

Articles
How Much Co2 Does A Kegerator Use
Modified: January 7, 2024
Discover the impact of kegerators on carbon emissions with informative articles. Learn how much CO2 a kegerator uses to make an environmentally conscious choice.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A kegerator is a popular appliance among beer enthusiasts and commercial establishments alike. It allows for the storage and dispensing of draft beer, eliminating the need for individual bottles or cans. While kegerators offer a convenient and cost-effective way to enjoy fresh beer, many people are concerned about their environmental impact, particularly in terms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
CO2 is a greenhouse gas responsible for global warming. It is released into the atmosphere through various human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels. The brewing and dispensing of beer also contribute to CO2 emissions, and kegerators play a role in this process.
Understanding the environmental impact of kegerators’ CO2 emissions can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions to reduce their carbon footprint. In this article, we will explore the energy consumption and CO2 emissions associated with kegerators, as well as ways to mitigate their environmental impact.
Key Takeaways:
- Kegerators contribute to CO2 emissions through energy consumption, beer production, and transportation. By optimizing energy efficiency, reducing carbonation levels, and supporting local breweries, individuals and businesses can minimize their environmental impact.
- Understanding and calculating the CO2 emissions of kegerators can guide informed decisions to reduce their carbon footprint. Implementing sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy, practicing responsible drinking, and promoting awareness, can make a meaningful impact in the fight against climate change.
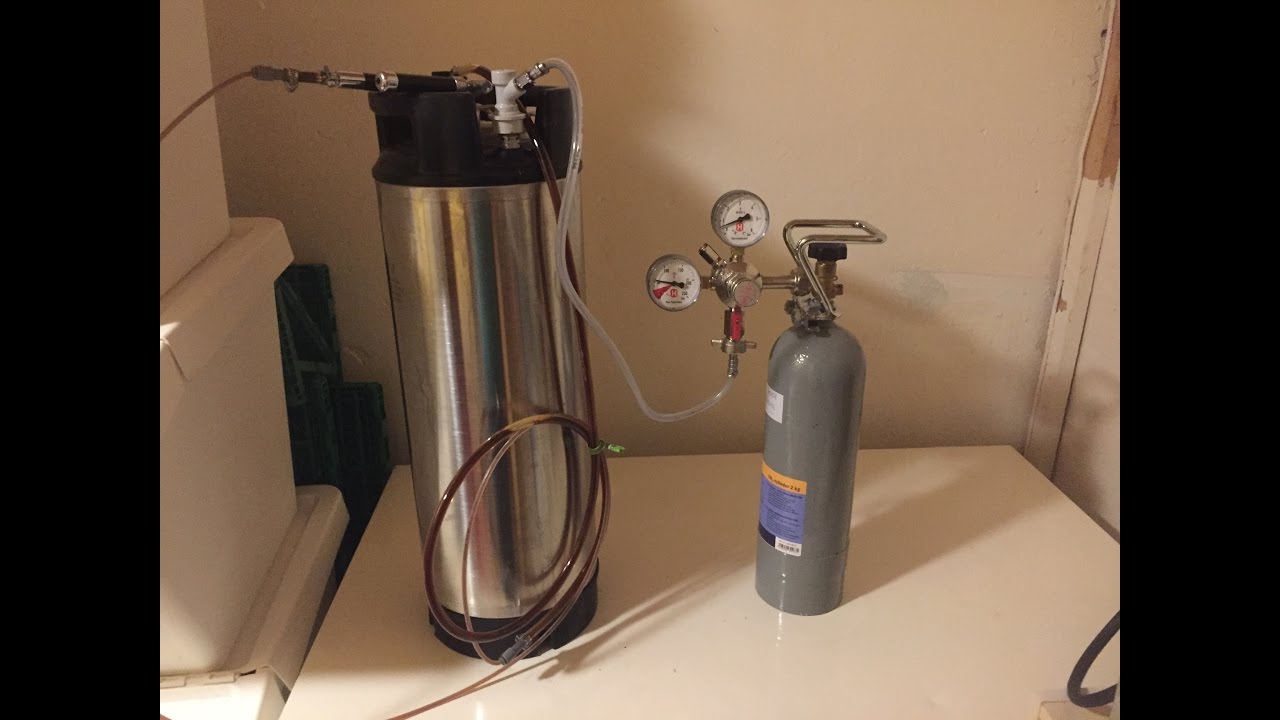
What is a Kegerator?
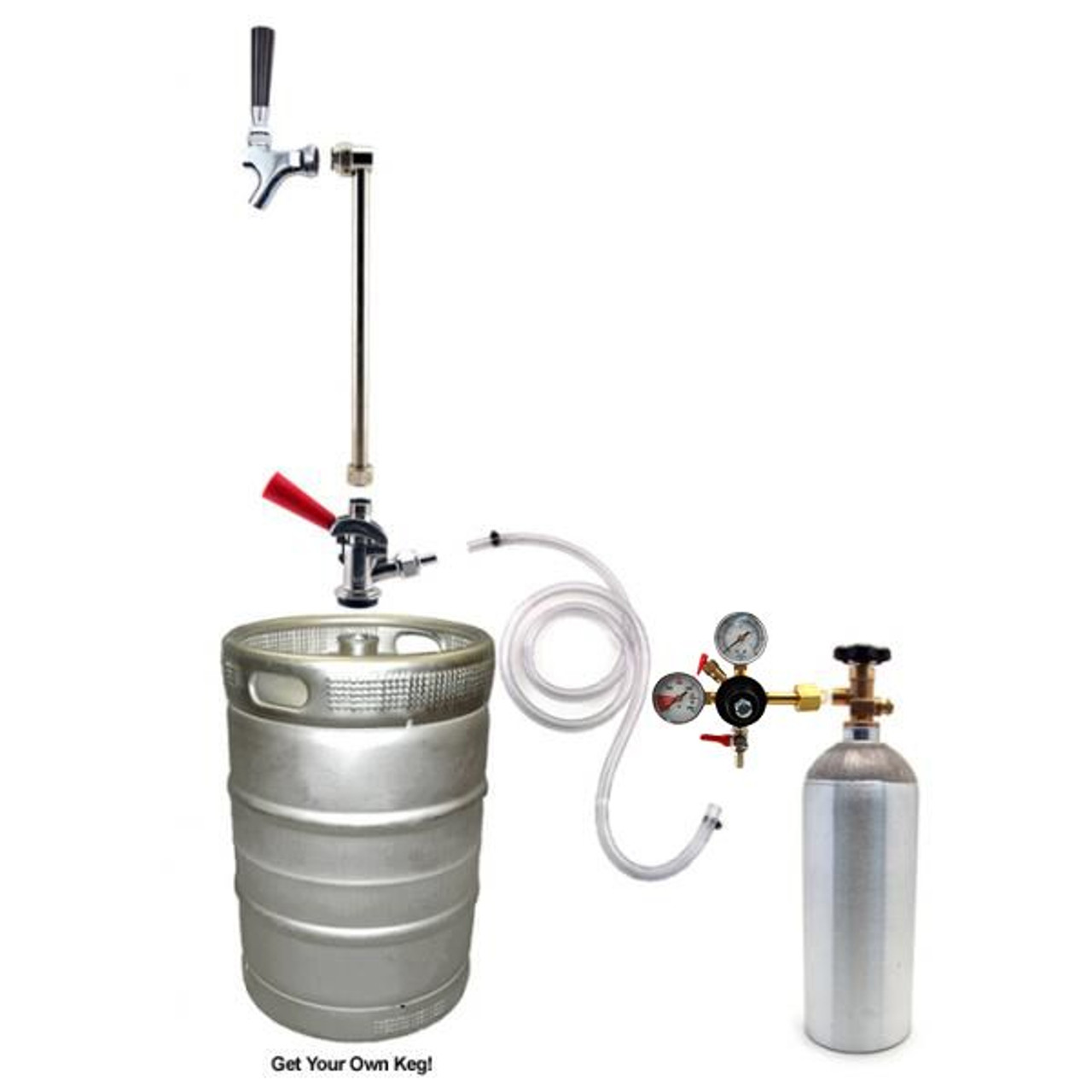
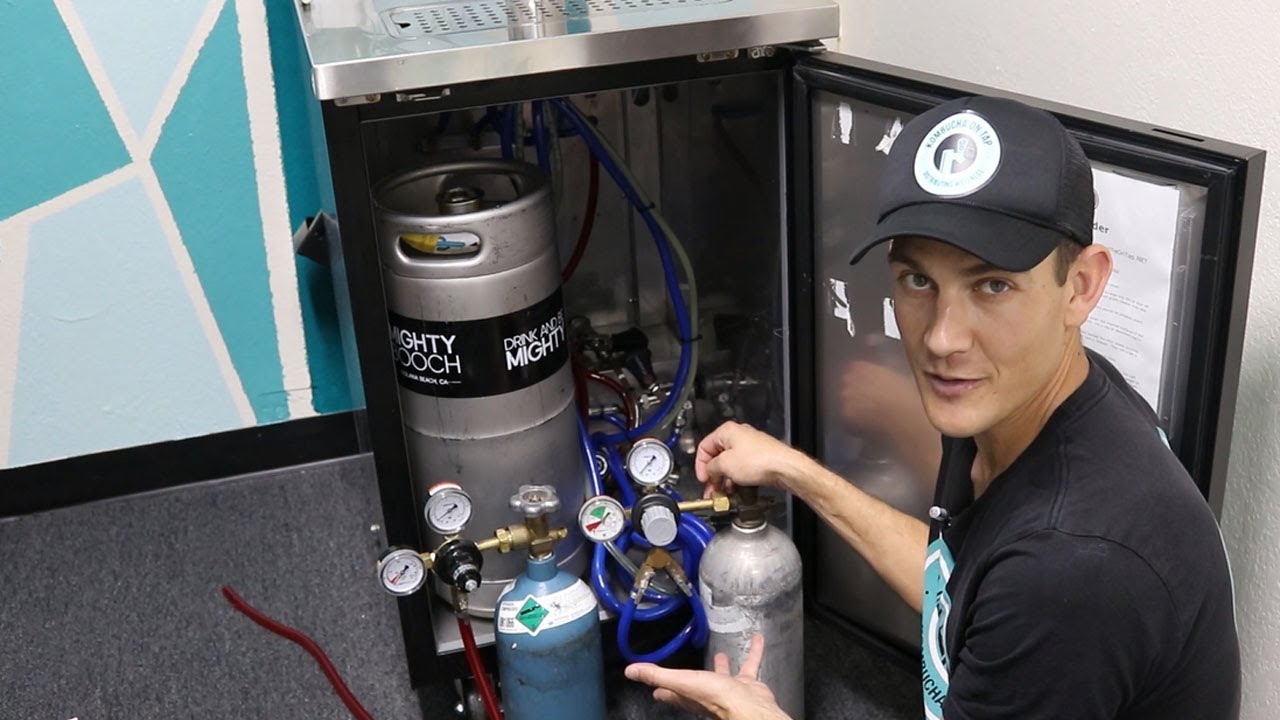
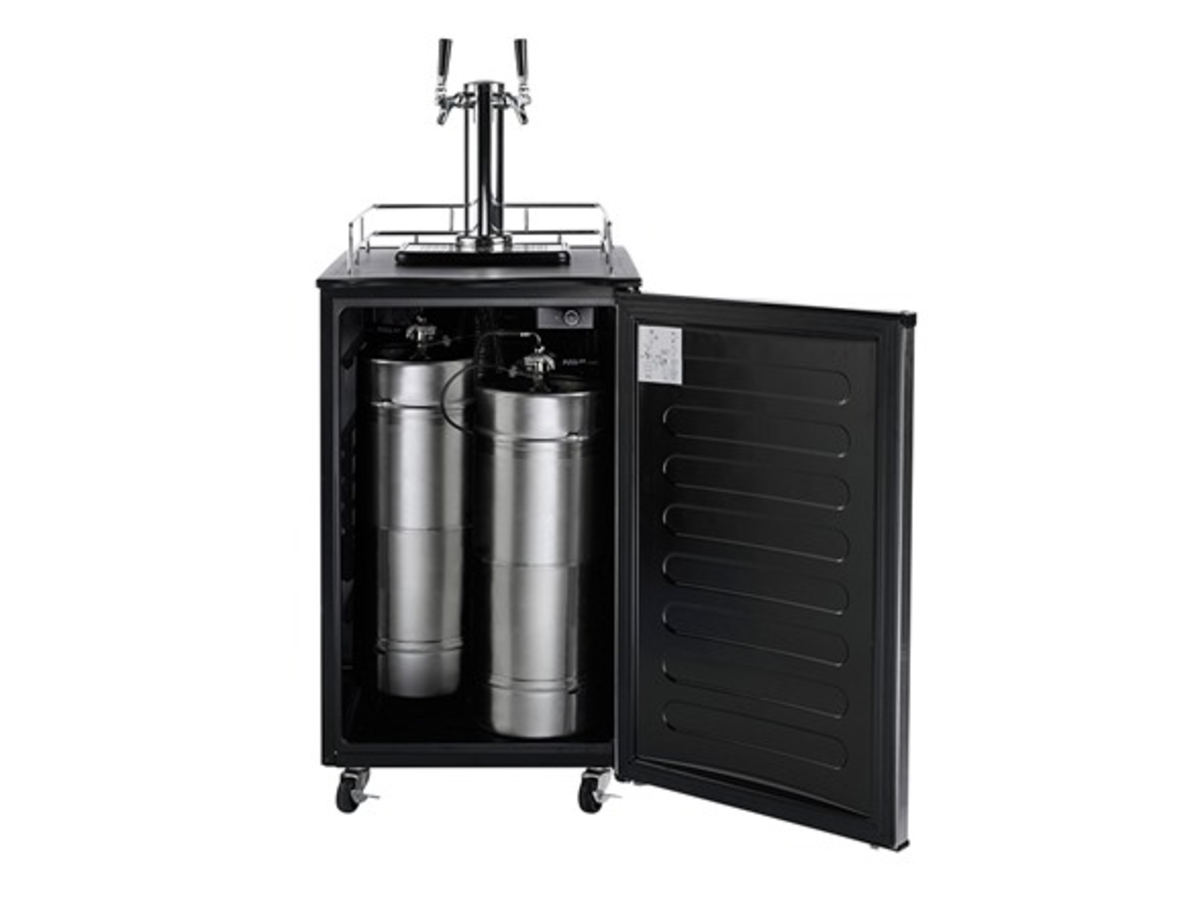
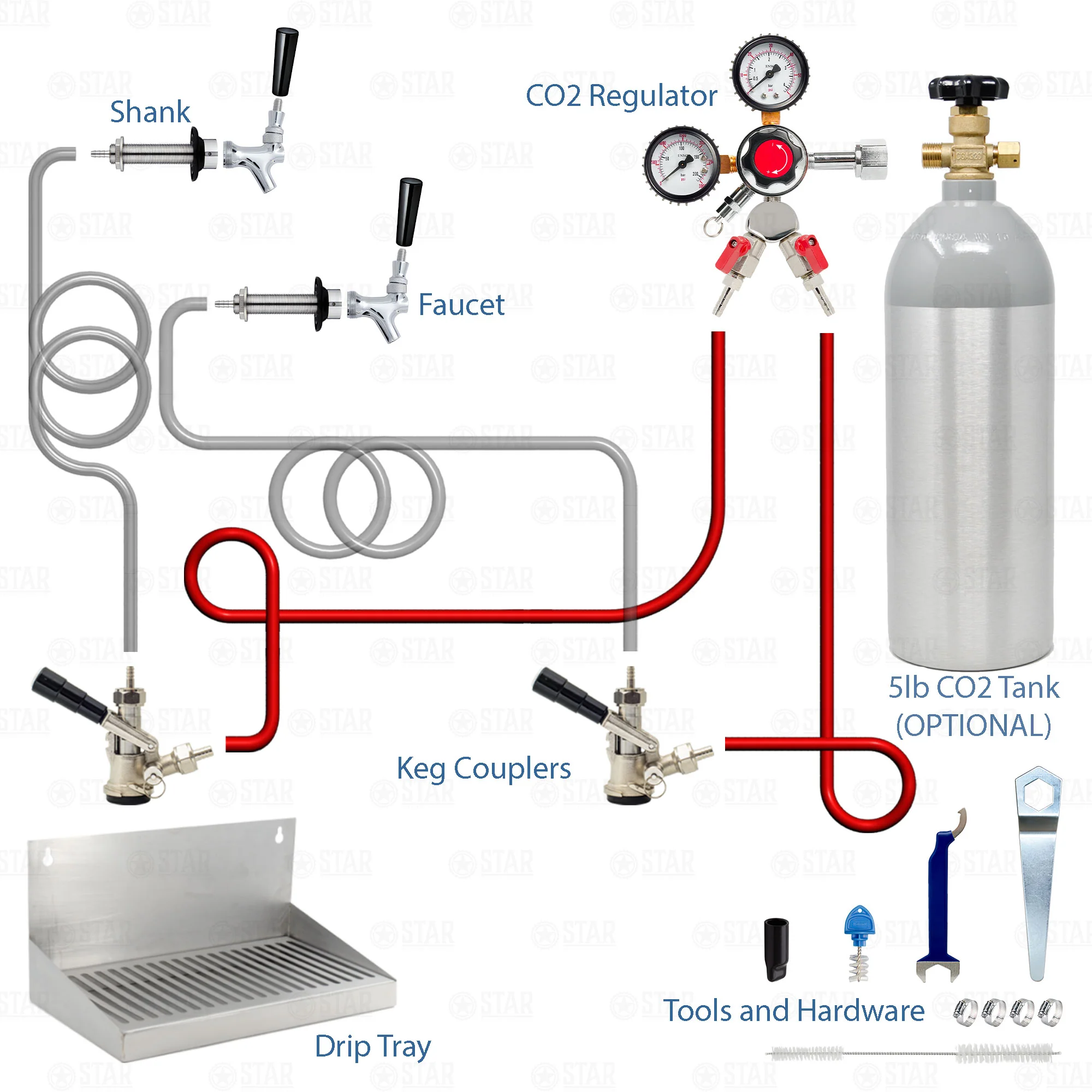
A kegerator is a specially designed refrigerator or freezer that is specifically built to store and dispense kegs of beer. It is equipped with a CO2 tank, a regulator, and a tap system to maintain the carbonation and temperature of the beer, ensuring a fresh and enjoyable drinking experience.
Kegerators come in various sizes and styles, ranging from small countertop units for home use to larger commercial-grade models used in bars, restaurants, and breweries. They are typically constructed with stainless steel or durable materials to withstand the rigors of keg storage and beer dispensing.
One of the key features of a kegerator is the ability to serve beer on tap, eliminating the need for individual bottles or cans. This not only saves money but also reduces packaging waste associated with traditional bottled or canned beer. Additionally, kegerators allow beer enthusiasts to enjoy a wide variety of beers from different breweries, as kegs offer a greater selection than pre-packaged beer options.
By having a kegerator at home, beer lovers can replicate the bar experience and entertain guests with fresh, perfectly carbonated beer. It also provides a convenient solution for beer consumers who prefer draft beer over bottled or canned varieties.
Overall, kegerators offer many benefits, including cost savings, convenience, and an environmentally friendly alternative to individual beer packaging. However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact associated with the use of kegerators, specifically the CO2 emissions involved in the process.
The Environmental Impact of CO2
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that plays a major role in climate change. When released into the atmosphere, CO2 traps heat and contributes to global warming. The excessive accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere is primarily caused by human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
In the context of kegerators, the environmental impact of CO2 is linked to the production and transportation of beer, as well as the operation of the kegerator itself. When beer is brewed, carbon dioxide is generated as a natural byproduct of the fermentation process. To ensure proper carbonation and flavor, breweries typically add additional CO2 during the brewing or kegging process.
Furthermore, the transportation of kegs from breweries to retail establishments or individuals’ homes also contributes to CO2 emissions. The energy consumed in refrigerating, storing, and dispensing beer in kegerators also adds to the overall environmental impact.
It is important to note that while CO2 emissions from beer-related activities make a relatively small contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions compared to other sectors, every effort to minimize these emissions is significant in the fight against climate change.
As awareness about the environmental impact of CO2 emissions grows, individuals and businesses are looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint, including finding ways to minimize the CO2 emissions associated with kegerators.
In the next sections, we will explore the energy consumption of kegerators and the various factors that influence CO2 emissions, as well as ways to calculate and reduce the environmental impact of kegerators.
Energy Consumption of Kegerators
Kegerators, like any other electrical appliance, consume energy during their operation. The energy consumption of a kegerator depends on various factors, including its size, insulation level, cooling mechanism, and usage patterns.
The primary energy consumption in a kegerator is attributed to maintaining the desired temperature inside the unit. The compressor, which is responsible for cooling the kegerator, consumes the most energy. It works by compressing refrigerant gases, causing them to release heat and cool down in the process. The cooled refrigerant then circulates through the system, absorbing heat from the keg and the surrounding environment.
Kegerators with better insulation and more energy-efficient compressors can help reduce energy consumption. Additionally, the frequency and duration of door openings can also impact energy usage. Keeping the kegerator door closed as much as possible helps maintain a stable temperature inside, minimizing the workload on the cooling system and reducing energy consumption.
It’s worth noting that the energy consumption of a kegerator can vary significantly depending on individual usage patterns. For example, a kegerator used in a commercial setting such as a busy bar or restaurant may consume more energy due to constant usage and frequent door openings. On the other hand, a kegerator used for occasional home use will have lower energy consumption.
To ensure energy efficiency, it is advisable to choose a kegerator with a high energy star rating. Energy star-rated appliances are designed to meet specific energy efficiency guidelines set by regulatory authorities, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings in the long run.
As consumers, being mindful of energy consumption and practicing energy-saving habits can make a significant difference in reducing the environmental impact of kegerators. Simple measures like setting the kegerator temperature to an optimal and stable level, cleaning the coils regularly, and minimizing door openings can help optimize energy efficiency.
In the next section, we will explore the various factors that affect CO2 emissions from kegerators and learn how to calculate the environmental impact of a kegerator in terms of CO2 emissions.
To reduce the CO2 usage of a kegerator, consider investing in a more energy-efficient model, insulating the kegerator to maintain temperature, and regularly checking for and repairing any leaks in the system.
Factors Affecting CO2 Emissions
Several factors influence the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with kegerators. Understanding these factors can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions to minimize their environmental impact. Let’s examine some of the key factors that affect CO2 emissions from kegerators:
1. Beer Production: The process of brewing beer produces CO2 as a byproduct of fermentation. Additionally, breweries often add additional carbonation to kegs before shipping them to retailers or consumers. The amount of CO2 released during the brewing and kegging process can vary depending on the brewing method, beer style, and the desired level of carbonation.
2. Transport: The transportation of kegs from breweries to retail establishments or individuals’ homes contributes to CO2 emissions. The distance traveled, mode of transportation, and packaging materials used can impact the carbon footprint associated with transporting kegs.
3. Energy Consumption: The energy consumption of the kegerator itself contributes to CO2 emissions. The type and efficiency of the cooling system, insulation levels, and usage patterns all influence the amount of energy consumed. Energy-efficient kegerators with better insulation and modern cooling mechanisms can help reduce CO2 emissions.
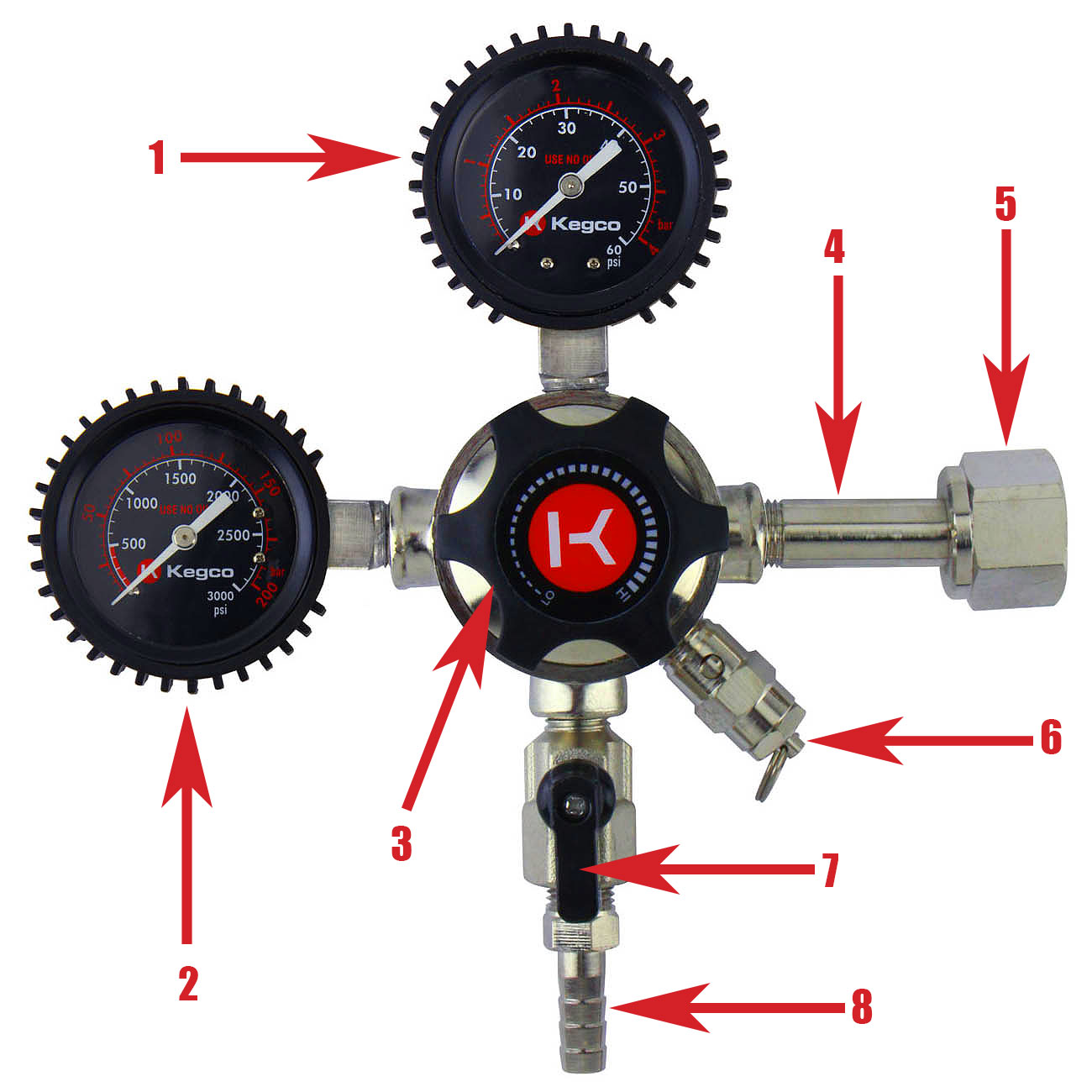
4. Carbonation: The amount of CO2 used to carbonate beer within the kegerator affects CO2 emissions. The carbonation level is controlled through the adjustment of the CO2 regulator. By calibrating the regulator to dispense the optimal level of carbonation for each beer style, excessive CO2 consumption and emissions can be minimized.
5. Usage Patterns: How often and for how long the kegerator is in use can influence CO2 emissions. Commercial establishments or individuals who frequently tap kegs and leave the kegerator running continuously will have higher CO2 emissions compared to those who use the kegerator sporadically.
6. Maintenance and Efficiency: Regular maintenance of the kegerator, including cleaning coils, checking seals, and ensuring efficient operation, can help optimize energy consumption and reduce CO2 emissions. Proper maintenance ensures that the kegerator operates at its highest efficiency, minimizing energy waste.
By considering these factors and implementing sustainable practices, individuals and businesses can take significant steps towards reducing the CO2 emissions associated with kegerators. In the next section, we will discuss how to calculate the environmental impact of a kegerator in terms of CO2 emissions.
Read more: How To Use A Kegerator Co2 Regulator
Calculating CO2 Emissions of a Kegerator
To determine the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with a kegerator, several factors need to be considered. While it may not be possible to calculate the exact emissions with absolute precision, estimating the CO2 footprint of a kegerator can provide valuable insight into its environmental impact. Here are the key steps involved in calculating CO2 emissions:
1. Beer Consumption: The first step is to determine the amount of beer consumed from the kegerator over a specific period. This can be measured by the number of kegs or the volume of beer dispensed in liters or gallons.
2. CO2 Usage: Next, you need to estimate the amount of CO2 used for carbonating the beer in the kegerator. This can be done by referring to the manufacturer’s guidelines or by consulting the supplier of the CO2 cylinders. The CO2 usage is typically measured in pounds or kilograms.
3. CO2 Emissions per Unit: Once you have the beer consumption and CO2 usage figures, you can calculate the CO2 emissions per unit of beer. Divide the amount of CO2 used by the volume of beer consumed to obtain the CO2 emissions per volume unit.
4. Energy Consumption: Consider the energy consumed by the kegerator during the same period. This can be measured using the electricity consumption (in kilowatt-hours) or by referring to the appliance’s energy rating, if available. The energy consumption is then converted to CO2 emissions using the average emission factor of the local electricity grid. This emission factor represents the amount of CO2 produced per kilowatt-hour of electricity generated in a particular region.
5. Transportation: If the kegs are transported from a brewery to the kegerator’s location, estimate the distance traveled and mode of transportation (e.g., truck, plane). Use emission factors specific to each transportation mode to calculate the CO2 emissions associated with the keg transportation.
6. Total Calculation: Add up the CO2 emissions from beer consumption, CO2 usage, energy consumption, and transportation to obtain the total CO2 emissions of the kegerator for the specified period.
It’s important to note that these calculations provide an estimate of the CO2 emissions and may not account for all variables and factors involved. However, they serve as a useful starting point for understanding and comparing the environmental impact of different kegerators or optimizing the usage of an existing kegerator to reduce its carbon footprint.
In the next section, we will explore strategies and practices to minimize CO2 emissions and reduce the environmental impact of kegerators.
Reducing CO2 Emissions from Kegerators
Reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from kegerators can have a positive impact on the environment and help mitigate climate change. Here are several strategies and practices that can be implemented to minimize the CO2 footprint of kegerators:
1. Optimize Energy Efficiency: Choose an energy-efficient kegerator with a high energy star rating. Look for models with good insulation, modern cooling mechanisms, and efficient compressors. Properly maintain the kegerator by cleaning coils regularly, ensuring good door seals, and setting the temperature at an optimal level to minimize energy consumption.
2. Use Renewable Energy: Consider powering the kegerator with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. This helps reduce the CO2 emissions associated with the electricity consumption of the kegerator. Installing solar panels or opting for renewable energy providers can be effective ways to achieve this.
3. Reduce Carbonation Levels: Adjust the CO2 regulator to dispense the minimum amount of carbonation required for each beer style. Avoid over-carbonation, as this can result in excess CO2 usage and emissions. Finding the right balance between maintaining the desired carbonation level and minimizing CO2 usage is crucial.
4. Opt for Local Breweries: Whenever possible, choose kegs from local breweries. This helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting kegs over long distances. Local breweries often have shorter supply chains, which can result in lower CO2 emissions during transportation.
5. Practice Responsible Drinking: Avoid wastage by ensuring that the kegerator is not left running unnecessarily. Turn off the kegerator when not in use or during periods of low demand. Additionally, practice responsible drinking to reduce overall beer consumption, thus minimizing the environmental impact associated with kegerator use.
6. Recycle and Reuse: Properly recycle keg shells, cylinders, and other materials used in the kegerator setup. Explore opportunities for reusing kegs instead of disposing of them, as this reduces waste and the need for new keg production, which can be resource-intensive and contribute to CO2 emissions.
7. Educate and Raise Awareness: Promote awareness among kegerator owners, businesses, and beer enthusiasts about the environmental impact of CO2 emissions and the importance of reducing carbon footprints. Encourage sustainable practices and highlight the benefits of energy efficiency and environmentally conscious choices.
By implementing these strategies and adopting environmentally friendly practices, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the CO2 emissions associated with kegerators. Remember, even small steps towards sustainability can make a meaningful impact in the fight against climate change.
Let’s conclude this article with a recap of the key points discussed.
Conclusion
Kegerators provide a convenient and enjoyable way to store and dispense draft beer. However, it’s important to be aware of their environmental impact, particularly in terms of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Understanding the factors contributing to CO2 emissions and taking steps to reduce them is crucial for minimizing our carbon footprint and mitigating climate change.
In this article, we explored the energy consumption of kegerators and how it contributes to CO2 emissions. We discussed the factors influencing CO2 emissions, including beer production, transportation, energy consumption, carbonation levels, usage patterns, and maintenance efficiency. By considering these factors, we can make informed decisions to reduce the environmental impact of kegerators.
We also learned about calculating the CO2 emissions of a kegerator by taking into account beer consumption, CO2 usage, energy consumption, and transportation. While these calculations provide estimates, they serve as valuable tools for understanding the environmental impact of kegerators and comparing their sustainability.
To minimize CO2 emissions from kegerators, we looked at various strategies and practices. These include optimizing energy efficiency, using renewable energy sources, reducing carbonation levels, supporting local breweries, practicing responsible drinking and waste management, and promoting education and awareness about sustainable practices.
By implementing these measures, we can reduce the carbon footprint of kegerators and contribute to a more sustainable future. Every effort counts in the fight against climate change, and making conscious choices regarding our kegerator use is one way to make a positive difference.
It’s important for individuals, businesses, and the brewing industry as a whole to prioritize environmental stewardship and embrace sustainability in all aspects of kegerator operations. By doing so, we can enjoy the convenience of kegerators while minimizing their impact on the environment.
Let’s strive to make greener choices and raise awareness about the importance of reducing CO2 emissions from kegerators. Together, we can create a more sustainable and thriving planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Much Co2 Does A Kegerator Use
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Much Co2 Does A Kegerator Use”