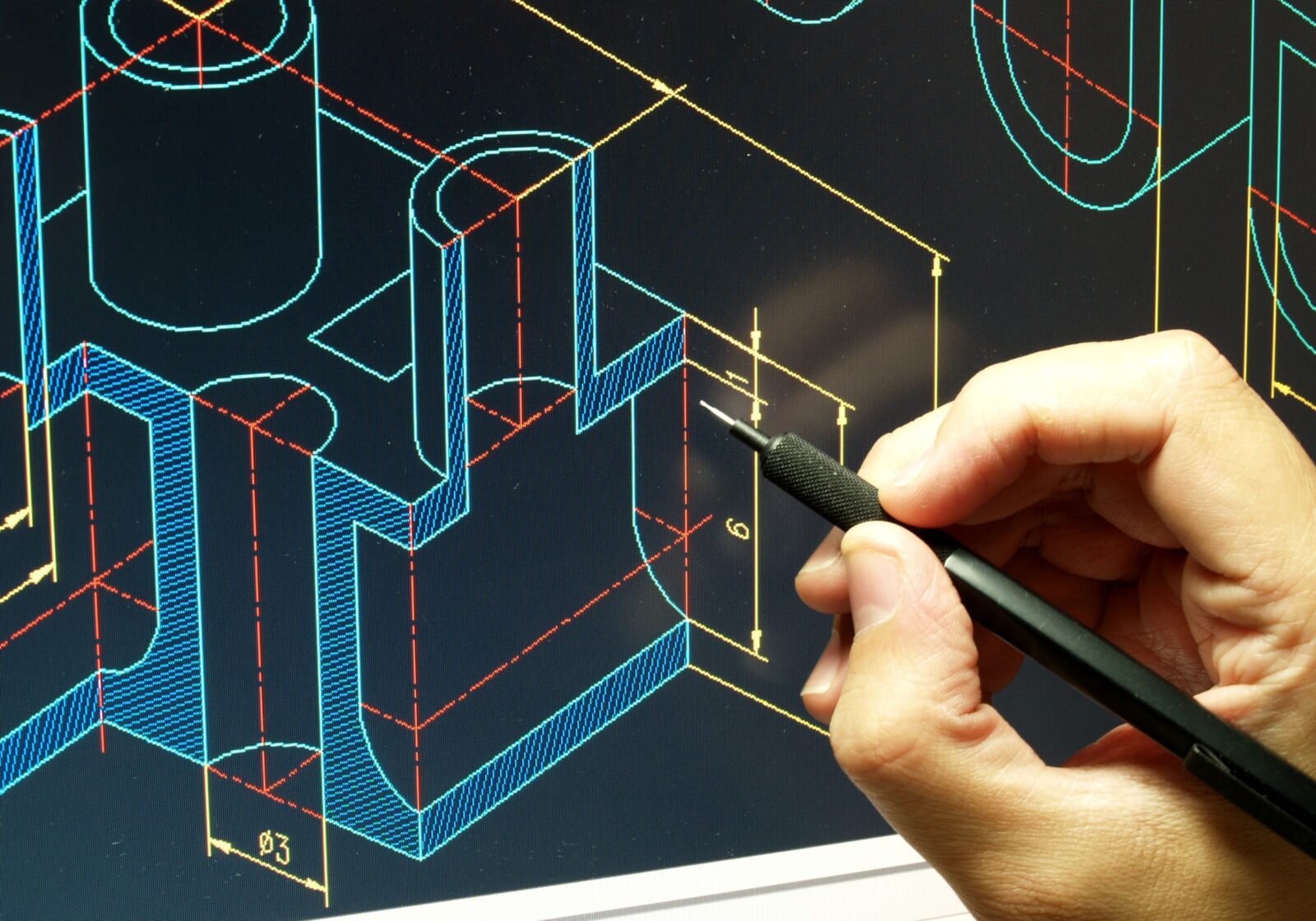
3D CAD, also known as three-dimensional computer-aided design, refers to the creation, modification, and analysis of digital models using specialized software. It allows designers and engineers to create virtual representations of objects or structures in a three-dimensional space, mimicking the real-world dimensions and properties of the physical object.
Unlike 2D CAD, which only allows for the creation of two-dimensional drawings, 3D CAD software provides a more immersive and realistic experience. Designers can construct complex shapes, manipulate objects in 3D space, and view their designs from different angles, providing a more accurate representation of the final product or structure.
3D CAD models consist of interconnected geometric elements, such as lines, curves, surfaces, and solids, which define the shape and characteristics of the design. These elements are created and manipulated using a variety of tools and commands within the CAD software, giving designers full control over the design process.
Moreover, 3D CAD allows for the addition of additional information to the model, such as material properties, tolerances, and assembly instructions. This enables designers to evaluate the performance and functionality of their designs and detect potential issues or conflicts before they arise in the physical world.
In summary, 3D CAD is a powerful design tool that enables designers and engineers to create, visualize, and analyze digital models in three dimensions. It provides a realistic representation of the design, facilitates collaboration among project stakeholders, and streamlines the design process from conception to production.
History of 3D CAD
The history of 3D CAD dates back to the early 1960s when the computer-aided design industry was in its infancy. During this time, simple 2D drafting systems were developed to assist designers in creating technical drawings. However, it wasn’t until the 1970s and 1980s that advancements in computer technology paved the way for the development of 3D CAD.
One of the pioneering systems in 3D CAD was Sketchpad, developed by Ivan Sutherland in 1963. Sketchpad allowed users to create and manipulate objects on a computer screen using a light pen, representing a significant leap forward in design technology. However, due to the limitations of hardware and processing power at the time, practical implementation of 3D CAD was still a distant dream.
In the early 1970s, with the rapid development of computer hardware, software, and graphics technology, companies like IBM and Lockheed began experimenting with more advanced 3D CAD systems. These early systems focused on wireframe modeling, where objects were represented as interconnected lines and curves in 3D space.
The breakthrough for 3D CAD came in the late 1970s with the introduction of the first solid modeling systems. It was during this period that pioneering companies such as United Computing, Applicon, and Computervision began developing software that allowed engineers to create complex 3D models with greater accuracy and realism.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, the use of 3D CAD systems became increasingly prevalent in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Companies like Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC) and Autodesk emerged as key players in the CAD software market, introducing innovative features such as parametric modeling, assembly design, and simulation capabilities.
With the advancement of computer processing power and the development of more user-friendly interfaces, 3D CAD systems became more accessible and affordable to designers, architects, and engineers of all backgrounds. This led to widespread adoption and integration of 3D CAD technology across various industries.
Today, 3D CAD software continues to evolve, integrating advanced features such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) capabilities, cloud-based collaboration, and integration with other design and engineering tools. The history of 3D CAD is a testament to the transformative power of technology in shaping the way we design and create in the modern world.
Importance of 3D CAD in Design
3D CAD has revolutionized the design process, becoming an essential tool in various industries. Its importance lies in its ability to enhance creativity, efficiency, and accuracy in design. Here are some key reasons why 3D CAD is crucial in the design field:
- Visualization and Communication: 3D CAD enables designers to create realistic and detailed visual representations of their designs. This allows clients, stakeholders, and team members to better understand the concepts and make informed decisions early in the design process. It bridges the communication gap by presenting designs in a way that is easily comprehensible.
- Design Exploration and Iteration: With 3D CAD, designers can quickly explore different design alternatives and variations. They can easily make changes and test out ideas without the constraints and costs associated with physical prototypes. This promotes innovation and enables designers to push boundaries and achieve optimal solutions.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: 3D CAD facilitates collaboration among multidisciplinary teams by providing a central platform in which design files can be shared, reviewed, and updated in real-time. It allows for efficient communication, reduces errors, and ensures everyone is on the same page throughout the design process.
- Simulation and Analysis: 3D CAD software often incorporates simulation and analysis tools that allow designers to test the functionality and performance of their designs virtually. This helps identify potential issues, optimize designs, and reduce the need for costly physical prototypes or rework later in the development process.
- Cost and Time Savings: By using 3D CAD, designers can streamline the design process, reducing lead times and minimizing errors. It eliminates the need for manual drafting and allows for easy documentation and revision control. This leads to significant cost savings in both time and materials.
- Integration with Manufacturing: 3D CAD models can be seamlessly integrated with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems, enabling a smooth transition from design to production. This integration ensures that the design intent is accurately translated into the manufacturing process, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Overall, 3D CAD plays a vital role in the design industry by empowering designers to create, communicate, and innovate in a more efficient and accurate manner. Its impact extends from the initial concept development stage to the final production, ensuring that designs are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional, cost-effective, and manufacturable.
Applications of 3D CAD
3D CAD has a wide range of applications across various industries, revolutionizing the way objects, structures, and products are designed and engineered. Here are some key areas where 3D CAD is extensively utilized:
- Architecture and Construction: In architectural design, 3D CAD allows architects to create detailed models of buildings, visualize interiors, and analyze structural elements. It helps in space planning, material selection, and evaluating the impact of design choices on energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Product Design and Manufacturing: 3D CAD is widely used in product design and manufacturing processes. It enables designers to create and refine product concepts, test functionality, and validate designs before moving into production. Manufacturers can utilize 3D CAD models for prototyping, tooling, and assembly instructions.
- Mechanical and Industrial Engineering: 3D CAD plays a crucial role in mechanical and industrial engineering, aiding in the design of complex machinery and equipment. It allows engineers to simulate movement, evaluate tolerances, and optimize performance. Additionally, it facilitates the integration of components and ensures proper functionality of assembly.
- Automotive and Aerospace: The automotive and aerospace industries heavily rely on 3D CAD for the design and development of vehicles, aircraft, and their components. 3D CAD software enables engineers to create aerodynamic shapes, analyze structural integrity, and simulate crash tests, leading to safer and more efficient designs.
- Medical Devices and Prosthetics: 3D CAD is utilized in the design and development of medical devices and prosthetics. It allows for the customization of products based on individual patient needs, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal functionality. 3D printing technologies can directly produce prototypes and even final products using CAD models.
- Animation and Visual Effects: In the entertainment industry, 3D CAD is extensively used in animation and visual effects. It provides the foundation for creating lifelike characters, virtual environments, and special effects in movies, video games, and virtual reality experiences.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of 3D CAD. In reality, the technology is applicable to any field that involves complex design, visualization, and engineering. From consumer products to infrastructure projects, 3D CAD has become an indispensable tool for professionals across industries, enabling them to bring their ideas to life and push the boundaries of what is possible.
When working with 3D CAD, it’s important to understand the concept of parametric modeling, which allows you to create designs with defined parameters that can be easily modified and updated. This can save you time and effort in the design process.
Read more: What Does CAD Stand For In 3D Printing
Advantages of 3D CAD
3D CAD offers numerous advantages over traditional 2D design methods, transforming the way designers and engineers approach their work. Here are some key benefits of using 3D CAD:
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D CAD allows designers to create realistic and immersive visual representations of their designs. This enables better visualization and understanding of the final product, making it easier for designers to communicate their ideas to clients, stakeholders, and team members.
- Improved Design Accuracy: With 3D CAD, designers can create precise and accurate models, ensuring that the final product or structure meets specifications and requirements. The ability to define exact measurements, tolerances, and material properties reduces errors in the design process, leading to higher quality designs.
- Design Exploration and Iteration: 3D CAD allows for easy exploration of design alternatives and variations. Designers can quickly modify and iterate their designs, test different configurations, and compare options before finalizing a design. This flexibility promotes innovation and leads to better-designed products.
- Faster Design Process: Compared to traditional drafting methods, 3D CAD significantly speeds up the design process. Design changes can be made easily and quickly, with automatic updates to all associated views and documentation. This saves time and eliminates the need for manual re-drawing, leading to improved productivity.
- Simulation and Analysis: 3D CAD software often integrates simulation and analysis tools, enabling designers to evaluate the performance and functionality of their designs before physical prototyping. This allows for early detection of potential issues or conflicts, reducing costly rework and ensuring designs meet desired criteria.
- Improved Collaboration: 3D CAD systems facilitate collaboration among team members, project stakeholders, and manufacturers. Design files can be easily shared, reviewed, and modified in real-time, promoting effective communication and reducing the chance of misinterpretation. This leads to better collaboration and smoother workflow.
- Integration with Manufacturing: 3D CAD models can be seamlessly integrated with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems, enabling a direct transition from design to production. This integration ensures that the design intent is accurately translated into the manufacturing process, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Cost and Waste Reduction: By using 3D CAD, designers can identify and resolve design issues early in the process, reducing the likelihood of costly errors during production. Additionally, the ability to simulate and optimize designs can lead to material and resource savings, minimizing waste and lowering overall production costs.
These advantages demonstrate the transformative impact of 3D CAD on the design process. Whether it’s improving accuracy, streamlining workflows, enabling better collaboration, or reducing costs, 3D CAD has become an essential tool for designers and engineers in a wide range of industries.
Disadvantages of 3D CAD
Although 3D CAD offers numerous advantages, it also comes with a few potential drawbacks. It’s important to be aware of these disadvantages when utilizing 3D CAD in the design process. Here are some key considerations:
- Steep Learning Curve: 3D CAD software can have a steep learning curve, especially for those new to the technology. Mastering the software and its various tools and features may require significant time and training, which can be a challenge for individuals or organizations with limited resources or tight deadlines.
- Software and Hardware Requirements: 3D CAD software often requires robust computer hardware and operating systems to run smoothly. Rendering complex models and performing simulations can be resource-intensive, necessitating powerful computers with ample storage, memory, and graphics capabilities.
- Cost of Software and Licenses: High-quality 3D CAD software can be expensive, especially for professional and commercial applications. Additionally, there may be additional costs associated with software licenses, maintenance, and updates. This can be a barrier for smaller businesses or individuals working on a tight budget.
- Dependency on Software: The reliance on 3D CAD software means that any technical issues, software bugs, or compatibility problems can disrupt the design process or hinder productivity. Software updates or changes can also introduce new features or workflows that require additional training and adaptation.
- Complexity of Models and File Size: As designs become more complex and detailed in 3D CAD, the file size of the models can increase significantly. This can pose challenges when sharing or transferring files, especially in cases where internet bandwidth or storage space is limited.
- Limitations in Physical Representation: While 3D CAD models can provide a highly accurate digital representation, they may not always capture the full physical properties or characteristics of the final product. Designers must consider factors such as material textures, lighting, and manufacturing processes that can influence the final appearance and functionality.
- Human Error and Misinterpretation: Despite the precision and accuracy offered by 3D CAD, human errors can still occur during the design process. Misinterpretation of design intentions or mistakes in inputting data can lead to significant design flaws or errors that might get overlooked during the review process.
While these disadvantages should be taken into account, with proper training, support, and planning, they can be effectively mitigated or minimized. The benefits of 3D CAD often outweigh these drawbacks, making it an invaluable tool for designers and engineers in a wide range of fields.
Future of 3D CAD
The future of 3D CAD holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance and evolve. Here are some key trends and developments that are shaping the future of 3D CAD:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technology is poised to have a significant impact on 3D CAD systems. AI algorithms can assist designers in automating repetitive tasks, generating design suggestions, and analyzing complex data. This integration will enhance productivity, accuracy, and creativity in the design process.
- Advancements in Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are becoming more accessible and affordable. Integration of 3D CAD with VR/AR platforms allows designers to experience their designs in immersive virtual environments or overlay digital models onto physical spaces. This facilitates better visualization, ergonomic evaluations, and real-time design feedback.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration and Storage: Cloud technology continues to improve, enabling real-time collaboration and seamless data sharing among team members. By leveraging the power of the cloud, designers can work together on 3D CAD projects simultaneously, regardless of their physical location. Cloud storage offers secure and scalable solutions for managing and accessing large CAD models and their associated data.
- Generative Design: Generative design is an emerging technology that uses algorithms and AI to explore vast design possibilities, optimizing designs for specific parameters and constraints. This approach enables designers to quickly generate and evaluate multiple design iterations, leading to innovative and optimized solutions.
- Advancements in Additive Manufacturing: With the growing popularity of 3D printing and other additive manufacturing technologies, 3D CAD will continue to play a crucial role in designing for these processes. Integration with 3D printers and materials libraries will enable designers to create complex geometries and customize designs for specific manufacturing methods and materials.
- Simulation and Digital Twins: Simulation capabilities within 3D CAD will become even more sophisticated, allowing designers to accurately predict and evaluate the behavior and performance of their designs. This will enable the creation of digital twins, where virtual models simulate real-world behavior, helping to optimize maintenance, performance, and operation of physical products and systems.
- Design for Sustainability: The focus on sustainability and environmental impact is growing. 3D CAD will continue to evolve to support sustainable design practices, enabling designers to evaluate energy efficiency, material usage, and recycling considerations. It will empower designers to make more informed decisions and create environmentally conscious designs.
The future of 3D CAD is filled with promise, as it embraces technologies such as AI, VR/AR, cloud computing, and additive manufacturing to enhance the design process. These advancements will further empower designers and engineers, enabling them to explore new frontiers, streamline collaboration, and create innovative and sustainable designs.
Conclusion
3D CAD has transformed the design industry, revolutionizing the way designers and engineers create, visualize, and communicate their ideas. From its early roots in the 1960s to the advanced systems of today, 3D CAD has become an indispensable tool in various fields, including architecture, manufacturing, engineering, and entertainment.
The advantages of 3D CAD are undeniable. Enhanced visualization, improved accuracy, faster design iterations, simulation capabilities, and better collaboration are just a few of the benefits it offers. Designers can explore and iterate designs efficiently, validate functionality and performance, and streamline collaboration among team members and clients.
Despite some potential drawbacks, such as a learning curve, hardware requirements, and software costs, 3D CAD remains an essential investment for organizations and professionals looking to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
The future of 3D CAD holds even more exciting possibilities. Integration with AI, VR/AR, cloud technologies, generative design, and additive manufacturing will further enhance the design process, efficiency, and innovation. Designers will have access to advanced tools and capabilities that enable them to push the boundaries of creativity and create sustainable, customized, and optimized designs.
In conclusion, 3D CAD has revolutionized the way we design. It has accelerated the design process, improved accuracy, facilitated collaboration, and empowered designers to bring their visions to life. As technology continues to advance, the future of 3D CAD looks bright, promising even greater potential for innovation, creativity, and efficiency in the world of design.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is 3D CAD
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Is 3D CAD”