Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How To Operate A 3D Printer


Smart Home Devices
How To Operate A 3D Printer
Modified: April 22, 2024
Learn how to operate a 3D printer for your smart home devices with our comprehensive guide. Get started on creating your own custom designs today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing! In this comprehensive guide, you will learn everything you need to know about operating a 3D printer with confidence and ease. Whether you are a hobbyist, a DIY enthusiast, or a professional looking to delve into the realm of additive manufacturing, this article will equip you with the essential knowledge to unleash your creativity and bring your designs to life.
The concept of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we approach prototyping, product development, and even manufacturing. With a 3D printer at your disposal, you have the power to transform digital designs into tangible objects, layer by layer, using a diverse range of materials such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and more. The versatility and precision of 3D printing technology have paved the way for groundbreaking innovations across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer goods.
As you embark on this enlightening journey, you will gain a profound understanding of the fundamental principles behind 3D printing, from selecting the right filament and calibrating your printer to troubleshooting common issues and maintaining optimal performance. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to unleash your creativity, unleash your creativity and maximize the potential of your 3D printer.
So, without further ado, let's dive into the captivating realm of 3D printing and unravel the intricacies of operating a 3D printer with precision and expertise. Whether you are a novice or an experienced enthusiast, this guide is tailored to empower you with the knowledge and skills needed to embark on a seamless 3D printing journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Operating a 3D printer involves understanding its components, preparing designs, and maintaining the printer. With attention to detail and creativity, you can bring digital designs to life with precision and finesse.
- To operate a 3D printer successfully, meticulous setup, design preparation, and troubleshooting are essential. Embracing the iterative nature of 3D printing fosters growth and innovation in the captivating world of additive manufacturing.
Read more: How To Build A 3D Printer
Understanding the Basics of 3D Printing
Before delving into the operational aspects of a 3D printer, it’s essential to grasp the foundational concepts that underpin this revolutionary technology. At its core, 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing that involves creating three-dimensional objects by depositing material layer by layer based on a digital model. This process stands in stark contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, where material is carved away from a solid block.
The key components of a 3D printer include the extruder, which melts and deposits the filament, the build platform, where the object is constructed, and the control system, which coordinates the movements and operations of the printer. Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for harnessing the full potential of your 3D printer.
One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its versatility in material usage. From biodegradable PLA and tough ABS to flexible TPU and engineering-grade PETG, the range of filaments available enables the creation of objects with diverse properties, strengths, and finishes. This versatility makes 3D printing suitable for a wide array of applications, including rapid prototyping, custom manufacturing, and even artistic expression.
Furthermore, familiarizing yourself with the various types of 3D printing technologies, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), will provide valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of each method. Each technology has its unique strengths, allowing for the creation of intricate designs, functional prototypes, and end-use parts with precision and efficiency.
As you delve deeper into the world of 3D printing, it’s essential to consider design principles that optimize the printability of your creations. Factors such as overhangs, tolerances, and support structures play a pivotal role in ensuring successful prints. Embracing these principles will empower you to unleash your creativity while maintaining the integrity and quality of your designs.
By understanding the fundamental principles of 3D printing, you will lay a solid foundation for harnessing the full potential of this transformative technology. With this knowledge in hand, you are poised to embark on an enriching journey into the realms of creativity, innovation, and limitless possibilities.
Setting Up Your 3D Printer
Setting up your 3D printer is a crucial initial step that lays the groundwork for successful and seamless printing experiences. Whether you are unboxing a new printer or fine-tuning an existing one, the setup process encompasses several essential aspects that warrant careful attention.
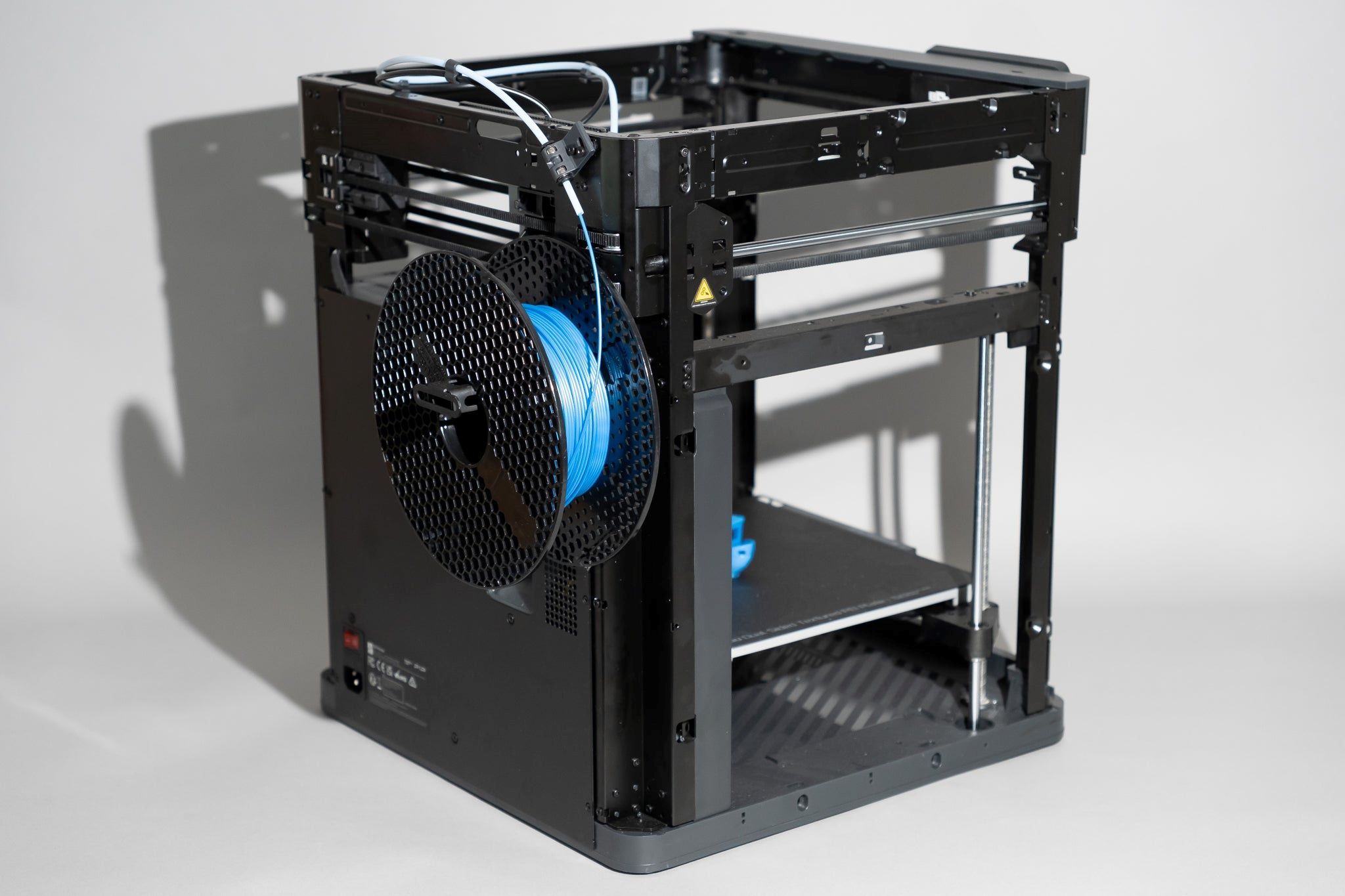
Assembly and Calibration:
Upon unboxing your 3D printer, meticulously follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble the various components with precision. This typically involves securing the frame, installing the build platform, and attaching the extruder assembly. Once assembled, the calibration process comes into play, ensuring that the printer’s axes are aligned, the build platform is leveled, and the extruder’s nozzle is at the optimal height above the platform. Proper calibration is vital for achieving accurate prints and preventing potential issues during the printing process.
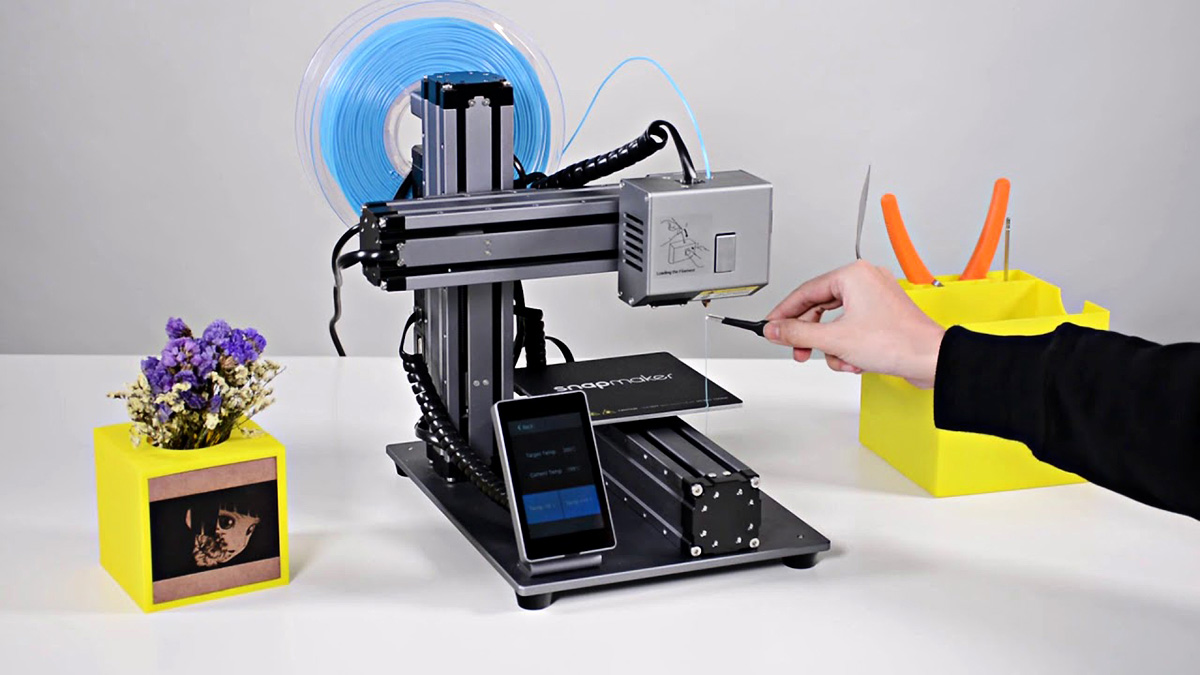
Filament Loading:
Next, load the filament of your choice into the printer’s extruder following the specified loading procedure. Whether it’s PLA, ABS, PETG, or a specialty filament, ensure that the filament is inserted securely and guided into the extruder’s pathway to facilitate smooth and consistent material flow during printing.
Software Installation and Configuration:
Most 3D printers are accompanied by dedicated slicing software, such as Cura, Simplify3D, or PrusaSlicer. Install the recommended software on your computer and configure it to match your printer’s specifications, including the print bed dimensions, filament type, and extruder temperature. Familiarize yourself with the software’s interface and settings to prepare your digital designs for printing with precision and efficiency.
Connectivity and Firmware Updates:
If your 3D printer features connectivity options, such as USB, Wi-Fi, or SD card compatibility, establish the preferred connection method to transfer your sliced models to the printer. Additionally, check for firmware updates for your printer to ensure that it operates with the latest enhancements and optimizations, enhancing its overall performance and reliability.
By meticulously setting up your 3D printer, you lay a solid foundation for embarking on a seamless and rewarding printing journey. Attention to detail during the setup process is instrumental in mitigating potential issues and maximizing the capabilities of your 3D printer, setting the stage for the successful realization of your creative visions.
Preparing Your Design for Printing
Before commencing the printing process, meticulous preparation of your digital designs is paramount to achieving optimal print quality and ensuring a smooth printing experience. Whether you are creating your designs from scratch or sourcing them from online repositories, the following steps will guide you through the crucial process of preparing your designs for 3D printing.
Design Software and File Formats:
Utilize specialized design software such as Tinkercad, Fusion 360, or Blender to create or modify your 3D models. These programs offer a range of tools for sculpting, modeling, and refining your designs, empowering you to bring your ideas to life with precision and creativity. Additionally, ensure that your designs are saved in compatible file formats, such as .STL or .OBJ, which are universally accepted by slicing software and 3D printers.
Slicing and Model Orientation:
Once your design is finalized, import the model into your preferred slicing software. Here, you have the opportunity to adjust crucial parameters such as layer height, infill density, and support structures. Carefully orient the model to optimize printability, minimize overhangs, and enhance overall structural integrity. Additionally, consider the placement of the model on the print bed to maximize stability and minimize the need for excessive support material.
Support Generation and Rafting:
For designs with overhangs or intricate geometries, the generation of support structures is essential to prevent print failures and ensure the fidelity of the final object. Configure your slicing software to generate supports where necessary, ensuring that they can be easily removed post-printing without compromising the design’s integrity. In some cases, utilizing a raft, a horizontal grid of material beneath the model, can enhance adhesion and stability during printing.
Material Selection and Print Settings:
Based on the specific requirements of your design, select the appropriate filament type and color to bring your vision to life. Adjust the print settings, including nozzle temperature, print speed, and cooling options, to align with the material’s characteristics and the intricacies of your design. Fine-tuning these settings will optimize print quality and minimize the risk of issues such as warping or stringing.
By meticulously preparing your designs for 3D printing, you set the stage for successful and rewarding printing experiences. Attention to detail during the preparation phase is instrumental in ensuring that your creations are translated from the digital realm to physical reality with precision, fidelity, and visual appeal.
When operating a 3D printer, always ensure that the print bed is level before starting a print. This will help to ensure that the first layer of your print adheres properly and prevents any printing issues.
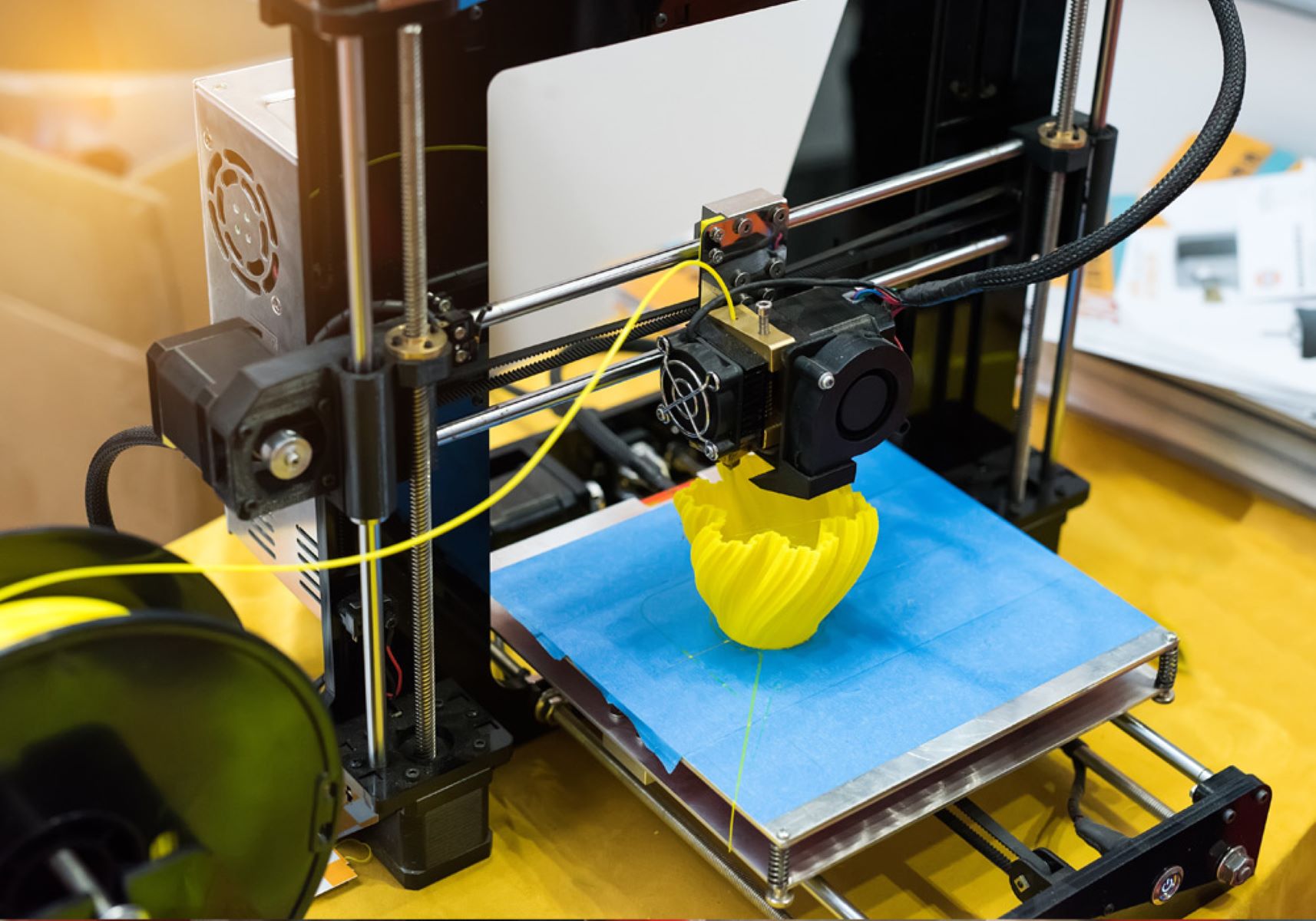
Operating Your 3D Printer
Operating a 3D printer involves a series of meticulous steps and considerations to ensure the successful realization of your digital designs. From initiating the print job to monitoring the progress and post-processing the printed object, each phase of the printing process demands attention to detail and a keen understanding of your printer’s capabilities.
Initiating the Print Job:
Once your design is prepared and loaded into the slicing software, transfer the sliced model to your 3D printer using the preferred connectivity method, such as SD card, USB, or Wi-Fi. Navigate the printer’s interface to select the appropriate print file and initiate the printing process. Pay close attention to the initial layer adhesion and extrusion to ensure that the print adheres securely to the build platform.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
Throughout the printing process, maintain a vigilant eye on the printer to identify any anomalies or issues that may arise. Monitor the layer-by-layer progression of the print, ensuring that each layer is deposited accurately and adheres to the preceding layers. Additionally, observe the extruder’s movements and filament flow to detect any signs of irregularities or potential print failures. Regular maintenance, such as ensuring the filament spool rotates freely and clearing any filament jams, is essential to sustain the printer’s optimal performance.
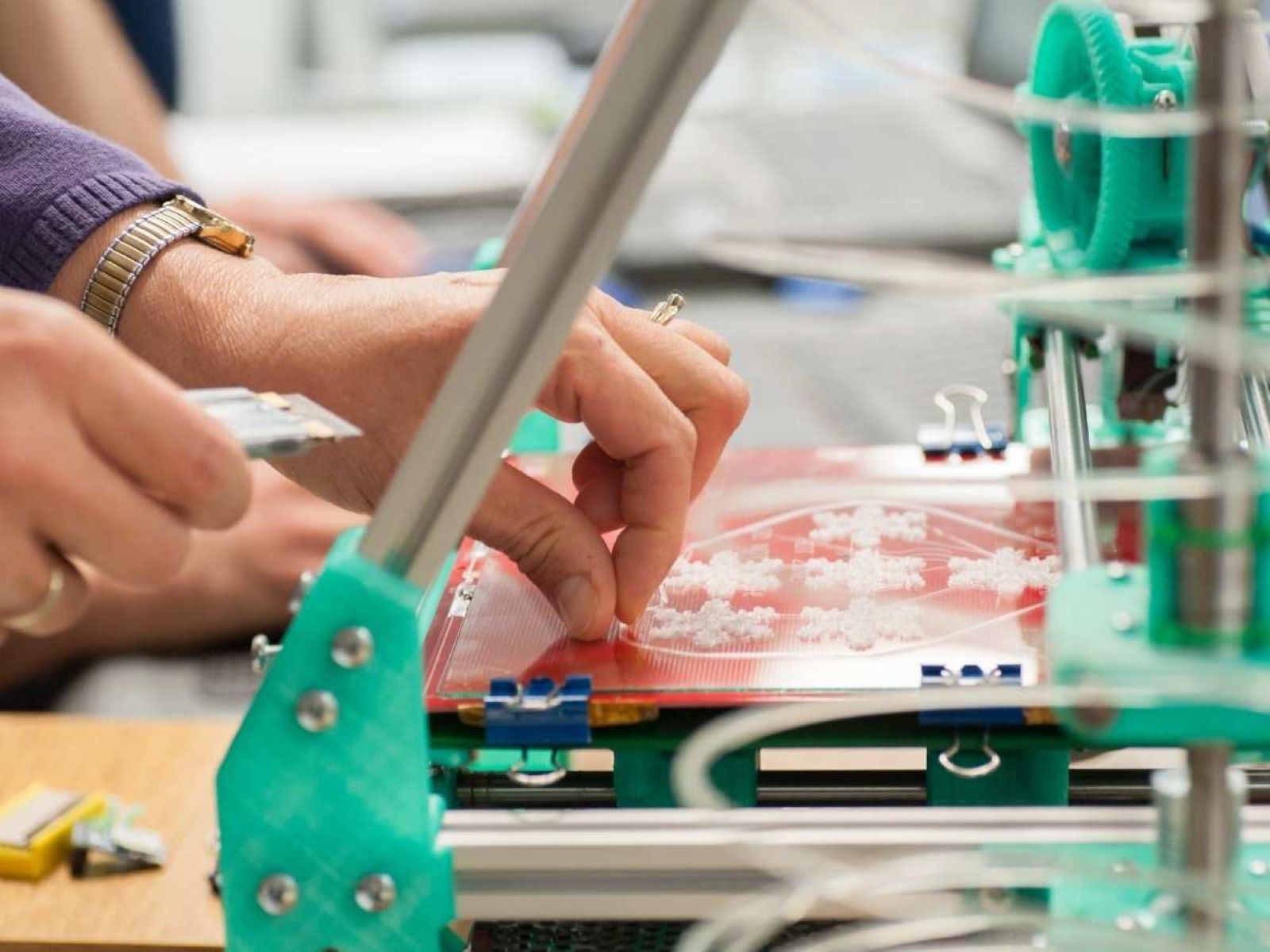
Post-Processing and Finishing:
Upon the completion of the print, carefully remove the object from the build platform, taking care to avoid damage or distortion. Depending on the print material and design intricacies, post-processing steps such as support removal, sanding, and surface finishing may be necessary to refine the object’s appearance and functionality. Embrace post-processing as an opportunity to add personal touches and enhancements to your printed creations, elevating them to a professional and polished standard.
Adhering to Best Practices:
Embracing best practices such as maintaining a clean and dust-free printing environment, storing filaments in dry and controlled conditions, and periodically calibrating and inspecting your printer will contribute to consistent and reliable printing results. Additionally, documenting the print settings and any modifications made during the printing process will serve as valuable references for future projects, enabling you to refine and optimize your printing workflows.
By mastering the art of operating your 3D printer with precision and diligence, you pave the way for a fulfilling and enriching printing journey. Each print serves as a testament to your creativity and technical prowess, bringing your digital designs to life with impeccable detail and craftsmanship.
Read more: Where To Put A 3D Printer
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While 3D printing offers boundless opportunities for creativity and innovation, it is not uncommon to encounter challenges and issues during the printing process. Understanding common issues and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies is essential for maintaining consistent print quality and resolving potential setbacks.
Layer Adhesion and Warping:
Poor layer adhesion and warping often stem from inadequate bed adhesion and suboptimal print settings. To address this, ensure that the print bed is leveled accurately and consider using adhesion aids such as a brim or raft to enhance the object’s stability during printing. Adjusting the print temperature, infill density, and cooling settings can also mitigate warping and improve layer adhesion.
Extrusion Problems and Stringing:
Extrusion-related issues, such as under-extrusion or stringing, can compromise print quality. Verify that the filament diameter and extrusion multiplier settings are calibrated correctly to facilitate consistent material flow. Additionally, optimizing retraction settings and minimizing the occurrence of stringing through temperature adjustments and print speed optimization can effectively address these issues.
Print Imperfections and Artifacts:
Identifying and rectifying print imperfections, such as z-axis artifacts, ghosting, or ringing, requires meticulous examination of the printer’s mechanical components and print settings. Tensioning belts, reducing print speeds, and fine-tuning acceleration and jerk settings can alleviate these imperfections, resulting in smoother and more refined prints.
Extruder Jams and Filament Issues:
Extruder jams and filament-related issues can disrupt the printing process and lead to failed prints. Regularly inspect the extruder assembly for any obstructions or filament entanglements, and ensure that the filament path is clear and unobstructed. Furthermore, storing filaments in dry and dust-free conditions and utilizing filament filters can minimize the risk of filament-related issues.
Software and Firmware Troubleshooting:
If you encounter anomalies during the slicing process or experience erratic printer behavior, consider updating the slicing software to the latest version and verifying that the printer’s firmware is up to date. Additionally, recalibrating the printer’s settings and performing test prints with different software configurations can help isolate and resolve software-related issues.
By familiarizing yourself with these common issues and implementing targeted troubleshooting measures, you are empowered to overcome challenges and elevate your 3D printing proficiency. Each troubleshooting endeavor serves as an opportunity for learning and refinement, ultimately enhancing your mastery of the 3D printing craft.
Maintenance and Care of Your 3D Printer
Maintaining and caring for your 3D printer is paramount to ensure its longevity, consistent performance, and the production of high-quality prints. By incorporating regular maintenance practices into your printing routine, you can mitigate potential issues, extend the lifespan of critical components, and optimize the overall reliability of your printer.
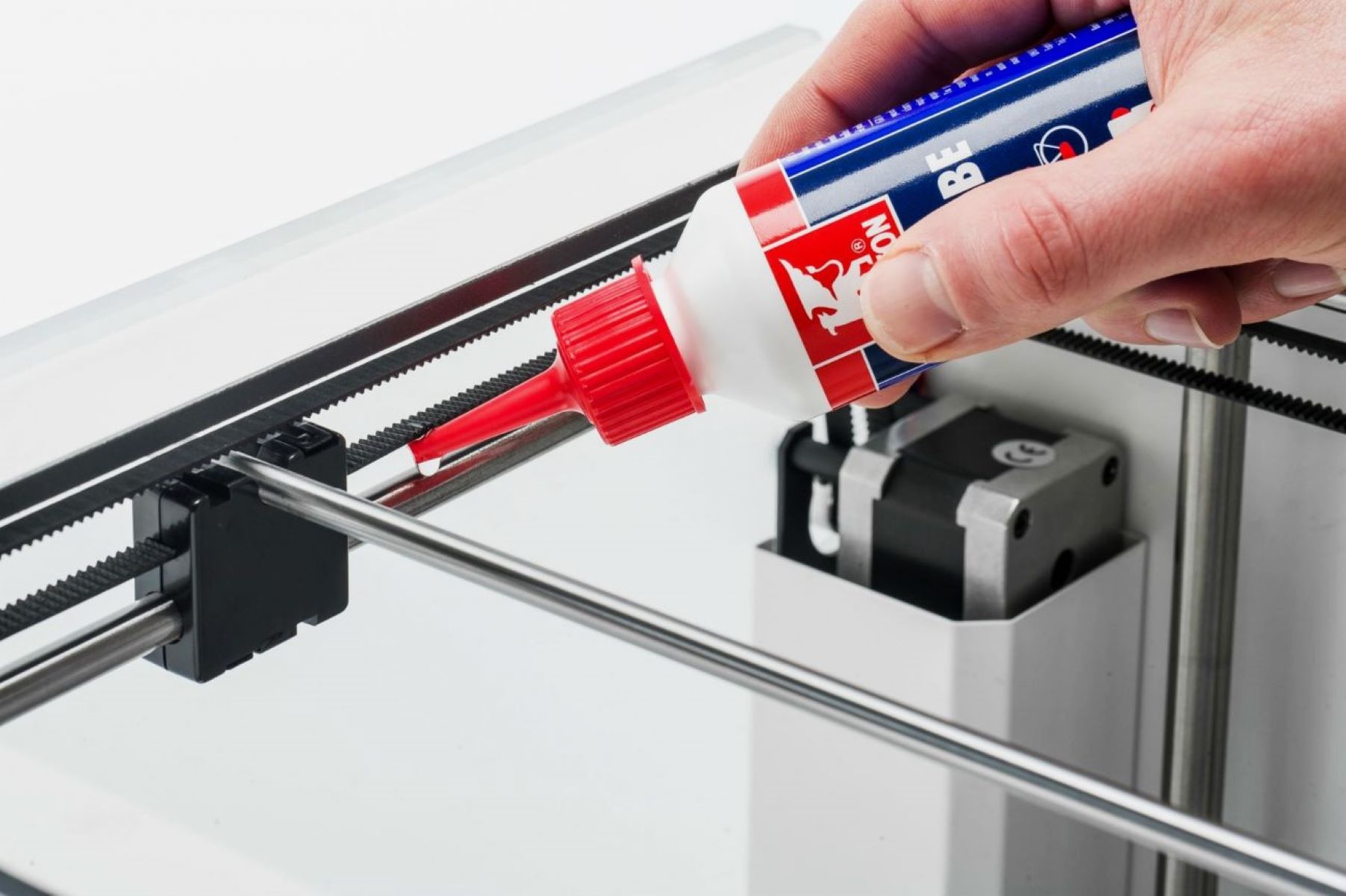
Regular Cleaning and Lubrication:
Periodically clean the build platform, print bed, and the printer’s exterior to remove dust, debris, and residual filament particles. Additionally, lubricate the printer’s moving components, such as the rods and lead screws, with a suitable lubricant to minimize friction and ensure smooth and precise movements during printing.
Calibration and Alignment:
Regularly calibrate and align the printer’s axes, including the X, Y, and Z axes, to maintain accurate and consistent print quality. Proper calibration ensures that the printer’s movements and positioning remain within specified tolerances, minimizing the risk of misaligned prints and inaccuracies.
Filament Storage and Handling:
Store filaments in a dry and dust-free environment, utilizing sealed containers or desiccant packs to prevent moisture absorption and filament degradation. Proper filament handling, such as avoiding sudden bends or kinks during spooling, contributes to smooth material flow and minimizes the risk of extrusion issues during printing.
Extruder and Nozzle Maintenance:
Regularly inspect the extruder assembly and nozzle for any accumulated debris, filament residue, or partial clogs. Clear any obstructions using suitable tools and ensure that the nozzle aperture remains unobstructed to facilitate precise material deposition during printing.
Electronics and Connectivity:
Inspect the printer’s electronic components, including the motherboard, wiring, and connectivity interfaces, to identify any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Periodically verify the integrity of the printer’s electrical connections and ensure that firmware updates are applied as recommended by the manufacturer.
Component Wear and Replacement:
Monitor critical components such as belts, pulleys, and bearings for signs of wear, deformation, or slackness. Replace worn components promptly to maintain the printer’s structural integrity and minimize the risk of print imperfections attributed to mechanical inconsistencies.
By integrating these maintenance practices into your 3D printing routine, you not only preserve the optimal functionality of your printer but also cultivate a deeper understanding of its intricacies. The commitment to proactive maintenance and care underscores your dedication to achieving exceptional print quality and sustained operational reliability from your 3D printer.
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on a captivating journey into the realm of 3D printing. Throughout this comprehensive guide, you have delved into the fundamental principles, operational intricacies, and maintenance essentials that define the art of operating a 3D printer. Armed with this knowledge, you are poised to unleash your creativity, innovate with confidence, and bring your digital designs to life with precision and finesse.
As you navigate the multifaceted landscape of 3D printing, remember that each print serves as a canvas for your imagination and technical prowess. Embrace the iterative nature of the printing process, where challenges are opportunities for growth, and triumphs are manifestations of your dedication and expertise.
With a keen understanding of the basics of 3D printing, meticulous attention to setup and preparation, adept operation of your printer, and a commitment to regular maintenance, you are well-equipped to traverse the exciting terrain of additive manufacturing. Whether you are crafting functional prototypes, artistic creations, or customized components, your 3D printer stands as a conduit for boundless innovation and tangible realization of your visions.
Remember, the world of 3D printing is a tapestry of innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning. Embrace the community of makers, designers, and enthusiasts, and share your experiences to contribute to the collective wealth of knowledge and inspiration.
As you embark on your 3D printing endeavors, may your creations inspire awe, spark curiosity, and leave an indelible mark on the ever-evolving landscape of additive manufacturing. Your journey as a 3D printing enthusiast is a testament to the harmonious fusion of artistry, technology, and boundless creativity.
Now, armed with the insights and expertise gained from this guide, venture forth with confidence, and let the rhythmic hum of your 3D printer echo the symphony of your ingenuity and passion.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Operate A 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “How To Operate A 3D Printer”