

Articles
What Is An Electric Motor Capacitor?
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn about the role and importance of capacitors in electric motors. Discover how capacitors enhance motor performance and efficiency. Read more in our informative articles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electric motors are essential components in various appliances and machinery, powering everything from household appliances to industrial equipment. While the basic principles of electric motors are widely understood, there are specific components that play crucial roles in their operation. One such component is the capacitor, which acts as a vital part of the motor’s starting and running processes.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of capacitors in electric motors and explore their functionalities. We will discuss the different types of motors that use capacitors and address common problems associated with capacitors in motors. By understanding the role that capacitors play in electric motors, we can gain a better appreciation for these remarkable devices.
Key Takeaways:
- Capacitors are essential for electric motor operation, providing phase shifts and power factor correction for efficient and reliable performance in both start and run processes.
- Capacitor issues, such as failure, leaking, or incorrect values, can impact motor performance. Timely troubleshooting and professional assistance are crucial for maintaining optimal motor functionality.
Read more: How To Check A Electric Motor Capacitor
Basics of Electric Motors
Before diving into the role of capacitors in electric motors, let’s briefly cover the basics of how electric motors work. Electric motors operate on the principle of electromagnetism, where the interaction between a magnetic field and an electric current produces motion. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling the movement of various mechanical components.
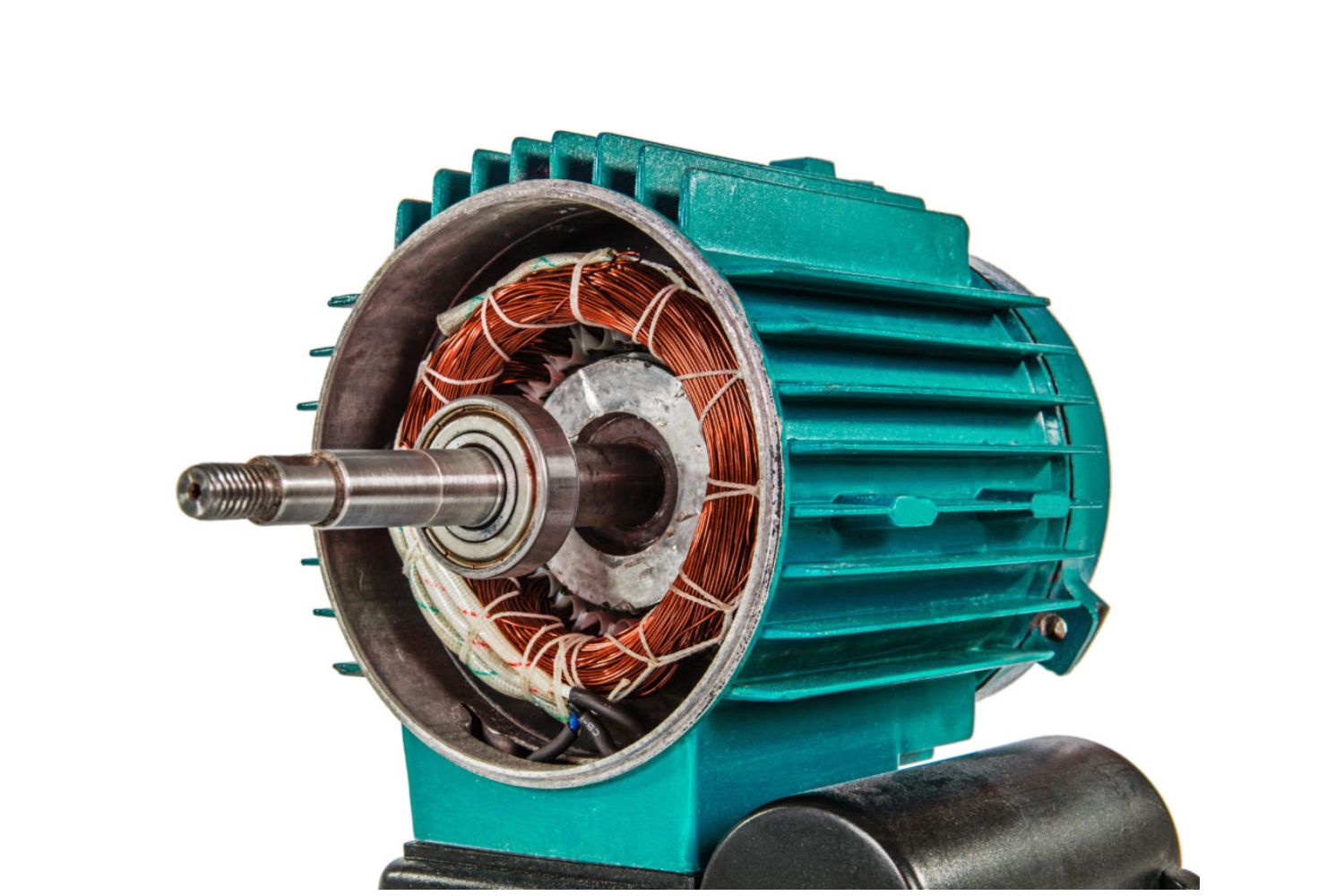
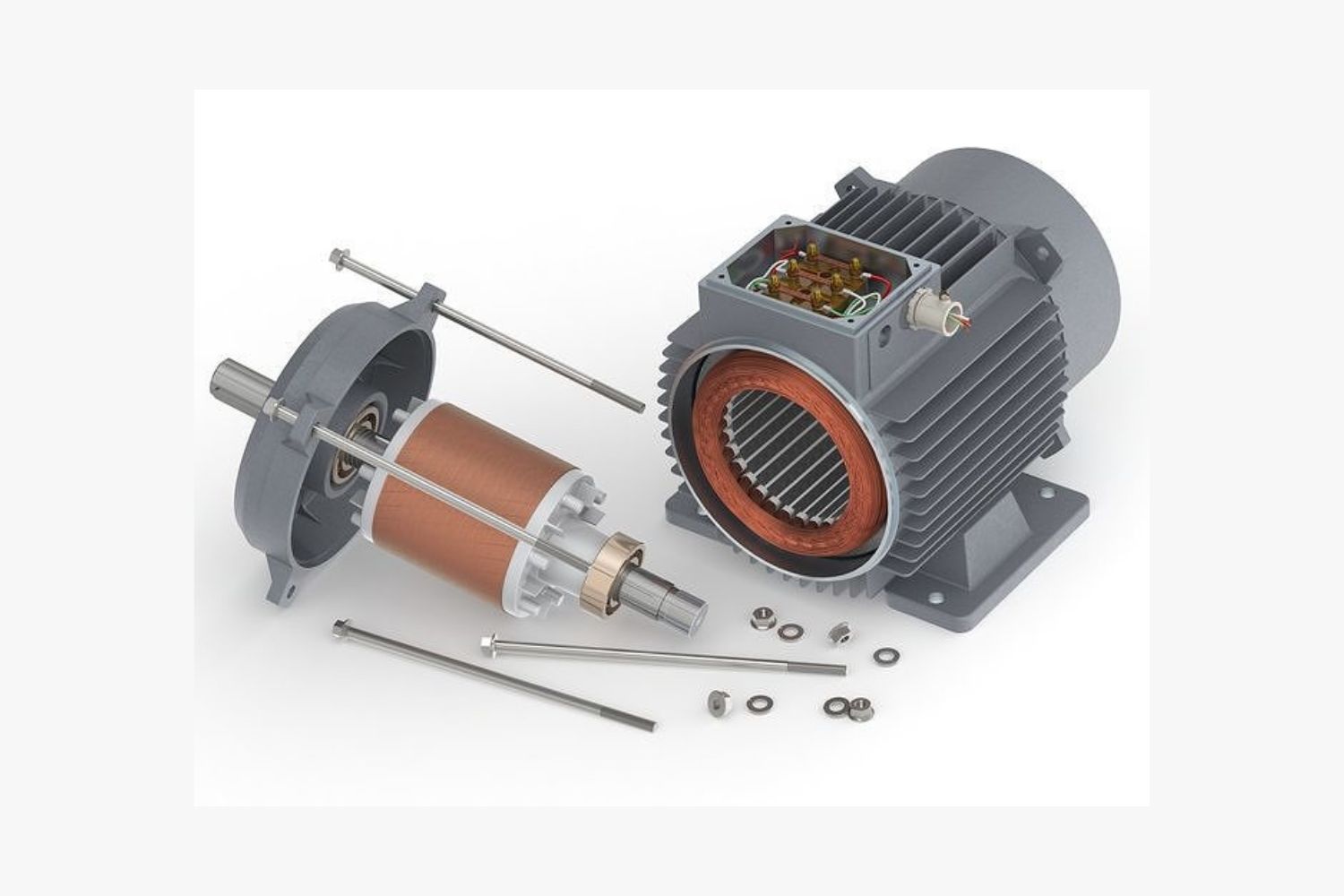
Electric motors consist of a stationary component called the stator and a rotating component called the rotor. The stator contains a series of wire windings that generate a magnetic field when an electric current passes through them. The rotor, on the other hand, is usually composed of permanent magnets or electromagnets that interact with the magnetic field generated by the stator.
When an electric current flows through the wire windings in the stator, it creates a magnetic field that induces a force on the magnets in the rotor. This force causes the rotor to rotate, resulting in the mechanical movement of the motor.
Electric motors can be categorized into two main types: AC (alternating current) motors and DC (direct current) motors. AC motors are commonly used in household appliances and industrial applications, while DC motors are often found in battery-operated devices and machinery.
Now that we have a basic understanding of electric motors, let’s explore the role that capacitors play in their operation.
Role of Capacitor in Electric Motors
Capacitors play a crucial role in electric motors, specifically in the starting and running processes. They help create the necessary phase difference between the motor’s starting winding and running winding to initiate and maintain rotational motion. The primary function of capacitors in electric motors is to improve the motor’s efficiency and performance by providing the necessary torque and power during start-up.
In single-phase AC motors, capacitors are used to create a phase shift in the electric current, which is required for starting the motor. These motors have two windings: the main winding and the auxiliary winding. The main winding generates the magnetic field that drives the rotor, while the auxiliary winding creates a phase difference using a start capacitor. This phase difference allows the motor to start rotating in the desired direction.
On the other hand, three-phase AC motors typically do not require capacitors for starting. These motors have three separate windings that are spaced equally apart, creating a rotating magnetic field. This rotating magnetic field induces the necessary torque for the motor to start without the need for capacitors.
In addition to the starting process, capacitors also play a role in improving the efficiency of running AC motors. Capacitor run motors utilize capacitors in conjunction with the main winding to optimize power factor and improve motor performance. By correcting the power factor, these motors operate more efficiently, consume less energy, and have a reduced risk of overheating.
Overall, capacitors act as essential components in electric motors by providing the necessary phase shifts for starting and enhancing the efficiency of running. Without capacitors, motors would struggle to start and may not operate at their full potential.
Capacitor Start Motors
Capacitor start motors are a type of single-phase AC motor that relies on capacitors to initiate rotational motion. These motors are commonly used in applications where high starting torque is required, such as air compressors, refrigeration equipment, and power tools.
A capacitor start motor consists of two windings: the main winding and the start winding. The main winding is responsible for generating the magnetic field that drives the rotor, while the start winding provides the necessary phase difference to initiate rotation.
During start-up, a start capacitor is connected to the start winding in series. This capacitor creates a phase shift between the current in the main winding and the current in the start winding. The phase shift results in a rotating magnetic field that induces the necessary torque for the motor to start rotating.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, a centrifugal switch disconnects the start capacitor from the circuit, allowing the motor to continue running with only the main winding. This switch prevents the start capacitor from overheating during continuous operation.
Capacitor start motors are known for their high starting torque, which makes them suitable for applications that require quick acceleration or heavy loads. The start capacitor provides the extra torque needed during start-up, improving the motor’s ability to overcome inertia and get the equipment up to speed efficiently.
However, capacitor start motors are generally less efficient than other types of motors and may have lower power factors. This is due to the additional power required to maintain the phase difference in the start winding. Despite their lower efficiency, capacitor start motors offer excellent starting performance, making them a popular choice in various industrial and commercial applications.
A capacitor on an electric motor helps to improve the motor’s starting torque and efficiency by providing a phase shift in the motor’s windings. It also helps to reduce power factor and improve the motor’s power factor correction.
Capacitor Run Motors
Capacitor run motors are another type of AC motor commonly used in a wide range of applications. Unlike capacitor start motors, capacitor run motors have a continuous running capacitor connected in parallel with the main winding. These motors are designed to enhance the efficiency and power factor of the motor during continuous operation.
The primary purpose of the capacitor in capacitor run motors is to correct the power factor. Power factor is a measure of how effectively the motor utilizes the electrical power it receives. A low power factor can result in inefficient power consumption and increased energy costs. By using a capacitor in parallel with the main winding, the power factor of the motor is improved, leading to higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Capacitor run motors are often utilized in applications where a constant and steady torque output is required, such as pumps, fans, and HVAC systems. The capacitor provides the necessary reactive power, which helps optimize the motor’s performance and maintain a steady rotational speed.
These motors are designed to operate continuously, and the capacitor run in parallel with the main winding ensures optimum power factor across various load conditions. The continuous running capacitor helps reduce power losses and minimizes the risk of overheating, resulting in improved motor reliability and longevity.
It is important to select the correct capacitor for capacitor run motors to ensure optimal motor performance. The capacitance value of the capacitor is carefully chosen to match the motor’s requirements and maintain the desired power factor. Incorrect capacitor selection can lead to inefficient motor operation, decreased performance, and even motor failure.
In summary, capacitor run motors offer improved power factor and efficiency compared to standard motors. They provide a steady torque output and are commonly used in applications that require continuous operation and a reliable motor performance. The use of capacitors in these motors helps optimize power utilization, reduces energy costs, and enhances overall motor efficiency.
Read also: 8 Best Electric Motor Capacitor for 2025
Common Capacitor Problems in Motors
While capacitors play a crucial role in the operation of electric motors, they can sometimes experience problems that can affect the motor’s performance and functionality. Here are some common capacitor problems that can occur in motors:
- Capacitor Failure: Capacitors can fail over time due to various factors such as age, overheating, voltage spikes, or manufacturing defects. When a capacitor fails, it may no longer provide the necessary capacitance value, resulting in reduced motor performance or complete motor failure.
- Capacitor Leaking: Capacitors can develop leaks, which can lead to a loss of electrolyte and reduced capacitance. Leaking capacitors may cause the motor to overheat, resulting in motor damage or premature failure.
- Capacitor Swelling: Swelling or bulging capacitors indicate internal damage or a build-up of gases, which can be caused by excessive heat or pressure. Swollen capacitors should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage to the motor.
- Wrong Capacitor Value: Incorrect capacitor values, either due to improper selection or replacement, can lead to motor inefficiency or excessive current draw. It is crucial to select and install capacitors with the correct specifications as specified by the motor manufacturer.
- Capacitor Wiring Issues: Faulty wiring connections or loose terminals can adversely affect capacitor performance. It is important to ensure that the capacitor is properly connected to the motor circuit and that all wiring connections are secure.
When faced with capacitor issues in motors, it is recommended to consult a professional technician or electrician with expertise in motor repair. They can diagnose the problem and determine whether the capacitor needs repair or replacement. Regular maintenance and inspection of capacitors can help identify potential issues early and prevent motor failures.
Overall, being aware of common capacitor problems in motors and taking proactive measures to address them can help ensure optimal motor performance and prolong the lifespan of the motor.
Troubleshooting Capacitor Issues in Motors
When experiencing capacitor problems in motors, it is essential to troubleshoot and diagnose the issue accurately to determine the appropriate course of action. Here are some troubleshooting steps to follow when dealing with capacitor issues in motors:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by inspecting the capacitor for any visible signs of damage, such as bulging, leaking, or corroded terminals. Also, check the wiring connections to ensure they are secure.
- Testing Capacitance: Use a capacitance meter or a multimeter with a capacitance function to measure the capacitance of the capacitor. Compare the measured value with the specified capacitance value indicated by the motor manufacturer. If the measured value deviates significantly from the specified value, it may indicate a faulty capacitor.
- Checking Voltage Ratings: Verify that the voltage rating of the capacitor matches or exceeds the motor’s voltage requirements. Using a capacitor with a lower voltage rating can cause premature failure or damage to the capacitor.
- Testing Resistance: Use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance of the capacitor. A low or zero resistance reading indicates a shorted capacitor, while a high resistance reading suggests an open circuit or a faulty capacitor.
- Replacing Damaged Capacitors: If visual inspection or testing reveals any signs of damage or if the capacitance or resistance values are significantly off, it is recommended to replace the capacitor with a new one that matches the specifications provided by the motor manufacturer.
- Professional Assistance: If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue or if you are unsure about the proper course of action, it is best to consult a professional technician or electrician with experience in motor repair. They can provide expert guidance and ensure the correct diagnosis and resolution of the capacitor problem.
Remember that working with electrical components can be dangerous. Always follow proper safety procedures and, if necessary, seek professional help to avoid any accidents or further damage.
By following these troubleshooting steps and addressing capacitor issues promptly, you can restore the optimal functionality of the motor and prevent any potential damage or failures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, capacitors play a vital role in the operation and performance of electric motors. Whether in capacitor start motors or capacitor run motors, these components provide the necessary phase shifts and power factor correction to ensure efficient and reliable motor operation.
Capacitor start motors are characterized by their high starting torque, making them ideal for applications that require quick acceleration or heavy loads. On the other hand, capacitor run motors excel in providing continuous torque output with improved power factor, making them suitable for applications that demand steady and efficient operation.
However, it is important to note that capacitors in motors can encounter various problems, including failure, leaking, swelling, incorrect values, and wiring issues. Timely troubleshooting and appropriate actions such as replacement or repair are crucial to maintain motor performance and prevent further damage.
By understanding the role of capacitors in electric motors and staying vigilant in identifying and addressing capacitor issues, users can optimize motor efficiency, enhance performance, and prolong the lifespan of the motor.
If you encounter persistent or complex capacitor issues in motors, it is always recommended to seek assistance from a professional technician or electrician with expertise in motor repair. Their specialized knowledge and skills can ensure accurate diagnosis and resolution of any problems.
Overall, capacitors are indispensable components in electric motors, contributing to their reliable starting, efficient operation, and overall performance. Their significance in ensuring smooth motor functionality cannot be underestimated, making it essential to give proper attention to capacitors when dealing with motor-related issues.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An Electric Motor Capacitor?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is An Electric Motor Capacitor?”