Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is A Conduit In Construction


Building & Construction
What Is A Conduit In Construction
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn about the role of a conduit in building construction and how it facilitates the safe and organized passage of electrical wiring and plumbing systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the field of construction, there are various components and systems that come together to create a functional and safe building. One such component that plays a crucial role in the construction process is a conduit. A conduit acts as a protective sleeve or channel that houses and guides different types of utilities and services within a building.
In simple terms, a conduit can be thought of as a pathway or tunnel that allows various utilities to be safely routed through the walls, floors, and ceiling of a structure. Whether it’s electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, HVAC ducts, or telecommunication cables, conduits serve as a means to organize and protect these essential systems.
Conduits are typically made of a rigid or flexible material such as metal, PVC (polyvinyl chloride), or HDPE (high-density polyethylene). The choice of material depends on the specific application and the requirements of the building. Regardless of the material used, conduits offer several benefits in terms of installation, maintenance, and overall functionality.
In this article, we will explore the different types of conduits used in construction, their specific applications, and the benefits they provide. We will also delve into the construction process of installing conduits and the importance of their regular maintenance to ensure smooth operation of the building’s utilities.
Key Takeaways:
- Conduits in construction protect, organize, and ensure efficient utility systems, enhancing safety, flexibility, and compliance with building codes. They are vital for creating secure and functional building infrastructure.
- Proper installation and regular maintenance of conduits are essential for sustained functionality, longevity, and safety of building utility systems. Careful planning, inspections, and repairs contribute to efficient and reliable infrastructure.
Read more: What Is An EMT Conduit
Definition of a Conduit
A conduit, in the context of construction, refers to a protective pathway or channel that is used to encase and guide various utilities and services within a building. It acts as a conduit for the safe and organized routing of electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, HVAC ducts, and telecommunication cables.
Conduits serve two main purposes: protection and organization. By enclosing these utilities within conduits, they are shielded from external elements such as moisture, dust, and physical damage. This not only ensures the longevity and reliability of the utilities but also minimizes the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
Additionally, conduits help in the organization of the building’s utility systems. They provide a systematic and structured approach to routing and managing the different utilities, making it easier for maintenance and repairs. With conduits in place, locating and accessing specific utility lines becomes more efficient, saving time and effort for technicians and contractors.
The use of conduits is regulated by building codes and standards to ensure the safety and compliance of the construction project. These standards specify the types of conduits to be used, the materials they should be made of, and the installation guidelines to be followed.
It is important to note that conduits are not limited to just one type of utility. They can accommodate a wide range of systems, making them a versatile component in the construction industry. Whether it’s electrical, plumbing, HVAC, or telecommunication, conduits provide a unified and organized approach to utility routing.
In the following sections, we will explore the different types of conduits used in construction and their specific applications in more detail.
Types of Conduits
There are various types of conduits used in construction, each designed to accommodate specific utilities and serve different purposes. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types of conduits:
- Electrical Conduits: Electrical conduits are used to encase and protect electrical wiring and cables. They ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electricity throughout the building, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks and short circuits. Electrical conduits can be made of metal, such as galvanized steel or aluminum, or non-metallic materials like PVC or HDPE. They are available in different sizes to accommodate various wire gauges and can be installed in both exposed and concealed locations.
- Plumbing Conduits: Plumbing conduits, commonly known as plumbing pipes, are used for the transportation of water, gas, and sewer lines within a building. These conduits ensure the proper flow and distribution of water and other fluids, allowing for efficient plumbing systems. Plumbing conduits are commonly made of materials such as copper, PVC, or PEX (cross-linked polyethylene). The choice of material depends on factors such as the type of fluid being transported, the pressure requirements, and the specific plumbing regulations.
- HVAC Conduits: HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) conduits are used to distribute conditioned air throughout a building and remove stale air. These conduits typically consist of ductwork made of materials like galvanized steel or flexible aluminum. HVAC conduits play a critical role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. They are sized and routed strategically to ensure efficient airflow and optimal performance of the HVAC system.
- Telecommunication Conduits: Telecommunication conduits are used for the installation and protection of telecommunication cables and data networks within a building. They provide pathways for the transmission of voice, data, and video signals. Telecommunication conduits are typically made of PVC or HDPE and can be installed alongside electrical conduits or in dedicated telecom shafts. The use of dedicated telecom conduits helps to segregate and protect the sensitive telecommunication infrastructure from interference and damage.
These are just a few examples of the many types of conduits used in construction. Other specialized conduits include fire-resistant conduits, which are designed to withstand high temperatures and protect electrical systems during a fire emergency. Additionally, there are waterproof conduits used in wet environments to prevent water ingress and corrosion.
By utilizing the appropriate conduits for each utility type, construction projects can ensure the efficient and safe operation of the building’s systems. It is essential to consult with professionals and adhere to building codes and regulations to determine the appropriate conduit types and installation methods for a specific project.
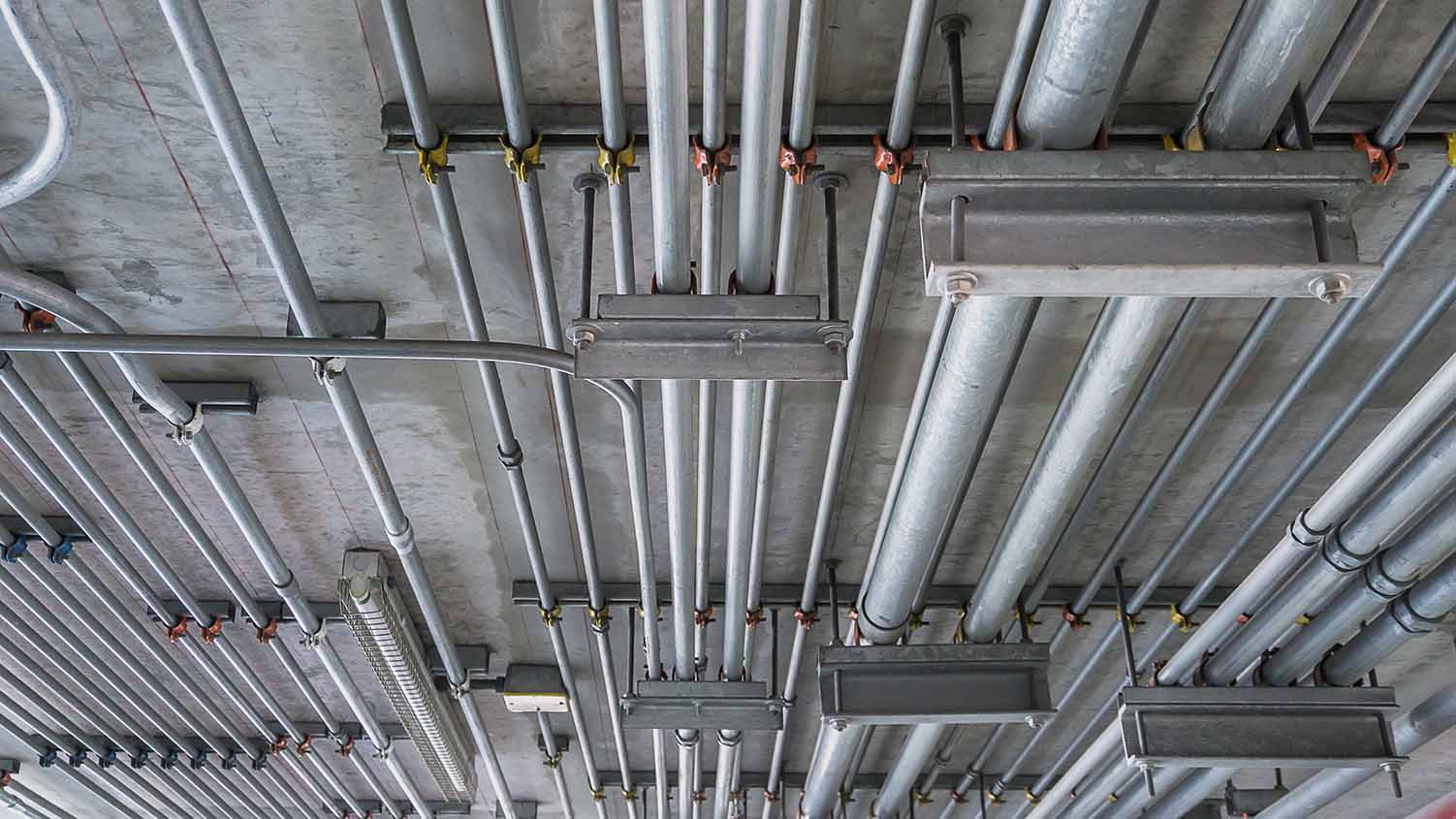
Electrical Conduits
Electrical conduits are an integral part of any building’s electrical system. They provide a safe and organized pathway for electrical wiring and cables, protecting them from damage and ensuring the efficient transmission of electricity throughout the structure. Electrical conduits come in various types and materials to suit different applications and installation requirements.
Some common types of electrical conduits include:
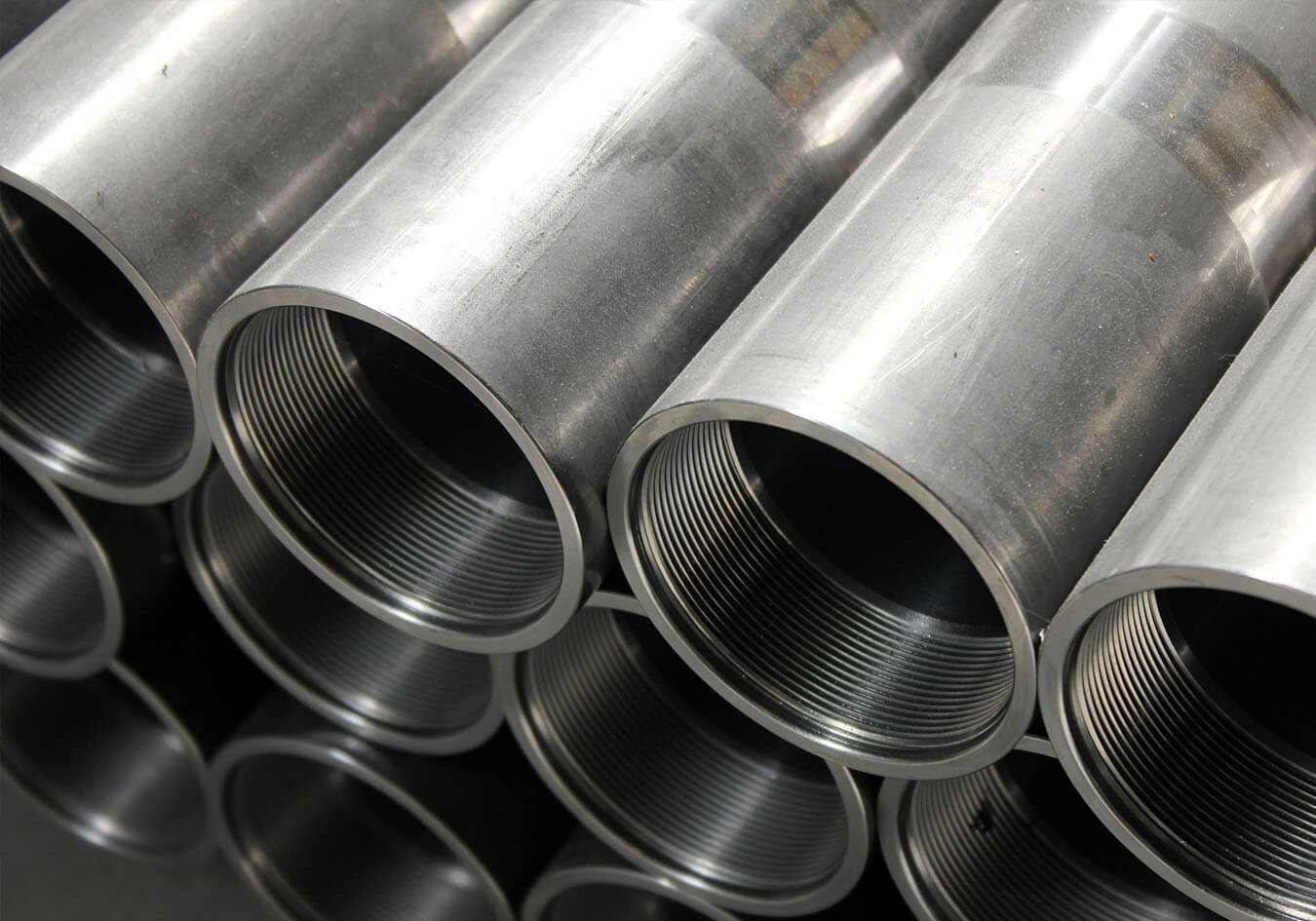
- Rigid Metal Conduits (RMC): Rigid metal conduits are made of steel or aluminum and provide maximum protection to electrical wiring. They are very durable and resistant to physical damage, making them suitable for outdoor and harsh environment installations. RMCs are threaded on both ends for easy connection and can withstand high temperatures.
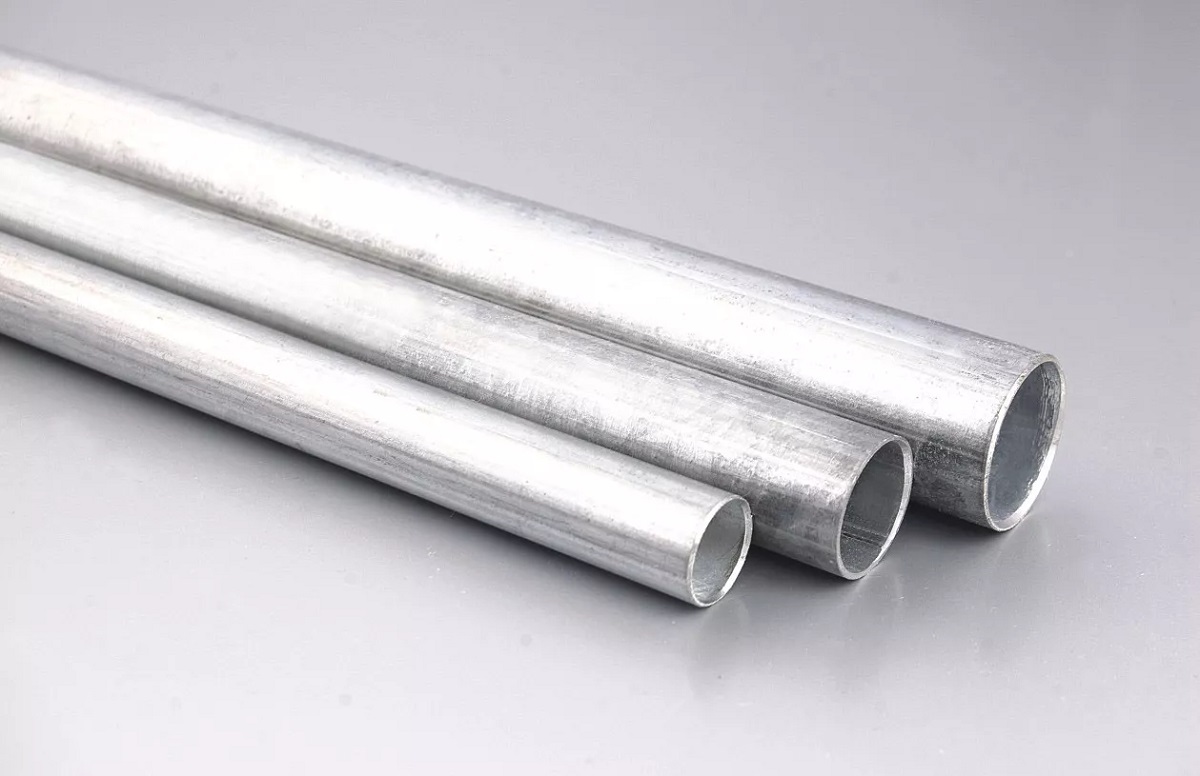
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT conduits are made of thin-walled steel and are lighter and easier to work with compared to RMCs. They are typically used in residential and commercial applications where the level of physical protection required is moderate. EMTs are often used in exposed electrical installations and can be bent easily to accommodate various routing configurations.
- Intermediate Metal Conduits (IMC): IMC conduits are similar to RMCs in terms of material but have a thinner wall. They provide a higher level of protection than EMTs and are commonly used in commercial and industrial settings. IMCs are corrosion-resistant and suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
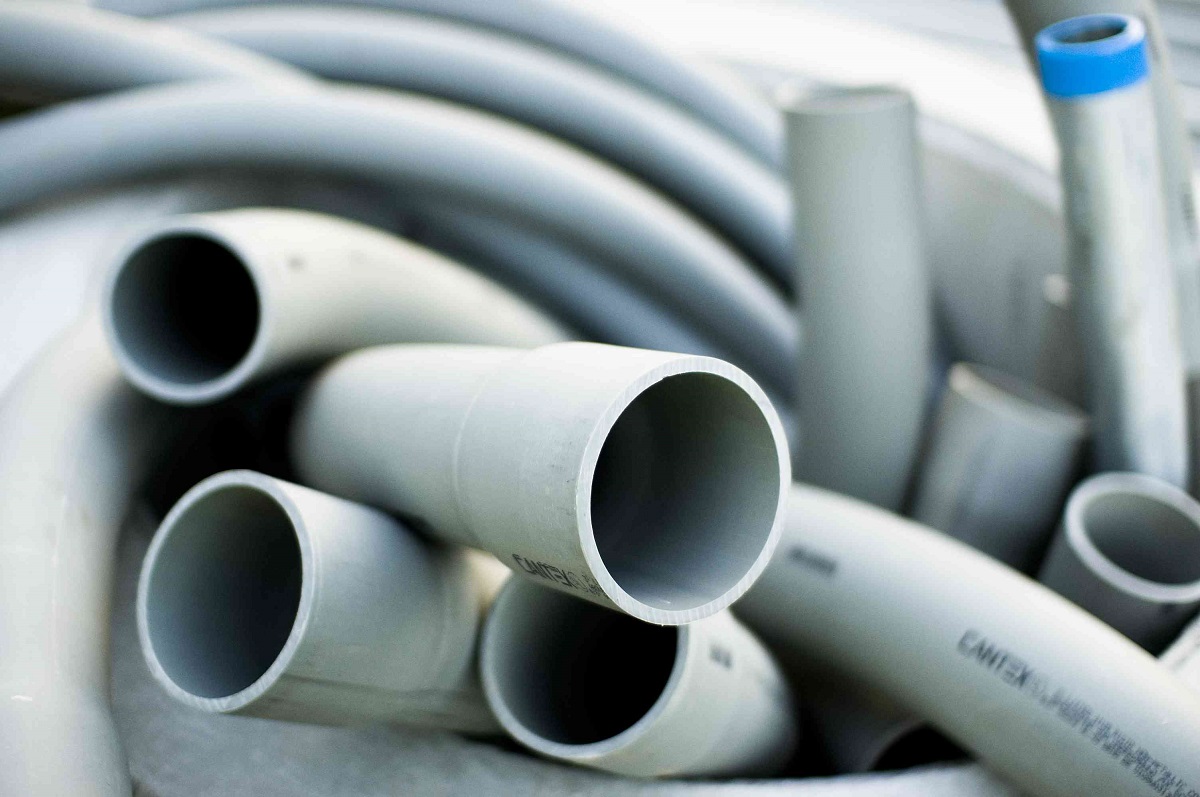
- PVC Conduits: PVC conduits are made of polyvinyl chloride and are a popular choice for electrical installations. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion and chemical damage. PVC conduits come in rigid or flexible forms, allowing for easy installation and routing in both exposed and concealed locations.
When selecting the appropriate electrical conduit, factors such as the environmental conditions, the type and gauge of wires to be used, and the specific requirements of the electrical system should be considered. Additionally, adherence to local electrical codes and regulations is essential to ensure safe and compliant installations.
The installation of electrical conduits involves several steps. First, the conduit route is planned, taking into account factors such as accessibility, clearance requirements, and proximity to other utilities. Then, the conduits are cut to the desired length and secured using appropriate connectors and fittings. The electrical wires are pulled through the conduit, and the conduits are properly sealed to prevent moisture ingress.
Regular maintenance of electrical conduits is crucial to ensure their continued functionality. Inspections should be carried out periodically to identify any signs of damage, corrosion, or deterioration. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be promptly addressed to prevent electrical hazards and maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
In summary, electrical conduits play a vital role in the safe and efficient distribution of electricity within a building. By choosing the appropriate type of conduit and following proper installation and maintenance practices, construction projects can ensure reliable and compliant electrical systems.
Plumbing Conduits
In construction, plumbing conduits refer to the pipes and tubing used to transport water, gas, and sewer lines within a building. Plumbing conduits serve the important function of ensuring the proper flow and distribution of fluids throughout the structure. They come in different materials, sizes, and configurations to accommodate specific plumbing needs and comply with building codes and regulations.
Here are some common types of plumbing conduits:
- Copper Pipes: Copper pipes are known for their durability, reliability, and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in both residential and commercial applications. Copper pipes are available in various sizes, including rigid and flexible options, to accommodate different plumbing configurations.
- PVC Pipes: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes are lightweight, affordable, and resistant to corrosion and chemical damage. They are widely used in plumbing systems, especially for water supply and drain lines. PVC pipes come in different diameters and are easy to work with, as they can be cut and connected using simple solvent-welded joints.
- PEX Pipes: PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) pipes are gaining popularity in residential and commercial plumbing systems. They are flexible, resistant to freezing and bursting, and can be easily installed using crimp or push-fit fittings. PEX pipes are suitable for both hot and cold water applications.
- Galvanized Steel Pipes: Galvanized steel pipes are known for their strength and durability. They are often used in older buildings or for specific applications where corrosion resistance is crucial. Galvanized steel pipes are threaded and can be connected using threaded fittings.
The choice of plumbing conduits depends on various factors, such as the type of fluid being transported, the pressure requirements, and the specific plumbing codes and regulations. It is important to select the right materials and sizes to ensure the proper functioning of the plumbing system and to prevent leaks, clogs, and other issues.
During the installation of plumbing conduits, careful planning and layout are essential. The conduits should be routed in a way that maximizes efficiency and minimizes the risk of leaks or damage. Proper supports and hangers should be used to secure the conduits in place, ensuring they are adequately supported and minimizing stress on the joints and connections.
Maintenance of plumbing conduits involves regular inspections to identify any leaks, corrosion, or blockages. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be carried out promptly to prevent water damage, mold growth, and plumbing system failures.
In summary, plumbing conduits play a crucial role in the functioning of a building’s plumbing system. By selecting the appropriate materials, following proper installation techniques, and conducting regular maintenance, construction projects can ensure reliable and efficient plumbing systems that meet the needs of the occupants.
Read more: What Is Electrical Conduit
HVAC Conduits
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) conduits are an essential component of a building’s HVAC system. They are responsible for distributing conditioned air throughout the structure and removing stale air. HVAC conduits come in various types and materials, allowing for efficient airflow and optimal performance of the HVAC system.
Here are a few common types of HVAC conduits:
- Ductwork: Ductwork is the most common type of HVAC conduit and is used to transport conditioned air to different rooms or areas within a building. It comprises a network of sheet metal or flexible aluminum tubes that are sealed and insulated to prevent air leakage and optimize energy efficiency. Ductwork can be rectangular, round, or oval-shaped, depending on the specific requirements of the HVAC system and the architectural constraints of the building.
- Plenums: Plenums are large air chambers that act as distribution points for the conditioned air from the HVAC system. They are often located above drop ceilings or in equipment rooms. Plenums allow for smooth airflow to multiple duct branches, ensuring proper distribution of air to various zones within the building.
- Ventilation Shafts: Ventilation shafts are vertical conduits that facilitate the movement of air within a building. They are commonly used for exhaust systems, such as bathroom or kitchen ventilation. Ventilation shafts can be made of sheet metal or PVC, depending on the specific requirements and building codes.
- Flexible Ducts: Flexible ducts, also known as flex ducts, are made of durable, lightweight materials such as plastic and wire coil. They are often used in applications where it is challenging to install rigid ductwork, such as in tight spaces or around corners. Flexible ducts allow for greater flexibility in routing and are typically insulated to minimize heat loss or gain.
Proper installation of HVAC conduits is crucial to ensure efficient airflow and optimal performance of the HVAC system. The ductwork should be designed and sized correctly, taking into consideration factors such as airflow requirements, building layout, and thermal loads. Sealants and insulation should be applied at joints and connections to prevent air leaks and reduce energy loss.
Maintenance of HVAC conduits involves regular inspections and cleaning to ensure the cleanliness of the ductwork and prevent the buildup of dust, debris, and microbial contaminants. Filtration systems should also be inspected and replaced periodically to maintain healthy indoor air quality.
In summary, HVAC conduits play a vital role in the efficient operation of a building’s HVAC system. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of HVAC conduits contribute to energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and the overall functionality of the HVAC system.
A conduit in construction is a pipe or tube used to protect and route electrical wiring. When installing conduits, make sure to follow local building codes and regulations to ensure safety and compliance.
Telecommunication Conduits
In the modern world, telecommunication is an integral part of our daily lives. From telephone lines to data networks, a reliable and efficient telecommunication infrastructure is essential in any building. Telecommunication conduits provide the necessary pathways and protection for the installation of telecommunication cables and data networks.
Here are some common types of telecommunication conduits:
- PVC Conduits: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduits are commonly used for telecommunication installations. They are lightweight, affordable, and resistant to corrosion and moisture. PVC conduits come in various sizes and can be installed both indoors and outdoors. They offer protection and flexibility for the routing of telecommunication cables.
- HDPE Conduits: HDPE (high-density polyethylene) conduits are durable and offer excellent protection for telecommunication cables. They are highly resistant to impact, chemicals, and moisture, making them suitable for underground or outdoor installations. HDPE conduits are available in a range of sizes and can accommodate multiple telecommunication cables within a single conduit.
- Innerducts: Innerducts are additional protective conduits installed within larger conduits or duct banks. They offer an extra layer of protection for telecommunication cables, helping to prevent damage from external forces or environmental conditions. Innerducts are commonly made of HDPE or PVC and can be installed alongside electrical conduits or in separate dedicated telecom shafts.
Telecommunication conduits are designed to ensure the reliable transmission of voice, data, and video signals. The conduits protect the cables from physical damage, moisture, and electrical interference, ensuring the quality and integrity of the communication signals.
The installation of telecommunication conduits involves careful planning and coordination with telecommunication service providers. The conduits should be routed strategically to ensure efficient cable management and minimize the risk of signal degradation or interference. Proper bends, access points, and pull boxes should be incorporated into the conduit system to facilitate cable installation and future maintenance.
Maintenance of telecommunication conduits primarily involves visual inspections to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks, bends, or exposed cables. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be carried out promptly to maintain the functionality and reliability of the telecommunication infrastructure.
In summary, telecommunication conduits are a vital component in the construction of a building’s telecommunication infrastructure. By selecting the appropriate conduits and following proper installation and maintenance practices, construction projects can ensure efficient communication systems that meet the needs of the occupants.
Benefits of Using Conduits in Construction
Using conduits in construction offers various benefits that contribute to the safety, efficiency, and overall functionality of a building. Here are some key advantages of incorporating conduits in construction projects:
- Protection: Conduits provide a protective barrier for utilities such as electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, HVAC ducts, and telecommunication cables. They shield these systems from external elements, including moisture, dust, and physical damage, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
- Organization: Conduits enable the organization and systematic routing of different utilities within a building. They ensure that the utilities are properly segregated and organized, making it easier to locate and access specific utility lines for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades.
- Safety: By encasing utilities within conduits, potential hazards such as electrical shocks, water leaks, or gas leaks are minimized. Conduits help prevent accidental contact with electrical wiring, reduce the risk of water damage from plumbing leaks, and ensure the proper containment of gas pipes.
- Flexibility: Conduits offer flexibility in terms of routing and re-routing utilities as needed. They allow for easy modifications and additions to the building’s systems, making renovations or expansions more manageable without having to completely overhaul the existing infrastructure.
- Maintenance: Conduits simplify maintenance and repair work by providing clear pathways for troubleshooting and inspections. Technicians can easily identify and address issues within the conduits, minimizing downtime and ensuring that the building’s utilities are operating at their optimal levels.
- Compliance: The use of conduits in construction helps ensure compliance with building codes and regulations. Conduits are designed and installed based on industry standards, ensuring the proper installation and protection of utilities to meet safety and performance requirements.
- Future-Proofing: Conduits allow for future expansion and technological advancements. By including additional conduits or larger conduit sizes during construction, the building is prepared to accommodate future upgrades or the incorporation of new utilities without significant disruption or costly renovations.
Overall, the use of conduits in construction provides a range of advantages that contribute to the efficiency, safety, and long-term functionality of a building’s utility systems. Whether it is electrical, plumbing, HVAC, or telecommunication, incorporating conduits into construction projects ensures a well-organized, protected, and adaptable infrastructure.
Construction Process of Installing Conduits
The installation of conduits in a construction project requires careful planning and execution to ensure the proper routing and protection of utilities. Here is an overview of the construction process involved in installing conduits:
- Design and Planning: The first step in installing conduits is to develop a detailed design and layout plan. This involves determining the locations where the conduits will be installed, taking into account factors such as accessibility, clearance requirements, and proximity to other utilities.
- Material and Equipment Procurement: Once the conduit plan is finalized, the necessary materials and equipment are procured. This includes the conduits themselves, connectors, fittings, supports, and any specialized tools or accessories required for the installation.
- Preparation of Conduits: The conduits are prepared by cutting them to the appropriate lengths according to the design plan. Any necessary holes, notches, or access points are made in the conduits to accommodate specific routing requirements or future access for maintenance.
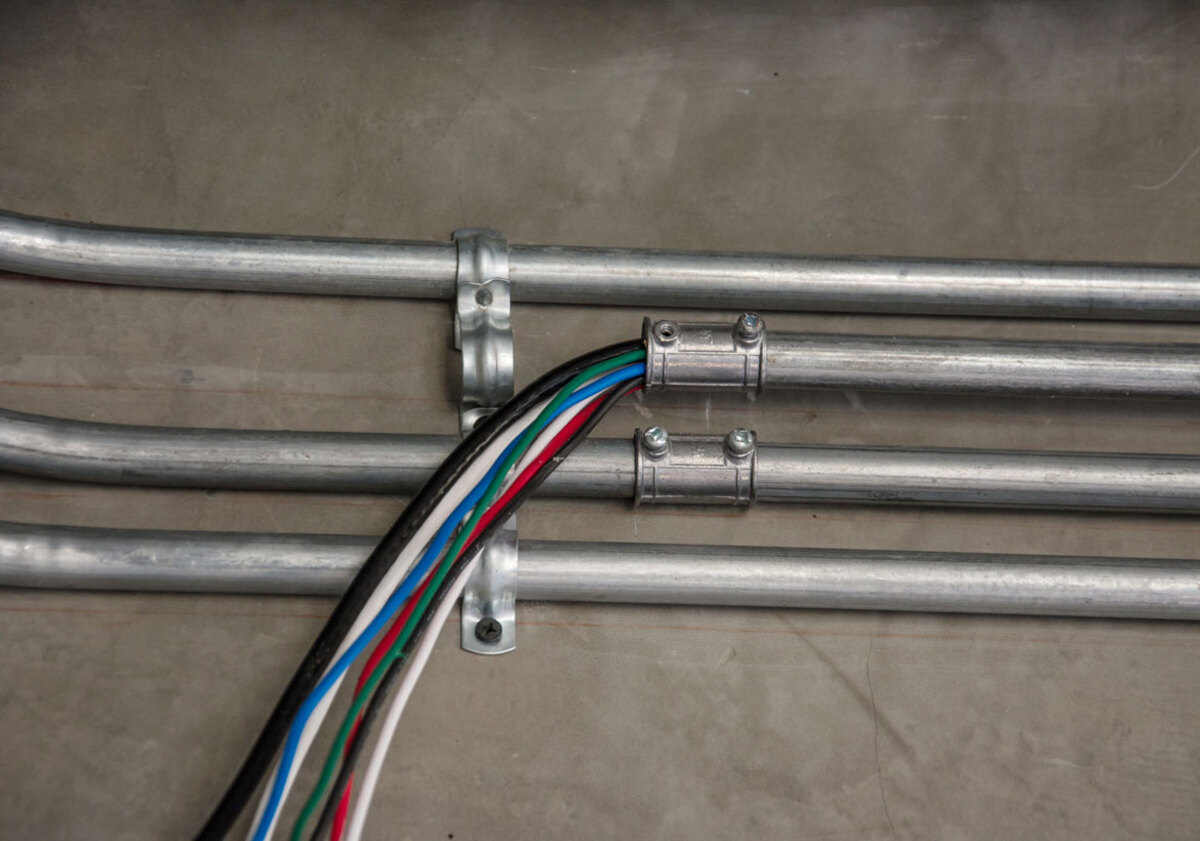
- Installation of Conduits: The conduits are then installed in the designated locations. They are secured to the building structure using appropriate supports, brackets, or hangers. Connections between conduits are made using connectors or fittings suitable for the specific conduit type and material.
- Pull-in Process: If the conduits need to accommodate wires, cables, or pipes, a pulling process is carried out. A pulling rope or fish tape is inserted through the conduits, and the utility lines are attached to the pulling mechanism. The lines are then carefully pulled through the conduits, ensuring they are not damaged or twisted during the process.
- Sealing and Insulation: Once the utility lines are pulled through the conduits, proper sealing and insulation measures are implemented. This helps prevent moisture ingress, air leaks, or heat loss/gain depending on the application. Sealants, tapes, or foams are used to seal any gaps or joints in the conduits, while insulation materials are applied to maintain temperature control.
- Verification and Testing: After the installation is complete, a thorough verification and testing process is conducted. This includes checking the integrity of all connections, inspecting for any signs of damage or leaks, and conducting tests to ensure proper functionality of the utilities routed through the conduits.
It is important to note that the construction process of installing conduits may vary depending on the specific project requirements, building codes, and the types of utilities being routed. It is recommended to consult with professionals experienced in conduit installation to ensure compliance with regulations and best practices.
By following proper installation techniques and protocols, construction projects can establish a well-organized and protected infrastructure that provides efficient and reliable utility distribution throughout the building.
Read more: What Is Conduit Used For
Maintenance of Conduits
Maintaining conduits is essential to ensure the long-term functionality and efficiency of a building’s utility systems. Regular maintenance helps identify and address any issues or damage that may occur within the conduits. Here are some important steps to consider when maintaining conduits:
- Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of the conduits to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or corrosion. Inspect the seals, joints, and connections for any leaks or gaps that may allow moisture or debris to enter the conduits.
- Cleaning: Clean the conduits periodically to remove any dirt, debris, or blockages that may restrict the flow of utilities. Use appropriate cleaning methods, such as compressed air or specialized conduit cleaning tools, to ensure thorough cleaning without causing damage.
- Repairs: Immediately address any identified issues or damage. Cracks or breaks in conduits should be repaired using appropriate materials or techniques to restore the structural integrity. Faulty or deteriorated seals, joints, or fittings should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage or leaks.
- Replacements and Upgrades: Over time, conduits may need to be replaced or upgraded to accommodate changes in utility requirements or to meet updated building codes and regulations. Evaluate the condition and capacity of existing conduits and consider replacements or upgrades as necessary.
- Documentation: Maintain a detailed record of maintenance and repairs performed on the conduits. Document the date, type of maintenance or repair, and any relevant observations or recommendations. This documentation can be valuable for reference, future maintenance, or if any warranty claims need to be made.
- Collaboration with Professionals: Engage the expertise of professionals and contractors experienced in conduit maintenance. They can provide guidance, conduct more in-depth inspections, and perform specialized tasks such as pressure testing or thermal imaging to identify hidden issues or potential risks within the conduits.
It is important to note that some conduits may require specialized maintenance procedures or regulations to follow. For example, fire-resistant conduits may need firestop maintenance to ensure the continued integrity of the fireproofing measures.
Furthermore, it is crucial to prioritize safety during conduit maintenance. Ensure that proper safety measures are followed, such as using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), following lockout/tagout procedures, and working in teams when necessary.
In summary, regular maintenance of conduits is essential to ensure their continued functionality and longevity. By conducting inspections, cleaning, and prompt repairs, construction projects can maintain the integrity of the conduits and minimize the risk of utility failures or other issues adversely impacting the building’s systems.
Conclusion
Conduits are a vital component in the construction industry as they play a crucial role in protecting, organizing, and ensuring the efficient functioning of utility systems within buildings. Whether it’s electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, HVAC ducts, or telecommunication cables, conduits provide a means to route and safeguard these utilities, contributing to the overall safety, functionality, and longevity of a building.
Throughout this article, we have explored the different types of conduits commonly used in construction. Electrical conduits protect and route electrical wiring, plumbing conduits transport water and gas, HVAC conduits distribute conditioned air, and telecommunication conduits facilitate the installation of telecommunication cables and data networks.
The benefits of using conduits in construction are numerous. They provide protection against external elements, facilitate organization and accessibility of utilities, enhance safety, offer flexibility for future modifications, and ensure compliance with building codes and regulations. By incorporating conduits into construction projects, building owners can enjoy a well-structured and secure infrastructure that allows for efficient utility distribution and facilitates maintenance and repairs.
When it comes to installing conduits, careful planning, design, and selection of appropriate materials are essential. The construction process involves preparing the conduits, securing them in place, pulling utility lines, sealing connections, and conducting thorough testing to ensure proper functioning. Adherence to industry standards and compliance with building codes are paramount in achieving successful conduit installations.
Regular maintenance of conduits is crucial to sustain their efficiency and longevity. This involves inspections, cleaning, repairs, replacements, and collaboration with professionals to identify issues and address them promptly. By conducting proper maintenance, building owners can prevent potential problems, minimize downtime, and prolong the lifespan of the conduits and associated utility systems.
In conclusion, conduits are integral to the construction of safe, functional, and reliable buildings. They provide a conduit for utilities, protecting and organizing them while allowing for flexibility and future modifications. Incorporating conduits into construction projects enhances the overall functionality and longevity of the building’s utility systems, ensuring occupant comfort and satisfaction for years to come.
Curious about taking your conduit knowledge into practical application? If installing conduits within walls seems daunting, fret not, as our detailed guide on conduit installation offers step-by-step insights. For those considering upgrades or new projects, our review of the top metal conduits for 2024 provides a comprehensive look at options that ensure safety and efficiency. Dive deeper into these topics to enhance your construction skills and make informed decisions on selecting the right materials for any task.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Conduit In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is A Conduit In Construction”