

Articles
How Many Circuits In A Conduit
Modified: March 2, 2024
Discover the answer to how many circuits can be installed in a conduit with this informative article. Learn about electrical safety and best practices.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to electrical installations, conduits play a crucial role in safeguarding and organizing the wiring systems. Conduits serve as protective channels that house electrical wires, protecting them from damage and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. But have you ever wondered how many circuits can be installed in a single conduit?
In this article, we will delve into the world of conduits and electrical circuits to understand the factors that determine the number of circuits that can be accommodated in a conduit. We will explore the basics of conduits and electrical circuits, the calculations involved in determining conduit fill, and the guidelines provided by the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure safe and efficient electrical installations.
By understanding the limitations, benefits, and safety considerations, you will be equipped with the knowledge to plan and execute electrical installations with multiple circuits in a conduit.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding conduit fill calculations and NEC guidelines is crucial for determining the number of circuits in a conduit. Prioritizing safety and compliance ensures efficient and safe electrical installations.
- While accommodating multiple circuits in a conduit offers space efficiency and cost savings, it’s essential to address limitations such as conduit fill capacity and potential interference. Prioritize safety and consult experts for informed decisions.
Understanding Conduits
Before we dive into the specifics of electrical circuits in conduits, let’s first establish a clear understanding of what conduits are and why they are used in electrical installations.
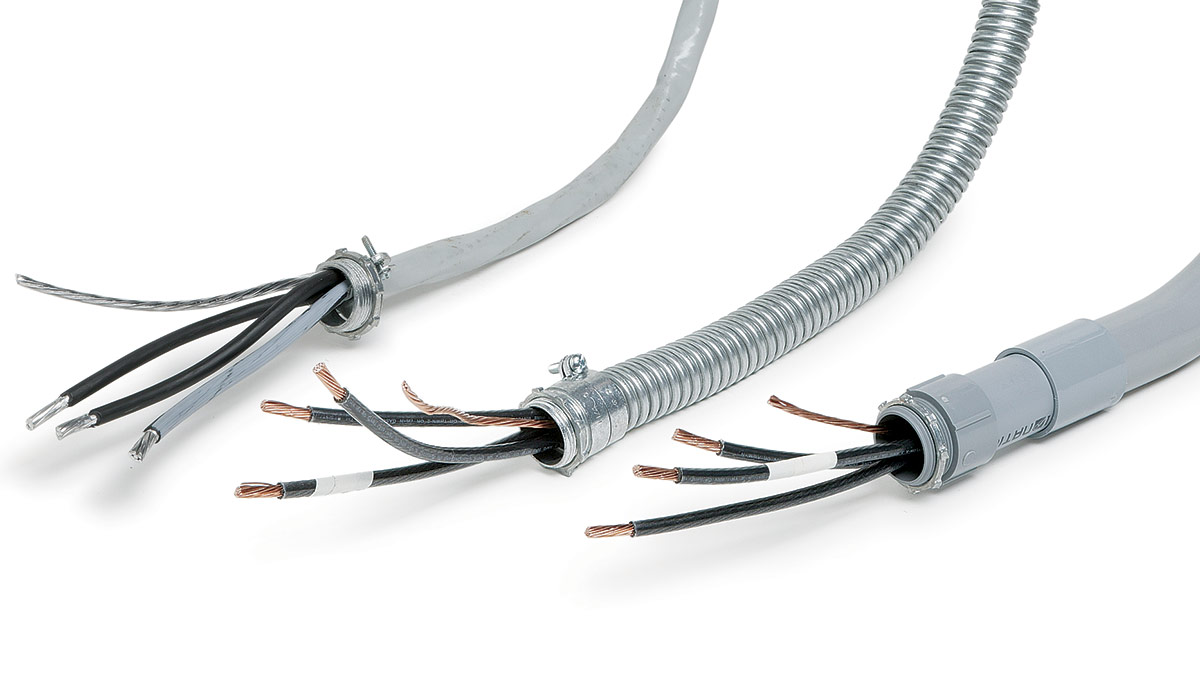
A conduit is a pipe or tube-like structure designed to contain and protect electrical wires and cables. It acts as a protective channel, shielding the wires from physical damage and exposure to environmental elements such as moisture and dust. Moreover, conduits serve another critical purpose in electrical installations, which is to organize and streamline the wiring system, facilitating maintenance and future modifications.
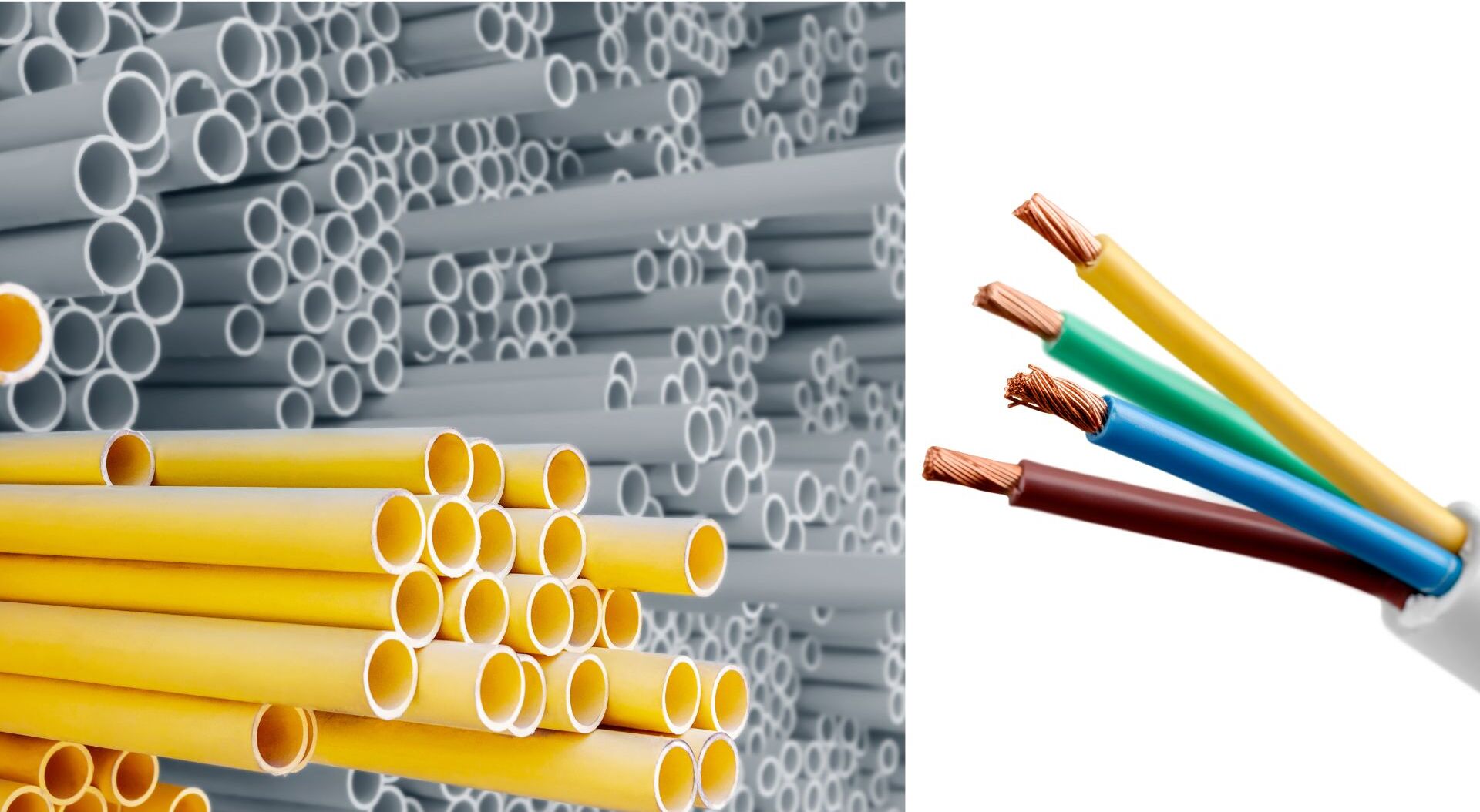
There are various types of conduits available, each designed for specific applications and environments. The most common types include:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): Made of galvanized steel, RMC is the most durable and rigid type of conduit. It provides excellent protection against physical impact and is suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT conduits are made of thin-wall steel or aluminum tubing. They are lighter and more flexible than RMC, making them easier to install in tight spaces or when a degree of flexibility is required.
- Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): FMC, also known as “greenfield,” is a flexible conduit made of interlocking metal strips. It is commonly used in exposed or areas with vibration, such as outdoor installations or machinery.
- PVC Conduit: PVC conduits are made of polyvinyl chloride, a sturdy and non-conductive material. They are popular for their affordability, ease of installation, and resistance to corrosion. PVC conduits are commonly used in residential and commercial applications.
- Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC): LFMC is similar to FMC but is additionally coated with a watertight jacket. It is commonly used in areas that require protection against moisture, such as outdoor installations or wet locations.
It’s important to choose the right conduit type based on the specific requirements of your installation, considering factors such as environmental conditions, level of protection needed, and local building codes.
Now that we have a solid understanding of conduits, let’s move on to unraveling the intricacies of electrical circuits and how they relate to conduits.
Basics of Electrical Circuits
Electrical circuits are the vital pathways that allow electricity to flow and power various electrical devices and systems. Understanding the fundamentals of electrical circuits is essential to comprehend how multiple circuits can be accommodated in a conduit.
Let’s begin by defining an electrical circuit. An electrical circuit is a closed loop or pathway that allows an electric current to flow from a power source to a load. It consists of various components that work together to facilitate the flow of electricity. Here are some key components of an electrical circuit:
- Power Source: The power source provides the electrical energy needed to drive the circuit. It can be a generator, battery, or even a power supply from the grid.
- Conductors: Conductors are materials, such as copper or aluminum wires, that carry the electric current from the power source to the load.
- Load: The load is the device or system that consumes electrical energy and performs a specific function. It can be a light bulb, motor, computer, or any other electrical device.
- Switches: Switches control the flow of electricity in the circuit. They can open or close the circuit, allowing or preventing the current from reaching the load.
- Protection Devices: Protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are installed to safeguard the circuit and connected devices from overcurrents or short circuits.
Electrical circuits can be classified into various types based on their configuration and purpose. Some common types of electrical circuits include:
- Series Circuits: In series circuits, the components are connected in a single path, forming a sequential loop. The same electrical current passes through each component, and the voltage is divided across them. If one component fails or is disconnected, the entire circuit is interrupted.
- Parallel Circuits: Parallel circuits have multiple paths for current flow, where components are connected across different branches. The same voltage is applied across each component, but the current may vary. If one component fails or is disconnected, other components continue to operate.
- Combination Circuits: Combination circuits are a mix of series and parallel circuits. They have both series and parallel connections to meet specific requirements or to control different parts of the circuit separately.
Understanding the different types of circuits is crucial when planning the wiring layout and determining the number of circuits that can be installed in a conduit.
Now that we have a solid grasp of the basics of electrical circuits, let’s explore the factors involved in determining the number of circuits that can be accommodated in a conduit.
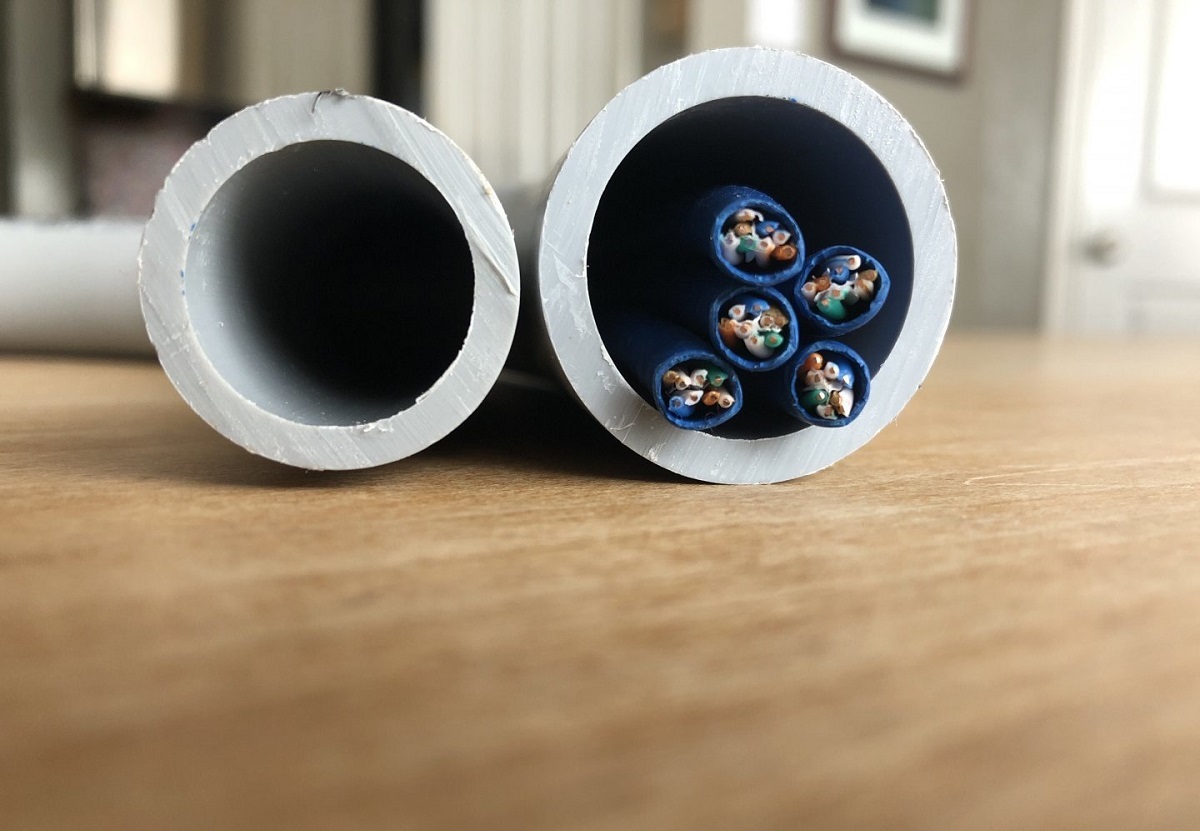
Number of Circuits in a Conduit
When it comes to determining the number of circuits that can be accommodated in a conduit, several factors come into play. It’s crucial to consider these factors to ensure compliance with safety standards, promote efficient operation, and avoid overload conditions.
Factors Determining the Number of Circuits in a Conduit
1. Conduit Size: The size of the conduit plays a vital role in determining the number of circuits that can be installed. Larger conduits provide more space for wires and allow for a higher number of circuits, while smaller conduits may limit the number of circuits due to space constraints.
2. Wire Size: The size of the wires being used also affects the number of circuits that can be accommodated. Larger gauge wires require more space, reducing the number of circuits that can fit within a given conduit size.
3. Conduit Fill Capacity: Every conduit has a specific “fill capacity,” which represents the maximum allowable amount of space occupied by the conductors inside the conduit. This capacity is determined based on the size and type of the conduit.
Read more: How Many Breakers In 100 Amp Panel
Conduit Fill Calculations
Conduit fill calculations help determine how many circuits can be safely installed in a conduit based on the sizes of the wires and the conduit itself. These calculations consider the size of the conductors, the type of insulation, and the conduit fill capacity.
Conduit fill calculations follow specific formulas and guidelines outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure safe and efficient installations. The NEC provides tables and formulas for calculating the maximum allowable fill for different types and sizes of conductors in various conduit types.
NEC Guidelines for Conduit Sizing
The NEC provides comprehensive guidelines for sizing conduits based on the number and size of the conductors being installed. These guidelines ensure that the conduit is not overfilled, preventing potential overheating, excess voltage drop, and fire hazards.
The NEC provides tables that outline the maximum allowable fill percentages for different conduit sizes and types, based on the diameter and type of the conductors being installed. These tables serve as a valuable resource when determining the appropriate conduit size for a specific installation.
It’s crucial to adhere to the NEC guidelines to ensure compliance with electrical safety regulations and promote optimal performance and longevity of the electrical system.
Now that we understand the factors involved in determining the number of circuits in a conduit and the importance of conduit fill calculations and NEC guidelines, let’s dive into an example to demonstrate the conduit fill calculation process and considerations involved.
Conduit Fill Calculation Example
Let’s walk through a step-by-step example of conduit fill calculations to determine the number of circuits that can be installed in a specific conduit. Keep in mind that this example is for illustration purposes, and actual calculations may vary based on specific installation requirements.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process:
- Identify the conduit size: Determine the size of the conduit in which you plan to install the circuits. For this example, we will assume a 1-inch PVC conduit.
- Refer to the NEC table: Consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) table for the conduit fill capacity of a 1-inch PVC conduit. The table provides values for different conductor sizes and types.
- Determine conductor sizes: Identify the sizes and types of conductors that will be installed in the conduit. As an example, let’s assume we have four 12-gauge THHN copper conductors.
- Calculate the fill percentage: Refer to the NEC table and find the fill percentage for 12-gauge THHN conductors in a 1-inch PVC conduit. Let’s assume the fill percentage is 40%.
- Calculate the available fill space: Multiply the conduit size by the fill percentage. In this case, 1 inch x 40% = 0.4 inches.
- Calculate the actual fill space: Determine the outer diameter of the conductors being used. The outer diameter of a 12-gauge THHN conductor is typically around 0.130 inches. Multiply the outer diameter by the number of conductors (4 in this example). So, 0.130 inches x 4 = 0.52 inches.
- Compare the actual fill space to the available fill space: Compare the actual fill space (0.52 inches) to the available fill space (0.4 inches). If the actual fill space is greater than the available fill space, you will need to reduce the number of conductors or increase the conduit size to ensure compliance.
Read more: How Many Circuit Breakers In A House
Assumptions and Considerations:
It’s important to note that this example simplifies the conduit fill calculations and considers a specific scenario. In real-world applications, there may be additional factors and considerations, such as different conductor types, insulation types, and installation requirements. Always consult the NEC and work with a qualified electrician or engineer to ensure accurate and compliant conduit fill calculations for your specific installation.
Furthermore, it’s essential to account for future expansion and maintenance when determining the number of circuits in a conduit. Leaving sufficient space for potential additions or modifications can save time, effort, and costs in the long run.
Remember to always prioritize safety and compliance when planning and executing electrical installations. Understanding conduit fill calculations and following the NEC guidelines will help ensure the integrity of the electrical system.
Now that we have explored the conduit fill calculation example and the assumptions involved, let’s discuss the benefits, limitations, and safety concerns related to having multiple circuits in a conduit.
Benefits and Limitations of Multiple Circuits in a Conduit
Installing multiple circuits in a conduit can offer several advantages, but it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. It is important to weigh these factors when determining the feasibility of accommodating multiple circuits in a conduit.
Advantages of Multiple Circuits in a Conduit:
1. Space Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of installing multiple circuits in a conduit is the efficient utilization of space. Rather than running separate conduits for each circuit, multiple circuits can share the same conduit, allowing for a more compact and organized wiring system.
2. Cost Savings: Using a single conduit for multiple circuits can reduce material costs compared to installing separate conduits for each circuit. Additionally, the compactness of a shared conduit can save on installation time and labor costs.
3. Simplicity of Installation: Having multiple circuits in a single conduit simplifies the installation process. Electricians can run all the necessary wires in one conduit, making it easier to route and secure the wiring system.
4. Easy Maintenance and Modifications: With multiple circuits in a conduit, future maintenance and modifications become more convenient. It simplifies troubleshooting and allows for easy modifications or additions in the future without the need for extensive rewiring.
Limitations and Challenges:
1. Conduit Fill Limitations: The primary limitation of accommodating multiple circuits in a conduit is the conduit fill capacity. Each conduit has a specified fill capacity, and exceeding it can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and compromised safety. It’s crucial to perform accurate conduit fill calculations and adhere to NEC guidelines to prevent overfilling.
2. Increased Complexity and Organization: Sharing a conduit for multiple circuits can introduce complexity in terms of organization and labeling. It’s vital to properly label and identify each circuit to avoid confusion during maintenance or troubleshooting. This requires meticulous documentation and clear identification practices.
3. Potential for Interference: Having multiple circuits in close proximity can potentially lead to interference or crosstalk between the wires. This interference can affect the performance and reliability of the circuits. Proper spacing, separation, and shielding may be required to mitigate the risk of interference.
Read more: How Many Romex Wires In Conduit
Safety Concerns:
When installing multiple circuits in a conduit, safety should always be a priority. Some key safety concerns to address include:
1. Overheating: Overfilling a conduit can cause excessive heat buildup, potentially leading to wire insulation deterioration, meltdowns, or even fires. Adhering to conduit fill capacity limits and performing proper conduit fill calculations is crucial to prevent overheating.
2. Voltage Drop: Multiple circuits sharing the same conduit can result in voltage drop, affecting the performance of connected devices and equipment. Careful consideration of wire sizes and circuit loads is necessary to minimize voltage drop and ensure proper operation.
3. Accessibility and Inspections: With multiple circuits in a single conduit, accessibility for maintenance and inspections can become challenging. Ensuring adequate access points, clear labeling, and proper documentation is essential to facilitate future inspections and maintenance activities.
It’s important to consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer to properly assess the feasibility and safety considerations when planning multiple circuits in a conduit.
Now that we have explored the benefits, limitations, and safety concerns related to multiple circuits in a conduit, let’s wrap up our discussion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of conduits and electrical circuits is crucial when determining the number of circuits that can be accommodated in a conduit. By considering the factors such as conduit size, wire size, and conduit fill capacity, you can ensure safe and efficient electrical installations.
While installing multiple circuits in a conduit offers advantages such as space efficiency, cost savings, and easier maintenance, it is important to be aware of the limitations and challenges involved. Conduit fill limitations, increased complexity, and potential for interference need to be carefully addressed to maintain system integrity and reliability.
Ensuring compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines is vital in determining conduit fill and sizing requirements. Adhering to these guidelines helps prevent overheating, voltage drop, and other electrical hazards that can jeopardize safety.
When planning multiple circuits in a conduit, it is essential to prioritize safety and consult with qualified electricians or engineers. They can provide expertise in conduit fill calculations, proper wire sizing, and safe installation practices to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your electrical system.
By understanding the benefits, limitations, and safety concerns related to multiple circuits in a conduit, you can make informed decisions and plan electrical installations that meet your specific requirements and comply with applicable regulations.
Remember, electrical installations require meticulous attention to detail and compliance with safety standards to ensure the protection of people and property. Stay informed, consult experts, and prioritize safety in all your electrical endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Circuits In A Conduit
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “How Many Circuits In A Conduit”