

Articles
How Many Romex Wires In Conduit
Modified: August 26, 2024
Looking for informative articles on how many Romex wires can be safely placed in a conduit? Get the answers you need to ensure electrical safety and compliance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Overview
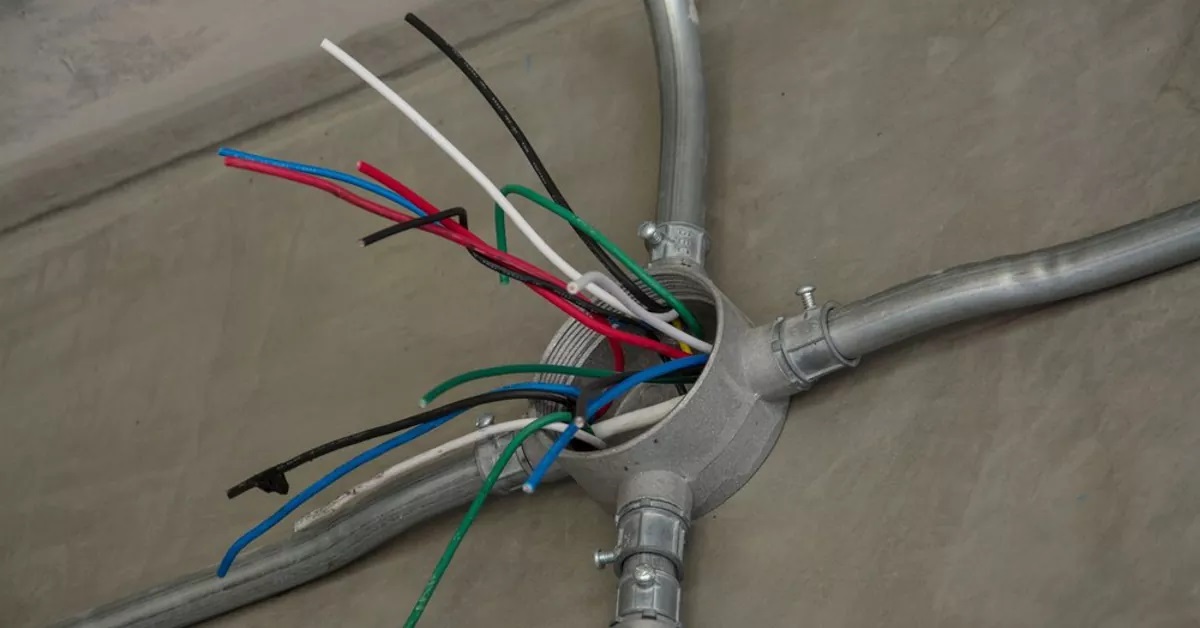
When it comes to electrical wiring, proper installation is crucial for ensuring the safety and functionality of your electrical system. One important consideration is the use of Romex wire and conduit. Romex wire, a popular type of non-metallic sheathed cable, is commonly used for residential electrical installations. Conduit, on the other hand, is a protective tubing system that can be used to house and route electrical wires.
In this article, we will delve into the topic of how many Romex wires can be safely installed in conduit. We will explore the purpose of using conduit, factors to consider, and the maximum number of Romex wires allowed in conduit. Additionally, we will touch upon conduit fill calculations, consequences of overfilling conduit, and important safety precautions.
Understanding these aspects can help you make informed decisions when it comes to your electrical wiring projects.
Key Takeaways:
- Properly calculating conduit fill ratios is crucial for safely installing Romex wires. Overfilling conduit can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and non-compliance with building codes, posing serious risks to the electrical system.
- Prioritize safety when working with Romex wires and conduit. Turn off power, wear protective gear, follow building codes, and consult a qualified electrician if needed. Safety precautions are essential for successful and secure electrical installations.
Read more: How Many Wires In A 3/4 Inch Conduit
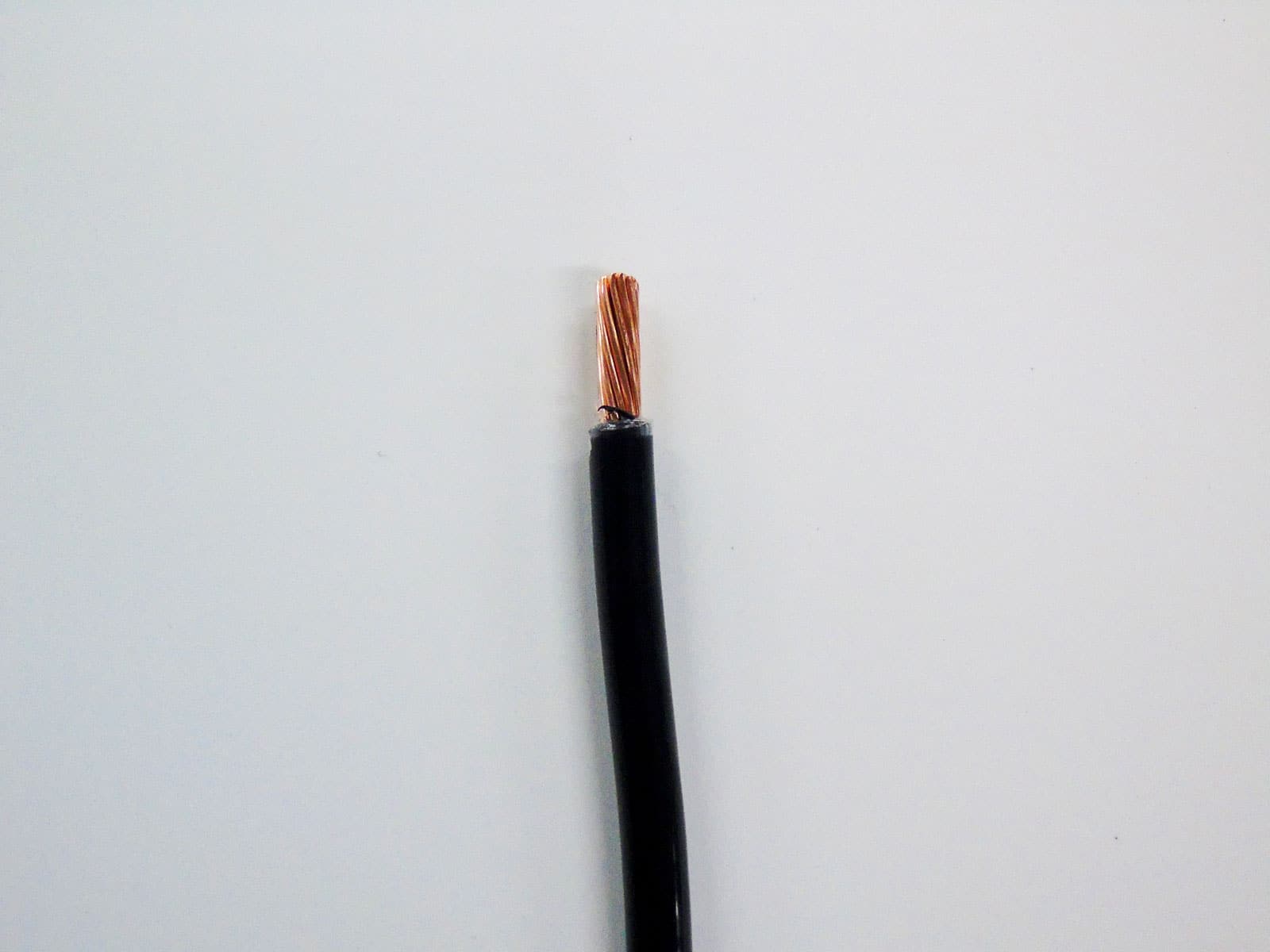
What is Romex Wire?
Romex wire, also known as NM-B cable, is a type of non-metallic sheathed cable commonly used for residential electrical installations. It is made up of several individual wires that are encased in a protective vinyl jacket. The outer jacket is typically color-coded to indicate the wire’s gauge and usage.
Romex wire is available in various sizes, ranging from 14 AWG (American Wire Gauge) to 6 AWG, with the smaller gauges being used for lower-amperage circuits and the larger gauges for higher-amperage circuits. Each individual wire within the cable is insulated to prevent any electrical contact or short circuits.
One of the advantages of Romex wire is its ease of installation. It can be easily run through wall cavities, attics, and other concealed spaces, making it ideal for residential applications. Additionally, Romex wire is less expensive compared to other types of wiring, making it a popular choice for homeowners and electricians alike.
It is important to note that Romex wire is only suitable for use in dry and non-metallic environments. If you need to run wiring in areas exposed to moisture or where conduit is required, it is necessary to use appropriate wiring methods and materials.
What is Conduit?
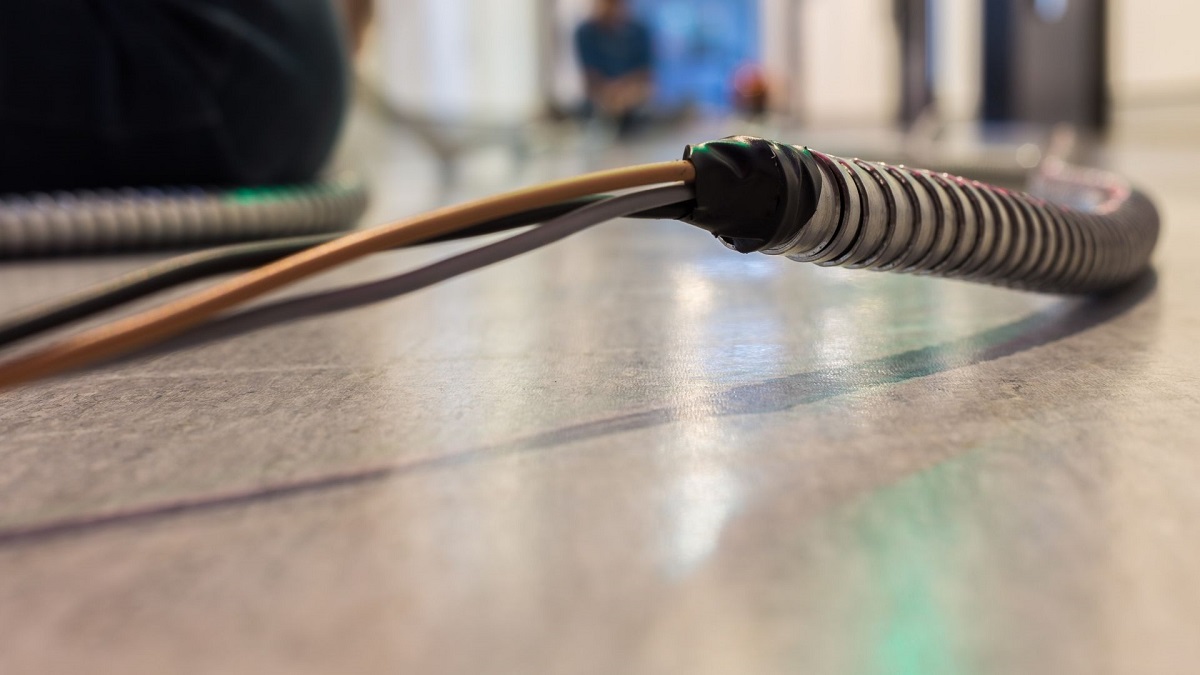
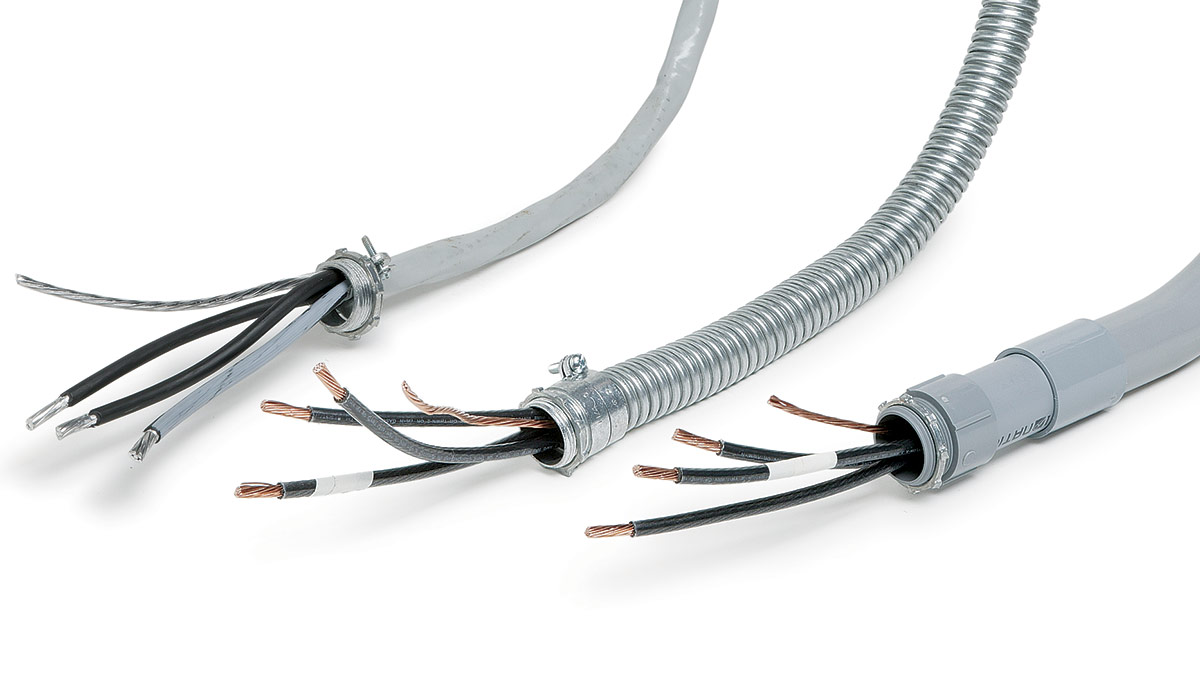
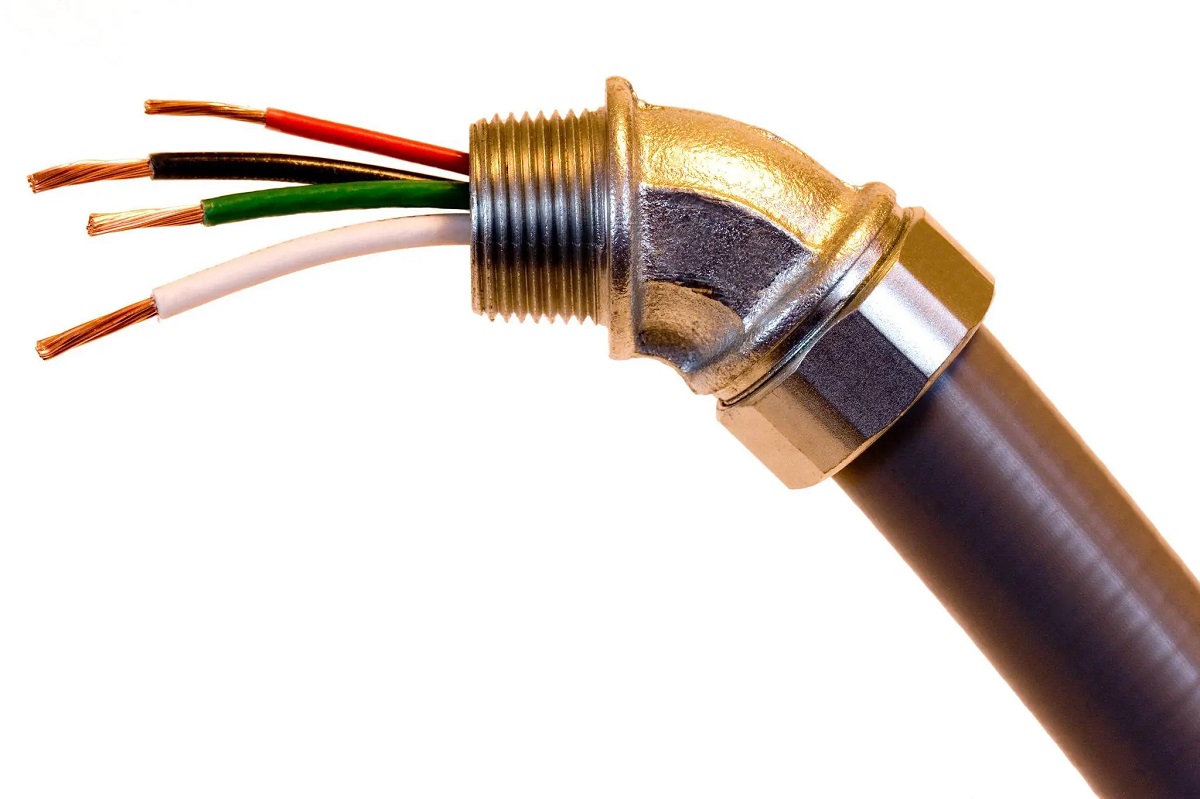
Conduit is a protective tubing system that is used to house and route electrical wires. It provides a sturdy and enclosed pathway for electrical cables, offering protection from physical damage, moisture, and other potential hazards. Conduits are typically made of metal or plastic and are available in various sizes and types to accommodate different wiring needs.
The primary purpose of using conduit is to ensure the safety and integrity of electrical wiring installations. By enclosing the wires within a conduit, they are shielded from external elements and are less prone to damage caused by impact, moisture, or excessive heat. Conduit also serves as a means of organizing and consolidating multiple wires, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot electrical systems.
There are two main types of conduit: rigid conduit and flexible conduit. Rigid conduit, as the name suggests, is a more rigid and durable option. It is typically made of metal, such as galvanized steel or aluminum, and offers excellent protection against physical damage. Flexible conduit, on the other hand, is more pliable and is commonly made of plastic or steel. It is a versatile option that is often used in situations where there are bends or curves in the wiring path.
In addition to protecting the wires, conduit also plays a role in code compliance. Many electrical codes require the use of conduit in certain applications, such as in commercial buildings or in areas with specific environmental conditions. Adhering to these codes helps ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
It’s important to note that conduit alone is not sufficient for electrical wiring. Wires must also be appropriately sized, grounded, and connected to electrical components to ensure proper function and safety. Consulting with a qualified electrician is recommended for any complex electrical installations involving conduit.
The Purpose of Using Conduit
Conduit serves multiple purposes when it comes to electrical installations. Its primary function is to protect electrical wires from potential damage and provide a safe pathway for their routing. Here are some key purposes and benefits of using conduit:
- Physical Protection: One of the main reasons for using conduit is to shield the electrical wires from physical damage. Conduit serves as a barrier against accidental impacts, such as from construction activities or moving objects, minimizing the risk of electrical faults, short circuits, or exposed wires.
- Moisture and Environmental Protection: Conduit offers protection against moisture, dust, and other environmental elements. This is particularly important in locations where electrical wiring may be exposed to high humidity, water, or corrosive substances. By preventing moisture ingress, conduit helps maintain the integrity and functionality of the electrical system.
- Fire Resistance: Certain types of conduit, such as rigid metallic conduit, have inherent fire-resistant properties. In the event of a fire, these conduits can help contain and limit the spread of flames, providing additional time for occupants to evacuate and minimizing property damage.
- Wiring Organization: Conduit allows for neat and organized routing of electrical wires. It helps to consolidate multiple wires into a single pathway, reducing the potential for tangles and confusion. This makes troubleshooting and future maintenance tasks more efficient and less time-consuming.
- Code Compliance: Many electrical codes and regulations mandate the use of conduit in specific applications. Adhering to these codes is essential for ensuring the safety and compliance of electrical installations. By using conduit where required, you can avoid potential legal issues and ensure that your electrical system meets the necessary standards.
It is worth noting that the type of conduit used may vary depending on the specific needs of the installation. Rigid conduit is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings due to its durability and strength. Flexible conduit, on the other hand, is more suitable for residential applications or situations where there are bends and curves in the wiring path.
Overall, conduit plays a vital role in protecting electrical wiring from physical damage, offering environmental resistance, enhancing organization, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes. It provides peace of mind and contributes to the overall safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Factors to Consider
When determining how many Romex wires can be safely installed in conduit, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration. These factors include:
- Conduit Size: The size of the conduit is an important factor in determining the number of Romex wires it can accommodate. Conduits are available in different sizes, typically measured in trade sizes or by their inner diameter. The larger the conduit size, the more wires it can hold. It is essential to select a conduit size that is appropriate for the number and size of Romex wires being installed.
- Conduit Type: The type of conduit you choose can also impact the number of Romex wires that can be safely installed. Rigid conduits usually have less space available compared to flexible conduits. Therefore, flexible conduits can typically accommodate more wires. However, it is important to consult applicable building codes to ensure the proper type of conduit is used for your specific application.
- Romex Wire Size: The size of the Romex wires being installed will also influence the number that can fit in a conduit. Different gauge sizes of Romex wire have different diameters, and larger gauge wires will require more space. Ensure you know the dimensions of the Romex wires you are working with and refer to industry standards or building codes for guidance on appropriate conduit fill calculations.
- Wire Spacing: Proper wire spacing must be maintained within the conduit to prevent overheating and maintain electrical safety. Different codes specify minimum distances that need to be maintained between the wires to allow for adequate airflow and dissipate heat. Failure to maintain proper wire spacing can lead to insulation damage, increased resistance, and potential electrical hazards.
- Conduit Fill Ratio: Building codes provide guidelines for the maximum allowable conduit fill ratio. This ratio specifies the maximum percentage of the conduit’s cross-sectional area that can be occupied by the wires. Exceeding the recommended conduit fill ratio can cause overheating, increased resistance, and potential damage to the insulation. It is crucial to adhere to the appropriate fill ratio calculations to ensure a safe and efficient installation.
It is important to note that these factors may vary depending on your specific jurisdiction and local building codes. Consulting with a qualified electrician or referring to specific regulations in your area is highly recommended to ensure compliance and safety.
Considering these factors will help you determine the appropriate conduit size and ensure that the number of Romex wires being installed falls within the recommended guidelines. By carefully planning and following industry standards, you can optimize the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
When determining how many Romex wires can fit in a conduit, remember to consider the size of the conduit and the gauge of the wires. Follow the National Electrical Code guidelines for proper sizing.
Read more: How Many #4 Wires In A 1 Inch Conduit
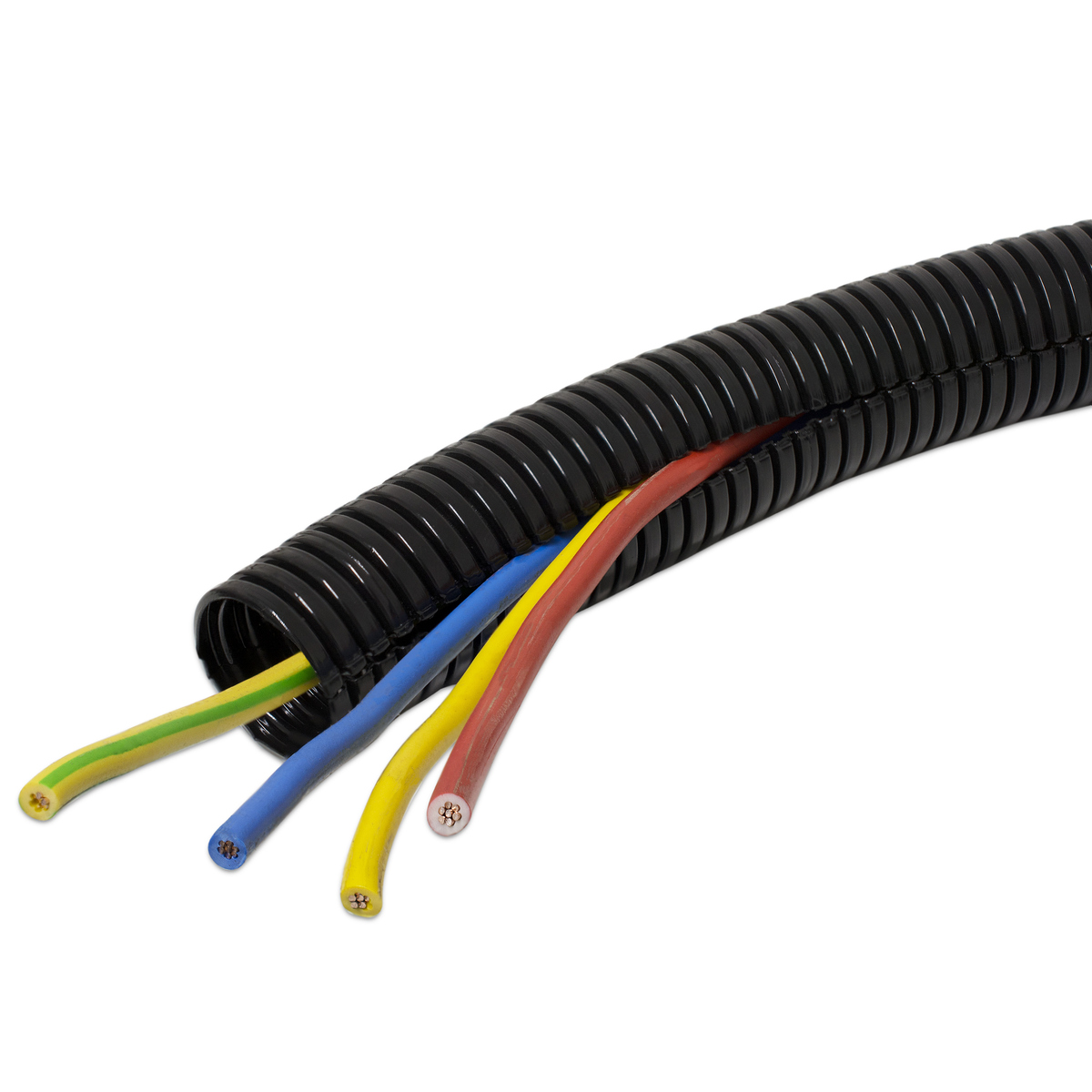
Maximum Number of Romex Wires Allowed in Conduit
The maximum number of Romex wires that can be safely installed in conduit depends on several factors, including the size of the conduit, the type of conduit being used, the size of the Romex wires, and the applicable building codes. Here are some general guidelines to consider:
- Conduit Size: Conduits come in various sizes, ranging from 1/2 inch to 6 inches or larger. The size of the conduit will determine how many wires it can accommodate. Building codes provide specific guidelines on conduit fill ratios, which determine the maximum allowable percentage of the conduit’s cross-sectional area that can be occupied by the wires. The fill ratio must be calculated based on the size of the conduit and the size of the Romex wires being used.
- Wire Size: Romex wires come in different gauge sizes, with each gauge having a different diameter. The larger the gauge number, the smaller the wire diameter. The size of the Romex wires will affect how many can be safely installed in a given conduit size. Smaller gauge wires take up less space, allowing more wires to be installed in the conduit.
- Conduit Type: The type of conduit being used can also impact the number of Romex wires that can be installed. Flexible conduits, such as flexible non-metallic conduits (FNMC) or liquid-tight flexible conduits, tend to have more available space compared to rigid metallic conduits. The flexibility of the conduit allows for easier installation of multiple wires.
- Code Requirements: It is crucial to consult the local electrical codes applicable to your area. Building codes often specify the maximum conduit fill ratios that must be followed to ensure the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. These codes provide guidelines on how to calculate the maximum number of wires allowed based on the conduit size and type, as well as wire size.
Calculating the maximum number of Romex wires allowed in conduit requires a careful assessment of these factors and adherence to the applicable building codes. Keep in mind that exceeding the recommended conduit fill ratios can lead to overheating, increased resistance, and potential damage to the wires and insulation.
It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified electrician or refer to specific regulations in your jurisdiction to ensure compliance with local codes and standards. A professional can accurately determine the maximum number of Romex wires that can be safely installed in your specific situation, taking into account the specific conduit size, wire size, and other relevant factors.
By following the guidelines and regulations, you can ensure a secure and efficient installation, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and maintaining the integrity of your electrical system.
Conduit Fill Calculations
Conduit fill calculations are a crucial step in determining the maximum number of Romex wires that are allowed to be installed in a conduit. These calculations ensure that the wires are not overly crowded, which could lead to safety hazards such as overheating or insulation damage. Here are the key steps involved in conduit fill calculations:
- Determine Conduit Size: Measure the inner diameter of the conduit or refer to the conduit size designation (e.g., 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch) to determine the conduit size for the calculation.
- Identify Wire Sizes: Determine the sizes (gauges) of the Romex wires that will be installed in the conduit. Wire gauges are typically marked on the cable jacket or can be measured using a wire gauge stripping tool.
- Refer to Conduit Fill Chart: Consult a conduit fill chart or the appropriate section of the local electrical code to determine the maximum allowable fill ratio based on the conduit size and the wire sizes being used. The fill ratio is expressed as a percentage and represents the maximum amount of the conduit’s cross-sectional area that can be occupied by the wires.
- Calculate the Fill Ratio: To calculate the fill ratio, divide the total cross-sectional area occupied by the Romex wires by the cross-sectional area of the conduit. Multiply the result by 100 to obtain the fill ratio percentage. Make sure to account for the insulation within the wires in your calculations.
- Compare to Maximum Allowable Fill Ratio: Compare the calculated fill ratio to the maximum allowable fill ratio specified in the conduit fill chart or local electrical code. If the calculated fill ratio exceeds the maximum allowable fill ratio, you will need to either reduce the number of wires or increase the conduit size to accommodate the wires properly.
It’s important to note that conduit fill calculations can vary depending on local codes and specific installations. Some factors, such as the type of conduit being used and the presence of other conductors, may require additional considerations in the calculations.
When performing conduit fill calculations, ensure accuracy by using the appropriate charts, consulting local electrical codes, and seeking guidance from a qualified electrician if necessary. Keeping the conduit fill ratio within the recommended limits will help maintain proper airflow, prevent insulation damage, and ensure the safety and performance of the electrical system.
Remember, safety should always be the top priority when working with electrical systems. Incorrect conduit fill can pose serious risks, so take the time to calculate and adhere to the appropriate fill ratios for your specific installation.
Consequences of Overfilling Conduit
Overfilling conduit, or exceeding the recommended conduit fill ratios, can have several negative consequences that compromise the safety and functionality of the electrical system. Here are some of the potential consequences of overfilling conduit:
- Overheating: When a conduit is overfilled, the wires inside can generate more heat, leading to overheating. Excessive heat can damage the insulation on the wires, increase resistance, and potentially cause short circuits or electrical fires.
- Reduced Airflow: Overfilled conduits restrict proper airflow, preventing the dissipation of heat. Without adequate airflow, the wires may not cool down, leading to heat buildup and potential damage to the insulation and wire conductors.
- Insulation Damage: Overfilling conduit can put excessive pressure and stress on the wires, potentially causing insulation damage. Damaged insulation increases the risk of electrical faults, short circuits, and the potential for shocks or electrocution.
- Difficulty Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Overfilled conduits make it challenging to identify and isolate specific wires or troubleshoot electrical issues. It becomes more difficult to access or remove wires for maintenance or repair purposes, potentially leading to increased costs and time spent on resolving electrical problems.
- Non-compliance with Building Codes: Building codes exist to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Overfilling conduit violates these codes and regulations, which can result in legal ramifications and may void insurance coverage. It is important to adhere to the specified conduit fill ratios to maintain compliance with local codes.
To prevent these negative consequences, it is essential to carefully calculate and adhere to the recommended conduit fill ratios specified in the local electrical codes. These ratios are designed to ensure proper spacing, airflow, and heat dissipation within the conduit, minimizing the risks associated with overfilling.
Remember that the conduit fill calculations should include considerations for the size of the conduit, the wire sizes, and any other conductors present. If the calculated fill ratio exceeds the recommended limits, adjustments should be made by either reducing the number of wires or increasing the conduit size.
By properly managing conduit fill and avoiding overfilling, you can mitigate the risks of overheating, insulation damage, and other potential hazards. This will help maintain the longevity, safety, and performance of your electrical system.
Important Safety Precautions
When working with Romex wires and conduit, it’s essential to prioritize safety to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries. Here are some important safety precautions to follow:
- Turn Off Power: Before starting any work on your electrical system, always turn off the power supply to the area where you will be working. This ensures that you won’t come into contact with live wires and reduces the risk of electric shock.
- Wear Protective Gear: When working with electrical wiring, wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves, safety glasses, and work boots. This protects you from sharp edges, electrical shocks, and other potential hazards.
- Use the Right Tools: Ensure you have the correct tools for the job. Working with Romex wires and conduit may require wire strippers, conduit benders, and other specialized tools. Using the right tools helps prevent accidents, damage to the wires, and ensures proper installation.
- Follow Building Codes and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local building codes and electrical regulations before starting any electrical work. Adhere to these guidelines to ensure the safety and compliance of your electrical installations.
- Properly Size Conduit: Select the appropriate conduit size based on the number and size of the Romex wires. Using a conduit that is too small can lead to overfilling and potential hazards. It is recommended to consult a professional or refer to conduit fill charts for proper size selection.
- Avoid Overfilling Conduit: Carefully calculate the conduit fill ratio to avoid overfilling. Overfilled conduits can lead to overheating, wire insulation damage, and other safety issues. Adhere to the recommended fill ratios specified in local electrical codes.
- Secure and Fasten Wires: Ensure that the Romex wires are properly secured and fastened within the conduit. Loose or improperly secured wires can cause electrical shorts, damage to the insulation, and potential safety hazards. Use appropriate clips, straps, or clamps to secure the wires in place.
- Hire a Qualified Electrician: If you are uncertain or uncomfortable with any aspect of your electrical project, it is always best to consult a qualified electrician. Professional electricians have the knowledge, expertise, and experience to carry out electrical installations safely and effectively.
Remember that electricity can be extremely dangerous, and even small mistakes can have serious consequences. By following these safety precautions and exercising caution, you can protect yourself, your property, and ensure the longevity and safety of your electrical system.
If you encounter any unexpected issues or are unsure about any part of the installation process, it is always best to seek professional advice from a licensed electrician.
Read more: How Many 8 AWG Wires In 1 Inch Conduit
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between Romex wire and conduit is essential for safe and effective electrical installations. Romex wire provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for residential wiring projects, while conduit offers protection and organization for the wires. By considering factors such as conduit size, wire size, and adhering to local building codes, you can determine the maximum number of Romex wires allowed in conduit.
Conduit fill calculations play a crucial role in ensuring that the wires are properly spaced within the conduit, allowing for adequate airflow and preventing overheating. Overfilling conduit can lead to serious consequences, including insulation damage, increased resistance, and potential safety hazards. It is important to abide by the recommended conduit fill ratios and consult local codes to ensure compliance and safety.
Throughout the installation process, it is vital to follow important safety precautions. This includes wearing appropriate protective gear, turning off power, using the right tools, and properly securing the wires within the conduit. However, if you are unsure or uncomfortable with any aspect of your electrical project, it is always advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician to ensure a safe and successful installation.
By understanding the purpose of using conduit, calculating conduit fill, and implementing necessary safety measures, you can ensure the functionality, integrity, and safety of your electrical system. Properly installed Romex wires in conduit provide a reliable and efficient electrical solution for residential applications.
Remember, electrical work should be approached with caution and knowledge. Following best practices and guidelines will not only protect you and your property but also ensure that your electrical installations pass inspections and comply with building codes.
Ultimately, by combining proper planning, adherence to regulations, and a focus on safety, you can confidently tackle your electrical wiring projects using Romex wire and conduit, knowing that the end result will be a reliable and secure electrical system in your home.
Curious about taking your DIY electrical skills further? Dive into our guide on how to run overhead electrical wire to garage, perfect for those planning to power up their garage with overhead lines. If you're aiming to tidy up those wires, our article on how to install conduit in wall offers practical steps for embedding conduits seamlessly within your walls. Both pieces are packed with easy-to-follow advice and essential safety tips to help you upgrade your home's electrical setups confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Romex Wires In Conduit
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “How Many Romex Wires In Conduit”