Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is A BIM Execution Plan?

Building & Construction
What Is A BIM Execution Plan?
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn the importance of a BIM Execution Plan in building construction. Discover how it ensures project success, collaboration, and efficient workflows.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
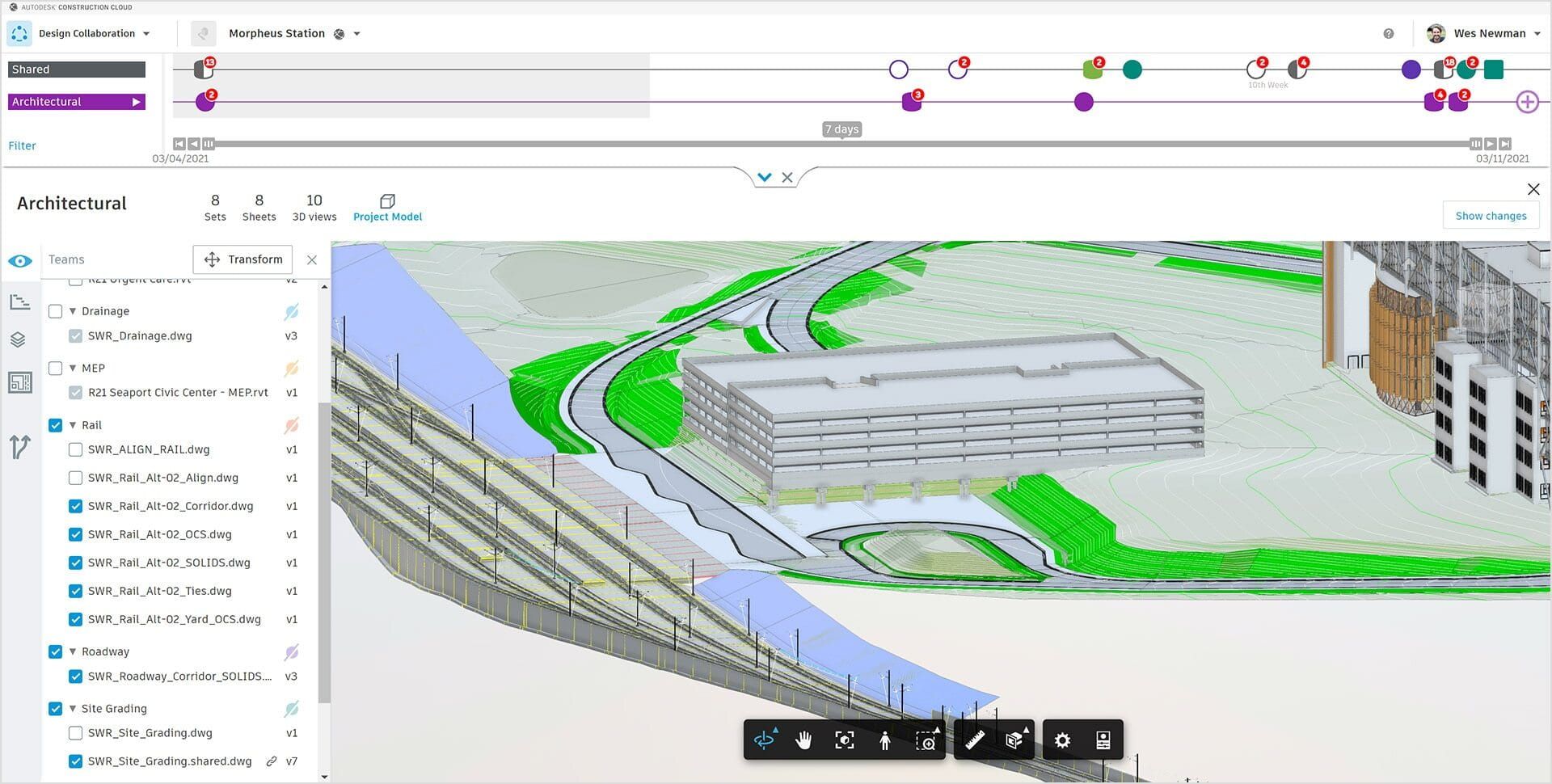
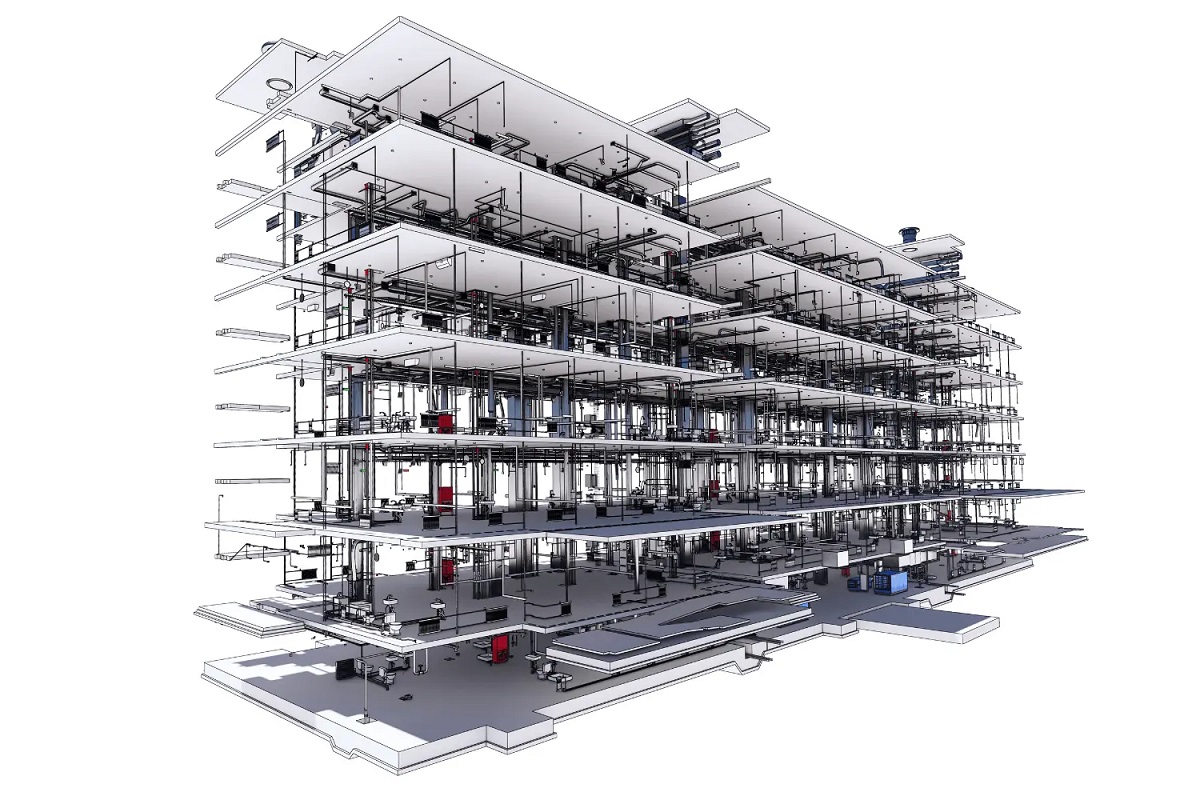
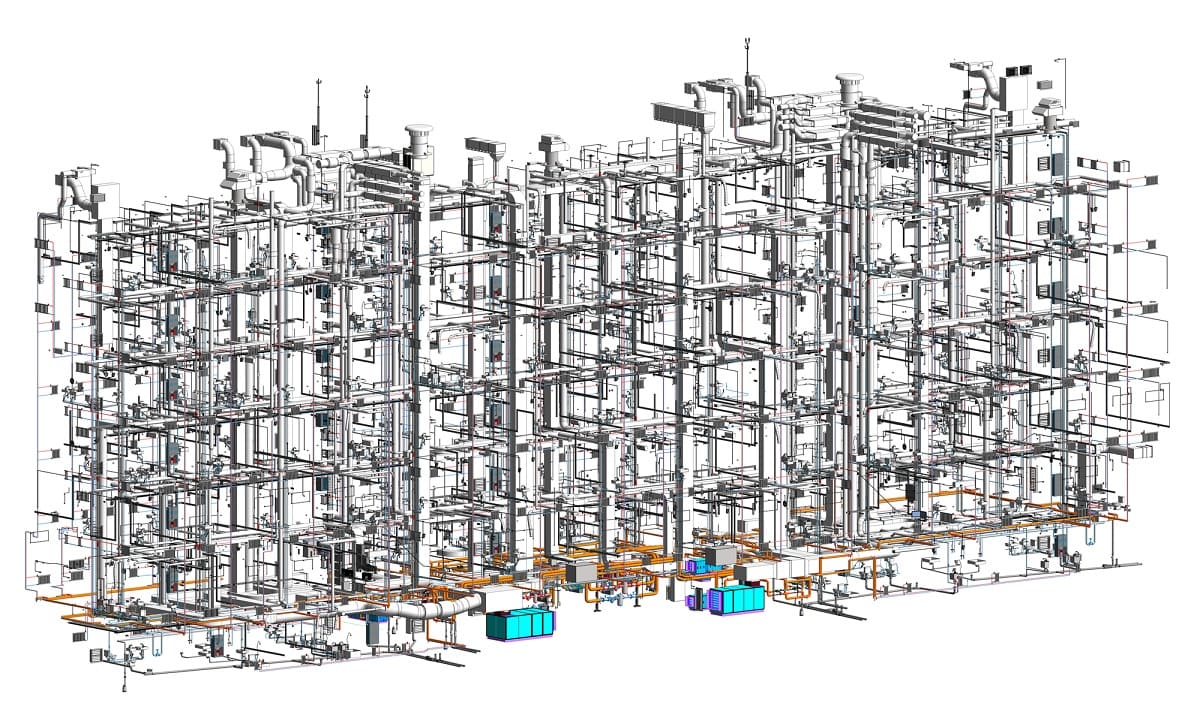
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the construction industry by enhancing collaboration, improving project efficiency, and reducing errors and rework. However, to effectively implement BIM on a construction project, a well-defined plan is essential. This is where a BIM Execution Plan (BEP) comes into play.
A BIM Execution Plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the strategies, processes, and procedures for implementing BIM on a construction project. It serves as a roadmap for all stakeholders involved, ensuring consistency, standardization, and successful execution of BIM throughout the project lifecycle.
The purpose of this article is to provide a deeper understanding of what a BIM Execution Plan entails, why it is important, and how to develop and implement one effectively. We will also explore the benefits of having a BIM Execution Plan and the challenges that may arise during its creation and implementation.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the significance of a BIM Execution Plan and how it can contribute to the success of your construction projects.
Key Takeaways:
- A BIM Execution Plan is crucial for successful BIM implementation in construction projects. It aligns stakeholders, sets standards, clarifies responsibilities, and promotes collaboration, leading to efficient project delivery and reduced errors.
- Developing a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan involves defining goals, establishing standards, providing training, and addressing challenges. Following best practices ensures successful BIM implementation, improved collaboration, and enhanced project outcomes.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Purpose of a BIM Execution Plan
A BIM Execution Plan serves several crucial purposes in the successful implementation of BIM on a construction project:
- Establishing project objectives: The BIM Execution Plan helps define the project objectives in terms of BIM deliverables, milestones, and overall project goals. It ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards a common vision.
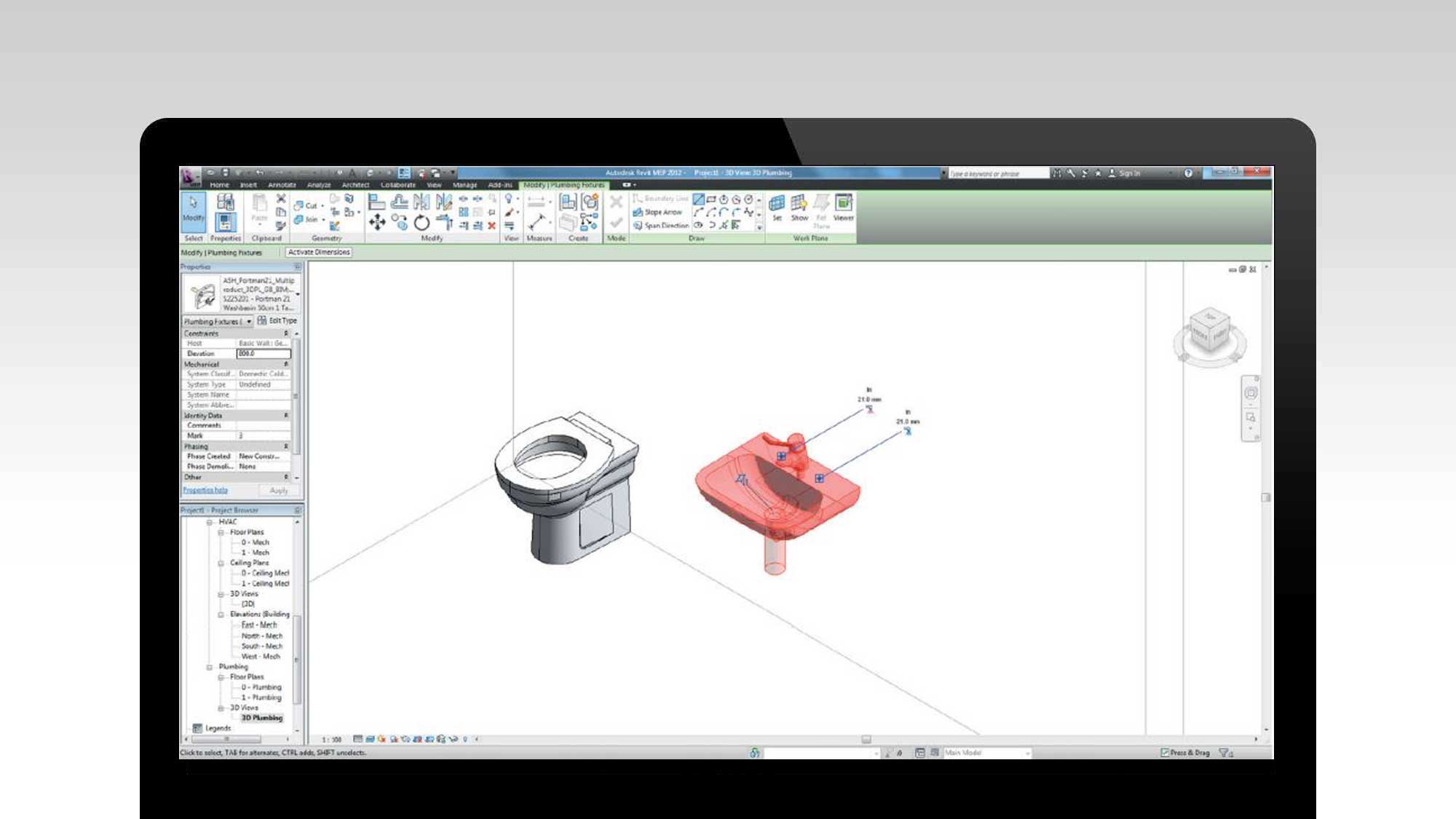
- Setting BIM standards and guidelines: The plan establishes the standards and guidelines for BIM usage throughout the project. It defines the required level of detail (LOD) for different project phases, naming conventions, data exchange protocols, and modeling requirements. This promotes consistency and interoperability among project participants.
- Clarifying roles and responsibilities: The BIM Execution Plan clearly defines the roles and responsibilities of each project participant regarding BIM implementation. It outlines the specific tasks and deliverables expected from architects, engineers, contractors, and other team members involved in the BIM process.
- Ensuring coordination and collaboration: The plan facilitates coordination and collaboration among project stakeholders by defining the workflows and communication protocols for BIM-related activities. It outlines how information will be shared, reviewed, and updated throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring seamless collaboration and reducing conflicts and clashes.
- Managing project information: The BIM Execution Plan provides guidelines for the management of project information. It outlines data standards, file naming conventions, version control processes, and information exchange formats. This ensures that project data is organized, accessible, and easily shared across disciplines and project phases.
In summary, the purpose of a BIM Execution Plan is to establish clear objectives, standardize BIM practices, assign roles and responsibilities, facilitate coordination and collaboration, and manage project information. By having a well-defined plan in place, construction projects can maximize the benefits of BIM implementation and ensure a smooth and efficient project delivery process.
Key Components of a BIM Execution Plan
A BIM Execution Plan comprises several essential components that collectively ensure the successful implementation of BIM on a construction project. The following are the key components of a BIM Execution Plan:
- Project Information: This section provides an overview of the project, including its objectives, scope, schedule, and budget. It also includes information about the project team and their roles and responsibilities.
- BIM Goals and Objectives: This component outlines the specific goals and objectives of the project regarding BIM implementation. It identifies the desired outcomes and benefits of using BIM on the project.
- BIM Standards and Guidelines: Here, the plan defines the BIM standards and guidelines to be followed throughout the project. It includes information about the level of detail (LOD) required for different project phases, naming conventions, modeling guidelines, and file formats for information exchange.
- BIM Roles and Responsibilities: This section outlines the roles and responsibilities of each project participant in relation to BIM implementation. It clearly defines the tasks and deliverables expected from architects, engineers, contractors, and other team members involved in the BIM process.
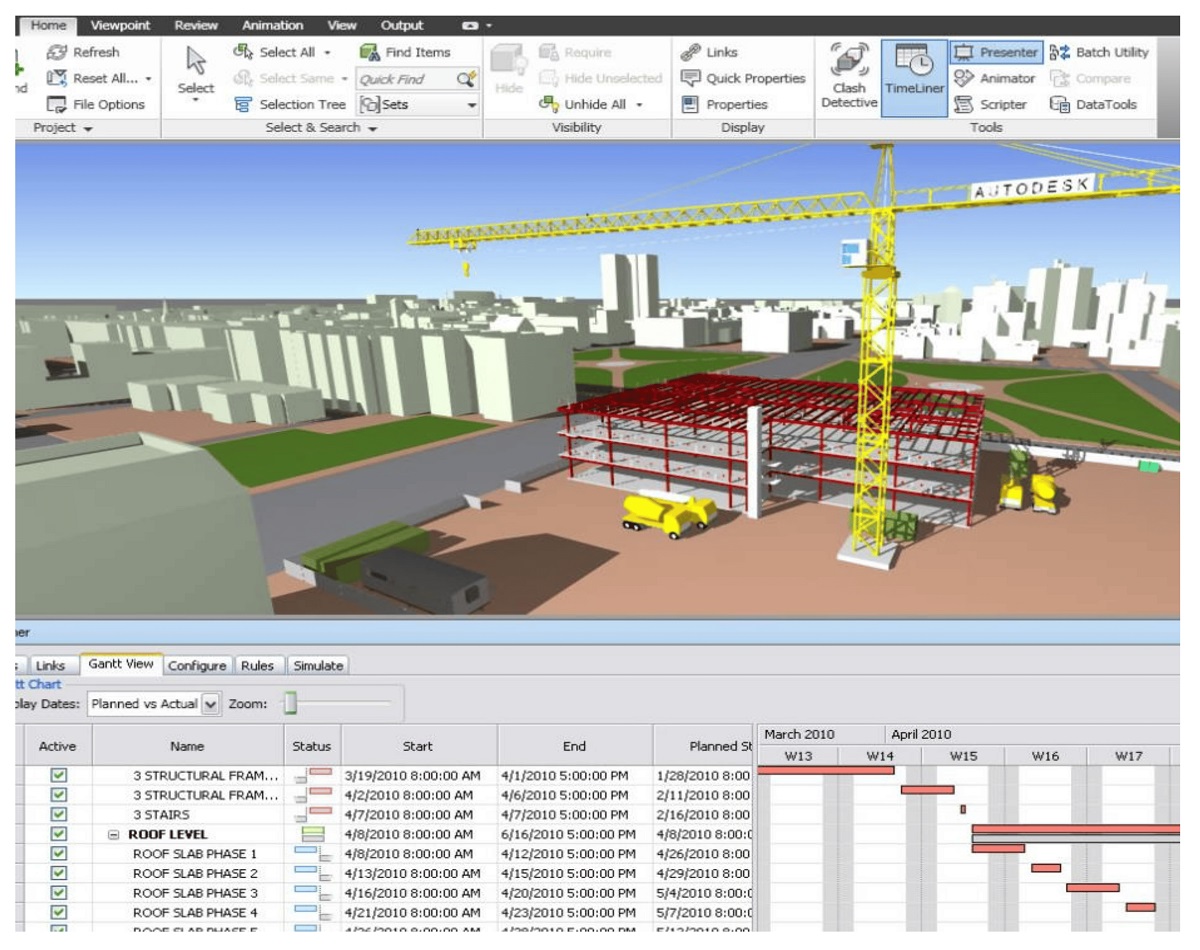
- BIM Workflows and Processes: Here, the plan describes the workflows and processes for BIM-related activities. It outlines how information will flow among project stakeholders, including the coordination and review processes. It also includes details about clash detection, model validation, and change management procedures.
- Data Management: This component addresses the management of project information and data. It includes guidelines for data organization, file naming conventions, information exchange protocols, and version control procedures. It also outlines the use of data platforms and collaboration tools for efficient data management.
- BIM Deliverables and Milestones: This section specifies the BIM deliverables required at different project stages. It identifies the key milestones related to BIM implementation and provides a timeline for their completion.
- BIM Training and Support: Here, the plan outlines the training needs of the project team in relation to BIM implementation. It identifies the BIM training requirements, resources, and support mechanisms to ensure that all team members are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge.
- BIM Coordination and Communication: This component focuses on the coordination and communication aspects of BIM implementation. It defines the communication protocols, meeting schedules, and reporting mechanisms to ensure effective collaboration and information exchange among project participants.
- BIM Implementation Strategy: Lastly, the plan includes a section dedicated to the overall BIM implementation strategy. It outlines the steps and milestones for implementing BIM on the project, identifies potential risks and mitigation measures, and ensures that the BIM execution aligns with the project timeline and goals.
By incorporating these key components into a BIM Execution Plan, construction projects can effectively manage BIM implementation, promote collaboration, set clear expectations, and maximize the benefits of BIM technology.
Benefits of Having a BIM Execution Plan
A well-developed BIM Execution Plan offers numerous benefits for construction projects implementing Building Information Modeling (BIM). The following are some of the key benefits of having a BIM Execution Plan:
- Enhanced Collaboration: A BIM Execution Plan promotes collaboration among project stakeholders. By establishing clear guidelines for communication, information exchange, and coordination, the plan ensures that all team members can work together effectively. This leads to improved collaboration and a better understanding of project requirements.
- Improved Efficiency: With a BIM Execution Plan, construction projects can streamline their processes and workflows. By defining standardized procedures and protocols, the plan facilitates a more efficient project delivery process. This results in reduced errors, rework, and delays, ultimately saving time and costs.
- Consistency and Standardization: The BIM Execution Plan establishes consistent practices and standards across the project. This ensures that all project participants follow the same guidelines for BIM implementation, including modeling practices, information sharing, and project documentation. Consistency and standardization promote interoperability and reduce conflicts and discrepancies.
- Risk Mitigation: By addressing potential risks and challenges upfront, a BIM Execution Plan helps mitigate project risks. The plan identifies potential conflicts, clashes, and coordination issues, allowing for proactive risk management. This minimizes the likelihood of costly issues arising during the construction phase.
- Improved Decision-Making: A well-defined BIM Execution Plan facilitates data-driven decision-making. By integrating accurate and up-to-date project information, the plan enables project teams to make informed decisions about design changes, construction sequencing, and material selections. This leads to better project outcomes and reduces the need for costly revisions.
- Increased Productivity: The BIM Execution Plan optimizes resource allocation and improves project team productivity. By providing clear roles and responsibilities, defining workflows, and outlining deliverables and milestones, the plan ensures that each team member knows their tasks and expectations. This leads to increased productivity and overall project efficiency.
- Effective Change Management: Change is an inevitable part of construction projects, but managing changes can be challenging. A BIM Execution Plan includes processes and procedures for change management, ensuring that project modifications are properly assessed, communicated, and implemented. This minimizes the impact of changes and maintains project integrity.
- Enhanced Facility Management: A BIM Execution Plan facilitates the transition from the construction phase to the facility management phase. By capturing accurate information about building systems, components, and maintenance requirements, the plan provides valuable data for facility managers. This enables efficient facility operations, maintenance, and future renovations.
In summary, a BIM Execution Plan offers a wide range of benefits to construction projects. It enhances collaboration, improves efficiency, promotes consistency, mitigates risks, facilitates decision-making, increases productivity, enables effective change management, and enhances facility management. By investing time and effort in developing a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan, construction projects can reap the rewards of successful BIM implementation.
A BIM Execution Plan (BEP) is a crucial document that outlines the processes, standards, and guidelines for implementing Building Information Modeling on a project. It helps ensure that all project stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same BIM goals.
Steps to Develop a BIM Execution Plan
Developing a BIM Execution Plan requires careful planning and collaboration among project stakeholders. The following are the key steps involved in developing a BIM Execution Plan:
- Define Project Goals and Objectives: Start by clearly defining the goals and objectives of the project regarding BIM implementation. Identify the desired outcomes and benefits that BIM will bring to the project.
- Identify Key Stakeholders: Identify all project stakeholders who will be involved in the BIM process. This includes architects, engineers, contractors, subcontractors, and any other relevant parties.
- Establish BIM Standards and Guidelines: Develop and document the BIM standards and guidelines for the project. This includes specifying the required level of detail (LOD) for different project phases, defining naming conventions, information exchange protocols, and modeling guidelines.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each project stakeholder regarding BIM implementation. This ensures that everyone understands their tasks and deliverables related to BIM.
- Define BIM Workflows and Processes: Map out the workflows and processes for BIM-related activities. This includes defining the coordination and review processes, clash detection procedures, model validation steps, and change management protocols.
- Establish Data Management Procedures: Develop procedures for data management, including file organization, naming conventions, version control, and information exchange formats. Determine the tools and platforms that will be used for efficient data management throughout the project.
- Identify BIM Deliverables and Milestones: Identify the BIM deliverables required at different project stages. Determine the key milestones related to BIM implementation and establish a timeline for their completion.
- Provide BIM Training and Support: Determine the BIM training needs of the project team and provide appropriate training resources. Ensure that all team members have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively use BIM on the project.
- Establish Communication and Collaboration Protocols: Define the communication protocols, meeting schedules, and reporting mechanisms for BIM-related activities. Establish channels for effective collaboration and information exchange among project stakeholders.
- Document the BIM Execution Plan: Compile all the information and guidelines into a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan document. Include all the components discussed earlier in this article, ensuring that it is well-structured and easy to understand.
- Review and Update: Regularly review and update the BIM Execution Plan as the project progresses. Adapt the plan to any changes in project requirements, team composition, or technology advancements.
By following these steps, construction projects can develop a well-rounded BIM Execution Plan that aligns with project goals, promotes collaboration, standardizes practices, and ensures successful BIM implementation.
Read more: What Is A BIM Coordinator?
Challenges in Creating and Implementing a BIM Execution Plan
While a BIM Execution Plan is crucial for the successful implementation of BIM on a construction project, there are several challenges that project teams may encounter during its creation and implementation. The following are some common challenges:
- Lack of Understanding: One of the major challenges is the lack of understanding about BIM and its potential benefits. This can make it difficult to create and implement a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan that effectively addresses the project’s specific needs.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing BIM requires a significant shift in workflows, processes, and collaboration methods. Resistance to change from project team members who are accustomed to traditional practices can hinder the development and implementation of the BIM Execution Plan.
- Coordination Issues: BIM relies on effective collaboration and coordination among various project stakeholders. However, coordinating different teams and disciplines can be challenging, particularly in large-scale projects with multiple stakeholders.
- Technical Challenges: BIM implementation involves the use of specialized software and technologies. Technical challenges such as learning curves, interoperability issues, and software compatibility can pose hurdles in creating and implementing the BIM Execution Plan.
- Data Management: Managing vast amounts of data generated through BIM can be complex. Challenges may include data organization, file naming conventions, information exchange protocols, and version control. Inadequate data management practices can impact the effectiveness of the BIM Execution Plan.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective collaboration and communication among project stakeholders are crucial for successful BIM implementation. However, challenges such as language barriers, lack of clear communication protocols, and inadequate collaboration tools can hinder the execution of the BIM Execution Plan.
- Cost and Resource Constraints: Developing and implementing a BIM Execution Plan requires investment in training, software licenses, and technology infrastructure. Limited financial resources or lack of support from project owners may create obstacles in creating and implementing the plan.
- Continuous Updating: BIM technology and industry practices are constantly evolving. Keeping the BIM Execution Plan updated with the latest standards, guidelines, and best practices can be challenging, especially on long-duration projects.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to invest in proper training and education for the project team, foster a culture of collaboration and openness to change, establish clear communication channels, and regularly review and update the BIM Execution Plan as needed.
By addressing these challenges proactively, construction projects can effectively create and implement a BIM Execution Plan that maximizes the benefits of BIM, improves project outcomes, and enhances overall project efficiency.
Best Practices for Developing and Implementing a BIM Execution Plan
Developing and implementing a BIM Execution Plan requires careful planning and consideration. By following best practices, construction projects can ensure an effective and successful implementation of BIM. The following are some key best practices to keep in mind:
- Early Involvement: Involve all relevant stakeholders from the early stages of the project. This includes architects, engineers, contractors, subcontractors, and facility managers. Their input and expertise will help shape the BIM Execution Plan to meet the project’s specific needs.
- Set Clear Goals and Objectives: Define clear and measurable goals and objectives for BIM implementation. This will guide the development of the BIM Execution Plan and align all project stakeholders towards a common vision.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster a culture of collaboration and open communication among project teams. Establish clear communication channels and protocols to ensure effective information exchange, coordination, and timely resolution of issues.
- Standardization: Establish standardized BIM practices and guidelines across the project. This includes defining naming conventions, modeling guidelines, file formats, and information exchange protocols. Standardization promotes consistency, interoperability, and streamlines project workflows.
- Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training and education on BIM tools and processes to the project team. This will equip them with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively utilize BIM technology and adhere to the BIM Execution Plan.
- Quality Control and Data Management: Implement robust quality control processes to ensure the accuracy and integrity of BIM data. Establish data management procedures, including file organization, version control, and information exchange protocols. This will enable efficient data sharing and collaboration throughout the project lifecycle.
- Regular Updates: Continuously review and update the BIM Execution Plan as the project progresses. This will ensure that the plan remains aligned with project objectives, incorporates changes in technology and industry best practices.
- Documentation and Training Materials: Document all aspects of the BIM Execution Plan and make them readily accessible to all project stakeholders. Provide training materials, guidelines, and resources to support the implementation of the BIM Execution Plan.
- Quality Assurance and Auditing: Conduct regular quality assurance checks and audits to ensure compliance with the BIM Execution Plan. This will help identify any deviations or shortcomings and allow for corrective actions to be taken promptly.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and learning. Encourage feedback from project teams, monitor performance metrics, and seek opportunities to enhance the BIM Execution Plan and its implementation.
By following these best practices, construction projects can develop and implement a robust BIM Execution Plan that maximizes the benefits of BIM, improves collaboration and efficiency, and delivers successful project outcomes.
Conclusion
The implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the construction industry by revolutionizing collaboration, increasing efficiency, and reducing errors and rework. However, to harness the full potential of BIM, a well-developed and implemented BIM Execution Plan is essential.
A BIM Execution Plan serves as a roadmap for BIM implementation, providing project stakeholders with clear guidelines, standards, and processes. It helps to align project objectives, set BIM standards and guidelines, assign roles and responsibilities, ensure effective coordination and collaboration, and manage project information efficiently.
Throughout this article, we have explored the key components of a BIM Execution Plan, highlighted the benefits of having one, and discussed the steps to develop and implement it. We have also addressed the challenges that may arise during its creation and implementation, as well as provided best practices to overcome these challenges.
By following best practices and investing time and effort into developing a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan, construction projects can reap the rewards of successful BIM implementation. Enhanced collaboration, improved efficiency, consistent practices, effective risk management, data-driven decision-making, increased productivity, and seamless facility management are among the many benefits that a well-implemented BIM Execution Plan can provide.
In conclusion, the adoption of a BIM Execution Plan is essential for any construction project seeking to leverage the power of BIM technology. It ensures that all project stakeholders are on the same page, working towards a common goal, and employing standardized practices and processes. The BIM Execution Plan acts as a guide, ensuring successful BIM implementation and delivering better project outcomes.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, embracing BIM and incorporating it into project workflows through a well-defined BIM Execution Plan will become increasingly crucial for success. By staying up to date with the latest technologies, industry standards, and best practices, construction professionals can navigate the complexities of BIM implementation and seize the many opportunities it presents.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A BIM Execution Plan?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.







0 thoughts on “What Is A BIM Execution Plan?”