Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Design Drainage For A House


Architecture & Design
How To Design Drainage For A House
Modified: October 19, 2024
Looking to design drainage for your house? Our architecture design experts can guide you through the process, ensuring proper and effective drainage solutions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Proper drainage is an essential aspect of any well-designed house. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity, longevity, and overall functionality of a building. Without an effective drainage system, a house is susceptible to various problems such as water damage, foundation issues, mold growth, and compromised landscape integrity.
In this article, we will explore the importance of proper drainage design and provide insights into the fundamental principles and components of a drainage system. We will also discuss how to assess a site, plan the drainage system, choose the right components, and install them effectively. Additionally, we will explore surface drainage solutions and provide tips for maintaining and troubleshooting drainage systems.
By comprehensive understanding the importance and intricacies of drainage design, homeowners, architects, and contractors can ensure that a house remains dry, secure, and well-maintained for years to come.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper drainage design is crucial for preventing water damage, protecting the foundation, and maintaining the integrity of the landscape in a well-designed house.
- Choosing the right drainage components, integrating surface drainage solutions, and regular maintenance are essential for ensuring an effective and long-lasting drainage system.
Importance of Proper Drainage Design
Proper drainage design is crucial for a variety of reasons. Let’s explore why it is essential to ensure effective drainage for your house.
1. Prevents Water Damage: One of the primary purposes of a drainage system is to redirect water away from the house. Without proper drainage, rainwater, groundwater, or runoff can accumulate around the foundation, leading to water seepage, cracks, and potential structural damage. Effective drainage design helps mitigate the risk of water damage to your home.
2. Protects Foundation: Excessive moisture around the foundation can cause the soil to swell and contract, leading to shifting and uneven settling of the foundation. This can result in cracks, foundation leaks, and compromised stability. Proper drainage design helps in maintaining a stable foundation, ensuring the longevity and structural integrity of the house.
3. Prevents Basement Flooding: Basement flooding can be a nightmare for homeowners, causing extensive damage to furnishings, appliances, and personal belongings. A well-designed drainage system helps prevent water from entering the basement, protecting it from potential flooding and associated problems.
4. Controls Soil Erosion: Improper drainage can lead to soil erosion in your yard or garden. When water accumulates and does not drain properly, it can wash away the topsoil, resulting in a barren and unattractive landscape. Adequate drainage helps prevent soil erosion, preserving the beauty and functionality of your outdoor space.
5. Prevents Mold and Mildew: Excessive moisture can create a favorable environment for mold and mildew growth. These fungi not only cause unpleasant odors and stains but also pose health risks. Proper drainage design helps in keeping moisture levels in check, minimizing the chances of mold and mildew infestation.
6. Preserves Landscape: Proper drainage is not only vital for the protection of the house but also for maintaining the health and beauty of the surrounding landscape. By preventing water accumulation and saturation, drainage design ensures that plants, trees, and grass receive adequate moisture without drowning or suffering from root rot.
7. Enhances Property Value: A well-designed drainage system is an essential component of a property’s functionality and infrastructure. It adds value to your home, as potential buyers appreciate the peace of mind that comes with knowing the house is protected from water damage and other related issues.
Overall, investing in proper drainage design is a smart choice that not only protects your home from potential damage but also contributes to its long-term sustainability and value.
Understanding the Basics of Drainage Systems
A drainage system is composed of various components that work together to redirect water away from the house and prevent water-related issues. Let’s delve into the basics of drainage systems to gain a better understanding of their functionality.
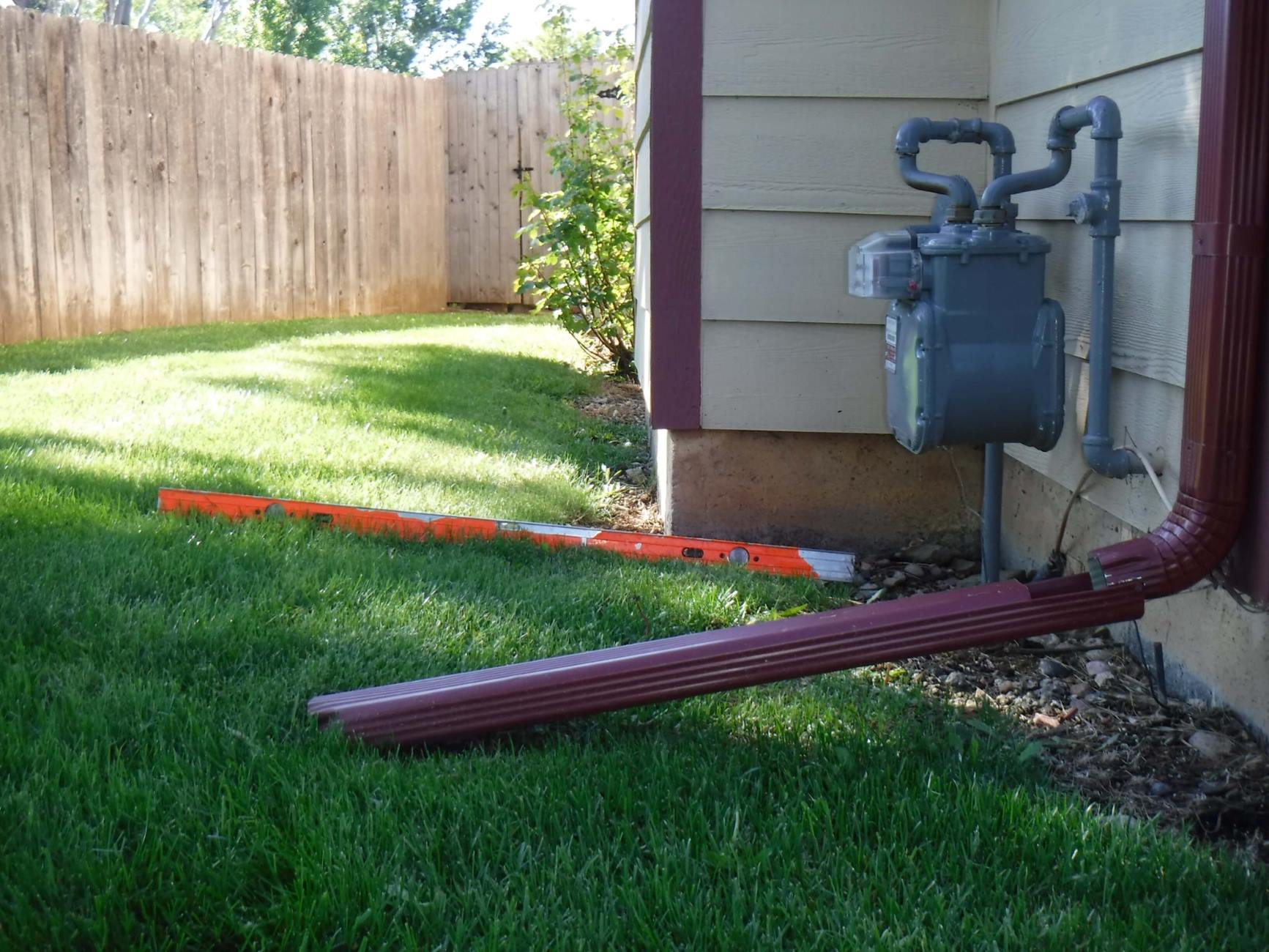
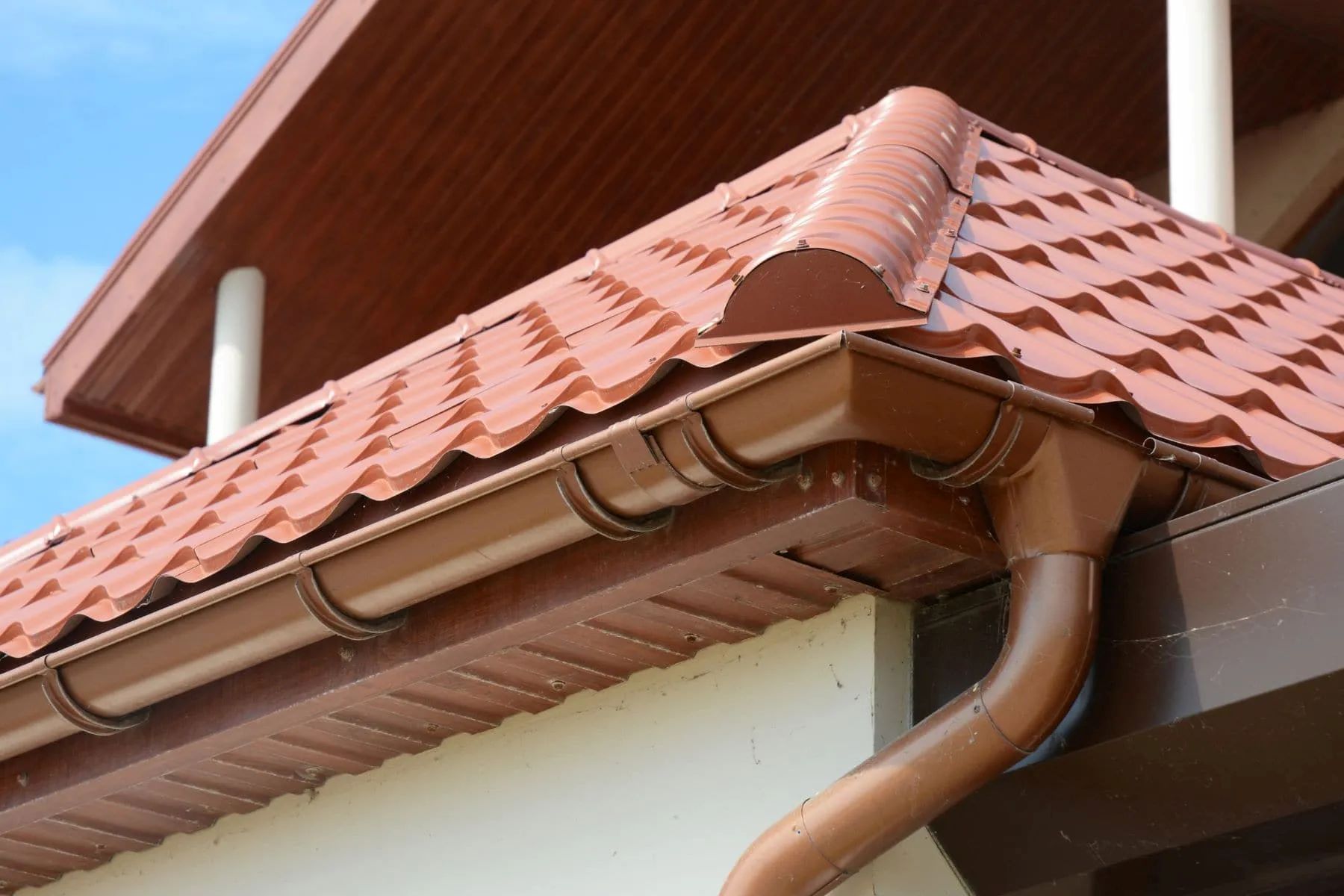
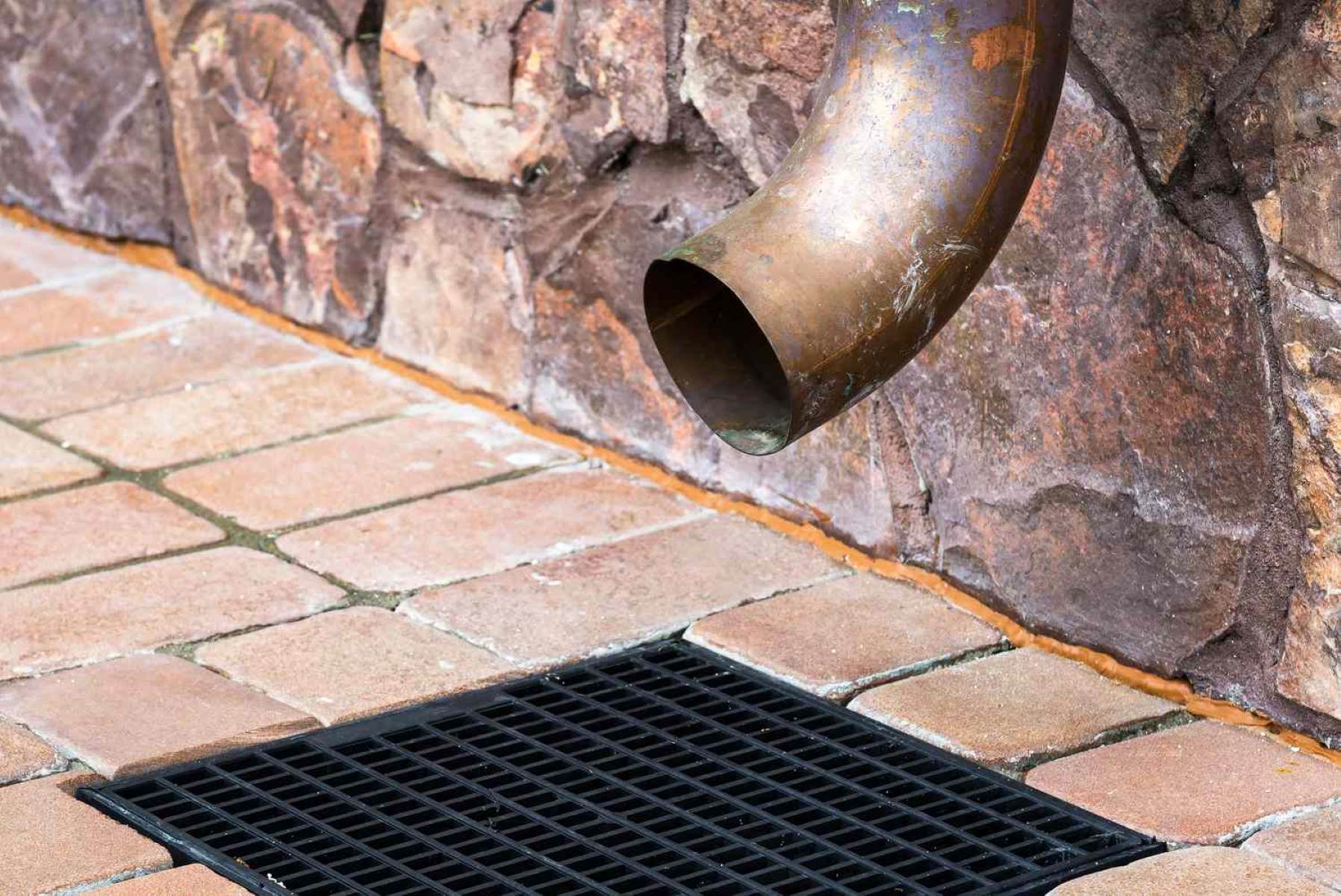
1. Gutters and Downspouts: Gutters are an essential part of a drainage system, collecting rainwater from the roof and directing it towards downspouts. Downspouts then channel the water away from the foundation and into the ground or a drainage system. Regular maintenance of gutters and downspouts is crucial to prevent clogs and ensure proper water flow.
2. Slope and Grading: Proper slope and grading of the land around the house are essential for effective drainage. The ground should be sloped away from the foundation to ensure that water drains away instead of collecting near the house. The ideal slope is usually around 6 inches per 10 feet, but this can vary depending on local regulations and terrain.
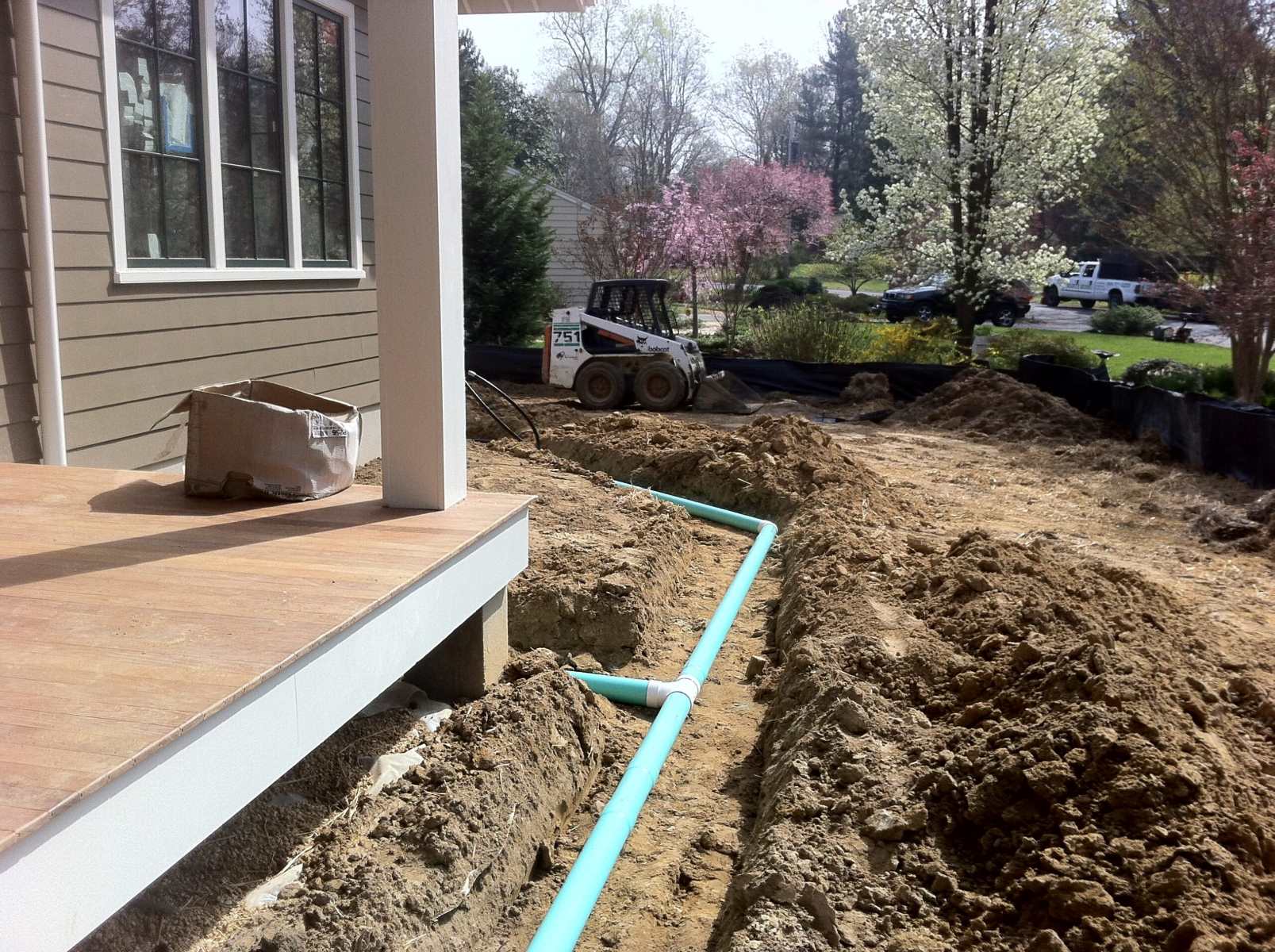
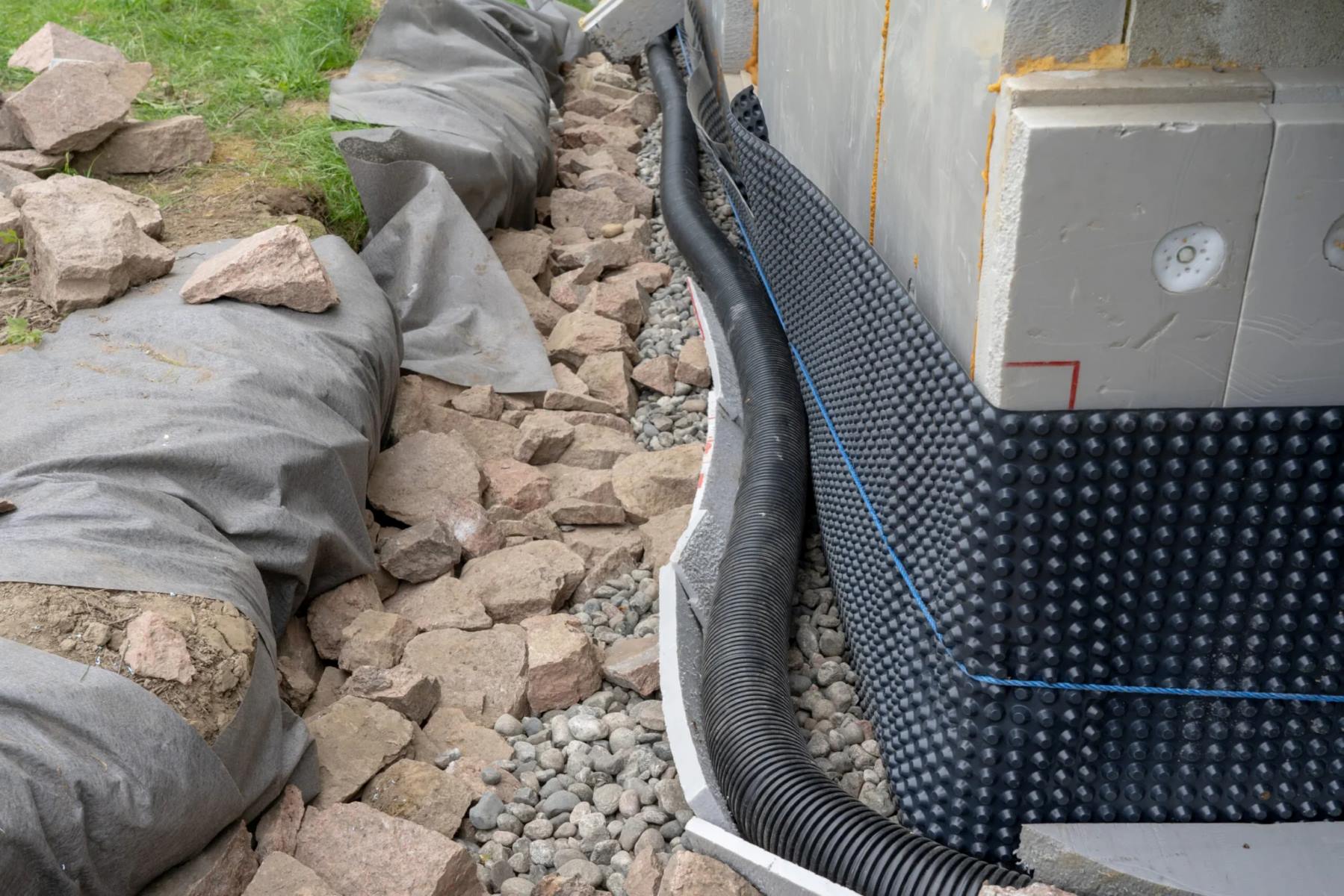
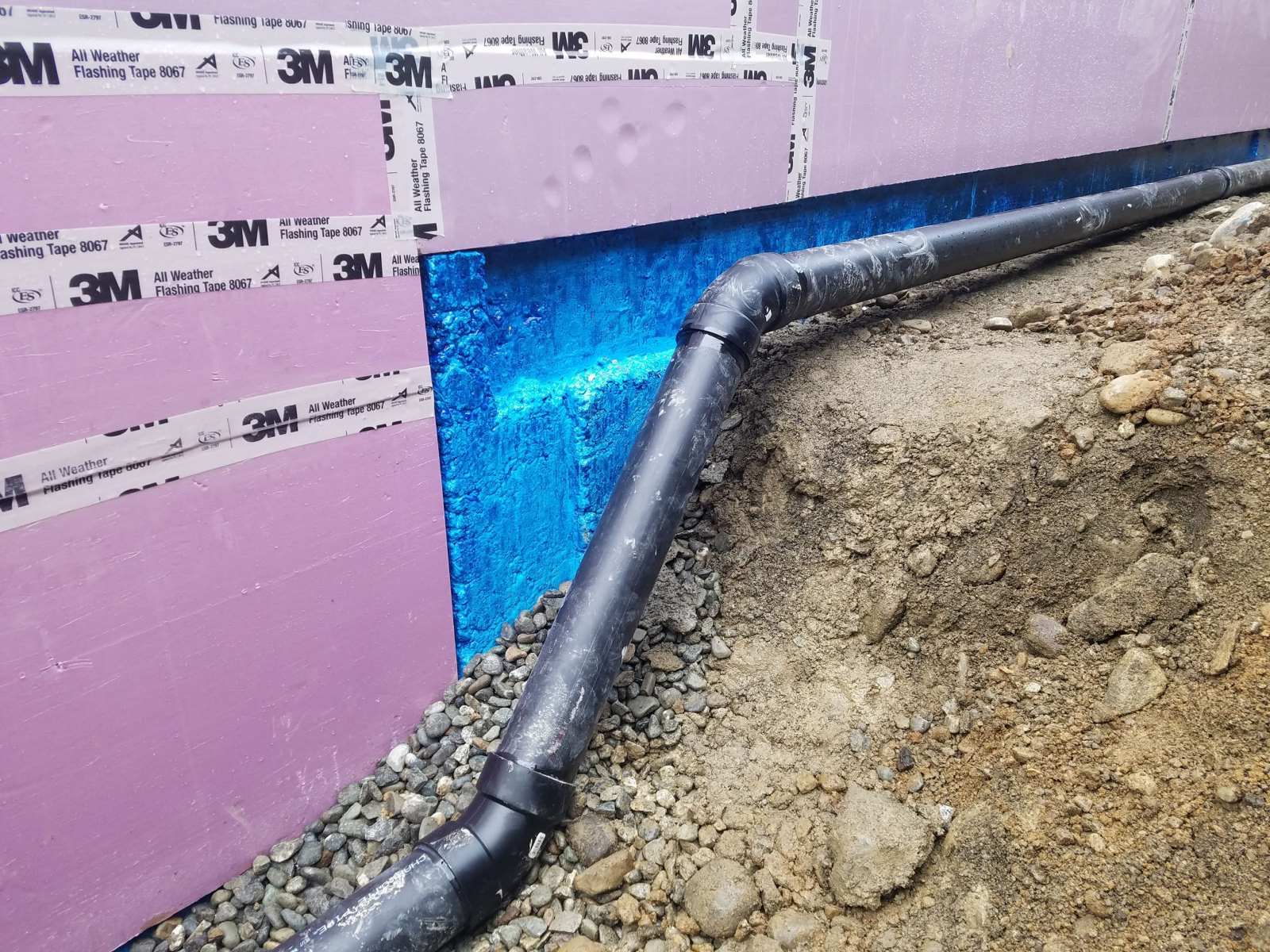
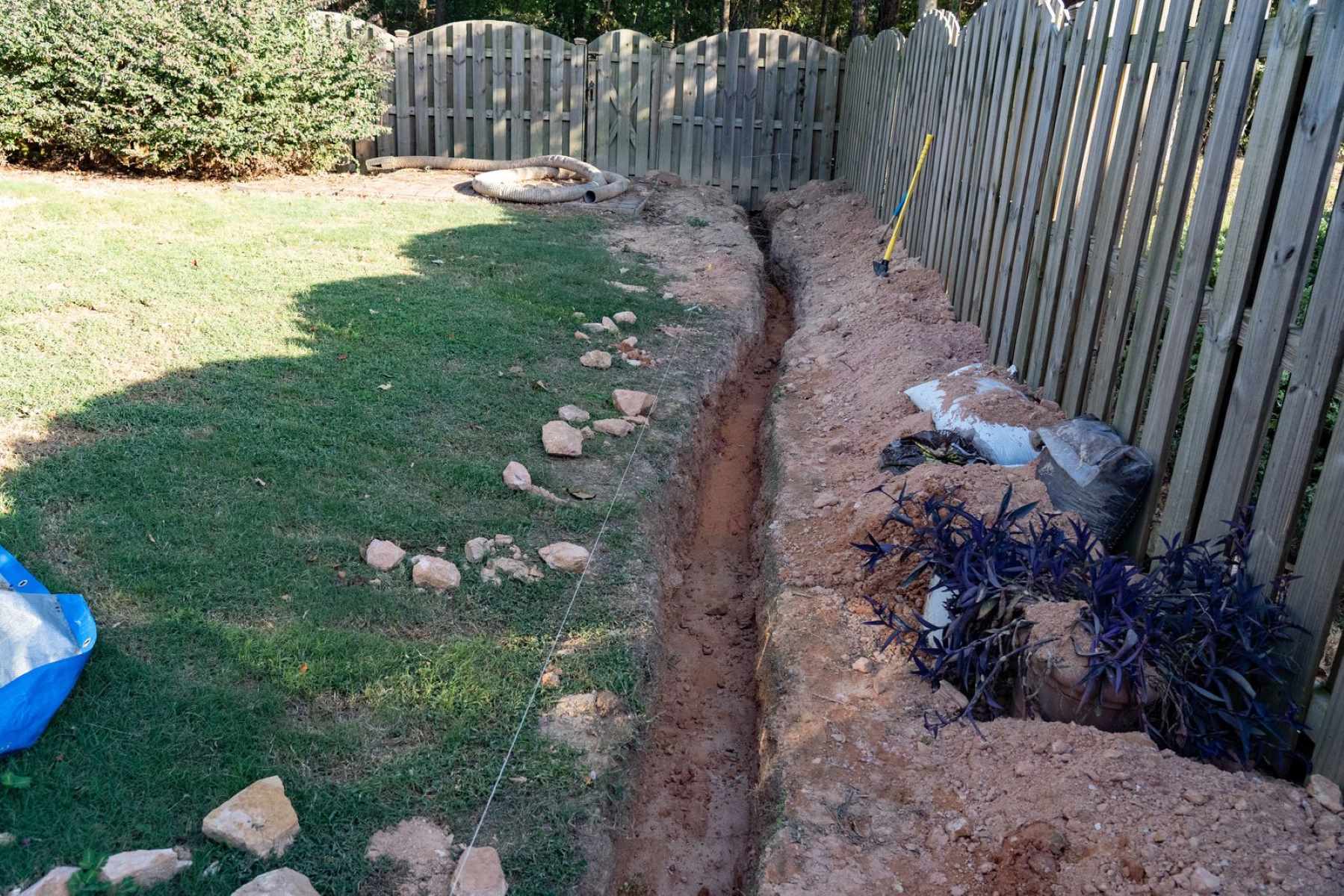
3. French Drains: French drains are underground drainage systems designed to divert excess water away from the house. They consist of a perforated pipe buried in a gravel-filled trench. The perforations allow water to enter the pipe, which then carries it away from the property. French drains are particularly useful in areas with high groundwater levels or heavy rainfall.
4. Sump Pumps: Sump pumps are commonly used in homes with basements. They are installed in a pit or sump basin below the basement floor. The sump pump collects and pumps out excess water that accumulates in the pit, preventing basement flooding. Ensuring proper maintenance and regular testing of sump pumps is crucial to their effective operation.
5. Catch Basins and Channel Drains: Catch basins and channel drains are surface drainage solutions that collect and channel water away from specific areas prone to water accumulation, such as driveways, walkways, or patios. They are connected to underground pipes and usually have a grate on top to capture debris and prevent clogging.
6. Dry Wells: Dry wells are underground structures designed to hold and slowly release excess water into the surrounding soil. They consist of a large pit filled with gravel or stone, allowing water to percolate through and replenish the groundwater table. Dry wells are particularly useful in areas with poor soil drainage.
7. Swales: Swales are shallow ditches or depressions designed to divert surface water away from the house and towards a designated drainage area. They are typically lined with grass or vegetation to slow down water flow and promote infiltration.
Understanding these basic components of a drainage system is essential for effective drainage design. By incorporating the right elements based on your specific needs and site conditions, you can ensure efficient water management and protection for your home.
Assessing the Site
Before designing a drainage system for your house, it is crucial to assess the site and understand the land’s characteristics. This assessment will help determine the specific drainage needs and identify any potential challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some key factors to consider when assessing the site:
1. Topography: Analyze the slope and contours of the land. Determine how water naturally flows and identify areas prone to water accumulation. Understanding the topography will guide the positioning of drainage components and help establish the appropriate drainage routes.
2. Soil Composition: Different soil types have varying drainage capacities. Assess the soil composition on your property to determine its permeability. Clay soils, for example, drain more slowly than sandy soils. Understanding the soil composition will help determine the proper drainage design, as well as the need for additional measures such as soil amendments or the installation of dry wells.
3. Water Sources: Identify potential sources of water that can affect the drainage around your house. This includes rainwater runoff from the roof, groundwater, and neighboring properties. Understanding the water sources will help determine the volume and intensity of water that needs to be managed by the drainage system.
4. Existing Drainage System: Assess any existing drainage features or systems on your property. This includes gutters, downspouts, French drains, or catch basins. Evaluate their condition and functionality to determine if any upgrades or repairs are necessary before implementing a new drainage system.
5. Landscaping and Property Features: Consider the existing landscaping elements and property features. Identify any structures, trees, or landscaping features that could affect the drainage, such as obstructing water flow or causing water pooling. Make note of any necessary modifications or additional drainage measures required to address these issues.
6. Local Regulations and Codes: Check the local regulations and codes regarding drainage design and installation. Different municipalities may have specific requirements and guidelines to follow. Ensure that your drainage system complies with these regulations to avoid any potential legal or compliance issues in the future.
By carefully assessing the site, you will gain valuable insights into the specific drainage requirements of your property. This knowledge will allow you to tailor the drainage design to effectively manage water flow and prevent potential drainage issues.
Planning the Drainage System
Once you have assessed the site and have a clear understanding of its drainage needs, it’s time to start planning the drainage system for your house. Proper planning is crucial to ensure that the system effectively manages water flow and prevents water-related issues. Here are the key steps to consider when planning your drainage system:
1. Define the Objectives: Start by clearly defining the objectives of your drainage system. Determine the specific problems you need to address, whether it is diverting rainwater away from the house, preventing basement flooding, or controlling water accumulation in specific areas of your property.
2. Determine Drainage Routes: Based on the site assessment, determine the best routes for diverting water away from your house. Consider the natural slope of the land and aim to direct water towards lower-lying areas, drainage ditches, or designated drainage points. This will help ensure efficient water flow and prevent standing water.
3. Establish Drainage Components: Choose the appropriate drainage components based on your specific needs. This may include gutters, downspouts, French drains, catch basins, channel drains, or sump pumps. Consider factors such as the volume of water to be managed, soil composition, and local regulations when selecting the components.
4. Determine Sizing and Capacity: Ensure that the drainage components are sized appropriately to handle the expected volume of water. This includes calculating the gutter capacity, downspout size, pipe diameter for French drains, or sump pump capacity. Proper sizing will ensure that the drainage system can effectively handle water flow without overwhelming the components.
5. Consider Maintenance Needs: Factor in maintenance requirements when planning your drainage system. Some components, such as gutters and downspouts, require regular cleaning to prevent clogs. Ensure that there is easy access to these components for maintenance purposes.
6. Incorporate Proper Slope and Grading: Ensure that the land around your house is properly sloped and graded. This will facilitate natural water flow and prevent water pooling. The ideal slope should be directed away from the foundation, with a minimum slope of 2% recommended. Proper grading will help maximize the effectiveness of the drainage system.
7. Consider Water Conservation Measures: While the primary goal of a drainage system is to manage excess water, you can also incorporate water conservation measures into your design. Consider capturing and reusing rainwater through rain barrels or incorporating permeable surfaces to allow water to infiltrate into the ground instead of being directed to the drainage system.
By carefully planning the drainage system, you can ensure that it is tailored to your specific needs and effectively addresses the drainage challenges of your property. Taking the time to plan upfront will save you potential headaches in the future and help protect your house from water-related issues.
When designing drainage for a house, make sure to slope the ground away from the foundation to prevent water from pooling and causing damage. Use gutters and downspouts to direct water away from the house.
Read more: What Is My House’s Standard Drainage Size
Choosing the Right Drainage Components
Choosing the right drainage components is critical for the effectiveness and efficiency of your drainage system. Each component serves a specific purpose in managing water flow and preventing water-related issues. Here are some key considerations when selecting drainage components:
1. Gutters and Downspouts: Select high-quality gutters that are durable and resistant to corrosion. Choose the appropriate size based on the expected water volume and the roof area they will cover. The downspouts should be wide enough to handle the flow of water and direct it away from the foundation.
2. French Drains: When installing French drains, choose perforated pipes made of durable materials such as PVC or HDPE. The pipe size should be sufficient to accommodate the expected water flow. Use filter fabric to prevent soil intrusion and clogging of the drainage system.
3. Catch Basins and Channel Drains: Consider the load-bearing capacity and durability of the catch basins and channel drains, especially if they will be in areas exposed to vehicular traffic. Choose grates that prevent debris from entering the system but still allow water to flow freely.
4. Sump Pumps: Look for sump pumps with sufficient horsepower and pumping capacity to handle the amount of water that can accumulate in your basement. Consider additional features such as battery backup systems to ensure functionality during power outages.
5. Dry Wells: Select the appropriate size and material for your dry well based on the expected water volume and soil conditions. The well should have sufficient capacity to store excess water and allow for slow infiltration into the ground.
6. Consider Local Regulations: Be aware of any local regulations or codes that dictate specific requirements for drainage components. Some areas may have restrictions on the types of materials or sizes allowed. Ensure that your chosen components comply with these regulations to avoid any issues in the future.
7. Consult with Professionals: If you are unsure about which drainage components to choose, consider consulting with a professional contractor or drainage expert. They can provide valuable insights and ensure that you select the right components for your specific needs and site conditions.
Remember that the effectiveness of your drainage system relies on the quality and functionality of the components you choose. Invest in high-quality materials and products that are specifically designed for drainage purposes to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your drainage system.
Installing Drainage Pipes
Proper installation of drainage pipes is crucial for the effective functioning of your drainage system. Whether you’re installing French drains, downspout extensions, or other types of drainage pipes, following these key steps will help ensure a successful installation:
1. Plan the Layout: Determine the layout of your drainage pipes based on the site assessment and the desired water flow path. Take into account factors such as the slope of the land, the location of existing structures, and any potential obstacles that may impede water flow.
2. Dig Trenches: Dig trenches for the drainage pipes following the planned layout. The depth of the trench will depend on the pipe size, soil conditions, and local regulations, but it is generally recommended to have a minimum depth of 12 inches to ensure proper functioning and protection of the pipes.
3. Grade the Trenches: Ensure that the bottom of the trench is properly graded to create a slope and facilitate water flow. The recommended slope is typically 1/8 to 1/4 inch per linear foot to ensure that water flows freely towards the desired drainage point.
4. Lay Geotextile Fabric: Place a layer of geotextile fabric along the bottom and sides of the trench. This fabric acts as a barrier, preventing soil particles from entering the drainage pipe and causing clogs. It also helps with filtration, allowing water to pass through while restricting the passage of debris.
5. Install the Drainage Pipes: Lay the drainage pipes in the trench on top of the geotextile fabric. Ensure that the pipes have a gentle slope following the layout plan to promote proper water flow. Connect the sections of pipe using appropriate connectors or fittings as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
6. Backfill the Trench: Once the pipes are in place, carefully backfill the trench with soil. Compact the soil in layers to provide stability and prevent settling. Be cautious not to damage or displace the drainage pipes during the backfilling process.
7. Extend Downspouts: If you are installing downspout extensions to divert water away from the house, connect them to the existing downspouts. Ensure that the extensions have a proper slope away from the foundation and are securely fastened to prevent displacement or damage.
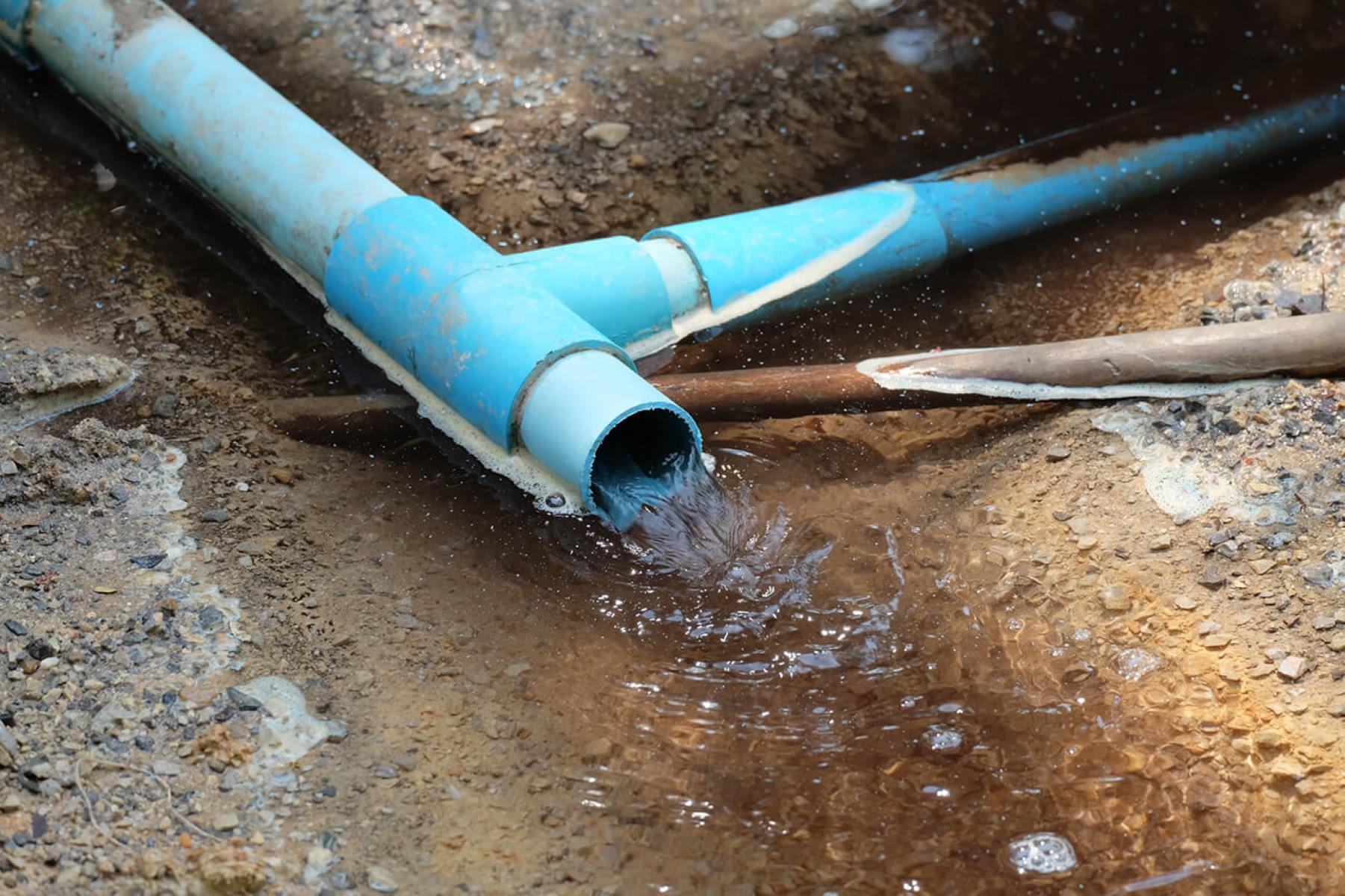
8. Test the System: After the installation is complete, test the drainage system by running water through the pipes. Check for any leaks, blockages, or improper water flow. This will allow you to identify and address any issues before they become more significant problems.
Proper installation of drainage pipes is essential for maintaining the functionality and longevity of your drainage system. If you are unsure or lack the necessary expertise, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a professional contractor or drainage expert to ensure a proper and efficient installation.
Creating Surface Drainage Solutions
In addition to underground drainage systems, surface drainage solutions play a crucial role in directing water away from specific areas prone to water accumulation. These solutions are particularly useful for managing rainwater runoff from driveways, walkways, patios, and other impermeable surfaces. Here are some effective surface drainage solutions to consider:
1. Grading and Sloping: Ensuring proper grading and sloping of surfaces is a fundamental surface drainage solution. The surface should be sloped away from structures and towards designated drainage points or areas. This allows water to naturally flow and prevents pooling.
2. Swales: Swales are shallow, broad, and gently sloping channels that help divert water away from specific areas. They are typically lined with grass or vegetation and can be strategically placed to direct water towards a desired drainage point or absorption area.
3. Permeable Paving: Using permeable paving materials is an excellent solution for managing surface water runoff. These materials allow water to infiltrate through the pavement rather than pooling on the surface. Examples of permeable paving include porous asphalt, permeable concrete, and permeable pavers.
4. Trench Drains: Trench drains, also known as linear drains, are long, narrow drains installed in areas prone to water accumulation, such as driveways or patio edges. They have a sloped surface that collects and channels water into an underground pipe or a designated drainage area.
5. Rain Gardens: Rain gardens are attractive and functional landscaping features designed to capture and absorb rainwater runoff. They are planted with native vegetation that can tolerate both wet and dry conditions. Rain gardens help slow down and filter water, allowing it to infiltrate into the ground gradually.
6. Catch Basins and Channel Drains: Catch basins and channel drains are also surface drainage solutions that collect and carry water away from specific areas. They can be connected to underground pipes or designed to discharge water into a designated drainage point.
7. Berms and Swales Combination: Creating a combination of berms (raised areas) and swales (depressions) can be an effective surface drainage solution. Berms can redirect water away from an area while swales catch and direct the water to a designated drainage area. This combination helps control and manage surface water runoff effectively.
When creating surface drainage solutions, it is essential to consider the specific needs of your property and the characteristics of the area. Proper design and implementation of these solutions will help prevent water pooling, erosion, and other related issues, ensuring a well-drained and functional outdoor space.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Drainage Systems
Maintaining and regularly inspecting your drainage system is essential to ensure its proper functioning and prevent any potential issues. By following some key maintenance tips and knowing how to troubleshoot common problems, you can keep your drainage system in optimal condition. Here are some guidelines to help maintain and troubleshoot your drainage system:
1. Regular Cleaning: Clean your gutters, downspouts, and catch basins regularly to remove any debris or obstructions that may impede water flow. Clogged components can lead to backups and water overflow, causing potential damage to your home’s foundation or landscape.
2. Inspect for Damage: Conduct routine inspections of your drainage system to check for any signs of damage, including cracks, leaks, or loose connections. Addressing small issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems later on.
3. Clear Vegetation: Trim back any vegetation, such as tree branches or overgrown shrubs, that may obstruct the flow of water through your drainage system. This will help maintain the proper water flow and prevent unnecessary blockages.
4. Ensure Proper Slope: Regularly check the slope and grading of your outdoor areas, ensuring that they remain properly sloped away from your home’s foundation. Over time, soil erosion or settling can affect the slope, leading to inefficient drainage. Make any necessary adjustments to maintain the desired slope.
5. Address Standing Water: If you notice areas of standing water in your yard or near your foundation, it may indicate a problem with your drainage system. Investigate and determine the cause of the standing water, and take appropriate actions, such as redirecting the water flow or installing additional drainage components if needed.
6. Monitor Basement Moisture: Keep an eye on the moisture level in your basement. Excessive moisture or signs of water intrusion may indicate a problem with your drainage system. Address any basement moisture issues promptly to prevent further damage and potential mold growth.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues: If you encounter issues such as slow or inadequate drainage, foul odors, or unusual water flow patterns, consider consulting with a professional to troubleshoot the problem. They can provide expert advice and help identify the root cause of the issue.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any drainage system issues will help ensure its effectiveness and longevity. By taking these proactive steps, you can prevent potential problems and enjoy a well-functioning drainage system that protects your home from water-related issues.
Read more: Drainage Considerations When Buying A House
Conclusion
Proper drainage design is a vital aspect of any well-designed house. It plays a crucial role in preventing water damage, protecting the foundation, and maintaining the integrity of the landscape. By understanding the basics of drainage systems, assessing the site, and planning accordingly, homeowners, architects, and contractors can create effective drainage solutions that meet their specific needs.
Choosing the right drainage components, such as gutters, downspouts, French drains, and catch basins, is essential for the functionality and efficiency of the drainage system. With proper installation techniques and regular maintenance, homeowners can ensure that their drainage system effectively manages water flow, prevents water-related issues, and extends the lifespan of their property.
Surface drainage solutions, such as grading and sloping, swales, permeable paving, trench drains, and rain gardens, further enhance the effectiveness of the drainage system by diverting water away from specific areas of concern. These solutions, when integrated into the overall drainage design, contribute to a well-drained and functional outdoor space.
Maintaining and troubleshooting the drainage system is crucial for its longevity and optimal performance. Regular cleaning, inspecting for damage, clearing vegetation, and addressing standing water are essential maintenance practices. Promptly addressing any issues or seeking professional help when troubleshooting ensures that the drainage system functions as intended, protecting the house from water damage and maintaining a healthy environment.
In conclusion, proper drainage design, installation, and maintenance are essential for the long-term stability, functionality, and value of a house. By investing time and effort into understanding the principles of drainage, choosing the right components, and implementing effective solutions, homeowners can rest assured that their property is well-protected from water-related issues, ensuring a dry, secure, and comfortable living space for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Design Drainage For A House
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Design Drainage For A House”