

Articles
How To Read Electrical Wire Numbers
Modified: January 6, 2024
Learn how to read electrical wire numbers with our informative articles. Get expert tips and guidance to understand wiring codes and markings.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of electrical wiring! Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, understanding electrical wire numbers is essential. Electrical wire numbers serve as a universal language in the electrical industry, allowing electricians to identify and work with different types of wires with ease.
In this article, we will explore the significance of electrical wire numbers and how they are used to ensure safe and efficient electrical installations. We will delve into the different types of wire numbers, explain how to interpret them, and demonstrate how to read wire numbers on electrical diagrams.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of electrical wire numbers and be well-equipped to confidently navigate the world of electrical wiring.
So, let’s jump right in and demystify electrical wire numbers!
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding electrical wire numbers is crucial for safe and efficient electrical installations. By decoding wire numbers, electricians can select the right wires, ensure proper connections, and maintain reliable electrical systems.
- Reading wire numbers on diagrams is essential for understanding electrical system layouts. By tracing wire connections and understanding their functions, professionals can troubleshoot effectively and ensure proper wiring.
Read more: How To Read A Metric Electrical Cord Numbers
Understanding Electrical Wire Numbers
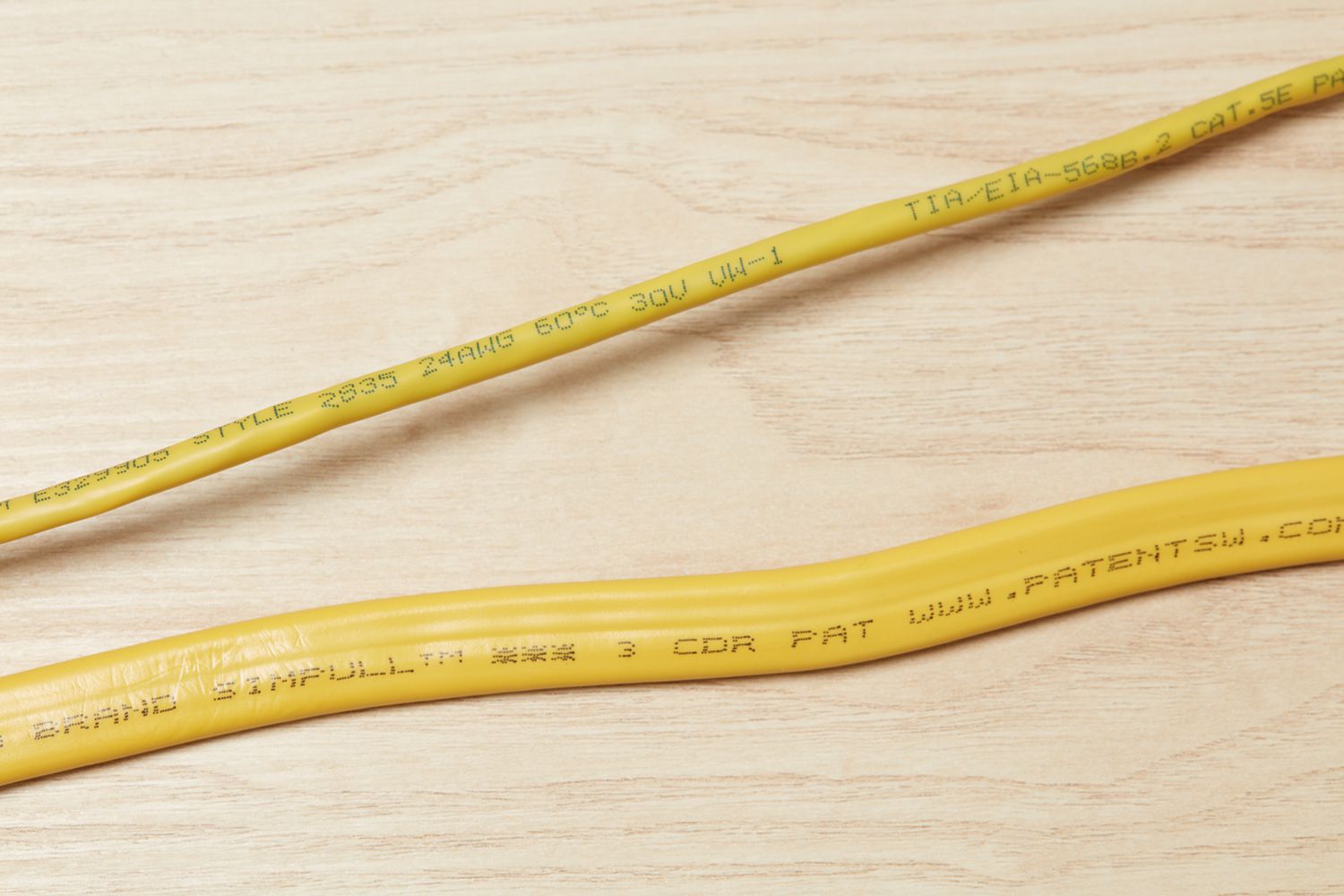
Electrical wire numbers are alphanumeric labels that are assigned to different types of wires used in electrical installations. These wire numbers provide vital information about the characteristics and purpose of each wire, making it easier to identify and work with them correctly.
Wire numbers consist of a combination of letters, numbers, or both, which represent specific attributes of the wire. They typically follow a standardized format established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) or the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
One of the most common systems used in North America is the NEMA standard, which assigns a unique number to each type of wire. The wire numbers provide information about the wire’s functionality, voltage rating, insulation type, and other essential characteristics.
By understanding these wire numbers, electricians can select the appropriate wire for a given application, ensure proper installations, and maintain a safe and reliable electrical system.
It’s important to note that wire numbers may vary depending on the specific industry or region. However, the fundamentals and principles behind these wire numbers remain relatively consistent.
Now that we have a basic understanding of electrical wire numbers, let’s dive into the different types of wire numbers you are likely to encounter.
Different Types of Wire Numbers
Electrical wire numbers can vary based on the specific application and industry. Here are some common types of wire numbers you may come across:
- Conductor Size: In many wire numbering systems, the size of the conductor is indicated by a numerical value. For example, a wire labeled as “14” indicates a 14-gauge wire, which has a specific diameter and carrying capacity. The larger the number, the smaller the wire size.
- Voltage Rating: Wire numbers may also indicate the voltage rating of the wire. This information is crucial to ensure that the wire can handle the electrical load without risk of overheating or damage. For instance, a wire labeled as “600V” is suitable for applications with a voltage of up to 600 volts.
- Insulation Type: Different insulation materials are used based on the environmental conditions and specific applications. Wire numbers may include a letter code that represents the type of insulation used. For example, “THHN” denotes a thermoplastic high-heat-resistant nylon-coated wire.
- Functionality: Wire numbers can also indicate the specific function of the wire within an electrical system. For instance, “G” may represent a ground wire, “X” could indicate a switch leg, and “T” might signify a traveler wire in a three-way switch configuration.
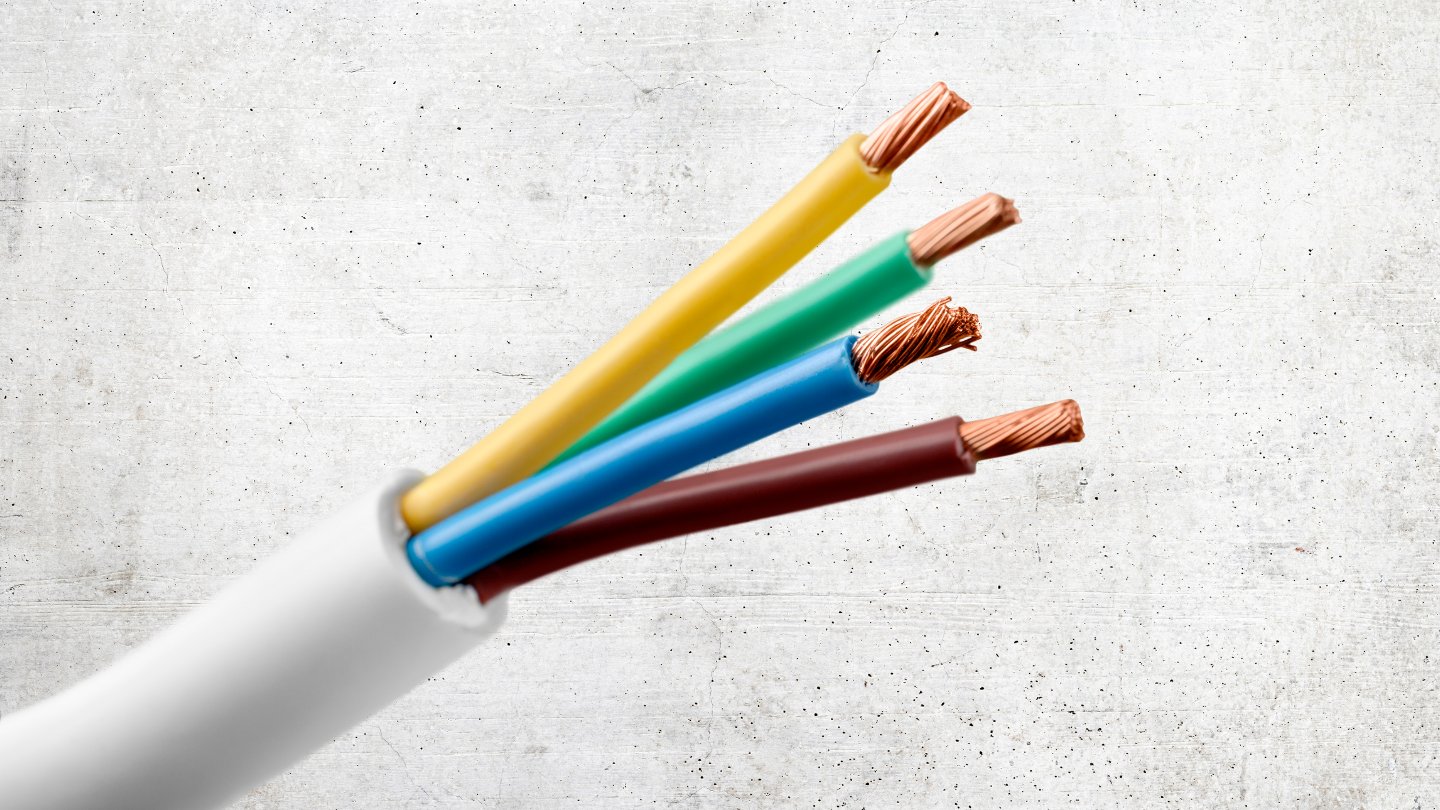
- Color Coding: In addition to numbers and letters, wire colors are often used as an additional means of identification. Different colors are assigned to wires based on their purpose or voltage level, following industry-standard color-coding practices.
Understanding these different types of wire numbers is essential for correctly selecting and installing electrical wires. It ensures proper functionality, compatibility, and compliance with safety standards.
Next, let’s explore how to interpret wire numbers and what they signify in electrical installations.
When reading electrical wire numbers, remember that the numbers indicate the wire gauge and the number of conductors. For example, 14/2 indicates a 14-gauge wire with 2 conductors.
Interpreting Wire Numbers
Interpreting wire numbers is crucial for understanding the characteristics and purpose of each wire in an electrical installation. By deciphering wire numbers, electricians can determine the appropriate wire for a specific application and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the electrical system.
Here are some key steps to interpret wire numbers:
- Referencing Wire Numbering Standards: Start by familiarizing yourself with the wire numbering standards specific to your region or industry. This could be the NEMA standard, IEC standard, or any other applicable standard. Understanding the format and conventions used in the wire numbering system will help you interpret the wire numbers accurately.
- Decoding the Numbers and Letters: Break down the wire number into its individual components (numbers and letters) and interpret their meanings based on the standards. For example, if a wire number is “14-2”, the “14” indicates the wire gauge size, and the “2” represents the number of conductors within the cable.
- Identifying Voltage Ratings: Look for any voltage rating information included in the wire number. This will indicate the maximum voltage that the wire can safely handle. It is crucial to select wires with voltage ratings appropriate for the electrical system they are being installed in.
- Understanding Insulation Types: Pay attention to any letters or codes in the wire number that represent the insulation type. Different insulation materials have varying properties, such as temperature resistance and flexibility, that make them suitable for specific applications.
- Consider Wire Color Coding: If wire colors are used alongside wire numbers, familiarize yourself with the color codes. Different colors may signify distinct functions or voltage levels. Ensure that the wire color aligns with its designated purpose.
By following these steps when interpreting wire numbers, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the wires’ characteristics and ensure proper installation in accordance with industry standards.
Next, let’s explore how wire numbers are used in electrical diagrams and how to read them accurately.
Reading Wire Numbers on Diagrams
Electrical diagrams, such as wiring diagrams, schematics, and blueprints, use wire numbers to represent the various wires and connections within an electrical system. Being able to read wire numbers on diagrams is essential for understanding the layout and functionality of the system.
Here are some key points to consider when reading wire numbers on diagrams:
- Locating the Wire Numbers: Locate the wire numbers on the diagram. They are typically adjacent to the lines representing the wires or connected to symbols representing devices or components. The wire numbers may be labeled directly on the diagram or referred to in a legend or key.
- Matching Wire Numbers: Identify the wire numbers on the diagram that correspond to the actual wires you are working with. This involves comparing the numbers on the diagram to the wire labels or marking on the physical wires.
- Following the Flow: Follow the path of the wire numbers on the diagram to understand the flow of electricity and the connections between different devices and components. This will help you visualize how the electrical system is interconnected.
- Identifying Wire Functions: Pay attention to any additional symbols or annotations associated with the wire numbers on the diagram. These may indicate the functionality or purpose of the wire, such as whether it is a power supply, ground, control wire, or signal wire.
- Tracing Wire Connections: Trace the wire numbers on the diagram to determine where they lead and which devices or components they are connected to. This will help you understand the wiring layout and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Reading wire numbers on diagrams requires careful attention to detail and the ability to interpret the diagram symbols and annotations. It is essential to cross-reference the wire numbers with the actual wires and components to ensure accurate identification and proper wiring.
Now that you have a solid understanding of how wire numbers are read on diagrams, let’s summarize what we’ve learned.
Read more: How To Read An Electrical Blueprint
Conclusion
Understanding electrical wire numbers is a fundamental skill for anyone working with electrical systems. Wire numbers provide valuable information about the characteristics and purpose of each wire, allowing for safe and efficient electrical installations. By deciphering wire numbers, electricians can select the appropriate wire for a specific application, ensure proper connections, and maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
In this article, we explored the significance of electrical wire numbers and how they are used in various industries. We discussed the different types of wire numbers, including conductor size, voltage rating, insulation type, functionality, and color coding. These wire numbers serve as a universal language within the electrical field, enabling clear communication and standardization.
We also covered the process of interpreting wire numbers, which involves referencing wire numbering standards, decoding the numbers and letters, identifying voltage ratings and insulation types, and considering wire color coding. This knowledge is crucial for correctly selecting and installing electrical wires based on their intended purpose and specifications.
Furthermore, we delved into the importance of reading wire numbers on diagrams, such as wiring diagrams and schematics. By learning to identify wire numbers on diagrams, trace wire connections, and understand their functions, professionals can effectively troubleshoot electrical systems and ensure proper wiring layouts.
Overall, electrical wire numbers play a vital role in the field of electrical engineering and are essential for maintaining safe and reliable electrical systems. By familiarizing yourself with wire numbering systems, interpreting wire numbers accurately, and reading wire numbers on diagrams, you will be well-equipped to navigate the world of electrical wiring with confidence and expertise.
So go ahead and embrace the world of electrical wire numbers, and may your electrical installations be seamless and successful!
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Read Electrical Wire Numbers
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “How To Read Electrical Wire Numbers”