Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is A CAD Designer


Architecture & Design
What Is A CAD Designer
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the role of a CAD designer in architecture design. Learn how CAD software is used to create precise and detailed architectural drawings.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
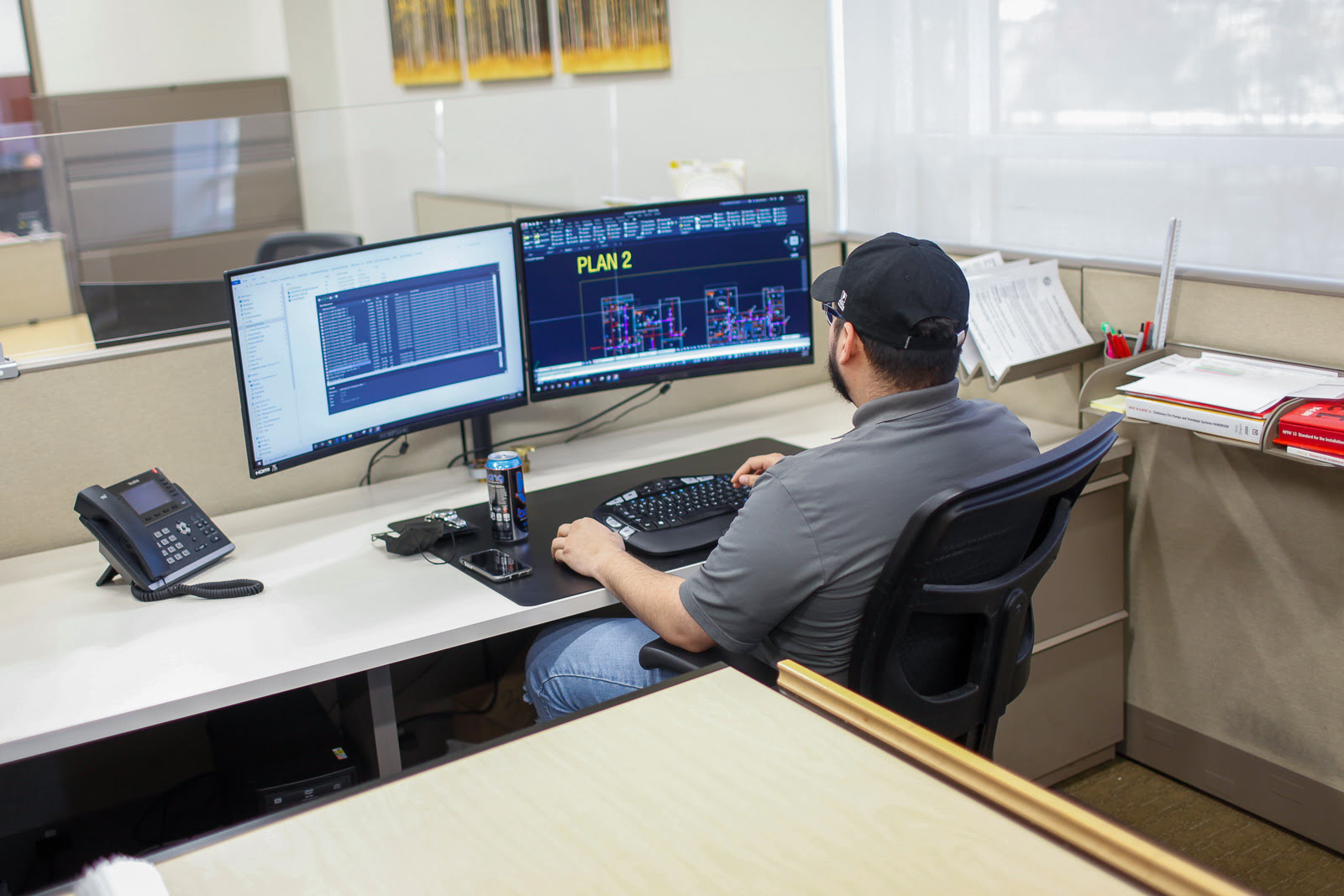
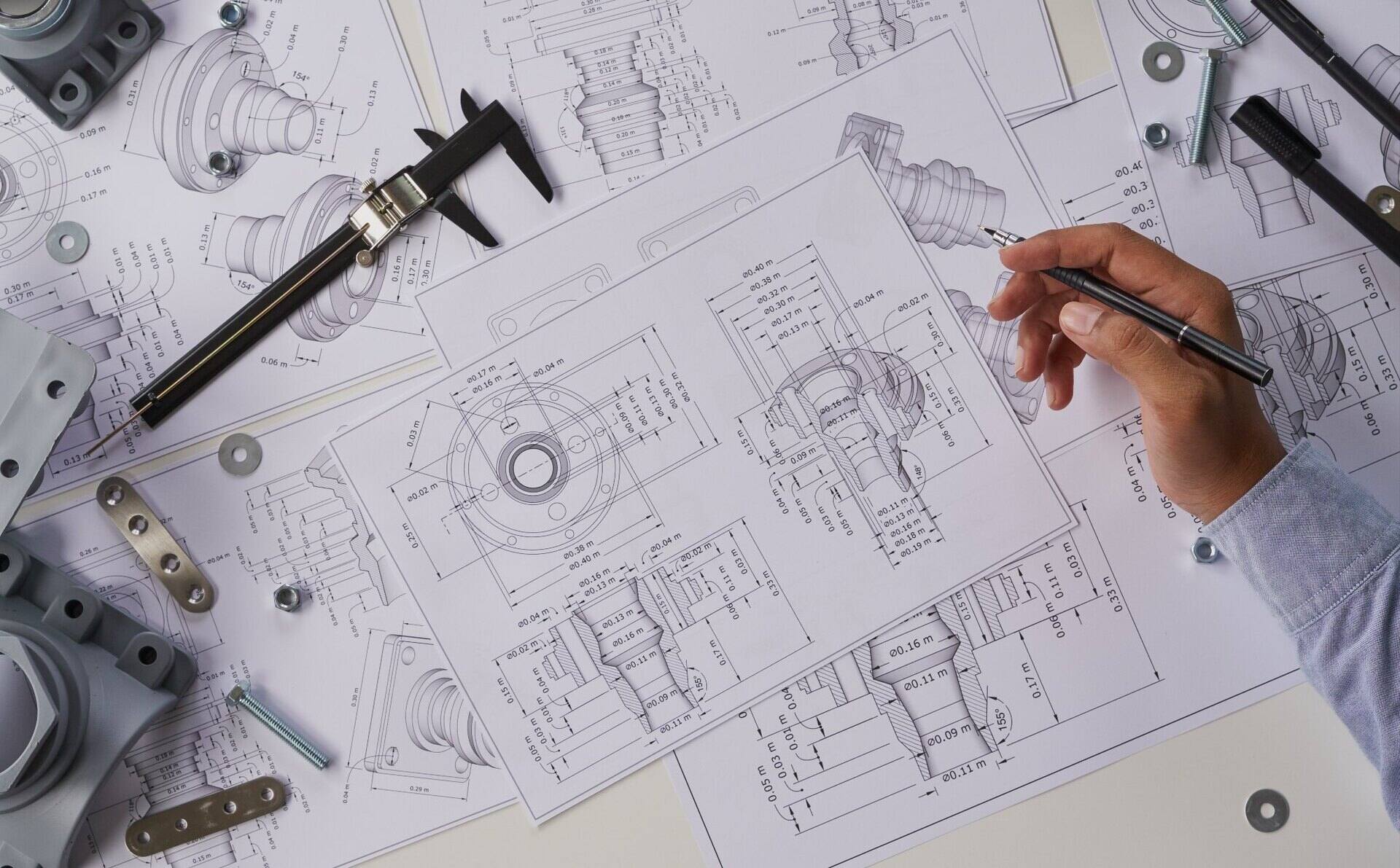
When it comes to designing and creating architectural masterpieces, a key figure behind the scenes is the CAD designer. These skilled professionals play a crucial role in the architecture and engineering industries by translating concepts and ideas into precise technical drawings and blueprints. But what exactly is CAD, and what does a CAD designer do?
CAD, short for Computer-Aided Design, refers to the use of computer software and specialized tools to create, modify, and analyze designs. CAD software allows designers to generate 2D and 3D models, incorporate accurate measurements, and simulate real-life scenarios for various purposes including architectural planning, product design, and engineering projects.
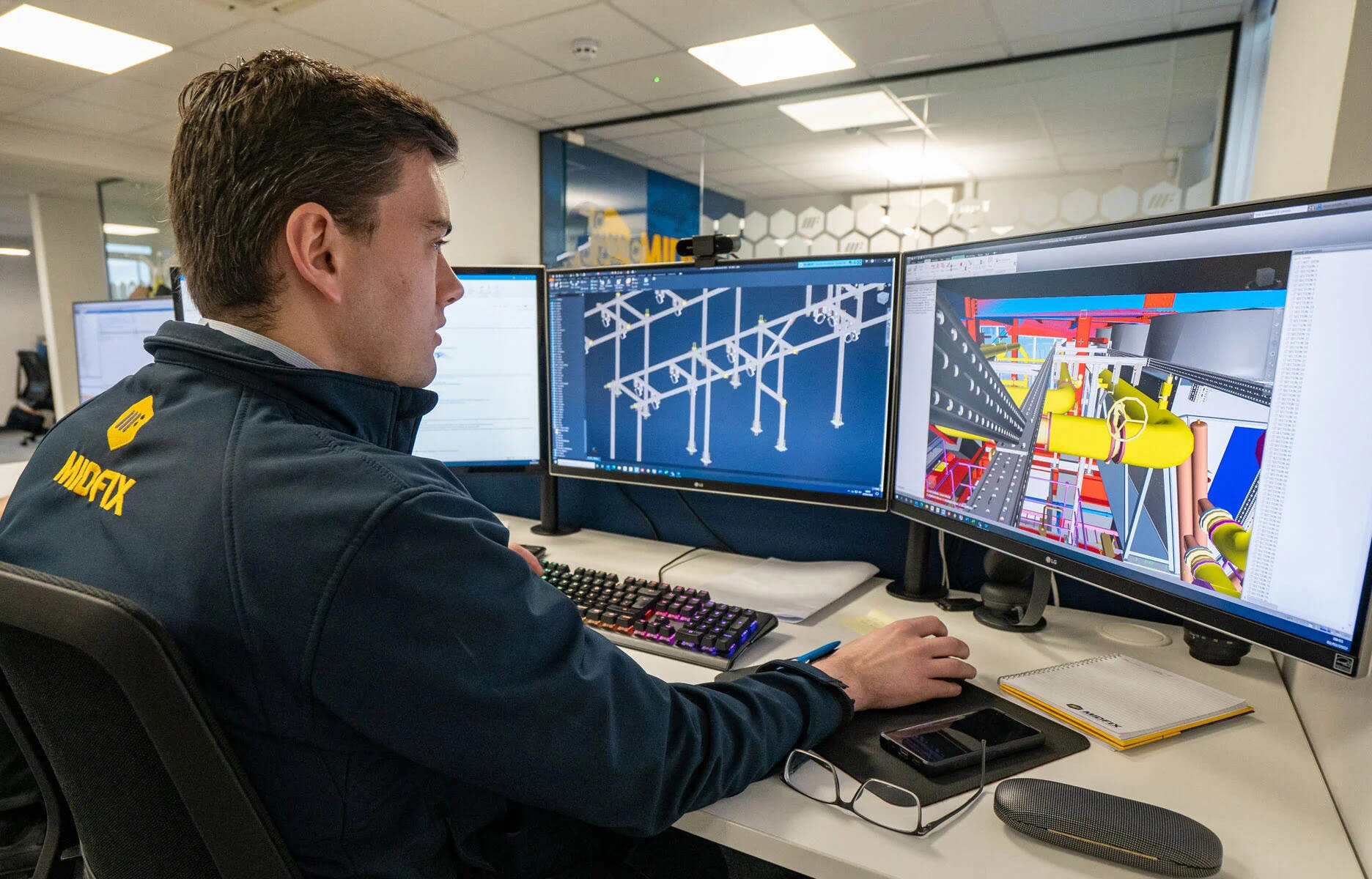
A CAD designer is the expert who harnesses the power of CAD software to transform abstract ideas and concepts into tangible design solutions. These professionals possess a combination of technical skills, artistic flair, and a deep understanding of architectural principles. They work closely with architects, engineers, and other stakeholders to create detailed drawings and models that serve as the blueprint for construction.
Becoming a CAD designer requires a specific set of skills and a keen eye for detail. Let’s take a closer look at what it takes to excel in this field.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD designers play a pivotal role in translating abstract ideas into precise technical drawings and models using CAD software. Their combination of technical skills, creativity, and attention to detail is essential in the design and construction process.
- The demand for CAD designers is on the rise across various industries, offering promising career opportunities. Continuous learning, collaboration, and staying updated with the latest CAD software advancements are crucial for success in this dynamic field.
Read more: What Is CAD?
Definition of CAD
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, is a technology that utilizes computer software and hardware to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, and optimization of various designs. It has revolutionized the field of design and engineering by providing a more efficient and accurate way to generate visual representations of ideas and concepts.
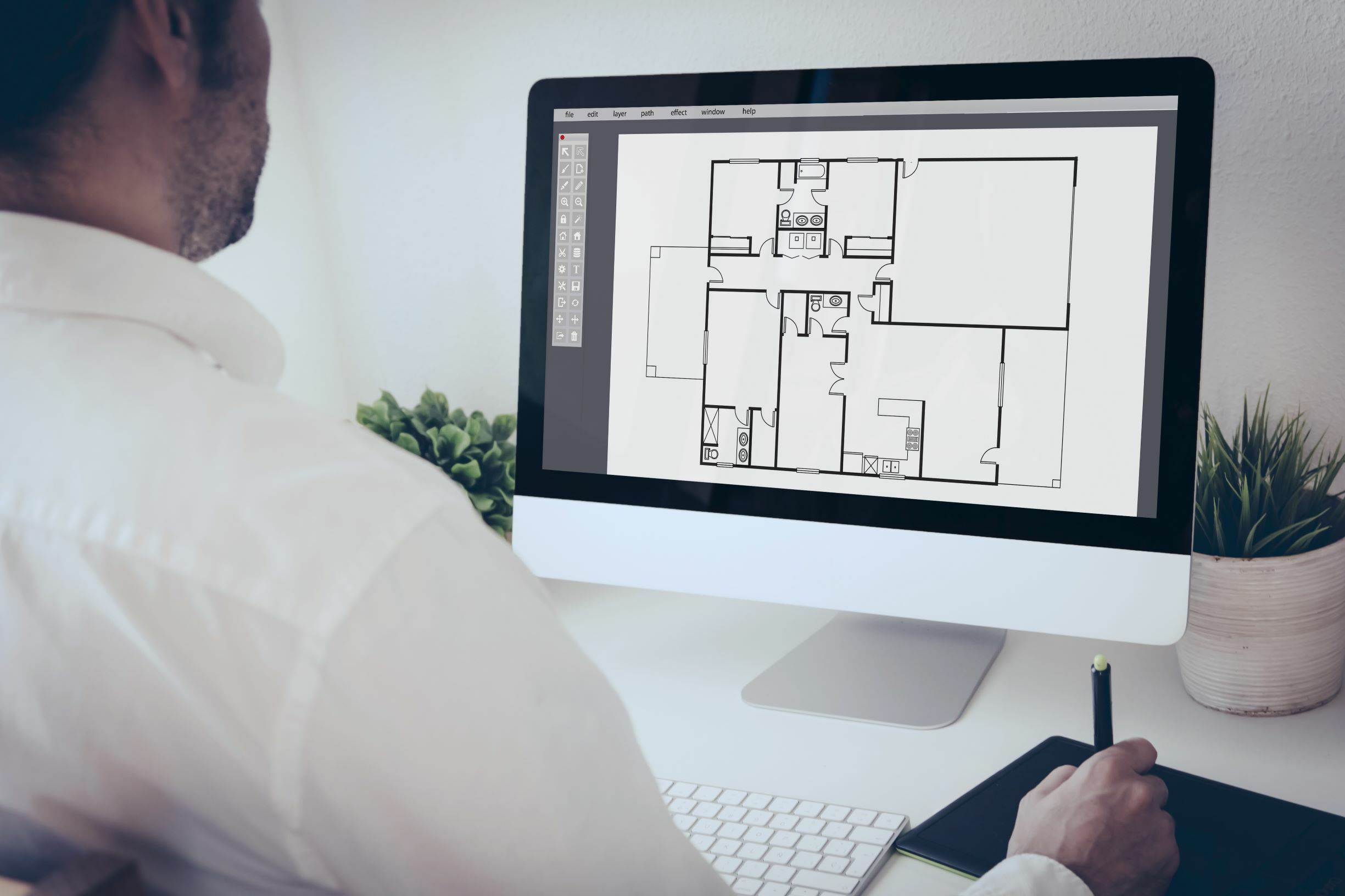
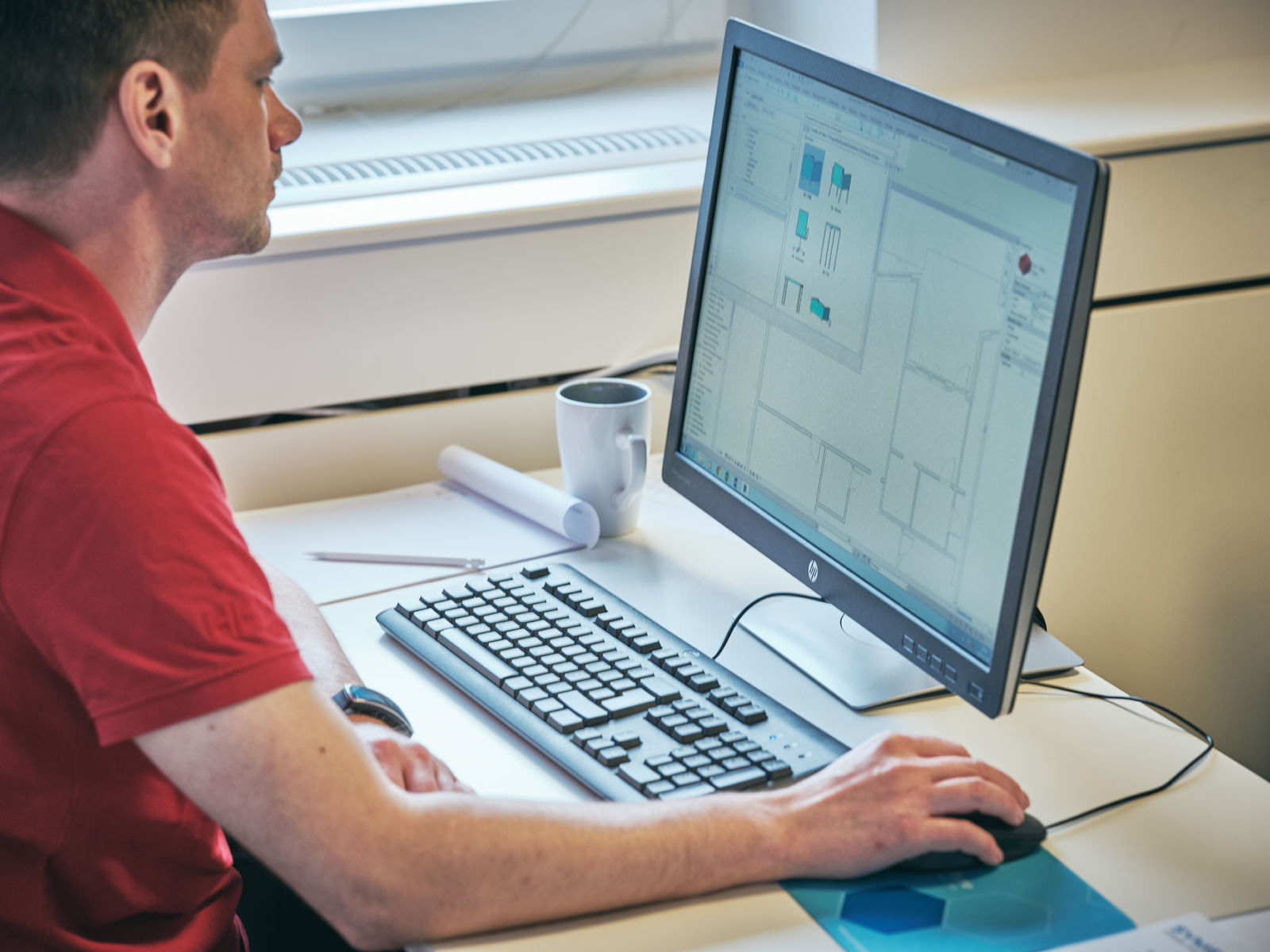
In the realm of architectural design, CAD has become an indispensable tool for architects, designers, and engineers. It allows for the creation of detailed and precise 2D and 3D models that can be easily manipulated and shared. CAD software provides a digital workspace where designers can draft, annotate, and simulate designs, enabling them to visualize the final product before it is built.
CAD software offers a wide range of features and functionalities that enhance the design process. These include the ability to incorporate accurate measurements, scale drawings, generate realistic renderings, perform structural analysis, and collaborate with other professionals involved in the project. With CAD, designers can easily modify and iterate on their designs, saving time and reducing errors.
Furthermore, CAD allows for better communication and collaboration between different stakeholders. Designers can easily share their work with clients, contractors, and other team members, facilitating a more efficient and streamlined workflow. Changes and revisions can be made in real-time, ensuring all parties are on the same page throughout the design process.
Overall, CAD has revolutionized the way designs are created and has significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of the design process. It has become an essential tool for architects, engineers, and designers in various industries, ranging from architecture and construction to product design and manufacturing.
Role of a CAD Designer
A CAD designer plays a critical role in the design and development process. They are responsible for transforming ideas and concepts into detailed technical drawings and models. Their work serves as the foundation for construction and manufacturing projects. Let’s delve deeper into the key responsibilities of a CAD designer:
1. Creating Detailed Drawings: CAD designers use specialized software to create precise and accurate 2D and 3D drawings. These drawings include floor plans, elevations, sections, and other technical details necessary for construction. CAD designers must have a strong understanding of architectural principles, as well as knowledge of building codes and regulations.
2. Design Modifications and Iterations: Throughout the design process, CAD designers collaborate with architects, engineers, and other professionals to make changes and modifications to the design. They incorporate client feedback, structural requirements, and aesthetic considerations to refine the design. CAD software allows designers to easily modify and iterate on their models, saving time and resources.
3. Technical Problem-Solving: CAD designers need to have a solid problem-solving mindset. They must be able to identify and resolve design issues, ensuring that the final product is both functional and safe. They work closely with engineers and architects to find practical solutions to technical challenges that may arise during the design process.
4. Collaborative Teamwork: CAD designers often work as part of a larger team, collaborating with architects, engineers, project managers, and contractors. They must effectively communicate and coordinate with team members to ensure that the design requirements are met and that the project progresses smoothly.
5. Keeping Up with Industry Standards: CAD designers need to stay updated with the latest industry trends, software updates, and advancements in technology. They must continuously expand their knowledge and skills to remain competitive in their field.
6. Quality Control: CAD designers are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and quality of their work. They must carefully review and check their drawings and models for errors and inconsistencies. Attention to detail is paramount to produce high-quality design documents.
7. Documentation and Archiving: CAD designers maintain a proper record of all design-related documents and files. This includes organizing and archiving drawings, models, and revisions for future reference and retrieval.
In summary, a CAD designer plays a pivotal role in the design and construction process. They are responsible for creating detailed and accurate drawings, collaborating with team members, problem-solving, and ensuring the high quality of their work.
Skills Required for CAD Designing
Being a CAD designer requires a specific set of skills, both technical and creative. Here are some of the essential skills that are necessary to excel in this field:
1. Proficiency in CAD Software: A CAD designer must have a deep understanding and proficiency in CAD software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Revit, or other industry-standard software. They should be able to navigate the software efficiently, utilize advanced features, and produce accurate and detailed drawings.
2. Technical Knowledge: CAD designers require a solid understanding of engineering and architectural principles. They need to comprehend construction techniques, materials, and building codes to ensure that their designs are practical and meet regulatory standards.
3. Attention to Detail: Precision is crucial in CAD designing. CAD designers must have a keen eye for detail and accuracy. They need to ensure that measurements, dimensions, and annotations are correct to avoid errors during the construction phase.
4. Problem-Solving: CAD designers must possess excellent problem-solving skills. They encounter complex design challenges and must find practical and efficient solutions. The ability to analyze and think critically is essential in order to overcome technical obstacles that may arise.
5. Creativity and Design Sensibility: While CAD designers work with technical drawings, they also need to have a creative mindset. They should be able to envision and create aesthetically pleasing designs that meet the functional requirements of the project.
6. Communication and Collaboration: CAD designers often work as part of a team, so effective communication and collaboration skills are crucial. They need to be able to clearly convey their ideas and designs to architects, engineers, and other stakeholders. Active listening and the ability to incorporate feedback are essential for working collaboratively.
7. Continuous Learning: The field of CAD designing is constantly evolving, with new software releases and updates. CAD designers need to stay updated with the latest industry trends and advancements. Continuous learning and willingness to adapt to new technologies are critical for professional growth.
8. Time Management: CAD designers often work on tight deadlines and multiple projects simultaneously. They need to effectively manage their time to meet project deadlines while maintaining quality and accuracy in their work.
9. Technical Drawing Skills: Although CAD software automates many aspects of drawing, having a background in manual or traditional technical drawing techniques is beneficial. It helps CAD designers understand the fundamentals of drafting and enables them to create more precise and detailed drawings.
10. Analytical Thinking: CAD designers need to analyze design requirements, interpret sketches and specifications, and translate them into practical and feasible designs. They must be able to think analytically to ensure that their designs can be successfully implemented.
These skills are essential for a CAD designer to excel in their field and deliver high-quality designs that meet client expectations. With a combination of technical expertise, creativity, and strong communication skills, CAD designers can bring ideas to life with precision and accuracy.
Responsibilities of a CAD Designer
A CAD (Computer-Aided Design) designer is responsible for several key tasks throughout the design process. Their role involves translating concepts and ideas into detailed technical drawings and models. Let’s explore the primary responsibilities of a CAD designer:
1. Creating Technical Drawings: The primary responsibility of a CAD designer is to create accurate and detailed technical drawings. They use CAD software to generate 2D and 3D models, incorporating measurements, dimensions, and annotations. These drawings serve as the basis for construction, manufacturing, or product development.
2. Incorporating Design Specifications: CAD designers work closely with architects, engineers, and clients to understand design specifications and requirements. They ensure that these specifications are incorporated into the design by accurately representing dimensions, materials, and other necessary details. They must have a keen eye for precision and accuracy.
3. Collaboration with Design Team: CAD designers often work as part of a larger design team, collaborating with architects, engineers, and other professionals. They contribute their technical expertise to design discussions, offer suggestions for improvements, and incorporate feedback from team members to refine the design.
4. Modifying and Iterating Designs: Throughout the design process, CAD designers receive feedback and requests for modifications. They must be able to make changes to the design quickly and accurately using CAD software. The ability to iterate on designs and accommodate changes is crucial for meeting project requirements.
5. Ensuring Design Compliance: CAD designers need to be knowledgeable about building codes, regulations, and industry standards. They are responsible for ensuring that the design complies with these requirements, such as fire safety, accessibility, and structural integrity. This helps to ensure that the final product is safe and functional.
6. Conducting Design Reviews: CAD designers participate in design reviews and meetings to present their work, discuss design options, and provide updates on the progress of the project. They may also collaborate with clients to review and gain approval for the design before moving forward with the construction phase.
7. Continuous Learning and Professional Development: CAD designers need to stay updated with the latest software advancements, design techniques, and industry trends. They should actively seek opportunities for professional development to enhance their skills and knowledge in CAD software and design principles.
8. Quality Control: CAD designers are responsible for ensuring the quality and accuracy of their work. They thoroughly review the drawings and models they create to identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies. Quality control is crucial to maintain the integrity of the design and prevent potential problems during construction.
9. Documenting and Archiving Design Files: CAD designers maintain proper documentation of their design files, including revisions and versions. This ensures that all design-related information is well organized and easily accessible for future reference or modifications.
10. Communication and Coordination: CAD designers need effective communication skills to collaborate with team members, clients, and stakeholders. They should be able to clearly convey design intent, explain technical concepts, and address any queries or concerns related to the design.
In summary, a CAD designer plays a crucial role in the design process by creating accurate technical drawings, collaborating with the design team, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining quality control. Their expertise and attention to detail contribute to the successful completion of architectural, engineering, and design projects.
A CAD designer uses computer software to create detailed technical drawings and 3D models for product design and manufacturing. It’s important to stay updated on the latest software and industry trends to excel in this field.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
CAD Software Used by CAD Designers
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is an essential tool for CAD designers, enabling them to create, modify, and analyze designs in a digital environment. There are several software options available, each with its own features and specialties. Let’s explore some of the widely used CAD software in the industry:
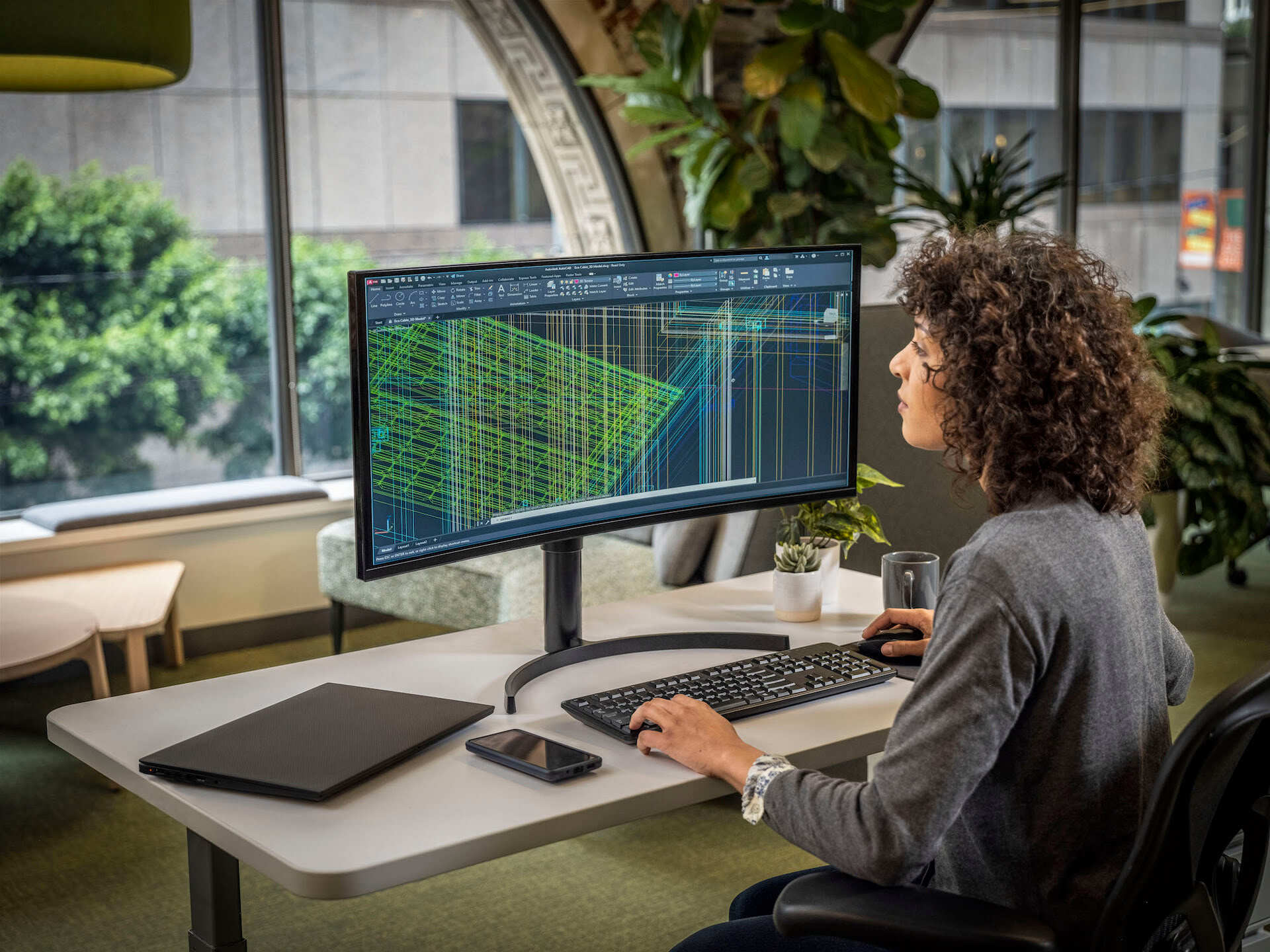
1. AutoCAD: AutoCAD is one of the most popular and widely used CAD software in the industry. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for 2D and 3D design, allowing CAD designers to create precise technical drawings, models, and animations. AutoCAD supports a wide range of industries, including architecture, engineering, and product design.
2. SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a powerful CAD software specifically designed for 3D mechanical design and engineering. It offers an extensive set of tools for creating complex 3D models, assemblies, and simulations. It is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace.
3. Revit: Revit is a building information modeling (BIM) software developed by Autodesk. It is widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Revit allows CAD designers to create intelligent 3D models that incorporate detailed information about the building elements. It enables collaboration among various disciplines and offers tools for architectural design, structural engineering, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems.
4. CATIA: CATIA is a CAD software developed by Dassault Systèmes. It is primarily used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial design. CATIA offers a wide range of tools for 3D modeling, surfacing, and analysis. It is known for its advanced capabilities in handling complex designs and assemblies.
5. Solid Edge: Solid Edge is a 3D CAD software developed by Siemens. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for design and engineering, including solid modeling, assembly modeling, and simulation. Solid Edge is widely used in mechanical and product design industries.
6. SketchUp: SketchUp is a user-friendly 3D modeling software known for its ease of use and intuitive interface. It is widely used for architectural design, interior design, and urban planning. SketchUp offers both free and paid versions with various features for different levels of users.
7. Fusion 360: Fusion 360, developed by Autodesk, is a cloud-based CAD software that combines design, engineering, and collaboration tools in a single platform. It offers a range of features for 3D modeling, simulation, and manufacturing. Fusion 360 is popular among small and medium-sized businesses as it provides an integrated workflow for product development.
8. Rhino: Rhino, or Rhinoceros 3D, is a versatile CAD software known for its ability to handle complex geometries and organic shapes. It is widely used in architectural design, industrial design, and jewelry design. Rhino offers a wide range of plugins and scripting capabilities to enhance its functionality.
These are just a few examples of the CAD software used by CAD designers. The choice of software depends on various factors, including industry, project requirements, and personal preferences. CAD designers should evaluate different software options to find the one that best fits their needs and enhances their productivity in creating accurate and detailed designs.
Industries That Employ CAD Designers
The demand for CAD (Computer-Aided Design) designers spans across various industries that rely on precise technical drawings and detailed design documentation. From architecture to manufacturing, CAD designers play a pivotal role in bringing concepts to life. Let’s explore some of the key industries that employ CAD designers:
1. Architecture and Construction: The architectural industry heavily relies on CAD designers to create detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models. CAD software allows architects to visualize and communicate their design ideas accurately. CAD designers collaborate closely with architects, ensuring that their designs adhere to building codes and regulations.
2. Engineering: CAD designers are integral to the engineering industry, where they create technical drawings and models that serve as the foundation for mechanical, electrical, civil, and structural engineering projects. CAD software enables engineers to analyze and validate their designs before they are implemented.
3. Manufacturing: In the manufacturing sector, CAD designers work on product design and development. They create 3D models and assembly drawings for manufacturing processes. CAD software assists in optimizing product designs for efficiency and manufacturability.
4. Automotive and Aerospace: The automotive and aerospace industries heavily rely on CAD designers for designing vehicle parts, components, and aircraft structures. CAD software allows designers to create complex designs and perform various analyses, such as aerodynamics and stress testing.
5. Industrial Design: Industrial designers utilize CAD software to create 3D models of products, appliances, and consumer goods. CAD designers play a crucial role in transforming design concepts into manufacturable products, considering both functional and aesthetic aspects.
6. Interior Design: CAD designers contribute to interior design projects by creating detailed drawings of spaces and developing 3D models. This helps interior designers visualize and present their design concepts to clients, ensuring accurate design implementation.
7. Civil and Infrastructure: CAD designers are involved in civil and infrastructure projects such as road and bridge construction, urban planning, and water management systems. They create technical drawings and models that aid in the planning and implementation of these projects.
8. Electronics and Electrical: The electronics and electrical industries employ CAD designers to create circuit board designs, electrical schematics, and layouts. CAD software helps in optimizing electronics design for functionality, signal integrity, and manufacturing processes.
9. Furniture and Product Design: In the furniture and product design industries, CAD designers create 3D models and technical drawings for product manufacturing. They ensure that the designs are feasible, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
10. Energy and Environmental Solutions: CAD designers are involved in energy-related projects like solar panel installations, wind turbine design, and energy-efficient system planning. CAD software aids in modeling and analyzing these systems for optimal energy performance.
These are just a few examples of industries that employ CAD designers. With the ever-increasing reliance on digital design and accurate documentation, the need for CAD designers continues to grow across various sectors. CAD designers are at the forefront of transforming design concepts into tangible, practical solutions that shape the world around us.
Career Outlook for CAD Designers
The career outlook for CAD (Computer-Aided Design) designers is promising, driven by the increasing demand for precise technical drawings and the continuous advancements in CAD software technology. CAD designers play a crucial role in various industries, including architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and product design. Let’s explore the career outlook for CAD designers:
1. Job Growth: The demand for CAD designers is expected to grow steadily in the coming years. As industries continue to rely on digital design and accurate documentation, CAD designers are essential in bridging the gap between concept and implementation. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 4% job growth for drafters, including CAD designers, from 2019 to 2029.
2. Technological Advancements: CAD software technology is evolving rapidly, offering new features and capabilities to enhance the design process. CAD designers need to stay updated with the latest software advancements and adapt to new technologies. The ability to leverage cutting-edge tools and techniques can provide a competitive edge in the job market.
3. Specialization Opportunities: CAD designers have the opportunity to specialize in specific industries or areas of expertise. For example, they can focus on architectural design, product design, or mechanical engineering. By developing specialized skills and knowledge, CAD designers can become sought-after professionals in their respective fields.
4. Collaboration and Teamwork: CAD designers often work as part of a team, collaborating with architects, engineers, and other stakeholders. They contribute their technical expertise to design discussions and incorporate feedback from team members. Strong communication and teamwork skills are crucial for success as a CAD designer.
5. Continuing Education: CAD designers need to stay updated with the latest industry trends and advancements. Continuous learning and professional development are essential for career growth. Pursuing certifications, attending workshops, and staying informed about emerging technologies can enhance job prospects and open up new opportunities.
6. Freelance and Consulting Opportunities: Many CAD designers choose to work as freelancers or consultants, providing their services to multiple clients or companies. This offers flexibility and the opportunity to work on a variety of projects. However, freelancers need to establish a strong professional network and market their skills effectively to secure projects.
7. Global Opportunities: The skills of CAD designers are transferable across different regions and industries, providing opportunities for international employment. As globalization continues to drive collaboration and outsourcing, CAD designers may find job prospects in different countries or with multinational companies.
8. Environmental and Sustainable Design: With the increasing focus on sustainability and eco-friendly design solutions, CAD designers who possess knowledge of green design principles and energy-efficient technologies will have an edge in the job market. The demand for CAD designers with expertise in environmentally conscious design is expected to grow.
9. Advancement Opportunities: With experience and additional training, CAD designers can advance their careers into roles such as senior CAD designer, CAD manager, or project manager. These positions often involve greater responsibility in managing design processes, leading teams, and overseeing larger-scale projects.
10. Entrepreneurship: CAD designers with an entrepreneurial spirit can start their own design firms or consultancy businesses. This allows them to take on projects independently, build their client base, and have creative control over their work.
The career outlook for CAD designers is promising, with ample opportunities for growth, specialization, and career development. By staying updated with industry trends, honing their technical skills, and nurturing their creativity, CAD designers can thrive in a dynamic and ever-evolving design landscape.
Conclusion
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) designers play a crucial role in the architecture, engineering, and design industries. Their expertise in utilizing CAD software allows them to transform ideas and concepts into precise technical drawings and models. The demand for CAD designers is growing, driven by the increasing reliance on digital design, accurate documentation, and advanced software technology.
Throughout this article, we have explored the world of CAD design, from understanding the definition of CAD to delving into the responsibilities and skills required for CAD designers. We have also discussed the industries that employ CAD designers and the promising career outlook for those in this field.
CAD designers must possess a combination of technical skills, creative thinking, precision, and a keen eye for detail. Their ability to create accurate technical drawings, collaborate effectively with team members, solve design problems, and adapt to new technologies sets them apart as key players in the design process.
The continuous advancements in CAD software technology provide ample opportunities for CAD designers to expand their skills and specialize in specific industries. From architecture and engineering to manufacturing and product design, CAD designers contribute to the creation of functional and visually appealing designs that meet the needs of clients and regulatory standards.
To thrive as CAD designers, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest industry trends and advancements. Continuous learning, professional development, and effective communication are key aspects of success in this field. CAD designers who embrace these opportunities and continuously refine their skills will find themselves at the forefront of the design industry.
In conclusion, the world of CAD design offers a promising career path for those with a passion for both technology and design. As industries continue to rely on precise technical drawings and accurate documentation, the role of CAD designers becomes increasingly important. With their expertise in CAD software and their ability to bring design concepts to life, CAD designers contribute to the creation of innovative and functional designs that shape the world we live in.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A CAD Designer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A CAD Designer”