Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Are CAD Models


Architecture & Design
What Are CAD Models
Modified: August 29, 2024
Learn how CAD models are used in architecture design and how they can enhance the design process. Discover the benefits of using CAD models in architectural projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
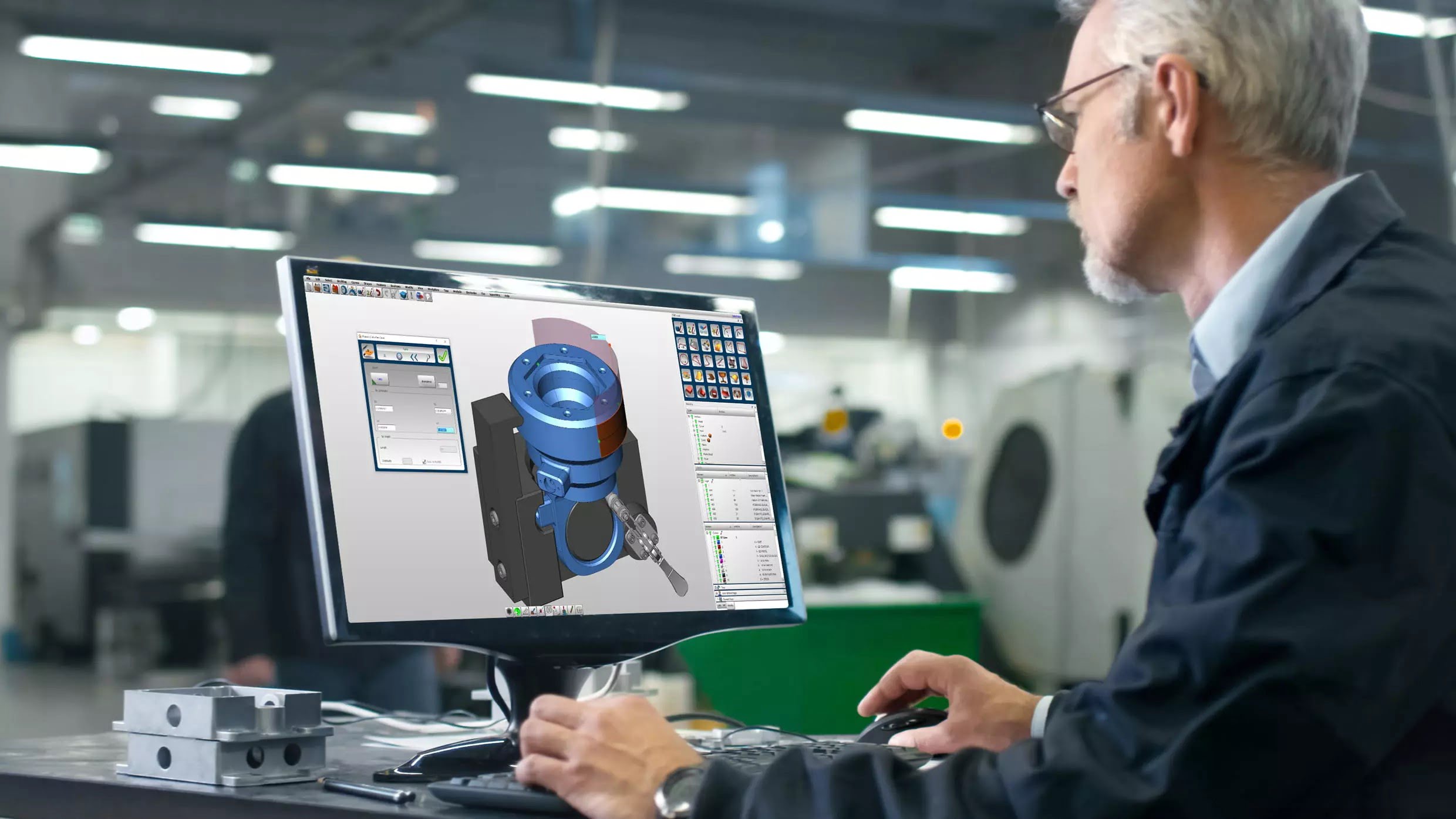
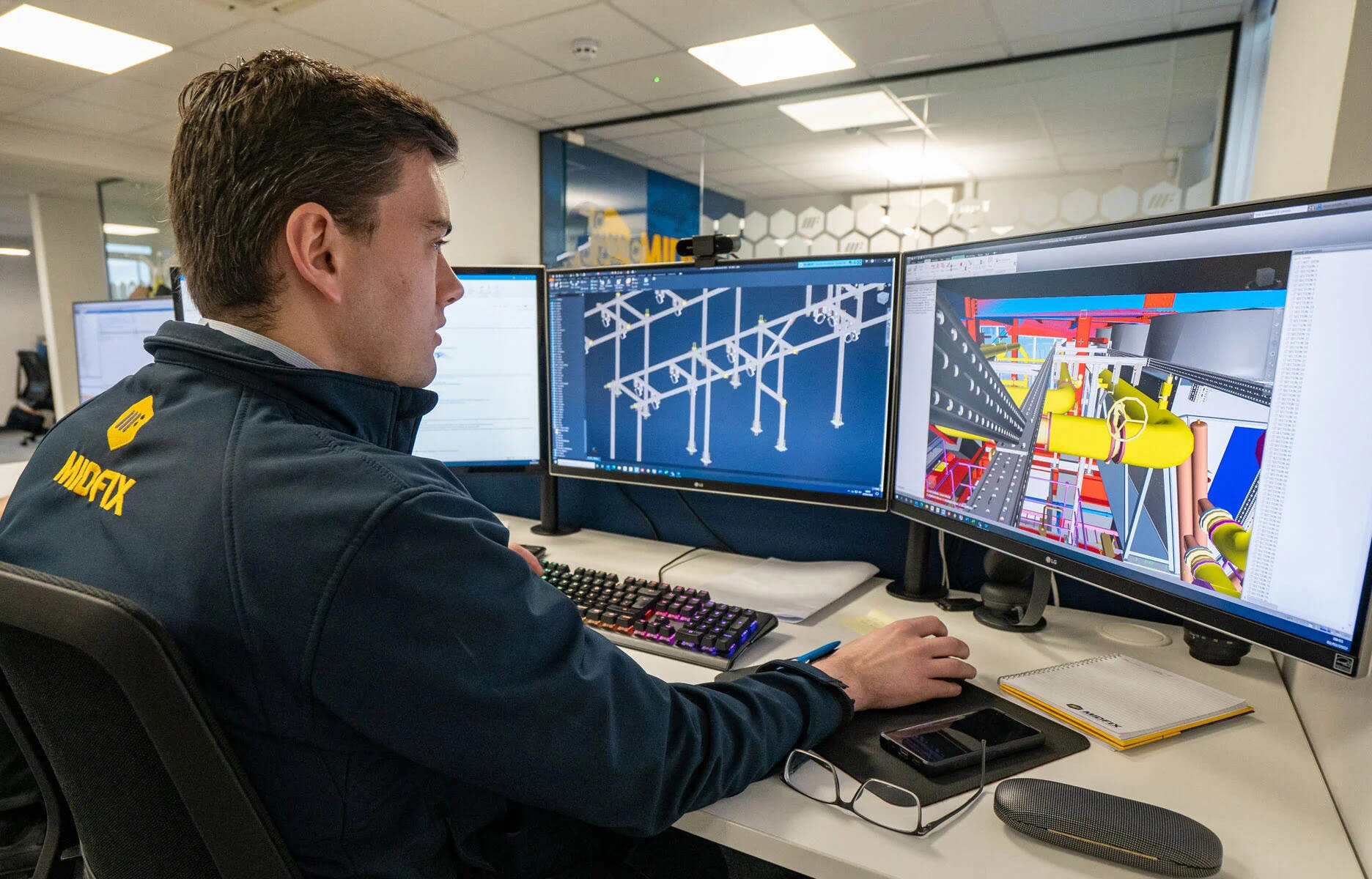
In the field of architecture and design, the use of CAD models has become increasingly prevalent. CAD, which stands for Computer-Aided Design, refers to the process of creating and manipulating digital representations of physical objects and spaces. These CAD models enable architects, engineers, and designers to visualize, analyze, and communicate their ideas in a virtual environment.
Over the years, CAD models have revolutionized the way architectural designs and plans are developed. With the help of advanced software tools, architects and designers can now create intricate and detailed 3D representations of buildings, interiors, landscapes, and more. This technology has significantly streamlined the design process, allowing for faster iterations, increased accuracy, and improved collaboration among professionals.
In this article, we will explore the definition, importance, types, advantages, and disadvantages of CAD models. We will also delve into the various applications of CAD models and the challenges involved in creating them. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of CAD models and their impact on the architecture and design industry.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD models revolutionize architecture and design by enhancing visualization, accuracy, collaboration, and efficiency. Despite challenges, they are indispensable for creating realistic visualizations and streamlining the design process.
- The widespread applications of CAD models across diverse industries, from architecture to urban planning, highlight their pivotal role in transforming the design process. Despite challenges, CAD models have become invaluable tools for designers.
Read more: How To Rotate CAD Model Space
Definition of CAD Models
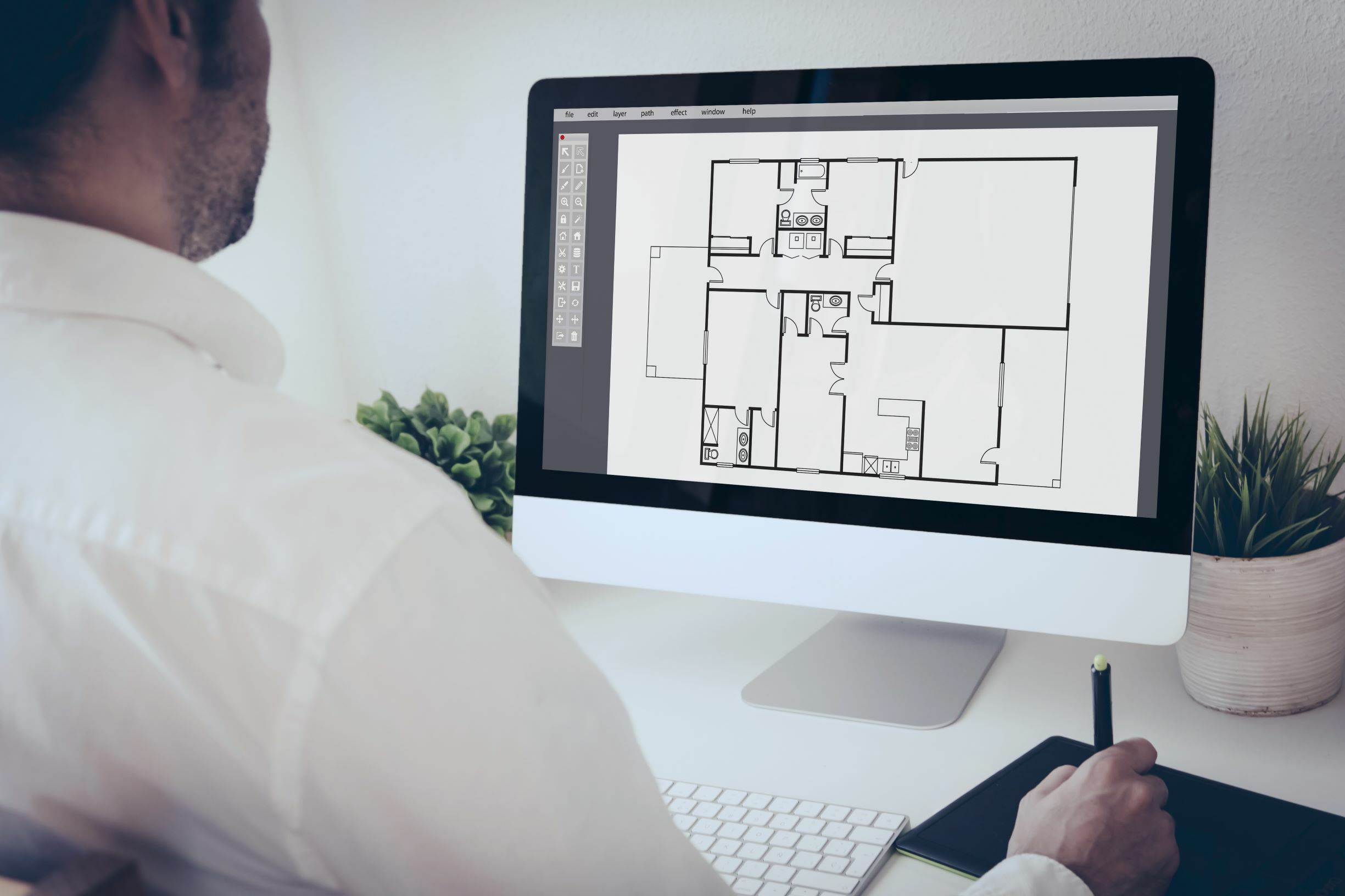
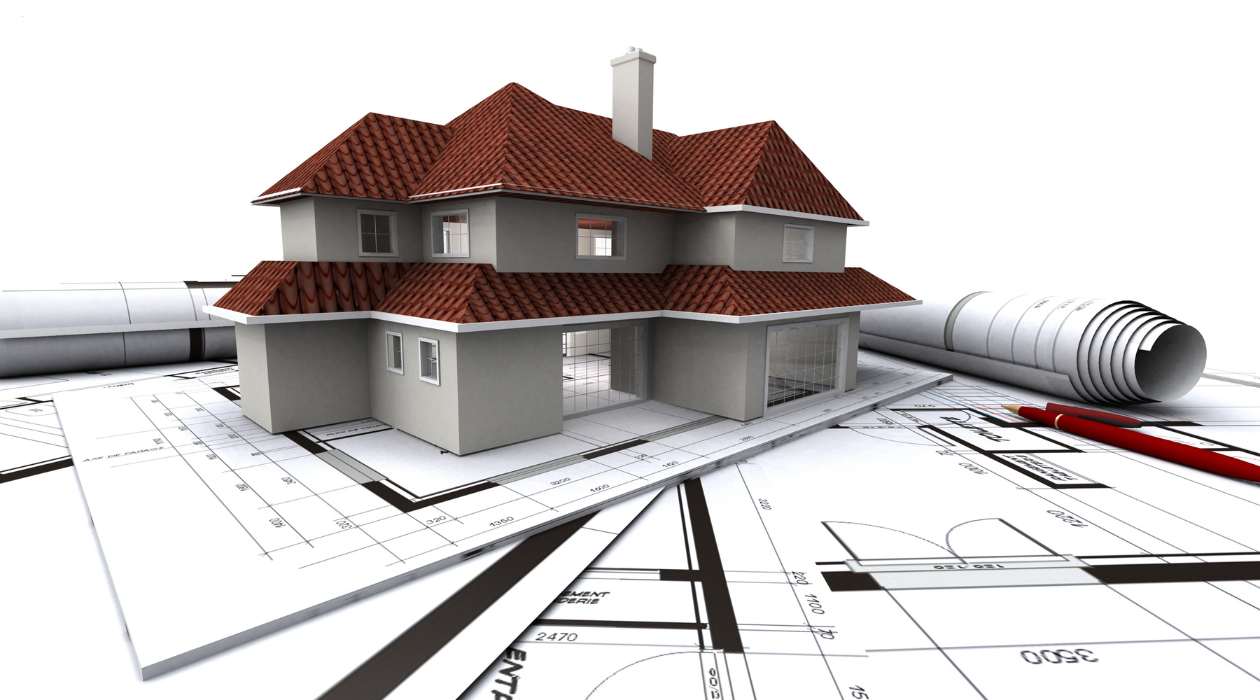
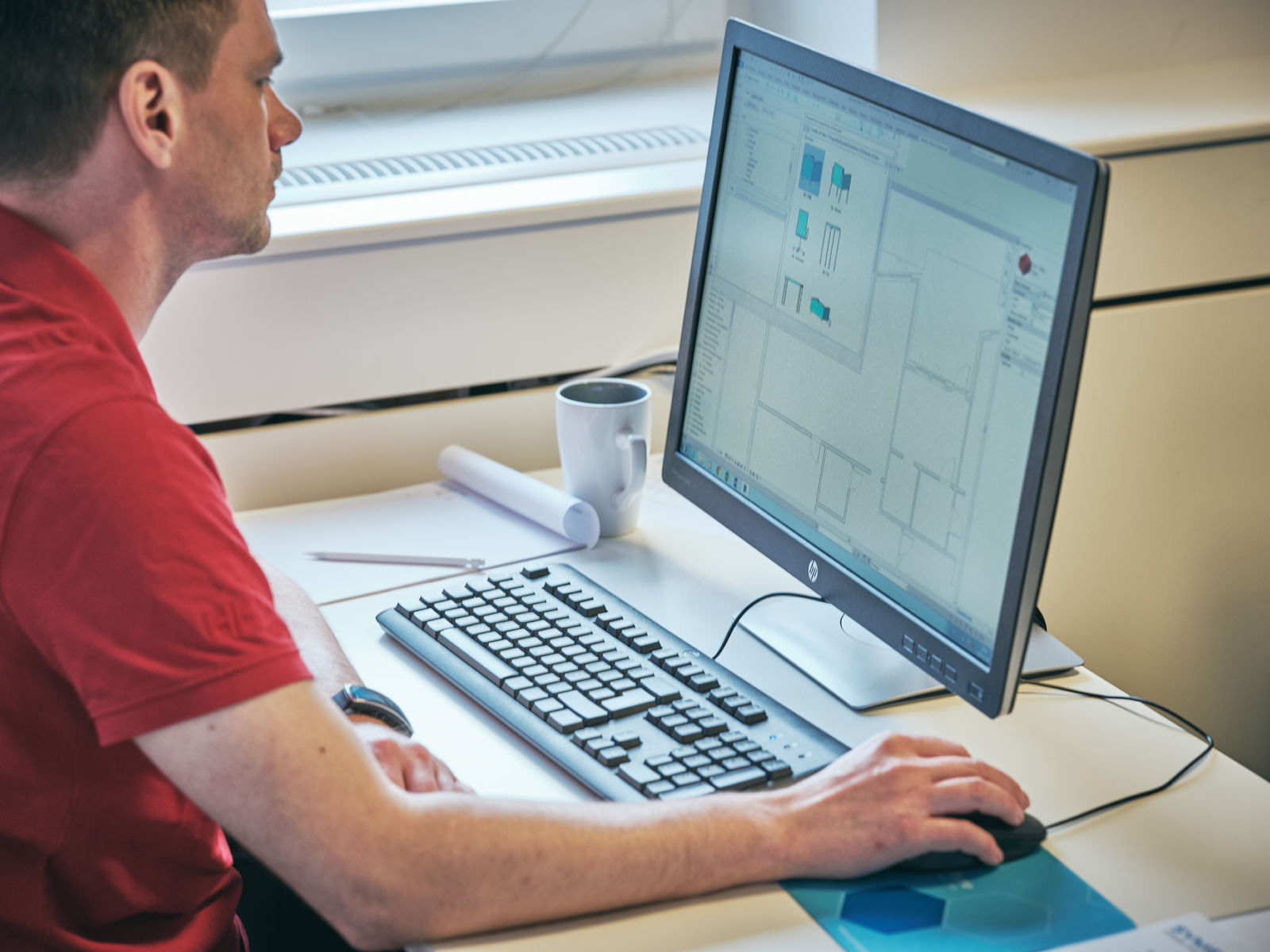
CAD models, as mentioned earlier, are digital representations of physical objects and spaces created using computer-aided design software. These models are created by architects, engineers, or designers to simulate the appearance and functionality of an object before it is fabricated or constructed. CAD models can range from simple 2D drawings to complex 3D visualizations, depending on the level of detail required.
CAD models are typically created using geometric modeling techniques, where the object is represented by mathematical formulas and algorithms. These models can be manipulated and modified in various ways, allowing for easy exploration of different design iterations. CAD software provides a range of tools and features that enable professionals to add dimensions, textures, colors, and other visual elements to the models, enhancing their realism and accuracy.
CAD models can encompass a wide range of objects, including buildings, furniture, electronic devices, and even entire cities. They can be used in different stages of the design process, from initial concept development to detailed construction plans. CAD models are also often used for virtual prototyping and simulation, allowing designers to test the performance and functionality of their designs before they are physically built.
One of the key aspects of CAD models is their parametric nature. Parametric modeling allows designers to define relationships and constraints between different elements of the model. For example, changing the height of a wall in a building model will automatically adjust the dimensions of connected walls, windows, and doors, ensuring overall consistency and eliminating the need for manual adjustments.
Overall, CAD models provide a powerful tool for architects, engineers, and designers to visualize and communicate their ideas effectively. They serve as a bridge between the conceptual and physical realms, facilitating better decision-making, collaboration, and innovation in the field of architecture and design.
Importance of CAD Models
CAD models have become an indispensable tool in the architecture and design industry. They offer numerous benefits and play a crucial role in the design and development process. Here are some of the key reasons why CAD models are important:
- Visualization: CAD models provide a realistic visual representation of the design concept. They enable architects, engineers, and clients to visualize how the final product will look, allowing for better decision-making and feedback.
- Accuracy and Precision: CAD models allow for precise measurements and dimensions, ensuring that the design is accurately captured. This reduces errors and inconsistencies that may occur during the construction phase, saving time and resources.
- Flexibility and Iteration: CAD models can be easily modified and iterated upon. Designers can quickly explore different options, make changes, and evaluate the impact of those changes in real-time. This flexibility promotes creativity and innovation in the design process.
- Collaboration: CAD models facilitate collaboration between different professionals involved in the design project. Multiple stakeholders can view and interact with the model, providing valuable input and feedback. This collaboration streamlines communication and improves coordination.
- Cost and Time Savings: By using CAD models, architects and designers can identify and resolve design issues early on. This minimizes costly rework during construction and reduces the overall project timeline. Additionally, CAD models enable efficient material estimation and optimized resource allocation.
- Sustainability: CAD models can aid in sustainable design practices by allowing designers to analyze energy efficiency, daylighting, and other environmental factors. This helps in creating greener and more sustainable buildings and spaces.
- Documentation: CAD models serve as a comprehensive and accurate documentation of the design intent. They can be used as a reference during the construction phase and for future maintenance and renovations.
- Marketing and Presentation: CAD models can be used for marketing purposes, showcasing the design to potential clients and investors. They provide a visually compelling representation that effectively communicates the design concept.
In summary, CAD models offer immense value in the architecture and design industry. They improve visualization, accuracy, collaboration, and efficiency. With their ability to facilitate creativity and innovation, CAD models have become an integral part of the design process, helping professionals bring their ideas to life.
Types of CAD Models
CAD models come in various types, each with its own purpose and level of complexity. Here are some of the commonly used types of CAD models in the architecture and design industry:
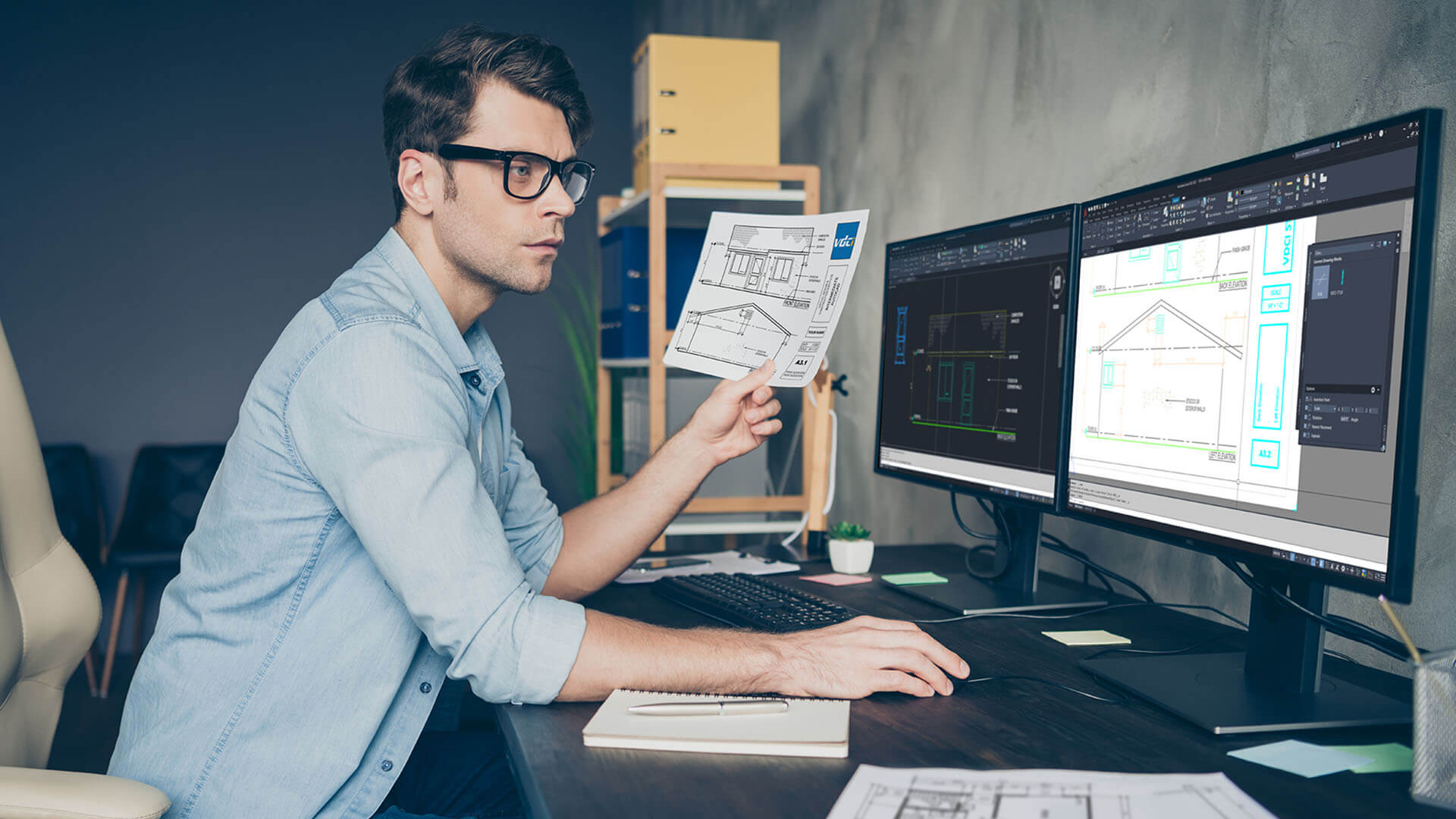
- 2D Models: 2D models are the most basic type of CAD models. They represent objects and spaces using only height and width dimensions, without any depth. 2D models are often used for creating floor plans, elevations, and other technical drawings. They provide a clear and concise representation of the design layout.
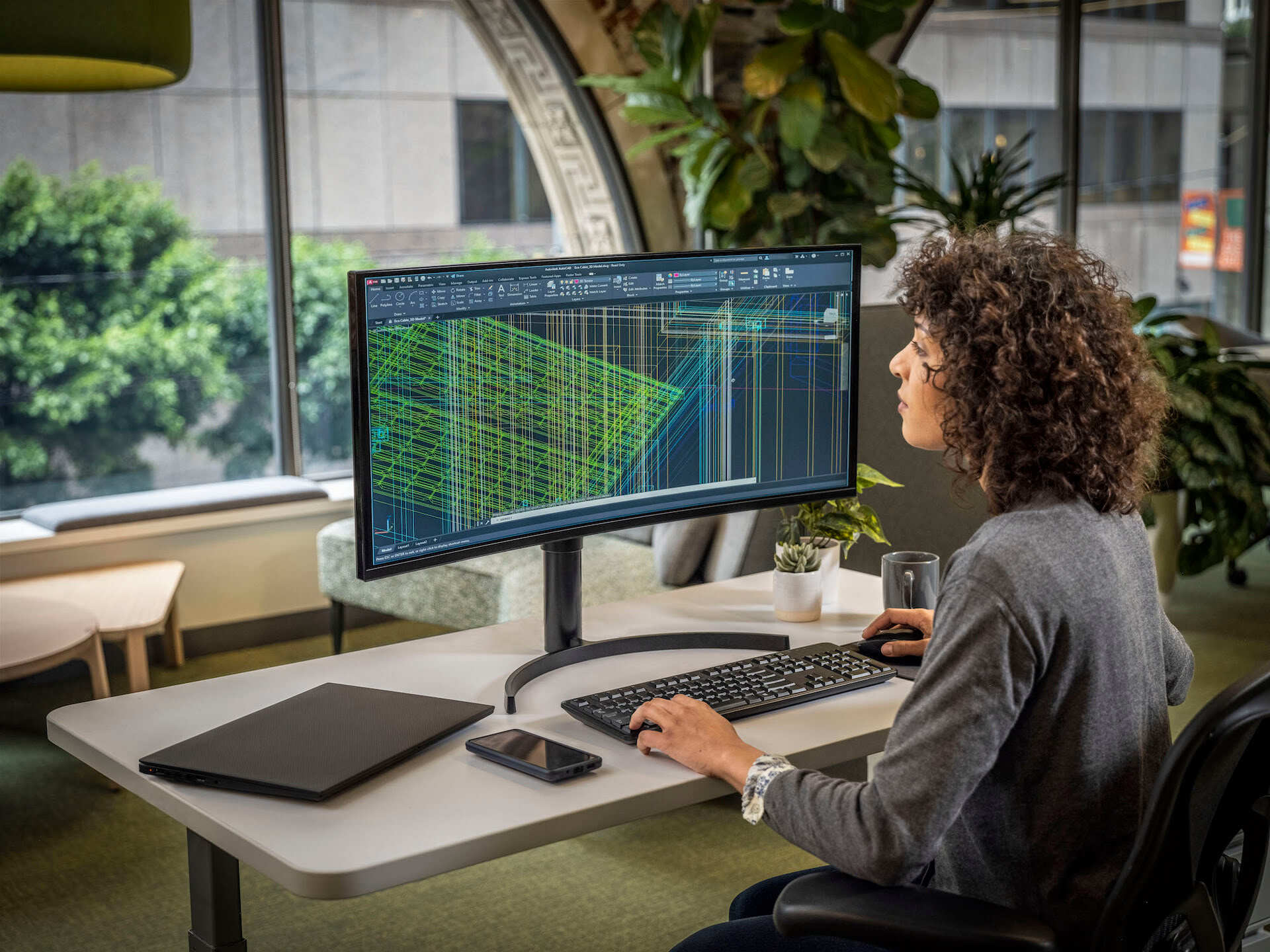
- 3D Models: 3D models add the element of depth to the design representation. They provide a more realistic and immersive view of the object or space. 3D models are commonly used for visualizing buildings, interiors, landscapes, and other architectural elements. They allow for a better understanding of spatial relationships and help in identifying design issues.
- Parametric Models: Parametric models are built using parametric modeling techniques, where the dimensions and attributes of the model are defined through parameters and relationships. Changes made to one parameter automatically update other related elements in the model. Parametric models enable designers to easily modify and adapt the design while maintaining consistency and accuracy.
- BIM Models: Building Information Modeling (BIM) models are comprehensive digital representations of a building project. BIM models include not only the physical aspects of the building, but also information about materials, costs, schedules, and more. BIM models allow for coordination and collaboration between different disciplines involved in the construction process, promoting efficiency and minimizing errors.
- Mesh Models: Mesh models are commonly used in digital sculpting and organic modeling. They are composed of interconnected polygons that create a mesh-like structure. Mesh models are highly detailed and can accurately represent complex and irregular shapes. They are often used in product design and character modeling.
- Surface Models: Surface models focus on the external surfaces of an object, rather than its internal structure. They are used to represent smooth and curvaceous designs, such as car bodies or furniture. Surface models provide a high level of aesthetic detail and are often used in industrial design and automotive industries.
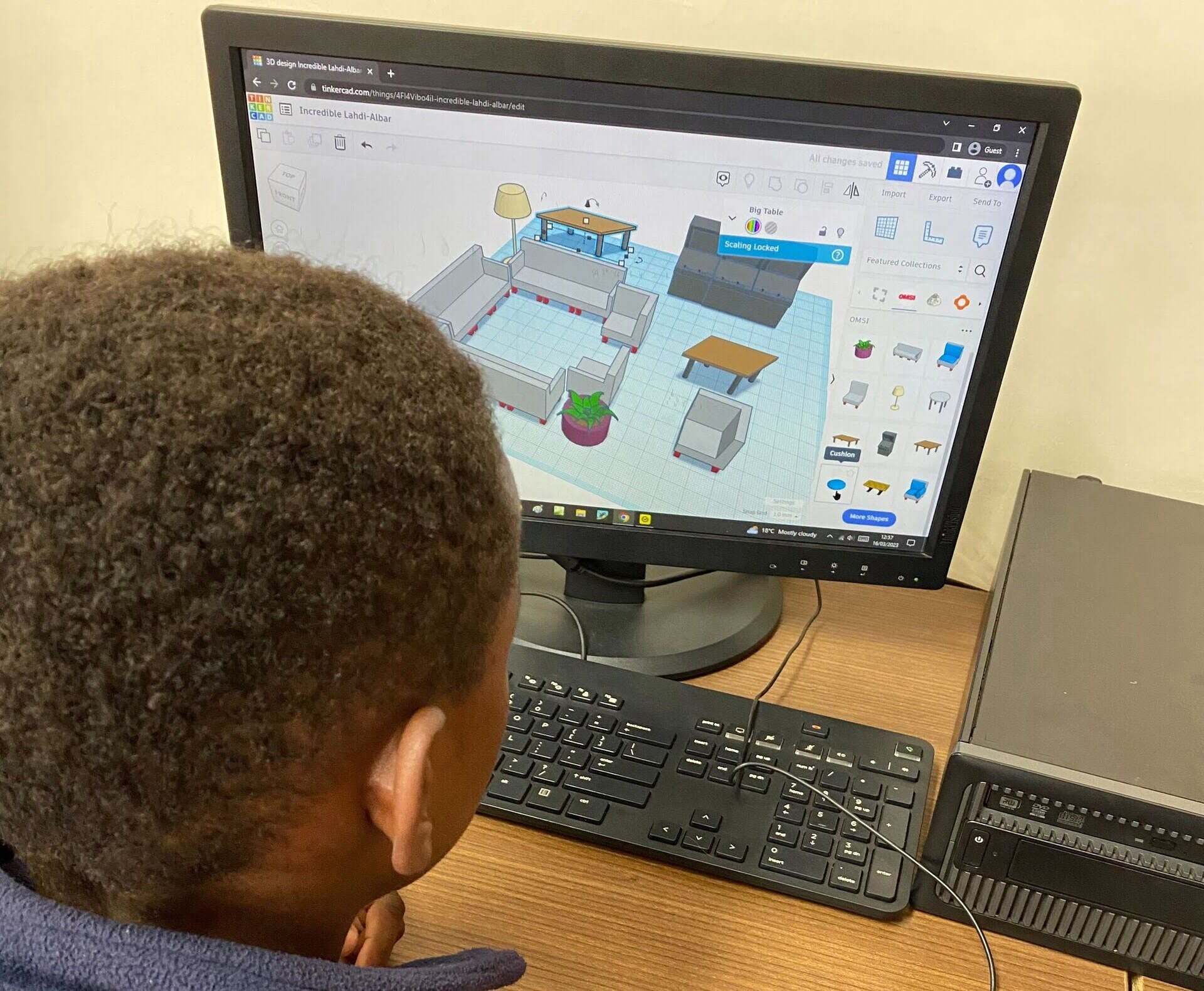
- Virtual Reality (VR) Models: VR models are designed specifically for virtual reality environments. These models enable users to experience the design in an immersive and interactive way. VR models are beneficial for client presentations, as they provide a realistic sense of scale and space.
These are just a few examples of the different types of CAD models available. The choice of model type depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired level of detail and functionality.
Advantages of CAD Models
CAD models offer numerous advantages that have transformed the architecture and design industry. These advantages have revolutionized the design process, enabling professionals to work more efficiently and effectively. Here are some key benefits of using CAD models:
- Improved Visualization: CAD models provide a realistic visual representation of the design concept, allowing architects, engineers, and clients to better understand and visualize the final product. This leads to better decision-making and more accurate feedback in the early stages of the design process.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: CAD models allow for precise measurements, ensuring that the design is accurately captured. Designers can easily modify dimensions, angles, and other parameters, reducing errors and inconsistencies that may occur during the construction phase.
- Efficient Design Iteration: CAD models enable quick and effortless exploration of design alternatives. Changes can be easily made and evaluated in real-time, promoting creativity and innovation. This flexibility in design iteration saves time and allows for the development of optimized and refined designs.
- Better Collaboration: CAD models facilitate collaboration between architects, engineers, and other project stakeholders. Multiple professionals can simultaneously work on the same model, making real-time changes and sharing feedback. This improves communication, coordination, and overall project efficiency.
- Cost and Time Savings: By using CAD models, potential design flaws can be identified and resolved early in the design process. This helps minimize costly rework during the construction phase. CAD models also enable efficient material estimation and resource allocation, leading to cost savings and improved project timelines.
- Virtual Prototyping and Simulation: CAD models can be used for virtual prototyping and simulation, allowing designers to analyze the performance and functionality of their designs. This helps identify potential issues before physical construction begins, saving time and resources.
- Sustainability: CAD models facilitate sustainable design practices by allowing designers to analyze energy efficiency, daylighting, and other environmental factors. This contributes to the creation of greener and more sustainable buildings and spaces.
- Documentation: CAD models serve as comprehensive and accurate documentation of the design intent. They can be used as a reference during the construction phase and for future maintenance and renovations.
Overall, CAD models offer significant advantages in terms of visualization, accuracy, collaboration, efficiency, and sustainability. They have transformed the way architects, engineers, and designers approach the design process, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced client satisfaction.
When creating CAD models, it’s important to use accurate measurements and consider the intended purpose of the design. This will ensure the model is functional and meets the necessary specifications.
Read more: What Is CAD?
Disadvantages of CAD Models
While CAD models offer numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge that there are also some disadvantages associated with their use. These disadvantages can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the level of expertise of the users. Here are some of the common disadvantages of CAD models:
- Steep Learning Curve: CAD software can be complex and require significant training to use effectively. Learning the intricacies of the software and mastering its features can take time and effort, especially for those who are new to CAD modeling.
- Initial Investment: Implementing CAD software and hardware can involve a significant upfront cost. This includes the cost of purchasing licenses, establishing required infrastructure, and training staff. For smaller design firms or individual designers, this initial investment can be a barrier.
- Technical Issues and Software Updates: CAD software and hardware can be prone to technical issues and incompatibilities. Updates to software versions may also require additional training or adaptation for users. This can lead to disruption or delays in the design process.
- Complexity of Design Process: Working with CAD models can sometimes lead to overcomplication of the design process. With the ease of making modifications, designers may be tempted to continuously refine and revise their designs, potentially leading to decision paralysis or loss of focus on the project goals.
- Dependency on Software: CAD models require software to create, modify, and view them. In the event of software compatibility issues, data loss, or technical failures, there is a risk of losing access to the CAD models and the associated work. Adequate backup measures and software compatibility checks are essential to mitigate this risk.
- Limitations in Creativity: While CAD models provide a platform for visualizing and manipulating designs, they can sometimes limit the creativity of designers. The constraints of the software and the reliance on predefined templates and elements may restrict the freedom to explore unconventional approaches.
- Lack of Physical Sensory Experience: CAD models are digital representations that lack the physical and sensory experience of real-world objects. This can make it challenging to fully understand the tactile qualities, materiality, and spatial perception of the design, which may impact the final outcome.
- Reliance on Technical Skills: Creating and manipulating CAD models requires technical skills and knowledge. Designers need to be proficient in using the software and understanding the underlying principles of computer-aided design. This can be a barrier for those without a technical background.
Despite these disadvantages, the benefits of CAD models still outweigh the drawbacks for most professionals in the architecture and design field. It is important to address these challenges through proper training, maintenance, and a balanced approach to utilizing CAD models in the design process.
Applications of CAD Models
CAD models have a wide range of applications across various industries. They are especially prevalent in the architecture and design field, where their versatility and functionality have transformed the way professionals create and communicate their designs. Here are some common applications of CAD models:
- Architectural Design: CAD models are extensively used in architectural design to create digital representations of buildings and structures. Architects can create detailed 3D models of exteriors and interiors, allowing them to visualize and refine the design before construction begins. These models aid in communicating design concepts to clients, ensuring that their vision is accurately captured.
- Interior Design: CAD models play a crucial role in interior design by enabling designers to plan and visualize the layout, furniture placement, and overall aesthetics of a space. Designers can create 3D models that accurately represent materials, colors, and lighting, helping clients understand the final look and feel of the interior design scheme.
- Product Design and Engineering: CAD models are widely used in product design and engineering to create digital prototypes and simulate product functionality. Designers can use CAD models to refine product concepts, test assembly procedures, and analyze mechanical properties. This allows for faster product development cycles and improved overall quality.
- Landscape Design: CAD models are employed in landscape design to create virtual representations of outdoor spaces, gardens, and parks. Designers can visualize the placement of trees, shrubs, pathways, and other landscape elements. This helps in creating aesthetically pleasing and functional outdoor environments.
- Urban Planning: CAD models are used in urban planning to analyze and simulate the impact of development projects on the existing landscape. Planners can create 3D models of cities, incorporating proposed buildings and infrastructure, to evaluate factors such as traffic flow, zoning regulations, and environmental impacts.
- Civil Engineering and Construction: CAD models are essential in civil engineering and construction for creating accurate design plans, analyzing structural integrity, and coordinating construction activities. Civil engineers can use CAD models to design roadways, bridges, and other infrastructure, while construction professionals can visualize and plan construction sequences.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): CAD models are utilized in VR and AR applications to create immersive and interactive experiences. Designers and clients can explore a virtual representation of a design in 360 degrees, giving a realistic sense of scale, proportion, and spatial relationships.
- Prototype Development: CAD models are used to create physical prototypes through 3D printing or CNC machining. These prototypes allow designers to test the functionality and usability of their designs before mass production, reducing costly iterations and potential product failures.
These are just a few examples of the countless applications of CAD models in various industries. As technology continues to advance, CAD models are likely to play an even greater role in design and innovation across different fields.
Challenges in Creating CAD Models
While CAD models offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges that need to be addressed in the process of creating them. Designers and architects often encounter these challenges when working with CAD software. Here are some common challenges faced in creating CAD models:
- Complexity: CAD software can be complex and require extensive training to use effectively. The multitude of features, tools, and functionalities can be overwhelming, especially for users who are new to CAD modeling.
- Data Management: Creating CAD models involves handling and managing a large amount of data. This includes the design files, associated textures, external references, and other related information. Ensuring proper organization and version control of data can be challenging, especially in collaborative environments.
- Model Accuracy: Achieving accurate measurements and precise modeling can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex geometries or irregular shapes. Designers must ensure that the CAD models accurately represent the intended design, taking into account all relevant dimensions and details.
- Performance and Speed: Advanced CAD models can be computationally intensive and may require powerful hardware to manipulate and view them smoothly. Large file sizes, intricate geometries, and high polygon counts can slow down the modeling process, impacting productivity and workflow.
- Software Compatibility: CAD models may need to be shared and collaborated upon with others who may be using different CAD software or versions. Ensuring compatibility and proper file exchange between different software platforms can be a challenge, as not all software programs have seamless interoperability.
- Design Iteration: While CAD models offer flexibility in design iterations, constantly refining and modifying designs can lead to decision paralysis or loss of focus. Designers need to strike a balance between exploring alternatives and making progress towards meeting project goals and deadlines.
- Design Consistency and Standards: CAD models must adhere to established design standards and industry best practices. Designers need to ensure consistency in naming conventions, layer organization, dimensioning, and other design elements for smooth collaboration and effective documentation.
- Technical Expertise: Creating complex CAD models requires technical knowledge and expertise. Designers need to grasp concepts like parametric modeling, surface modeling, and other advanced techniques to effectively utilize CAD software. Continuous learning and skill development are essential to overcome this challenge.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technical proficiency, training, efficient workflows, and effective communication among team members. By addressing these challenges, designers and architects can fully harness the advantages of CAD models and maximize their potential in the design process.
Conclusion
CAD models have revolutionized the architecture and design industry, providing architects, engineers, and designers with powerful tools to visualize, analyze, and communicate their ideas. The benefits of CAD models are evident in their ability to improve visualization, accuracy, collaboration, and efficiency throughout the design process. From creating complex 3D models to simulating product functionality, CAD models have become an indispensable part of modern design workflows.
Despite the advantages, it is important to acknowledge the challenges associated with creating CAD models. These challenges include the complexity of the software, data management issues, accuracy concerns, and software compatibility. However, with proper training, efficient data management practices, and continuous skill development, designers can overcome these challenges and fully leverage the capabilities of CAD models.
The application of CAD models is widespread across diverse industries, including architecture, interior design, product design, engineering, landscaping, and urban planning. CAD models have significantly improved the design process, enabling designers to visualize concepts, iterate design ideas, and communicate their vision effectively. These digital models have also promoted sustainable design practices, cost savings, and better decision-making.
As technology continues to advance, CAD models are expected to play an even more significant role in the future. Integration with virtual reality and augmented reality technologies will further enhance the immersive experience of CAD models. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may unlock new possibilities, automating tasks and enhancing the design capabilities of CAD software.
In conclusion, CAD models have transformed the architecture and design industry. They have become invaluable tools for creating realistic visualizations, improving accuracy, promoting collaboration, and streamlining the design process. Despite the challenges, the benefits of CAD models far outweigh the drawbacks, making them an essential component of modern design practices.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are CAD Models
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Are CAD Models”