Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is A BIM Specialist?


Building & Construction
What Is A BIM Specialist?
Modified: February 25, 2024
Discover the role and responsibilities of a BIM specialist in the building construction industry. Enhance project efficiency and accuracy with their expertise.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry, and at the heart of this digital transformation is the role of a BIM Specialist. In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, the demand for professionals who can effectively navigate and leverage BIM software and tools is on the rise.
A BIM Specialist plays a crucial role in the successful implementation of BIM workflows and processes throughout the construction project lifecycle. They are responsible for coordinating and managing the digital models and data that serve as the foundation for planning, designing, constructing, and operating buildings.
This article will delve into the role and responsibilities of a BIM Specialist, the skills and qualifications required to excel in this field, the software and tools they need to be familiar with, as well as the collaborative work and communication skills essential for success. Furthermore, we will explore their understanding of the building lifecycle and project management, BIM implementation and coordination, and the benefits of hiring a BIM Specialist.
Whether you are a construction professional looking to gain insights into this emerging field or a project owner aiming to optimize your construction projects, understanding the role of a BIM Specialist is crucial for staying competitive in today’s industry.
So, let’s dive in and explore the world of BIM Specialists!
Key Takeaways:
- A BIM Specialist is crucial for successful BIM implementation in construction projects, bringing expertise in coordination, clash detection, data extraction, and collaboration, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and efficiency.
- Hiring a BIM Specialist offers benefits such as enhanced project coordination, cost savings, improved collaboration, and efficient construction processes, making it a strategic investment for construction projects seeking success in the digital era.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Role and Responsibilities of a BIM Specialist
A BIM Specialist plays a pivotal role in the successful implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in construction projects. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that the BIM process is effectively integrated into all stages of the project, from design and construction to facility management.
Here are some of the key roles and responsibilities of a BIM Specialist:
- Coordinating and managing BIM projects: A BIM Specialist is responsible for overseeing the coordination and management of BIM projects. This includes collaborating with various stakeholders such as architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers to ensure that the project requirements are met.
- Developing and maintaining BIM standards and protocols: BIM Specialists are tasked with developing and maintaining BIM standards and protocols within the organization. This involves creating guidelines for BIM use, naming conventions, file organization, and data exchange between different software platforms.
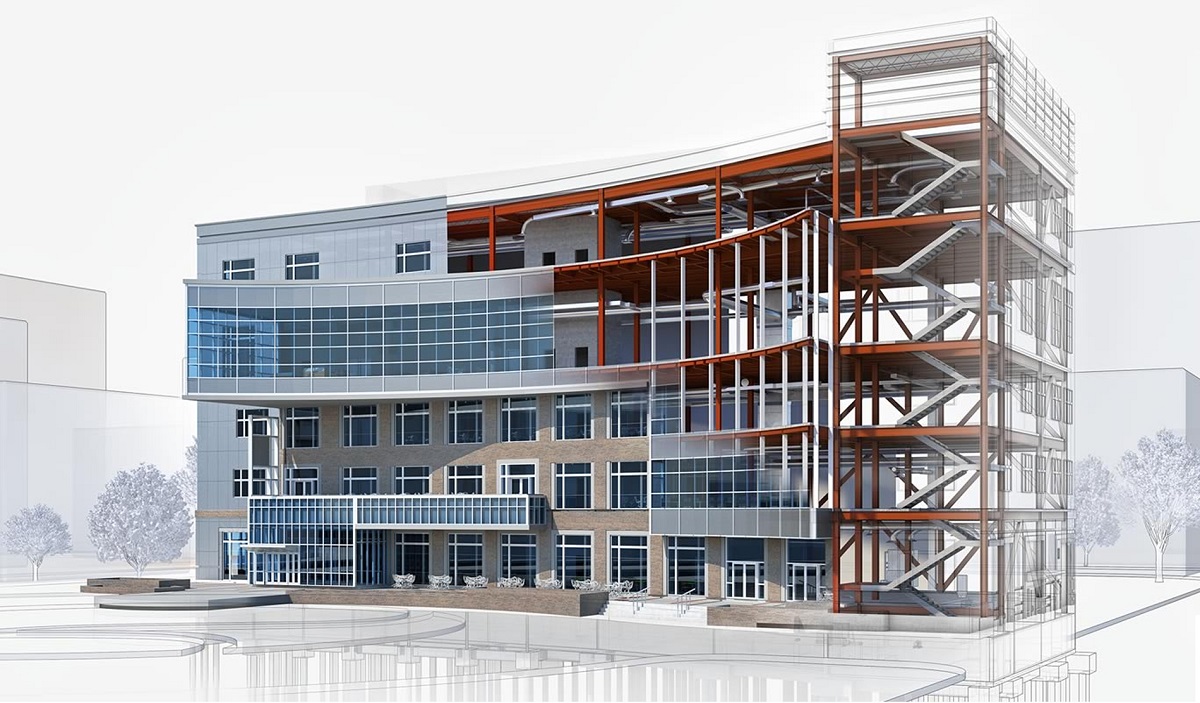
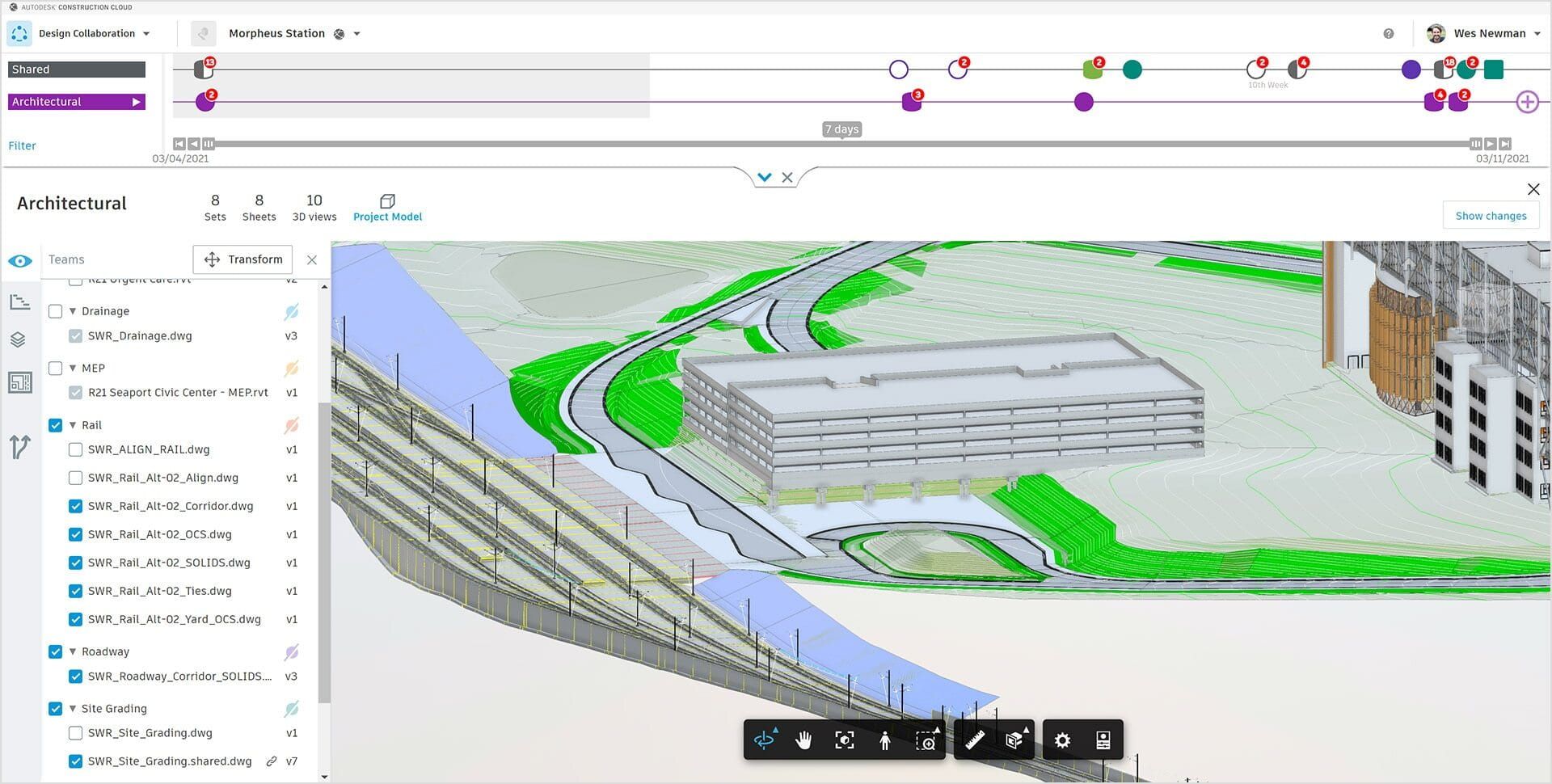
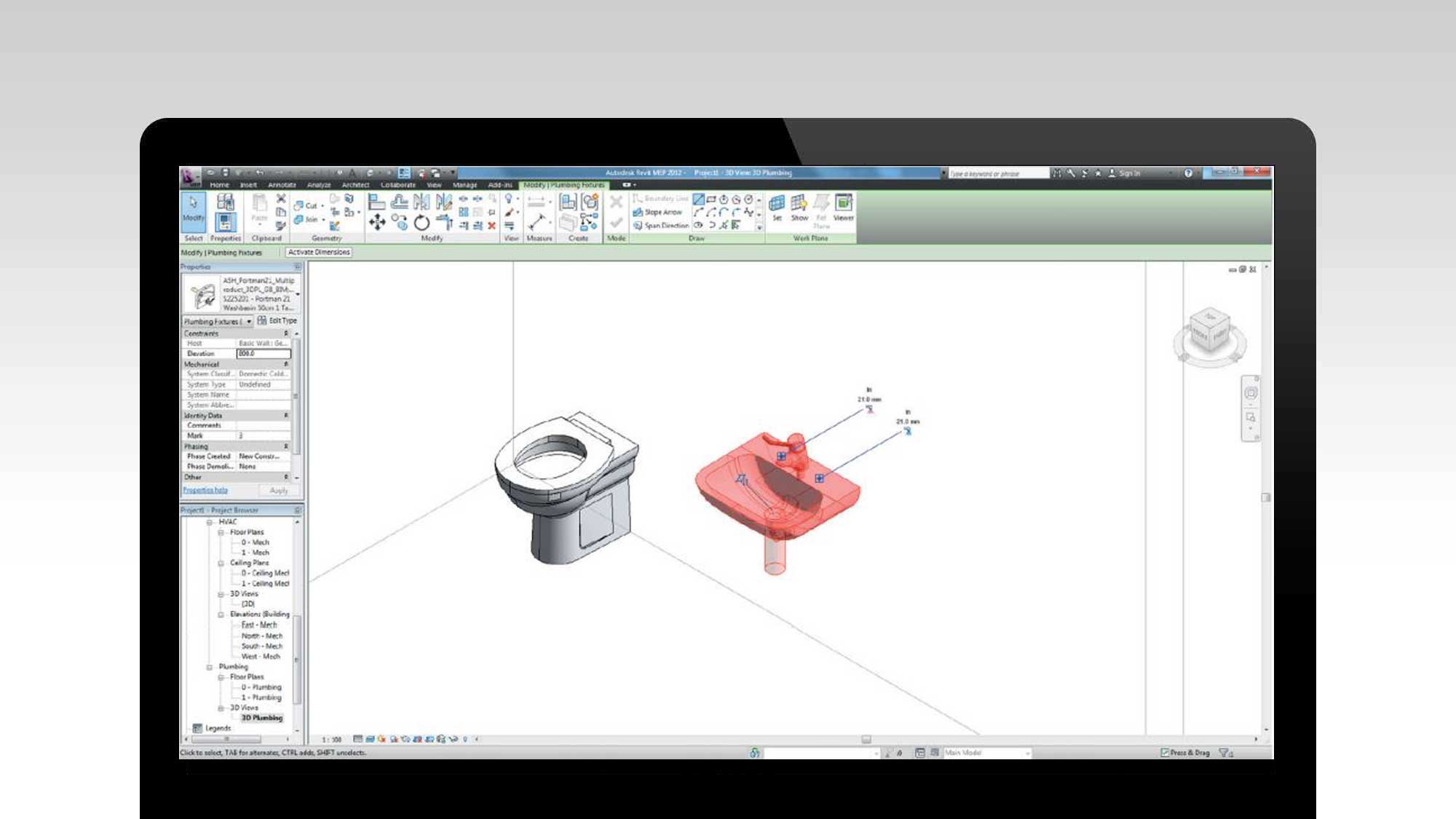
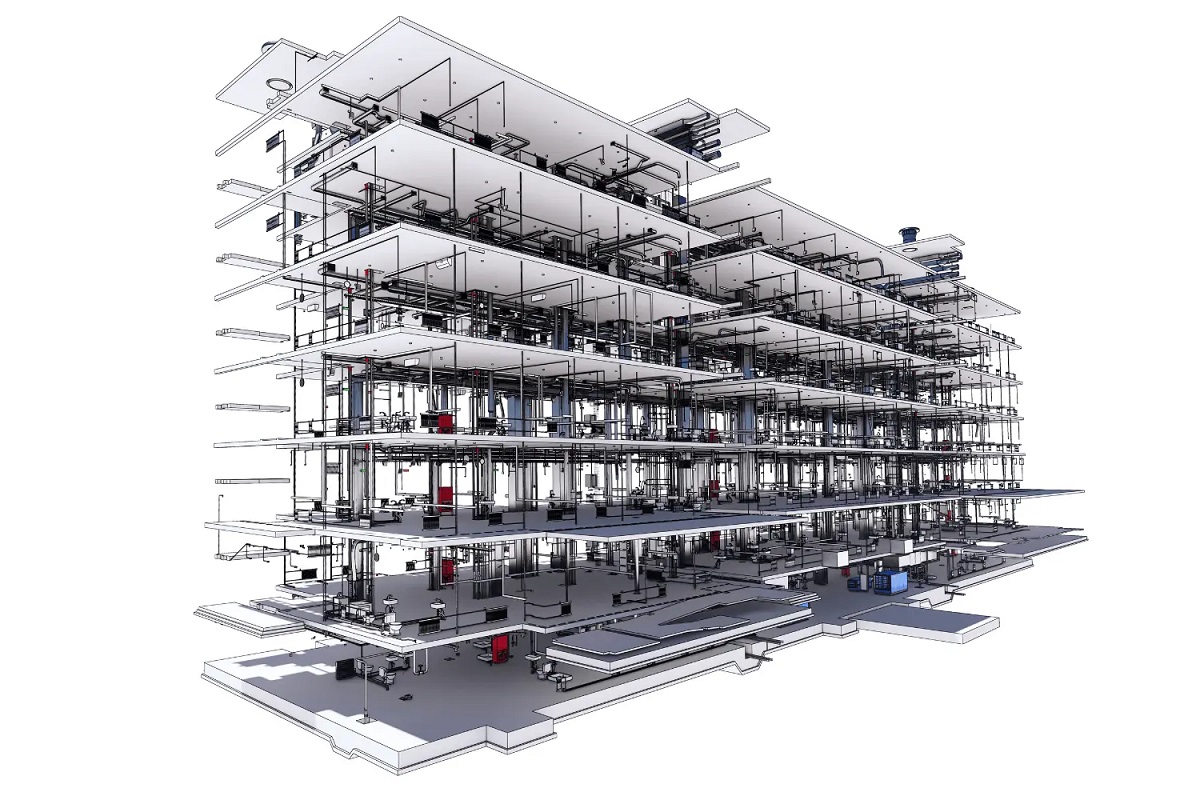
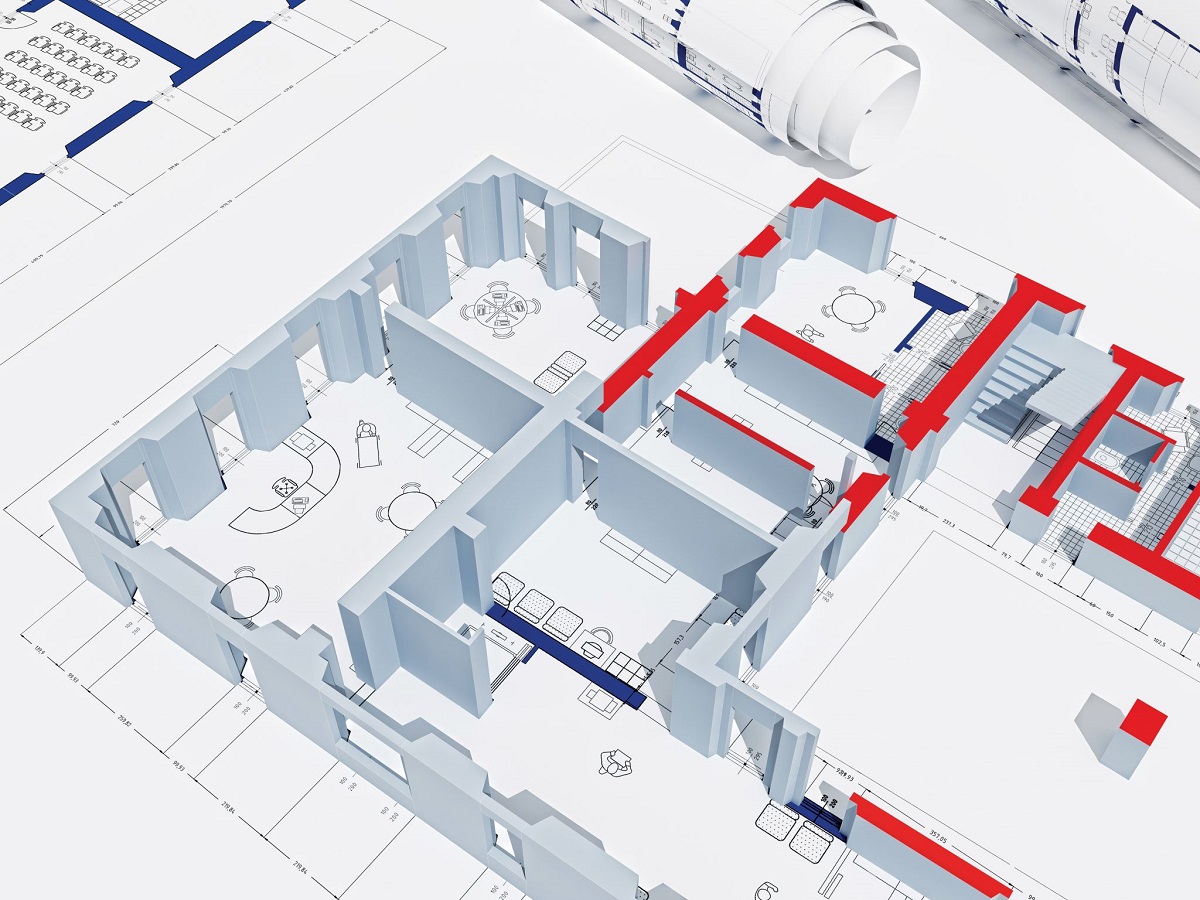
- Creating and managing BIM models: BIM Specialists are experts in creating and managing 3D digital models using BIM software such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, or Bentley AECOsim. They are responsible for accurately modeling the building components and systems, assigning properties and attributes, and ensuring data integrity throughout the project.
- Performing clash detection and coordination: One of the critical responsibilities of a BIM Specialist is to perform clash detection and coordination. They identify and resolve clashes and conflicts between the various building systems (e.g., HVAC, electrical, plumbing) in the virtual model, preventing costly issues during construction.
- Extracting data and generating reports: BIM Specialists have the expertise to extract valuable data from the BIM models and generate reports for different project phases. This includes quantity takeoffs, cost estimates, construction schedules, and facility management information, allowing for better decision-making and improving project efficiency.
- Providing training and support: BIM Specialists are responsible for providing training and support to project team members in the use of BIM software and tools. They facilitate workshops, conduct hands-on training sessions, and offer technical assistance to ensure that everyone involved understands how to effectively utilize BIM technology.
- Staying updated with industry trends: BIM technology is continuously evolving, and a BIM Specialist must stay updated with the latest industry trends, software updates, and emerging technologies. They actively engage in professional development, attend conferences, and join industry groups to expand their knowledge and skills.
Overall, a BIM Specialist plays a crucial role in streamlining communication, improving collaboration, and ensuring the successful implementation of BIM processes in construction projects. Their expertise in managing BIM projects, developing and maintaining standards, creating and coordinating models, extracting data, and providing training makes them invaluable assets to any construction team.
Skills and Qualifications Required for a BIM Specialist
Being a BIM Specialist requires a unique blend of technical skills, industry knowledge, and effective communication abilities. Here are some of the key skills and qualifications that are crucial for success in this role:
- Proficiency in BIM software: A BIM Specialist should have a deep understanding of BIM software such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Navisworks, or Bentley AECOsim. They should be proficient in creating and manipulating 3D models, performing clash detection, generating construction documentation, and utilizing advanced features and tools.
- Knowledge of building design and construction: A strong foundation in building design and construction is essential for a BIM Specialist. They should have a comprehensive understanding of architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems to accurately model and coordinate the building components.
- Attention to detail: BIM Specialists must have a keen eye for detail to ensure accuracy and completeness in their work. They should be able to identify potential clashes, errors, and inconsistencies in the model and rectify them before they escalate into costly problems during construction.
- Analytical and problem-solving skills: BIM Specialists need strong analytical and problem-solving skills to identify and resolve clashes, coordinate different systems, and optimize the building design for better efficiency. They should be able to think critically and find innovative solutions to complex issues that arise during the BIM process.
- Collaborative mindset: BIM Specialists work in multidisciplinary teams, so they need to have excellent teamwork and collaboration skills. They should be able to effectively communicate, coordinate, and negotiate with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to ensure smooth project execution.
- Understanding of data management and visualization: BIM involves the management and manipulation of massive amounts of data. A BIM Specialist should have a solid understanding of data management principles and the ability to visualize and present data in a clear and concise manner to facilitate decision-making.
- Continuous learning: The field of BIM is dynamic and constantly evolving. A BIM Specialist needs to have a thirst for knowledge and a commitment to continuous learning. Staying updated with the latest BIM technologies, industry trends, and software advancements is crucial to perform effectively in this role.
- Professional certifications: While not mandatory, certifications such as Autodesk Certified Professional in Revit or BIM Management can add credibility to a BIM Specialist’s skillset. These certifications validate their expertise in BIM software and demonstrate their commitment to professional development.
These skills and qualifications lay the foundation for a successful career as a BIM Specialist. By developing and honing these abilities and staying abreast of industry advancements, a BIM Specialist can make a significant impact on construction projects and contribute to the overall success of the team.
BIM Software and Tools Familiarity
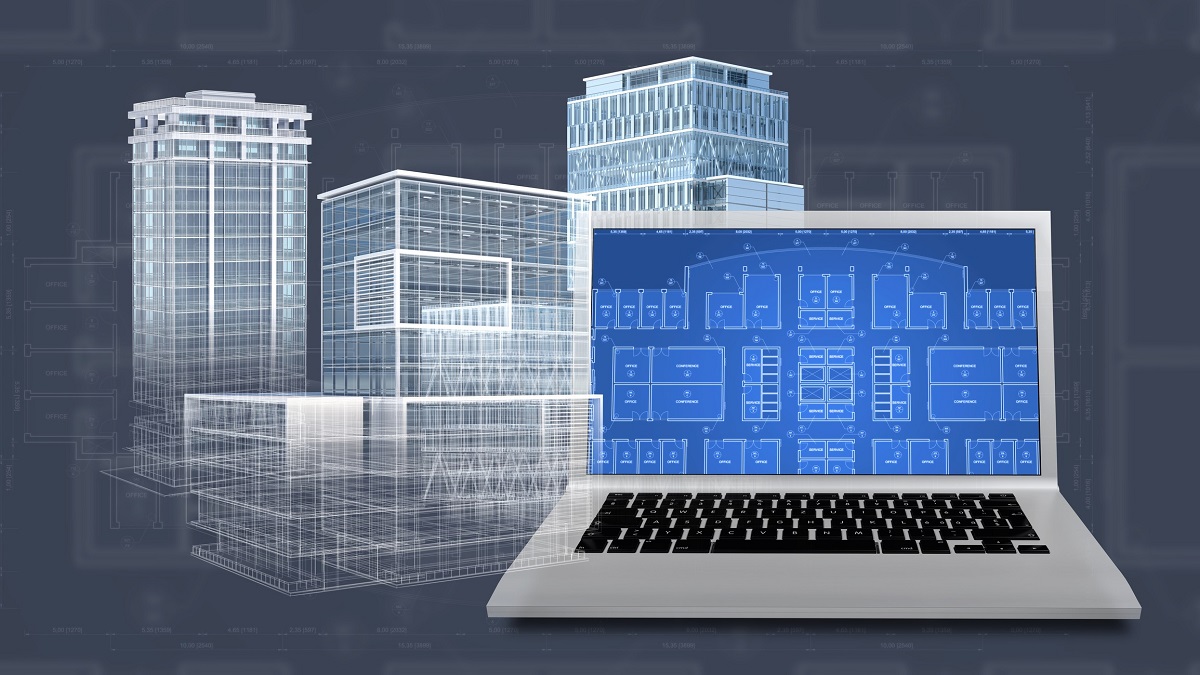
As a BIM Specialist, having a strong familiarity with various BIM software and tools is essential. These software and tools are the backbone of the digital revolution in the construction industry and enable BIM Specialists to create, manage, and collaborate on building information models.
Here are some of the key BIM software and tools that a BIM Specialist should be familiar with:
- Autodesk Revit: Revit is one of the most widely used BIM software in the industry. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for architectural, structural, and MEP design and coordination. BIM Specialists should have in-depth knowledge of Revit’s modeling capabilities, family creation, parametric design, and collaboration features.
- ArchiCAD: ArchiCAD is another popular BIM software that offers a range of features for architectural design and documentation. BIM Specialists should be proficient in using ArchiCAD’s modeling tools, generating construction drawings, and leveraging its BIMx platform for interactive 3D navigation and documentation.
- Bentley AECOsim Building Designer: AECOsim Building Designer is a powerful BIM software for comprehensive building design and analysis. BIM Specialists should be familiar with its parametric modeling capabilities, clash detection, and integration with other Bentley software, such as MicroStation and OpenBuildings Designer.
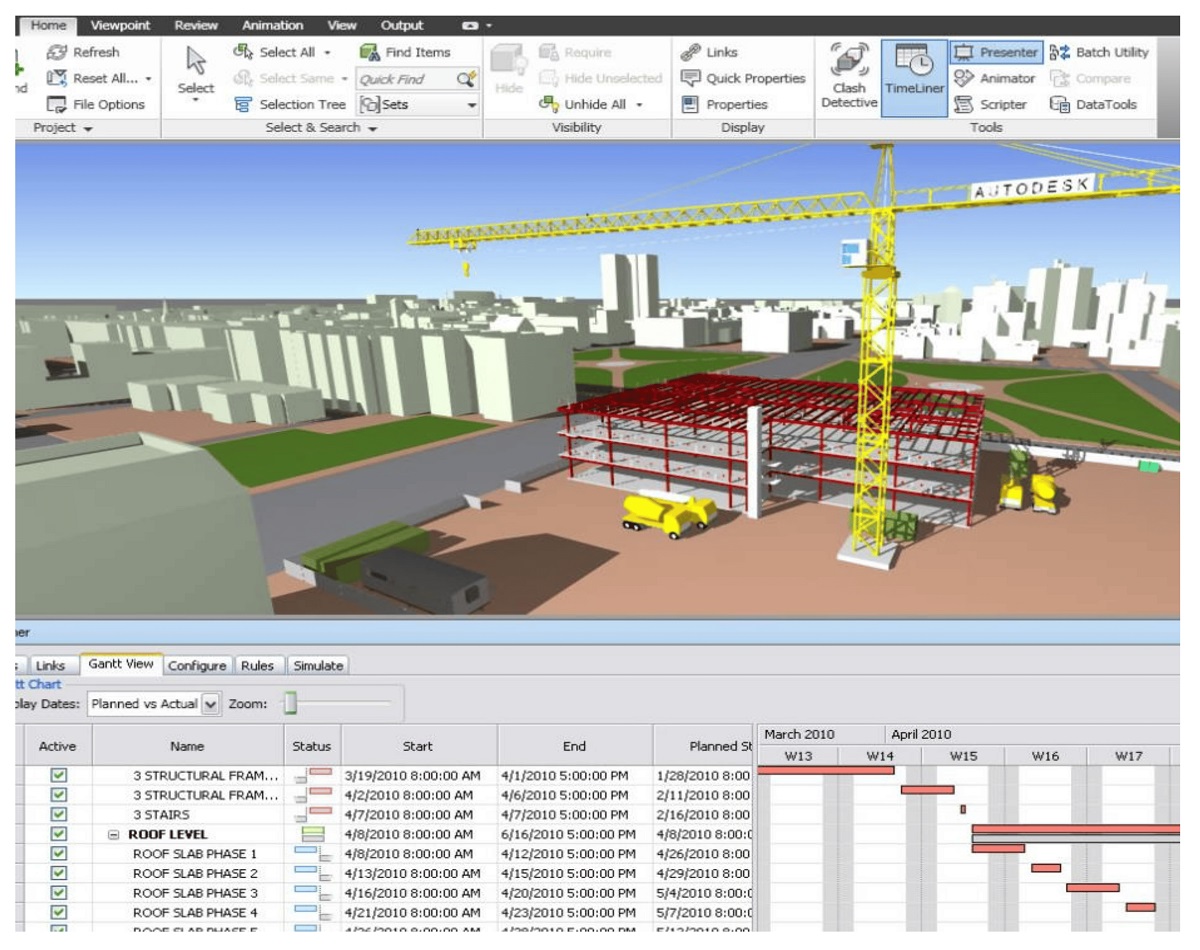
- Navisworks: Navisworks is a project review software that allows BIM Specialists to combine and visualize models from different disciplines, perform clash detection, and generate 4D construction simulations. Familiarity with Navisworks’ navigation tools, coordination workflows, and clash resolution techniques is essential.
- Bluebeam Revu: Bluebeam Revu is a PDF-based collaboration software that simplifies document management and markups. BIM Specialists should be proficient in using Revu’s features to collaborate on construction drawings, review and track changes, and generate RFIs (Requests for Information).
- Autodesk BIM 360: BIM 360 is a cloud-based platform that facilitates collaboration and project management in the BIM process. BIM Specialists should be familiar with its document management, issue tracking, and model coordination features to streamline communication and enhance project efficiency.
Along with these specific software, a BIM Specialist should also be familiar with file formats like IFC (Industry Foundation Classes), which enables interoperability between different BIM software. Additionally, knowledge of scripting languages like Dynamo for Revit or Grasshopper for Rhino can enhance automation and customization capabilities.
Staying up-to-date with the latest versions and enhancements of these software and tools is crucial for a BIM Specialist to leverage their full potential. Regular training, certifications, and participation in industry forums or user groups can help BIM Specialists expand their expertise in these software and maximize their effectiveness in managing BIM projects.
In summary, a thorough familiarity with BIM software and tools empowers BIM Specialists to create, manage, and collaborate on building information models, significantly improving project coordination and efficiency.
Collaborative Work and Communication Skills
In addition to technical expertise, collaborative work and effective communication skills are integral for BIM Specialists. The nature of their role demands close collaboration with various stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle. Strong interpersonal skills and the ability to communicate clearly and concisely are essential for successful BIM implementation and coordination.
Here are some key collaborative work and communication skills that a BIM Specialist should possess:
- Teamwork: BIM Specialists work as part of multidisciplinary teams, including architects, engineers, contractors, and project managers. They need to have a collaborative mindset, actively contribute to discussions, and be open to different perspectives and ideas.
- Interdisciplinary coordination: Effective coordination is crucial for successful BIM implementation. BIM Specialists should have the ability to collaborate with different disciplines, understand their requirements, resolve conflicts, and ensure that the models and data accurately represent the design intent.
- Active listening: Active listening is a vital communication skill for BIM Specialists. They must attentively listen to the needs and concerns of team members, clients, and other stakeholders. This enables them to address issues effectively and ensure that everyone’s requirements are met.
- Clear and concise communication: BIM Specialists need to communicate complex technical information in a clear and concise manner. They should have excellent verbal and written communication skills to explain BIM concepts, present design options, and share project updates with team members and stakeholders.
- Negotiation and conflict resolution: BIM Specialists often encounter conflicts and differences of opinion during the coordination process. They should possess strong negotiation skills to find mutually acceptable solutions and resolve conflicts amicably, ensuring the smooth progress of the project.
- Presentation and visualization: BIM Specialists should be adept at presenting BIM models and data to various stakeholders. Whether it’s through 3D visualizations, virtual reality (VR) walkthroughs, or construction simulations, they should be able to effectively communicate the design intent and project progress.
- Documentation and reporting: Clear and organized documentation is essential for effective communication in BIM projects. BIM Specialists should be proficient in preparing comprehensive reports, construction documentation, and recording meeting minutes to ensure accurate information flow and project transparency.
- Conflict management: Conflicts may arise in BIM projects due to differing priorities, design conflicts, or schedule constraints. BIM Specialists should have the ability to manage conflicts professionally, mediate discussions, and find compromises that satisfy all parties involved.
By nurturing these collaborative work and communication skills, BIM Specialists can foster effective teamwork, minimize misunderstandings, and maintain a harmonious project environment. This helps ensure that BIM processes are successfully implemented, and project objectives are achieved.
Furthermore, BIM Specialists should be open to ongoing feedback and actively seek clarity whenever necessary. Their receptive attitude towards feedback and willingness to communicate openly contribute to a positive working environment and facilitate successful project outcomes.
A BIM Specialist is responsible for managing and implementing Building Information Modeling (BIM) processes on construction projects. They should have a strong understanding of BIM software and be able to collaborate with various stakeholders to ensure successful project delivery.
Read more: What Is BIM In Revit?
Understanding of Building Lifecycle and Project Management
A BIM Specialist’s understanding of the building lifecycle and project management is crucial for the successful implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) throughout construction projects. Having knowledge of the various stages of the building lifecycle and project management methodologies enables BIM Specialists to align their work with project goals, optimize processes, and deliver high-quality results.
Here are some key aspects of building lifecycle and project management that a BIM Specialist should be familiar with:
- Pre-construction phase: BIM Specialists should have a clear understanding of the pre-construction phase, which encompasses the conceptual design, feasibility studies, and early-stage coordination. They should be able to collaborate with architects and engineers to address project requirements and develop an accurate digital representation of the building design.
- Construction phase: During the construction phase, BIM Specialists should have a comprehensive understanding of the sequencing and coordination of construction activities. They should be able to utilize BIM models to assist with clash detection, monitor construction progress, and facilitate communication between different teams to ensure construction aligns with the design intent.
- Post-construction phase: BIM plays a vital role in the post-construction phase for facilities management and maintenance. BIM Specialists should understand how to leverage the data-rich BIM models to facilitate asset management, routine maintenance, and facility operation. This knowledge allows for improved efficiency and cost savings in the building’s lifecycle.
- Project management methodologies: BIM Specialists should be familiar with project management methodologies such as Agile, Waterfall, or Lean Construction. Understanding these methodologies allows them to effectively collaborate with project managers and align their work within the project constraints, timelines, and goals.
- Building codes and regulations: BIM Specialists must have knowledge of relevant building codes, regulations, and sustainability standards. They should ensure that the BIM models comply with these requirements and facilitate the generation of accurate reports and documentation necessary for compliance.
- Risk management and quality assurance: BIM Specialists should have a strong grasp of risk management practices and quality assurance procedures. They should actively identify potential risks in the BIM process, implement mitigation measures, and collaborate with stakeholders to ensure that quality standards are met throughout the project.
- Integrated project delivery: BIM Specialists should understand and be able to collaborate effectively within an Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) environment. This approach emphasizes early engagement of all project stakeholders and promotes collaborative decision-making, resulting in improved project outcomes.
- Change management: Construction projects often undergo changes due to client requests, design modifications, or unforeseen circumstances. BIM Specialists should be equipped to handle change management effectively, ensuring that BIM models and associated documentation are up to date and accurately reflect the revised project details.
By having a solid understanding of the building lifecycle and project management principles, BIM Specialists can align their work with the project objectives, collaborate effectively with stakeholders, and contribute to the overall success of the construction project.
Moreover, as BIM continues to evolve and integrate with other areas of project management, such as cost estimating and scheduling, BIM Specialists who understand these intricate connections can provide valuable insights and optimize the project’s overall performance.
BIM Implementation and Coordination
BIM implementation and coordination are vital aspects of a BIM Specialist’s role. They are responsible for ensuring the seamless integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) processes into all stages of a construction project and facilitating effective coordination among project stakeholders. Successful BIM implementation and coordination require careful planning, collaboration, and technical expertise.
Here are some key points to consider for BIM implementation and coordination:
- Establishing BIM standards and protocols: BIM Specialists play a crucial role in developing and implementing BIM standards and protocols within an organization. These standards define best practices, naming conventions, file organization, and data exchange processes to ensure consistency and interoperability among team members.
- Collaborating with project stakeholders: BIM implementation requires collaboration with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders. BIM Specialists foster effective communication, set clear expectations, and promote collaboration throughout the project lifecycle to ensure full participation and maximize the benefits of BIM.
- Creating and maintaining BIM models: BIM Specialists are responsible for creating and maintaining accurate and up-to-date BIM models. They integrate architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems into the models, ensuring that all components are coordinated and clash-free. Regular model updates and revisions help improve project efficiency and accuracy.
- Clash detection and coordination: BIM Specialists use clash detection software to identify and resolve clashes and conflicts between different building systems. They analyze clashes, coordinate with relevant stakeholders, propose solutions, and make necessary adjustments to the BIM models to ensure smooth construction and minimize costly errors.
- Facilitating construction sequencing: BIM models can assist with construction sequencing and visualization. BIM Specialists work closely with project managers and contractors to analyze the construction sequence, optimize workflows, and simulate construction activities using the BIM models. This enables better coordination, resource management, and scheduling.
- Data management and integration: BIM Specialists manage vast amounts of data within the BIM models. They ensure data integrity, validate inputs and outputs, and integrate additional data sources where necessary. This allows for comprehensive analysis, visualization, and reporting, leading to improved decision-making and project outcomes.
- Training and support: BIM Specialists provide training and support to project team members who may be new to BIM processes or software. They conduct workshops, create training materials, and offer technical assistance to ensure that all team members understand the benefits of BIM and can effectively utilize BIM tools and technologies.
- Continuous improvement and innovation: BIM implementation is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and innovation. BIM Specialists stay updated with the latest industry trends, software enhancements, and emerging technologies. They actively seek opportunities to improve workflows, streamline processes, and apply new BIM methodologies to deliver better project outcomes.
By effectively implementing BIM workflows, coordinating project stakeholders, and leveraging the power of BIM tools and technologies, BIM Specialists contribute to the efficient execution of construction projects. Their expertise in BIM implementation and coordination helps drive collaboration, improve communication, and optimize project outcomes.
Benefits and Advantages of Hiring a BIM Specialist
Hiring a skilled and experienced BIM Specialist brings numerous benefits and advantages to construction projects. They play a critical role in successfully implementing Building Information Modeling (BIM) processes and leveraging advanced technologies to enhance project coordination, efficiency, and overall project outcomes.
Here are some key benefits of hiring a BIM Specialist:
- Improved project coordination: BIM Specialists excel in coordinating and managing complex project data and models. They ensure seamless communication between project stakeholders, minimizing clashes, and conflicts in the design and construction phases. This leads to improved project coordination and reduces errors and rework.
- Enhanced collaboration: BIM Specialists foster collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and other project team members. By utilizing BIM tools and facilitating effective communication, they create an environment that promotes information sharing, teamwork, and collaborative decision-making, resulting in more streamlined and efficient project execution.
- Increased cost savings: With their expertise in clash detection and construction sequencing, BIM Specialists help identify and resolve clashes and conflicts early in the design stage. This reduces costly rework during construction, leading to significant cost savings. Additionally, accurate quantity takeoffs and cost estimation from BIM models enable better budget control and cost forecasting.
- Improved project visualization: BIM Specialists leverage 3D modeling and visualization tools to provide clients, stakeholders, and project teams with a vivid representation of the project. This enhances understanding, clarity, and decision-making, ensuring that everyone involved has a clear vision of the final product and can make more informed choices.
- Increased construction efficiency: BIM Specialists help optimize construction workflows and sequencing, reducing errors, and improving efficiency. By simulating construction activities and analyzing resource allocation, they identify potential bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement. This enables the project team to streamline construction processes, meet deadlines, and deliver projects on time.
- Improved facility management and maintenance: BIM models created and managed by BIM Specialists serve as a valuable resource for facility management and maintenance. With accurate and up-to-date information about the building’s systems, components, and equipment, facility managers can optimize maintenance schedules, plan renovations, and efficiently manage the building throughout its lifecycle.
- Enhanced data analysis and reporting: BIM Specialists possess strong data management skills and can extract valuable insights from BIM models. By performing data analysis, generating reports, and utilizing advanced analytics tools, they help project teams make data-driven decisions, identify trends, and improve overall project performance.
- Adaptability to evolving technologies: BIM Specialists stay abreast of the latest trends and advancements in BIM technology. They adapt to evolving software tools and methodologies, enabling project teams to harness the full potential of emerging technologies. This ensures that construction projects remain at the forefront of technological innovation.
Ultimately, hiring a BIM Specialist is a strategic investment that can significantly improve project outcomes. Their expertise in BIM implementation, coordination, collaboration, and data management provides a competitive edge, saves time and costs, and enhances the overall efficiency and success of construction projects.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the construction industry, and the role of a BIM Specialist has become increasingly critical in implementing and leveraging BIM processes to enhance project outcomes. A BIM Specialist brings a unique set of skills, knowledge, and expertise to construction projects, leading to improved project coordination, collaboration, efficiency, and overall success.
In this article, we explored the role and responsibilities of a BIM Specialist, highlighting their ability to coordinate and manage BIM projects, develop and maintain BIM models, perform clash detection, extract data, and provide training and support. We also discussed the skills and qualifications required, including proficiency in BIM software, understanding of the building lifecycle and project management, and effective communication and collaboration skills.
Furthermore, we emphasized the importance of a BIM Specialist’s familiarity with BIM software and tools such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Navisworks, and more. Their expertise in these tools enables them to create, manage, and coordinate building information models effectively, improving project visualization, cost savings, and construction efficiency.
We also addressed the collaborative work and communication skills necessary for a BIM Specialist to successfully engage with project stakeholders and promote effective teamwork and coordination. The ability to actively listen, communicate clearly, facilitate collaboration, and resolve conflicts contributes to the seamless implementation of BIM processes and enhances project outcomes.
Moreover, we discussed the BIM Specialist’s understanding of the building lifecycle, project management methodologies, and risk management, all of which enable them to align their work with project goals, manage changes, and optimize project performance.
Finally, we highlighted the benefits and advantages of hiring a BIM Specialist, including improved project coordination, enhanced collaboration, cost savings, increased construction efficiency, better visualization, improved facility management, and the ability to harness evolving technologies.
In conclusion, the role of a BIM Specialist is pivotal in the successful implementation of BIM in construction projects. Their technical expertise, collaborative work approach, strong communication skills, and understanding of the building lifecycle and project management contribute to streamlining processes, reducing costs, and delivering high-quality projects. By embracing the skills and knowledge of a BIM Specialist, construction professionals and project owners can unlock the full potential of BIM and stay at the forefront of the industry’s digital revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A BIM Specialist?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “What Is A BIM Specialist?”