

Articles
How Many Wires In 1/2 Inch Conduit
Modified: February 28, 2024
Looking for articles about how many wires can fit in a 1/2 conduit? Find answers and expert guidance on this topic.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
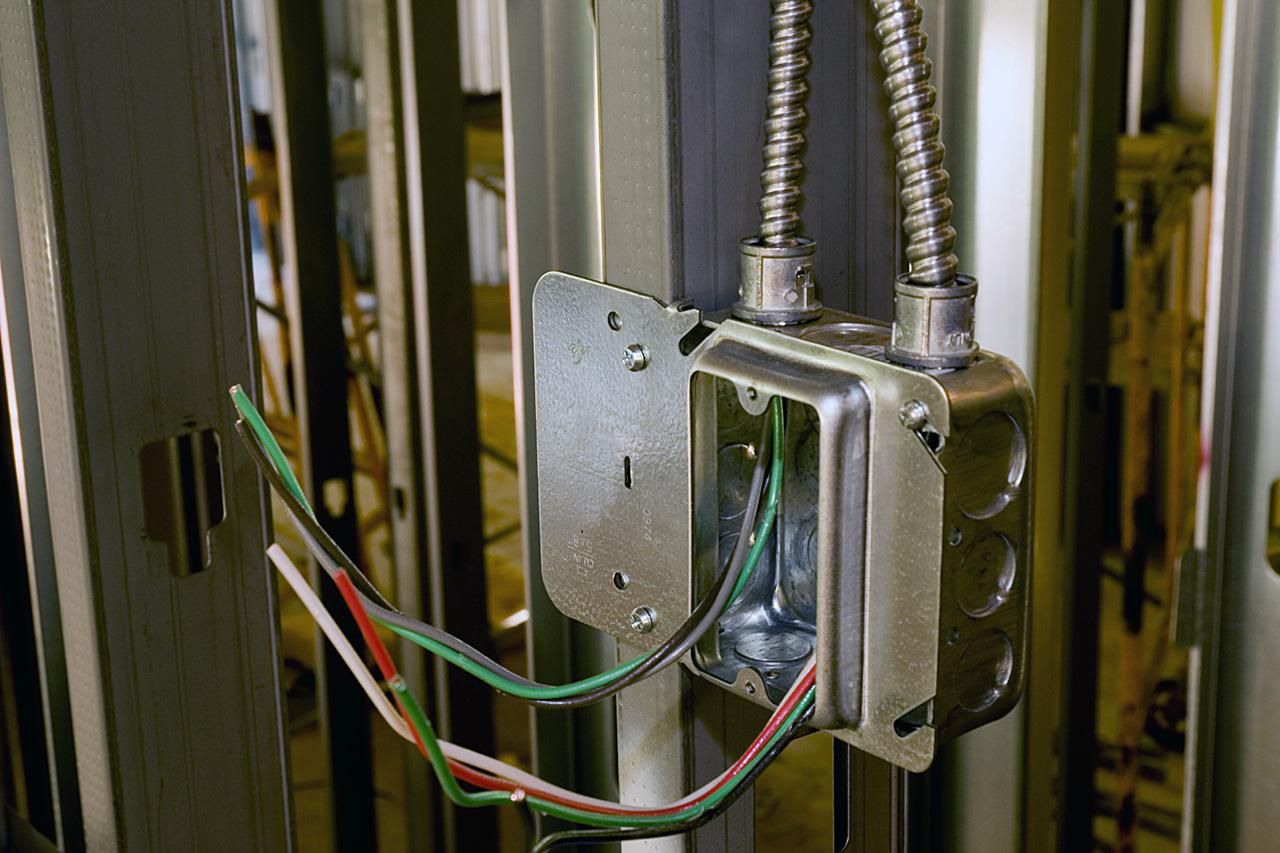
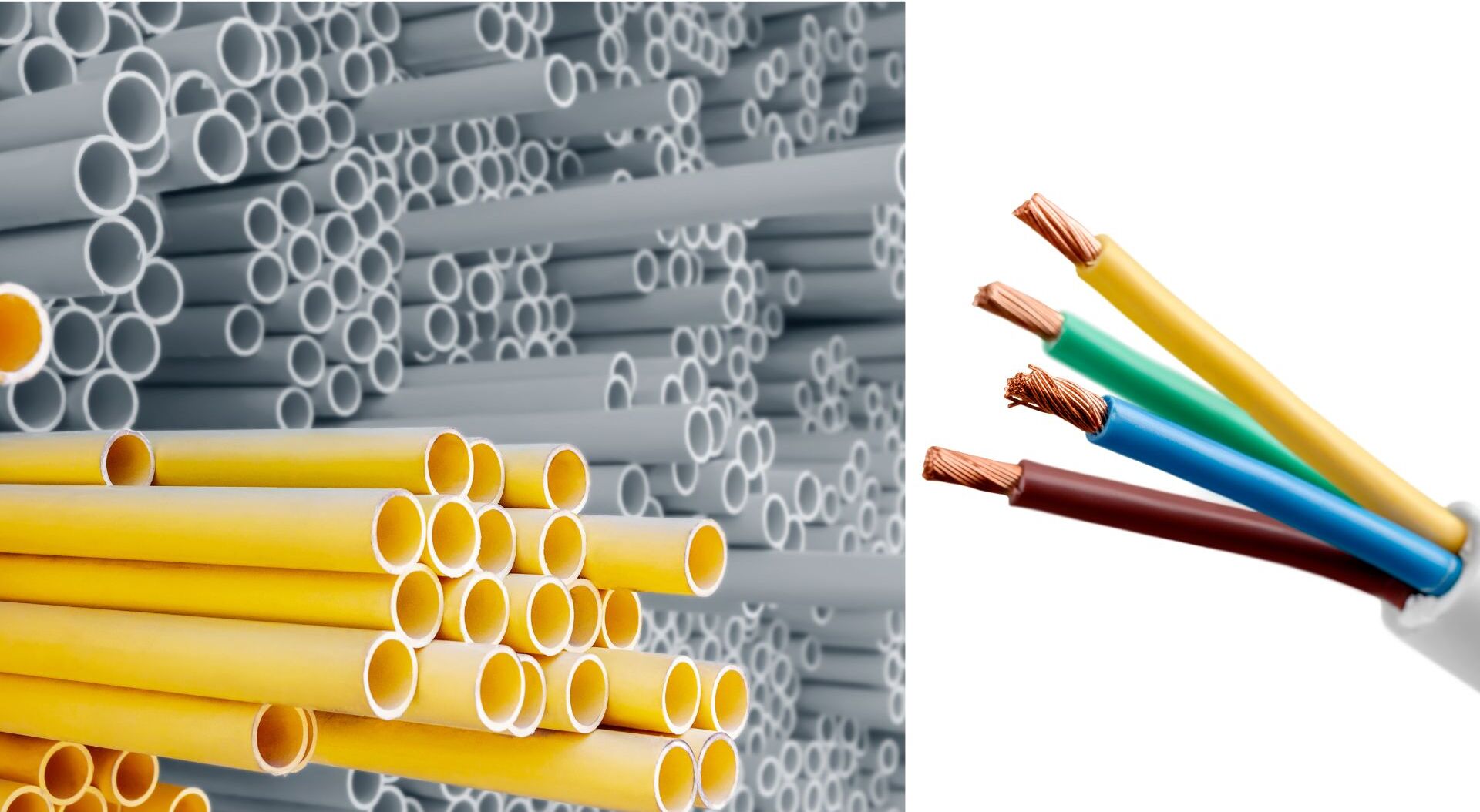
When it comes to electrical installations, proper conduit usage plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and functionality of the system. Conduit is a protective tubing used to encase electrical wires, providing insulation and shielding against external elements. It also helps in organizing and routing wires, making it easier to maintain and troubleshoot electrical systems.
Understanding the different types of conduit and their capabilities is crucial for electricians and anyone involved in electrical work. One popular size of conduit is the 1/2″ conduit. In this article, we will explore what 1/2″ conduit is and delve into the standard number of wires that can be accommodated within it.
Whether you’re a professional electrician or a DIY enthusiast, having a clear understanding of conduit sizing and wire capacity will aid you in planning and executing electrical installations smoothly and efficiently. So, let’s dive in and discover the world of 1/2″ conduit and its wire capacity.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper conduit sizing and fill calculations are crucial for ensuring efficient wire routing, preventing overheating, and complying with safety standards in electrical installations.
- Understanding the factors that affect the number of wires in conduit, such as wire size, insulation type, and conduit material, is essential for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system.
Read more: How Many 12/2 Wires In 1/2 Inch Conduit
Understanding Conduit
Conduit is a critical component in electrical installations as it provides a protective pathway for electrical wires. It shields the wires from physical damage and safeguards them from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. By enclosing the wires in conduit, the risk of accidents and electrical hazards are reduced.
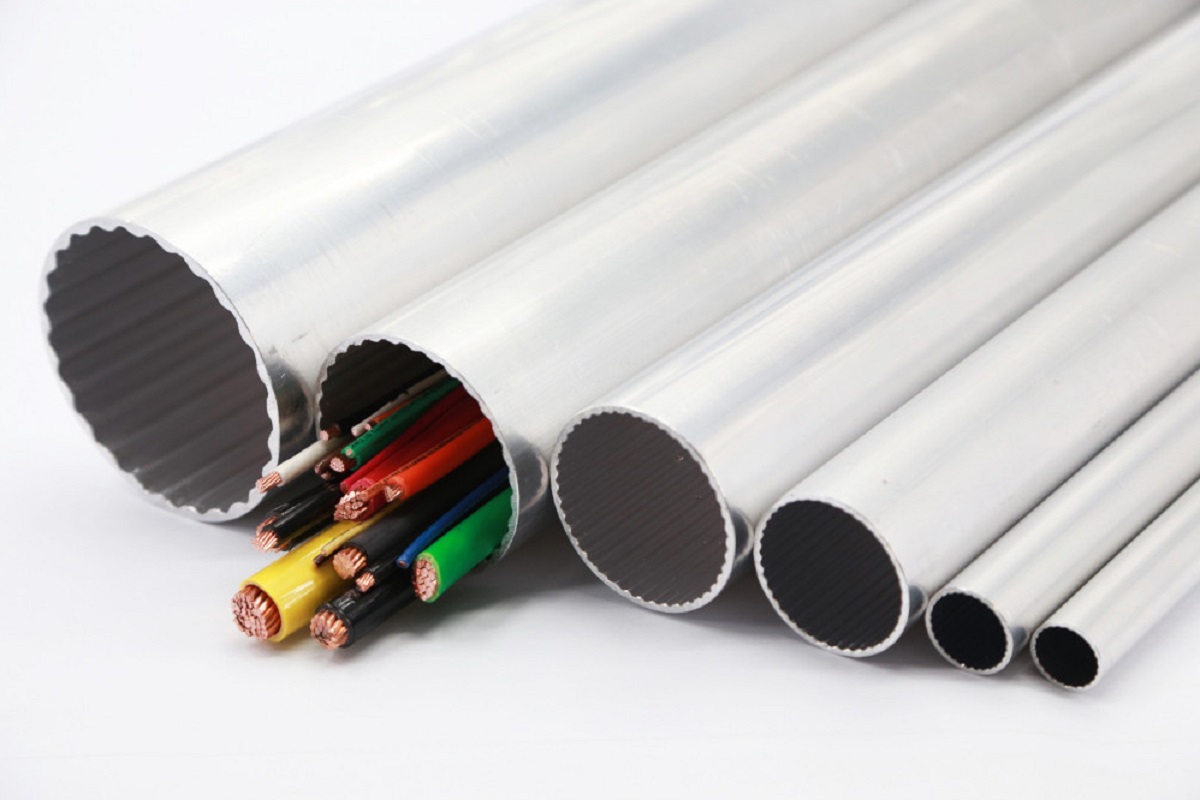
Conduit can be made from different materials such as metal, PVC (polyvinyl chloride), or flexible conduit. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the level of protection required. Metal conduit, such as rigid steel conduit (RSC) or intermediate metal conduit (IMC), is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings due to its durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions. PVC conduit is more popular in residential installations due to its affordability and ease of installation.
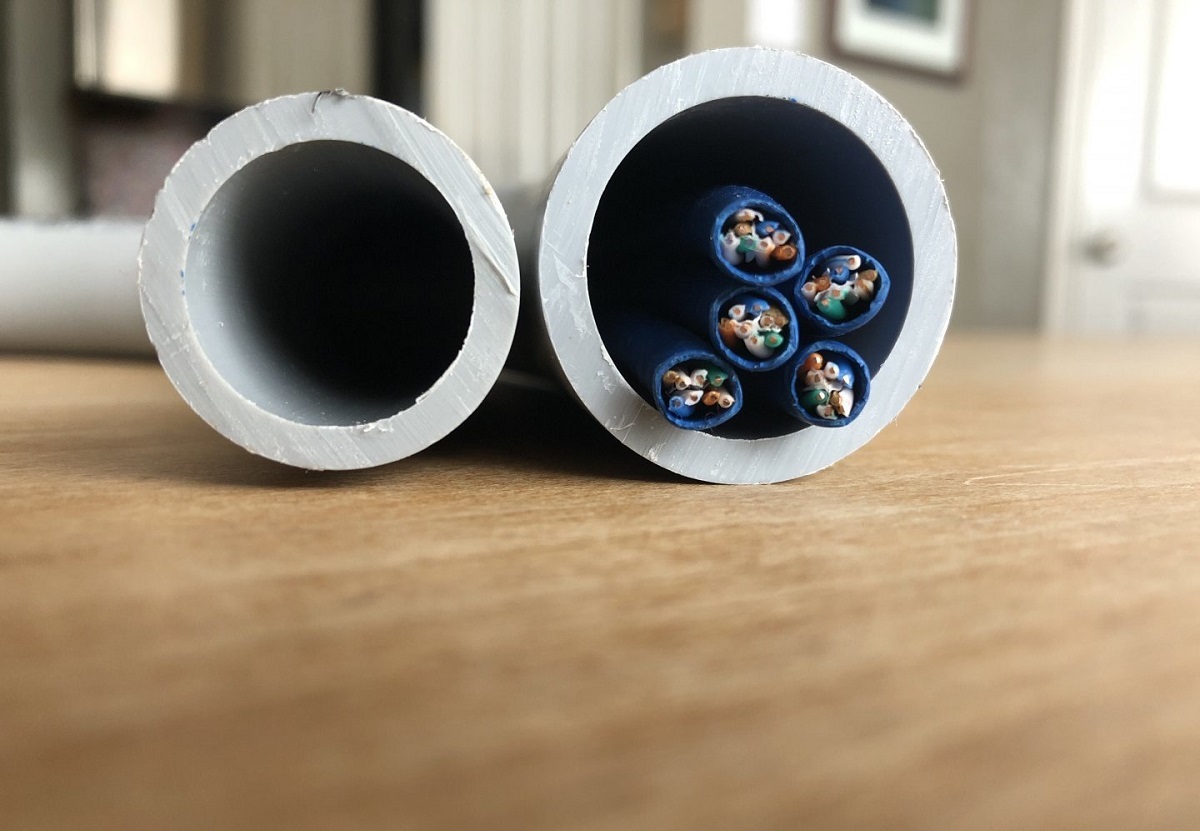
Conduit also comes in various sizes, ranging from as small as 1/2″ to as large as several inches in diameter. The size of the conduit determines the number of wires it can accommodate and the ease of installation. It is essential to choose the right conduit size to ensure efficient wire routing and compliance with electrical codes and regulations.
Properly installed conduit not only protects the wires but also allows for future expansions or modifications. In case an issue arises within the electrical system, the conduit can be easily accessed for troubleshooting or rewiring. It also aids in cable management and prevents tangling or entanglement of wires, making it easier to identify specific circuits during maintenance or repairs.
In summary, conduit is an integral part of electrical installations, providing protection, organization, accessibility, and flexibility. Understanding the different types of conduit and their applications is crucial for ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical systems.
Types of Conduit
Conduit comes in various types to cater to different applications and installation requirements. Let’s take a look at the most common types of conduit:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): RMC is one of the most durable and rigid types of conduit. It is made of galvanized steel and is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings where protection against physical damage is crucial. RMC is threaded on both ends and requires special fittings for installation.
- Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC): IMC is another type of metal conduit that is less rigid than RMC. It is made of galvanized steel and provides excellent protection for electrical wires. IMC is typically used in exposed or outdoor installations, as it is corrosion-resistant and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is a lightweight and easy-to-install conduit that is made of thin-walled galvanized steel. It is commonly used in residential installations, where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are important factors. EMT is often used indoors or in concealed locations.
- PVC Conduit: PVC conduit is made of polyvinyl chloride and is a popular choice for residential installations due to its affordability and ease of installation. It is available in different wall thicknesses and can be used both indoors and outdoors. PVC conduit is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and corrosion.
- Flexible Conduit: As the name suggests, flexible conduit is a type of conduit that provides flexibility for wire routing in tight or irregular spaces. It is often made of flexible metal or plastic material and is commonly used in applications that require frequent modifications or bends in the conduit.
Each type of conduit has its own advantages and applications. The choice of conduit will depend on factors such as the environment, installation requirements, and budget constraints. It is important to consult local electrical codes and regulations to ensure compliance when selecting and installing conduit.
Now that we have a better understanding of the different types of conduit, let’s explore what 1/2″ conduit is and its wire capacity.
What is 1/2″ Conduit?
1/2″ conduit, also known as half-inch conduit, is a common size of conduit used in electrical installations. The measurement refers to the internal diameter of the conduit. It is important to note that the actual outer diameter of the conduit may be slightly larger due to the thickness of the conduit walls.
1/2″ conduit is widely used in both residential and commercial applications. Its compact size makes it ideal for running wires in tight spaces or areas where larger conduit sizes are not necessary. It is suitable for routing electrical wires for lighting circuits, outlets, switches, and other low-voltage applications.
The material for 1/2″ conduit can vary depending on the specific application and the level of protection required. It can be made of metal, such as galvanized steel or aluminum, or non-metallic materials like PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Each material has its own advantages and considerations in terms of durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
When selecting 1/2″ conduit, it is essential to take into account the electrical codes and regulations in your area. These codes specify the maximum fill capacity of conduit, which determines the number and size of wires that can be accommodated safely. Proper conduit sizing and fill calculations are crucial to ensure efficient wire routing, prevent overheating, and comply with safety standards.
Now that we have a basic understanding of 1/2″ conduit, let’s discuss the standard number of wires that can be accommodated within it.
When determining how many wires can fit in a 1/2″ conduit, you can use the NEC guidelines which state that for a 1/2″ conduit, the maximum number of conductors allowed is 4. This includes all insulated conductors and grounding conductors.
Standard Number of Wires in 1/2″ Conduit
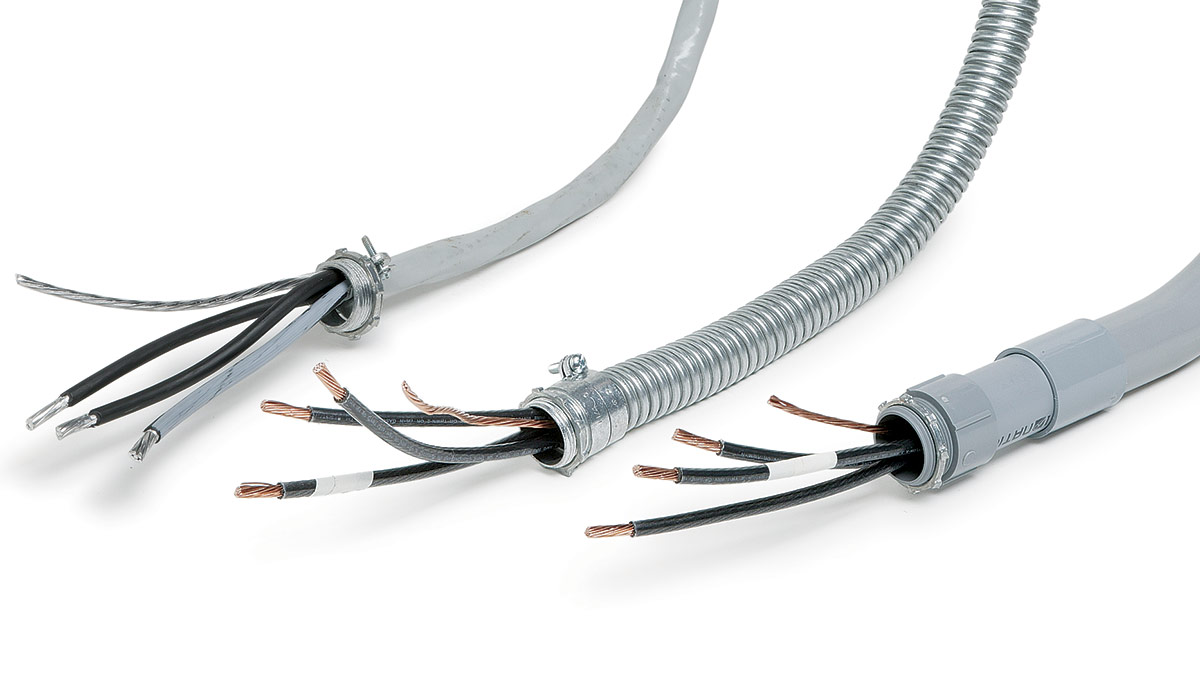
The number of wires that can be safely and effectively installed in 1/2″ conduit depends on various factors such as the type of wires, insulation type, and the electrical codes and regulations in your area. It is important to consult local codes and guidelines to ensure compliance and safety in your specific installation.
As a general guideline, the standard number of wires that can be installed in 1/2″ conduit is limited. In most cases, you can expect to accommodate a maximum of 4 to 6 wires, depending on their size and the type of conduit being used. It is important to note that this number refers to the number of “current-carrying” conductors, which are wires that carry the electrical load.
However, it’s essential to consider the fill capacity of the conduit to determine its suitability for your specific installation. The fill capacity refers to the percentage of space within the conduit that the wires occupy. Different wire sizes and types have different fill capacities, and exceeding the recommended fill capacity can lead to overheating, decreased airflow, and potential safety hazards.
To accurately determine the fill capacity of 1/2″ conduit for your specific wiring setup, you can refer to conduit fill calculation tables provided by electrical codes or consult an electrical professional. These tables take into account factors such as wire size, insulation type, and number of conductors to provide a precise calculation of the fill capacity.
It is crucial to follow the recommended fill capacity and avoid overcrowding the conduit to ensure proper heat dissipation, prevent excessive friction between wires, and facilitate future modifications or additions. Additionally, be aware that bundling or grouping multiple wires together can affect the fill capacity and may require adjustments in conduit size or the installation of multiple conduits.
Remember, proper wire sizing, conduit fill calculations, and adherence to local electrical codes are essential to ensure the safety, functionality, and compliance of your electrical installation.
Now that we understand the standard number of wires that can be accommodated in 1/2″ conduit, let’s explore the factors that can affect the number of wires in conduit.
Read more: How Many 12 GA Wires In 1/2 Inch Conduit
Factors Affecting the Number of Wires
Several factors come into play when determining the number of wires that can be safely installed in 1/2″ conduit. It is crucial to consider these factors to ensure compliance with electrical codes, prevent overheating, and maintain the integrity of the electrical system. Let’s take a closer look at the key factors that can affect the number of wires in conduit:
- Wire Size: The size of the wires being installed is a critical factor. Larger wire sizes, such as #10 AWG or #12 AWG, may require more space within the conduit, reducing the number of wires that can be accommodated. Smaller wire sizes, like #14 AWG or #16 AWG, typically allow for more wires to fit due to their smaller diameter.
- Insulation Type: The insulation type of the wires also affects the amount of space required within the conduit. Certain insulation types may have thicker walls, increasing the overall size of the wire. This can reduce the number of wires that can fit in the limited space of a 1/2″ conduit.
- Conduit Type and Material: Different types of conduit have varying internal diameters, which can impact the capacity to accommodate wires. Additionally, the material of the conduit can affect the available space for wires. For example, metal conduit may have thicker walls compared to PVC conduit, reducing the inner space for wire routing.
- Bundling and Grouping: When multiple wires are bundled or grouped together, they occupy more space within the conduit. This reduces the overall fill capacity and limits the number of wires that can be safely installed. It is important to consider the fill capacity guidelines and adjust conduit size or separate conduit runs if necessary.
- Conduit Fill Requirements: Electrical codes provide specific requirements for conduit fill, which dictate the maximum allowable percentage of the conduit’s cross-sectional area that can be filled with wires. It is crucial to adhere to these guidelines to prevent overheating, minimize voltage drops, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
By taking these factors into account, electricians and installers can determine the appropriate number of wires to be installed in 1/2″ conduit. It is essential to consult local electrical codes and guidelines, conduct conduit fill calculations, and ensure proper wire sizing to maintain a safe and efficient electrical installation.
Now that we understand the factors that affect the number of wires, let’s delve into the process of conduit fill calculation.
Conduit Fill Calculation
Conduit fill calculation is a method used to determine the maximum number of wires that can be safely and effectively installed in a given conduit. It involves considering the size of the conduit, the size of the wires, insulation type, and other factors to ensure compliance with electrical codes and prevent issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and installation difficulties.
To perform a conduit fill calculation, you can follow these general steps:
- Gather necessary information: Begin by collecting the required information, such as the size of the conduit, the type and size of the wires, and their insulation type. Consult local electrical codes and guidelines for specific requirements in your area.
- Determine wire size and fill capacity: Use wire sizing charts and conduit fill tables provided by electrical codes to find the appropriate wire size and its corresponding fill capacity. These charts take into account different wire sizes, insulation types, and conduit types to provide accurate fill capacity values.
- Calculate fill percentages: Calculate the percentage of fill for each wire and add them together. This can be done by dividing the cross-sectional area occupied by each wire by the total cross-sectional area of the conduit and multiplying by 100. Ensure that the total fill percentage does not exceed the recommended fill capacity specified in electrical codes.
- Consider bundling and grouping: If you are bundling or grouping multiple wires together within the conduit, factor in the derating requirements. Derating is the reduction in the fill capacity due to the increased heat generated by bundled or grouped wires. Refer to electrical codes for the derating factors to apply in your calculations.
- Make adjustments if necessary: If the calculated fill percentage exceeds the recommended fill capacity, you may need to make adjustments. Options include using a larger conduit size, installing additional conduits, or reducing the number of wires in the conduit.
It is important to note that conduit fill calculations may vary based on local electrical codes and regulations. Some jurisdictions may have specific requirements or restrictions that must be followed. It is crucial to consult the appropriate local authorities or an electrical professional for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
By performing conduit fill calculations, you can ensure that the appropriate number of wires are safely installed within the conduit, promoting proper airflow, minimizing heat buildup, and maintaining the integrity of the electrical system.
Now that we’ve familiarized ourselves with the conduit fill calculation process, let’s wrap up our discussion.
Conclusion
Understanding conduit and its capacity to accommodate wires is essential for anyone involved in electrical installations. In this article, we have explored the world of 1/2″ conduit and the factors that affect the number of wires it can safely contain.
Conduit serves as a protective pathway for electrical wires, shielding them from physical damage and environmental factors. It comes in various types, including rigid metal conduit, intermediate metal conduit, electrical metallic tubing, PVC conduit, and flexible conduit, each with its own advantages and applications.
1/2″ conduit is a common size used in residential and commercial installations, offering compact dimensions suitable for tight spaces. However, the standard number of wires that can be installed in 1/2″ conduit is limited, typically ranging from 4 to 6 wires. It is crucial to consider factors such as wire size, insulation type, conduit material, bundling, and conduit fill requirements to determine the optimal number of wires that can be safely accommodated.
Conduit fill calculation plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper installation of wires within the conduit. By following the steps of conduit fill calculation and consulting local electrical codes, installers can determine the maximum fill capacity and make necessary adjustments to ensure compliance and safety.
Remember, proper conduit usage is vital for the functionality and safety of electrical systems. Adhering to electrical codes, consulting professionals when needed, and considering factors like wire size, insulation type, and conduit fill capacity will help you create efficient, reliable, and safe electrical installations.
Now that you have a better understanding of 1/2″ conduit, wire capacity, and the importance of conduit fill calculation, you can confidently embark on your electrical projects, ensuring effective wire routing and compliance with electrical codes.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Wires In 1/2 Inch Conduit
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Many Wires In 1/2 Inch Conduit”