
Articles
When To Use Conduit For Electrical Wiring
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn when to use conduit for electrical wiring with our informative articles. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, our expert advice will help ensure safe and code-compliant installations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical wiring plays a crucial role in our modern world, providing power to our homes, offices, and various infrastructures. It is essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems, and one method to achieve this is by using conduit for electrical wiring. Conduit is a protective system that encloses and safeguards electrical cables and wires, ensuring their longevity and minimizing potential hazards. In this article, we will explore what conduit is, the benefits of using conduit for electrical wiring, when it should be used, the various types of conduit available, the installation process, and important considerations when choosing conduit for your electrical system.
Key Takeaways:
- Conduit for electrical wiring provides protection, flexibility, and compliance, making it ideal for industrial, outdoor, and sensitive environments. It ensures safety, durability, and efficient electrical systems, meeting diverse needs.
- Choosing the right conduit involves considering application, protection, flexibility, environment, compliance, installation, budget, and future expansion. Consulting with professionals ensures a safe, efficient, and reliable electrical system for long-term use.
Read more: How To Pull Electrical Wire Through Conduit
What is Conduit?
Conduit is a protective pathway or channel that is used to enclose electrical cables, wires, and other conductors. It is typically made of durable materials such as metal or plastic and is designed to provide physical protection against damage, moisture, and other external factors that can impact the performance and safety of electrical wiring.
The primary purpose of conduit is to protect the wires from mechanical damage, such as accidental impact, abrasion, or penetration by sharp objects. It also helps to contain and control any potential fire or electrical hazards that may arise from faulty wiring or short circuits.
Conduit provides an added layer of protection for electrical wiring, making it especially beneficial in environments where the risk of damage is high, such as construction sites, industrial facilities, or areas with high foot traffic. Additionally, conduit ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations, providing a safe and reliable electrical system.
Conduit also offers the flexibility to easily add or replace wiring as needed. By having the wires enclosed within the conduit, it becomes simpler to modify or expand the electrical system without the need for extensive rewiring. This is particularly advantageous in commercial buildings or facilities where the infrastructure may require frequent modifications to accommodate changing needs.
Furthermore, conduit provides a shield against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This is particularly important in sensitive applications such as data centers or medical facilities, where the presence of stray electromagnetic signals can negatively affect the performance of sensitive equipment or disrupt critical systems.
In summary, conduit serves as a protective pathway for electrical wiring, safeguarding it from damage, moisture, and other external factors. It provides flexibility for modifications, ensures compliance with electrical codes, and protects against electromagnetic and radio frequency interference. Understanding what conduit is and its benefits helps to enhance the safety, durability, and efficiency of electrical systems.
Benefits of Using Conduit for Electrical Wiring
When it comes to electrical wiring, utilizing conduit offers a range of advantages that enhance safety, functionality, and ease of maintenance. Let’s explore the key benefits of using conduit for electrical wiring:
- Protection: One of the primary benefits of conduit is its ability to protect electrical wiring from various external factors. Conduit shields the wires from physical damage, moisture, and chemicals, reducing the risk of short circuits, fires, and other hazards.
- Durability: Conduit is constructed from robust materials such as metal or PVC, offering long-lasting protection for electrical wiring. It can withstand harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and exposure to UV radiation, ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system over an extended period.
- Flexibility: Using conduit provides flexibility when it comes to installing and modifying electrical systems. The conduit acts as a conduit (pun intended!) for running and organizing multiple wires in a neat and orderly manner, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot wiring issues. Additionally, conduit allows for future expansions or modifications without the need for significant rewiring.
- Easier Troubleshooting and Maintenance: With conduit, locating and addressing wiring problems becomes more accessible. The enclosed wires are protected from accidental damage or tampering, and it is easier to trace and identify specific wires within the conduit. This simplifies troubleshooting tasks and reduces downtime during maintenance or repairs.
- Compliance: Conduit systems adhere to electrical codes and regulations set by authorities. By using conduit, you ensure that your electrical wiring meets these standards, ensuring the safety and legality of your electrical installations.
- Noise Mitigation: In certain applications, conduit can help reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This is especially critical in environments sensitive to such interferences, such as audio studios or medical facilities.
- Aesthetics: Conduit can enhance the visual appeal of a space by concealing and organizing electrical wiring. With various conduit finishes and styles available, you can choose conduit that blends seamlessly with the decor or architectural design of the building.
- Safe and Reliable Network: By using conduit, you create a secure path for electrical wires, minimizing potential hazards and ensuring proper grounding. This reduces the risk of electrical shocks, equipment failures, or interruptions in power supply.
Overall, the benefits of using conduit for electrical wiring are multifold, ranging from enhanced protection and durability to improved troubleshooting capabilities and compliance with regulations. These advantages make conduit an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from residential homes to commercial buildings and industrial facilities.
When Should You Use Conduit for Electrical Wiring?
The decision to use conduit for electrical wiring depends on several factors. While conduit offers numerous benefits, it may not be necessary in every situation. Here are some scenarios where using conduit for electrical wiring is recommended:
- Industrial and Commercial Environments: In high-risk environments such as factories, warehouses, or manufacturing plants, where the risk of physical damage or exposure to harsh conditions is high, conduit is highly recommended. The added protection provided by conduit helps safeguard the electrical system in these demanding settings.
- Outdoor Applications: Outdoor installations are subject to various weather conditions, including rain, snow, extreme temperatures, and UV exposure. Conduit is essential for protecting wires from moisture, corrosion, and damage caused by exposure to these elements.
- Above-Ground Installations: When electrical wiring is installed above ground, such as on walls or ceilings, it is exposed to potential impact or accidental damage. Conduit provides an extra layer of protection to prevent physical damage and prolong the lifespan of the wiring.
- Exposed Areas: In areas where electrical wiring is subject to potential damage due to human activities or machinery, using conduit is advisable. Examples include garages, workshops, or areas with heavy foot traffic, where accidental impact or abrasion can occur.
- Retrofitting and Renovations: During retrofitting or renovation projects, when modifications are made to existing electrical systems, using conduit can simplify the process. Conduit allows for easier installation of new wiring or modifications without significantly disturbing the existing structure.
- Sensitive Environments: Certain environments require a high level of electrical noise mitigation or protection against electromagnetic interference. Data centers, hospitals, or research laboratories can benefit from using conduit to shield wires from external electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable and accurate performance of sensitive equipment.
- Long Cable Runs: When there is a need for running electrical wires over long distances, conduit provides an organized and efficient solution. It helps to minimize voltage drop, manage cable runs effectively, and simplifies troubleshooting in case of any issues.
- Mandatory Regulatory Compliance: In some jurisdictions, local electrical codes or regulations may require the use of conduit in specific applications or environments. It is essential to be familiar with these requirements and ensure compliance to meet safety standards and avoid potential legal issues.
While conduit is not always necessary for every electrical wiring project, considering the factors mentioned above can help determine when its use is beneficial. Consulting with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer is recommended to assess the specific needs of your project and make an informed decision.
Typical Applications for Conduit
Conduit is widely used in various applications to protect and organize electrical wiring. Its versatility and protective capabilities make it suitable for a range of environments and situations. Here are some typical applications where conduit is commonly used:
- Residential Buildings: In homes, conduit is often employed to ensure the safety and organization of electrical systems. It is commonly used for wiring installations in basements, garages, outdoor lighting, and areas where the wiring is exposed to potential damage.
- Commercial Buildings: Conduit finds extensive use in commercial spaces such as offices, retail stores, restaurants, and hotels. It is utilized for various applications including powering lighting fixtures, electrical outlets, data and communication cables, and security systems.
- Industrial Installations: Industries such as manufacturing, warehouses, and factories require robust electrical systems that can withstand demanding conditions. Conduit is employed in these environments to protect wiring from hazards such as machinery vibrations, chemicals, moisture, and other potential damage sources.
- Outdoor Lighting: Conduit is commonly utilized for outdoor lighting installations, whether it’s for residential landscapes, commercial buildings, or public spaces. It protects the wiring from weather elements, UV radiation, and physical damage caused by landscaping or maintenance activities.
- Data Centers and IT Facilities: Data centers and IT facilities necessitate impeccable electrical systems to maintain uninterrupted operations. Conduit is used to protect and organize an extensive network of data cables, fiber optics, power cables, and other critical infrastructure.
- Colleges and Universities: Educational institutions often have complex electrical systems to cater to their diverse needs. Conduit is employed for wiring installations in classrooms, laboratories, administration buildings, sports facilities, and dormitories, ensuring safety and flexibility for future upgrades.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: In healthcare settings, where precision and reliability are paramount, conduit protects electrical wiring in critical areas such as operating rooms, laboratories, diagnostic imaging rooms, and patient care areas.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Conduit is widely used in transportation infrastructure such as airports, train stations, and subway systems. It supports electrical wiring for lighting, signaling, security systems, and communication networks.
This is just a snapshot of some typical applications for conduit; however, its usage extends to various other settings as well. Essentially, any environment where electrical wiring needs protection, durability, flexibility, or compliance with regulations can benefit from using conduit.
It is important to consult with electrical professionals to assess the specific requirements of your project and select the appropriate conduit type and installation methods for optimal performance and safety.
When running electrical wiring in exposed or potentially hazardous areas, such as outdoors or in a garage, it’s best to use conduit to protect the wires from damage and reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
Types of Conduit for Electrical Wiring
There are several types of conduit available for electrical wiring, each offering unique features and benefits. The choice of conduit depends on factors such as the application, environment, and specific requirements of the electrical system. Here are some common types of conduit used for electrical wiring:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): Rigid metal conduit, also known as RMC or rigid steel conduit, is a durable and robust option for heavy-duty applications. It is typically made of steel and provides excellent mechanical protection for electrical wiring. RMC is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where wiring is exposed to potential damage or challenging environments.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): Electrical metallic tubing, or EMT, is a lightweight conduit made of thin-wall galvanized steel. It is easy to install, bendable, and cost-effective. EMT is commonly used in residential and commercial applications where wiring protection is required but heavy-duty protection is not necessary.
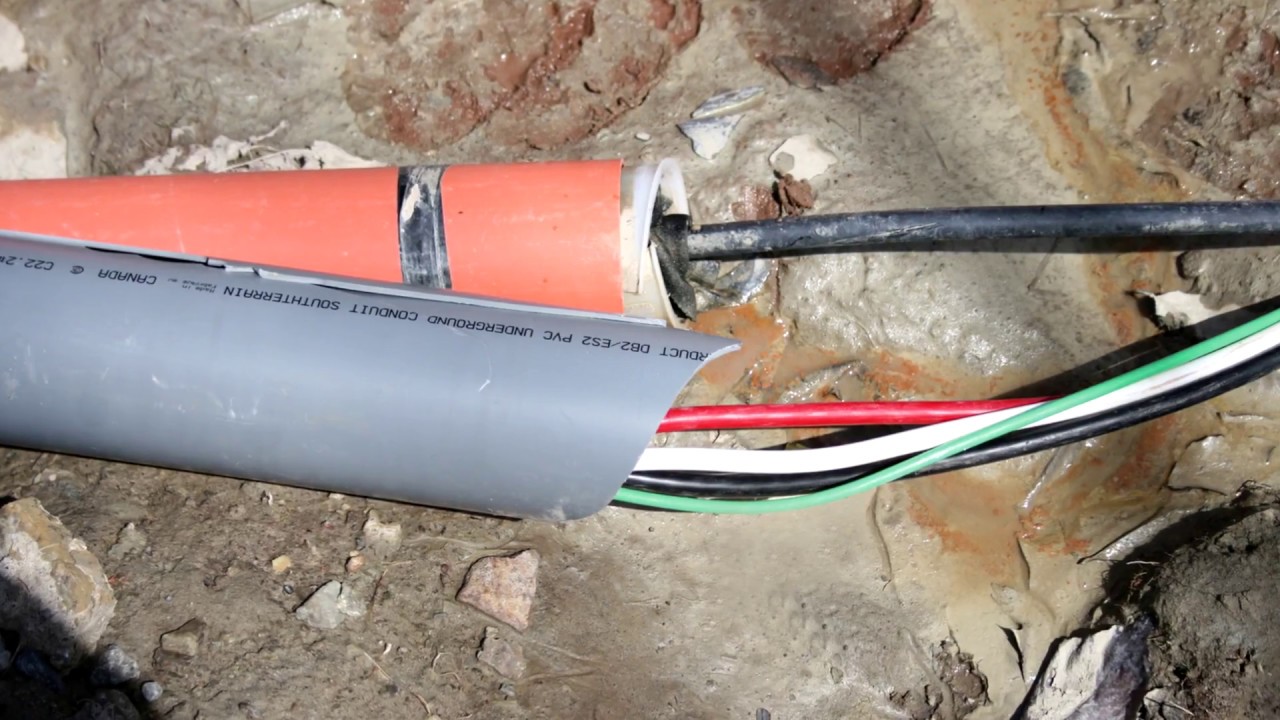
- Rigid Non-Metallic Conduit (RNC): Rigid non-metallic conduit, also known as PVC conduit, is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) material. It is lightweight, affordable, and resistant to corrosion and chemical exposure. RNC is commonly used in both indoor and outdoor applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): Flexible metal conduit, or FMC, is a versatile and flexible option for wiring installations that require some degree of movement or flexibility. It is constructed with a spiral metal strip and provides good protection against physical damage. FMC is commonly used in areas where wiring requires bends or twists, such as in machinery or equipment installations.
- Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC): Liquidtight flexible metal conduit, also known as LFMC or LFNC, is a flexible conduit that is designed to provide protection against liquids, moisture, and corrosive elements. It is commonly used in outdoor installations, wet locations, or areas where wiring is exposed to water or chemicals.
- Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC): Intermediate metal conduit, or IMC, is a lighter-weight alternative to RMC. It is made of galvanized steel and provides a higher level of protection compared to EMT. IMC is commonly used in commercial and industrial applications where added protection is required, but the rigidity of RMC is not necessary.
- Flexible Non-Metallic Conduit (FNC): Flexible non-metallic conduit, or FNC, is made of a flexible plastic material like PVC or nylon. It is lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion. FNC is commonly used in exposed or concealed installations where flexibility and low cost are important factors.
These are just a few examples of the types of conduit available for electrical wiring. Each type has its own set of advantages and is suited for specific applications. It is crucial to consult with electrical professionals to determine the most appropriate conduit type for your project, ensuring optimal protection and compliance with regulations.
Installation Process for Conduit Wiring
Installing conduit for electrical wiring requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure a safe and successful electrical system. Here is a general overview of the installation process for conduit wiring:
- Planning and Design: Begin by assessing the specific requirements of your electrical system and determining the appropriate type of conduit to use. Consider factors such as the environment, the number of cables or wires to be installed, and any specific regulations that need to be followed.
- Marking and Measurements: Before starting the installation, mark the path where the conduit will be installed on the walls, floors, or ceilings. Take accurate measurements to determine the lengths of conduit required and the locations of junction boxes or outlet boxes.
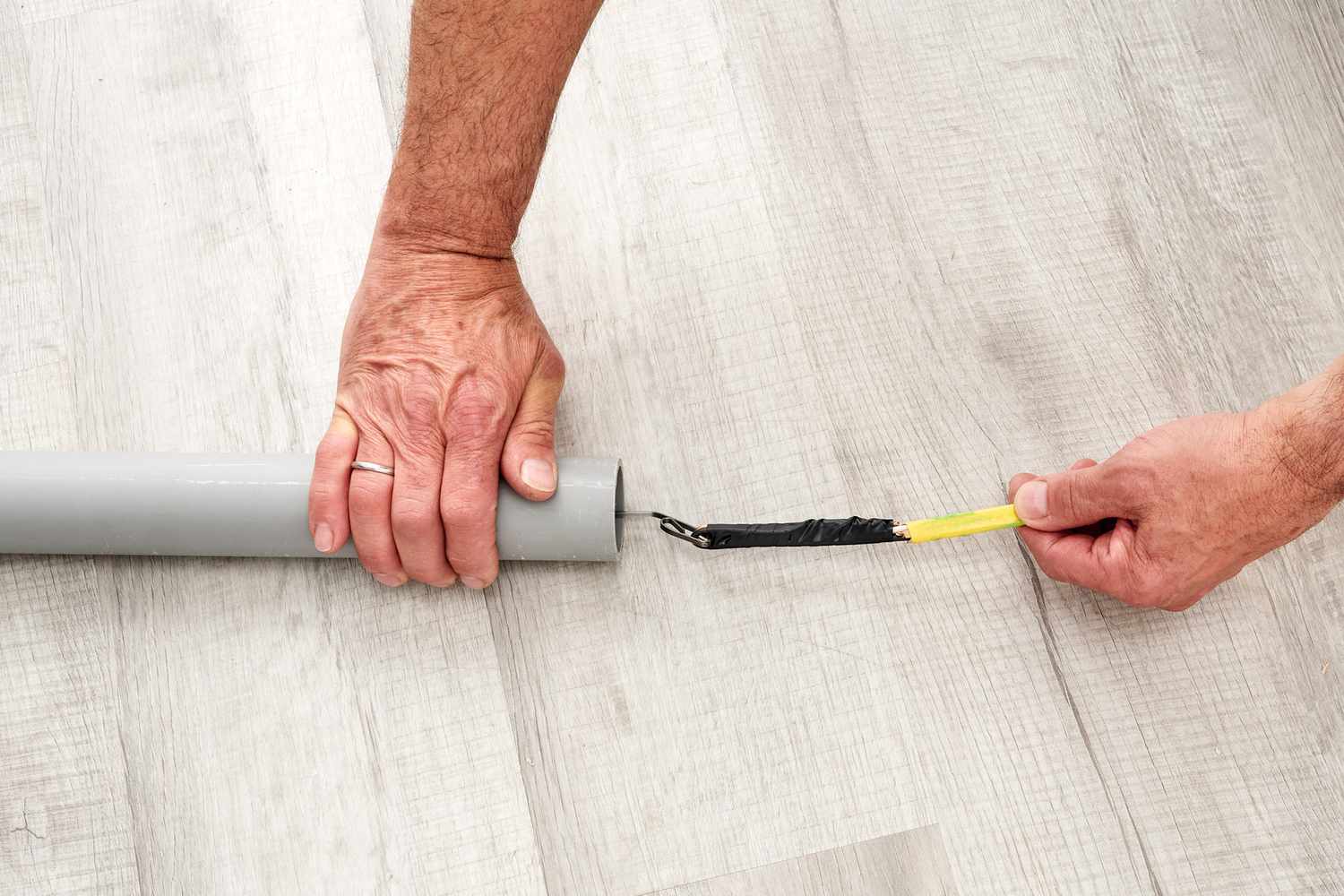
- Preparing the Conduit: Cut the conduit to the desired lengths using a conduit cutter or a hacksaw. Remove any burrs from the cut ends and ensure that the conduit is clear of debris or obstructions.
- Mounting: Install conduit supports such as straps or hangers at regular intervals along the marked path. Make sure to securely fasten the supports to the surface using appropriate hardware.
- Running the Wires: If necessary, pre-wire the cables or wires before inserting them into the conduit. Feed the wires through the conduit, starting from one end and pushing them carefully through the entire length. Use fish tape or a pull string to guide the wires through bends, turns, or longer runs.
- Connectors and Fittings: Install connectors or fittings as needed to join sections of conduit together or for connections to junction boxes or outlet boxes. Make sure to use appropriate connectors that match the type and size of conduit being used.
- Bending: If you need to make bends in the conduit, use a conduit bender or a conduit bending machine. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate and proper bending angles without damaging the conduit.
- Securing: Secure the conduit to the supports using appropriate conduit straps or hangers. Ensure that the conduit is properly aligned and straight without any unnecessary tension or stress.
- Junction Boxes and Outlets: Install junction boxes or outlet boxes at appropriate locations along the conduit run. Make necessary connections between the conduit and the boxes using suitable connectors or fittings.
- Finalizing: Once all the wiring is installed, check for any loose connections or improper alignments. Double-check that all the wires are securely in place and free from any damage or excessive tension.
It is important to note that electrical work should be carried out by qualified professionals who are familiar with local electrical codes and regulations. They have the knowledge and expertise to ensure that the installation is done safely and according to the required standards.
By following these general steps and consulting with professionals, you can ensure a successful and reliable conduit wiring installation that provides the necessary protection and functionality for your electrical system.
Considerations When Choosing Conduit for Electrical Wiring
Choosing the right conduit for electrical wiring is essential to ensure the safety, functionality, and longevity of your electrical system. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind when selecting conduit:
- Type of Application: Consider the specific application and environment where the conduit will be installed. Different types of conduit are better suited for certain applications. For example, in industrial settings, rigid metal conduit (RMC) or intermediate metal conduit (IMC) may be more appropriate, while in residential or light commercial settings, electrical metallic tubing (EMT) or rigid non-metallic conduit (RNC) could be sufficient.
- Physical Protection: Assess the level of physical protection needed for the wiring. If the wiring is exposed to potential damage, such as in high-traffic areas or harsh environments, choose a conduit material that provides robust protection and durability, such as RMC or PVC conduit.
- Flexibility: Determine whether flexibility is necessary for your wiring installation. Flexible conduit options like flexible metal conduit (FMC) or flexible non-metallic conduit (FNC) are suitable for installations that require bends or twists in the conduit.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the environmental conditions the conduit will be exposed to. If the conduit will be installed outdoors or in an area with high moisture levels, choose a conduit material that is resistant to corrosion and moisture, such as PVC or liquidtight flexible metal conduit (LFMC).
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): If the electrical system is sensitive to EMI or RFI, consider using conduit that offers good shielding properties, such as metal conduit options.
- Installation Ease: Evaluate the ease of installation for the conduit type you are considering. Different conduit materials and styles have varying installation methods, so choose one that aligns with the available resources and installation requirements.
- Code Compliance: Ensure that the chosen conduit meets local electrical codes and regulations. Familiarize yourself with the requirements for your specific jurisdiction to ensure compliance and avoid potential issues in the future.
- Budget and Cost: Take into account your budget and the cost considerations associated with various conduit options. Different conduit materials have different price points, so select one that best fits your budget while still meeting the necessary requirements of your project.
- Future Expansion: Consider whether your electrical system might require future expansions or modifications. Choosing conduit that allows for easy access, modifications, and additions can save time and effort in the future.
It is essential to consult with qualified electricians or electrical engineers who are familiar with conduit installations. They can provide expert advice specific to your project’s requirements, ensuring the appropriate conduit is chosen and installed correctly.
By considering these factors and seeking professional guidance, you can make an informed decision when choosing conduit for your electrical wiring, leading to a safe, efficient, and reliable electrical system.
Conclusion
Conduit plays a crucial role in protecting and organizing electrical wiring, ensuring the safety, longevity, and optimal performance of electrical systems. By encasing wires in a durable and protective pathway, conduit safeguards against physical damage, moisture, and other external factors that can compromise the integrity of the wiring.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of conduit for electrical wiring. We have discussed what conduit is, the benefits it offers, the scenarios where its use is recommended, typical applications, the different types of conduit available, the installation process, and important considerations when selecting conduit.
Using conduit for electrical wiring offers numerous advantages, including protection against physical damage, durability, flexibility for future modifications, ease of troubleshooting and maintenance, compliance with electrical codes, and the mitigation of electromagnetic interference. These benefits make conduit an ideal choice for a range of applications, from residential homes to industrial facilities.
When choosing conduit, it is crucial to consider factors such as the type of application, required physical protection, flexibility, environmental factors, code compliance, installation ease, budget, and potential for future expansions. Consulting with qualified professionals who have expertise in electrical systems and conduit installations is highly recommended to ensure the appropriate conduit is chosen and installed correctly.
In conclusion, conduit is an indispensable component in electrical wiring, offering both protective and organizational benefits. By selecting the right conduit and following proper installation practices, you can create a safe, reliable, and efficient electrical system that serves your needs for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about When To Use Conduit For Electrical Wiring
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “When To Use Conduit For Electrical Wiring”