Home>diy>Building & Construction>How Do Quantity Surveyors Use BIM?


Building & Construction
How Do Quantity Surveyors Use BIM?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how quantity surveyors in the building construction industry utilize BIM technology to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their project estimations and management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of quantity surveying in the digital age! With the advent of technology, the traditional role of quantity surveyors has evolved to incorporate new tools and methodologies. One such innovation that has revolutionized the field is Building Information Modeling (BIM).
But before we dive into how quantity surveyors use BIM, let’s first understand who they are and what their role entails.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM empowers quantity surveyors to enhance collaboration, improve accuracy in cost estimation, and streamline communication with other project stakeholders, revolutionizing the construction industry.
- While BIM offers significant benefits, quantity surveyors face challenges such as initial costs, software compatibility, and data integrity, requiring careful planning and adaptation to fully leverage its potential.
Read more: What Is A Quantity Surveyor In Construction?
Definition of Quantity Surveyors
Quantity surveyors, also known as construction economists, are professionals who are responsible for managing and controlling the costs of construction projects. They specialize in estimating and managing the financial aspects of the construction process, from initial feasibility studies to final account settlements.
Their role encompasses a wide range of activities, including cost estimating, cost planning, tendering, contract administration, and value engineering. Quantity surveyors work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other project stakeholders to ensure that projects are completed within budget and meet the required quality standards.
Introduction to BIM (Building Information Modeling)
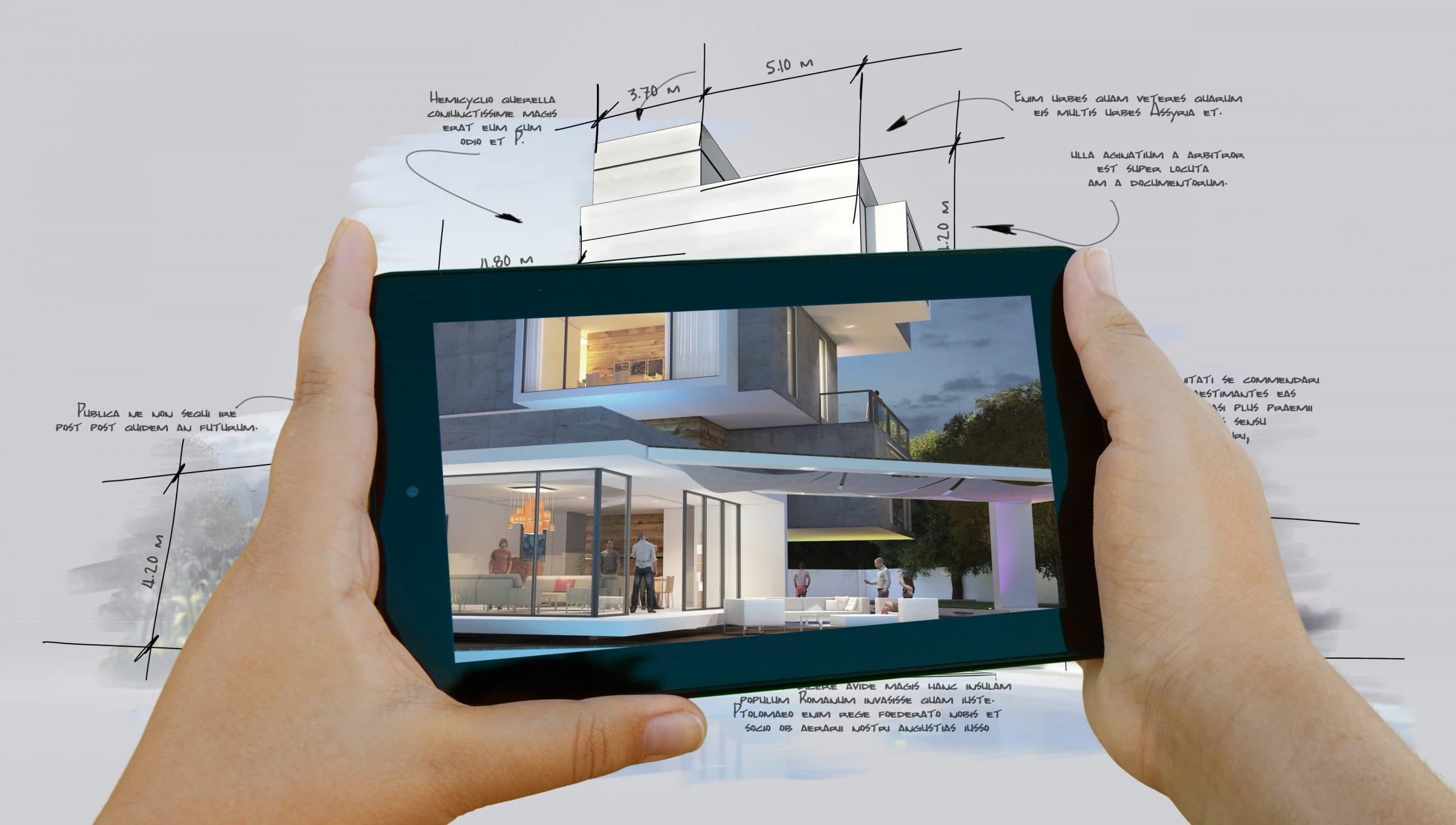
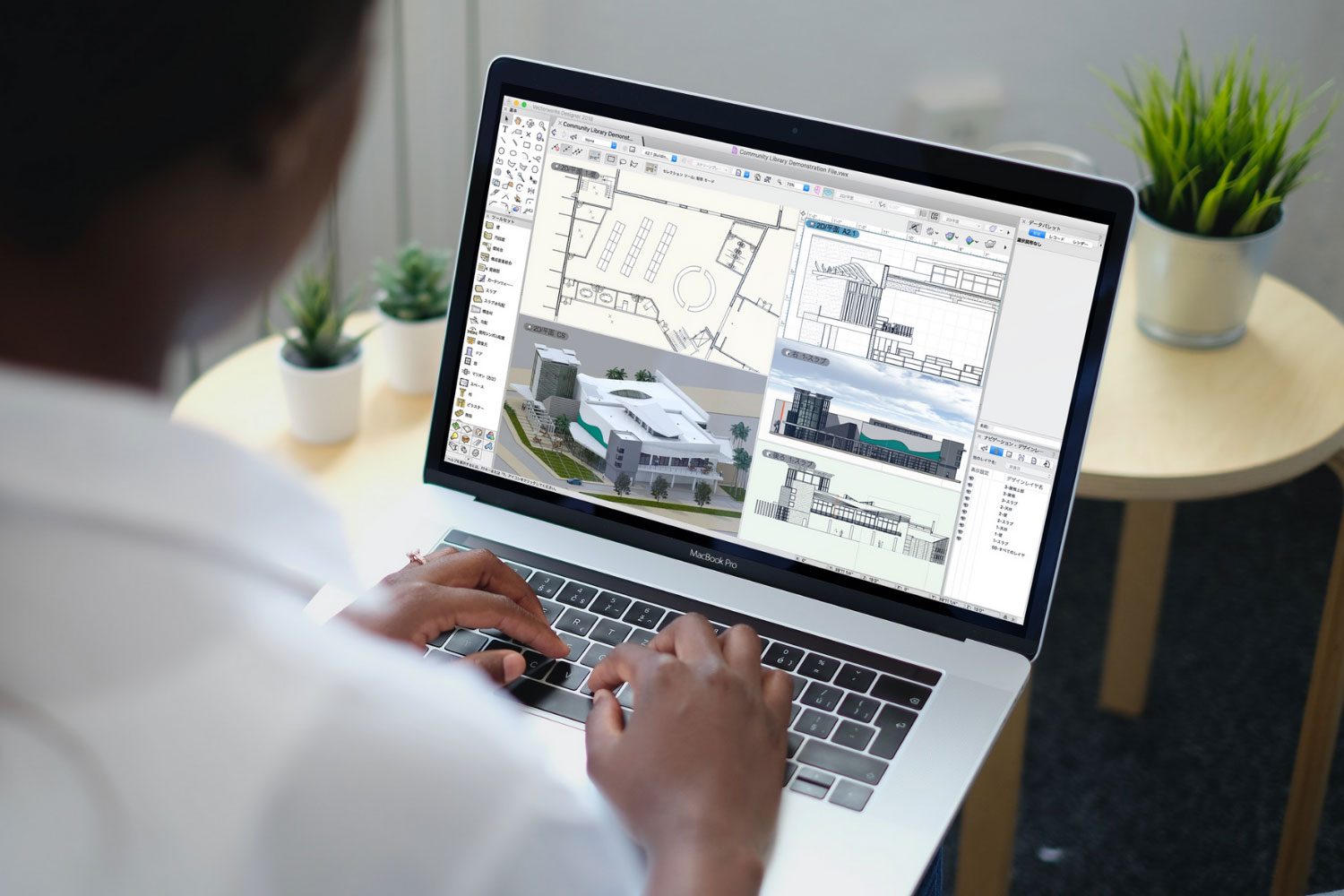
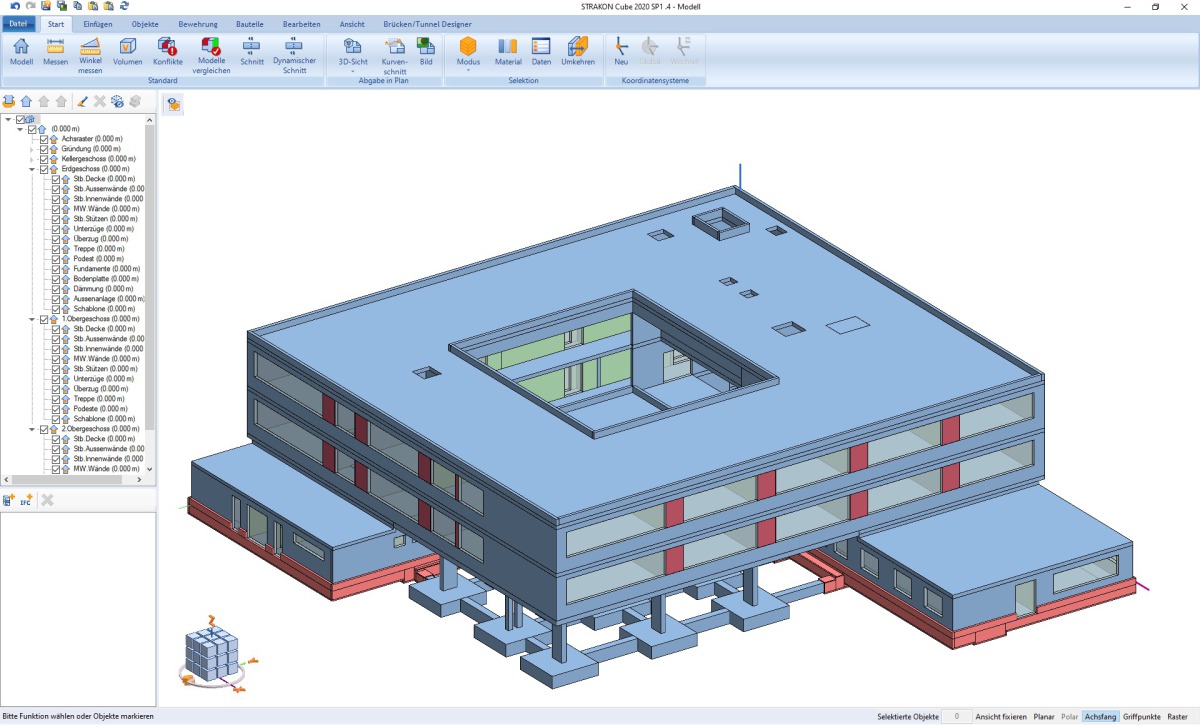
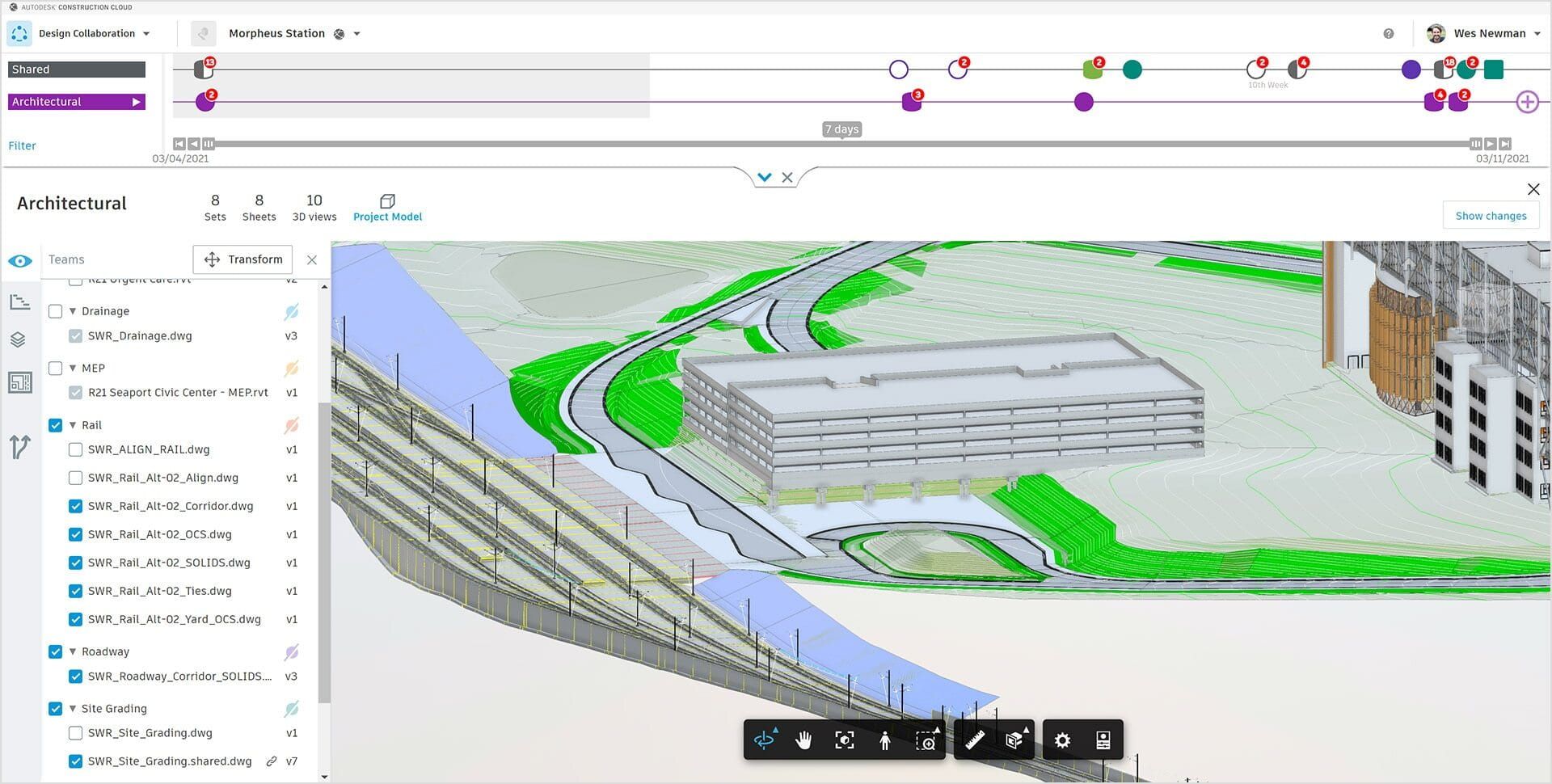
Building Information Modeling, commonly referred to as BIM, is a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project. It is a collaborative process that involves the creation and management of the physical and functional characteristics of a project in a unified digital model.
BIM allows for the integration of various components, such as 3D geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, quantities, and properties of building elements. This digital model serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about the project, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
BIM has gained popularity in the construction industry due to its ability to improve collaboration, reduce conflicts, enhance visualization, and streamline project delivery. Now, let’s explore how quantity surveyors leverage the power of BIM in their work.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM empowers quantity surveyors to enhance collaboration, improve accuracy in cost estimation, and streamline communication with other project stakeholders, revolutionizing the construction industry.
- While BIM offers significant benefits, quantity surveyors face challenges such as initial costs, software compatibility, and data integrity, requiring careful planning and adaptation to fully leverage its potential.
Read more: What Is A Quantity Surveyor In Construction?
Definition of Quantity Surveyors
Quantity surveyors, also known as construction economists, are highly skilled professionals who play a crucial role in the construction industry. They are responsible for managing and controlling the costs involved in construction projects. Quantity surveyors possess a unique combination of technical, financial, and legal expertise.
The primary goal of a quantity surveyor is to ensure that construction projects are completed within budget and meet the required quality standards. They work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other project stakeholders to optimize the financial aspects of a project from inception to completion.
One of the key responsibilities of a quantity surveyor is cost estimating. They use their extensive knowledge of construction materials, labor costs, equipment, and other factors to estimate the overall cost of a project. This involves analyzing architectural and engineering drawings, conducting site visits, and considering various factors that may impact costs.
Quantity surveyors also play a vital role in cost planning. They develop detailed budgets for projects, taking into account all the necessary elements, such as labor, materials, equipment, overheads, and contingencies. These budgets serve as a baseline for tracking and monitoring project costs throughout the construction process.
Another important aspect of a quantity surveyor’s role is tendering. They prepare tender documents, which include detailed project specifications, bills of quantities (BOQs), and other relevant information. They also evaluate bids from contractors and make recommendations based on their expertise in cost analysis and value for money.
During the construction phase, quantity surveyors are responsible for contract administration. They ensure that all parties involved in the project adhere to the terms and conditions of the contract. This includes managing variations, valuing work done, and certifying payments to contractors.
Value engineering is another area where quantity surveyors excel. They identify opportunities to reduce costs without compromising the quality or functionality of the project. This involves analyzing alternative materials, construction techniques, and design solutions to achieve optimal value for resources.
Quantity surveyors are also involved in the final account settlement. They negotiate and settle the final payments with contractors based on the actual work done and any agreed variations. This ensures fair and transparent financial transactions at the end of the project.
Overall, quantity surveyors hold a critical role in the construction industry, combining technical knowledge with financial acumen to ensure the successful delivery of construction projects within budgetary constraints. Through their expertise and attention to detail, they contribute to the overall efficiency and profitability of the construction process.
Introduction to BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Building Information Modeling, commonly referred to as BIM, is a transformative technology that has revolutionized the architecture, engineering, and construction industry. BIM is a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project that allows for the integration and coordination of various components into a unified model.
At its core, BIM is a collaborative process that enables project stakeholders to create, manage, and exchange information about a project in a digital format. This digital model contains not only 3D geometry but also valuable data about the project’s physical and functional characteristics.
One of the key advantages of BIM is its ability to enhance collaboration and communication among project teams. Through the use of a shared digital model, architects, engineers, contractors, quantity surveyors, and other stakeholders can work together in real-time, accessing and updating information as needed. This improved collaboration helps to reduce conflicts, minimize errors and potential rework, and streamline project delivery.
BIM enables better visualization of the project, allowing stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of the design, construction, and operation of a building or infrastructure before it is even built. Through advanced 3D modeling capabilities, BIM helps stakeholders to visualize the spatial relationships between various building elements, identify potential clashes or clashes, and evaluate the overall design aesthetic.
The digital nature of BIM also allows for improved accuracy and efficiency in quantity takeoff and cost estimation, which are essential aspects of a quantity surveyor’s role. By extracting accurate quantities directly from the BIM model, quantity surveyors can generate more precise and detailed cost estimates, reducing the margin for error and improving cost control throughout the project lifecycle.
BIM also supports value engineering by providing greater insight into the performance, functionality, and lifecycle costs of a building or infrastructure. With access to comprehensive data about the project, quantity surveyors can analyze alternative design options and construction methods, identifying opportunities for cost savings without compromising quality.
Furthermore, BIM facilitates the integration of sustainability and energy analysis into the design process. Quantity surveyors can use BIM to assess the environmental impact of different design decisions and evaluate the long-term operational costs of a building. This enables them to make informed recommendations for sustainable design strategies and optimize energy efficiency.
In summary, BIM is a powerful tool that has transformed the construction industry. As quantity surveyors embrace BIM, they can leverage its benefits to enhance collaboration, improve accuracy in cost estimation and quantity takeoff, support value engineering, and contribute to the development of sustainable and efficient buildings. BIM is undoubtedly shaping the future of quantity surveying and revolutionizing the way construction projects are planned, designed, and executed.
Read more: When Is BIM Used?
Benefits of BIM for Quantity Surveyors
Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers numerous benefits to quantity surveyors, enabling them to enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness in managing construction projects. Let’s explore some of the key advantages that BIM brings to the field of quantity surveying.
1. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: BIM enables seamless collaboration and information sharing among project teams. Quantity surveyors can work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders in a coordinated and integrated manner. This improved communication streamlines decision-making processes, reduces conflicts, and enhances overall project coordination.
2. Increased Accuracy in Cost Estimation: BIM provides quantity surveyors with a comprehensive and accurate source of project data. By extracting quantities directly from the BIM model, quantity surveyors can generate precise cost estimates. This eliminates the need for manual measurement and reduces the potential for errors, improving the overall accuracy of cost estimation.
3. Efficient Quantity Takeoff: Quantity takeoff, the process of quantifying and measuring the materials required for a construction project, is greatly streamlined with BIM. Automated quantity takeoff tools integrated with BIM software allow quantity surveyors to extract quantities directly from the model, eliminating manual measurement and reducing time and effort.
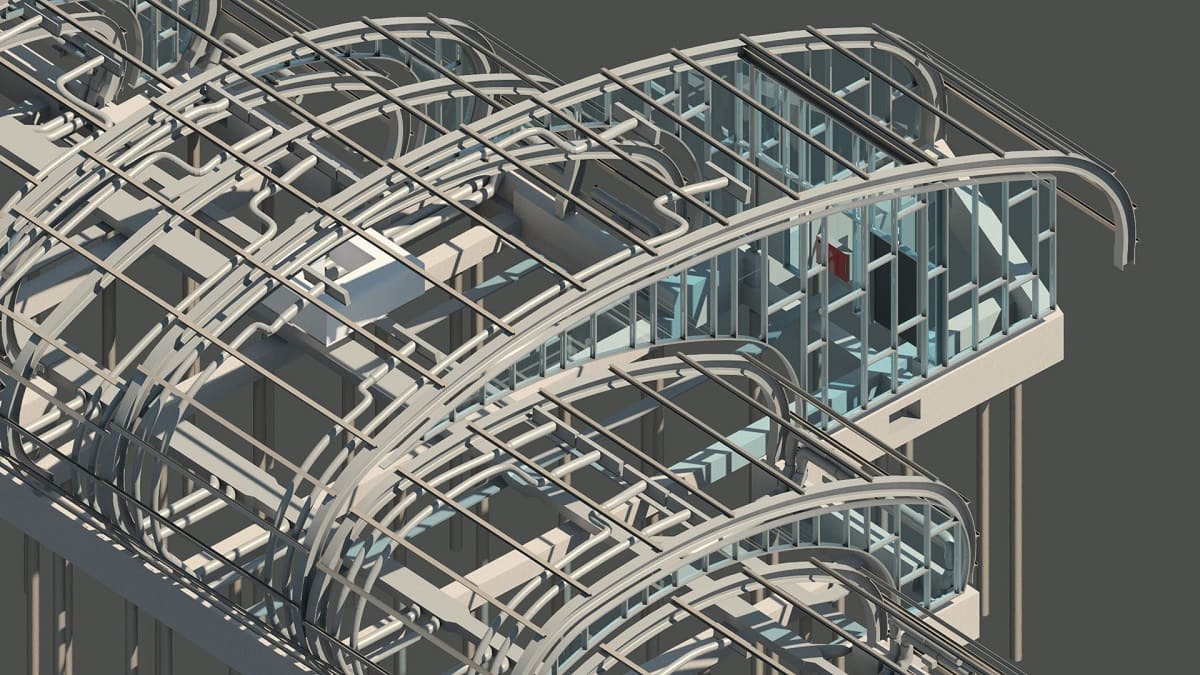
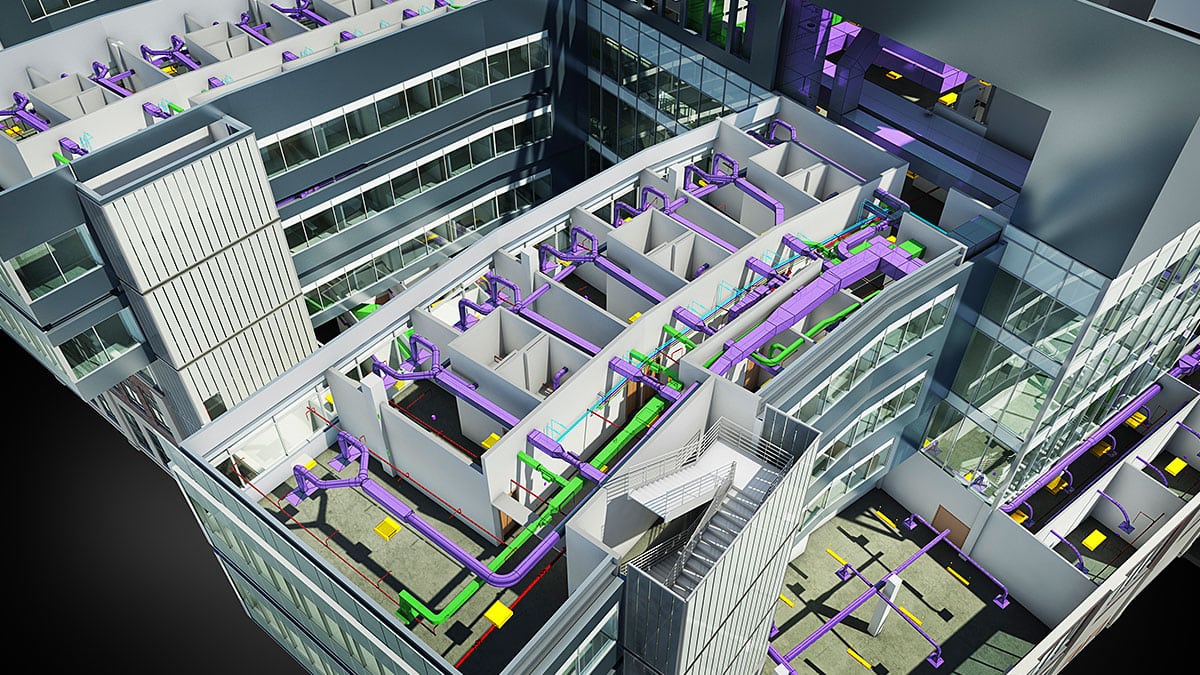
4. Improved Visualization and Clash Detection: BIM models provide quantity surveyors with a visual representation of the project. This allows them to identify clashes or interferences between building components, such as pipes and structural elements, before construction begins. By resolving potential clashes early on, quantity surveyors can minimize the risk of rework and associated costs.
5. Value Engineering and Design Optimization: BIM enables quantity surveyors to analyze alternative design options and construction techniques. By exploring different scenarios in the digital model, quantity surveyors can identify opportunities for cost savings without compromising quality. They can evaluate different materials, systems, and construction methods to optimize value while meeting project requirements.
6. Accurate and Timely Cost Reporting: BIM facilitates real-time cost reporting by integrating quantities and cost data into the digital model. Quantity surveyors can generate reports directly from the BIM software, providing accurate and up-to-date information on project costs. This enables better cost control and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
7. Enhanced Change Management: BIM supports efficient change management by allowing quantity surveyors to quickly assess the impact of design changes on costs and quantities. With the ability to visualize and analyze changes in the digital model, quantity surveyors can accurately evaluate the cost implications and provide timely cost advice to project stakeholders.
8. Improved Sustainability and Lifecycle Cost Analysis: BIM enables quantity surveyors to consider sustainability and lifecycle costs during the early stages of a project. They can analyze energy performance, carbon emissions, and maintenance costs using the data available in the BIM model. This helps in making informed decisions to optimize energy efficiency and reduce long-term operational costs.
Overall, BIM empowers quantity surveyors to become more efficient, accurate, and collaborative in their role. By leveraging the benefits of BIM, quantity surveyors can contribute to the successful delivery of construction projects, ensuring that they are completed within budget and to the highest quality standards.
Role of Quantity Surveyors in BIM Implementation
Quantity surveyors play a vital role in the successful implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM). They bring their expertise in cost management, quantity takeoff, and contract administration to leverage the benefits of BIM throughout the project lifecycle. Let’s explore the key aspects of the quantity surveyor’s role in BIM implementation.
1. Collaboration and Integration: Quantity surveyors collaborate closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other project stakeholders to implement BIM effectively. They actively participate in project meetings, contribute to design discussions, and provide valuable inputs related to cost analysis and value engineering. Through their collaboration, quantity surveyors help integrate BIM into the overall project workflow.
2. BIM Execution Planning: Quantity surveyors are involved in developing the BIM Execution Plan (BEP) for a project. The BEP outlines the strategies, protocols, and processes for BIM implementation. Quantity surveyors contribute to the development of the BEP by identifying the required level of detail for cost estimation, defining the information exchange requirements, and establishing the framework for quantity takeoff from the BIM model.
3. Standardization and Template Development: Quantity surveyors contribute to the standardization of BIM processes and the development of templates and libraries for cost analysis. They collaborate with other project team members to establish guidelines for BIM model development, ensuring consistency and uniformity in quantity takeoff and cost reporting. This standardization streamlines the BIM workflow and enhances efficiency.
4. Quantity Takeoff and Cost Estimation: Quantity surveyors use BIM to perform accurate quantity takeoff and cost estimation. They extract quantities directly from the BIM model, saving time and reducing errors associated with manual measurement. Quantity surveyors can link cost information to the BIM elements, enabling accurate cost estimation and better cost control throughout the project lifecycle.
5. Clash Detection and Design Coordination: Quantity surveyors collaborate with other project team members to identify clashes and interferences in the BIM model. They actively participate in design coordination meetings, providing valuable insights into constructability and cost implications. Through contribution to clash detection and design coordination, quantity surveyors help in reducing potential conflicts and minimizing rework.
6. Change Management: Quantity surveyors play a crucial role in change management within the BIM environment. They assess the impact of design changes on quantities and costs, ensuring that any variations are accurately captured and communicated. By providing timely cost advice and evaluating change requests, quantity surveyors help in maintaining cost control and managing project budgets effectively.
7. Cost Reporting and Analysis: Quantity surveyors use the BIM model to generate accurate and comprehensive cost reports. They leverage the information available in the BIM model to provide detailed cost breakdowns, cost projections, and cost analysis. Quantity surveyors ensure that the cost reports are aligned with the project requirements and provide valuable insights to stakeholders for decision-making.
8. Value Engineering and Sustainability: Quantity surveyors contribute to value engineering and sustainability initiatives within the BIM environment. They analyze alternative design options, construction methods, and materials to optimize cost and enhance sustainability. Through their expertise, they identify opportunities to reduce costs, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the overall value of the project.
In summary, quantity surveyors bring their specialized skills and knowledge to support and drive the effective implementation of BIM. They collaborate with the project team, leverage BIM for quantity takeoff and cost estimation, ensure accurate cost reporting, facilitate change management, and contribute to value engineering and sustainability initiatives. Their role is instrumental in maximizing the benefits of BIM and ensuring successful project outcomes.
Quantity surveyors can use BIM to extract accurate quantities for cost estimation, identify clashes for coordination, and visualize construction sequencing for better project planning.
BIM Tools and Software Used by Quantity Surveyors
Quantity surveyors employ a variety of BIM tools and software to effectively carry out their roles in the construction industry. These tools enable them to streamline their workflows, improve accuracy in quantity takeoff and cost estimation, and enhance collaboration with other project stakeholders. Let’s explore some of the commonly used BIM tools and software by quantity surveyors.
1. BIM Modeling Software: Quantity surveyors utilize BIM modeling software, such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, or Bentley MicroStation, to access and analyze the digital representations of construction projects. These software applications allow quantity surveyors to extract quantities, visualize the model, and perform clash detection to identify any conflicts or interferences within the design.
2. BIM Quantity Takeoff Software: Quantity surveyors utilize specialized software applications like Navisworks Manage, CostX, or Vico Office for BIM quantity takeoff. These tools allow quantity surveyors to extract precise quantities directly from the BIM model, eliminating the need for manual measurement. Additionally, these software applications typically provide features for cost estimation, reporting, and integration with other construction management systems.
3. Cost Estimating Software: Quantity surveyors use cost estimating software applications to develop accurate cost estimates based on the quantities extracted from the BIM model. Software tools like Candy CCS, CostOS, or Buildsoft Estimating allow quantity surveyors to allocate costs to various building elements, produce detailed cost reports, and facilitate cost analysis and comparisons.
4. BIM Collaboration Platforms: Quantity surveyors rely on collaboration platforms, such as BIM 360 or Trimble Connect, to enhance communication and coordination with other project stakeholders. These platforms facilitate real-time access to the BIM model, allow for the exchange of information, and provide a centralized location for discussions, markups, and issue tracking.
5. Project Management Software: Quantity surveyors use project management software applications like Procore, PlanGrid, or Primavera P6 to track project progress, manage project timelines, and monitor cost control. These tools provide features for project scheduling, task management, document management, and budget tracking, ensuring effective project management within the BIM environment.
6. Cost Management Software: Quantity surveyors utilize cost management software applications such as CostX, WinEst, or QSPro to facilitate cost control and financial management throughout the project lifecycle. These tools allow quantity surveyors to track costs, produce budget reports, manage variations, and generate accurate cost forecasts based on the data extracted from the BIM model.
7. Building Performance Analysis Software: Quantity surveyors leverage building performance analysis software applications such as Autodesk Insight or EnergyPlus to evaluate the energy efficiency and sustainability of a building design within the BIM environment. These tools allow for the analysis of energy consumption, daylighting, thermal performance, and other sustainable design factors, helping quantity surveyors identify opportunities for cost savings and energy optimization.
It is worth mentioning that the choice of BIM tools and software may vary based on the specific needs and preferences of quantity surveyors and the software requirements of the project. These tools and software applications are continually evolving and improving, empowering quantity surveyors with advanced functionalities to optimize their work processes and deliver successful construction projects.
Use of BIM in Cost Estimation
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has significantly transformed the way cost estimation is carried out in the construction industry. Quantity surveyors leverage the power of BIM to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of cost estimation processes. Let’s explore the key ways in which BIM is utilized in cost estimation.
1. Accurate Quantity Extraction: BIM enables quantity surveyors to extract quantities directly from the digital model. By linking the model elements to their associated quantities, quantity surveyors can automatically generate accurate and detailed quantity takeoff reports. This eliminates the need for manual measurement, reducing errors and improving the overall accuracy of the cost estimation process.
2. Cost Data Integration: BIM allows for the integration of cost data into the digital model. Quantity surveyors can assign cost information to various building components, including walls, floors, doors, and windows, within the BIM software. This integration of cost data provides a comprehensive overview of the project’s financial aspects, enabling more accurate cost estimation and budget control.
3. Parametric Cost Estimation: With BIM, quantity surveyors can use parametric cost estimation techniques to quickly and accurately estimate costs based on predefined cost parameters. By creating cost libraries within the BIM software, quantity surveyors can assign cost values to various elements and assemblies. This streamlines the cost estimation process, especially during the early stages of a project when limited information is available.
4. 4D and 5D Cost Estimation: BIM allows for the integration of time and cost data, enabling quantity surveyors to perform 4D and 5D cost estimation. Through the incorporation of scheduling information into the BIM model, quantity surveyors can visualize the construction sequence and analyze the associated costs at different stages of the project. This dynamic visualization enhances cost estimation accuracy and facilitates better decision-making.
5. Value Engineering Analysis: BIM facilitates value engineering analysis, a systematic process of evaluating design alternatives and construction methods to optimize value without compromising quality. Quantity surveyors can use BIM to simulate different design options, evaluate the associated costs, and identify opportunities for cost savings and value enhancement. This helps in making informed decisions during the cost estimation process.
6. Cost Reporting and Analysis: BIM enables quantity surveyors to generate detailed cost reports directly from the digital model. By extracting cost data from the BIM software, quantity surveyors can produce accurate and comprehensive reports, including cost breakdowns, material quantities, labor expenses, and more. These reports provide valuable insights for project stakeholders during the cost estimation and budgeting processes.
7. Change Impact Assessment: BIM supports quantity surveyors in assessing the impact of design changes on costs. By linking cost information to the BIM elements, quantity surveyors can quickly and accurately evaluate the cost implications of design variations. This assists in managing change requests, providing stakeholders with timely cost advice, and maintaining cost control throughout the project.
Overall, the use of BIM in cost estimation empowers quantity surveyors to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration in the estimation process. By leveraging the capabilities of BIM, quantity surveyors can produce more accurate cost estimates, improve budget control, and make informed decisions to optimize value and ensure the successful delivery of construction projects.
Read more: What Does A Construction Surveyor Do
Use of BIM in Quantity Takeoff
Quantity takeoff is a critical aspect of the quantity surveyor’s role in the construction industry, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized this process. BIM brings significant advantages to quantity takeoff, enabling quantity surveyors to streamline their workflows, improve accuracy, and enhance collaboration. Let’s explore the key ways in which BIM is utilized in quantity takeoff.
1. Direct Quantity Extraction: BIM allows quantity surveyors to extract quantities directly from the digital model. Instead of manually measuring and counting building components, quantity surveyors can leverage the intelligent data within the BIM model to generate accurate and detailed quantity takeoff reports. This significantly reduces time and effort while minimizing the risk of errors associated with manual measurement.
2. Automated Quantities: BIM software provides automated quantity calculation features, which expedite the quantity takeoff process. Quantity surveyors can define rules and parameters within the BIM software to automatically calculate quantities based on established measurement standards. This automation ensures consistency and reduces human error, resulting in more reliable and efficient quantity takeoff.
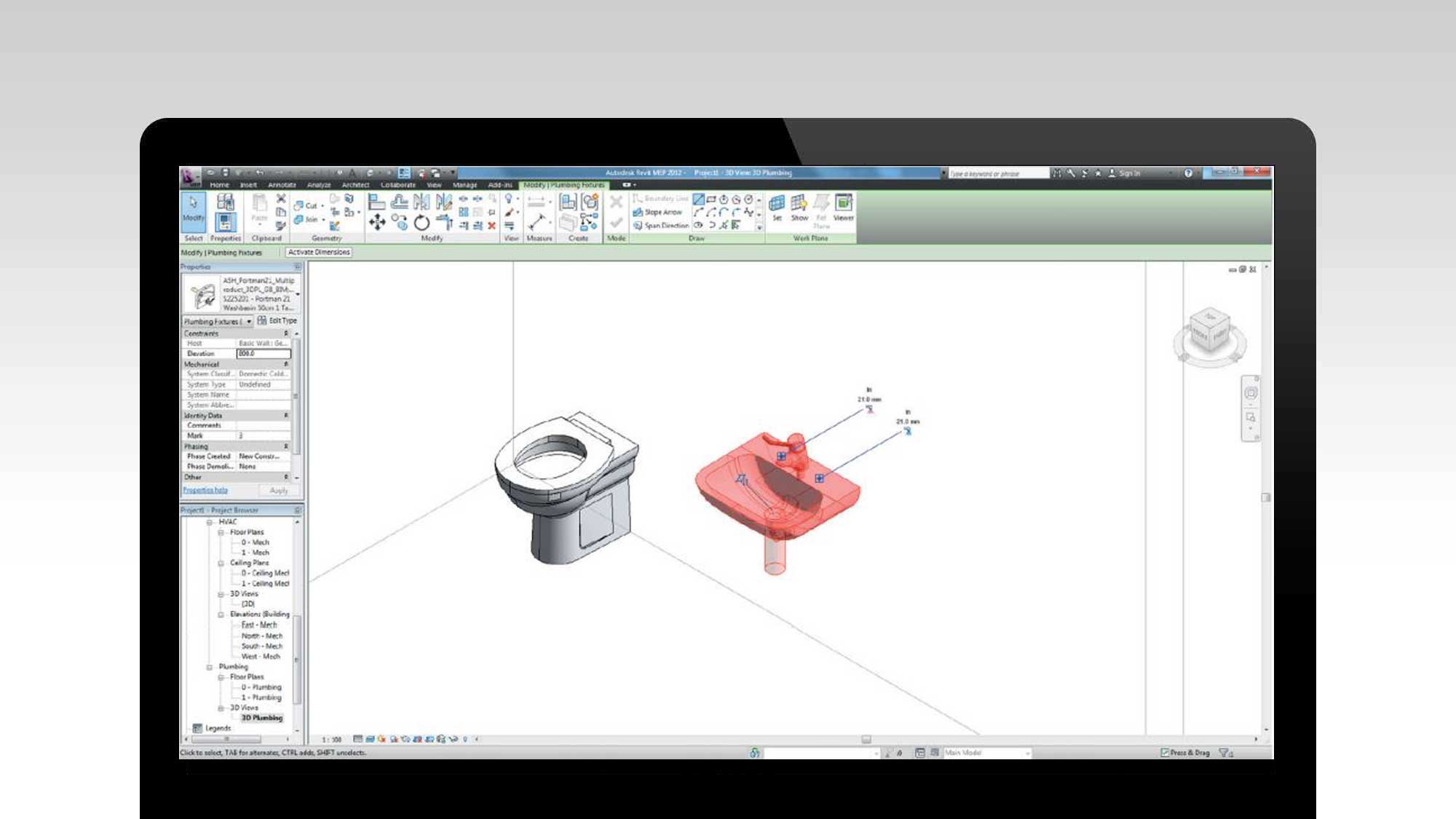
3. Visual Representation: BIM models provide a visual representation of the construction project, allowing quantity surveyors to easily identify and visualize the building components during the quantity takeoff process. With 3D models, quantity surveyors can navigate through the virtual building, visually verifying the quantities extracted and detecting any missing or duplicated items more easily than traditional 2D drawings or manual measurements.
4. Clash Detection: BIM facilitates clash detection during quantity takeoff. Quantity surveyors can analyze the BIM model to identify clashes or interferences between different building components, such as clashes between pipes and structural elements. By resolving these clashes early on, quantity surveyors can ensure that the quantities extracted are accurate and that potential construction issues are addressed before they become costly problems on-site.
5. Database Integration: BIM allows quantity surveyors to integrate external databases, such as cost databases or material databases, into the quantity takeoff process. By linking the BIM model with relevant databases, quantity surveyors can access up-to-date cost and material information, thereby ensuring accurate and consistent quantity calculations and cost estimations.
6. Enhanced Collaboration: BIM fosters improved collaboration between quantity surveyors and other project stakeholders during the quantity takeoff process. The shared BIM model serves as a central repository of project data, enabling real-time collaboration and information exchange between quantity surveyors, architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers. This collaborative environment facilitates smoother communication, reduces information gaps, and improves the accuracy and completeness of quantity takeoff data.
7. Increased Accuracy and Consistency: BIM significantly improves the accuracy and consistency of quantity takeoff. With automated quantity calculations and visual representations, quantity surveyors are less prone to errors and discrepancies that can arise from traditional manual methods. The standardized measurement rules and parameters embedded in the BIM software ensure consistent quantity measurement and reporting across the project.
By leveraging the capabilities of BIM in quantity takeoff, quantity surveyors can streamline their workflows, reduce errors, improve collaboration, and enhance the accuracy and reliability of quantity measurements. The integration of BIM in the quantity takeoff process ultimately contributes to more efficient and successful construction projects.
Use of BIM in Value Engineering
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become an invaluable tool for quantity surveyors in value engineering, a systematic process of evaluating design alternatives and construction methods to optimize value without sacrificing quality. BIM facilitates value engineering by providing quantity surveyors with advanced capabilities to analyze, visualize, and optimize the value of a construction project. Let’s explore the key ways in which BIM is utilized in value engineering.
1. Visualizing Design Options: BIM allows quantity surveyors to create and manipulate 3D models, enabling visualization of various design options. By virtually exploring alternative design scenarios, quantity surveyors can assess the impact of design changes on project costs, functionality, and aesthetics. BIM’s visual representation enhances the understanding of design possibilities, enabling quantity surveyors to identify the most cost-effective and value-maximizing solutions.
2. Clash Detection: BIM’s clash detection capabilities support value engineering by identifying clashes or interferences between building components. Quantity surveyors can use clash detection tools within the BIM software to identify potential conflicts, such as structural clashes or clashes between mechanical and electrical systems. Resolving these clashes early on ensures smoother construction, reduces rework, and contributes to cost savings and improved project efficiency.
3. Cost Analysis and Optimization: BIM enables quantity surveyors to perform cost analysis and optimization during the value engineering process. By integrating cost information into the BIM model, quantity surveyors can evaluate the cost implications of different design options and construction methods. They can compare material costs, labor expenses, and associated costs over the project lifecycle, enabling informed decision-making to achieve the best value for resources.
4. Lifecycle Cost Assessments: BIM supports quantity surveyors in performing lifecycle cost assessments, which involve evaluating the costs associated with the entire lifespan of a building. Quantity surveyors can leverage the data stored within the BIM model to assess long-term operating costs, maintenance costs, and energy consumption. By considering lifecycle costs, quantity surveyors can help optimize value by identifying energy-efficient solutions, minimizing long-term expenses, and enhancing the overall sustainability of a project.
5. Collaborative Environment: BIM fosters collaboration among various project stakeholders, which is critical in value engineering. Quantity surveyors can work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers within the BIM environment to evaluate alternative design options and construction methods. The shared BIM model facilitates real-time communication, information exchange, and informed decision-making, ensuring that all stakeholders contribute to maximizing value while meeting project goals.
6. Integrated Project Data: BIM integrates multiple data sources into a single platform, enhancing the value engineering process. Quantity surveyors can access and analyze data related to materials, costs, energy efficiency, and performance characteristics from within the BIM software. This integrated project data provides a comprehensive understanding of the project’s value drivers, enabling quantity surveyors to make informed decisions that optimize value while considering multiple factors simultaneously.
7. Early Cost Feedback: BIM allows quantity surveyors to provide early cost feedback during the design phase. By linking cost information to the BIM elements, quantity surveyors can estimate the cost implications of design decisions and communicate them to the project team. This early cost feedback is valuable for architects and designers, enabling them to make informed design choices that strike the right balance between cost-efficiency and quality.
BIM’s capabilities in visualization, clash detection, cost analysis, collaboration, and integrated project data make it a powerful tool for quantity surveyors in value engineering. By leveraging BIM, quantity surveyors can optimize value, minimize costs, enhance sustainability, and contribute to the successful delivery of construction projects.
Collaboration and Communication with Other Project Stakeholders
Collaboration and communication are vital elements in the successful execution of construction projects, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) has greatly enhanced the ability of quantity surveyors to collaborate and communicate with other project stakeholders. Through BIM, quantity surveyors can actively engage and collaborate with architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers, leading to improved project outcomes. Let’s explore the key ways in which BIM facilitates collaboration and communication with other project stakeholders.
1. Shared Information Platform: BIM provides a shared information platform that serves as a central repository for project data. This shared platform enables quantity surveyors to access, share, and exchange project-related information, reducing information gaps and ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the latest and most accurate information. By having a centralized and up-to-date source of information, quantity surveyors can collaborate more effectively with other project team members.
2. Real-Time Collaboration: BIM facilitates real-time collaboration among project stakeholders. Through the shared BIM model, quantity surveyors can work simultaneously with architects, engineers, and contractors, eliminating the need for multiple versions of drawings and design documents. Real-time collaboration allows for immediate feedback, faster decision-making, and quicker resolution of issues, leading to improved project efficiency and productivity.
3. Clash Detection and Coordination: BIM’s clash detection capabilities enable quantity surveyors to identify clashes or interferences between different building systems and components. By using clash detection tools within the BIM software, quantity surveyors can collaborate with other stakeholders to coordinate design changes and resolve conflicts before construction commences. This collaborative approach helps reduce conflicts, minimizes rework, and ensures that the project progresses smoothly.
4. Enhanced Visualization: BIM provides a visual representation of the project, allowing quantity surveyors to easily communicate and present complex information to other stakeholders. The visual nature of BIM enables quantity surveyors to illustrate quantities, costs, and design changes in a more understandable and relatable manner. This enhanced visualization facilitates better understanding, collaboration, and decision-making among all project stakeholders.
5. Improved Design Coordination: BIM enables quantity surveyors to actively participate in design coordination meetings and discussions. By having access to the BIM model, quantity surveyors can provide valuable inputs regarding potential cost implications, constructability, and value engineering opportunities. Their expertise in cost management and quantity takeoff contributes to optimizing the design process and ensuring that designs align with the project budget and goals.
6. Seamless Information Exchange: BIM promotes seamless information exchange between quantity surveyors and other project stakeholders. By integrating quantity takeoff data and cost information into the BIM model, quantity surveyors can share relevant cost data, reports, and analysis with architects, engineers, and contractors. This seamless exchange of information fosters transparency, facilitates collaboration, and ensures that all stakeholders are well-informed and aligned throughout the project lifecycle.
7. Value Engineering Discussions: BIM enables quantity surveyors to actively participate in value engineering discussions with architects, engineers, and other stakeholders. Through the BIM model, they can evaluate different design options, construction methods, and material choices, providing valuable insights into cost optimization without compromising quality. This collaborative approach encourages creativity and innovation, leading to the development of more cost-effective and value-enhancing solutions.
Overall, BIM empowers quantity surveyors to collaborate and communicate effectively with other project stakeholders. By utilizing the shared information platform, real-time collaboration, clash detection, enhanced visualization, improved design coordination, seamless information exchange, and active involvement in value engineering discussions, quantity surveyors can contribute to the success of construction projects by ensuring alignment, reducing conflicts, and optimizing project outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Using BIM for Quantity Surveying
While Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers significant benefits to quantity surveyors, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for its effective implementation. Understanding and anticipating these challenges can help quantity surveyors optimize the use of BIM and overcome potential obstacles. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and limitations of using BIM for quantity surveying.
1. Cost and Learning Curve: The initial costs associated with implementing BIM can be a challenge for smaller firms or projects with limited budgets. Acquiring BIM software licenses, training staff, and establishing new workflows require an upfront investment. Additionally, incorporating BIM into existing processes requires a learning curve for quantity surveyors and other project stakeholders. Adequate time, resources, and training are essential to overcome this challenge.
2. Software Compatibility and Collaboration: BIM requires collaboration and information exchange among various project stakeholders. However, compatibility issues can arise when different parties use different BIM software or versions. This can hinder smooth collaboration and data interoperability. Establishing common file formats, protocols, and communication channels is crucial to ensure effective collaboration and seamless information exchange.
3. Model Accuracy and Data Consistency: The accuracy and consistency of the BIM model are pivotal for quantity surveyors in their cost estimation and quantity takeoff processes. Any errors or inconsistencies in the BIM model can lead to incorrect quantity calculations or inaccurate cost estimations. Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the BIM model requires regular quality control checks, data verification, and coordination among project team members.
4. Model Complexity and Level of Detail: BIM models can become increasingly complex as projects progress and more information is added. This complexity can pose challenges for quantity surveyors, especially in extracting accurate quantities and performing cost estimations. Determining the appropriate level of detail for the BIM model becomes critical to strike a balance between the complexity of the model and the efficiency of the quantity surveyor’s work.
5. Data Integrity and Maintenance: BIM relies on accurate and up-to-date data to produce reliable results. Maintaining the integrity of data in the BIM model throughout the project lifecycle can be challenging. Ensuring that all project stakeholders update and maintain the BIM model with the most current information is essential to avoid discrepancies and errors in quantity takeoff and cost estimation.
6. Limited Industry Adoption: Although BIM is gaining momentum in the construction industry, there is still a level of resistance and limited adoption by some stakeholders. Working with project team members who are not fully embracing BIM can pose challenges in terms of data exchange, collaboration, and integration. Building awareness, promoting the benefits of BIM, and advocating for its adoption are important steps in addressing this limitation.
7. Legal and Contractual Issues: As BIM is relatively new, legal and contractual frameworks may still be catching up. The responsibility for errors or omissions in the BIM model, ownership of intellectual property rights, and liability issues can be challenging to resolve. Clarity and agreement on these legal and contractual aspects are crucial to mitigate potential risks and ensure the effective use of BIM in quantity surveying.
8. Data Security and Confidentiality: BIM involves the exchange and storage of large amounts of project data. Ensuring data security and confidentiality becomes essential to protect sensitive project information. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, data access controls, and non-disclosure agreements are necessary to address potential risks associated with the use of BIM.
Despite these challenges and limitations, the benefits of using BIM for quantity surveying outweigh the obstacles. With careful planning, effective collaboration, training, and adaptation of processes, quantity surveyors can navigate these challenges and harness the power of BIM to enhance their work processes, improve accuracy, and contribute to successful construction projects.
Read more: What Is BIM Used For In Construction
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the field of quantity surveying, offering significant benefits and opportunities for construction industry professionals. Through the integration of BIM into their workflows, quantity surveyors have witnessed improved collaboration, enhanced accuracy in cost estimation and quantity takeoff, and streamlined communication with other project stakeholders.
With BIM, quantity surveyors can leverage advanced tools and software to extract quantities directly from the digital model, eliminating manual measurement and reducing errors. The visual representations provided by BIM enable quantity surveyors to better understand and communicate complex information, facilitating efficient decision-making and optimized project outcomes.
BIM’s clash detection capabilities help quantity surveyors identify clashes or interferences between building components, enabling early resolution and reducing costly rework. Integration with cost databases and automation of quantity calculations enhance the accuracy and consistency of cost estimations, supporting better cost control and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Moreover, BIM promotes collaboration and communication among project stakeholders. Quantity surveyors can actively engage with architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers, exchanging information, participating in design discussions, and contributing valuable insights. This collaborative environment fosters innovation, enhances value engineering, and ensures alignment with project goals and budgets.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and limitations associated with implementing BIM in quantity surveying. The initial costs, learning curve, compatibility issues, model complexity, and data integrity are obstacles that require careful attention and planning. Additionally, legal and contractual frameworks, limited industry adoption, and data security concerns need to be addressed to fully leverage the benefits of BIM in quantity surveying.
In conclusion, the integration of BIM in quantity surveying has transformed the industry, empowering professionals to become more efficient, accurate, and collaborative. By embracing BIM and addressing the challenges, quantity surveyors can optimize their work processes, improve project outcomes, and contribute to the sustainable and successful delivery of construction projects. The continuous advancement of BIM technology and increased industry adoption will further enhance the role of quantity surveyors and shape the future of construction project management.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Do Quantity Surveyors Use BIM?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.





0 thoughts on “How Do Quantity Surveyors Use BIM?”