

Articles
How To Test An AC Compressor
Modified: January 7, 2024
Learn how to test an AC compressor with these informative articles. Gain valuable insights and troubleshooting tips to ensure your compressor is running efficiently.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
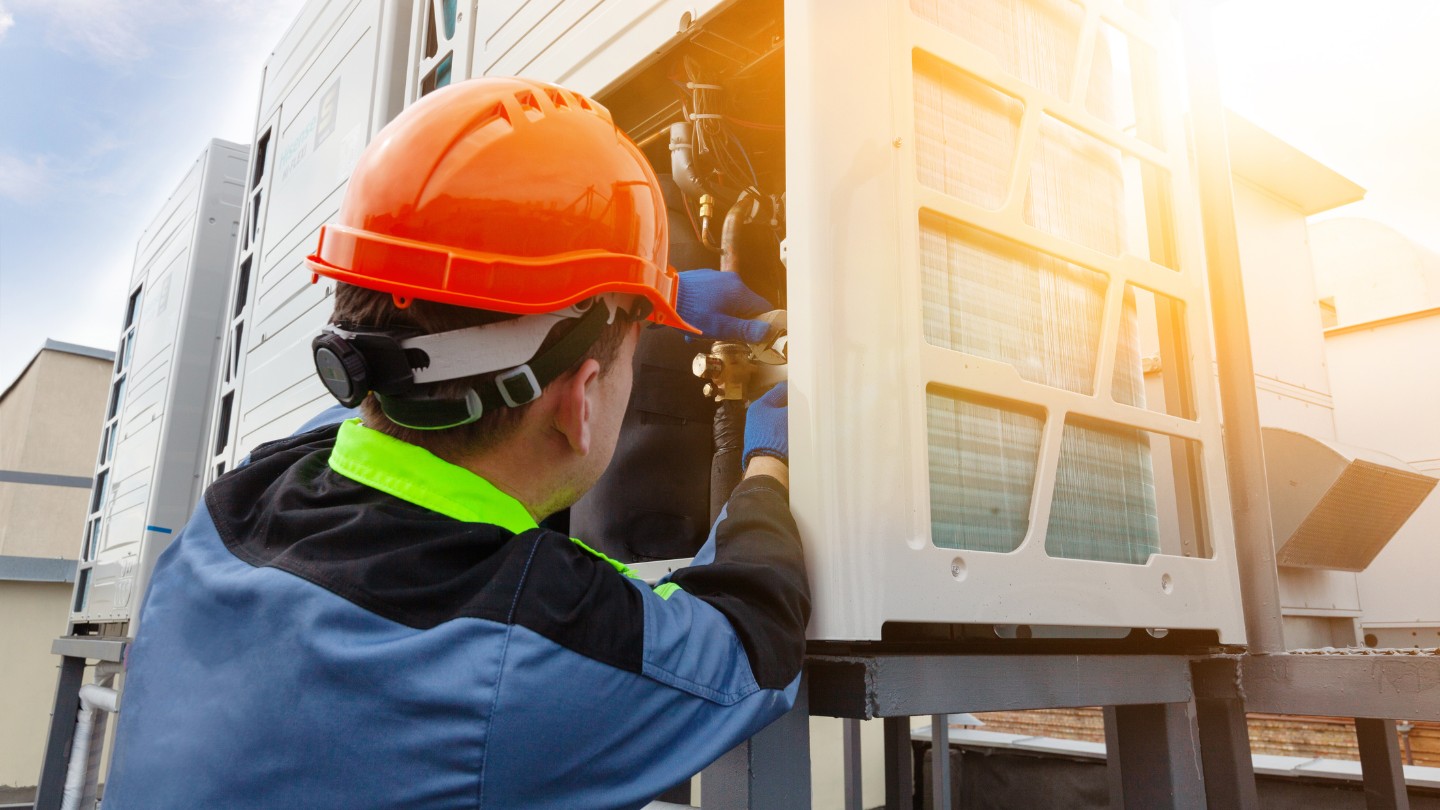
Welcome to our guide on how to test an AC compressor. The AC compressor is a vital component of your air conditioning system, responsible for compressing and circulating the refrigerant that cools and dehumidifies the air inside your vehicle or home.
Over time, an AC compressor may develop issues that can affect its performance, such as electrical problems, refrigerant leaks, or mechanical failures. Testing the AC compressor can help you identify these issues early on, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
In this article, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of testing an AC compressor. We will cover everything from gathering the necessary tools and equipment to interpreting the test results. So whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and guidance you need.
Before we dive into the testing process, it is important to note that working with an AC compressor requires some technical knowledge and safety precautions. If you do not feel comfortable or confident in performing these tests, it is best to seek the assistance of a qualified professional.
Now, let’s get started with the first step: gathering the necessary tools and equipment.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular testing and maintenance of your AC compressor are crucial for identifying potential issues early on, ensuring efficient cooling, and avoiding costly repairs or replacements.
- If you encounter abnormalities during testing, seek professional assistance to accurately diagnose and address any issues with your AC compressor, ensuring the longevity of your air conditioning system.
Read more: How To Test AC Compressor In Car
Step 1: Gather the necessary tools and equipment
Before you begin testing the AC compressor, it is important to gather all the tools and equipment you will need. Having these items handy will ensure a smooth and efficient testing process. Here are the essential tools and equipment you will need:
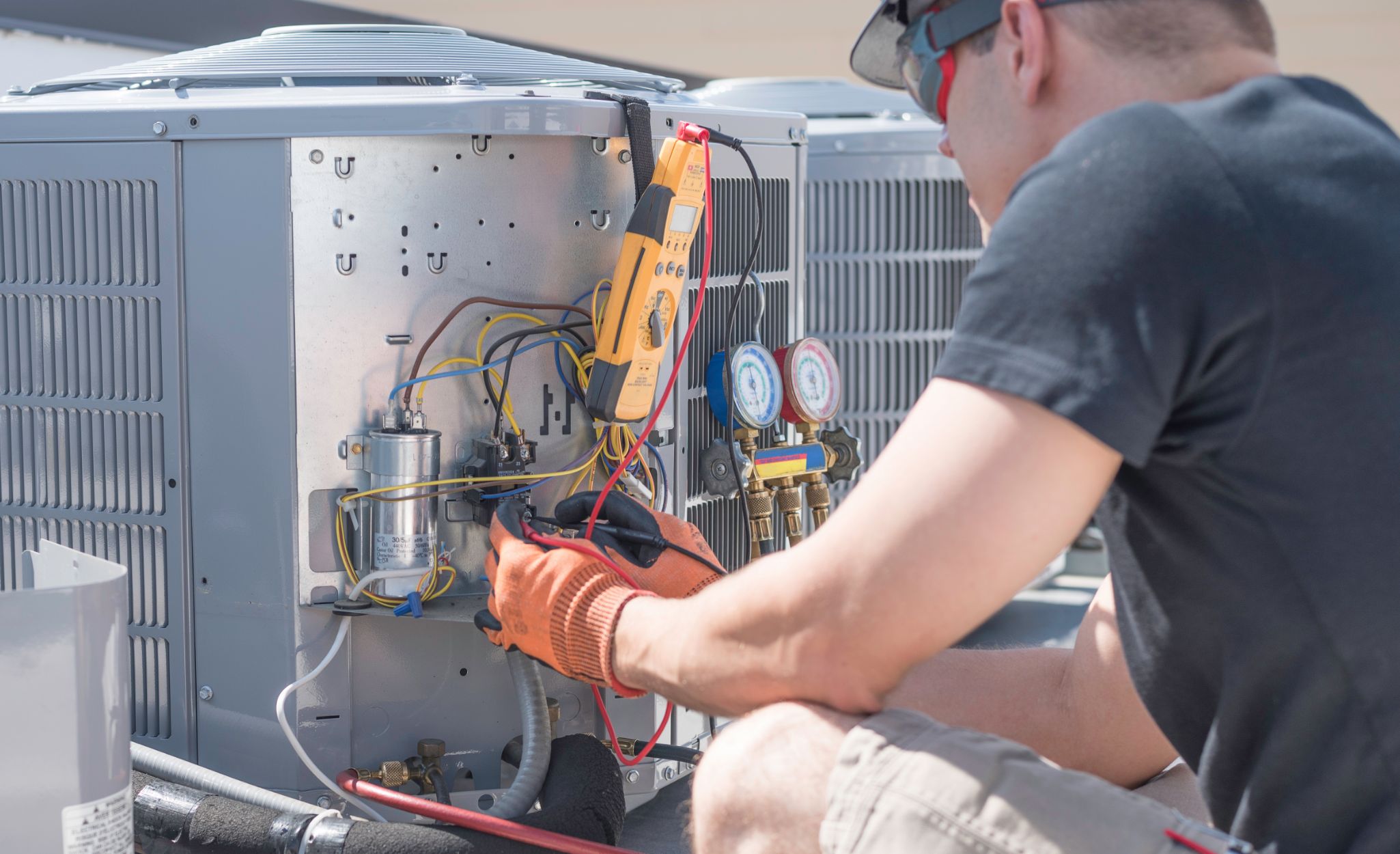
- AC manifold gauge set: This set includes pressure gauges, hoses, and connectors that allow you to measure the pressure of the refrigerant in the system.
- Multimeter: A digital multimeter is used to measure voltage, resistance, and continuity. It is an essential tool for testing electrical connections.
- AC leak detection kit: This kit includes a UV dye and a UV flashlight. It helps you identify refrigerant leaks by detecting the presence of the dye under UV light.
- Noise and vibration detector: This tool is optional but can be useful for detecting abnormal noises or vibrations in the compressor.
- Protective gear: It is important to prioritize your safety while working with AC compressors. Make sure to wear safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing to protect yourself from potential hazards.
Once you have gathered all the necessary tools and equipment, ensure that they are in good working condition. Check the gauges on the manifold gauge set for any signs of damage or wear. Verify that the multimeter is functioning properly by testing it on a known electrical source. The accuracy and reliability of your testing depend on the quality and functionality of your tools.
With the tools and equipment prepared, you are now ready to move on to the next step, which involves performing a visual inspection of the AC compressor.
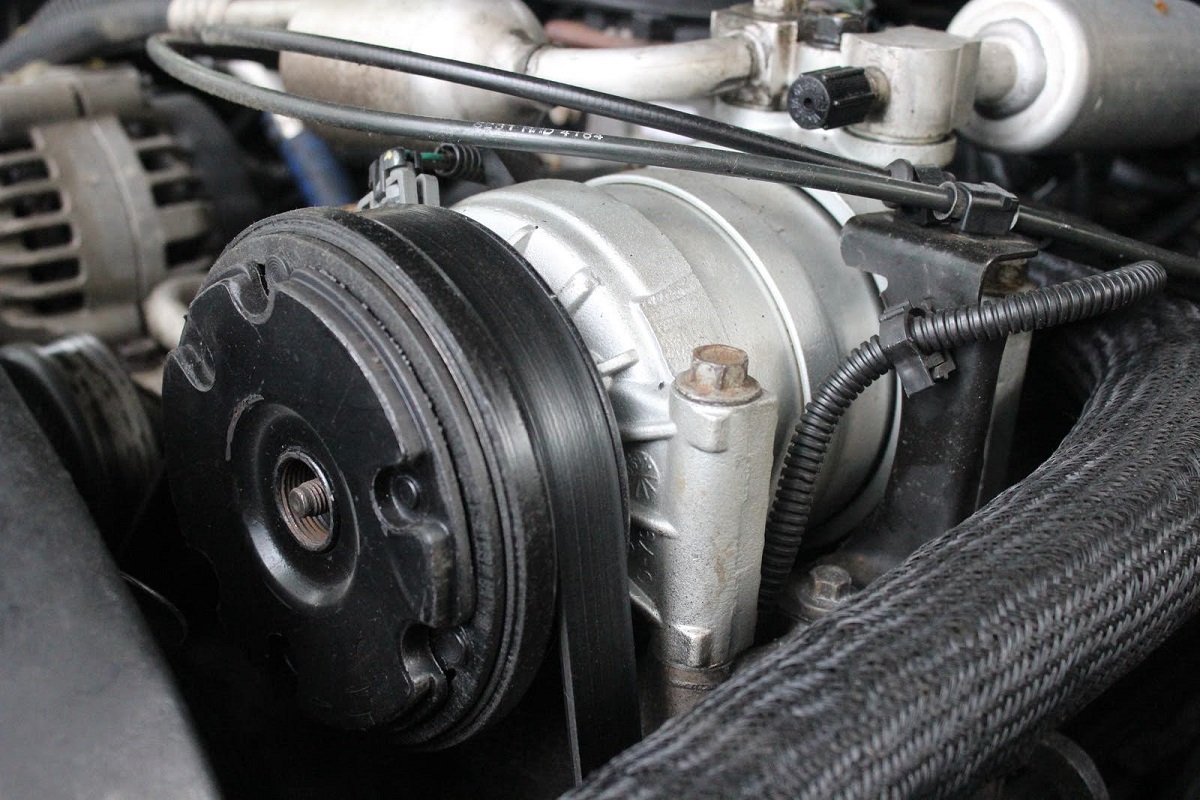
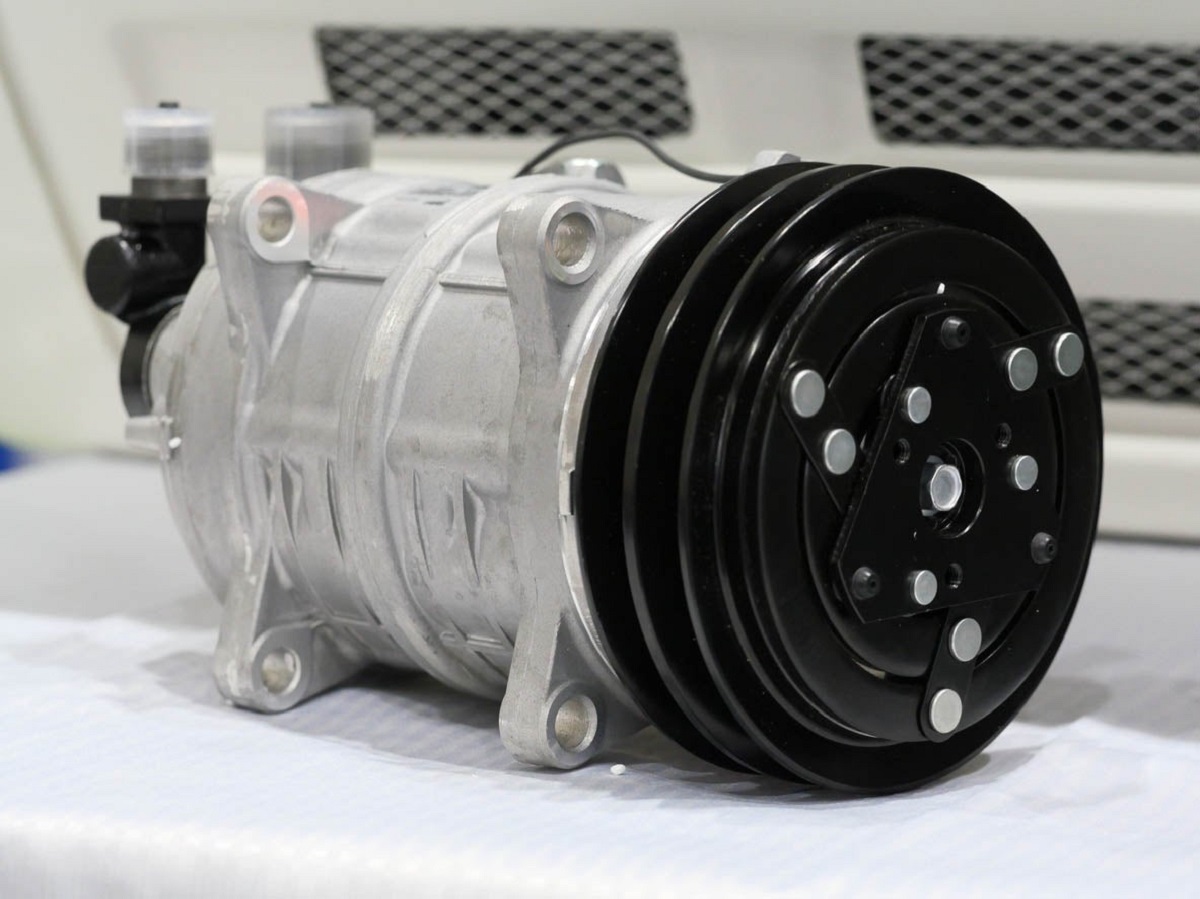
Step 2: Perform a visual inspection of the AC compressor
Before diving into the more technical tests, it’s important to start with a visual inspection of the AC compressor. This step allows you to identify any visible signs of damage, leaks, or excessive wear.
Here’s how to perform a visual inspection of the AC compressor:
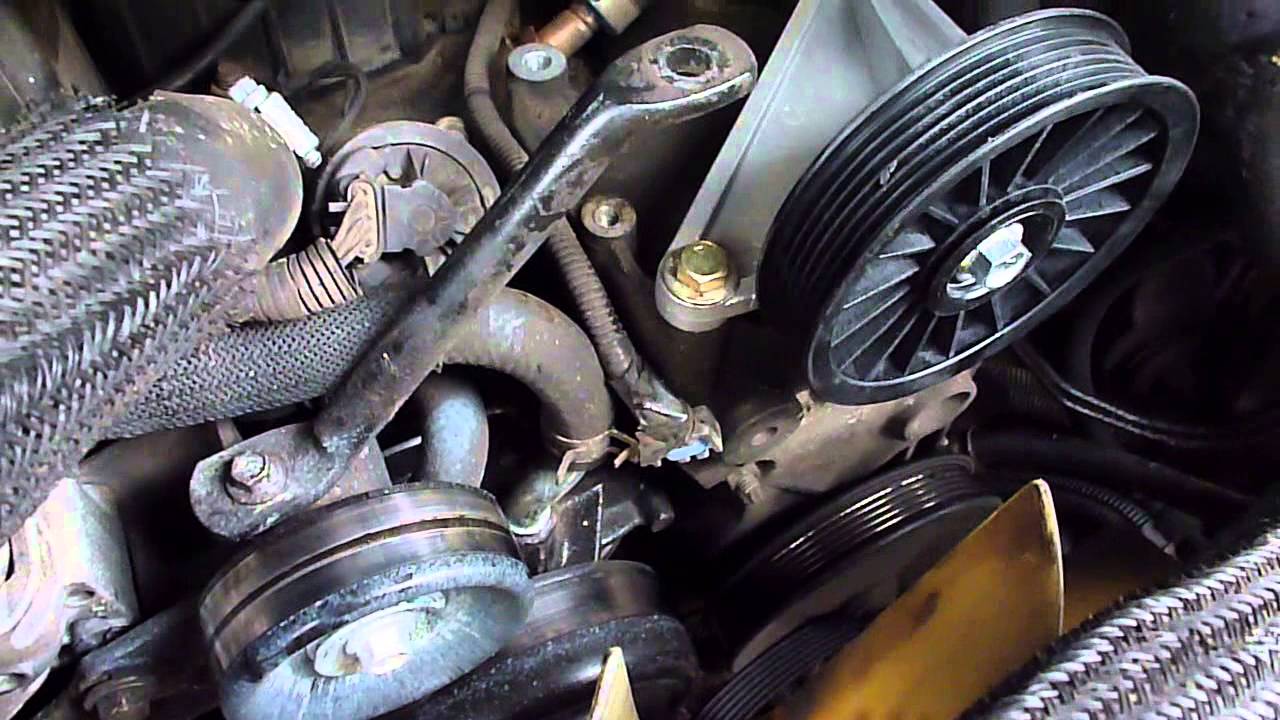
- Start by locating the AC compressor. In most vehicles, the compressor is located near or on the engine. It typically has a pulley and a belt connected to it.
- Inspect the compressor for any signs of physical damage, such as dents, cracks, or broken components. Pay close attention to the compressor housing, fittings, and connectors.
- Check for any signs of refrigerant leaks. Look for oil stains or greasy residue around the compressor or its connections. This could indicate a refrigerant leak.
- Inspect the compressor’s electrical connections. Ensure that the wires are properly connected and that there are no signs of fraying, burnt insulation, or loose connections.
- Examine the compressor pulley and belt for any wear or damage. Look for cracks, fraying, or excessive slack in the belt. A damaged belt may cause the compressor to malfunction.
- Take note of any abnormal noises or vibrations coming from the compressor. Unusual sounds like grinding, squealing, or knocking may indicate internal mechanical issues.
If you notice any significant damage, leaks, or abnormalities during the visual inspection, it is recommended to consult with a professional for further diagnosis and repair. They will have the expertise and tools necessary to address complex issues with the AC compressor.
Once you have completed the visual inspection, you can proceed to the next step: testing the electrical connections of the AC compressor.
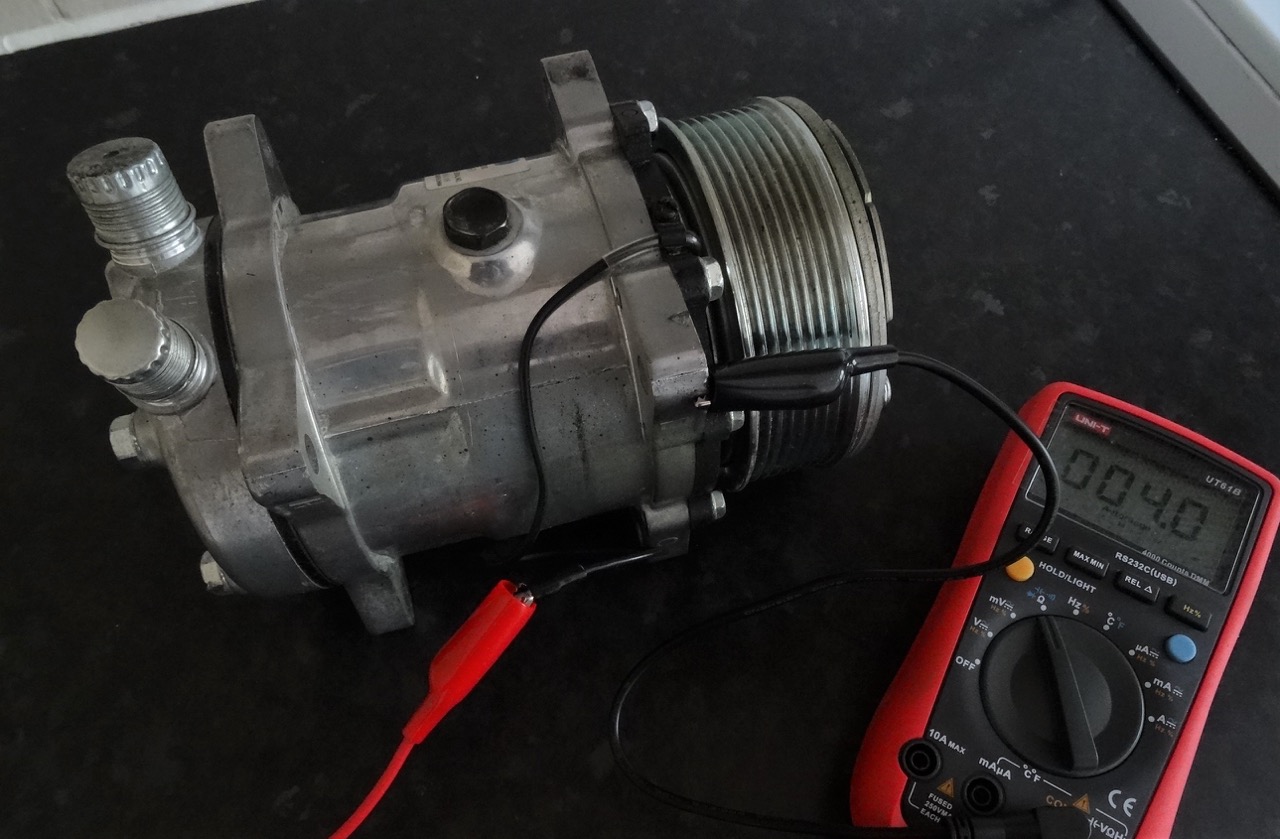
Step 3: Test the electrical connections
Testing the electrical connections of the AC compressor is an important step in diagnosing any electrical issues that may be affecting its performance. Faulty wiring or loose connections can result in the compressor not functioning properly.
Follow these steps to test the electrical connections:
- Start by disconnecting the power supply to the AC compressor. This can usually be done by locating the AC compressor relay in the fuse box and removing the corresponding fuse or relay.
- Using a multimeter set to the continuity mode, test the resistance across the compressor’s electrical connections. This will help identify any open circuits or high resistance in the wiring.
- Check each connection point of the compressor, including the wiring harness, plugs, and terminals. Ensure that they are securely connected and free from corrosion or damage.
- If you find any loose or corroded connections, clean them using electrical contact cleaner and reconnect them securely.
- Next, test the continuity of the compressor’s clutch coil. This is done by connecting one lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the compressor’s clutch connector and the other lead to a good ground. The multimeter should display low resistance if the clutch coil is functioning properly.
- If the clutch coil has high resistance or no continuity, it may be faulty and require replacement.
- Lastly, reconnect the power supply to the AC compressor and turn on the AC system. Monitor the compressor for any signs of abnormal operation, such as excessive noise or failure to engage.
If you encounter any issues during the electrical connections test or find that the AC compressor is not functioning correctly, it is recommended to consult with a professional technician who can further diagnose and resolve the problem.
Once you have finished testing the electrical connections, you can move on to the next step: checking the refrigerant levels in the AC compressor.
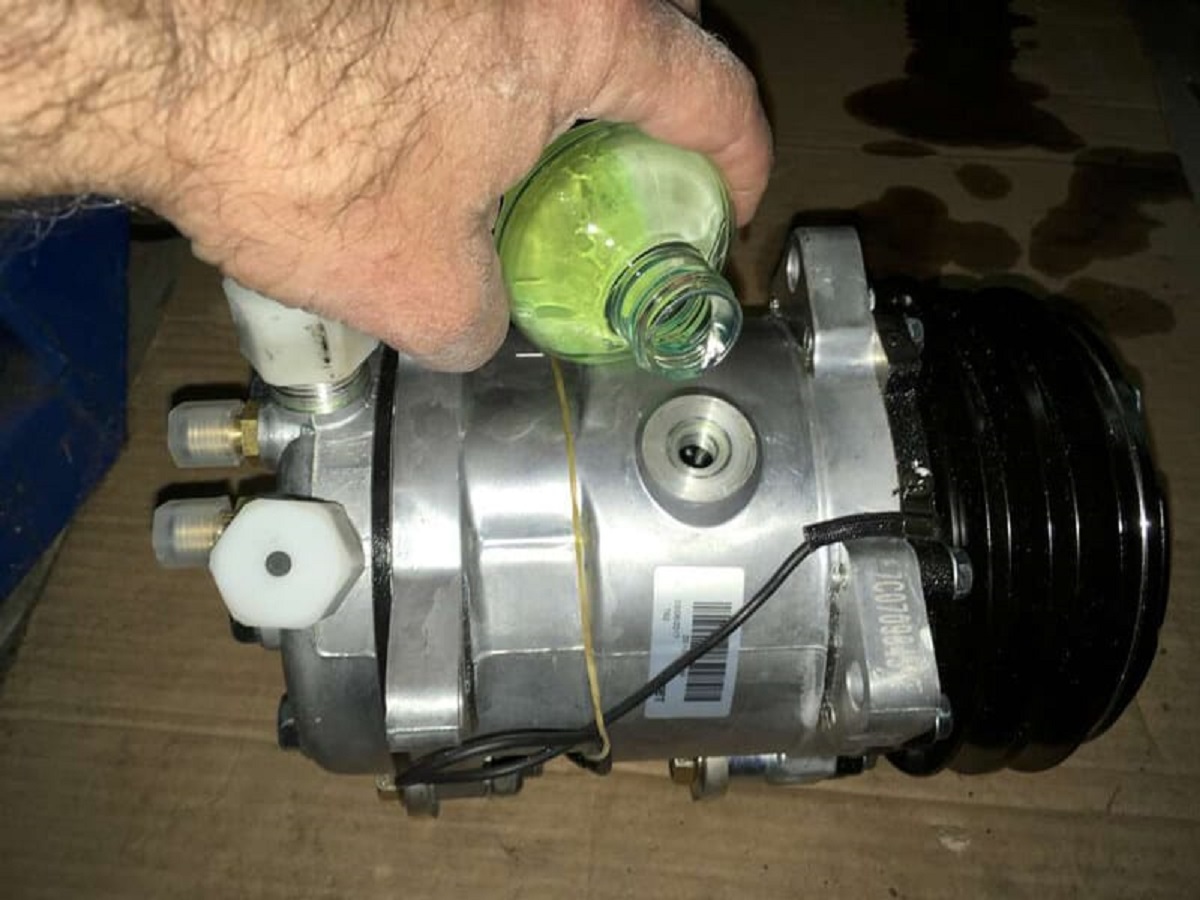
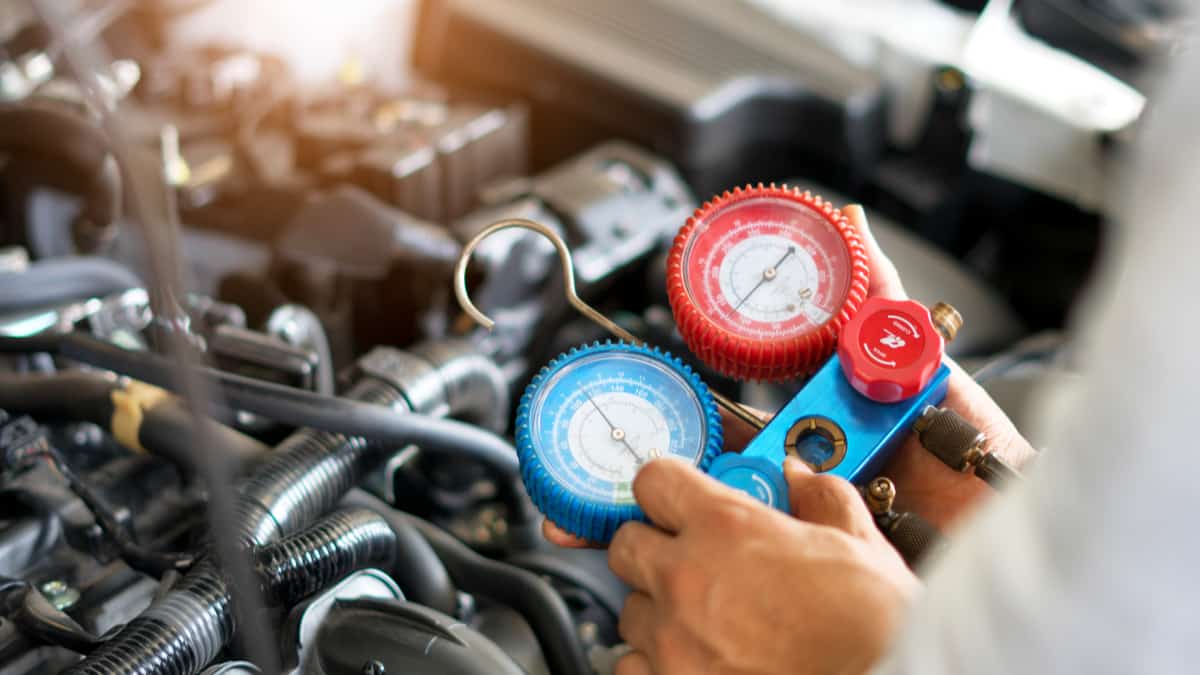
Step 4: Check the refrigerant levels
Checking the refrigerant levels in the AC compressor is crucial for proper operation and cooling efficiency. Insufficient refrigerant can lead to poor cooling performance, while excessive refrigerant can cause damage to the compressor and other components of the AC system.
Follow these steps to check the refrigerant levels:
- Start by locating the service ports on the AC compressor. These ports are usually labeled as low-pressure and high-pressure ports.
- Attach the AC manifold gauge set to the service ports. Connect the blue hose to the low-pressure port and the red hose to the high-pressure port. The yellow hose is connected to the refrigerant canister.
- Ensure that the valves on the manifold gauge set are closed before attaching the hoses to the service ports.
- Now, open the valves on the manifold gauge set. This will allow the pressure readings to be displayed on the gauges.
- Observe the pressure readings on both the low-pressure and high-pressure gauges. These readings will help determine if the refrigerant levels are within the recommended range.
- If the pressure readings are too low, it indicates a refrigerant leak or insufficient refrigerant levels. In this case, it is best to consult with a professional technician to locate and repair the leak before adding refrigerant.
- If the pressure readings are too high, it indicates excessive refrigerant levels. In this case, it is recommended to have a professional technician evacuate the excess refrigerant to prevent damage to the compressor and other components.
It is important to note that handling refrigerant requires proper training and certification. If you are not qualified or do not have the necessary equipment, it is best to leave the refrigerant-related tasks to a professional technician.
Once you have checked the refrigerant levels, you can move on to the next step: testing the compressor clutch.
Read more: How To Change AC Compressor
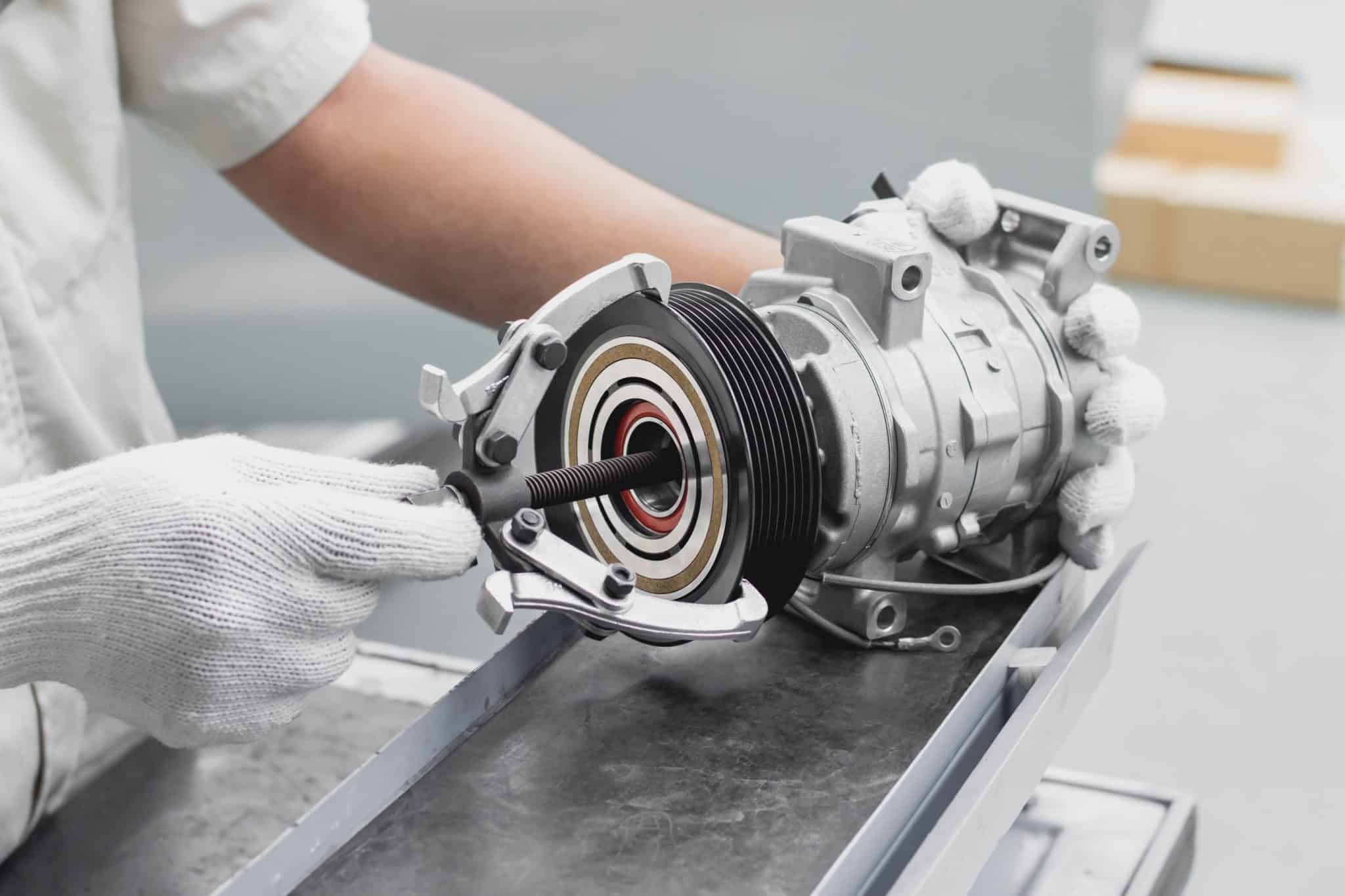
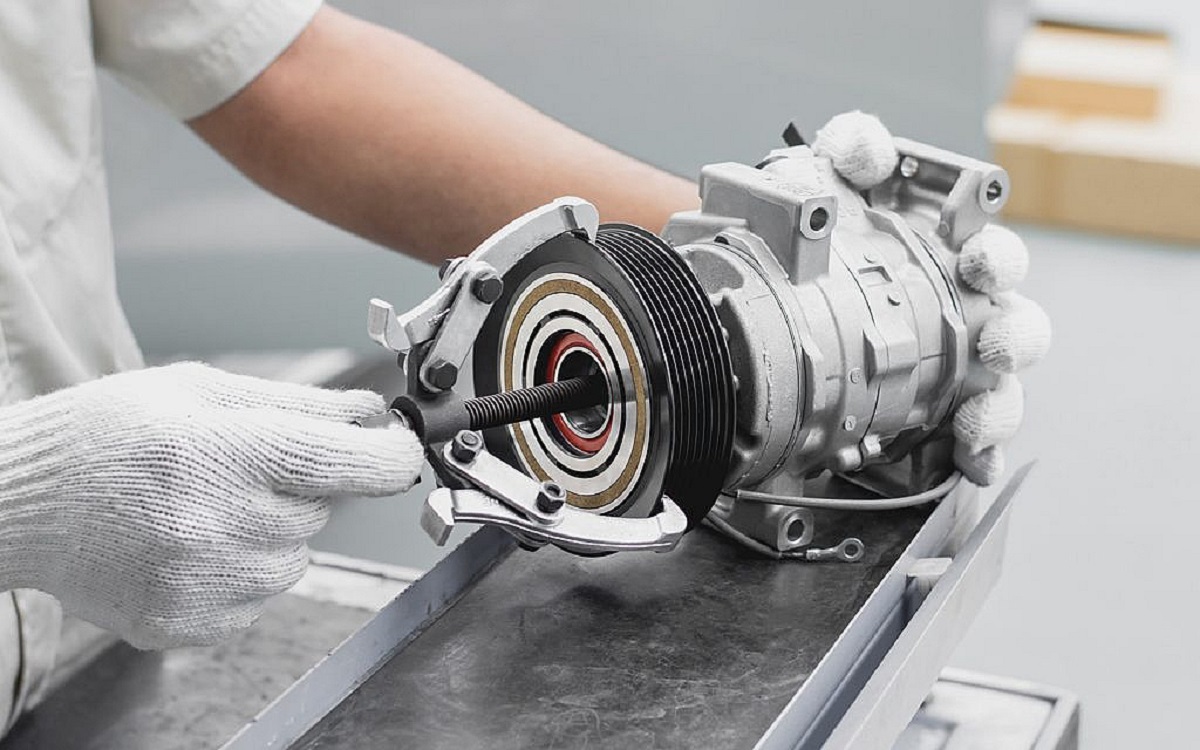
Step 5: Test the compressor clutch
The compressor clutch plays a crucial role in the operation of the AC compressor. It engages and disengages the compressor as needed to maintain the desired cooling temperature. Testing the compressor clutch will help you determine if it is functioning properly.
Follow these steps to test the compressor clutch:
- Start by locating the compressor clutch. It is usually located at the front of the AC compressor and is connected to the drive belt.
- With the engine off, visually inspect the compressor clutch for any signs of damage, such as worn-out or cracked components.
- Inspect the clutch coil wiring for any signs of fraying or damage. Ensure that the wiring is securely connected and free from corrosion.
- Turn on the engine and set the AC controls to the maximum cooling setting.
- Observe the compressor clutch as the AC system is turned on. The clutch should engage and start spinning as the system activates.
- If the clutch does not engage, it may indicate an electrical issue, a faulty clutch coil, or a problem with the AC control module. Further testing or professional assistance may be required.
- Listen for any abnormal noises coming from the compressor clutch while it is engaged. Unusual sounds like grinding, squealing, or rattling may indicate a mechanical issue that requires attention.
If you suspect that the compressor clutch is not functioning correctly, it is recommended to have it inspected by a professional technician. They will have the expertise and tools to diagnose and resolve any issues with the clutch.
Once you have finished testing the compressor clutch, you can move on to the next step: measuring the voltage output of the AC compressor.
When testing an AC compressor, use a multimeter to check for continuity between the compressor terminals. If there is no continuity, the compressor may be faulty and in need of replacement.
Step 6: Measure the voltage output
Measuring the voltage output of the AC compressor is an important test to determine if it is receiving the correct electrical power. This test helps identify any issues with the electrical supply or the compressor itself.
Follow these steps to measure the voltage output:
- Start by locating the electrical connections of the AC compressor. These connections are typically located near the compressor itself.
- Ensure that the power supply to the AC compressor is turned off. This can be done by disconnecting the AC compressor relay or removing the appropriate fuse from the fuse box.
- Set your multimeter to the voltage mode and select a range suitable for the expected voltage value. In most vehicles, the AC compressor operates on a 12V or 24V system, so select the appropriate range.
- Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the compressor’s electrical connection.
- Connect the black lead of the multimeter to a good ground point, such as a metal part of the vehicle’s chassis.
- Turn on the engine and set the AC controls to the maximum cooling setting.
- Observe the multimeter display for the voltage reading. Ideally, the voltage reading should match the specified voltage for your vehicle’s AC system (e.g., 12V or 24V).
- If the voltage reading is significantly lower or higher than the specified value, it indicates an electrical issue that needs to be addressed. Consult with a professional technician to further diagnose and resolve the problem.
Keep in mind that working with electrical components can be dangerous. If you are not confident or experienced in performing electrical tests, it is best to seek the assistance of a qualified professional.
Once you have measured the voltage output of the AC compressor, you can proceed to the next step: checking for abnormal noises or vibrations.
Step 7: Check for abnormal noises or vibrations
Abnormal noises or vibrations coming from the AC compressor are often indicators of underlying mechanical issues or imbalances. Checking for these abnormal signs can help identify potential problems and prevent further damage to the compressor.
Follow these steps to check for abnormal noises or vibrations:
- Start the engine and allow it to idle.
- Turn on the AC system and set it to the maximum cooling setting.
- Listen carefully for any unusual noises coming from the AC compressor. Pay attention to sounds like grinding, squealing, rattling, or knocking.
- If you hear any of these abnormal noises, it could indicate internal mechanical issues, such as a damaged bearing or a failing compressor. In such cases, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair.
- Observe the compressor closely for any excessive vibrations. Place your hand on the compressor and feel for any unusual movements or vibrations.
- Excessive vibrations may be a sign of imbalances or loose components within the compressor. Consult with a professional technician to address these issues before they cause further damage.
If you encounter any abnormal noises or vibrations during these tests, it is crucial to have the AC compressor inspected by a qualified professional. They will have the knowledge and expertise to identify and address any mechanical issues.
Once you have checked for abnormal noises or vibrations, you can move on to the next step: testing the compressor under load.
Step 8: Test the compressor under load
Testing the AC compressor under load is a critical step to assess its performance and efficiency when operating in real-world conditions. This test helps determine if the compressor can handle the workload and provide effective cooling.
Follow these steps to test the compressor under load:
- Start the engine and allow it to reach normal operating temperature.
- Turn on the AC system and set it to the maximum cooling setting.
- Monitor the compressor’s performance while under load. Observe how quickly it engages, how smoothly it operates, and how effectively it cools the interior of the vehicle.
- Pay attention to any changes in performance compared to previous tests. Look for signs of the compressor struggling to maintain the desired cooling temperature or any decreased cooling capacity.
- If you notice any significant issues or a decline in performance, it could indicate a problem with the compressor, such as a worn-out clutch, a faulty valve, or a refrigerant leak. In such cases, it is recommended to have the compressor inspected and repaired by a professional technician.
Testing the compressor under load allows you to assess its functionality in real-world conditions. This step is particularly important if you have previously identified any issues during the earlier tests. A comprehensive evaluation will help ensure that the compressor is operating at its optimal capacity.
Once you have completed the test under load, you can proceed to the final step: interpreting the test results and determining the necessary course of action.
Read more: What Is An AC Compressor
Step 9: Interpret the test results
After performing all the previous steps and conducting the necessary tests on the AC compressor, it’s time to interpret the results. This step involves analyzing the data you’ve collected and determining the next course of action based on the findings.
Here’s how to interpret the test results:
- Review all the tests you have performed, including the visual inspection, electrical connections test, refrigerant level check, compressor clutch test, voltage output measurement, and evaluation under load.
- Compare the results to the expected performance standards for your specific AC system. Consult the vehicle or equipment manufacturer’s guidelines for reference.
- If all the tests indicate normal operation, the AC compressor is likely functioning correctly with no significant issues identified. Routine maintenance and regular inspections should suffice to keep it in good condition.
- If any of the tests reveal abnormalities, such as leaks, electrical faults, excessive wear, or poor performance, it indicates potential problems with the AC compressor. Consult with a professional technician to further diagnose and address the specific issues.
- Consider the age, overall condition, and cost of repairs when deciding whether to repair or replace the AC compressor. In some cases, it may be more practical and cost-effective to replace the compressor.
- If you are not confident in interpreting the test results or making the necessary decisions, it is advisable to seek the expertise of a qualified professional who can provide accurate analysis and guidance.
Remember, maintaining the optimal performance of your AC compressor is crucial for efficient cooling and comfort. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and timely repairs or replacements will ensure the longevity and reliability of your AC system.
With a clear understanding of the test results, you can take the appropriate steps to address any issues and ensure the continuous operation of your AC compressor.
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the testing process for an AC compressor. By following these steps and interpreting the test results, you are now equipped with the knowledge to maintain and troubleshoot your AC system effectively.
Remember, if you are unsure about any aspect of the testing process or if you encounter persistent issues, seeking professional assistance is always recommended.
Thank you for using our guide, and we hope it has been helpful in your AC compressor testing journey!
Conclusion
Testing an AC compressor is an essential process for ensuring the efficient operation of your air conditioning system. By following the step-by-step guide we have provided, you can identify potential issues and take the necessary steps to repair or replace the compressor as needed.
Throughout the testing process, we covered various aspects, including gathering the necessary tools and equipment, performing a visual inspection, testing the electrical connections, checking the refrigerant levels, evaluating the compressor clutch, measuring the voltage output, checking for abnormal noises or vibrations, and testing the compressor under load. Each step serves a crucial purpose in assessing the overall health and performance of the AC compressor.
Interpreting the test results allows you to make informed decisions on whether further repairs or replacements are necessary. It is important to consult with a professional technician for a comprehensive analysis and guidance, especially when faced with complex issues.
Remember, regular maintenance, inspections, and prompt repairs are crucial for keeping your AC compressor in optimal condition. Addressing any issues promptly will help avoid costly repairs and ensure the longevity of your AC system.
We hope this guide has been informative and helpful in your journey to test an AC compressor. By following the steps outlined and seeking professional assistance when necessary, you can keep your air conditioning system running smoothly and comfortably.
Thank you for reading, and we wish you success in testing and maintaining your AC compressor!
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Test An AC Compressor
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “How To Test An AC Compressor”