

Articles
What Is A RTU HVAC System
Modified: August 27, 2024
Curious about RTU in HVAC? Read our articles to learn more about this essential component in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, there are various components that work together to ensure optimal indoor comfort. One essential component is the rooftop unit (RTU). In this article, we will explore what a RTU is and its role in HVAC systems.
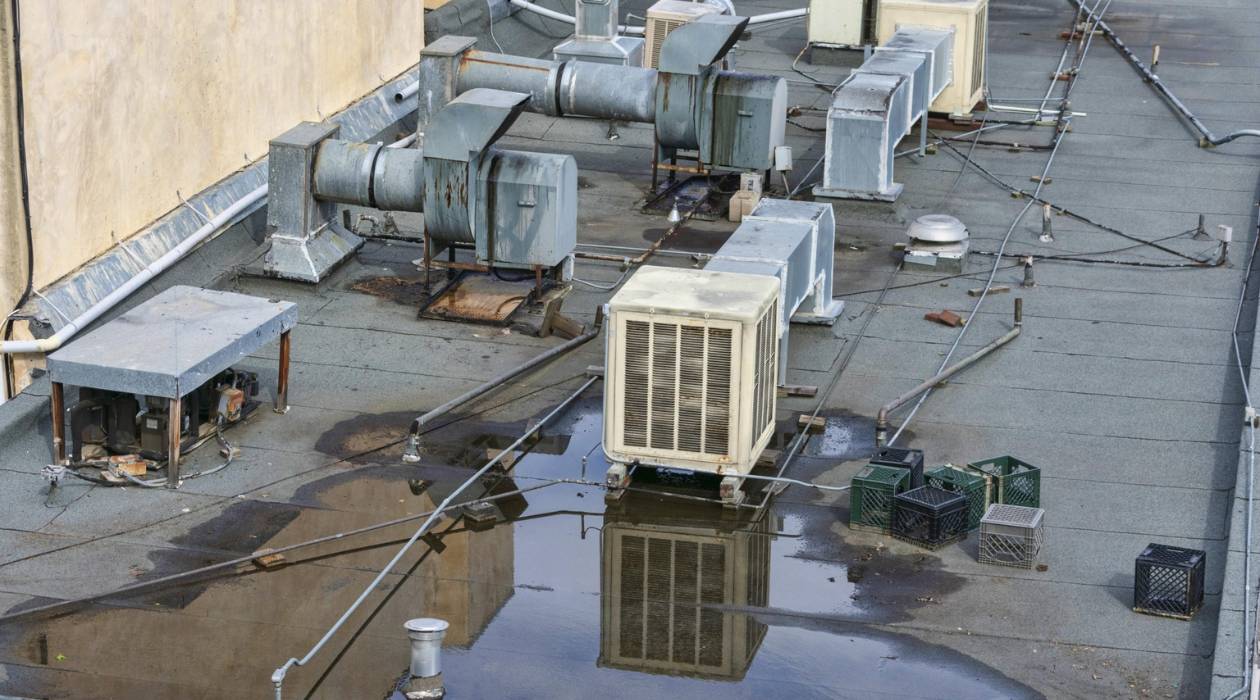
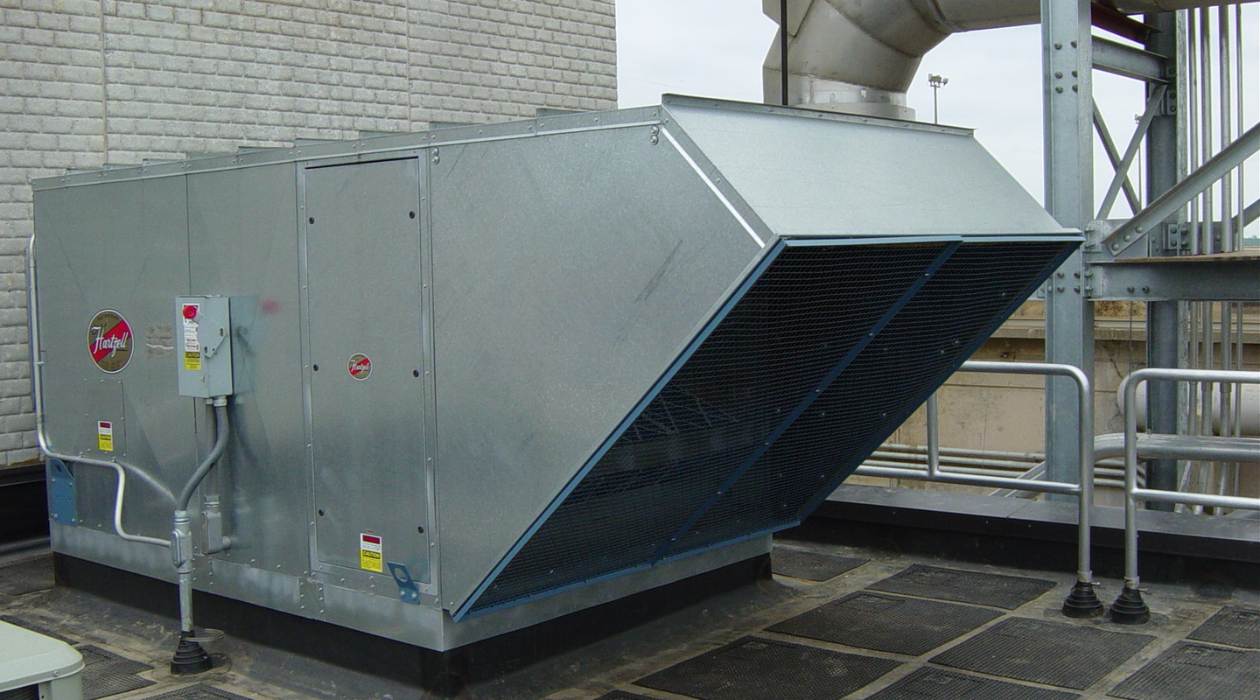
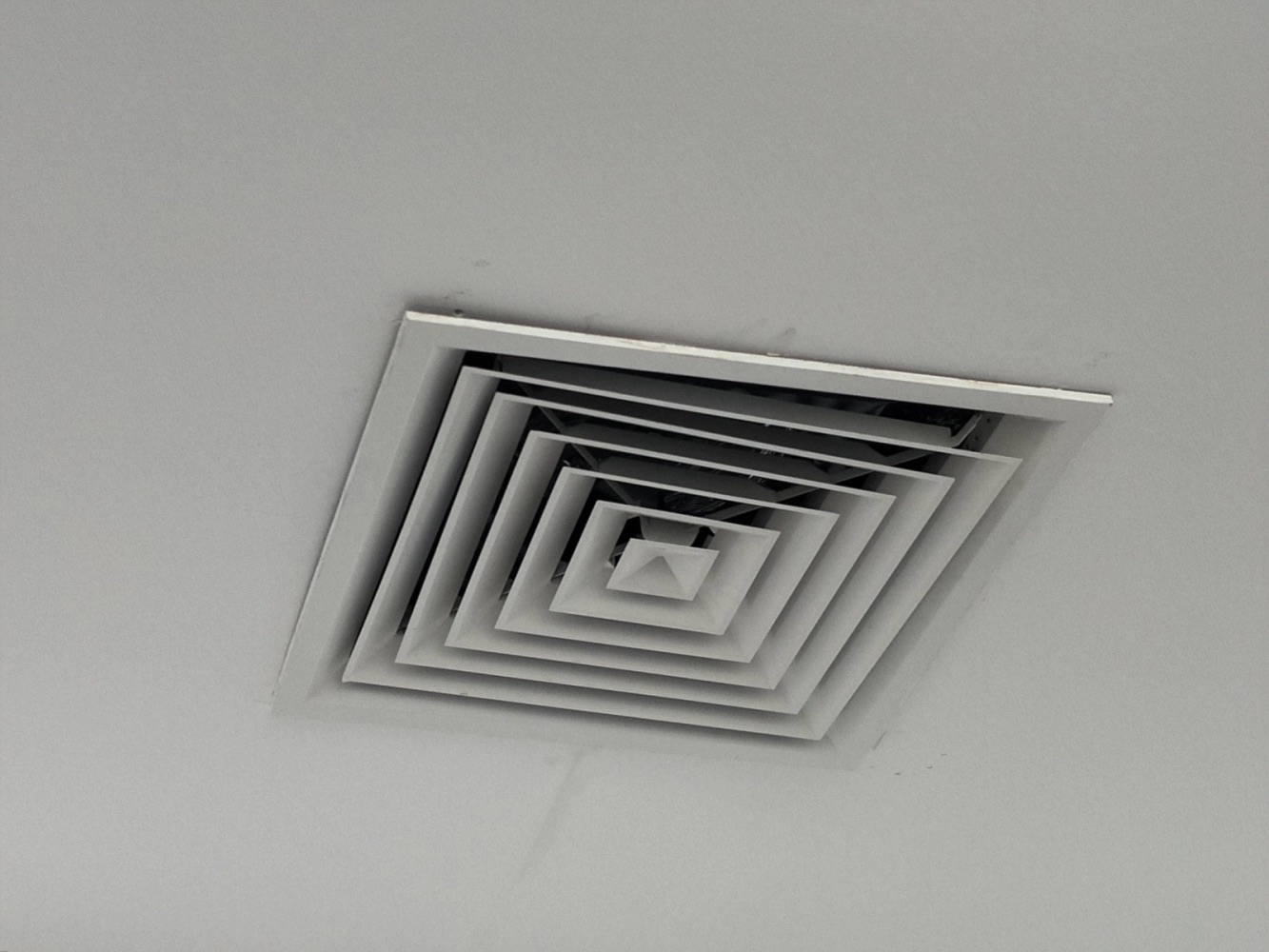
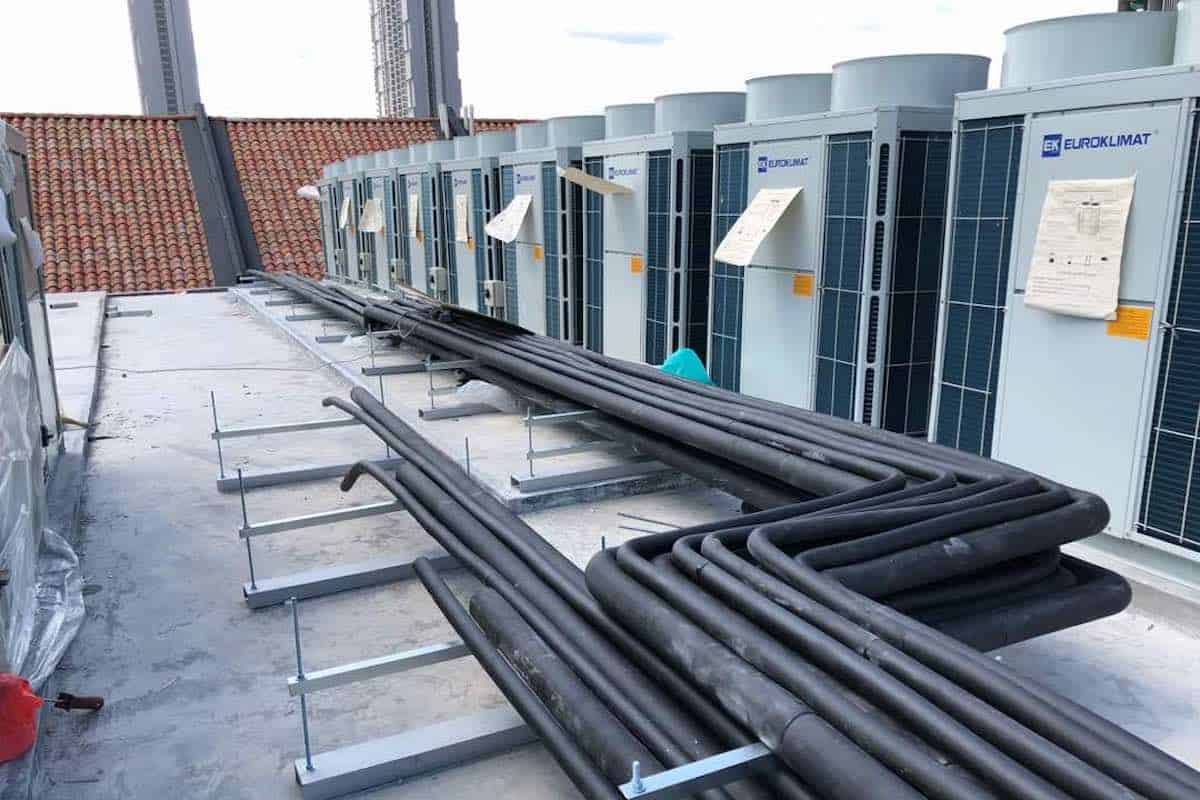
A rooftop unit, commonly referred to as an RTU, is a self-contained HVAC system that is installed on the roof of a building. It is designed to deliver heating and cooling to a specific area or zone within the building. RTUs are commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, where they offer several advantages in terms of efficiency, space utilization, and ease of maintenance.
Key Takeaways:
- RTUs are self-contained HVAC systems installed on building rooftops, offering space efficiency, easy installation, and flexibility in zoning for efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation in commercial and industrial settings.
- Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for optimizing RTU performance, preventing breakdowns, and extending lifespan. Despite some disadvantages, RTUs provide reliable HVAC solutions with energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Read more: What Is Saturation In HVAC
Definition of RTU
A rooftop unit (RTU) is a standalone HVAC system that is mounted on the roof of a building. It is a self-contained unit that includes all the necessary components for heating, cooling, and ventilation. The RTU is designed to provide conditioned air to a specific area or zone within the building, such as an office space, retail store, or restaurant.
The key feature of an RTU is its ability to function independently without the need for extensive ductwork or a central HVAC system. This makes it a popular choice for buildings where space constraints or architectural limitations prevent the installation of a traditional HVAC system.
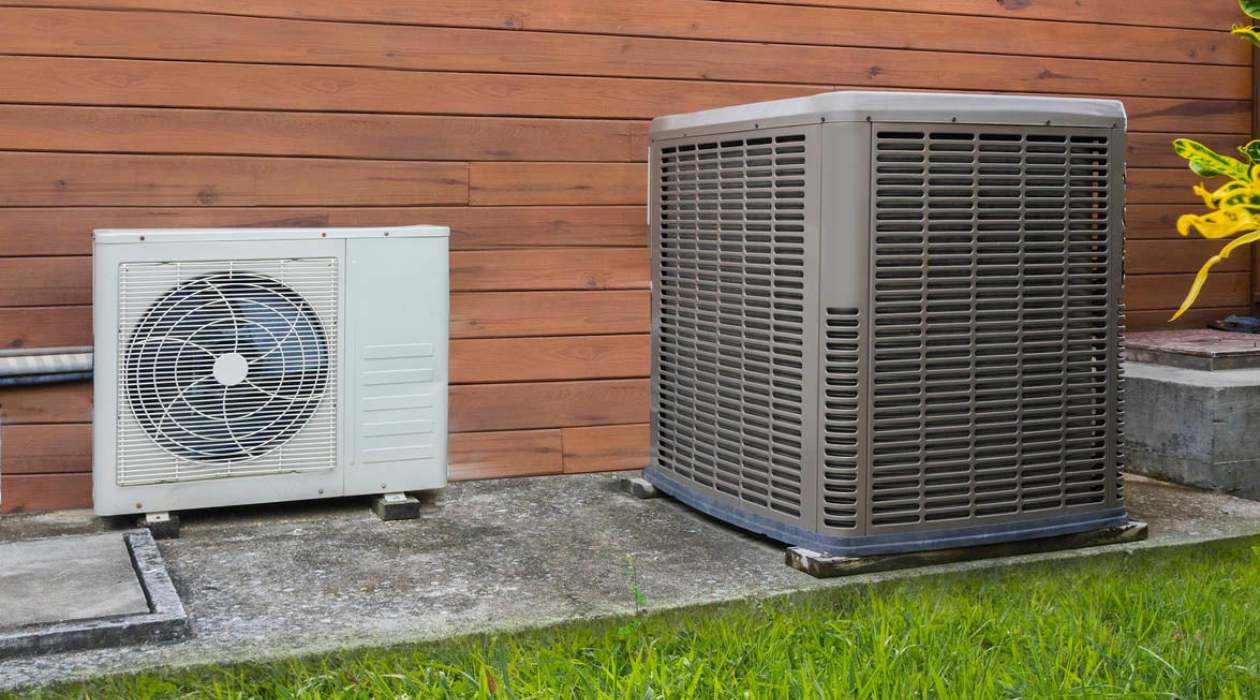
RTUs come in various sizes, ranging from small units that can cool a single room to larger units that can handle the climate control needs of an entire building. They are available in both packaged and split system configurations. In a packaged RTU, all the components are housed in a single unit, while in a split system RTU, the condenser and compressor are located outside, separate from the air-handling unit.
These units are typically powered by electricity, but they can also be fueled by natural gas, propane, or oil, depending on the specific requirements of the building. They are equipped with controls that allow for precise temperature and humidity control, ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. Additionally, most RTUs are designed to be compatible with building automation systems, enabling centralized control and monitoring of multiple units.
Components of an RTU
An RTU comprises several key components that work together to provide efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation. Understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are the main components found in an RTU:
- Compressor: The compressor is responsible for circulating the refrigerant throughout the system. It compresses the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant and raises its temperature and pressure, allowing it to release heat.
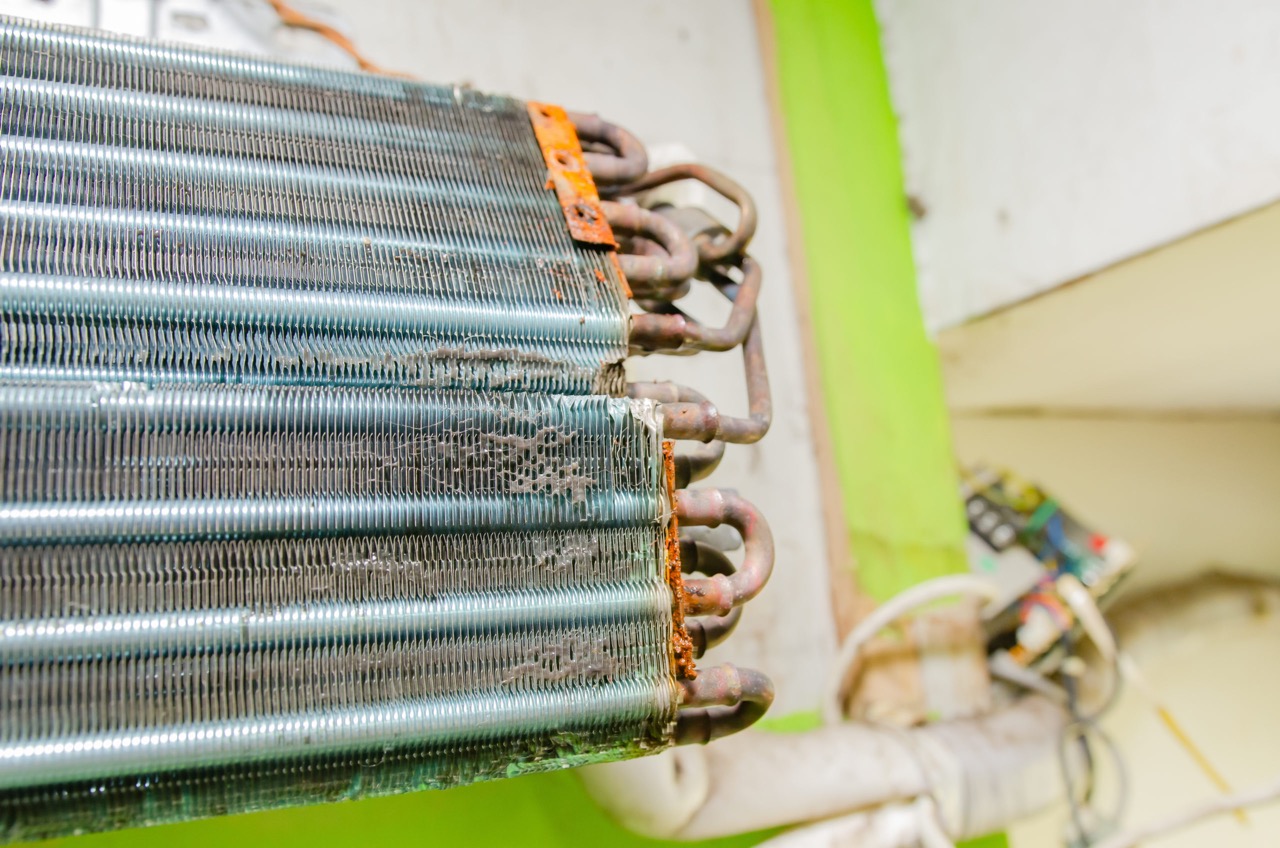
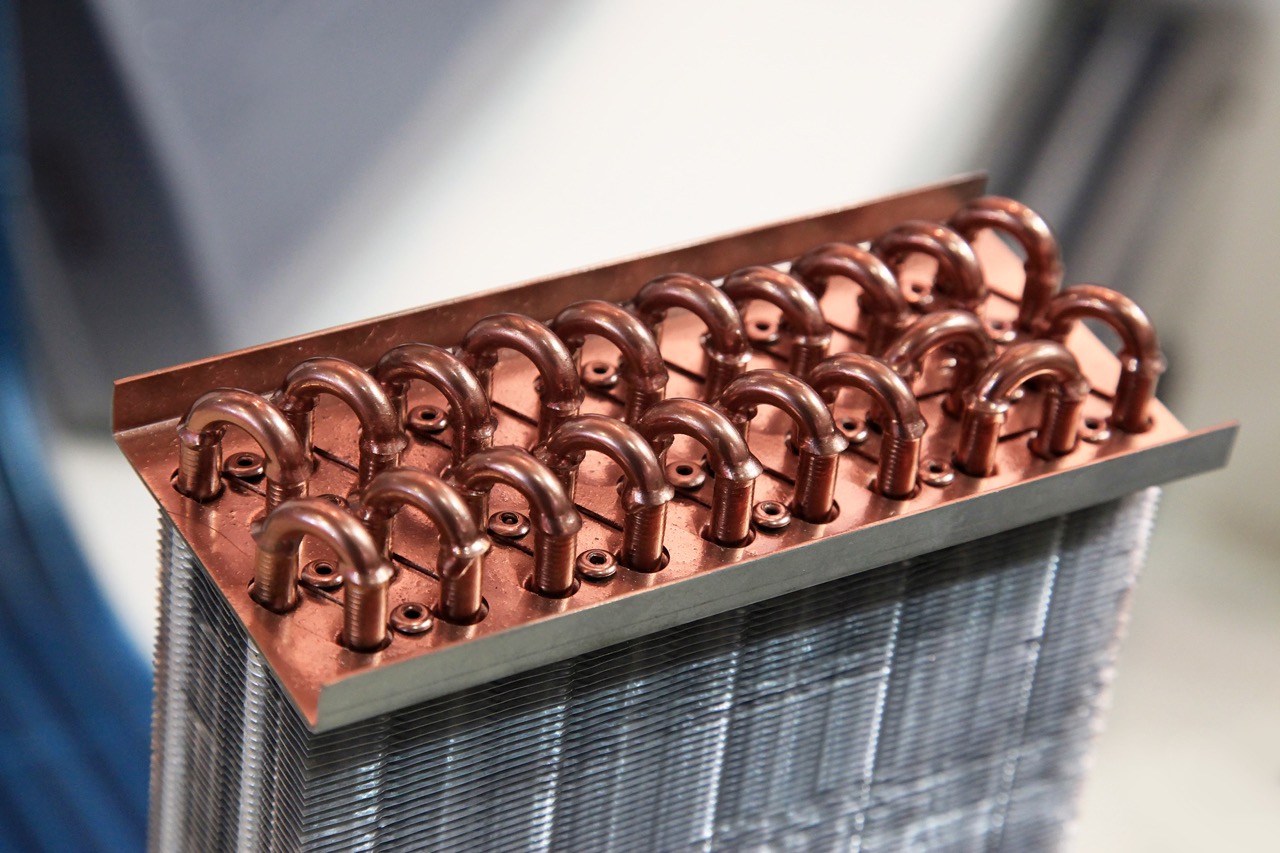
- Condenser: The condenser is where the high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant releases heat to the outdoor air. It cools down the refrigerant, causing it to change from a gas to a liquid state.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is located indoors and absorbs heat from the air. It facilitates the heat exchange process, where the refrigerant evaporates, absorbing heat from the surrounding air and cooling it down.
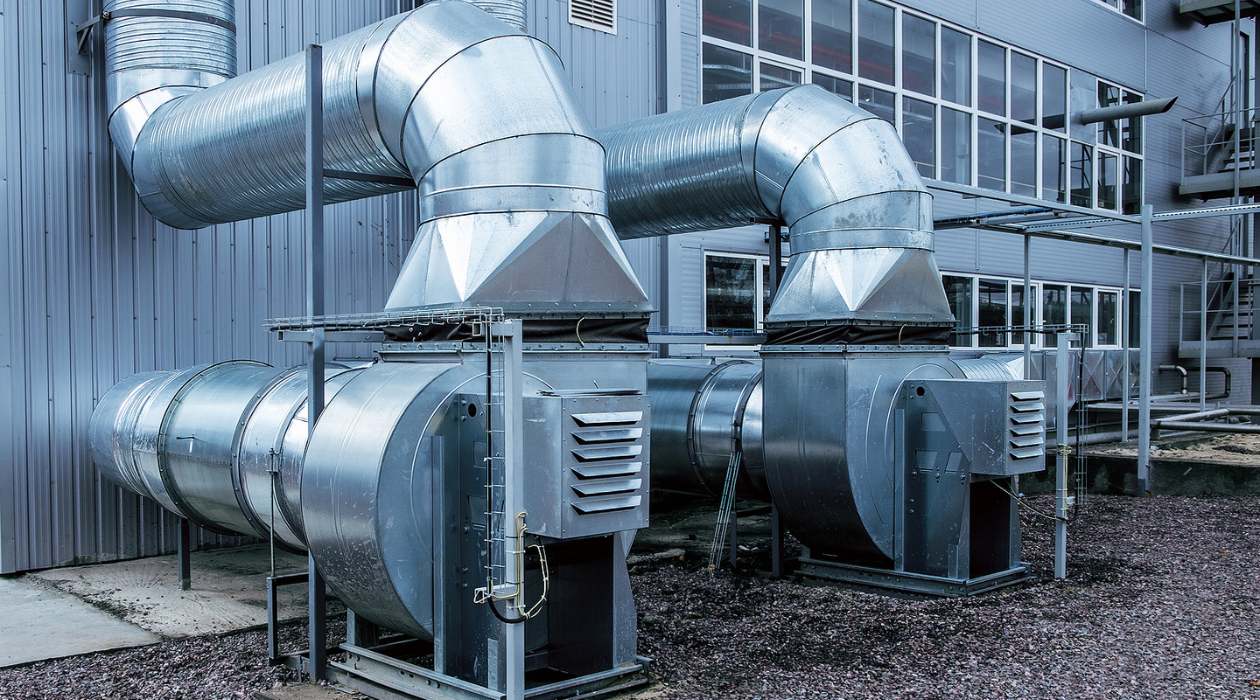
- Air Handling Unit: The air handling unit (AHU) is responsible for circulating the conditioned air throughout the building. It consists of a blower fan that draws in air from the space, passes it over the evaporator coil to cool or heat it, and then distributes it through the supply vents.
- Filters: Filters are used to remove dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air before it is circulated throughout the building. They help maintain good indoor air quality and protect the HVAC system from dirt accumulation.
- Ductwork: Ductwork is the system of ducts that distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. It ensures efficient airflow and directs the air to different areas or rooms as needed.
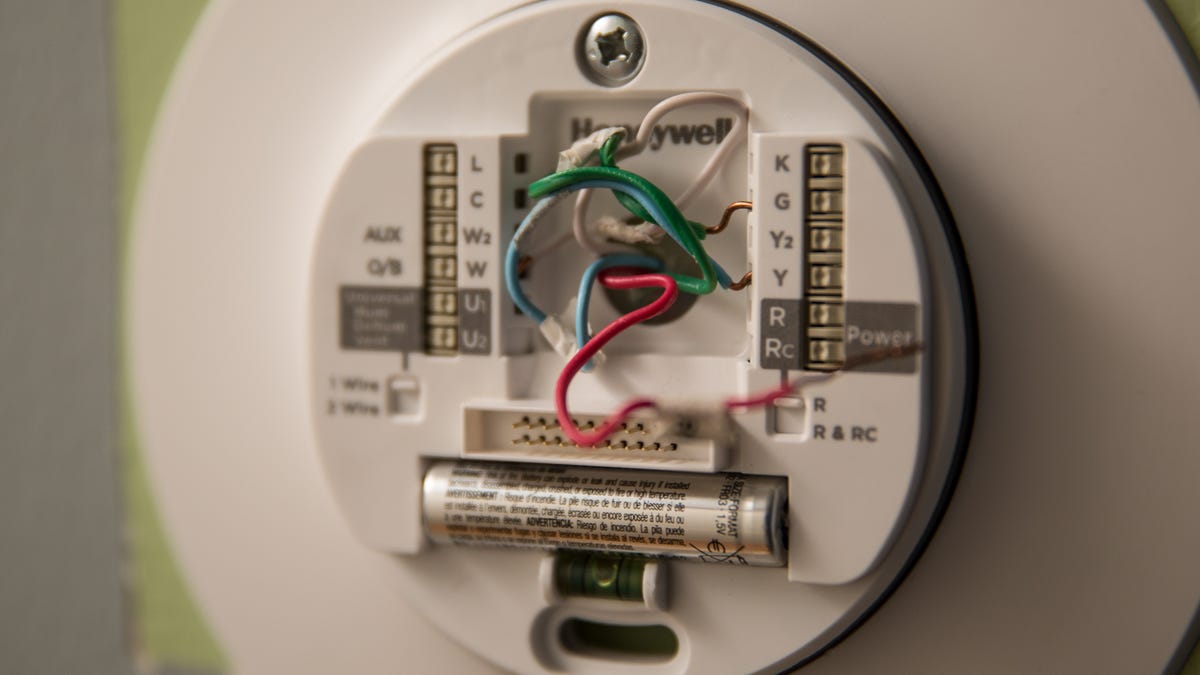
- Thermostat: The thermostat is the control device that allows users to adjust the temperature and settings of the RTU. It senses the temperature in the space and signals the RTU to turn on or off to maintain the desired temperature.
- Exhaust Fan: In addition to providing conditioned air, some RTUs are equipped with exhaust fans to remove stale air, odors, and pollutants from the space.
- Electrical Panel: The electrical panel houses the electrical connections, circuit breakers, and controls for the RTU. It ensures the safe operation of the unit and allows for easy access during maintenance or repairs.
These components work together harmoniously to deliver efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation to the building. Regular maintenance, including cleaning filters, inspecting ductwork, and ensuring proper functioning of all components, is essential to keep the RTU operating at optimal efficiency.
How RTUs work
Rooftop units (RTUs) are designed to provide heating, cooling, and ventilation to a specific area or zone within a building. Understanding how RTUs work can help in optimizing their performance and ensuring efficient operation. Here’s a breakdown of how RTUs work:
- Cooling Mode: In cooling mode, the RTU collects warm air from the space through the return air duct. This warm air passes through the filters to remove any impurities. The air then flows over the evaporator coil, which contains cold refrigerant. As the air passes over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air, cooling it down. The cooled air is then circulated back into the space through the supply vents, while the heated refrigerant goes to the condenser unit located outside. In the condenser, the heat is released to the outdoor air, and the refrigerant returns to its liquid state, ready to repeat the cooling cycle.
- Heating Mode: In heating mode, the RTU collects cool air from the space and circulates it through the return air duct. This air passes through the filters to remove any pollutants. The air then flows over the heating elements, which can be electric coils or a gas burner, depending on the RTU’s fuel source. The heating elements warm up the air, and the warm air is then distributed back into the space through the supply vents. Meanwhile, exhaust gases produced by the combustion process are safely vented outside the building.
- Ventilation: In addition to cooling and heating, RTUs also provide ventilation. They have provisions to introduce fresh outdoor air into the space, ensuring proper air exchange and maintaining good indoor air quality. Ventilation can be achieved through an integrated fresh air damper that allows a controlled amount of outdoor air to mix with the conditioned air. Some RTUs also have exhaust fans to remove stale air and maintain a balanced airflow.
- Controls and Thermostat: The operation of the RTU is controlled by a thermostat located within the building. The thermostat monitors the temperature in the space and sends a signal to the RTU to turn on or off to maintain the desired temperature. The control system also allows for programming and scheduling of temperature settings to optimize energy efficiency.
RTUs are designed to be efficient and reliable HVAC systems. They are typically self-contained units that are easy to install and maintain. Regular maintenance, including filter cleaning/replacement, coil cleaning, and inspections, is essential to ensure proper operation and prevent any issues that could affect performance.
Advantages of using RTUs in HVAC systems
Rooftop units (RTUs) offer several advantages when it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These advantages make RTUs a popular choice for commercial and industrial buildings. Here are some of the key advantages of using RTUs:
- Space Efficiency: RTUs are designed to be compact and self-contained, allowing for efficient use of space. By being installed on the roof, they free up valuable indoor space that would have been occupied by traditional HVAC systems. This is especially beneficial in buildings with limited space or when retrofitting older structures.
- Easy Installation: RTUs are relatively easy to install compared to other HVAC systems. They are typically pre-assembled and factory-tested, reducing the installation time and labor costs. Since they are self-contained units, there is no need for extensive ductwork or complicated infrastructure, making them a cost-effective and time-efficient option.
- Flexibility: RTUs offer flexibility in terms of zoning and control. They can be configured to provide heating, cooling, and ventilation to specific areas or zones within a building. This allows for precise temperature control and energy management. Additionally, RTUs are often compatible with building automation systems, enabling centralized control and monitoring of multiple units.
- Energy Efficiency: RTUs are designed to be energy-efficient. They are equipped with advanced controls, such as programmable thermostats and variable speed fans, to optimize energy consumption. Additionally, some models offer energy recovery systems, which allow for the transfer of heat or coolness between outgoing and incoming air streams, further improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs.
- Maintenance and Accessibility: RTUs are designed for easy maintenance and accessibility. Most components, such as filters and coils, are easily accessible, making regular servicing and cleaning simpler. The location on the roof also allows for easy access during inspections and repairs without disrupting the building’s occupants.
- Cost-Effective: Due to their ease of installation, space efficiency, and energy efficiency, RTUs can result in cost savings. They require less upfront investment compared to complex HVAC systems, and their energy-efficient operation can lead to reduced energy bills over time. Additionally, the simplicity of maintenance and repairs means lower maintenance costs.
RTUs offer practical solutions for HVAC needs in various commercial and industrial settings. Their space efficiency, ease of installation, flexibility, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive choice for building owners and facility managers.
When selecting a RTU (packaged rooftop unit) for HVAC, consider factors such as the unit’s size, energy efficiency, and compatibility with your building’s layout and needs. Regular maintenance is also crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Read more: What Is A Condenser In HVAC
Disadvantages of using RTUs in HVAC systems
While rooftop units (RTUs) offer several advantages for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, they also have certain disadvantages to consider. Understanding these disadvantages can help in making informed decisions when choosing an HVAC system. Here are some of the main disadvantages of using RTUs:
- Limited Capacity: RTUs have a limited capacity compared to larger central HVAC systems. This means they may not be suitable for large or complex buildings with extensive cooling or heating needs. In such cases, multiple RTUs may be required, which can increase equipment and installation costs.
- Maintenance Challenges: While RTUs are designed for easy maintenance, their location on the roof can present challenges. Servicing rooftop units may require specialized equipment and safety precautions. Additionally, ongoing maintenance tasks, such as filter replacements and coil cleaning, can be more difficult and time-consuming compared to indoor systems.
- Noise and Vibration: RTUs can generate noise and vibrations that may be disruptive, especially if the unit is located near occupied spaces. Although efforts are made to minimize noise levels, it is important to consider the potential impact, particularly in settings that require quiet environments like offices or hospitals.
- Aesthetics: The installation of RTUs on the roof can impact the visual aesthetics of a building. Some may find the presence of rooftop units unsightly, especially in architectural designs where the rooftop is visible from ground level. Proper planning and architectural considerations can mitigate this issue, but it is an aspect to be aware of.
- Weather Exposure: RTUs installed on the roof are exposed to various weather conditions, including extreme temperatures, rain, and snow. This exposure can lead to increased wear and tear on the unit over time, requiring more frequent maintenance and potential repairs.
- Energy Loss: In certain climates, RTUs may experience energy loss due to the exposure of ductwork and uninsulated parts on the roof. This can lead to heat gain or heat loss, reducing the overall efficiency of the system. Proper insulation and regular inspections can help mitigate this issue.
Despite these disadvantages, RTUs continue to be a practical choice for many buildings, particularly in commercial and industrial settings. Evaluating the specific needs and constraints of a project is essential in determining whether RTUs are the best HVAC solution.
Common Applications of RTUs in HVAC
Rooftop units (RTUs) are widely used in various applications, offering reliable heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) solutions for different settings. Here are some of the common applications where RTUs are utilized:
- Commercial Buildings: RTUs are commonly employed in commercial buildings such as office complexes, retail stores, restaurants, and small to medium-sized businesses. They provide efficient climate control for individual spaces or zones within the building, making them ideal for multi-tenant buildings where different areas may have varying HVAC requirements.
- Industrial Facilities: Many industrial facilities, such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution centers, benefit from the use of RTUs. These units offer flexibility in addressing the unique cooling, heating, and ventilation needs of large spaces, ensuring a comfortable working environment for employees and optimal performance of machinery and equipment.
- Education Institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities often rely on RTUs for HVAC needs. RTUs provide effective temperature control, ventilation, and comfort in classrooms, administrative areas, and other educational spaces. With the ability to provide zoned control, RTUs allow for individualized comfort settings in different areas of educational buildings.
- Healthcare Facilities: RTUs play a vital role in healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and medical offices. The units offer precise temperature control, ventilation, and humidity management, ensuring optimal patient comfort and maintaining sterile conditions. RTUs can be designed to accommodate specialized requirements, such as air purification and isolation room controls.
- Hospitals: Hospitals also benefit from the use of RTUs in non-medical areas, such as administrative offices, waiting rooms, and cafeterias. These units provide efficient and cost-effective HVAC solutions, ensuring a comfortable environment for staff, patients, and visitors.
- Retail and Hospitality: RTUs are widely utilized in the retail and hospitality industries, including shopping malls, hotels, restaurants, and entertainment complexes. RTUs offer the ability to maintain consistent temperatures and efficient climate control, creating a comfortable and inviting atmosphere for customers and guests.
- Multi-Residential Buildings: RTUs are often chosen for HVAC systems in apartment buildings, condominiums, and other multi-residential properties. The units can provide individual control over each dwelling unit, allowing residents to adjust the temperature according to their preferences and ensuring energy efficiency.
Thanks to their versatility, efficiency, and ease of installation, RTUs are a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s a commercial office space, a healthcare facility, an educational institution, or a retail establishment, RTUs offer reliable and effective HVAC solutions to meet specific requirements and provide optimal indoor comfort.
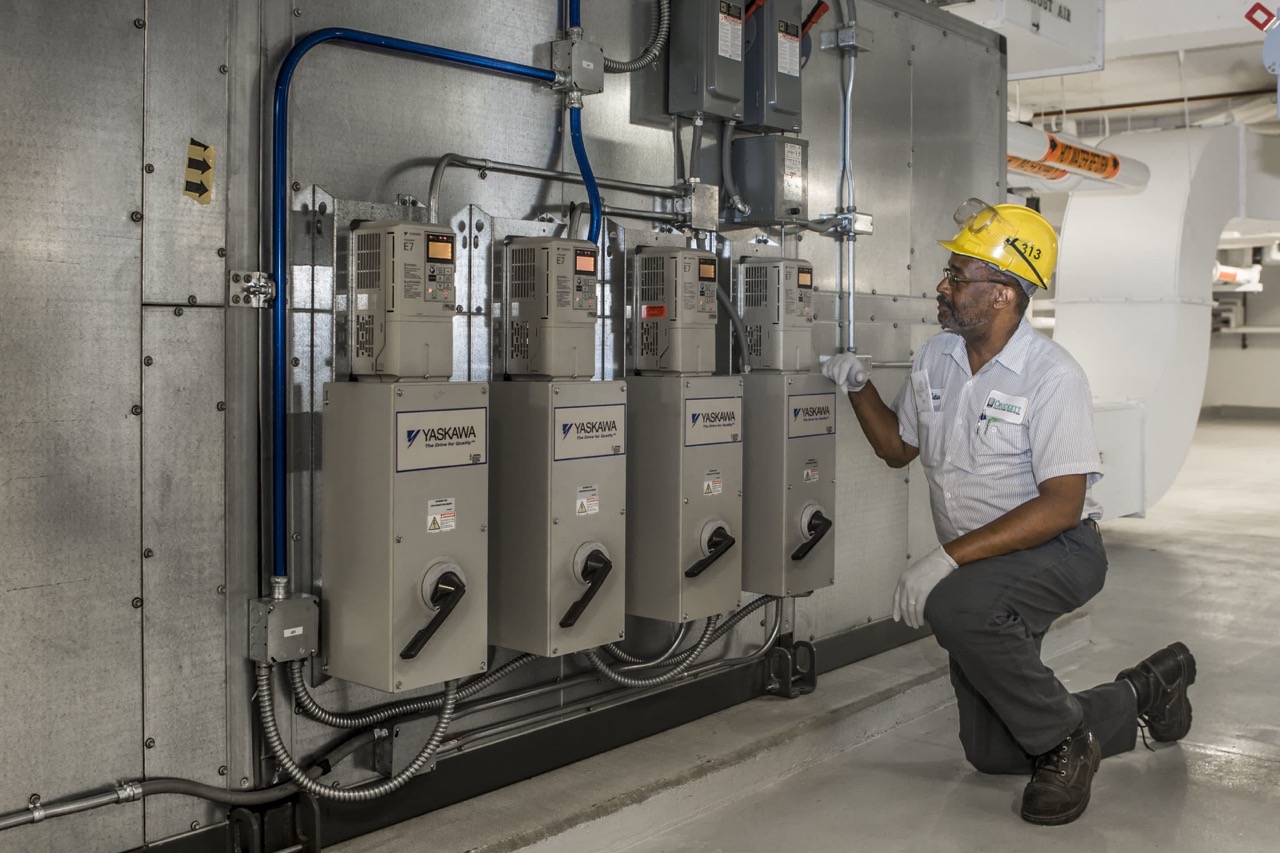
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of RTUs
Maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of rooftop units (RTUs) in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Regular maintenance helps to optimize energy efficiency, prevent breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of the unit. Here are some key maintenance tasks and troubleshooting tips for RTUs:
- Regular Filter Cleaning/Replacement: Clogged or dirty filters restrict airflow and reduce the efficiency of the unit. It is important to clean or replace the filters regularly, typically every 1-3 months, depending on usage and indoor air quality.
- Inspect and Clean Coils: The condenser and evaporator coils should be inspected and cleaned annually. Dirty coils reduce heat transfer efficiency and can lead to increased energy consumption. Care should be taken to use appropriate cleaning agents and techniques to avoid coil damage.
- Check and Clean Condensate Drain: The condensate drain should be inspected regularly to ensure it is clear of any obstructions. A clogged drain can cause water leakage, leading to potential water damage or mold growth. Additionally, check the drain pan for any signs of corrosion or damage.
- Inspect Belts, Bearings, and Motors: Inspect and tighten belts, check for proper alignment, and lubricate bearings as necessary. Also, monitor motor performance, looking for any unusual noises, vibrations, or overheating. Promptly address any issues to prevent further damage or motor failure.
- Inspect Fan Blades and Blower: Regularly inspect fan blades for damage, buildup of dirt or debris, and balance. Clean fan blades and blower assembly to maintain proper airflow. Unbalanced fans can cause excessive vibrations and noise.
- Verify Thermostat and Controls: Check the thermostat settings and calibration to ensure accurate temperature control. Test all control functions, including programming and scheduling, to ensure proper operation. Replace batteries in battery-powered thermostats as needed.
- Inspect and Seal Ductwork: Inspect ductwork for leaks, loose connections, or damaged insulation. Properly seal any leaks to prevent air loss and reduce energy waste. Consider having the ductwork professionally cleaned periodically to remove accumulated dirt and debris.
- Monitor Energy Consumption: Regularly monitor energy consumption trends to identify any spikes or abnormalities in energy usage. Sudden increases in energy consumption may indicate a problem with the RTU, such as a malfunctioning component or inefficient operation.
- Document and Keep Records: Maintain a maintenance log to document all maintenance tasks, repairs, and inspections performed on the RTUs. This log can help track the system’s performance over time and provide a reference for future maintenance requirements.
Troubleshooting RTUs involves identifying and addressing common issues that may arise. It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and seek professional assistance if needed. Some common troubleshooting steps include checking power supply, inspecting control settings, cleaning filters, and verifying the integrity of components.
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are vital for maintaining the performance and efficiency of RTUs. By following these maintenance tasks and troubleshooting tips, building owners and facility managers can ensure uninterrupted operation and prolong the lifespan of their RTUs.
Conclusion
Rooftop units (RTUs) play a significant role in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, offering efficient and reliable solutions for a wide range of applications. The self-contained nature of RTUs, along with their space efficiency, ease of installation, and flexibility, make them a popular choice in commercial, industrial, and institutional settings.
RTUs provide heating, cooling, and ventilation to specific areas or zones within buildings, ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. They offer advantages such as space efficiency, easy installation, flexibility in zoning, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. These units are designed to be easily maintained and serviced, although their location on the roof may present challenges in terms of access.
While RTUs come with certain disadvantages, including limited capacity, maintenance challenges, and weather exposure, these can often be mitigated through proper planning, maintenance, and architectural considerations. It is essential to evaluate the specific needs and constraints of each project when deciding on the best HVAC solution.
Maintenance is vital for optimal performance and longevity of RTUs. Regular tasks such as filter cleaning/replacement, coil cleaning, inspections, and system testing should be performed to ensure energy efficiency, prevent breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of the unit. Troubleshooting common issues promptly is also crucial to maintain the uninterrupted operation of RTUs.
In conclusion, RTUs provide effective and practical HVAC solutions for various applications. Their space efficiency, ease of installation, flexibility, and energy efficiency make them a reliable choice for heating, cooling, and ventilation. By implementing regular maintenance, troubleshooting, and adhering to manufacturer guidelines, users can maximize the performance and lifespan of RTUs, ensuring optimal indoor comfort in commercial and industrial buildings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A RTU HVAC System
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A RTU HVAC System”