

Articles
Why Does An Extension Cord Get Hot
Modified: August 27, 2024
Discover why extension cords can get hot and learn how to prevent dangerous overheating. Read our informative articles on extension cord safety.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
An extension cord is a convenient and versatile tool that allows us to power devices and appliances in areas where the electrical outlets are not easily accessible. Whether it’s in your workshop, backyard, or during outdoor activities, extension cords have become a common part of our daily lives.
However, have you ever noticed that after prolonged use, an extension cord can get quite hot? This phenomenon might leave you wondering why it happens and whether it poses any safety risks.
In this article, we will dive into the reasons why an extension cord gets hot and explore the various factors that contribute to this phenomenon. Understanding the underlying causes can help you prevent overheating issues and ensure the safe and efficient use of extension cords.
So, let’s unravel the mystery of why an extension cord gets hot!
Key Takeaways:
- Extension cords get hot due to resistance, overloading, length, gauge, poor connections, and insulation quality. Understanding these factors and taking precautions can prevent overheating and ensure safe use.
- Overloading an extension cord with excessive current can lead to overheating, potentially causing damage or fire hazards. Choosing the right cord, inspecting for damage, and prioritizing safety are crucial for safe use.
Read more: Why Would An Electrical Cord Get Hot
Understanding Extension Cords
Before we delve into the reasons behind the heat generated by extension cords, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of how they work. An extension cord is essentially a flexible electrical cable that allows electrical current to flow from the power source to your devices or appliances.
Extension cords are designed with a male plug on one end, which connects to the power outlet, and one or multiple female sockets on the other end, where you can plug in your devices. The length of the cord can vary, providing flexibility and the ability to reach areas that are a distance away from the power source.
Extension cords are typically made up of three conductors, each enclosed in its own insulation. These conductors include a live (hot) wire, a neutral wire, and a ground wire. The live wire carries the current from the power source to your devices, while the neutral wire provides the return path for the current. The ground wire, on the other hand, is a safety feature that provides an alternate path for electricity to dissipate in case of a fault.
It’s important to note that extension cords come in various types and sizes, each with its own specific purpose and limitations. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of different types of extension cords can help prevent overheating and potential safety hazards.
Now that we have a basic understanding of extension cords, let’s explore the factors that can contribute to the heat generated by these cords.
Factors Affecting Extension Cord Temperature
There are several factors that can contribute to the temperature rise in an extension cord during use. It’s important to be aware of these factors to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your extension cords. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key factors:
- Resistance: Extension cords have a certain level of electrical resistance due to the conductive material used in their construction. When current flows through the cord, it encounters resistance, which results in the generation of heat. The resistance increases with the length of the cord and the gauge (thickness) of the wires used. Higher resistance means more heat produced.
- Overloading: Overloading an extension cord by plugging in devices or appliances that draw more current than the cord is rated for can cause excessive heat buildup. The cord may not be able to handle the power demands, leading to overheating and potential damage.
- Length and Gauge: As mentioned earlier, the length and gauge of an extension cord can influence its temperature. Longer cords have higher resistance, leading to more heat generation. Additionally, using a thinner gauge (higher AWG number) cord for high-power devices can cause increased resistance and heat buildup.
- Poor Connections: Loose or damaged connections between the extension cord plugs and the power outlet or the devices being powered can result in resistance and heat buildup. It’s important to ensure proper and secure connections to minimize overheating risks.
- Insulation Quality: The insulation material used in the construction of an extension cord plays a crucial role in heat dissipation. High-quality insulation helps in dissipating the generated heat effectively, reducing the chances of overheating. Damaged or worn-out insulation can hinder heat dissipation and increase the temperature of the cord.
By understanding these factors and taking necessary precautions, you can minimize the risk of overheating and ensure the safe and efficient use of your extension cords. In the next sections, we will further explore the concepts of resistance and overheating, as well as discuss measures to prevent heat-related issues.
Resistance and Joule Heating
One of the fundamental principles behind the heat generation in extension cords is the concept of resistance and Joule heating. In simple terms, resistance refers to the opposition that electrical current encounters as it flows through a conductor like a wire.
When electric current passes through an extension cord, it encounters resistance due to the properties of the cord’s conductive material. This resistance causes a portion of the electrical energy to be converted into heat energy. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating, named after the physicist James Prescott Joule, who first discovered this relationship between resistance and heat.
According to Joule’s law, the heat generated (H) in a conductor is directly proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor, the current (I) flowing through it, and the time (t) during which the current flows. Mathematically, this relationship is expressed as:
H = I^2 * R * t
This equation shows us that the heat produced is dependent on the square of the current passing through the conductor, meaning that even a small increase in current can lead to a significant rise in heat generation.
Extension cords with higher resistance, such as longer cords or those with thinner gauge wires, will generate more heat due to the increased opposition to the current flow. This heat can accumulate over time, potentially leading to excessive temperatures and safety risks.
It’s important to understand that exceeding the recommended current capacity of an extension cord, also known as overloading, can significantly increase the resistance and heat production. Overloading the cord with appliances or devices that draw more power than the cord can handle can cause it to overheat, potentially resulting in damage to the cord or even electrical fires.
Now that we have explored the concept of resistance and Joule heating, let’s move on to understanding the relationship between overloading and extension cord overheating.
Overloading and Overheating
Overloading an extension cord is a common cause of overheating. When you plug in devices or appliances that draw more current than the cord is designed to handle, it puts a strain on the cord and can lead to excessive heat buildup.
Each extension cord has a maximum current rating, commonly referred to as its ampacity. This rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current that the cord can safely carry without overheating. Exceeding this current capacity can cause the cord to overheat and potentially lead to dangerous situations.
Overloading can occur in different ways. It could be caused by plugging too many high-power devices into the cord, exceeding the rated wattage of the cord, or daisy-chaining multiple cords together to reach a distant power source.
When a cord is overloaded, the increased current flowing through it encounters higher resistance, leading to more heat generation. Additionally, the excess heat can also cause the cord’s insulation to deteriorate, further increasing the risk of overheating and potential electrical hazards.
To prevent overloading and overheating, it is crucial to assess the power requirements of the devices you are connecting to the extension cord. Make sure that the total wattage of all the devices does not exceed the maximum wattage capacity of the cord.
If you find that you frequently need to power multiple high-power devices, it may be beneficial to use a heavy-duty extension cord with a higher ampacity. These cords are designed to handle larger electrical loads and are less prone to overheating.
A general rule of thumb is to avoid using extension cords as a permanent power solution for high-power devices. If you have devices or appliances that require a substantial amount of power, it is better to have dedicated wiring installed to support their needs.
By being mindful of the power requirements of your devices and avoiding overloading, you can significantly reduce the risk of overheating and ensure the safe use of your extension cords.
Next, let’s explore the impact of the length and gauge of extension cords on their temperature.
Make sure to use the right gauge extension cord for the job. Using a cord with a lower gauge number (thicker wire) can help reduce heat buildup.
Length and Gauge of Extension Cords
The length and gauge of an extension cord are two crucial factors that can impact its temperature during use. It’s essential to understand how these factors can contribute to overheating and make informed decisions when choosing the right extension cord for your needs.
Length: One of the primary factors affecting the temperature of an extension cord is its length. As the length of the cord increases, so does its electrical resistance. This increased resistance leads to more heat generation as the current passes through the cord.
Longer extension cords can experience a more significant temperature rise due to the higher resistance. Consequently, it’s important to choose the appropriate cord length to minimize the risk of overheating. Avoid using unnecessarily long cords when a shorter one would suffice, as this can help reduce resistance and mitigate heat buildup.
Gauge: The gauge, or thickness, of the wires within an extension cord also plays a role in the cord’s temperature. Extension cords are available in different gauges, typically measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG) numbers. A lower AWG number indicates a thicker wire and a lower resistance, while a higher AWG number represents a thinner wire and higher resistance.
Thicker gauge wires have lower resistance, resulting in less heat generated as the current flows through the cord. They are better suited for carrying higher currents without significant temperature increase. On the other hand, thinner gauge cords have higher resistance, leading to more heat dissipation and a greater risk of overheating when used with high-power devices.
When selecting an extension cord, consider the power requirements and the distance from the power source to your devices. Using a thicker gauge cord for longer distances or high-power devices can help minimize resistance and reduce the risk of excessive heat buildup.
It’s important to note that the maximum recommended length for extension cords may vary based on the gauge and ampacity of the cord. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and follow proper safety practices to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating.
By selecting the appropriate cord length and gauge based on your specific needs, you can minimize resistance and reduce the chances of your extension cord overheating. In the next section, we will discuss how poor connections can contribute to heat buildup.
Poor Connections and Heat Buildup
Poor connections between the extension cord plugs and the power outlet or the devices being powered can contribute to heat buildup. When the connections are loose or damaged, they create additional resistance in the circuit, which leads to an increase in heat generation.
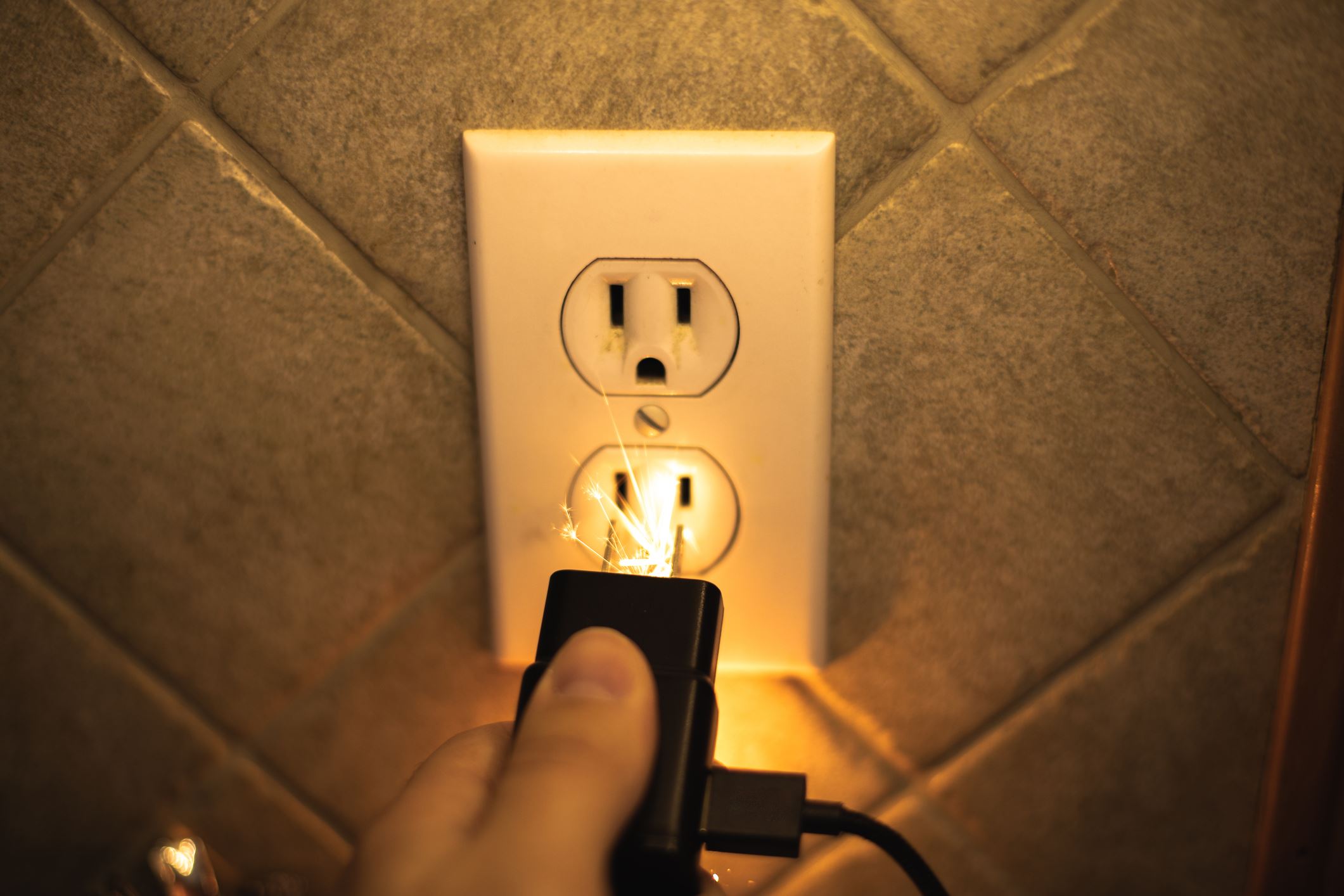
Loose connections can cause gaps between the plug and the socket, resulting in arcing or sparking. These electrical arcing phenomena not only generate heat but also pose a significant fire hazard. Loose connections can occur due to wear and tear, repeated unplugging and plugging, or simply using incompatible plugs and sockets.
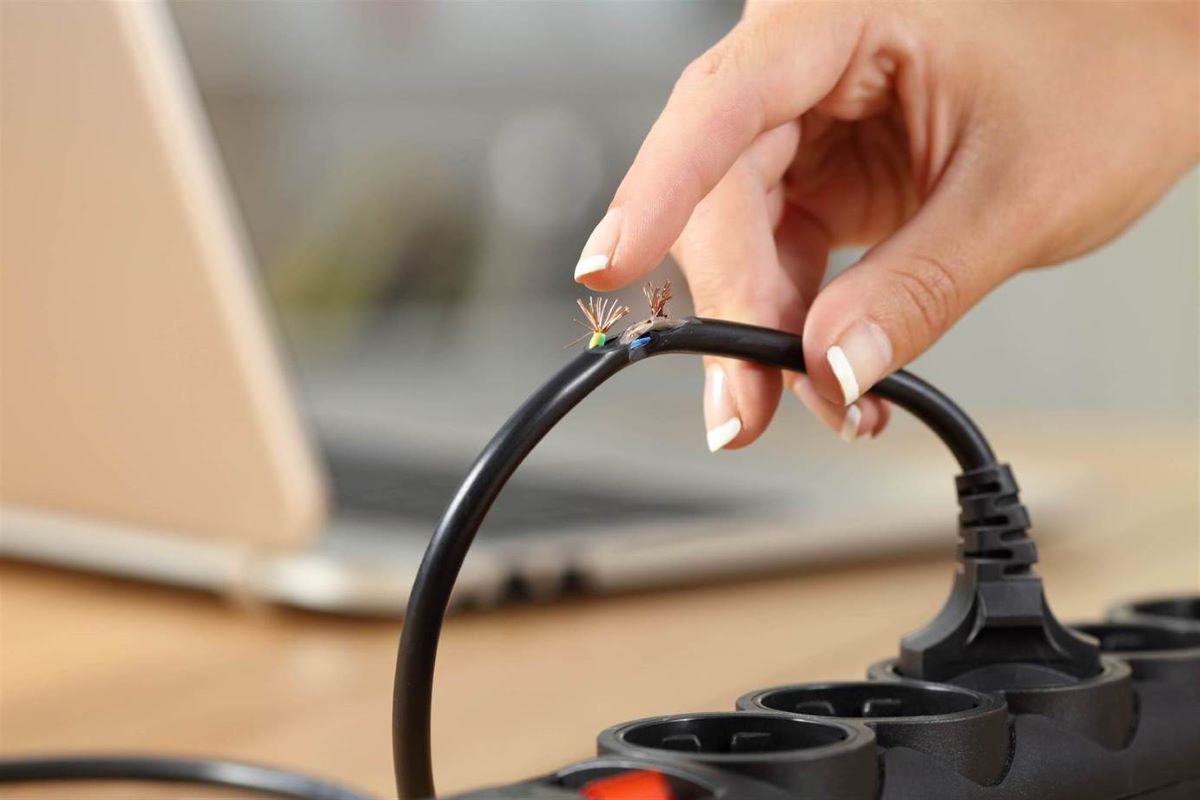
Damaged connections, such as frayed or exposed wires, can also result in increased resistance and heat production. Over time, the heat from these damaged areas can cause further deterioration, leading to potential electrical hazards.
To prevent heat buildup due to poor connections, it’s crucial to ensure proper and secure connections when using extension cords. Follow these tips to maintain safe and reliable connections:
- Inspect the plugs and sockets of your extension cords regularly. Look for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Replace any damaged cords or plugs immediately.
- When plugging in, ensure that the cord is fully inserted into the socket or device. Firmly push and secure the plug to ensure a tight connection.
- Avoid using adapters, multiple plug adaptors, or extension cords within extension cords. These setups can increase the chances of loose connections and create excessive heat buildup.
- Do not overload the sockets or power strips as it can put additional strain on the connections and increase the risk of overheating. Spread the load evenly across different outlets if needed.
By maintaining secure and proper connections, you can minimize resistance and prevent heat buildup. This not only ensures the safe operation of your extension cords but also reduces the risk of electrical hazards.
Now, let’s explore the role of insulation quality in heat dissipation and its impact on extension cord temperature.
Insulation Quality and Heat Dissipation
The insulation material used in the construction of an extension cord plays a crucial role in heat dissipation. High-quality insulation not only protects the wires from damage but also helps in effectively dissipating the heat generated during electrical operation.
The insulation surrounding the wires acts as a barrier, preventing direct contact between the conductors and other external objects. This insulation material is designed to have good thermal resistance, meaning it can withstand high temperatures without melting or degrading.
When an extension cord is in use, heat is generated due to resistance in the wires. The insulation around the wires helps to contain and dissipate this heat, preventing it from building up excessively. High-quality insulation provides better thermal properties, allowing for efficient heat dissipation.
If the insulation quality is compromised, such as due to wear and tear, damage, or improper manufacturing, it can hinder the heat dissipation process. This can lead to the insulation overheating and potentially causing the cord to fail or even result in electrical fires.
When purchasing an extension cord, it’s important to choose one with high-quality insulation. Look for cords that are certified by recognized safety organizations and comply with relevant safety standards. These cords are designed and tested to ensure proper insulation quality and heat dissipation capabilities.
Additionally, proper care and maintenance of the extension cords can help maintain the insulation effectiveness. Regularly inspect the cord for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frayed wires, or exposed insulation. Replace or repair any damaged cords to ensure the safety and reliability of the insulation.
It’s also important to avoid excessive bending or twisting of the cords, as this can damage the insulation and compromise its ability to dissipate heat effectively. Store the cords properly by coiling them loosely to prevent kinks or stress on the insulation.
By choosing extension cords with high-quality insulation and properly maintaining them, you can ensure efficient heat dissipation and reduce the risk of overheating and associated hazards.
In the next section, we will discuss important safety concerns and prevention strategies related to extension cord overheating.
Safety Concerns and Prevention
Extension cord overheating can pose significant safety risks if not addressed promptly. To ensure the safe and efficient use of extension cords, it’s crucial to be aware of the following safety concerns and implement appropriate preventative measures:
Fire Hazards: Overheating extension cords can potentially lead to electrical fires. The heat generated can ignite flammable materials or cause the cord’s insulation to melt, exposing the live wires. It’s essential to monitor the temperature of the cord and take immediate action if you notice excessive heat or burning smells.
Frequent Circuit Tripping: If your extension cord frequently causes circuit breakers to trip or fuses to blow, it’s a clear indication that the cord is overloaded or experiencing significant heat buildup. Continuing to use an overloaded cord can lead to electrical damage and pose safety risks.
Electrical Shocks: Overheating cords may increase the chances of electrical shocks, especially if the insulation is compromised or damaged. Exposure to live wires can result in serious injury or even fatality. It is crucial to replace damaged cords and avoid using them until they are repaired or replaced.
To prevent these safety concerns and maintain the longevity of your extension cords, consider the following prevention strategies:
- Choose the Right Cord: Select an extension cord with the appropriate ampacity and gauge for your specific needs. Ensure that it can handle the power requirements of the devices you are connecting, and avoid using cords that are undersized or damaged.
- Avoid Overloading: Never exceed the maximum current capacity of the extension cord. Distribute electrical loads across multiple cords or outlets if necessary. If you frequently need to power high-power devices, consider installing dedicated circuits to support them.
- Regular Inspection: Routinely inspect your extension cords for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Replace or repair damaged cords immediately to prevent overheating and potential hazards.
- Proper Storage: Coiling the cords loosely when not in use and avoiding kinks or twists can help prevent damage to the insulation. Store the cords in a cool and dry place to maintain their integrity.
- Safety Awareness: Educate yourself and others about the safe use of extension cords. Avoid running cords under rugs or carpets, through doorways, or in high-traffic areas where they can be tripped over or damaged.
By implementing these safety measures and being vigilant about the condition and usage of your extension cords, you can mitigate the risk of overheating and ensure a safe electrical environment.
Remember, ensuring electrical safety is paramount, and taking proactive steps to prevent extension cord overheating is crucial to protect both yourself and your property.
Now, let’s wrap up our discussion.
Read more: What To Do If Extension Cord Gets Wet
Conclusion
An extension cord is a valuable tool that allows us to access electrical power in various settings, but it’s important to be aware of the factors that can lead to overheating. Understanding the causes behind extension cord temperature rise can help us prevent potential safety hazards and ensure efficient operation.
We explored the factors that contribute to extension cord heat, including resistance, overloading, length and gauge, poor connections, and insulation quality. Resistance and the resulting Joule heating play a significant role in generating heat within the cord. Overloading the cord with excessive current can cause it to overheat, potentially leading to damage or fire hazards. The length and gauge of the cord also influence its temperature, with longer cords and thinner gauge wires producing more heat. Poor connections can increase resistance and heat buildup, while high-quality insulation aids in effective heat dissipation.
To ensure safety, it’s crucial to choose the right cord for your needs, consider the power requirements of your devices, and avoid overloading the cord. Regularly inspecting the cord for damage, securing proper connections, and storing it correctly can also prevent overheating. Being mindful of these safety concerns and implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of fires, electric shocks, and other hazards.
Always prioritize electrical safety and make informed decisions when using extension cords. If you notice excessive heat, burning smells, or other signs of overheating, immediately disconnect the cord and seek professional assistance.
By understanding the factors affecting extension cord temperature and taking necessary precautions, you can confidently and safely use extension cords to power your devices and appliances in various environments.
Remember, proper care and attention are essential for the reliable and efficient operation of extension cords. Stay informed, be cautious, and prioritize safety for a secure electrical setup.
Curious about how long you can safely use an extension cord before needing a break? Or maybe you're wondering which electrical cord battles more resistance? Our next articles cover these intriguing topics in detail. While managing extension cord usage effectively ensures safety and efficiency, understanding electrical resistance in different cords can help optimize your home setup. Dive into these reads to keep your home running smoothly without a hitch.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Does An Extension Cord Get Hot
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Why Does An Extension Cord Get Hot”