Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How To Program A 3D Printer

Smart Home Devices
How To Program A 3D Printer
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn how to program a 3D printer for smart home devices with our comprehensive guide. Master the art of 3D printing and bring your smart home ideas to life.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing! Whether you are a hobbyist, a professional designer, or an enthusiast eager to explore the endless possibilities of this cutting-edge technology, learning how to program a 3D printer is an essential skill that can unlock a realm of creativity and innovation.
In the realm of 3D printing, the ability to transform digital designs into physical objects is truly remarkable. From intricate prototypes to personalized gadgets and decorative items, the potential for bringing imagination to life is virtually limitless. As we embark on this journey, I will guide you through the fundamental aspects of 3D printing, including understanding the technology, selecting the right printer, setting it up, mastering basic and advanced printing techniques, and troubleshooting common issues.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have the knowledge and confidence to unleash your creativity and embark on exciting 3D printing projects. So, let's delve into the world of 3D printing and discover the magic of programming a 3D printer!
Key Takeaways:
- 3D printing is a revolutionary technology that turns digital designs into physical objects, offering endless creative possibilities for hobbyists, designers, and innovators.
- Choosing the right 3D printer, mastering setup and printing techniques, and troubleshooting common issues are essential for unleashing creativity and embarking on a fulfilling 3D printing journey.
Read more: How To Operate A 3D Printer
Understanding 3D Printing
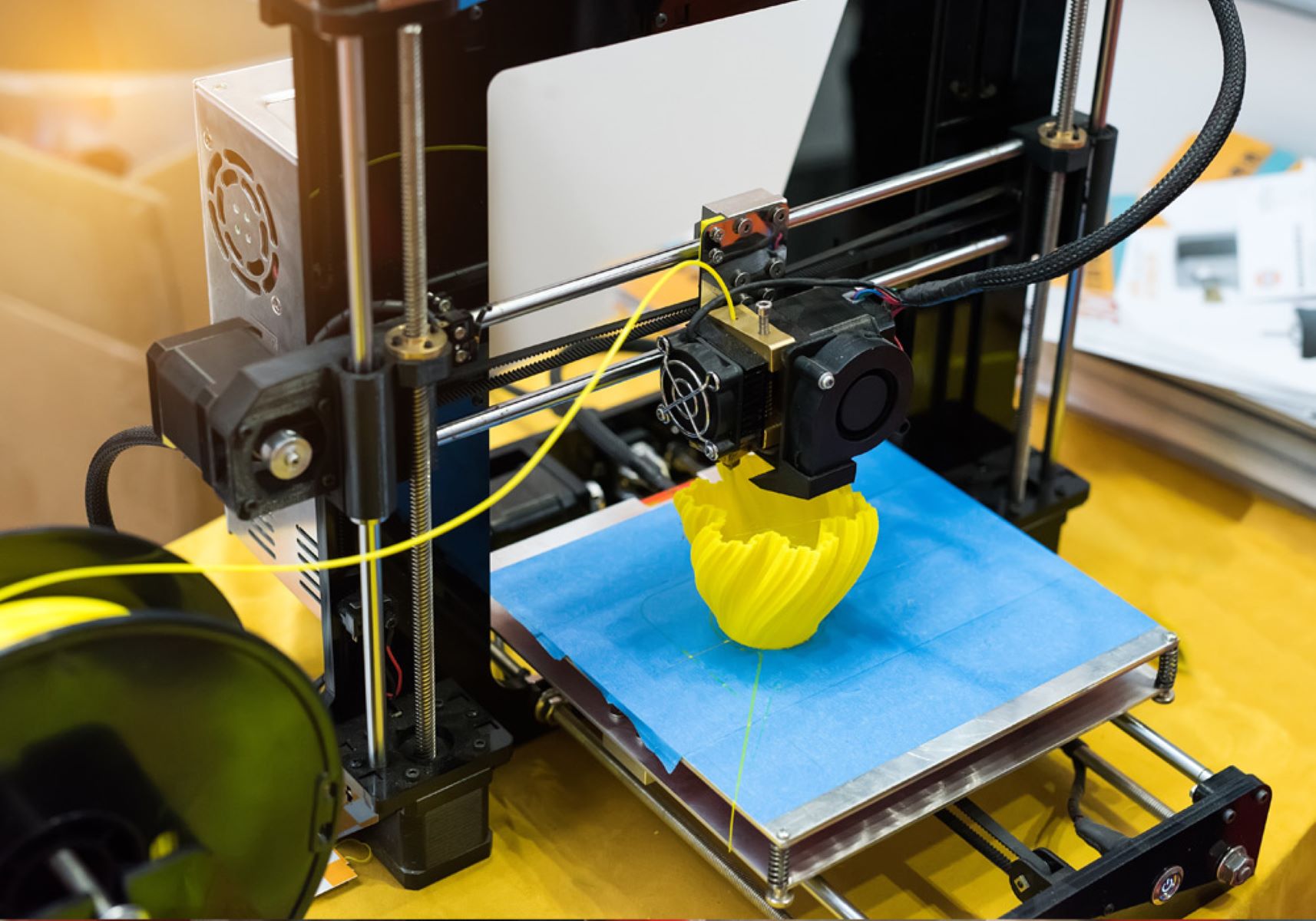
Before diving into the intricacies of programming a 3D printer, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of 3D printing technology. At its core, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material based on a digital model. This revolutionary method enables the production of complex and customized objects with precision and efficiency.
The process begins with a digital 3D model, which serves as the blueprint for the physical object. This model is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or obtained from online repositories that host a myriad of designs. The 3D model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software, which generates a set of instructions for the 3D printer to follow during the printing process.
3D printers utilize various materials, including plastics, metals, resins, and even composites, to bring the digital designs to life. The most common method involves the extrusion of thermoplastic filaments, which are heated and deposited layer by layer to form the object. Other techniques, such as stereolithography and selective laser sintering, employ photopolymerization and laser sintering, respectively, to solidify liquid resin or powder materials into precise shapes.
One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its versatility. From rapid prototyping in industrial settings to crafting intricate jewelry and fashion accessories, the technology has found applications across diverse industries. It empowers designers, engineers, artists, and innovators to materialize their concepts swiftly, iterate designs with ease, and customize products according to specific requirements.
Understanding the underlying principles of 3D printing sets the stage for harnessing its full potential. As we delve deeper into the realm of 3D printing, we will explore the nuances of selecting the right printer, setting it up, and mastering the art of programming to bring your creations to life.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
When embarking on your 3D printing journey, selecting the right printer is a pivotal decision that significantly influences your printing capabilities and the quality of your creations. With a myriad of options available in the market, understanding the key factors to consider will empower you to make an informed choice.
Printer Type: 3D printers come in various types, each catering to specific needs. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are ideal for beginners and are widely used for hobbyist projects. Stereolithography (SLA) printers excel in producing high-resolution prints and are favored for intricate designs. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) printers are suitable for industrial-grade applications, offering robust and durable prints.
Build Volume: The build volume determines the maximum size of objects that the printer can produce. Consider the dimensions that align with your intended projects, ensuring that the printer can accommodate your envisioned creations without limitations.
Resolution and Print Quality: Assess the printer’s resolution capabilities, which dictate the level of detail and intricacy achievable in your prints. Higher resolution equates to finer details and smoother surfaces, ideal for intricate designs and professional prototypes.
Material Compatibility: Evaluate the range of materials compatible with the printer. Whether you intend to work with standard filaments like PLA and ABS or explore advanced materials such as flexible filaments and composite blends, ensuring compatibility with your desired materials is crucial.
Software and Connectivity: The software ecosystem accompanying the printer plays a vital role in the printing process. User-friendly slicing software, firmware compatibility, and connectivity options, including Wi-Fi and USB, contribute to a seamless printing experience.
Support and Community: Consider the availability of customer support, comprehensive documentation, and an active user community. Access to troubleshooting resources, forums, and tutorials can be invaluable, especially for beginners navigating the intricacies of 3D printing.
Cost and Value: While budget considerations are important, it’s essential to weigh the printer’s cost against its features, capabilities, and long-term value. Investing in a reliable printer equipped with essential features often proves to be a prudent choice in the long run.
By carefully evaluating these factors and aligning them with your specific requirements and aspirations, you can confidently select a 3D printer that empowers you to unleash your creativity and embark on a fulfilling 3D printing journey.
Setting Up Your 3D Printer
As you embark on your 3D printing endeavors, setting up your printer correctly is crucial for achieving optimal results and a seamless printing experience. Whether you have just unboxed a brand-new printer or are fine-tuning an existing one, following these essential steps will ensure that your printer is primed for producing exceptional prints.
Assembly and Calibration: If your printer arrives in a kit form, meticulously follow the assembly instructions provided by the manufacturer. Pay close attention to the alignment of components, proper tensioning of belts, and calibration of the print bed to guarantee precise and consistent prints.
Leveling the Print Bed: Ensuring that the print bed is perfectly level is critical for successful adhesion and uniform layer deposition. Most printers feature manual or assisted bed leveling procedures, where the print head is adjusted to achieve an optimal distance from the bed surface across all points.
Extruder and Nozzle Setup: Calibrate the extruder and ensure that the nozzle is clean and free from any residual material. Properly setting the extrusion multiplier and flow rate in the printer’s firmware or software contributes to accurate filament deposition during printing.
Firmware and Software Configuration: Update the printer’s firmware to the latest version to benefit from performance enhancements and bug fixes. Additionally, configure the slicing software settings to align with your printer’s specifications, including filament type, print speed, layer height, and infill density.
Temperature Calibration: Verify and calibrate the extruder and heated bed temperatures to ensure consistency and accuracy during the printing process. This step is crucial for achieving optimal adhesion and preventing issues such as warping and layer separation.
Test Prints and Fine-Tuning: Before embarking on complex projects, conduct test prints to evaluate the printer’s performance and make necessary adjustments. Fine-tune parameters such as retraction settings, cooling fan speed, and print speed to optimize print quality and minimize imperfections.
Safety Measures: Prioritize safety by positioning the printer in a well-ventilated area and adhering to recommended operating temperatures. Familiarize yourself with the printer’s emergency stop procedures and fire safety precautions, ensuring a secure and controlled printing environment.
By meticulously setting up your 3D printer and adhering to best practices, you lay a solid foundation for achieving consistent and high-quality prints. This attention to detail not only enhances the printing experience but also fosters a deeper understanding of the printer’s capabilities, empowering you to unleash your creativity with confidence.
When programming a 3D printer, make sure to accurately calibrate the printer’s settings such as nozzle temperature, bed leveling, and filament type. This will ensure precise and successful 3D prints.
Basic 3D Printing Techniques
Mastering basic 3D printing techniques is pivotal for bringing your digital designs to life with precision and finesse. Whether you are venturing into 3D printing for the first time or seeking to refine your foundational skills, familiarizing yourself with these fundamental techniques will elevate your printing proficiency and the quality of your creations.
Layer Height and Resolution: Adjusting the layer height, which determines the thickness of each printed layer, directly impacts print quality. Finer layer heights result in smoother surfaces and finer details, albeit at the expense of longer print times. Balancing layer height with print speed and quality requirements is essential for achieving optimal results.
Infill Density and Patterns: The infill density dictates the internal structure of the printed object, ranging from solid (100% infill) to sparse infill percentages. Understanding infill patterns, such as grid, honeycomb, and gyroid, allows you to tailor the object’s strength, weight, and material usage according to its intended purpose.
Support Structures and Overhangs: When printing designs with overhanging features, support structures prevent drooping and ensure accurate layer deposition. Familiarize yourself with generating and removing support structures, optimizing their placement to minimize post-processing efforts while maintaining print integrity.
Bridging and Cooling: Mastering bridging techniques is essential for printing horizontal spans without the need for support structures. Adjusting cooling fan settings and print speeds during bridging segments contributes to clean and precise bridging, enhancing print quality and structural integrity.
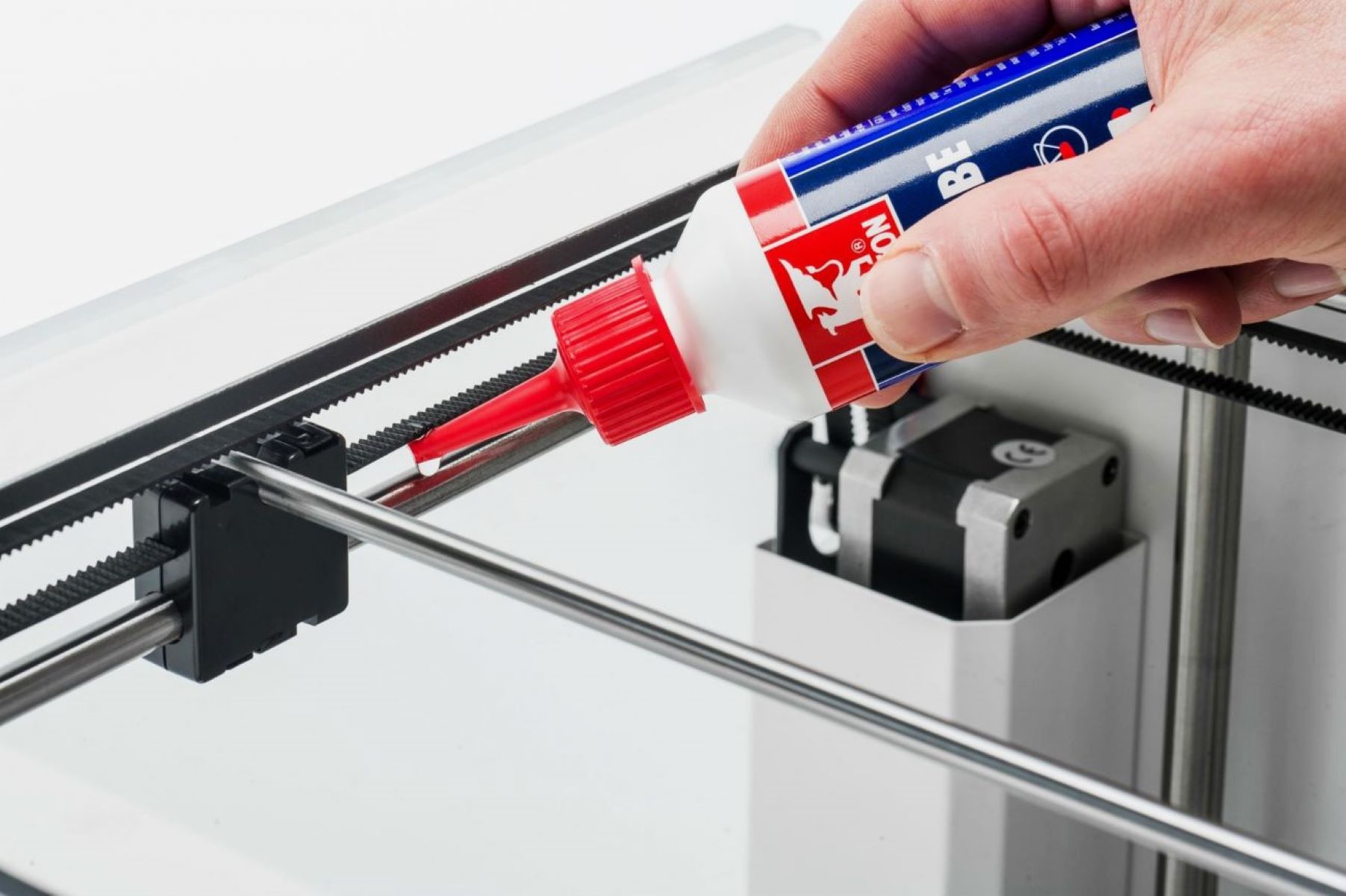
Adhesion and Bed Preparation: Achieving optimal adhesion between the print and the bed surface is crucial for preventing warping and ensuring print stability. Experiment with bed surface materials, such as BuildTak, PEI sheets, and glass, and employ adhesion aids like glue sticks and 3D printing adhesives to enhance print adhesion.
Post-Processing and Finishing: Refine your prints through post-processing techniques, including sanding, painting, and surface smoothing. Exploring finishing methods such as acetone vapor smoothing for ABS prints or resin curing for SLA prints elevates the visual appeal and tactile quality of your creations.
By honing these fundamental 3D printing techniques, you lay the groundwork for producing exceptional prints with precision and finesse. Embrace experimentation, learn from each print’s nuances, and leverage these techniques to realize your creative vision with unparalleled proficiency.
Read more: How Loud Is A 3D Printer
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques
Delving into advanced 3D printing techniques unlocks a realm of possibilities, enabling you to push the boundaries of creativity and precision in your prints. As you ascend to the realm of advanced printing, mastering these techniques empowers you to tackle intricate designs, optimize print quality, and explore innovative applications of additive manufacturing.
Multi-Material and Multi-Nozzle Printing: Embrace the versatility of multi-material and multi-nozzle printing, where intricate designs and functional prototypes benefit from the use of dissolvable support materials, flexible filaments, and composite blends. Leveraging dual-extrusion or multi-nozzle setups expands your design freedom and facilitates the creation of complex, multi-component objects.
Volumetric and Pressure-Advance Calibration: Fine-tuning volumetric extrusion and pressure-advance settings enhances print accuracy and mitigates issues such as oozing and stringing. Understanding these advanced calibration techniques optimizes filament flow dynamics, resulting in cleaner, more precise prints.
Hybrid Printing and Multi-Process Workflows: Explore hybrid printing approaches that combine the strengths of different 3D printing technologies, such as FDM and SLA, within a single print. Integrating multi-process workflows empowers you to capitalize on the unique attributes of each technology, achieving superior surface finish, intricate details, and functional diversity within a single print.
Variable Layer Height and Adaptive Slicing: Implement variable layer height techniques to dynamically adjust layer thickness based on the object’s geometry, optimizing print speed and detail resolution. Harness adaptive slicing algorithms to automatically enhance print quality in complex regions, ensuring uniform precision across the entire print.
Topology Optimization and Lattice Structures: Embrace advanced design principles such as topology optimization to create lightweight, structurally efficient objects. Incorporating lattice structures and generative design methodologies not only reduces material usage but also unlocks unprecedented design freedom and functional optimization.
Bioprinting and Functional Materials: Venture into the realm of bioprinting and functional materials, where 3D printing extends beyond rigid plastics to encompass bio-compatible resins, conductive filaments, and specialized materials tailored for specific applications. This frontier opens avenues for medical prototypes, electronic components, and advanced functional prototypes.
By embracing these advanced 3D printing techniques, you elevate your proficiency as a 3D printing enthusiast or professional, expanding your creative horizons and unlocking the potential to materialize intricate, innovative, and functionally diverse designs with unparalleled precision and sophistication.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While 3D printing offers a gateway to creativity and innovation, encountering occasional challenges is an inherent part of the printing process. Familiarizing yourself with common issues and their remedies equips you to navigate potential hurdles with confidence, ensuring that your printing endeavors remain smooth and rewarding.
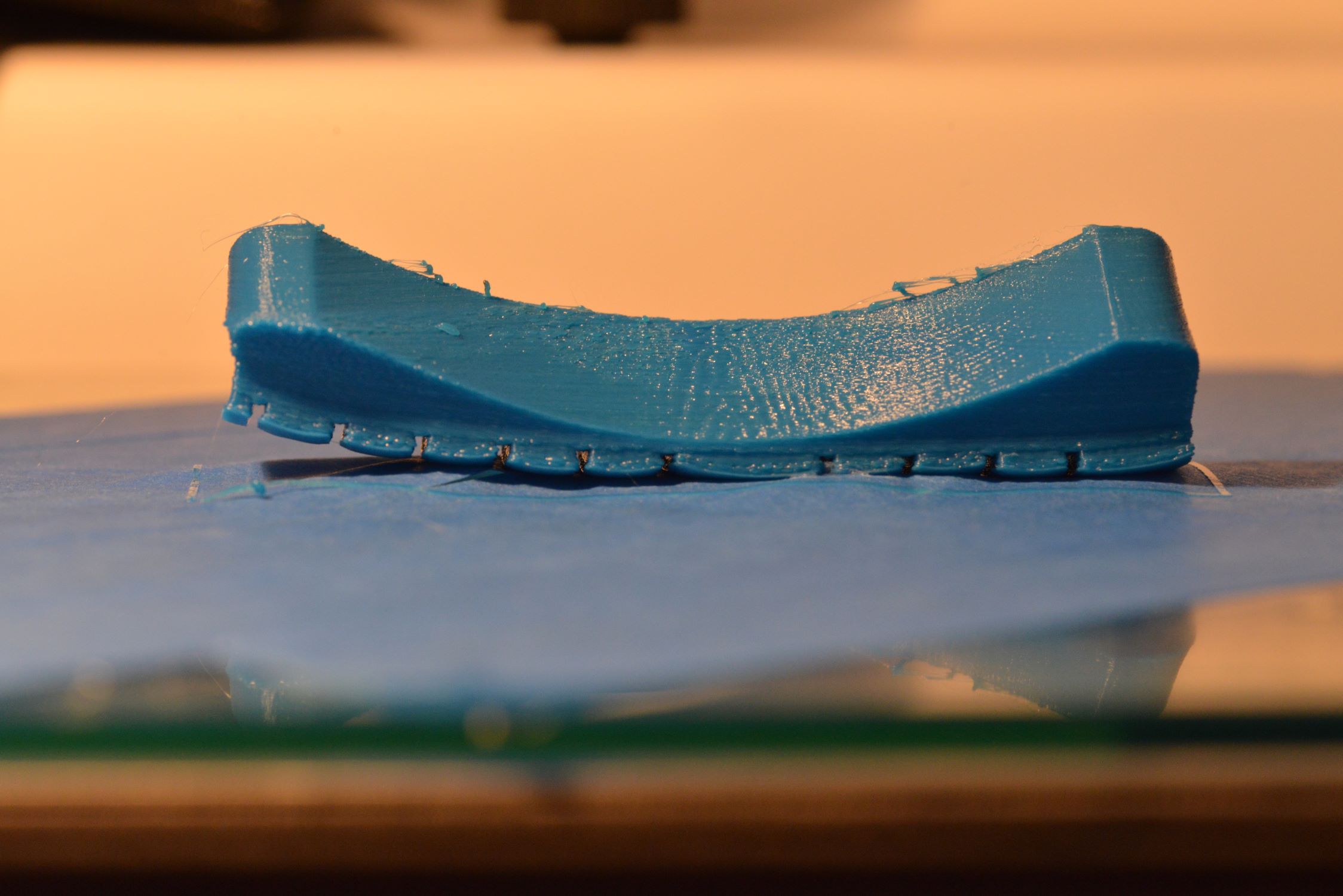
Print Adhesion and Warping: Inadequate adhesion between the print and the bed surface can lead to warping and detachment. Address this issue by optimizing the print bed temperature, employing adhesion aids such as glue sticks or specialized bed adhesives, and ensuring a level print bed to promote uniform adhesion across the print’s base layers.
Layer Misalignment and Shifting: Misaligned layers or sudden shifts during printing can result from loose belts, insufficient belt tension, or mechanical obstructions. Regularly inspect and adjust belt tension, verify the integrity of pulleys and drive mechanisms, and ensure that the printer’s frame and components are securely fastened to prevent unwanted movement.
Extrusion Issues and Under-Extrusion: Inconsistent extrusion or under-extrusion, characterized by gaps or incomplete layers, may stem from partial clogs, improper filament tension, or inadequate nozzle temperature. Clearing nozzle obstructions, calibrating extrusion settings, and verifying filament diameter and quality mitigates under-extrusion, fostering uniform and reliable filament deposition.
Stringing and Oozing: Stringing, manifested as thin filament strands between printed features, and oozing, where excess material is deposited during non-print moves, can be mitigated by fine-tuning retraction settings, adjusting print temperatures, and optimizing travel movements to minimize material deposition during non-print segments.
Print Imperfections and Zits: Surface imperfections, such as zits, blobs, or artifacts, can result from inconsistent cooling, improper retraction, or irregular filament flow. Tailoring cooling fan settings, optimizing retraction distances and speeds, and calibrating extrusion parameters fosters smoother, blemish-free prints.
Print Quality and Resolution: Achieving optimal print quality and resolution necessitates meticulous calibration of print settings, including layer height, print speed, and cooling. Fine-tuning these parameters, conducting test prints, and leveraging advanced slicing software features enhances print precision and visual appeal.
By proactively addressing these common issues and implementing targeted solutions, you fortify your troubleshooting acumen and cultivate a deeper understanding of your 3D printer’s nuances. Embrace each challenge as an opportunity to refine your skills and enhance the quality of your prints, ultimately enriching your 3D printing journey with resilience and expertise.
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on a captivating journey into the realm of 3D printing. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve navigated the intricacies of 3D printing, from understanding its foundational principles to mastering advanced techniques and troubleshooting common challenges. As you conclude this immersive exploration, it’s essential to reflect on the transformative potential of 3D printing and the boundless opportunities it presents.
At its core, 3D printing transcends traditional manufacturing paradigms, empowering individuals and industries to materialize innovative concepts, iterate designs with agility, and customize products with unparalleled precision. The fusion of digital creativity and tangible craftsmanship epitomizes the essence of 3D printing, fostering a dynamic ecosystem of creativity, innovation, and limitless possibilities.
By delving into the nuances of choosing the right printer, setting it up with precision, and mastering fundamental and advanced printing techniques, you have equipped yourself to embark on a fulfilling 3D printing journey. The fusion of technical proficiency, creative vision, and problem-solving acumen positions you to realize a myriad of projects, from artistic expressions to functional prototypes, and from intricate designs to utilitarian innovations.
As you navigate the ever-evolving landscape of 3D printing, remember that experimentation, resilience, and continuous learning are the cornerstones of mastery. Embrace the iterative nature of 3D printing, where each print serves as a canvas for refinement and innovation. Seize the opportunity to collaborate with a vibrant community of creators, share insights, and draw inspiration from diverse perspectives, enriching your journey with camaraderie and collective growth.
Ultimately, your foray into 3D printing transcends the mere act of programming a printer; it embodies a profound convergence of artistry, engineering, and boundless imagination. Embrace the transformative power of 3D printing as a catalyst for innovation, a medium for self-expression, and a gateway to shaping a future where creativity knows no bounds.
As you embark on your 3D printing odyssey, may your creations inspire, your discoveries ignite curiosity, and your journey unfold with the awe-inspiring magic of bringing imagination to life, layer by layer.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Program A 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “How To Program A 3D Printer”