

Articles
What Is Electrical Conduit
Modified: October 28, 2024
Learn all about electrical conduit and its importance in this collection of informative articles. Discover the different types of conduit, installation tips, and more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical conduit is an essential component in any electrical system. It provides a protective pathway for electrical wiring, ensuring safety and efficiency. Understanding what electrical conduit is and its significance in electrical installations is crucial for homeowners, electricians, and anyone involved in the construction industry.
Electrical conduit, also known as electrical pipe, is a system that consists of tubing or ducts used to protect and route electrical wiring. It is typically made of metal or plastic materials and is installed either exposed or concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of electrical conduit, including its definition, types, uses, installation process, advantages and disadvantages, common materials used, and maintenance requirements.
Whether you are planning a renovation or construction project or simply want to expand your knowledge on electrical systems, this article will serve as a valuable resource.
So let’s dive in and explore the world of electrical conduit!
Key Takeaways:
- Electrical conduit is a protective pathway for wiring, safeguarding against damage and hazards. It offers flexibility, durability, and compliance with electrical codes, ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations.
- Regular maintenance and inspection of electrical conduit are essential for ongoing safety and reliability. Visual inspections, moisture protection, mechanical checks, and professional assessments contribute to a secure electrical infrastructure.
Read more: What Is An IMC Electrical Conduit
Definition of Electrical Conduit
Electrical conduit is a system of tubing or ducts that provides a protected pathway for electrical wiring. It is designed to safeguard electrical cables from damage, environmental factors, and potential hazards.
The primary purpose of electrical conduit is to contain and protect electrical wires, preventing them from being exposed to moisture, dust, chemicals, physical impact, and electromagnetic interference. It acts as a barrier, shielding the wires and reducing the risk of electrical accidents, fire, and short circuits.
Conduits come in various sizes and materials, allowing flexibility in installation and offering different levels of protection based on the specific application and environment. They can be rigid or flexible, depending on the wiring needs and the location’s requirements.
Electrical conduit is a critical component in both residential and commercial settings. In homes, it is commonly used for routing electrical wiring from the main panel to various outlets, switches, and appliances throughout the property. In industrial and commercial buildings, conduit systems are employed for extensive electrical installations, connecting different areas and accommodating power distribution needs.
By enclosing electrical wires in conduit, the risk of accidental contact, abrasion, and damage is minimized. This ensures that the electrical system remains safe, reliable, and compliant with industry regulations and electrical codes.
Overall, the definition of electrical conduit can be understood as a protective channel that houses electrical wiring, providing insulation, organization, and structural support for the electrical system. It enhances the overall performance and longevity of the wiring infrastructure, contributing to a safer and more efficient electrical installation.
Types of Electrical Conduit
There are several types of electrical conduit available, each with its own characteristics and uses. The choice of conduit depends on factors such as the application, environment, and specific requirements of the electrical installation. Here are some common types of electrical conduit:
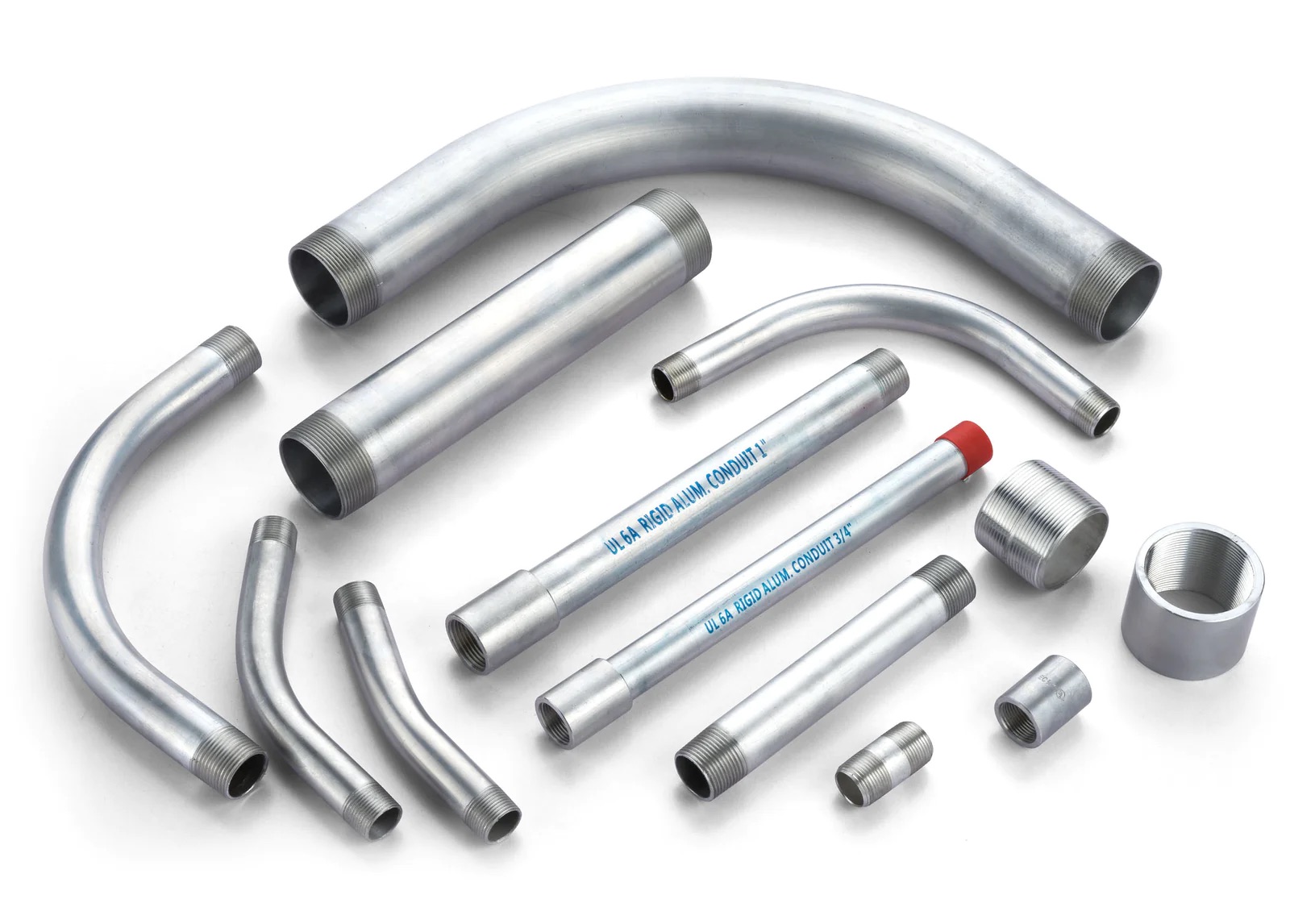
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): RMC is a heavy-duty conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is the most durable and rigid type of conduit, providing excellent protection for wiring in high-impact and corrosive environments. RMC is typically used in industrial, commercial, and outdoor applications.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is a lightweight and easy-to-install conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is commonly used in residential and commercial applications, where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are important. EMT is suitable for concealed installations and can be bent with specialized tools to accommodate complex routing.
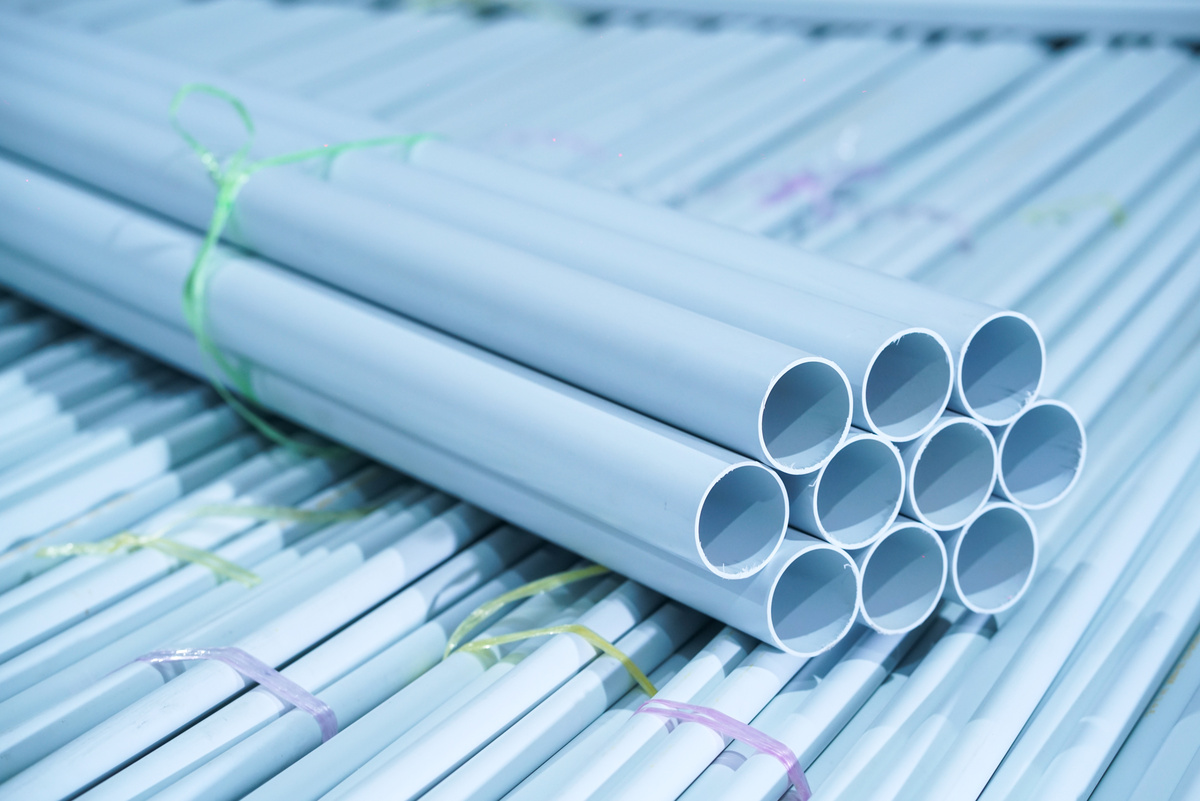
- Rigid Non-Metallic Conduit (RNC): RNC, also known as PVC conduit, is made of rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It is lightweight, affordable, and resistant to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals. RNC is often used in residential applications for underground or outdoor installations, as it provides good protection against the elements.
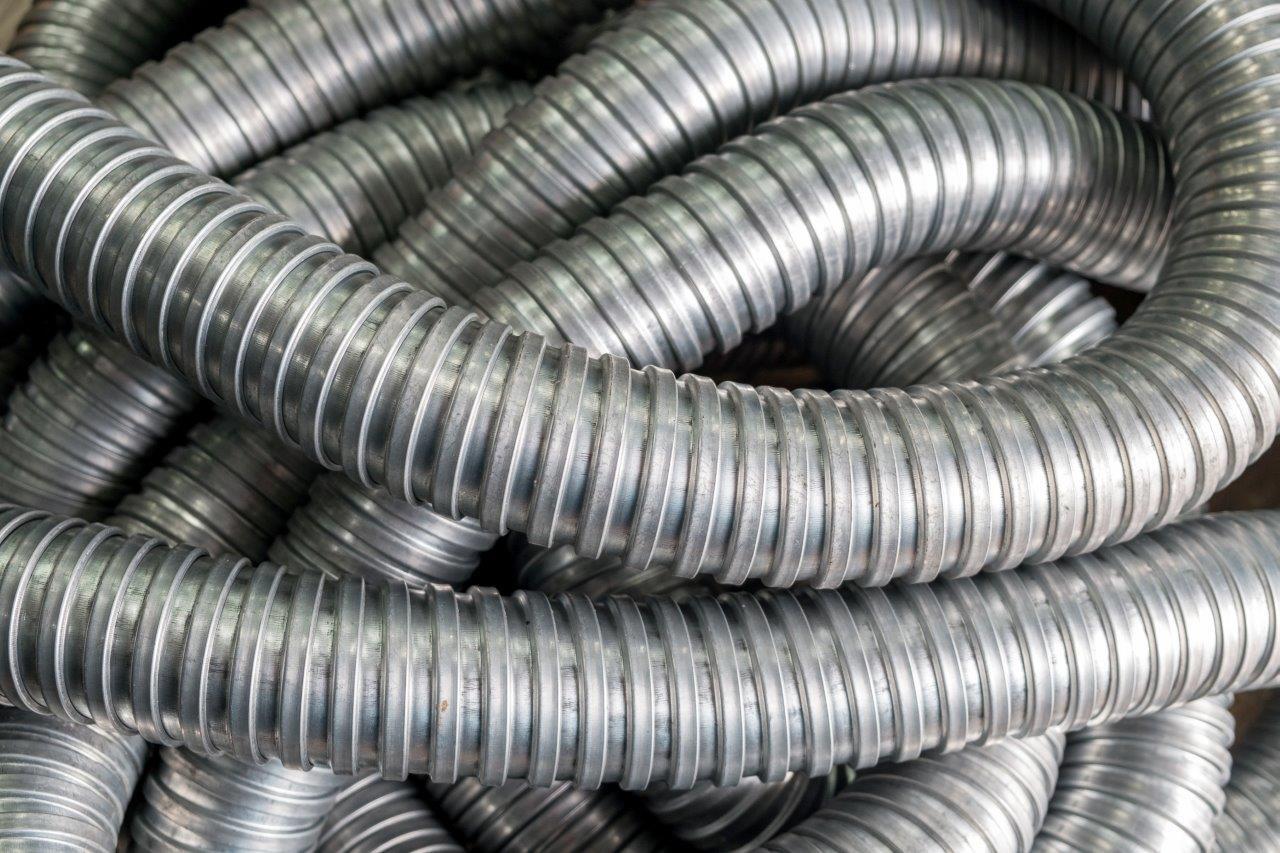
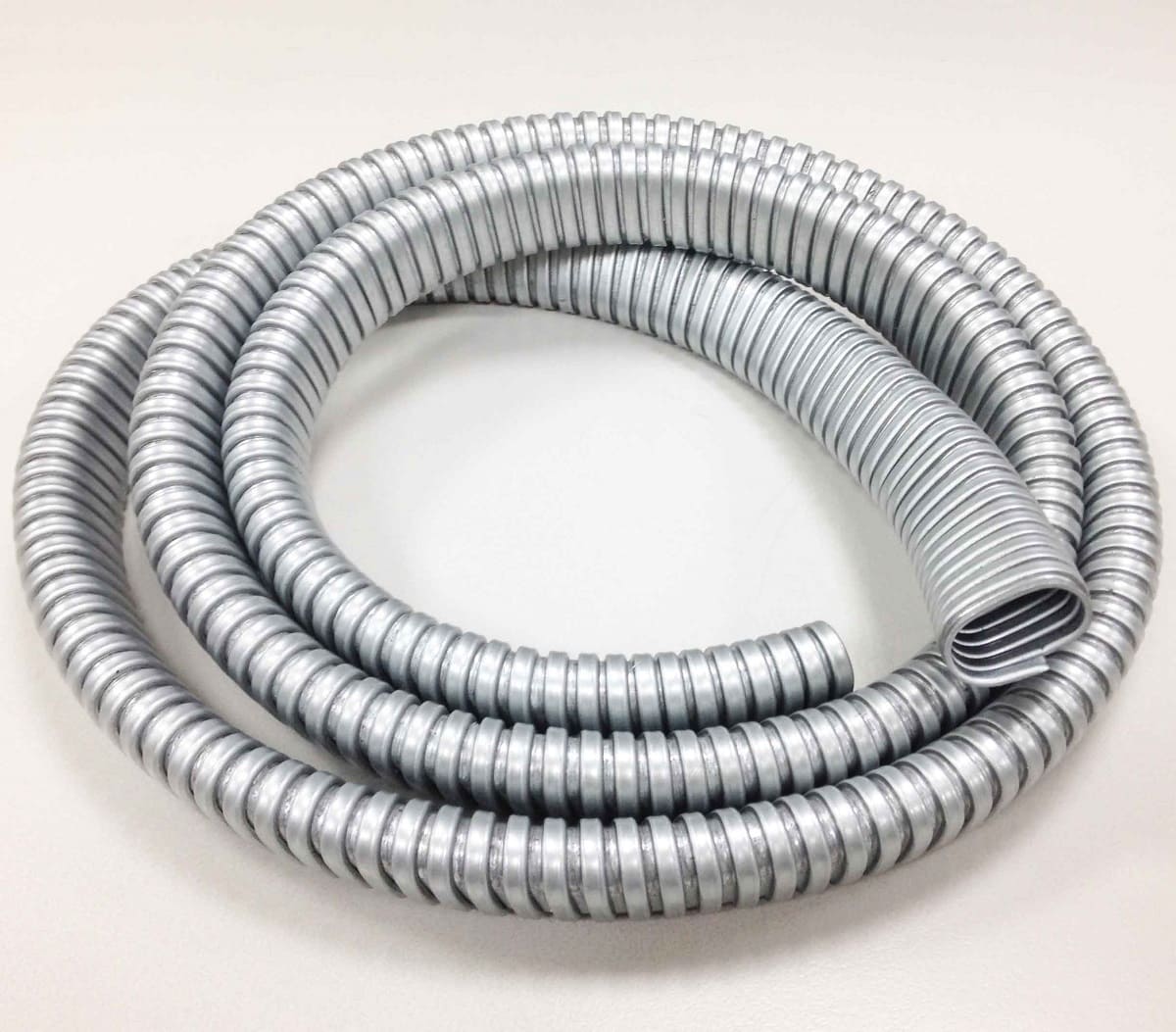
- Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): FMC, also known as “Greenfield,” is a flexible conduit made of interlocking, spiral-wound metal strips. It offers excellent flexibility, making it ideal for installations that require bending around corners or obstacles. FMC is commonly used in commercial and industrial applications where vibration or movement may occur.
- Flexible Non-Metallic Conduit (FNMC): FNMC, also known as “flex conduit,” is a flexible, waterproof conduit made of non-metallic materials such as PVC or nylon. It is suitable for wet locations and is commonly used in outdoor and underground applications, providing protection against moisture and chemical exposure.
These are just a few examples of the types of electrical conduit available. It is important to consult with a qualified electrician or refer to local electrical codes and regulations to determine the most suitable type of conduit for your specific project.
Remember, choosing the right type of conduit is crucial to ensure proper protection, durability, and efficient installation of electrical wiring.
Uses of Electrical Conduit
Electrical conduit is widely used in various applications to provide protection, organization, and flexibility for electrical wiring. Here are some common uses of electrical conduit:
- Residential Electrical Wiring: Electrical conduit is commonly used in residential properties to route wiring from the main electrical panel to outlets, switches, light fixtures, and appliances throughout the house. It ensures proper organization and protection of the electrical system, reducing the risk of accidents and damage.
- Commercial and Industrial Buildings: Conduit systems are extensively used in commercial and industrial buildings for both power distribution and data communication. They provide a reliable and flexible pathway for electrical wiring, accommodating the complex wiring needs of large-scale installations and enabling future modifications or upgrades.
- Outdoor Installations: Electrical conduit is essential for outdoor electrical installations where exposed wiring is susceptible to environmental elements. It protects the wiring from moisture, UV radiation, and physical damage caused by weather conditions or human activities. Examples include outdoor lighting systems, security cameras, and power connections for outdoor equipment or appliances.
- Underground Wiring: When electrical wiring needs to be installed underground, such as in underground power lines or irrigation systems, electrical conduit is used to provide protection against moisture, soil movement, and mechanical damage. Conduit ensures the longevity and reliability of the wiring infrastructure in these applications.
- Data and Communication Cabling: Conduit is also utilized in networking and communication installations to route data cables and fiber optics. It offers protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and allows for easy replacement or upgrade of cables, supporting the ever-evolving technology demands of modern communication systems.
- Security Systems: Electrical conduit plays a crucial role in security system installations, such as intrusion alarms, access control systems, and CCTV systems. It conceals and protects the wiring, preventing tampering and ensuring the secure operation of these critical components.
These are just a few examples of the uses of electrical conduit. Its versatility and reliability make it an essential part of any electrical installation, providing safety, organization, and protection for the entire electrical system. Whether for residential, commercial, or outdoor applications, electrical conduit enhances the performance and lifespan of electrical wiring, contributing to a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Installation Process of Electrical Conduit
The installation process of electrical conduit involves several steps to ensure proper placement, secure attachment, and effective routing of electrical wiring. While it is recommended to hire a licensed electrician for conduit installation, having a basic understanding of the process can be helpful. Here is a general overview of the installation process:
- Planning and Design: Start by determining the specific requirements of your electrical installation, including the number of circuits, types of wires, and locations of outlets and devices. This will help you create a detailed plan and decide on the appropriate type and size of conduit to use.
- Locating Wall Studs: Before marking the conduit’s path on the wall, identify and mark the locations of wall studs. This will help you avoid unnecessary holes and ensure a secure attachment of conduit to the structure.
- Marking Conduit Path: Use a measuring tape and a pencil to mark the path where the conduit will run. Consider factors such as obstructions, corners, and access points. Ensure that the path is clear of obstacles and interference.
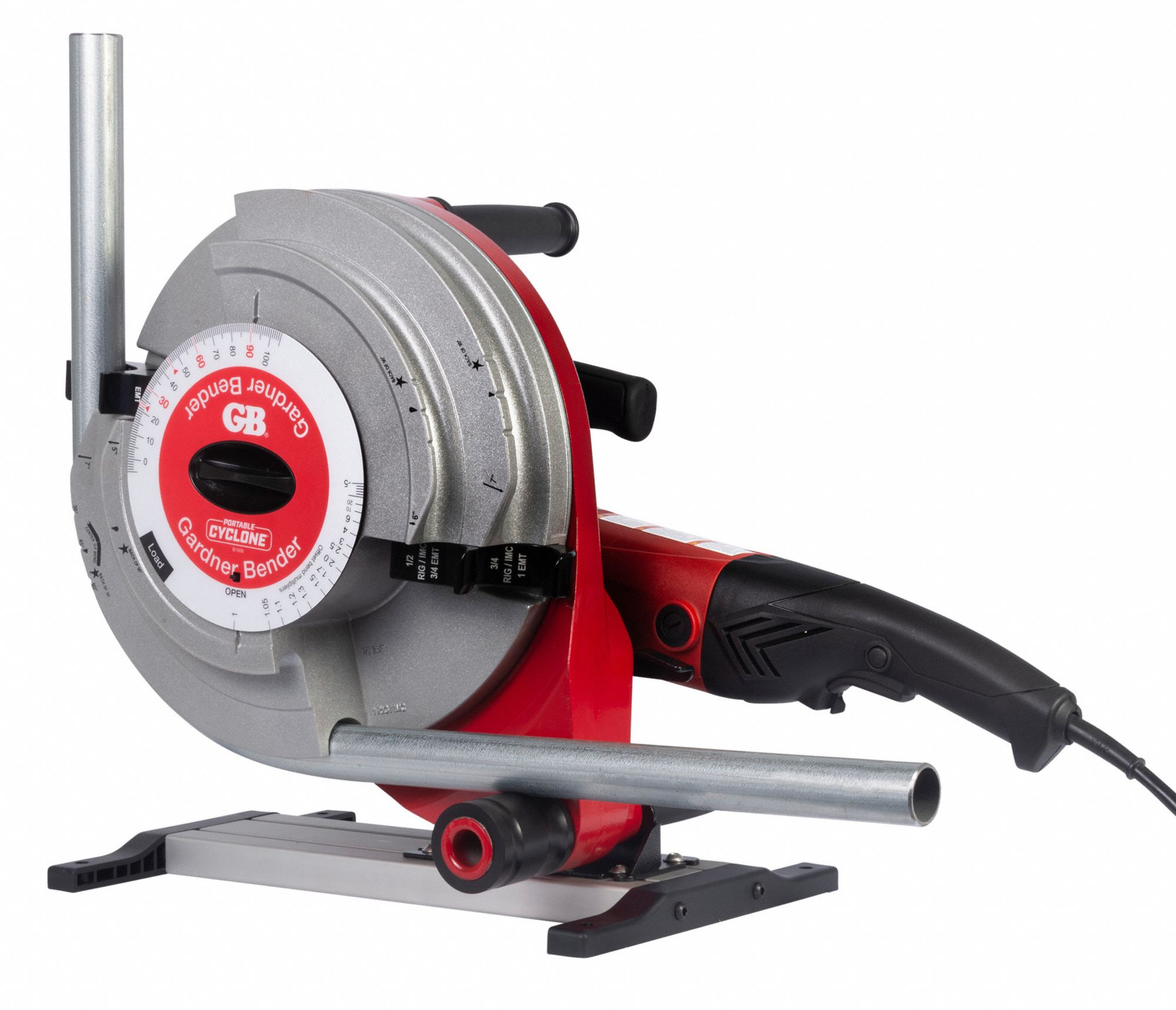
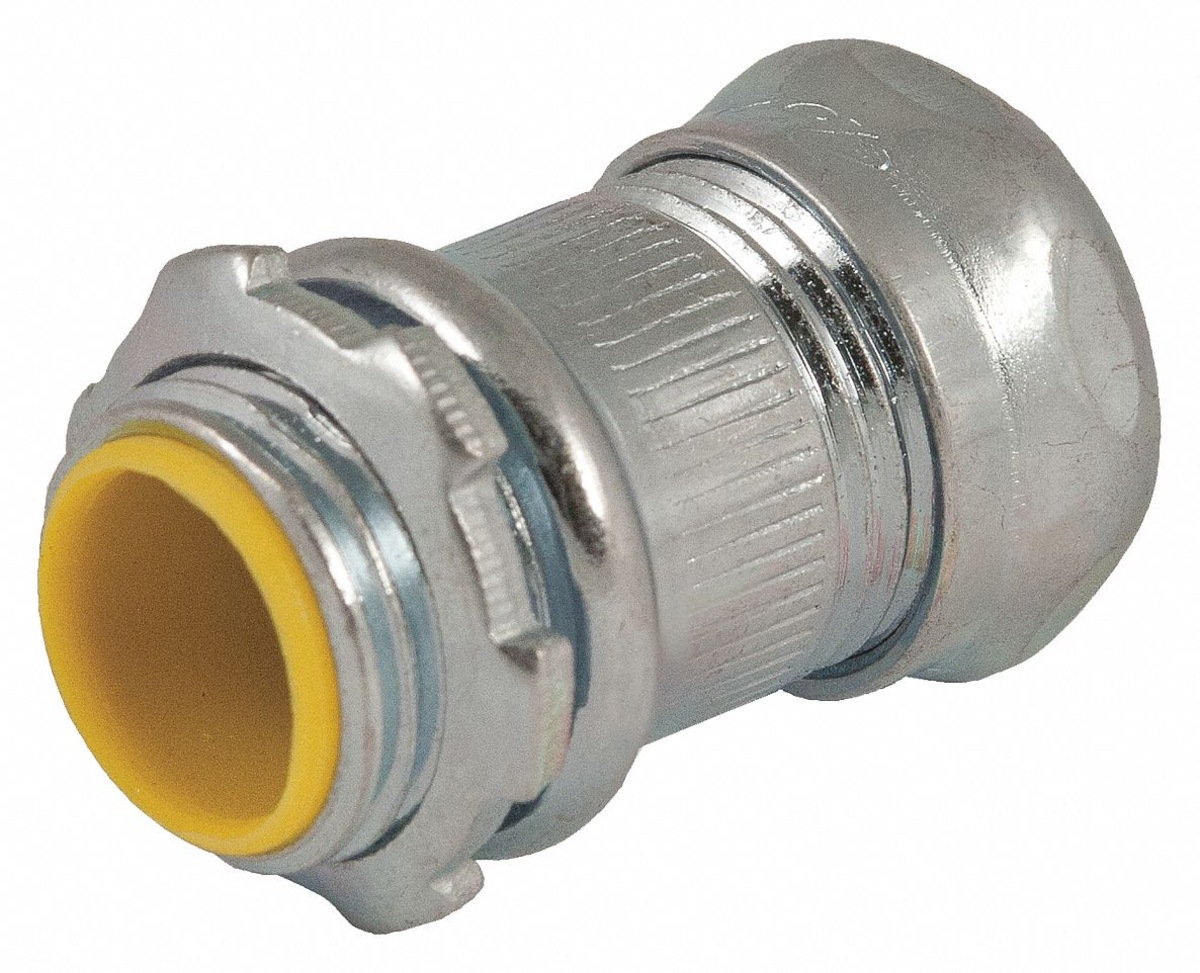
- Cutting and Preparing Conduit: Measure the required lengths of conduit and use a pipe cutter or hacksaw to cut them to size. Smooth out any sharp edges with a file or deburring tool. If necessary, use connectors, couplings, or elbows to create bends or connect multiple sections of conduit.
- Securing Conduit: Attach conduit straps or hangers to secure the conduit along the marked path. Ensure that the straps are properly spaced, providing adequate support and preventing excessive sag or strain on the conduit.
- Fishing Wires: Once the conduit is securely attached, use a fish tape or wire pulling tool to guide the electrical wires through the conduit. Attach the wires to the fish tape and carefully thread them through the conduit, taking care to avoid any sharp bends or kinks.
- Sealing and Grounding: Depending on the type of conduit and local electrical codes, you may need to seal the conduit ends using appropriate fittings or sealing compounds to prevent moisture ingress. Additionally, ensure that the conduit is properly grounded using grounding clamps and fittings.
- Inspection and Testing: After the installation is complete, it is crucial to have a qualified electrician inspect the conduit system for compliance with electrical codes and ensure the proper wiring connections. Perform thorough testing of the electrical system to ensure its functionality and safety.
It is important to note that the installation process may vary based on the specific requirements, conduit type, and local electrical codes. Always consult with a licensed electrician or refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for detailed guidance on the installation process.
Electrical conduit installation requires attention to detail, precision, and compliance with safety regulations. Proper installation ensures the integrity and performance of the electrical wiring system, offering long-term protection and efficiency.
Read more: How To Bend An Electrical Conduit
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electrical Conduit
Electrical conduit offers several advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when planning an electrical installation. Understanding these pros and cons can help you make informed decisions and select the most appropriate wiring method for your specific needs. Here are the key advantages and disadvantages of electrical conduit:
Advantages:
- Protection: Electrical conduit provides excellent protection for electrical wiring. It shields the wires from moisture, chemicals, physical damage, and electromagnetic interference, reducing the risk of accidents, short circuits, and fire hazards.
- Durability: Conduit, especially rigid metal conduit, is highly durable and can withstand harsh environments, impacts, and corrosion. It provides long-lasting protection for wiring, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical system.
- Flexibility: Certain types of conduit, such as flexible metal conduit, offer flexibility in routing electrical wiring. This allows for easy installation around corners, through tight spaces, and in areas where movement or vibration is present.
- Organized and Neat Appearance: Conduit systems provide a clean and organized appearance by concealing and organizing electrical wires. This is beneficial for both residential and commercial installations, improving aesthetics and ease of maintenance.
- Easy Maintenance and Modifications: With conduit, it is relatively simple to access and replace individual wires or add new wiring without major disruption. This flexibility is advantageous when modifications or upgrades are needed in the future.
- Compliance with Electrical Codes: Electrical conduit installations conform to electrical codes and regulations, ensuring compliance and safety. This is particularly important in commercial, industrial, and public settings.
Disadvantages:
- Increased Cost: The installation of electrical conduit can be more expensive compared to other wiring methods, such as surface wiring or cable trays. This additional cost is attributed to materials, labor, and the complexity involved.
- Requires Skilled Installation: Proper installation of electrical conduit requires skilled labor and expertise, especially when dealing with rigid conduit or complex routing. Inadequate installation can lead to inefficiencies, maintenance issues, and safety hazards.
- Time-Consuming Installation: Compared to simpler wiring methods, installing electrical conduit can be time-consuming. This is because the conduit needs to be properly mounted, wires need to be pulled through, and connectors or fittings may be required at various points.
- Limited Flexibility: Rigid conduit systems do not offer the same level of flexibility as cable trays or surface wiring. This can make it challenging to accommodate changes in the electrical layout or future additions to the system.
- Possibility of Condensation: In certain environments, particularly with underground or outdoor installations, condensation may occur inside the conduit. This can lead to moisture-related issues, such as corrosion or damage to electrical components.
Considering the advantages and disadvantages of electrical conduit will help you weigh the benefits versus the potential drawbacks. It is important to evaluate your specific requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals in order to make an informed decision on whether electrical conduit is the right choice for your electrical installation.
Common Materials Used for Electrical Conduit
Electrical conduit is available in a variety of materials, each chosen based on specific requirements such as durability, flexibility, cost, and environmental factors. The choice of materials depends on the type of installation, the level of protection needed, and compliance with electrical codes. Here are some common materials used for electrical conduit:
Read more: How To Run An Electrical Conduit
1. Metal Conduit:
- Galvanized Steel: This is the most commonly used material for rigid metal conduit (RMC). It offers excellent durability, strength, and protection against physical damage and corrosion.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is often used for rigid and intermediate metal conduit (IMC) due to its lightweight nature. It is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel conduit is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for corrosive environments and outdoor applications. It is commonly used in chemical plants, coastal areas, and other areas exposed to harsh conditions.
2. Non-Metallic Conduit:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC conduit, also known as rigid non-metallic conduit (RNC), is the most common type of non-metallic conduit. It is lightweight, relatively inexpensive, and resistant to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals. PVC conduit is commonly used in residential applications and areas where cost-effectiveness is important.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): HDPE conduit is a flexible form of non-metallic conduit that offers excellent resistance to impact, chemicals, and UV radiation. It is commonly used for underground and outdoor installations.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP): FRP conduit is a durable and non-conductive option for electrical installations. It is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and high temperatures, making it suitable for corrosive environments and industrial applications.
3. Flexible Conduit:
- Metallic: Flexible metallic conduit (FMC) is commonly made of interlocking metal strips, such as steel or aluminum. It provides flexibility and allows for easy installation around corners, in tight spaces, or where movement is expected.
- Non-Metallic: Flexible non-metallic conduit (FNMC) is made of materials like PVC or nylon. It is flexible, waterproof, and suitable for outdoor or wet locations. FNMC is commonly used in swimming pools, outdoor lighting, and irrigation systems.
When selecting the appropriate material for electrical conduit, consider factors such as the installation environment, exposure to moisture or corrosive substances, flexibility requirements, and overall cost. It is important to refer to local electrical codes and consult with professionals to ensure compliance and the best choice for your specific application.
Maintenance and Inspection of Electrical Conduit
Maintaining and inspecting electrical conduit is crucial to ensure the ongoing safety, efficiency, and reliability of the electrical system. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify issues, prevent potential hazards, and extend the lifespan of the conduit. Here are some key considerations for the maintenance and inspection of electrical conduit:
Read more: How To Glue Electrical Conduit
1. Visual Inspection:
Perform regular visual inspections of the conduit system to check for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Look for any cracks, dents, or dislodged fittings that may compromise the integrity of the conduit. Inspect the conduit supports and hangers for secure attachment and proper spacing. Ensure that all seals, fittings, and covers are in place and in good condition.
2. Moisture and Water Intrusion:
Inspect the conduit system for any signs of moisture or water intrusion. Moisture can cause corrosion, insulation degradation, and electrical malfunctions. Check for leaks, condensation, or pooling water near the conduits. Address any sources of moisture, repair leaks promptly, and consider the use of waterproof seals or fittings in areas prone to water exposure.
3. Mechanical Protection:
Ensure that the conduit system has adequate mechanical protection. Inspect the conduit for any signs of physical damage, such as dents, bends, or scratches. Assess the surroundings for potential hazards that could impact the conduit. Take necessary measures to protect the conduit from impacts, vibrations, or other mechanical stresses.
4. Access Points and Junction Boxes:
Inspect access points, junction boxes, and connection points to ensure they are secure and properly sealed. Check for loose or exposed wires, improper connections, or signs of overheating. Verify that the proper fittings and covers are in place to prevent dust, moisture, or accidental contact with live wires.
Read more: Why Is Electrical Conduit So Expensive
5. Electrical Testing:
Periodically test the electrical system to ensure its proper functioning. Conduct tests such as voltage testing, insulation resistance testing, and continuity testing to identify any issues with the wires, connections, or conduit itself. Perform these tests in accordance with industry standards and regulations.
6. Regular Cleaning:
Keep the conduit system clean and free from debris, dust, or foreign objects that may impede its performance. Use appropriate cleaning tools and methods to remove any blockages or accumulated dirt. Be cautious when cleaning around live wires and follow proper safety precautions.
7. Professional Inspection:
Consider involving a qualified electrician for periodic professional inspections of the electrical conduit system. Professionals have the expertise to identify potential risks, ensure compliance with electrical codes, and address any underlying issues. They can provide a comprehensive assessment and recommend necessary maintenance or repair actions.
Maintaining and inspecting electrical conduit will help identify any potential issues, ensure compliance with regulations, and enhance the overall safety and performance of the electrical system. By implementing a regular maintenance and inspection routine, you can mitigate risks, prevent electrical failures, and extend the lifespan of the conduit system.
Conclusion
Electrical conduit plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, organization, and longevity of electrical wiring systems. It provides protection against moisture, physical damage, and other potential hazards, while also offering flexibility and ease of maintenance. Understanding the various aspects of electrical conduit is essential for homeowners, electricians, and anyone involved in the construction industry.
In this article, we learned about the definition of electrical conduit and its significance in electrical installations. We explored the different types of electrical conduit, including rigid metal conduit (RMC), electrical metallic tubing (EMT), rigid non-metallic conduit (RNC), flexible metal conduit (FMC), and flexible non-metallic conduit (FNMC).
We also discussed the wide range of uses for electrical conduit. It is commonly used in residential, commercial, industrial, and outdoor applications, serving as a protective pathway for electrical wiring, underground installations, data communication systems, and security systems.
The installation process of electrical conduit involves careful planning, marking, securing, and routing of the conduit, along with fishing the wires through it and completing the necessary sealing and grounding procedures. It is important to follow electrical codes and regulations to ensure a proper and safe installation.
Examining the advantages and disadvantages of electrical conduit highlighted the benefits of enhanced protection, durability, flexibility, and compliance with electrical codes. However, it also mentioned factors such as increased cost, required skilled installation, and limited flexibility compared to other wiring methods.
Common materials used for electrical conduit were discussed, including metal conduit options like galvanized steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, as well as non-metallic conduit materials such as PVC, HDPE, and fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP).
The importance of maintenance and inspection for electrical conduit cannot be overstated. Regular visual inspections, addressing moisture intrusion, mechanical protection, maintaining access points, electrical testing, regular cleaning, and involving professionals for inspections contribute to the ongoing safety and performance of the conduit system.
In conclusion, electrical conduit is a crucial component of electrical systems, providing necessary protection, organization, and flexibility for electrical wiring. It ensures the safe and efficient operation of electrical installations, whether in homes, commercial buildings, or industrial settings. By understanding the different aspects of electrical conduit, we can make informed decisions, ensure compliance with regulations, and maintain a reliable and secure electrical infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Electrical Conduit
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Is Electrical Conduit”