Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is A Resin 3D Printer


Smart Home Devices
What Is A Resin 3D Printer
Modified: August 17, 2024
Discover how resin 3D printers work and their applications for creating smart home devices. Learn about the benefits of using resin 3D printing technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Read more: How Toxic Is 3D Printer Resin
Introduction
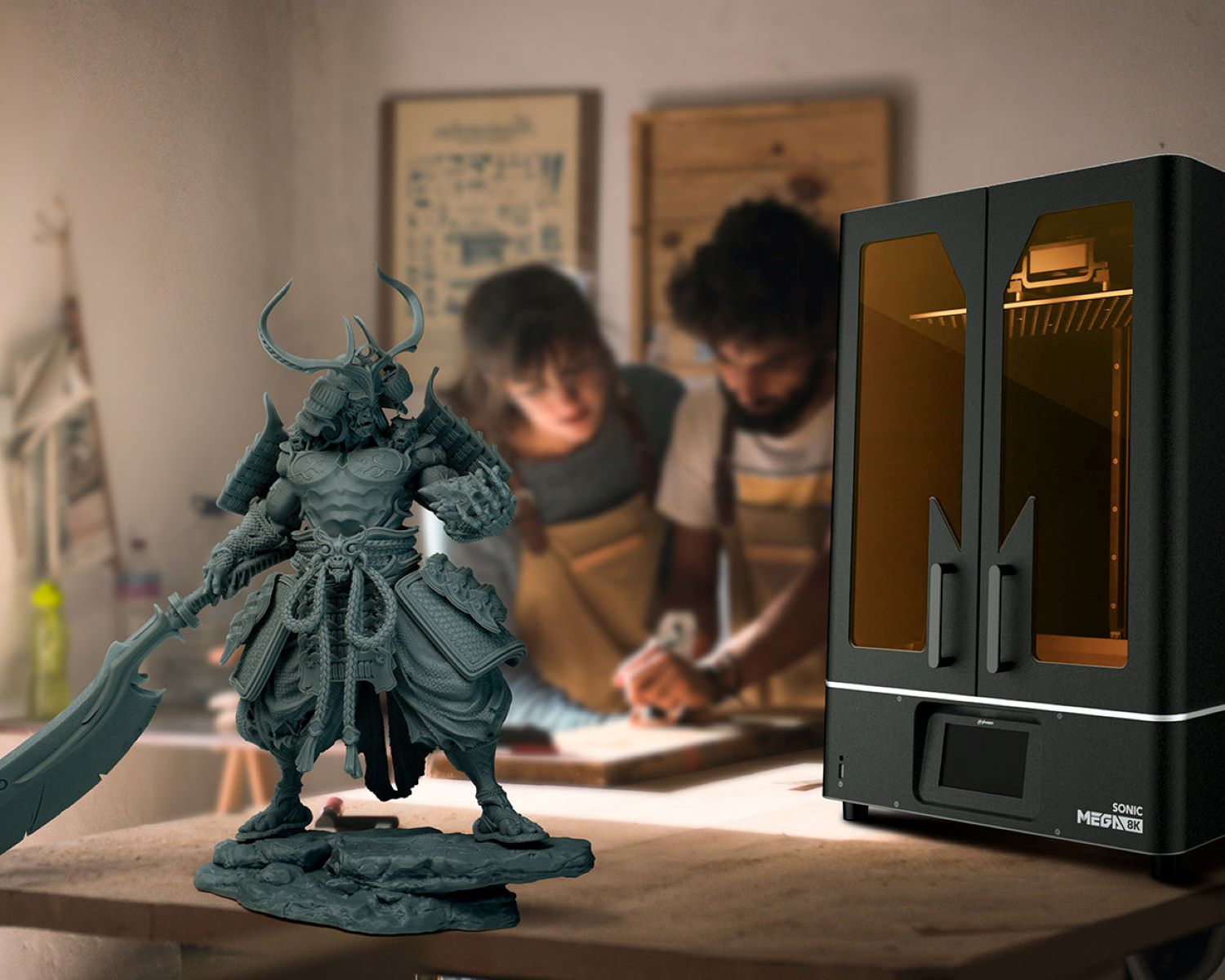
Welcome to the fascinating world of resin 3D printing! This cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the realm of additive manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision and versatility. Unlike traditional 3D printers that utilize filaments, resin 3D printers employ a liquid photopolymer resin to craft intricate, high-resolution objects with exceptional detail. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the inner workings of resin 3D printers, explore the different types available, and uncover the myriad applications and advantages of this innovative technology.
Resin 3D printing, also known as stereolithography (SLA) or digital light processing (DLP), has gained widespread acclaim for its ability to produce intricate and finely detailed objects with smooth surface finishes. This process involves the use of a liquid resin that solidifies when exposed to a specific wavelength of light, typically ultraviolet (UV) light. The resin is contained in a vat, and a build platform gradually lifts the object out of the resin as each layer is cured, resulting in precise and complex three-dimensional models.
In the following sections, we will explore the intricate mechanics of resin 3D printing, the various types of resin printers available, the advantages and limitations of this technology, as well as its diverse applications across different industries. Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a newcomer to the world of 3D printing, this guide will provide valuable insights into the captivating realm of resin 3D printing. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to uncover the inner workings and boundless potential of resin 3D printing technology.
Key Takeaways:
- Resin 3D printing uses UV light to create intricate objects with exceptional detail, making it perfect for jewelry, dental appliances, and artistic figurines.
- Resin 3D printing offers precision, material versatility, and speed, but requires careful consideration of post-processing, material properties, and print size limitations.
How Does a Resin 3D Printer Work?
Resin 3D printing operates on the principle of photopolymerization, a process in which liquid resin is transformed into a solid object through the use of light. The intricate mechanics of a resin 3D printer involve several key components working in harmony to bring digital designs to life in physical form.
Firstly, the 3D model to be printed is sliced into thin layers using specialized software, which then generates a series of two-dimensional cross-sectional images. These images are subsequently sent to the resin 3D printer, which begins the printing process by solidifying each layer of the object.
The printer consists of a build platform that descends into a vat of liquid resin, with the first layer of the object being formed at the bottom. A precise UV light source, such as a laser or a digital light projector (DLP), is then employed to selectively cure and solidify the resin in accordance with the pattern of the current layer. As the layer solidifies, the build platform gradually lifts the object to allow the next layer of resin to be cured, ultimately constructing the three-dimensional object layer by layer.
One of the key elements in this process is the resin itself, which plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and properties of the final print. Different resins offer varying characteristics, such as transparency, flexibility, or durability, allowing for a diverse range of applications and end products. Additionally, post-processing steps, such as rinsing the printed object in a solvent and curing it under UV light, may be required to achieve the desired mechanical properties and surface finish.
The precision and intricacy achievable with resin 3D printing make it an ideal choice for producing detailed prototypes, jewelry, dental appliances, and intricate figurines. The ability to create complex geometries and intricate details sets resin 3D printing apart from other additive manufacturing technologies, making it a preferred choice for applications that demand exceptional precision and surface quality.
Now that we have unveiled the inner workings of resin 3D printing, let’s delve into the diverse types of resin 3D printers available and explore their unique features and capabilities.
Types of Resin 3D Printers
Resin 3D printers are available in various configurations, each offering distinct features and capabilities tailored to different applications and user requirements. The two primary types of resin 3D printers are stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP) printers, each employing unique techniques to solidify the liquid resin and create three-dimensional objects.
Stereolithography (SLA) Printers: SLA printers utilize a precise UV laser to solidify the liquid resin, layer by layer, to form the desired object. These printers feature a laser that scans across the surface of the resin, selectively curing it to create each layer of the print. SLA printers are renowned for their exceptional precision and ability to produce high-resolution, detailed prints with smooth surface finishes. They are widely used in industries such as engineering, product design, and jewelry manufacturing, where intricate details and precise dimensions are crucial.
Digital Light Processing (DLP) Printers: DLP printers use a digital light projector to expose an entire layer of the print to UV light simultaneously, solidifying the entire layer in a single pass. This results in faster print times compared to SLA printers, making DLP technology well-suited for applications that prioritize speed and efficiency. DLP printers are often favored for producing dental models, custom orthodontic devices, and other applications where rapid prototyping is essential.
Both SLA and DLP printers offer exceptional print quality and are capable of producing intricately detailed objects with smooth surface finishes. When choosing between these two types of resin 3D printers, it is essential to consider factors such as print speed, resolution, and post-processing requirements to determine the most suitable option for a specific application or project.
Additionally, within the realm of resin 3D printing, there are variations in the types of resins used, such as standard, engineering, and castable resins, each designed to meet specific performance and material requirements. These diverse resin formulations further enhance the versatility and applicability of resin 3D printing technology across a wide range of industries and applications.
Now that we have explored the different types of resin 3D printers available, let’s uncover the numerous advantages of resin 3D printing and its transformative impact on the realm of additive manufacturing.
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing offers a multitude of advantages that have positioned it as a preferred choice for numerous applications across various industries. The following are some of the key advantages of resin 3D printing:
- Precision and Detail: Resin 3D printing excels in producing highly detailed and intricate objects with exceptional precision. The technology is capable of achieving fine features and smooth surface finishes, making it ideal for applications that demand high levels of detail, such as jewelry design, dental prosthetics, and intricate prototypes.
- Material Versatility: Resin 3D printers support a wide range of specialized resin formulations, including standard, engineering, and castable resins, each tailored to specific performance requirements. This versatility allows for the creation of objects with diverse material properties, such as transparency, flexibility, and durability, expanding the scope of potential applications.
- Speed and Efficiency: Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers, in particular, offer rapid print times by solidifying entire layers of resin simultaneously. This accelerated printing process enhances efficiency and productivity, making resin 3D printing well-suited for applications that require quick turnaround times and rapid prototyping.
- Complex Geometries: Resin 3D printing enables the fabrication of complex geometries and intricate structures that may be challenging or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. This capability unlocks new design possibilities and fosters innovation across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
- High Resolution: The technology’s ability to produce high-resolution prints with fine details allows for the creation of visually stunning and aesthetically appealing objects. This makes resin 3D printing an ideal choice for producing artistic sculptures, figurines, and customized consumer products.
- Prototyping and Iterative Design: Resin 3D printing facilitates rapid prototyping and iterative design processes, enabling designers and engineers to quickly iterate on concepts and refine designs with minimal lead time. This iterative approach accelerates product development cycles and fosters innovation in product design and development.
These advantages collectively position resin 3D printing as a versatile and powerful additive manufacturing technology, driving advancements in product design, prototyping, and production across a wide spectrum of industries. The technology’s ability to deliver precise, detailed, and visually striking objects has elevated its status as a transformative force in the realm of manufacturing and design.
As we continue our exploration of resin 3D printing, we will uncover the limitations associated with this technology and gain insights into its diverse applications across industries.
When using a resin 3D printer, make sure to wear gloves and work in a well-ventilated area, as the resin can be toxic. Clean up any spills immediately and dispose of waste properly.
Read also: 8 Amazing Resin 3D Printer For 2025
Limitations of Resin 3D Printing
While resin 3D printing offers a host of advantages, it is important to acknowledge the limitations and considerations associated with this innovative technology. Understanding these limitations is crucial for making informed decisions regarding its application and implementation. Here are some key limitations of resin 3D printing:
- Material Properties: The material properties of resin-based 3D prints may differ from those of traditional manufacturing materials, impacting factors such as strength, durability, and heat resistance. It is essential to carefully assess the suitability of resin-based materials for specific functional applications and environments.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Resin 3D prints often require post-processing steps, such as cleaning, support removal, and curing under UV light, to achieve the desired mechanical properties and surface finish. These additional steps can increase production time and necessitate careful handling of the printed objects.
- Print Size and Build Volume: Resin 3D printers typically have smaller build volumes compared to filament-based printers, limiting the size of objects that can be produced in a single print. Large-scale manufacturing or prototyping of sizable objects may require alternative manufacturing methods or assembly of multiple printed components.
- Material Handling and Safety: Liquid resin used in 3D printing processes can pose safety considerations, such as skin irritation and the need for proper ventilation when handling uncured resin. It is important to adhere to safety guidelines and best practices for handling and disposing of resin-based materials.
- Material Selection and Compatibility: The selection of suitable resin materials for specific applications is critical, as different resins offer varying properties and characteristics. Compatibility with the intended use case, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements must be carefully evaluated.
- Cost of Materials: Specialized resin materials used in 3D printing processes may have higher material costs compared to traditional manufacturing materials. Assessing the cost-effectiveness of resin-based 3D printing for a given application is essential for budget-conscious projects.
By recognizing these limitations and considerations, stakeholders can make informed decisions when integrating resin 3D printing into their design, prototyping, and manufacturing workflows. Despite these limitations, the technology’s unique capabilities and advantages make it a valuable asset in various industries, driving innovation and enabling the creation of intricate, high-quality objects.
As we move forward, we will explore the diverse applications of resin 3D printing, showcasing its impact across industries and its potential to revolutionize manufacturing and design processes.
Applications of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology with diverse applications across industries, revolutionizing the way intricate objects are designed, prototyped, and manufactured. The precision, detail, and material versatility offered by resin 3D printing have paved the way for innovative solutions in numerous domains. Let’s explore some of the compelling applications of resin 3D printing:
- Jewelry and Fashion: Resin 3D printing is widely utilized in the jewelry and fashion industries to produce intricate and customizable pieces, including finely detailed jewelry, ornate accessories, and unique fashion designs. The technology’s ability to create complex geometries and delicate structures aligns perfectly with the demands of these industries, enabling the production of stunning and personalized items.
- Medical and Dental: In the medical and dental fields, resin 3D printing plays a pivotal role in fabricating precise dental prosthetics, orthodontic devices, anatomical models, and surgical guides. The capability to produce patient-specific, high-precision medical components has significantly advanced the fields of dentistry, orthodontics, and personalized healthcare solutions.
- Prototyping and Product Development: Resin 3D printing is instrumental in rapid prototyping and iterative product development processes across various industries. Designers and engineers leverage the technology to create detailed prototypes, functional models, and concept designs with exceptional accuracy, accelerating the product development lifecycle and fostering innovation.
- Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors harness the capabilities of resin 3D printing to bring their imaginative creations to life with intricate details and expressive forms. The technology enables the realization of elaborate sculptures, artistic installations, and visually captivating artworks that push the boundaries of traditional artistic expression.
- Engineering and Aerospace: Resin 3D printing finds application in engineering and aerospace sectors for producing intricate components, lightweight structures, and complex prototypes. The technology’s ability to fabricate high-precision parts and intricate geometries supports advancements in aerospace engineering, prototyping of mechanical components, and the development of specialized tools and fixtures.
- Educational and Research: Resin 3D printing serves as a valuable tool in educational institutions and research facilities, facilitating the creation of detailed anatomical models, scientific prototypes, and educational aids. The technology enhances hands-on learning experiences, aids in medical research, and fosters innovation in academic and research settings.
These diverse applications underscore the far-reaching impact of resin 3D printing across creative, industrial, and scientific domains. The technology’s ability to produce intricate, high-resolution objects with diverse material properties has redefined traditional manufacturing processes and unlocked new possibilities in design, healthcare, and artistic expression.
As we conclude our exploration of resin 3D printing, it is evident that this innovative technology continues to drive innovation, creativity, and advancements in numerous fields, shaping the future of additive manufacturing and design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resin 3D printing stands as a transformative force in the realm of additive manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, material versatility, and intricate detail that have revolutionized the creation of three-dimensional objects. From its intricate photopolymerization process to the diverse applications across industries, resin 3D printing has redefined the boundaries of design, prototyping, and manufacturing.
By harnessing the power of precise UV light and specialized resin formulations, resin 3D printers bring digital designs to life with exceptional detail and fidelity, enabling the production of complex geometries, high-resolution prototypes, and customized components. The technology’s ability to create intricate jewelry, precise dental prosthetics, and visually stunning artworks showcases its impact across creative and industrial domains.
While resin 3D printing offers compelling advantages, such as speed, precision, and material versatility, it is important to consider the associated limitations, including post-processing requirements, material properties, and print size constraints. Understanding these considerations is essential for informed decision-making and successful integration of resin 3D printing into diverse workflows and applications.
As resin 3D printing continues to evolve, its impact extends into diverse domains, including jewelry design, medical innovation, product development, artistic expression, and academic research. The technology’s ability to foster innovation, accelerate prototyping, and enable the creation of intricate, high-quality objects underscores its significance in shaping the future of manufacturing and design.
Whether in the hands of artists, engineers, healthcare professionals, or educators, resin 3D printing has unlocked new frontiers of creativity, precision, and material exploration, driving advancements and pushing the boundaries of traditional manufacturing processes. As we look to the future, the continued evolution of resin 3D printing promises to further expand the possibilities of additive manufacturing, ushering in a new era of intricate, high-fidelity object creation across industries and disciplines.
With its transformative capabilities and boundless potential, resin 3D printing continues to inspire innovation, creativity, and exploration, shaping the landscape of design and manufacturing in profound and captivating ways.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Resin 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is A Resin 3D Printer”