

Articles
What Is An AC Compressor
Modified: February 26, 2024
Looking for articles on what an AC compressor is? Read our comprehensive guide to learn about the function and importance of AC compressors in air conditioning systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of air conditioning! AC compressors are an essential component of any air conditioning system, playing a vital role in cooling your home or office during the sweltering summer months. But what exactly is an AC compressor and how does it work?
In this article, we will explore the inner workings of an AC compressor, its components, types, common issues, troubleshooting tips, and maintenance practices. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of AC compressors and be better equipped to handle any issues that may arise.
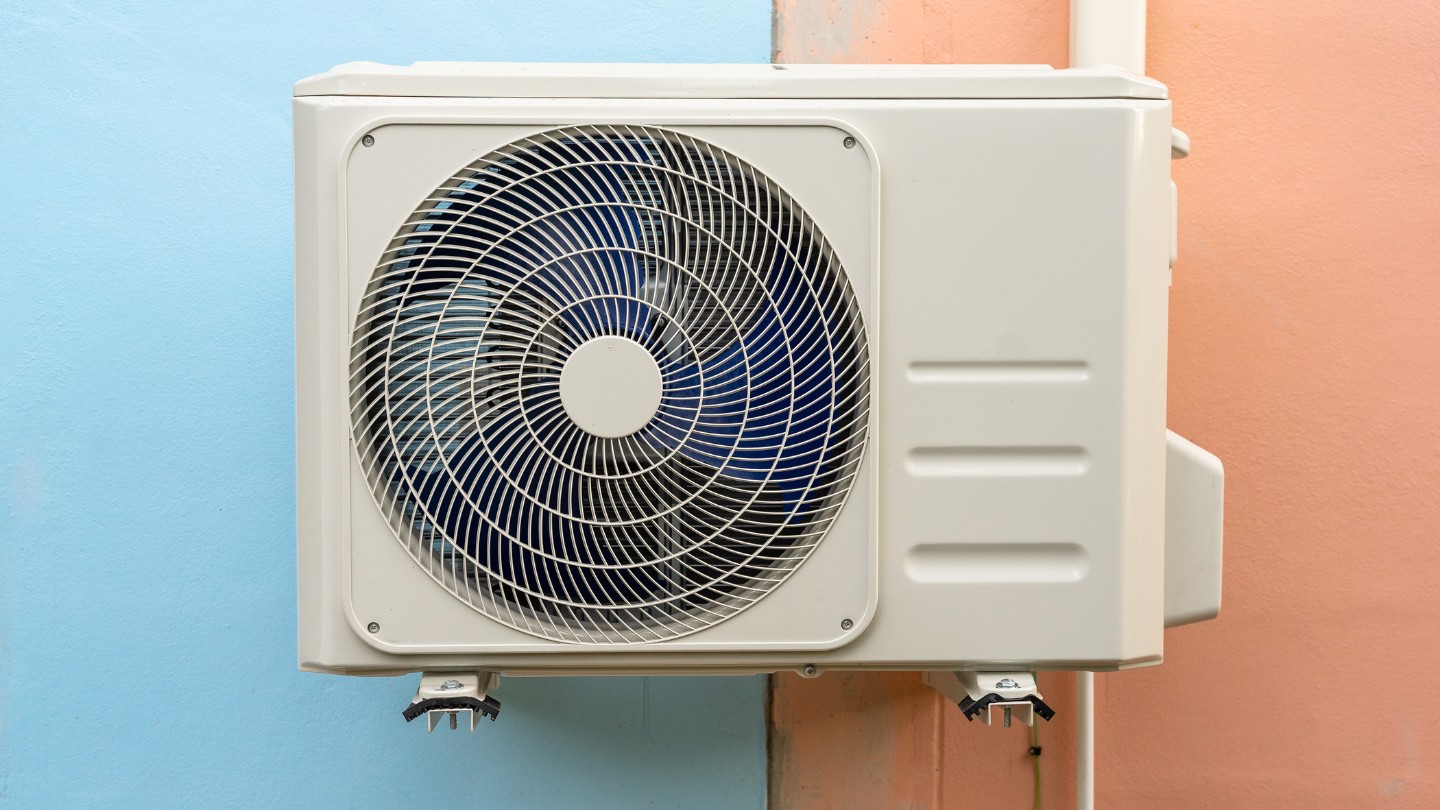
An AC compressor is the heart of an air conditioning system, responsible for compressing and circulating refrigerant gas to cool the air. Without it, your AC system would be unable to cool the air efficiently and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
The compressor performs the crucial task of compressing low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator coil into high-pressure gas. This compressed gas then flows through the condenser coil to release heat and transform back into a cool liquid. The liquid refrigerant then returns to the evaporator to repeat the cooling cycle.
To fully grasp how an AC compressor works, it’s essential to understand the various components that make up this complex system.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the inner workings of an AC compressor, its components, and the cooling process is essential for maintaining an efficient air conditioning system. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can extend the lifespan of the compressor and ensure a comfortable indoor environment.
- Common issues such as overheating, refrigerant leaks, and mechanical failures can impact the performance of AC compressors. Following maintenance tips, troubleshooting problems, and seeking professional assistance when needed are crucial for keeping the compressor running smoothly and maintaining optimal cooling.
Read more: What Is A Scroll Compressor For HVAC
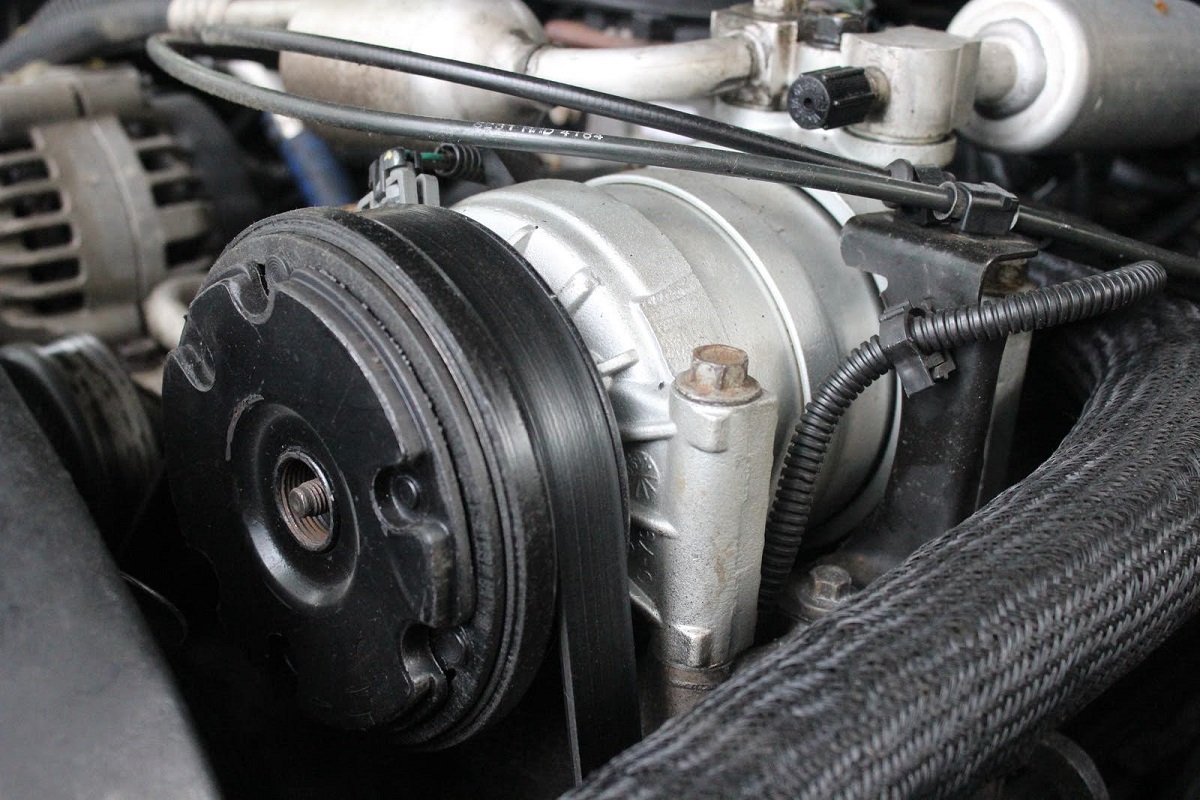
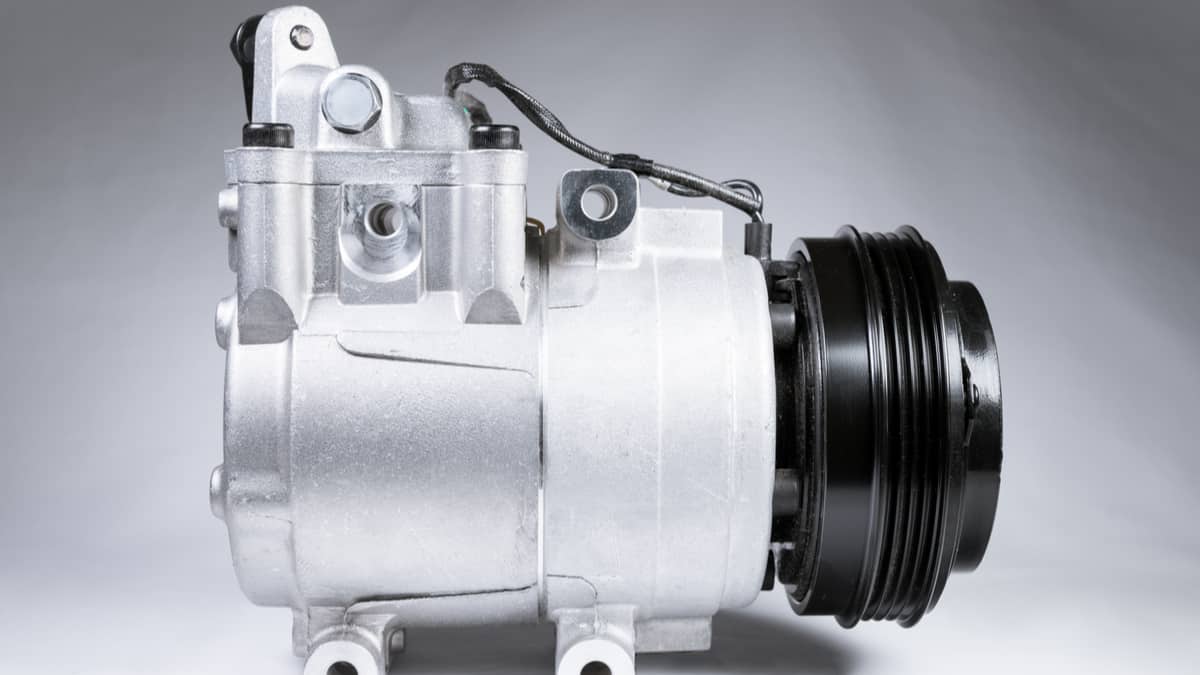
Definition of an AC Compressor
An AC compressor is a mechanical device that is responsible for circulating and compressing refrigerant gas in an air conditioning system. It is the crucial component that enables the cooling process by extracting heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside, keeping your space comfortable and cool.
The primary function of an AC compressor is to increase the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas, transforming it from a low-pressure vapor state into a high-pressure gas. This compression process allows the refrigerant to release heat as it flows through the system, ensuring effective cooling.
AC compressors are typically powered by an electric motor, which drives a piston or rotary engine. The engine compresses the refrigerant gas by creating high-pressure zones and low-pressure zones within the compressor. This compression cycle enables the refrigerant to circulate through the AC system, absorbing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside.
In simpler terms, think of the AC compressor as the heart of your air conditioning system. It takes in the refrigerant gas, compresses it, and pumps it through the system to cool down your space. Without a functioning compressor, your AC system would not be able to provide the cooling relief you expect.
AC compressors come in various sizes and capacities to accommodate different air conditioning systems. They are designed to handle specific refrigerants, such as R-410A or R-22, depending on the age and type of system. It’s important to ensure that the correct compressor is used for your specific AC unit to optimize performance and efficiency.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what an AC compressor is, let’s delve deeper into how it works and the components that make up this essential part of your air conditioning system.
How an AC Compressor Works
An AC compressor plays a critical role in the cooling process of an air conditioning system. It works in conjunction with other components to efficiently cool the indoor air. Let’s take a closer look at the step-by-step process of how an AC compressor works:
- 1. Refrigerant vapor enters the compressor: The AC system begins with the compressor receiving low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator coil. This vapor is typically in a gaseous state after absorbing heat from the indoor air.
- 2. Compression of the refrigerant: Once inside the compressor, the low-pressure refrigerant vapor is compressed by either a piston or rotary engine. As the compressor mechanically compresses the vapor, its pressure and temperature increase significantly.
- 3. High-pressure gas is generated: Through the compression process, the refrigerant vapor transforms into a high-pressure gas. This high-pressure gas contains a significant amount of thermal energy, which will be released later in the cooling process.
- 4. Refrigerant flows to the condenser coil: The high-pressure gas then flows through the condenser coil, a heat exchange component located outside the building. In the condenser coil, the refrigerant releases its accumulated heat to the surrounding air, causing it to condense into a high-pressure liquid state.
- 5. Heat dissipation and cooling: As the refrigerant condenses, it releases large amounts of heat to the outdoors, effectively cooling down. The condenser fan helps expedite this heat dissipation process by blowing air over the condenser coil.
- 6. Liquid refrigerant enters the expansion valve: After the heat dissipation process, the high-pressure liquid refrigerant travels to the expansion valve, a metering device located inside the indoor unit of the AC system.
- 7. Pressure reduction and evaporation: Inside the expansion valve, the high-pressure liquid refrigerant undergoes a pressure reduction. This reduction causes the refrigerant to evaporate and transform back into a low-pressure vapor.
- 8. Cooling cycle repeats: The low-pressure refrigerant vapor then re-enters the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air. This heat absorption process cools down the air, which is then distributed back into the space via the AC ducts. The cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation continues until the desired temperature is reached.
This continuous refrigerant cycle facilitated by the AC compressor is what enables your air conditioning system to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Each component of the AC system plays a crucial role, with the compressor at the center, ensuring the efficient cooling of the air.
Understanding how an AC compressor works allows you to appreciate the complexity and importance of this component. However, like any mechanical device, AC compressors are prone to issues and malfunctions. In the next section, we will explore common problems that can arise with AC compressors and how to troubleshoot them.
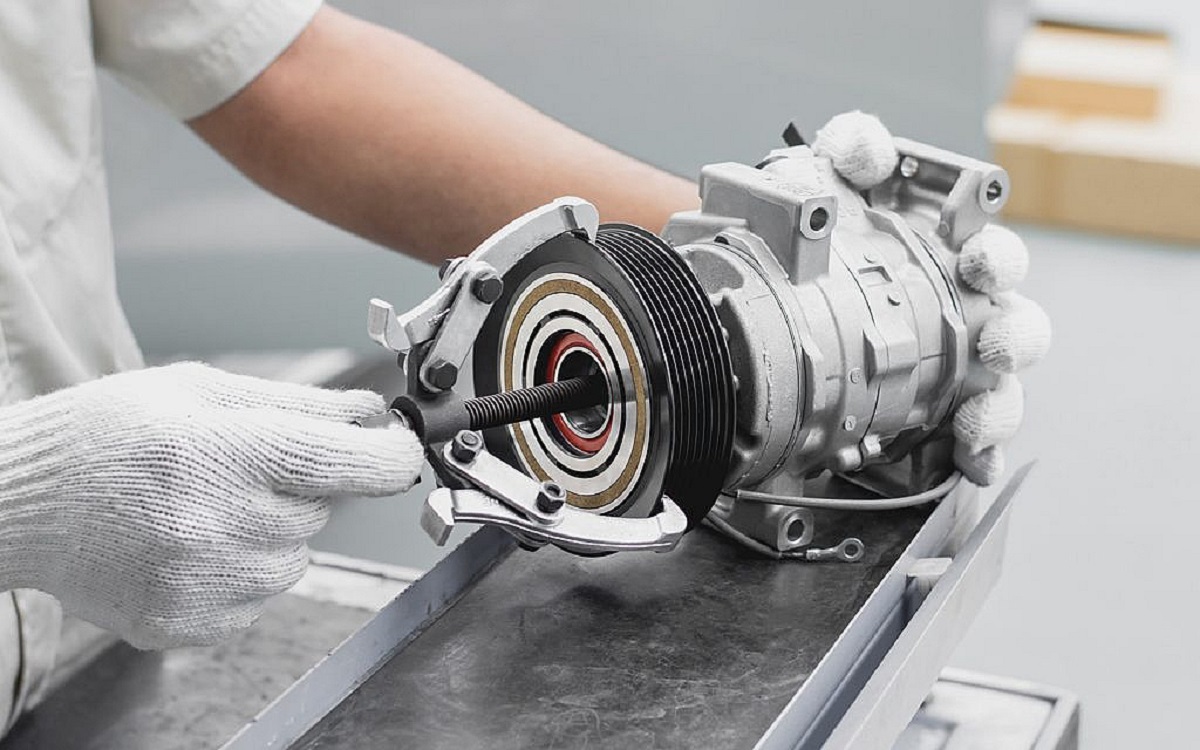
Components of an AC Compressor
An AC compressor consists of several key components that work together to compress the refrigerant gas and facilitate the cooling process. Understanding these components will give you a better understanding of how the compressor functions. Let’s explore the main components of an AC compressor:
- 1. Piston or Rotary Engine: The piston or rotary engine is the main mechanical component responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas. It creates the necessary high-pressure zones and low-pressure zones within the compressor to facilitate the compression process.
- 2. Compressor Housing: The compressor housing contains and protects the internal components of the compressor. It is made of durable materials that can withstand high pressure and temperature conditions.
- 3. Discharge Port: The discharge port is an outlet through which the high-pressure refrigerant gas exits the compressor and flows towards the condenser coil.
- 4. Suction Port: The suction port is an inlet through which the low-pressure refrigerant vapor enters the compressor from the evaporator coil. It provides the necessary flow of refrigerant into the compressor for the compression process.
- 5. Reed Valves: Reed valves are small flaps or plates located in the compressor that allow the refrigerant gas to enter and exit the compression chamber. These valves open and close in response to pressure differentials, ensuring that the refrigerant flows in the desired direction.
- 6. Bearings: Bearings are essential for smooth operation of the compressor. They provide support and reduce friction between moving parts, allowing the piston or rotary engine to rotate efficiently.
- 7. Oil Separator: The oil separator is a component that separates oil from the compressed refrigerant gas before it flows into the condenser coil. This helps ensure that only the refrigerant gas enters the condenser, preventing any potential damage or inefficiencies caused by the presence of oil.
- 8. Electric Motor: In most AC compressors, an electric motor provides the power to drive the piston or rotary engine. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to facilitate the compression process.
These components work in harmony to compress the refrigerant gas and facilitate the cooling process in an air conditioning system. Any issues or malfunctions with these components can impact the performance and efficiency of the AC compressor, leading to problems with cooling.
Now that we have explored the components of an AC compressor, let’s delve into the different types of AC compressors commonly found in air conditioning systems.
Types of AC Compressors
There are different types of AC compressors used in air conditioning systems, each with its own unique design and functionality. The type of compressor used in a particular AC system depends on factors such as system efficiency, cooling capacity, and the refrigerant being utilized. Let’s explore some of the most common types of AC compressors:
- 1. Reciprocating Compressor: Reciprocating compressors are the most common type of AC compressors. They use a piston-cylinder mechanism to compress the refrigerant gas. As the piston moves in a back-and-forth motion, it compresses the gas by reducing the volume of the cylinder. Reciprocating compressors are known for their reliability and durability, making them suitable for a range of cooling applications.
- 2. Scroll Compressor: Scroll compressors utilize two interlocking spiral-shaped scrolls – one fixed and one orbiting – to compress the refrigerant gas. As the orbiting scroll moves, it traps and compresses the gas between the scrolls, gradually decreasing the volume. Scroll compressors are known for their quiet operation and improved energy efficiency compared to reciprocating compressors.
- 3. Rotary Compressor: Rotary compressors use a rotating shaft with vanes or blades to compress the refrigerant gas. The rotating motion creates high-pressure zones and low-pressure zones, allowing the gas to be compressed. Rotary compressors are compact, lightweight, and known for their smooth operation. They are commonly used in smaller air conditioning systems and portable units.
- 4. Screw Compressor: Screw compressors consist of two interlocking rotors – a male and a female rotor – with helical grooves. As the rotors rotate, they push the refrigerant gas from the suction side to the discharge side, compressing it along the way. Screw compressors are known for their high efficiency and are often used in large-scale commercial and industrial air conditioning systems.
- 5. Centrifugal Compressor: Centrifugal compressors use high-speed rotating impellers to accelerate the refrigerant gas and increase its pressure. The impellers direct the gas towards a diffuser, where it is further compressed. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in large commercial HVAC systems and offer high cooling capacities.
Each type of compressor has its own advantages and considerations, and the choice of compressor depends on specific requirements and system characteristics. Understanding the different types of AC compressors can help you make informed decisions when it comes to selecting or troubleshooting your air conditioning system.
Now that we have explored the types of AC compressors, let’s delve into some common issues that may arise with these compressors and how to troubleshoot them.
Regular maintenance of your AC compressor is essential to ensure its efficiency and longevity. This includes cleaning the coils, checking for refrigerant leaks, and replacing air filters regularly.
Read more: What Causes An AC Compressor To Stop Working
Common Issues with AC Compressors
AC compressors, like any other mechanical component, can experience problems over time. These issues can affect the performance and efficiency of your air conditioning system. It’s important to be aware of common compressor problems and know how to troubleshoot them. Let’s explore some of the most frequently encountered issues with AC compressors:
- 1. Compressor Overheating: One common issue is compressor overheating, which can be caused by restricted airflow, low refrigerant levels, dirty condenser coils, or a malfunctioning fan. Overheating can lead to compressor failure, so it’s crucial to address this issue promptly.
- 2. Refrigerant Leaks: Refrigerant leaks can occur in the compressor or other parts of the AC system. These leaks can result in reduced cooling capacity, inefficient operation, and potential damage to the compressor. Identifying and repairing refrigerant leaks is important to ensure optimal system performance.
- 3. Electrical Problems: Electrical issues, such as faulty wiring, capacitor problems, or a failing motor, can affect the operation of the AC compressor. These problems may cause the compressor to fail to turn on, operate intermittently, or make unusual noises.
- 4. Compressor Clutch Failure: The compressor clutch engages and disengages the compressor according to the cooling demands. A failed clutch can prevent the compressor from engaging, leading to no cool air from the AC system.
- 5. Compressor Contamination: Contaminants like dirt, debris, or moisture can enter the compressor and compromise its functionality. Contamination can affect the lubrication of internal components, leading to increased wear and tear, reduced efficiency, and potential compressor damage.
- 6. Mechanical Failure: Over time, wear and tear can cause mechanical failure in the compressor. This can result in various issues, including compressor noise, reduced cooling capacity, or complete compressor failure.
If you encounter any of these issues with your AC compressor, it’s essential to address them promptly. However, troubleshooting and resolving AC compressor issues can be complex and require professional expertise. It’s recommended to seek assistance from a trained HVAC technician to diagnose and repair compressor problems effectively.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser coils, checking refrigerant levels and connections, and ensuring proper airflow, can help prevent many compressor issues. Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting can extend the lifespan of your AC compressor and ensure efficient cooling performance.
Now that we have explored common issues with AC compressors, let’s discuss some troubleshooting tips to help you address these problems effectively.
Troubleshooting AC Compressor Problems
When you encounter issues with your AC compressor, it’s essential to troubleshoot the problem to determine the cause and find a solution. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you address AC compressor problems effectively:
- 1. Check Power Supply: Ensure that the AC unit is receiving power by checking the circuit breaker and confirming that the power switch is turned on. If there is no power, reset the breaker or replace any blown fuses.
- 2. Check Thermostat Settings: Make sure the thermostat is set to the desired temperature and the cooling mode is activated. Incorrect thermostat settings can prevent the compressor from turning on.
- 3. Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty or clogged air filters can restrict airflow to the AC system, causing the compressor to work harder. Clean or replace the filters regularly to ensure optimal air circulation.
- 4. Check for Refrigerant Leaks: Perform a visual inspection of the AC system to check for any signs of refrigerant leaks, such as oil stains or frost buildup. If you suspect a leak, contact a professional technician to locate and repair it.
- 5. Clean Condenser Coils: Over time, the condenser coils can accumulate dirt, debris, and other contaminants, reducing their ability to dissipate heat effectively. Clean the coils using a soft brush or hose to remove any buildup and improve cooling performance.
- 6. Listen for Unusual Noises: Strange noises coming from the compressor, such as grinding, buzzing, or squealing sounds, could indicate mechanical problems. In such cases, it is best to consult with a trained technician to diagnose and address the issue.
- 7. Inspect Electrical Connections: Check for loose or damaged electrical connections leading to the compressor. Tighten any loose connections and replace any faulty wiring to ensure the proper flow of electricity.
- 8. Monitor Cooling Performance: Observe the cooling performance of the AC system. If the air is not sufficiently cool or if there are noticeable temperature variations, it could indicate a compressor problem that needs further investigation.
While these troubleshooting tips can help you identify and address some common AC compressor issues, it’s important to note that complex problems may require professional assistance. HVAC technicians have the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair compressor problems effectively.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to preventing many compressor issues. Schedule annual maintenance checks with a qualified technician to ensure your AC system is clean, properly lubricated, and functioning optimally. This will help extend the lifespan of your compressor and maintain the efficiency of your air conditioning system.
Now that we have explored troubleshooting tips, let’s move on to discussing some maintenance practices to keep your AC compressor in optimal condition.
Maintenance Tips for AC Compressors
Maintaining your AC compressor is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your AC compressor running smoothly and avoid potential issues:
- 1. Regularly Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty or clogged air filters restrict airflow, forcing the compressor to work harder. Clean or replace the filters every one to three months, depending on usage, to maintain proper airflow and improve energy efficiency.
- 2. Keep the Surrounding Area Clean: Clear any debris, leaves, or other obstructions around the outdoor unit. Ensure that the area is free from dirt and foliage, allowing adequate airflow to the condenser coil and preventing overheating.
- 3. Clean the Condenser Coil: Over time, the condenser coil can accumulate dirt and debris, reducing its efficiency. Use a soft brush or hose to gently clean the coil and remove any buildup. Regular cleaning improves heat transfer and helps maintain efficient cooling.
- 4. Inspect and Clean the Fan: Check the fan blades for any dirt, dust, or damage. Clean the blades and ensure they are balanced. Lubricate the fan motor if necessary, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- 5. Monitor Refrigerant Levels: Have a professional technician check the refrigerant levels regularly. Improper refrigerant levels can lead to compressor inefficiency and cooling problems. If the refrigerant level is low, it may indicate a leak that needs to be addressed.
- 6. Check and Tighten Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect electrical connections leading to the compressor for any loose or damaged wires. Tighten any loose connections and replace any faulty wiring to ensure a consistent power supply.
- 7. Schedule Professional Maintenance: Arrange annual maintenance visits with a qualified HVAC technician. They will inspect and service the entire AC system, including the compressor, to detect and prevent any potential issues.
- 8. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations, including lubrication procedures, filter replacement intervals, and any other guidelines relevant to your AC system.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the lifespan of your AC compressor and maintain its efficiency. Regular maintenance not only helps prevent major issues but also improves energy efficiency, saves money on utility bills, and ensures a comfortable indoor environment throughout the year.
Remember, if you encounter any significant problems or suspect a malfunctioning compressor, it’s best to contact a professional HVAC technician for assistance. They have the knowledge and expertise to handle complex compressor issues and perform any necessary repairs or replacements.
Now that we have covered maintenance tips for AC compressors, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
An AC compressor is a vital component of any air conditioning system, responsible for compressing refrigerant gas to cool the air. Understanding how an AC compressor works, its components, and the various types is essential for maintaining the efficiency and functionality of your AC system.
Common issues with AC compressors, such as overheating, refrigerant leaks, and mechanical failures, can impact cooling performance and require timely troubleshooting. Regular maintenance practices, including cleaning or replacing air filters, cleaning condenser coils, and scheduling professional inspections, are crucial for preventing problems and ensuring optimal compressor performance.
By following maintenance tips and troubleshooting issues promptly, you can extend the lifespan of your AC compressor and maintain a comfortable indoor environment. However, it’s important to seek professional assistance for complex compressor problems or when in doubt about any maintenance or repair tasks.
Remember, your AC compressor relies on a network of components working together, and regular maintenance is key to keeping it running smoothly. By taking care of your AC compressor, you can enjoy reliable cooling and a comfortable atmosphere in your home or office.
Now that you are equipped with knowledge about AC compressors, their functionality, common issues, troubleshooting tips, and maintenance practices, you are better prepared to handle any potential compressor-related problems that may arise. Stay proactive in your maintenance efforts, and your AC system will continue to keep you cool and comfortable for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An AC Compressor
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Is An AC Compressor”