

Articles
How To Determine Electrical Wire Size
Modified: September 2, 2024
Get expert tips on determining the right electrical wire size with our informative articles. Upgrade your knowledge and make informed decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to electrical wiring, choosing the correct wire size is of utmost importance. Using the wrong size wire can lead to a multitude of problems, including overheating, voltage drop, and even electrical hazards like fires. It is crucial to understand how to determine the appropriate wire size for your electrical applications.
In this article, we will delve into the world of electrical wire gauges, factors to consider when choosing wire size, and how to calculate the correct wire size. We will also discuss the relevant guidelines provided by the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure electrical safety. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to determine the right wire size for your next electrical project.
So let’s begin our journey by exploring the concepts of wire gauges and why they are essential in electrical installations.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding wire gauges and factors like voltage, current load, and environment are crucial in determining the right electrical wire size for safe and efficient operations.
- Calculating wire size using methods like current-carrying capacity and voltage drop ensures proper handling of expected loads and maintenance of voltage levels. Adhering to NEC guidelines and practical considerations further optimize electrical installations.
Read more: How To Determine Bathtub Size
Understanding Wire Gauges
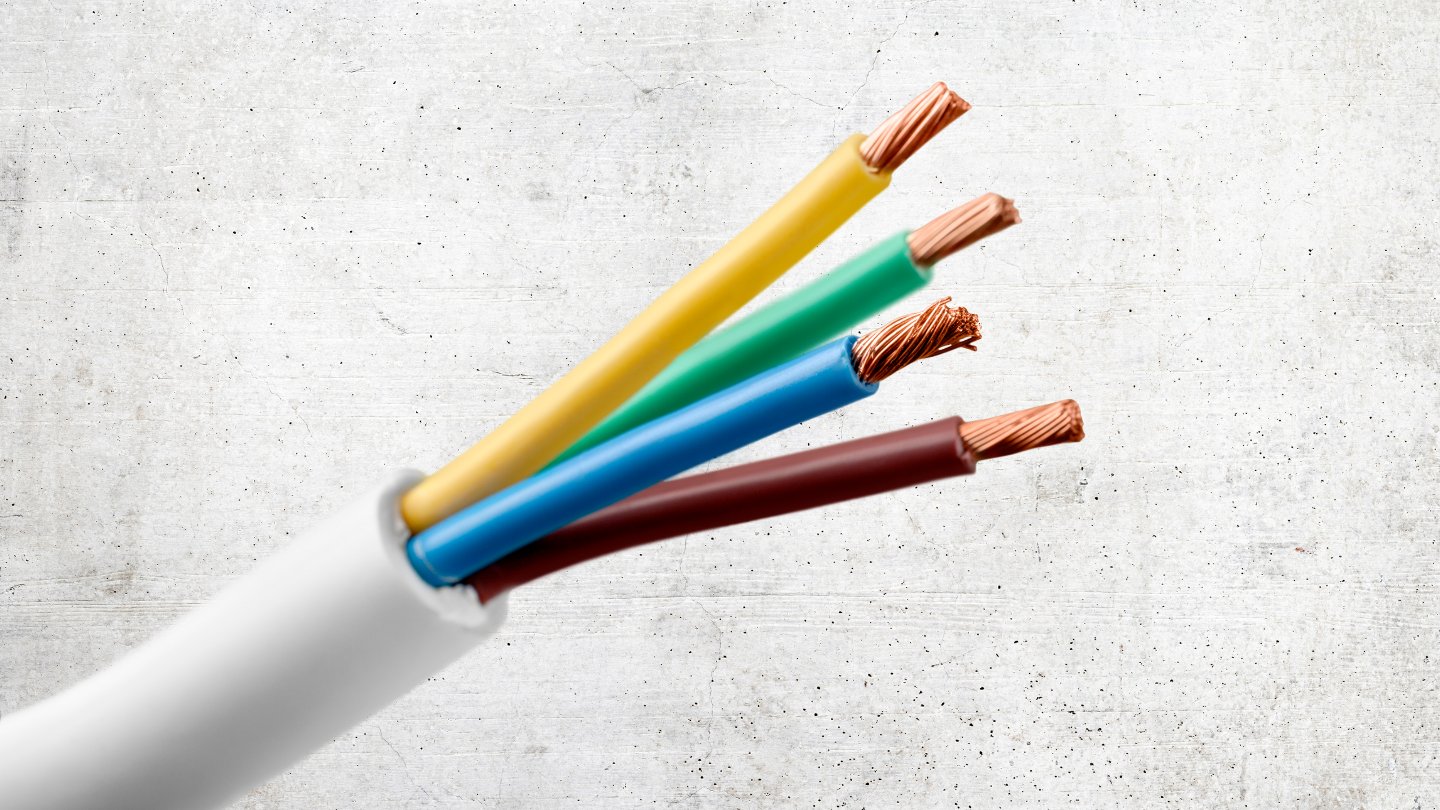
In the world of electrical wiring, wire gauges refer to the size of the wire. The gauge of a wire represents its diameter or cross-sectional area. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is commonly used in North America to standardize wire sizes. The AWG system assigns a specific number to each wire gauge, with a smaller number indicating a larger wire size.
Wire gauges range from 0000 (4/0) to 40, with 0000 being the thickest wire and 40 being the thinnest. As the wire gauge increases numerically, the wire diameter decreases, resulting in a smaller cross-sectional area. It’s important to note that different wire sizes have different ampacity ratings, which determine the maximum amount of current the wire can safely carry.
To better understand wire gauges, it may be helpful to visualize them in relation to everyday objects. For instance, a 12-gauge wire, which is commonly used for household electrical wiring, has a diameter similar to that of a standard clothes hanger. On the other hand, a 22-gauge wire, which is much thinner, is comparable to the thickness of a paperclip.
When choosing the appropriate wire size for a specific electrical application, it’s crucial to consider factors such as the voltage, current load, and wire length. These factors will play a significant role in determining the optimal wire gauge to ensure safe and efficient electrical operations.
Factors to Consider
When determining the right wire size for your electrical project, several factors need to be taken into consideration. Here are some important factors to keep in mind:
1. Voltage: The voltage of the electrical circuit is a critical factor in selecting the appropriate wire size. Higher voltage circuits require thicker wires to prevent excessive voltage drop and ensure efficient power transmission.
2. Current Load: The amount of current that will be flowing through the wire is another crucial factor. Current load is measured in amperes (A) and determines the ampacity rating of the wire. It is essential to choose a wire gauge that can handle the expected current without overheating.
3. Wire Length: The length of the wire also affects its resistance and voltage drop. As the wire length increases, resistance increases, which can lead to voltage drop. When dealing with longer wire runs, it may be necessary to choose a larger wire size to compensate for the voltage drop.
4. Environment: Consider the environment in which the wire will be installed. If the wire will be exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals, it may require specific types of insulation or coatings to ensure its durability and safety.
5. Wire Type: Different wire types have specific applications and specifications. For example, solid wire is suitable for permanent installations, while stranded wire is more flexible and better suited for applications that require frequent movement or flexing.
6. Overcurrent Protection: Consult the appropriate overcurrent protection device, such as circuit breakers or fuses, to ensure that the wire selected can handle the expected current load within the safety limits.
By taking into account these factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting the right wire size for your electrical project. A thorough understanding of these considerations will help ensure the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your electrical installations.
Calculating Wire Size
Determining the correct wire size for a specific electrical application requires calculations based on the expected current load and wire length. Here are two commonly used methods to calculate wire size:
1. Current-Carrying Capacity Method: This method involves determining the ampacity rating of the wire based on the expected current load. The ampacity rating is the maximum allowable current that a wire can carry without exceeding its temperature rating. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for ampacity ratings based on wire size and insulation type.
To calculate the wire size using the current-carrying capacity method, follow these steps:
a. Determine the expected current load in amperes (A).
b. Check the NEC or manufacturer’s tables to find the ampacity rating for the wire’s insulation type and installation conditions.
c. Choose a wire size (gauge) that has an ampacity rating equal to or greater than the expected current load.
2. Voltage Drop Method: This method involves calculating the acceptable voltage drop across the wire based on the length of the wire run and the allowable voltage drop for the specific application. The voltage drop is determined by the resistance of the wire, which increases with the wire length and decreases with the wire size.
To calculate the wire size using the voltage drop method, follow these steps:
a. Determine the length of the wire run in feet (ft).
b. Determine the expected current load in amperes (A).
c. Determine the allowable voltage drop (usually a percentage) for the specific application. Typical values range from 2% to 5%.
d. Use Ohm’s law (V = I x R) to calculate the resistance, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
e. Calculate the maximum acceptable resistance by multiplying the voltage drop percentage by the supply voltage.
f. Choose a wire size (gauge) that has a resistance per unit length (usually given in Ohms/ft) lower than the calculated maximum acceptable resistance.
Both methods require careful consideration of the expected current load, wire length, and voltage drop. It is recommended to consult the NEC, a qualified electrician, or use online wire size calculators to ensure accurate results.
Remember, it is always safer to choose a slightly larger wire size to account for unexpected increases in current load and minimize voltage drop.
When determining electrical wire size, consider the ampacity of the circuit, the length of the wire run, and the type of insulation. Use a wire size calculator or consult the National Electrical Code for guidance.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Guidelines
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for electrical installations in the United States. These guidelines include specifications and requirements for wire sizes based on the intended application and installation conditions. Here are some key NEC guidelines to keep in mind when determining wire sizes:
1. Ampacity Ratings: The NEC provides tables that specify the ampacity ratings for different wire sizes and insulation types. These ratings are based on the maximum temperature that the wire can safely withstand without deteriorating or posing a hazard. Be sure to select a wire size that has an ampacity rating equal to or greater than the expected current load.
2. Conductor Sizing: The NEC provides specific requirements for conductor sizing based on the type of circuit and its intended use. For example, branch circuits that serve general-purpose outlets in a dwelling unit generally require a minimum of 15 or 20-amp rated conductors.
3. Voltage Drop: The NEC allows for a certain amount of voltage drop across a wire based on the type of circuit and the sensitivity of the connected devices. For example, circuits supplying dwelling units with power must have a maximum allowable voltage drop of 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeder circuits.
4. Derating Factors: In certain conditions, such as when wires are bundled together or installed in a conduit, derating factors may need to be applied. These factors reduce the ampacity rating of the wire to account for increased heat buildup due to reduced airflow or proximity to other heat sources.
5. Grounding and Bonding: The NEC provides guidelines for grounding and bonding conductors, which are essential for safety in electrical systems. These guidelines ensure that proper-size grounding and bonding conductors are installed to minimize the risk of electrical shock and facilitate fault clearances.
6. Environmental Factors: The NEC takes into consideration environmental factors that may affect wire sizing requirements. For example, specific requirements exist for wiring in wet or corrosive environments, such as outdoor installations or areas exposed to chemicals or moisture.
It is crucial to consult the NEC guidelines specific to your region, as they may have some variations or additional requirements. Following NEC guidelines helps ensure the safety, efficiency, and compliance of electrical installations.
Remember, while the NEC provides essential guidelines, it is always prudent to consult a licensed electrician or electrical engineer to ensure compliance with local codes and regulations.
Read more: How To Determine Conduit Size
Practical Considerations
When determining the wire size for your electrical project, there are several practical considerations to keep in mind. These considerations can help optimize the installation process and ensure the overall functionality and safety of the electrical system. Here are some practical aspects to consider:
1. Wire Availability: Check the availability of the desired wire size in your local area or online. It’s important to choose a wire size that is readily accessible and affordable. If a specific wire size is difficult to source, consider alternatives that meet the same ampacity requirements.
2. Wire Color Coding: Electrical wires are usually color-coded to indicate their specific function. It is important to adhere to the standard color coding conventions to ensure proper identification and ease of future maintenance or troubleshooting. Check the NEC guidelines or local regulations for the recommended color coding practices.
3. Wire Insulation: Consider the insulation type required for your specific application. Different environments may necessitate different types of insulation, such as heat-resistant, moisture-resistant, or UV-resistant insulation. Selecting the appropriate insulation ensures the longevity and reliability of the wiring.
4. Wire Management: Proper wire management is crucial for both safety and aesthetics. Ensure that wires are neatly organized, properly labeled, and secured in conduit or cable trays where necessary. This helps prevent accidental damage, minimizes the risk of overheating, and simplifies future maintenance or modifications.
5. Wire Length and Routing: Plan the wire routing and determine the length of wire required for each circuit. Minimize wire lengths where possible to reduce voltage drop and save on material costs. Consider potential obstacles or obstructions that may require longer wire runs or specific routing techniques.
6. Future Expansion: Anticipate potential future expansion or modifications when selecting wire sizes. If there is a possibility of increased electrical loads or the need to accommodate additional circuits, it may be wise to choose a slightly larger wire size from the start to avoid the need for rewiring in the future.
7. Safety Precautions: Always prioritize safety when working with electrical systems. Follow proper installation techniques, use appropriate protective equipment, and adhere to local electrical codes and regulations. If you are unsure about any aspect of the installation, consult a licensed electrician for guidance.
Taking these practical considerations into account will help ensure a successful and efficient electrical installation. By considering wire availability, insulation types, wire management, routing, future expansion, and safety precautions, you can create a well-designed and reliable electrical system for your specific application.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct wire size for your electrical project is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe operations. By understanding wire gauges, considering various factors, and following relevant guidelines, you can determine the appropriate wire size for any application.
Understanding wire gauges allows you to grasp the concept of wire diameter and its relation to ampacity. By familiarizing yourself with the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, you can easily distinguish between different wire sizes and make informed decisions during wire selection.
Factors such as voltage, current load, wire length, environment, and wire type must be carefully considered. These factors directly impact the wire size and influence the overall performance and safety of the electrical system. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure optimal electrical conductivity, efficient power transmission, and minimize the risk of voltage drop and hazards.
Calculating wire size involves using methods such as the current-carrying capacity and voltage drop. These methods help determine the appropriate wire gauge based on the expected current load, wire length, and voltage drop tolerance. By accurately calculating the wire size, you can ensure that it can handle the intended load and maintain proper voltage levels.
It is important to adhere to the guidelines provided by the National Electrical Code (NEC) for wire sizing. The NEC specifies ampacity ratings, conductor sizing requirements, voltage drop allowances, grounding, and bonding guidelines, among other crucial aspects. These guidelines are designed to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical installations.
Practical considerations, such as wire availability, color coding, insulation type, wire management, wire length, routing, and future expansion, should also be taken into account. These considerations contribute to the functionality, aesthetics, and longevity of the electrical system.
In conclusion, selecting the correct wire size for electrical applications is a critical aspect of any project. By understanding wire gauges, considering various factors, following NEC guidelines, and taking practical considerations into account, you can confidently determine the appropriate wire size for any electrical installation. Always prioritize safety, adhere to local regulations, and consult professionals if needed to ensure a successful and reliable electrical system.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Determine Electrical Wire Size
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Determine Electrical Wire Size”