Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is Level 2 BIM?


Building & Construction
What Is Level 2 BIM?
Modified: January 24, 2024
Discover what Level 2 BIM means in the realm of building construction, and how it enhances collaboration and coordination throughout the project lifecycle.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
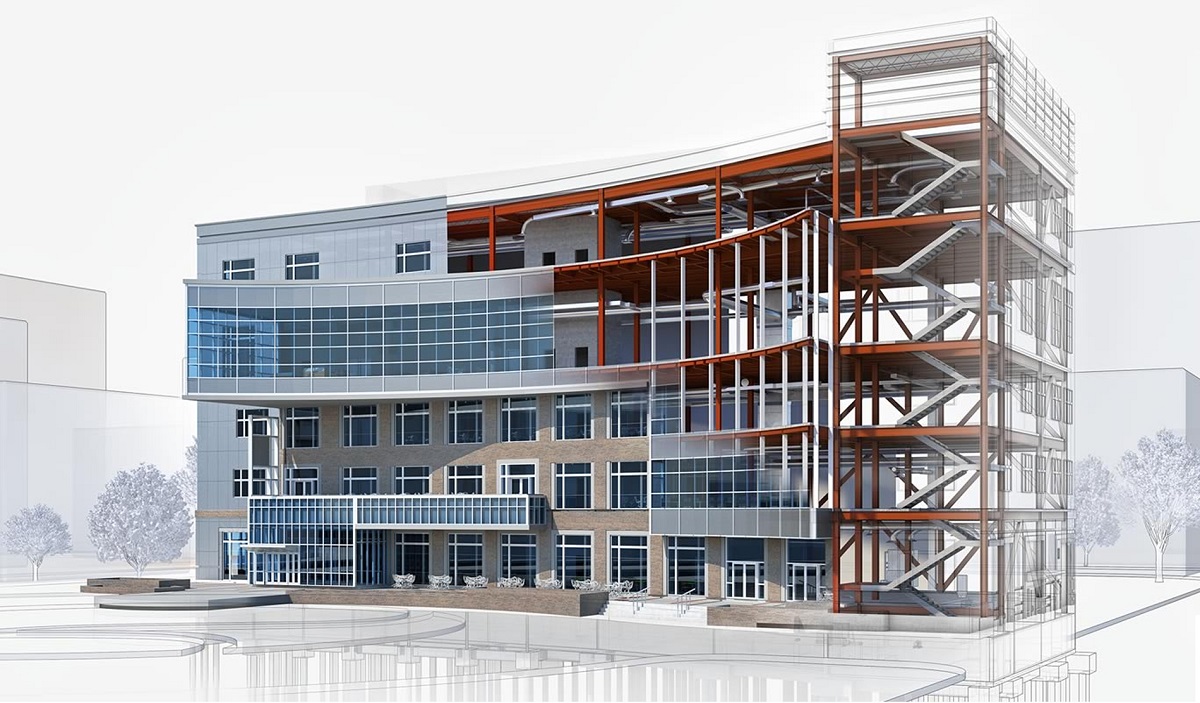
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the construction industry, making projects more efficient, accurate, and collaborative. In recent years, the concept of Level 2 BIM has emerged as a crucial milestone in the implementation of BIM processes.
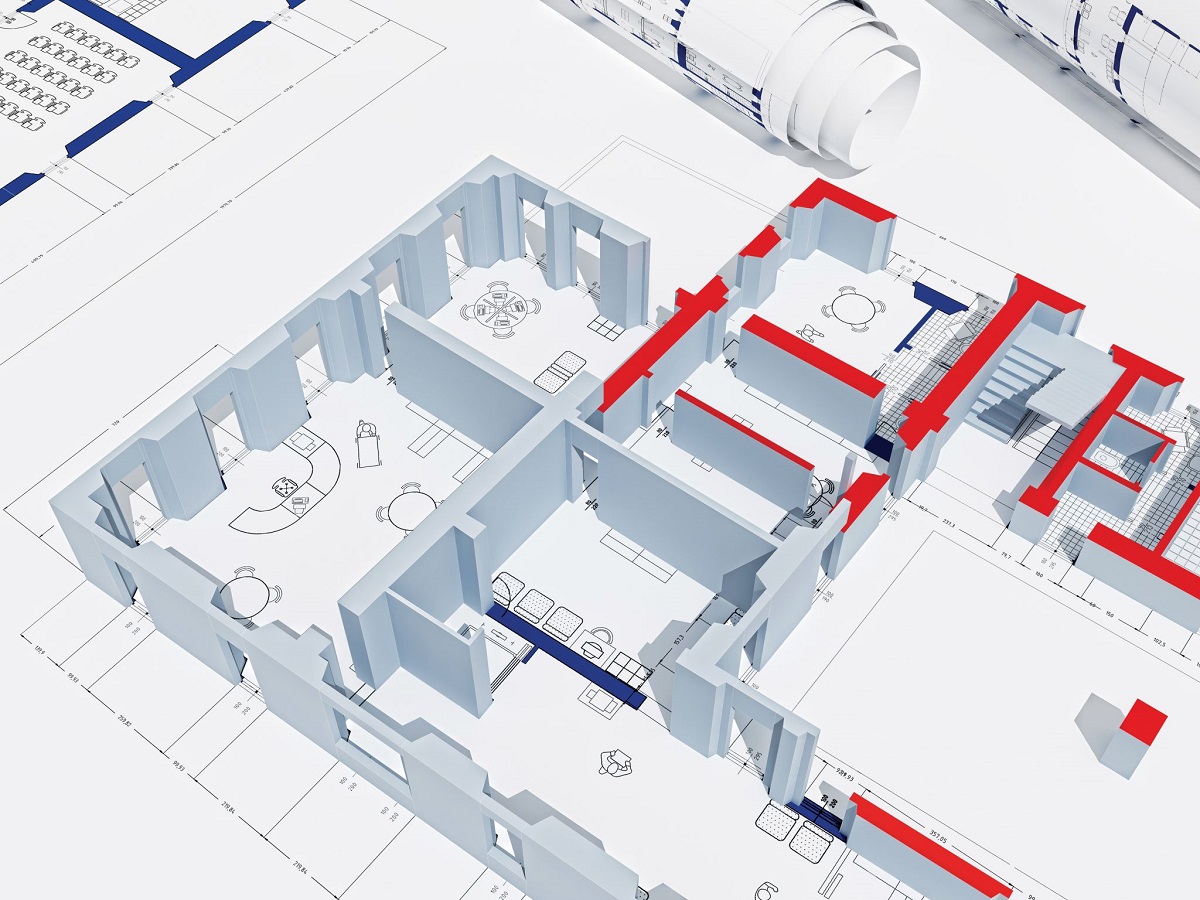
Level 2 BIM refers to the collaborative sharing of 3D digital models and associated project information between different parties involved in the construction project. It enables stakeholders to work together seamlessly, integrating their expertise and contributing to a unified, coordinated project design.
Implemented in the United Kingdom in 2016, Level 2 BIM has since gained international recognition and become a benchmark for BIM adoption. It sets the standard for collaboration and information sharing in the construction industry, facilitating efficient project delivery and improved asset management.
In this article, we will explore the key characteristics of Level 2 BIM, the benefits it offers, the challenges faced in its implementation, and best practices for successful adoption.
Key Takeaways:
- Level 2 BIM revolutionizes construction by enabling seamless collaboration and information sharing, leading to improved project outcomes and streamlined delivery processes.
- Successful Level 2 BIM adoption requires clear objectives, robust collaboration, standardized data exchange, and a culture of continuous improvement to maximize its benefits.
Read more: What Is A Level 2 EV Charger
Definition of Level 2 BIM
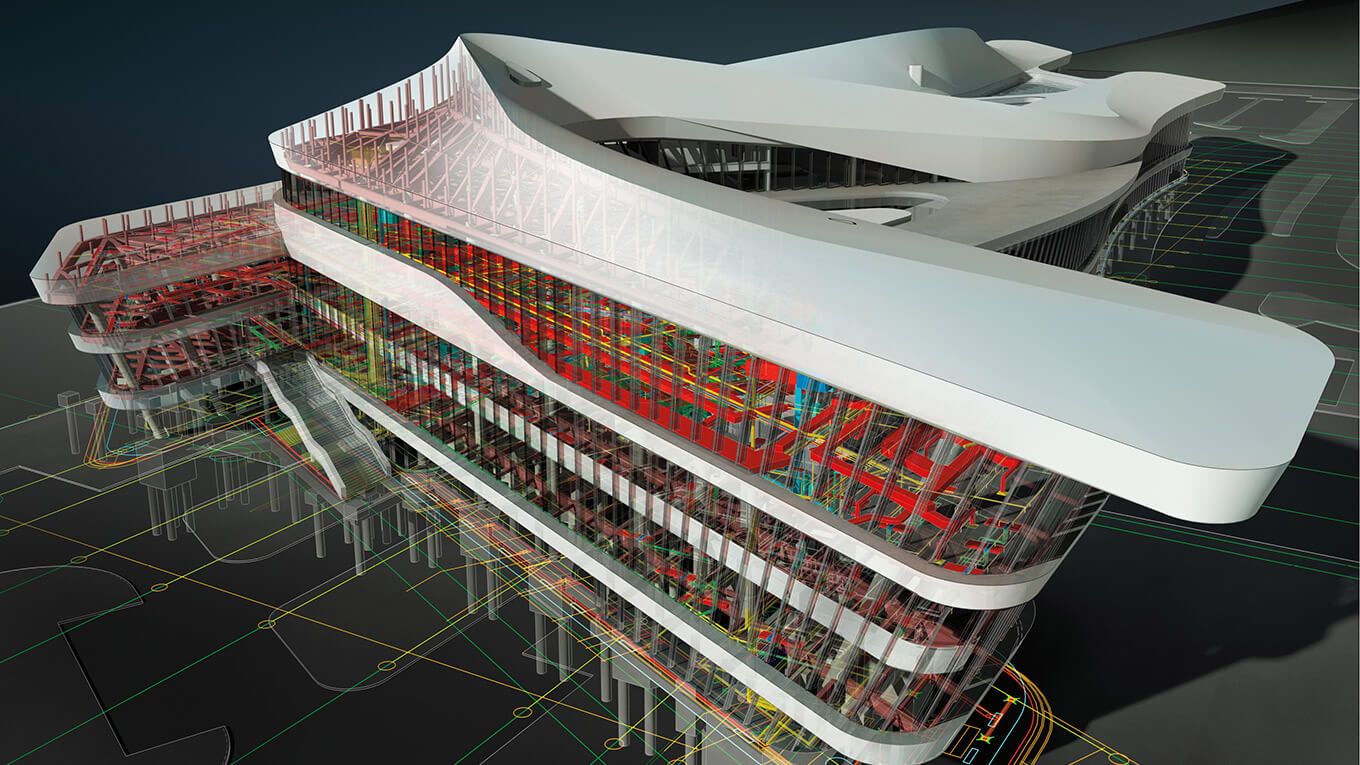
Level 2 BIM is a collaborative working methodology that enables the sharing of structured digital information between various stakeholders in a construction project. It involves the creation, management, and exchange of 3D models containing intelligent data, allowing for better decision-making and coordination throughout the project lifecycle.
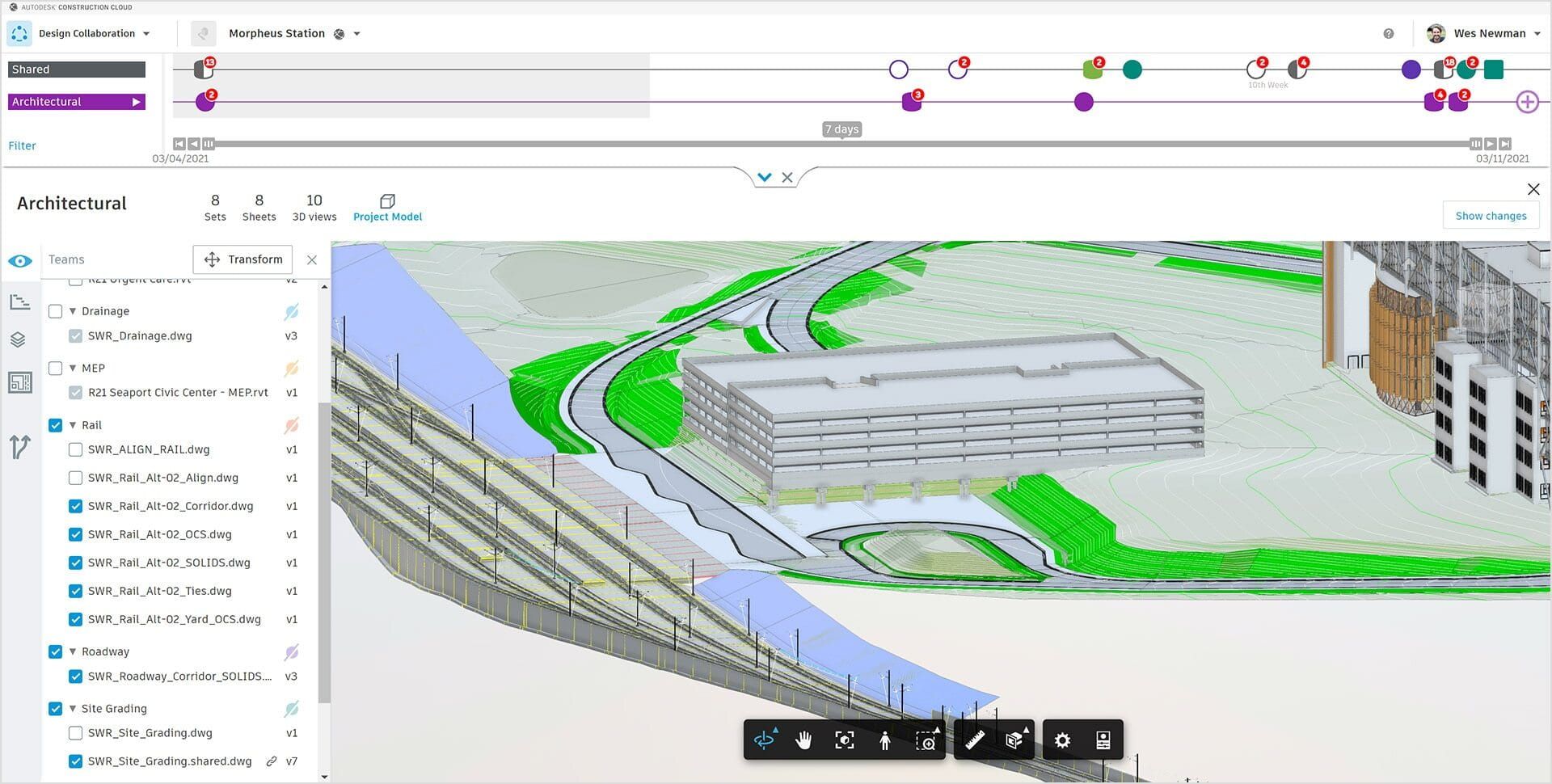
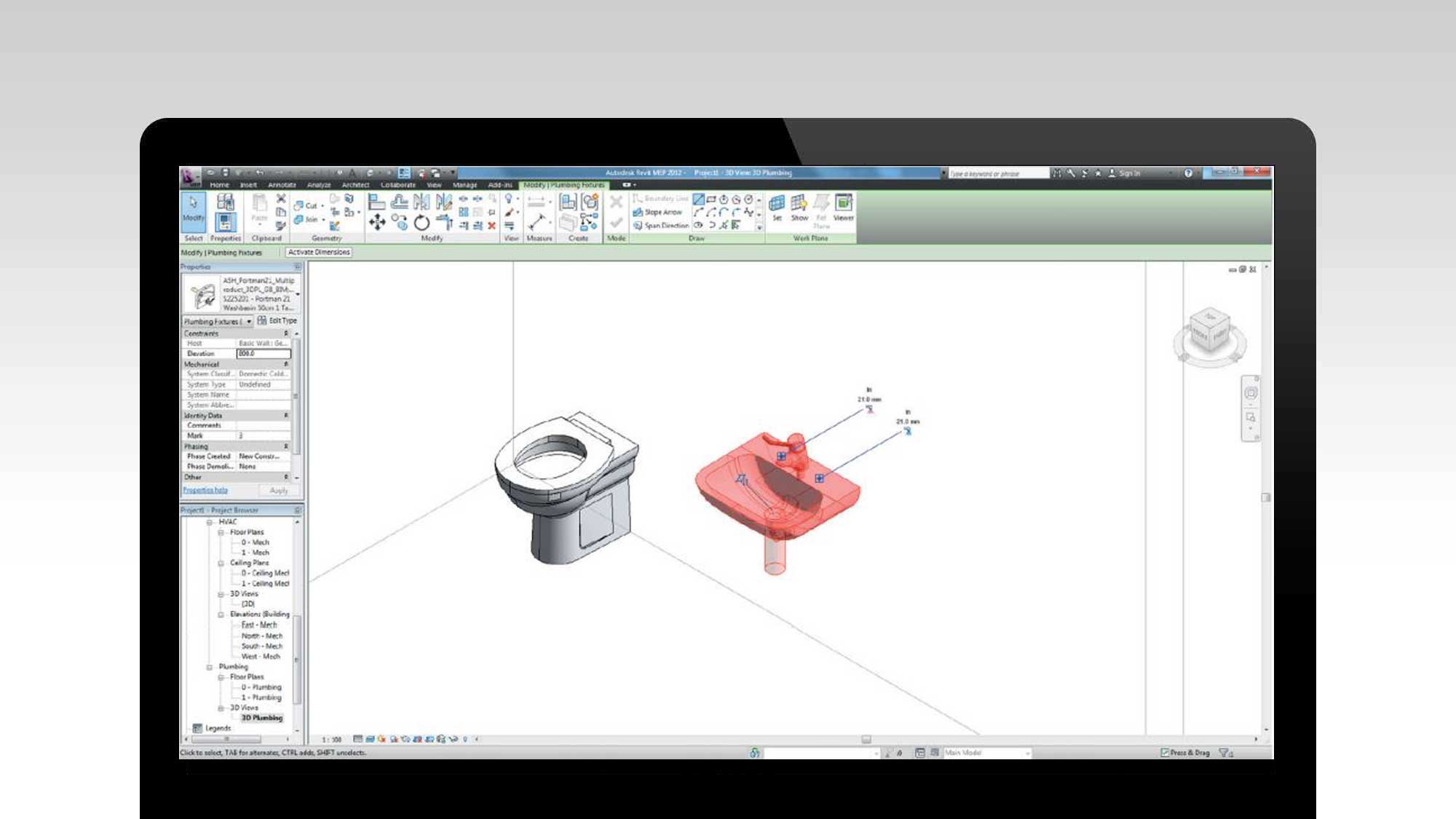
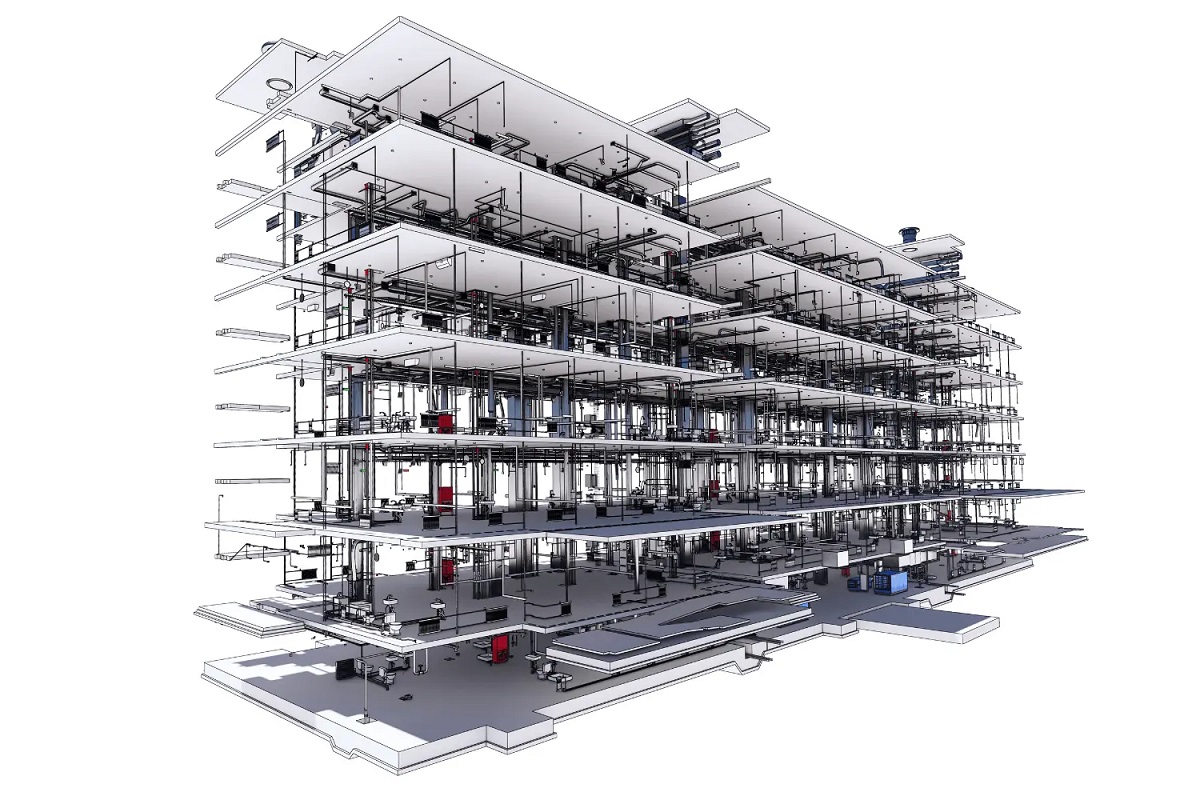
In Level 2 BIM, each discipline manages its own 3D models using their respective software tools. These models are then shared and federated in a common data environment (CDE), which acts as a central repository for all project information. The CDE ensures that every stakeholder has access to the most up-to-date and accurate information, promoting collaboration and minimizing conflicts.
One of the essential aspects of Level 2 BIM is the use of standardized file formats and data exchange protocols. This ensures that information can be seamlessly shared and integrated across different software platforms. Common file formats include Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) for 3D models and COBie (Construction Operations Building Information Exchange) for non-graphical data.
Another key element of Level 2 BIM is the incorporation of a common data environment that supports version control, document management, and collaboration tools. This centralized platform allows stakeholders to access and contribute to the project information in real-time, regardless of their physical location. It promotes transparency, communication, and coordination among all parties involved.
Level 2 BIM also emphasizes the importance of collaborative working practices and well-defined information exchange protocols. This ensures that information flows smoothly and consistently throughout the project, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date data.
Overall, Level 2 BIM represents a significant step forward in the adoption of BIM methodologies. It enables better collaboration, coordination, and data integration among all project stakeholders, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and more efficient asset management.
Key Characteristics of Level 2 BIM
Level 2 BIM is characterized by several key features that differentiate it from other levels of BIM implementation. These characteristics are essential for effective collaboration and information exchange throughout the construction project. Let’s explore them:
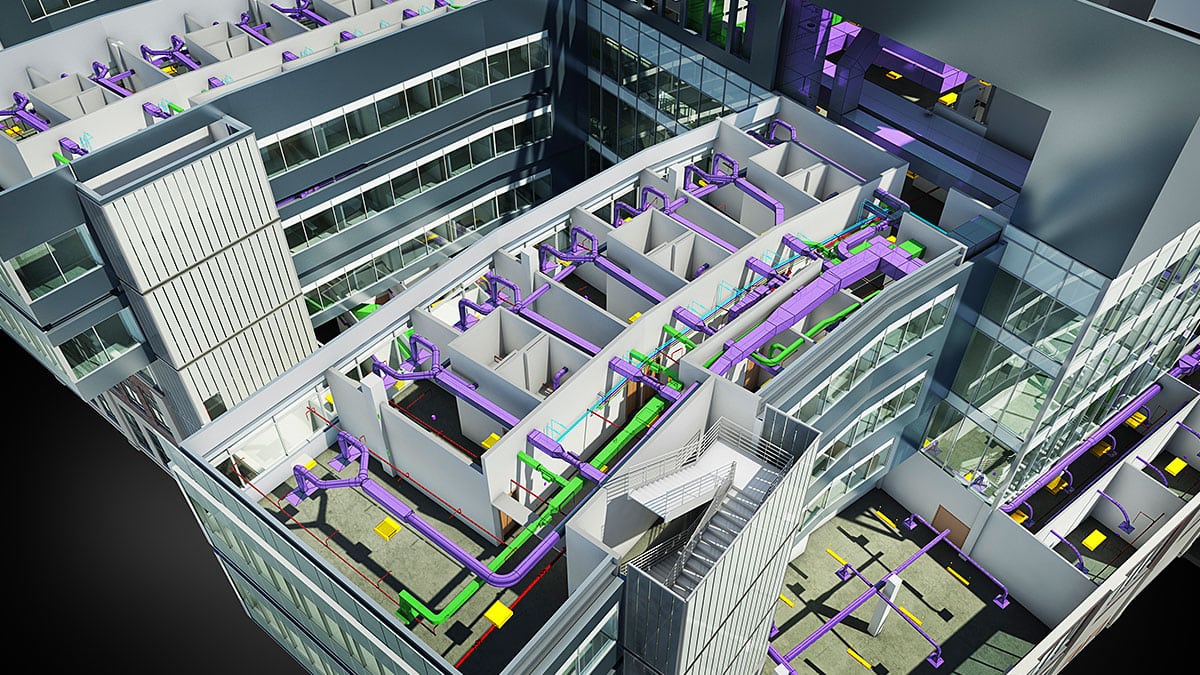
- Shared 3D Models: Level 2 BIM involves the creation and sharing of 3D models by different stakeholders. These models represent the physical and functional aspects of the building, including architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems.
- Collaborative Working: Level 2 BIM emphasizes collaboration among project parties. Stakeholders share and integrate their models in a common data environment, allowing for multidisciplinary coordination and identifying and resolving clashes early in the project lifecycle.
- Information Exchange: In Level 2 BIM, the sharing of information goes beyond 3D models. It encompasses data related to cost estimation, scheduling, material specifications, and operation and maintenance of the building. This holistic approach ensures that all relevant project information is readily available to all parties involved.
- Open Standards and Protocols: Level 2 BIM heavily relies on open standards and protocols for data exchange and interoperability. This ensures that different software tools can communicate and seamlessly integrate the shared information. Standards like IFC and COBie play a crucial role in achieving this interoperability.
- Common Data Environment: Level 2 BIM requires the establishment of a common data environment (CDE) where all project information is stored and managed. The CDE acts as a single source of truth, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date and accurate data.
- Version Control and Document Management: Level 2 BIM incorporates robust version control and document management practices. This ensures that previous versions of models and documents are preserved and can be accessed if needed. It also helps track changes and revisions made by different stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
These key characteristics of Level 2 BIM promote collaboration, information transparency, and efficient project delivery. By embracing these principles, construction projects can overcome the limitations of traditional design and construction processes, experiencing improved coordination, reduced errors, and enhanced risk management.
Benefits of Level 2 BIM
Level 2 BIM offers several significant benefits for construction projects, impacting various aspects of the project lifecycle. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Improved Collaboration: Level 2 BIM promotes collaboration among project stakeholders, fostering a more integrated and cohesive approach to project delivery. By sharing 3D models and associated data, teams can work together more effectively, identifying and resolving clashes and conflicts early in the design stage.
- Enhanced Coordination and Clash Detection: With Level 2 BIM, multiple disciplines can collaboratively work on the same platform, reducing coordination issues and clashes between architectural, structural, and MEP systems. Clash detection algorithms and tools help identify conflicts in the design phase, minimizing costly rework during construction.
- Accurate Cost Estimation: By integrating cost-related information into the BIM model, Level 2 BIM enables more accurate cost estimation and quantity take-offs. This improves cost forecasting and helps manage project budgets effectively, reducing the risk of overruns.
- Efficient Construction Processes: Level 2 BIM streamlines construction processes by providing a clear and visual understanding of the project. Builders have access to accurate and updated information, reducing errors, improving productivity, and minimizing construction delays.
- Better Facility Management: Level 2 BIM enables the creation of a comprehensive digital asset that includes all relevant information about the building, including maintenance requirements, warranties, and operating manuals. This information improves facility management and allows for efficient operation and maintenance of the building throughout its lifecycle.
- Improved Sustainability: Level 2 BIM helps optimize energy performance, enable better material selection, and enhance the overall sustainability of the building. By simulating different design options and analyzing their environmental impacts, stakeholders can make informed decisions that reduce energy consumption and lower the project’s carbon footprint.
These benefits clearly demonstrate the positive impact of Level 2 BIM on construction projects. By embracing this collaborative and data-oriented approach, stakeholders can create more efficient and sustainable buildings, reduce costs, and improve the overall project delivery process.
Level 2 BIM refers to the collaborative use of 3D models and shared project data. It requires all project and asset information to be created and managed in a common environment, enabling better collaboration between different parties involved in a construction project.
Challenges in Implementing Level 2 BIM
While Level 2 BIM offers numerous benefits, its implementation can pose several challenges. Let’s explore some of the key hurdles that organizations may face when adopting Level 2 BIM:
- Change Management: Implementing Level 2 BIM requires a significant shift in the way organizations work. It involves new processes, technologies, and collaboration methods, which may face resistance from employees accustomed to traditional practices. Effective change management strategies and training programs are essential to overcome this challenge.
- Interoperability Issues: Achieving seamless data exchange and interoperability among different software tools and platforms can be a complex task. Organizations may encounter challenges in standardizing file formats, ensuring compatibility between various software solutions, and maintaining data integrity throughout the project lifecycle.
- Lack of BIM Standards: While Level 2 BIM relies on open standards like IFC and COBie, the construction industry still lacks universally accepted BIM standards. This can lead to inconsistencies in information exchange, making collaboration and data integration more challenging.
- Cost and Resource Constraints: Implementing Level 2 BIM involves investing in software tools, infrastructure, and training. Organizations with limited financial resources or lack of technology expertise may find it challenging to allocate the necessary funds and staff to support the implementation process.
- Legal and Contractual Issues: Collaborative working, data sharing, and intellectual property ownership can raise legal and contractual concerns. Organizations need to address these issues by establishing clear agreements and contracts that define responsibilities, liabilities, and rights of all involved parties.
- Cultural and Organizational Resistance: Organizations with long-established practices and processes may face resistance to change when implementing Level 2 BIM. It requires a cultural shift towards embracing collaboration, information sharing, and interdisciplinary coordination, which may be met with resistance from stakeholders.
Despite these challenges, organizations that successfully overcome them can reap the benefits offered by Level 2 BIM. By recognizing these challenges and proactively addressing them through proper planning, training, and communication, organizations can navigate the implementation process more effectively.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Case Studies of Level 2 BIM Implementation
Several construction projects around the world have successfully implemented Level 2 BIM, showcasing its capabilities and benefits. Let’s explore some notable case studies:
1. Crossrail – London, UK: Crossrail, the largest infrastructure project in Europe, utilized Level 2 BIM to successfully deliver a new railway line under the streets of London. The project involved integrating various disciplines and managing complex underground infrastructure. Level 2 BIM played a crucial role in coordinating the design, construction, and operation of the project, ensuring efficient collaboration and minimizing clashes between different systems.
2. Muscat International Airport – Oman: The expansion of Muscat International Airport in Oman employed Level 2 BIM to manage the design and construction processes. BIM models were utilized to optimize space utilization, coordinate MEP systems, and streamline construction sequencing. The implementation of Level 2 BIM resulted in improved coordination, enhanced communication among project stakeholders, and reduced project delivery time.
3. Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture – Washington, D.C., USA: The construction of the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, D.C., utilized Level 2 BIM to coordinate the complex architectural and structural elements. BIM models were used to integrate the intricate design features, analyze structural performance, and enhance coordination among multiple contractors. The implementation of Level 2 BIM facilitated efficient collaboration and resulted in cost savings and reduced construction conflicts.
4. The Shard – London, UK: The iconic Shard skyscraper in London employed Level 2 BIM to successfully deliver this landmark project. BIM tools were used to coordinate the complex geometry of the building, analyze structural performance, and optimize construction sequencing. The use of Level 2 BIM contributed to better coordination among various disciplines, reducing errors, and ensuring a streamlined construction process.
5. Tampere Tramway – Tampere, Finland: The Tampere Tramway project in Finland utilized Level 2 BIM to manage the design and construction of the tramway network. BIM models were used to coordinate the track alignment, utility coordination, and clash detection. The implementation of Level 2 BIM improved collaboration among different project stakeholders, leading to reduced design changes, improved construction efficiency, and enhanced project delivery.
These case studies highlight the successful implementation of Level 2 BIM in various construction projects worldwide. They demonstrate how Level 2 BIM contributes to improved collaboration, streamlined processes, and better project outcomes.
Best Practices for Level 2 BIM Adoption
Implementing Level 2 BIM requires careful planning, coordination, and commitment from all stakeholders involved. To ensure successful adoption and maximize the benefits, it is important to follow these best practices:
- Establish Clear Objectives: Define clear goals and objectives for the implementation of Level 2 BIM. Identify the specific benefits you aim to achieve, such as improved collaboration, reduced errors, or enhanced project delivery.
- Create a BIM Execution Plan: Develop a comprehensive BIM Execution Plan (BEP) that outlines the project’s BIM requirements, standards, workflows, and responsibilities. This will serve as the roadmap for successful implementation and coordination among all project stakeholders.
- Invest in Training and Education: Provide training and education to all team members involved in the project. Ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively use BIM tools and understand the collaborative workflows required for Level 2 BIM.
- Collaborate Early and Often: Foster a collaborative environment where project stakeholders engage in early-stage coordination and communication. Encourage interdisciplinary meetings, information sharing, and clash detection to minimize errors and conflicts in the design phase.
- Utilize a Common Data Environment: Implement a robust common data environment (CDE) to centralize project information, 3D models, and associated data. Ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date and accurate information and establish protocols for version control and data management.
- Standardize Data Exchange: Adopt and enforce the use of industry-standard file formats, such as IFC and COBie, to ensure interoperability among different software tools. Establish data exchange protocols that define how information should be shared and communicated between project parties.
- Implement Clash Detection and Resolution: Utilize clash detection tools to identify and resolve collisions and clashes among different systems early in the design phase. Regularly review and update clash detection results to ensure smooth coordination and minimize construction conflicts.
- Regularly Update and Maintain BIM Models: Continually update and maintain the BIM models throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly synchronize the models in the CDE, incorporating changes and revisions made by different stakeholders. Ensure that the models accurately represent the as-built condition of the project.
- Promote a Culture of Collaboration: Foster a culture of collaboration, information sharing, and interdisciplinary coordination among all project stakeholders. Encourage open communication, mutual respect, and a willingness to embrace new technologies and collaborative workflows.
- Evaluate and Learn from Each Project: Continuously evaluate the implementation of Level 2 BIM and learn from each project. Identify areas for improvement, gather feedback from team members, and adapt your processes and workflows to enhance future projects.
By following these best practices, organizations can successfully adopt Level 2 BIM and maximize the benefits it offers. Effective communication, collaboration, and adherence to set standards and protocols are key to achieving successful BIM implementation.
Conclusion
Level 2 BIM represents a significant milestone in the adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) processes in the construction industry. It emphasizes collaboration, information exchange, and coordination among project stakeholders, leading to improved project outcomes and streamlined project delivery.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of Level 2 BIM, its key characteristics, the benefits it offers, the challenges in its implementation, and best practices for successful adoption.
Level 2 BIM enables the sharing of 3D models and associated project information, promoting collaboration, reducing errors, and enhancing coordination among different disciplines. It empowers stakeholders to work together seamlessly, integrating their expertise and contributing to a unified, coordinated project design.
Implementing Level 2 BIM does present challenges, such as change management, interoperability issues, and resource constraints. However, organizations that overcome these hurdles can reap the benefits of improved collaboration, accurate cost estimation, enhanced construction processes, better facility management, and increased sustainability.
Successful case studies, such as Crossrail, Muscat International Airport, the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, the Shard, and Tampere Tramway, highlight the potential of Level 2 BIM in delivering successful construction projects.
To ensure the successful adoption of Level 2 BIM, it is crucial to establish clear objectives, create a BIM execution plan, invest in training and education, foster collaboration, utilize a common data environment, standardize data exchange, implement clash detection and resolution, regularly update and maintain BIM models, promote a culture of collaboration, and evaluate and learn from each project.
In conclusion, Level 2 BIM offers immense potential for the construction industry, enabling efficient collaboration, accurate information exchange, and streamlined project delivery. By embracing Level 2 BIM and following best practices, organizations can unlock its numerous benefits and pave the way for a more integrated and successful construction process.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Level 2 BIM?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “What Is Level 2 BIM?”