Home>Garden Essentials>How Much Infill For ABS


Garden Essentials
How Much Infill For ABS
Modified: March 7, 2024
Discover how much infill is needed for ABS in your garden. Find out the optimal amount to ensure a sturdy and long-lasting surface.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
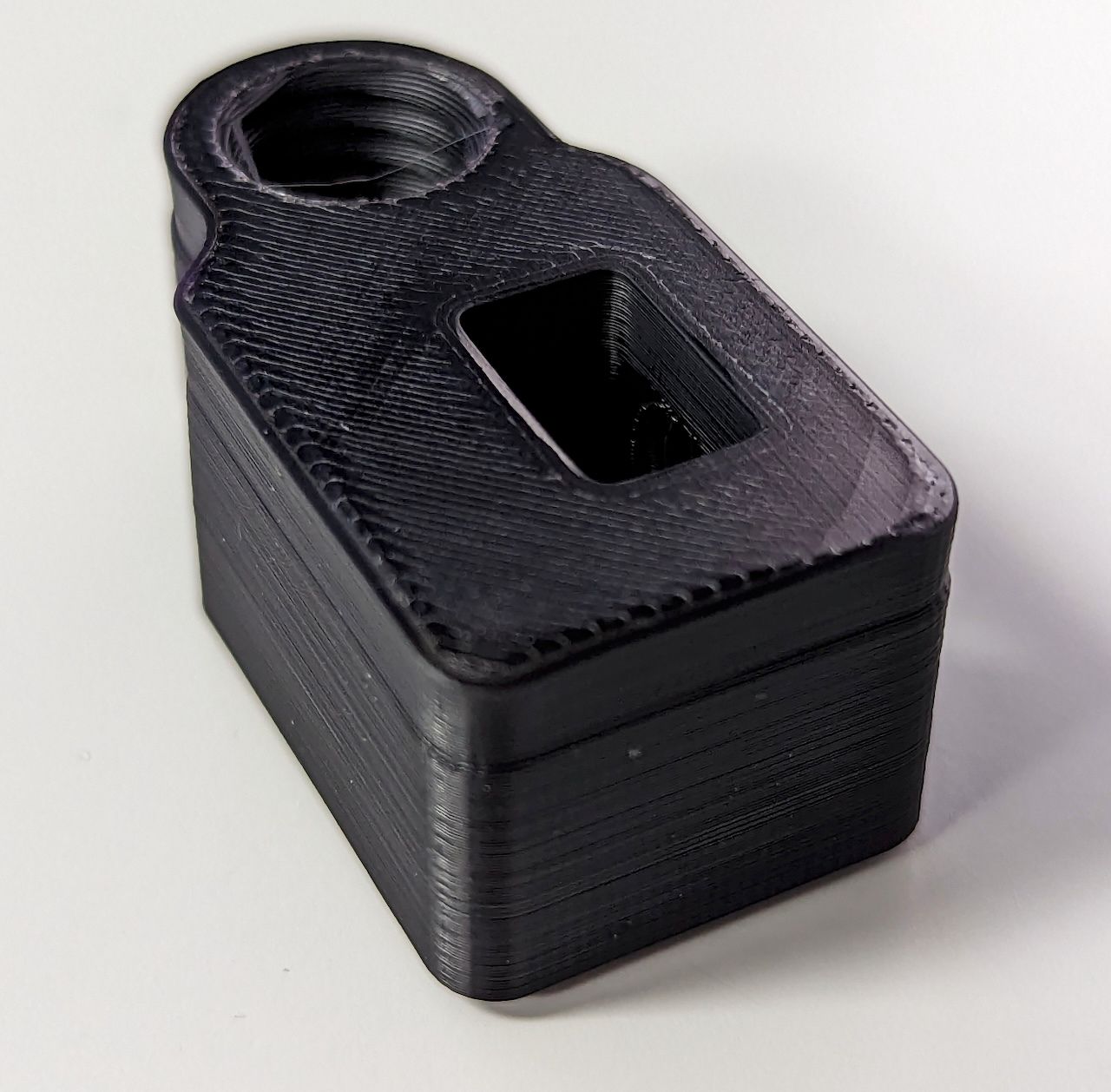
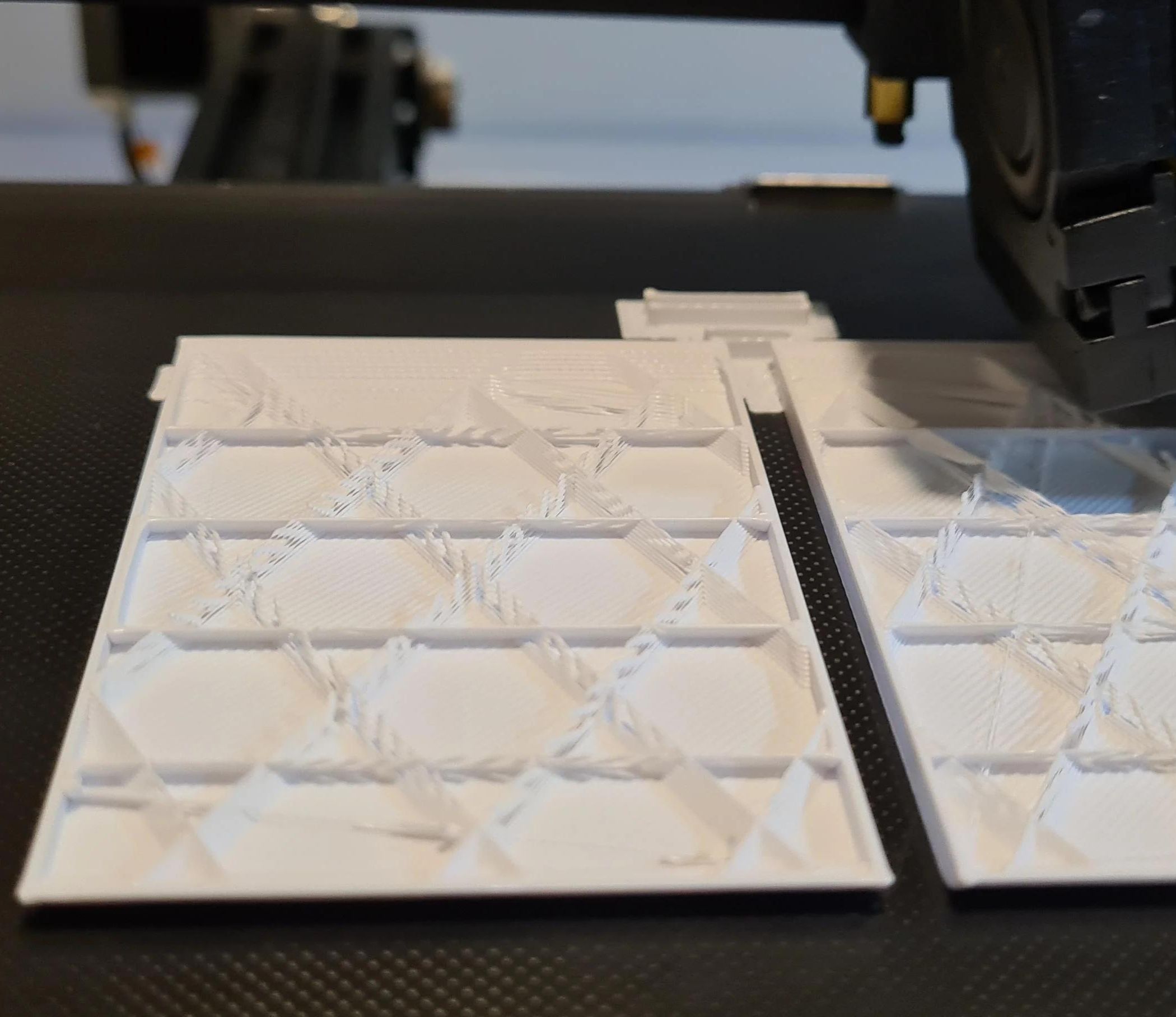
When it comes to 3D printing with ABS filament, one important factor to consider is the infill amount. Infill refers to the internal structure of a printed object, which fills the empty space between the outer walls. Determining the appropriate infill percentage for ABS is crucial for achieving the desired strength, durability, and print quality.
ABS, short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular thermoplastic material known for its strength, impact resistance, and high temperature tolerance. It is commonly used for producing functional parts, prototypes, and various consumer products. To fully exploit the potential of ABS in 3D printing, understanding the role of infill is essential.
The infill amount directly affects the strength, weight, and material usage of a 3D printed object. The infill pattern determines the distribution of the internal structure, which can be solid, honeycomb, grid, or other patterns. By controlling the infill percentage, you can balance the internal strength and weight of the object based on its intended application.
Finding the right infill percentage for ABS depends on several factors, such as the intended use of the printed object, the desired strength-to-weight ratio, the available printing time, and the capabilities of your 3D printer.
With this in mind, let us delve deeper into the importance of infill amount for ABS prints and explore the recommended infill percentages for different scenarios. We will also discuss how to test and adjust infill settings and examine the impact of infill density on print quality. Additionally, we will explore infill strategies for various applications to help you make informed decisions when printing with ABS filament.
Key Takeaways:
- Finding the right infill percentage for ABS 3D prints is crucial for balancing strength, material usage, and print time. Experiment and test different infill amounts to optimize the performance of your prints.
- Consider the specific application needs when choosing infill strategies for ABS prints. Whether it’s for functional parts, decorative objects, or heat dissipation, the right infill percentage and pattern can enhance the strength and visual appeal of your 3D prints.
Read more: How Much Does ABS Repair Cost
Understanding ABS Infill
Before we delve into the specifics of infill amount for ABS prints, let’s first understand what infill is and why it is important. Infill refers to the internal structure of a 3D printed object that provides support and stability to the outer walls. It is essentially a pattern of material that fills the empty space inside the object, making it solid and structurally sound.
With ABS filament, infill plays a crucial role in determining the overall strength and durability of the printed object. Unlike hollow prints, which are lightweight but more prone to breakage, solid infill creates a sturdy internal structure that enhances the mechanical properties of the object.
However, printing a solid infill is not always practical or necessary. Solid infill can be time-consuming, increase material usage, and result in a heavier object than desired. Therefore, it is important to strike a balance between infill percentage and the specific needs of your print.
The infill pattern is also worth considering. Common infill patterns include honeycomb, grid, triangles, and gyroid, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The pattern chosen can affect factors such as print speed, material usage, and overall strength.
By adjusting the infill amount, you can customize the internal structure to meet the requirements of your specific application. For example, if you are printing a decorative object that doesn’t require much strength, a lower infill percentage may be sufficient. On the other hand, if you are creating functional parts that need to withstand significant stress or load, a higher infill percentage would be recommended.
It is worth noting that the infill amount affects not only the strength but also the flexibility of the printed object. A higher infill percentage can result in a more rigid and robust print, while a lower infill percentage can produce a more flexible and lightweight object. Considering the desired characteristics and the intended use of the print is important when determining the appropriate infill amount.
Importance of Infill Amount
The infill amount for ABS prints is of utmost importance for several reasons. Let’s explore why determining the right infill percentage is crucial for achieving optimal print quality and functionality.
1. Strength and Durability: The infill amount directly impacts the strength and durability of 3D printed objects. A higher infill percentage will result in a stronger and more robust print, suitable for parts that require structural integrity and can withstand heavy loads or stress. Conversely, a lower infill percentage may be sufficient for prints that don’t require high strength, allowing for faster and more material-efficient prints.
2. Weight: The infill amount also affects the weight of the printed object. Solid infill creates a heavier print, while a lower infill percentage produces a lighter and more hollow print. By adjusting the infill, you can strike a balance between strength and weight, ensuring that the printed object meets the desired specifications without unnecessary bulk.
3. Material Usage: Controlling the infill percentage is essential for efficient material usage. Solid infill consumes more filament compared to lower infill percentages, resulting in increased material costs. By optimizing the infill amount, you can minimize material wastage and reduce printing costs while maintaining the necessary structural integrity.
4. Printing Time: The infill amount also affects the printing time. A solid infill requires more printing layers, leading to longer print durations. On the other hand, lower infill percentages reduce the number of layers, resulting in faster print speeds. Consider your time constraints and project deadlines when determining the appropriate infill percentage for your ABS prints.
5. Heat Dissipation: Infill plays a vital role in heat dissipation within the printed object. High infill percentages provide better internal heat distribution, which can be beneficial for parts that generate a significant amount of heat during operation. This helps prevent heat buildup and improves the overall performance and longevity of the print.
6. Support Structures: Infill also serves as a support structure for overhanging or complex geometries. By having a higher infill percentage, you can ensure better support for such features and minimize the risk of print failures or deformations during the printing process.
By considering these factors, you can determine the optimal infill amount for your ABS prints. The right infill percentage will not only provide the necessary strength and functionality but also optimize material usage, printing time, and overall performance of your 3D printed objects.
Factors to Consider
When determining the appropriate infill amount for ABS prints, there are several factors to take into consideration. These factors can help guide your decision-making process and ensure that you choose the infill percentage that best meets your specific needs. Let’s explore these factors:
1. Intended Use: The first factor to consider is the intended use of the printed object. What purpose will it serve? Is it a functional part that requires high strength and durability, or is it a decorative item that doesn’t need to withstand significant stress? Understanding the application of the print will help you determine the necessary infill percentage to achieve the desired outcome.
2. Strength Requirements: Consider the strength requirements of the object. Parts that need to bear weight or endure external forces require a higher infill percentage for added structural integrity. On the other hand, prints that don’t require high strength can utilize a lower infill percentage to save on material and reduce print time.
3. Print Time: Time is another crucial factor to consider. Prints with higher infill percentages result in more solid and time-consuming prints. If time is of the essence, opting for a lower infill percentage can significantly decrease the print duration.
4. Material Usage: The infill amount directly impacts material usage. Higher infill percentages consume more filament, increasing material costs. On the other hand, lower infill percentages economize material usage and reduce costs. Assess your budget and material availability to determine the most cost-effective infill percentage.
5. Print Quality: Consider the desired print quality. Higher infill percentages result in smoother and more solid prints, whereas lower infill percentages may lead to a more porous or hollow appearance. Evaluate the level of detail and surface finish required for your print to select the infill amount that achieves the desired visual outcome.
6. Heat Dissipation: If the printed object generates or needs to dissipate heat, such as in electronic enclosures, the infill amount plays a crucial role. A higher infill percentage can aid in better heat diffusion and improve the overall thermal performance.
7. Support Structures: Complex or overhanging geometries may require a higher infill percentage to provide sufficient support. Consider the design of your print and determine if a higher infill percentage is necessary to prevent print failures or deformations during the printing process.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select an appropriate infill percentage for your ABS prints that balances strength, time, material usage, print quality, thermal performance, and support requirements. Remember that finding the ideal infill amount may require some experimentation and adjustment to find the perfect balance for your specific needs.
Recommended Infill Percentages for ABS
When it comes to determining the ideal infill percentage for ABS prints, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. The recommended infill percentage can vary depending on the specific application, desired strength, print time, material usage, and other factors. However, here are some general guidelines to consider:
1. Low Infill Percentage (10-20%): A lower infill percentage is suitable for decorative prints or objects that don’t require much strength. These prints are often lightweight and can be completed relatively quickly. The lower infill also reduces material usage, making it a cost-effective option. However, it’s important to note that prints with low infill percentages may sacrifice some structural integrity.
2. Standard Infill Percentage (20-40%): This infill range is commonly used for average strength requirements. It provides a good balance between print time, material usage, and overall strength. The standard infill percentage is suitable for most functional prints, prototypes, and everyday objects where a balance of strength and efficiency is desired.
3. High Infill Percentage (40-80%): For parts that require maximum strength and durability, a higher infill percentage is recommended. This range is suitable for load-bearing components, mechanical parts, or objects that will undergo significant stress. However, keep in mind that high infill percentages can increase print time and material usage.
It’s worth mentioning that these percentages are not set in stone and can be adjusted based on your specific needs. You may find that certain prints require a higher or lower infill percentage to achieve the desired outcome. It’s always a good idea to conduct test prints and evaluate the results to fine-tune the infill percentage for your specific application.
Additionally, the choice of infill pattern can also impact the overall strength and print quality. Different patterns, such as honeycomb, grid, triangles, or gyroid, have varying strengths and material usage. Experimenting with different infill patterns, while keeping the infill percentage constant, can help you optimize the strength and performance of your prints.
Remember that finding the right infill percentage is a balance between achieving the desired strength, minimizing material usage, optimizing print time, and considering the specific requirements of your project. Don’t hesitate to make small adjustments and conduct test prints to find the perfect combination that meets your needs.
For ABS, a good starting point for infill percentage is around 20-30%. This will provide a good balance between strength and material usage. Adjust as needed based on your specific project requirements.
Read more: How Much Is Infill Percentage
Testing and Adjusting Infill Amount
Testing and adjusting the infill amount for ABS prints is an essential process to optimize the strength, print quality, and functionality of your 3D printed objects. Here are some steps you can take to test and fine-tune the infill amount:
1. Start with a Baseline: Begin by selecting a baseline infill percentage based on the recommended ranges mentioned earlier. This can serve as a starting point for your prints.
2. Conduct Test Prints: Print a few test pieces with different infill percentages within a range that aligns with your intended application. For example, you might print objects with 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% infill to compare their strength and quality.
3. Evaluate Strength and Print Quality: Once the test prints are complete, assess the strength and print quality of each object. Perform stress tests if needed or subject them to the expected loads and forces in their intended use environment. Also, visually inspect each print for any signs of weaknesses or imperfections.
4. Adjust the Infill Percentage: Based on the results of your evaluation, make adjustments to the infill percentage. For example, if a print with 10% infill is not strong enough for your application, try increasing it to 20% or higher. Conversely, if a print with 40% infill is excessively heavy and requires more material, consider reducing the infill percentage.
5. Reprint and Reevaluate: Repeat the printing process with the adjusted infill percentages. Compare the new prints to the previous ones and evaluate the improvements in strength and print quality. Continue iterating and adjusting until you achieve the desired outcome.
6. Consider Infill Pattern: Additionally, explore different infill patterns as an alternative to adjusting only the infill percentage. Changing the pattern, such as switching from a grid to a honeycomb, can impact the strength and material usage of the prints. Test prints with different patterns and evaluate the results alongside the infill percentages to find the optimal combination.
7. Document and Save Settings: Once you have identified the infill percentage and pattern that yield the best results, document these settings for future reference. Keeping a record of successful infill configurations can save time and provide a reference point for future prints.
By going through this testing and adjusting process, you can fine-tune the infill amount to achieve the desired balance of strength, weight, material usage, and print quality for your ABS prints. Remember that experimentation and iterations are key to finding the optimal infill settings for different applications and objects.
Impact of Infill Density on Print Quality
The infill density, or the amount of infill material packed within a specific area, has a significant impact on the overall print quality of ABS objects. Understanding this impact is crucial for achieving the desired level of strength, stability, and visual appeal in your 3D prints.
1. Strength and Stability: Increasing the infill density improves the overall strength and stability of the printed object. A higher density means more solid internal structure, resulting in better load-bearing capabilities and resistance to external forces. This is crucial for functional parts or objects that will be subjected to stress.
2. Surface Finish: Higher infill densities contribute to smoother and more refined surface finishes. With more infill material connecting the outer walls, there is less likelihood of gaps or inconsistencies in the surface texture. This is particularly important for objects with visible or aesthetic features.
3. Print Resolution: The infill density can also affect the level of detail and print resolution. Higher densities allow for intricate and precise details to be captured, resulting in a sharper and more accurate print. Lower densities, on the other hand, may result in a slightly rougher or less defined appearance.
4. Material Usage: Increasing the infill density will lead to higher material consumption. This can be a consideration if you want to minimize material usage and reduce printing costs. Finding the right balance between achieving the desired strength and stability while optimizing material usage is essential.
5. Print Time: It’s important to note that higher infill densities typically result in longer print times. This is because more layers need to be printed to achieve the desired density. If time is a constraint, finding the optimal infill density that balances print quality and print duration is crucial.
6. Support Requirements: The infill density can also influence the need for additional support structures. Prints with lower infill densities may require added support to maintain the integrity of overhanging or complex features. By increasing the infill density, you may reduce the need for additional supports.
Overall, understanding the impact of infill density on print quality allows you to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate density for your ABS prints. Finding the right balance between strength, visual appeal, material usage, and print time is essential. Experimentation and iterative testing can help you determine the optimal infill density to achieve the desired outcome for your specific application.
Infill Strategies for Different Applications
When it comes to selecting the infill strategy for ABS prints, different applications require different considerations. Here are some infill strategies to consider based on specific application needs:
1. Functional Parts and Load-Bearing Objects: For parts that will bear weight or undergo significant stress, a higher infill percentage is recommended. Aim for infill densities in the range of 40% to 80%. This will provide the necessary strength and stability to ensure the longevity and reliability of the printed object.
2. Prototyping and Testing: When creating prototypes or test parts, a mid-range infill percentage of around 20% to 40% is often suitable. This range balances strength, print time, and material usage, allowing for efficient testing and validation of design concepts without excessive material consumption.
3. Decorative Objects and Display Prints: Prints that are primarily for decorative purposes or display can utilize lower infill percentages. Ranges between 10% and 20% can produce lightweight prints with adequate structural integrity for their purpose while minimizing material usage and reducing print time.
4. Large-Scale Prints: For large-scale prints, such as architectural models or furniture, it’s important to consider print time and material usage. Opting for a lower infill percentage, coupled with a sturdy outer shell, can help reduce print duration and material costs while still maintaining the necessary strength for the size of the print.
5. Heat Dissipation Applications: If the printed object is intended to generate or dissipate heat, such as electronic enclosures or ventilation systems, a higher infill percentage can aid in better thermal management. Consider using infill percentages on the higher end of the recommended range (40% to 80%) to ensure better heat diffusion and overall thermal performance.
6. Artistic and Sculptural Prints: When creating artistic or sculptural prints, the infill strategy can be flexible. Depending on the desired visual effect and weight considerations, you can experiment with varying infill patterns and densities. Hollowing out certain areas while maintaining higher densities in load-bearing sections can provide an aesthetically pleasing and structurally stable print.
Remember, these are general guidelines, and specific applications may require unique approaches. It’s always vital to consider the specific requirements of your print, including strength, weight, aesthetics, material usage, and print time. Conducting test prints and evaluating the results is an effective way to fine-tune the infill strategy for your particular application.
By choosing the appropriate infill strategy, you can optimize the strength, functionality, and cost-efficiency of your ABS prints, ensuring they meet the specific needs of your intended application.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of infill amount in ABS prints is essential for achieving optimal strength, print quality, and functionality in 3D printed objects. By finding the right balance between infill percentage, infill pattern, and specific application needs, you can maximize the benefits of ABS filament in your prints.
When determining the infill amount, factors such as intended use, strength requirements, print time, material usage, print quality, and support structures should be carefully considered. It’s important to strike a balance between achieving the desired strength and stability while optimizing material usage, print time, and overall print quality.
To determine the ideal infill percentage, conducting test prints with different infill densities within the recommended ranges is crucial. Evaluating the strength, stability, surface finish, material usage, print time, and support requirements of each print can help you fine-tune the infill settings to meet your specific needs.
Additionally, considering the infill pattern can further enhance the performance and appearance of your prints. Different patterns, such as honeycomb, grid, triangles, or gyroid, have varying strengths, material usage, and visual effects. Experimenting with different patterns alongside the infill percentages can help you find the optimal combination for your intended application.
Remember, infill strategies can vary based on different applications. Understanding the specific requirements of functional parts, prototypes, decorative objects, large-scale prints, heat dissipation applications, and artistic prints can guide you in selecting the appropriate infill strategy for each scenario.
Ultimately, finding the right infill amount for ABS prints involves a process of experimentation, adjustment, and evaluation. By refining your infill settings, you can optimize the strength, print quality, and functionality of your ABS prints, ensuring they meet your specific requirements and expectations.
With a thorough understanding of ABS infill and a willingness to explore different options, you can unlock the full potential of your ABS prints and create high-quality, durable, and visually impressive objects through 3D printing.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Much Infill For ABS
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Much Infill For ABS”