Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How Hard Is 3D Modeling

Architecture & Design
How Hard Is 3D Modeling
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the challenges of 3D modeling in architecture design and explore how difficult it can be to master this complex skill.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
3D modeling is a fundamental aspect of modern architecture and design. It allows architects, designers, and engineers to create detailed and realistic virtual representations of physical objects or spaces. With the advancement of technology, 3D modeling has become an indispensable tool in various industries, including architecture, manufacturing, entertainment, and gaming.
Whether it’s creating a stunning architectural visualization, designing a product prototype, or developing lifelike characters for movies and video games, 3D modeling brings ideas to life in a visually captivating manner. But have you ever wondered how hard it is to master the art of 3D modeling? In this article, we will explore the intricacies of 3D modeling, the challenges faced by professionals in the field, and the skills required to excel in this creative discipline.
Key Takeaways:
- Mastering 3D modeling requires a blend of technical expertise and artistic vision, enabling professionals to bring virtual creations to life with stunning realism and captivating detail.
- From architectural visualization to medical applications, 3D modeling revolutionizes industries, enhancing communication, streamlining design processes, and pushing the boundaries of creativity in countless real-world applications.
Read more: What Is 3D Modeling?
What is 3D modeling?
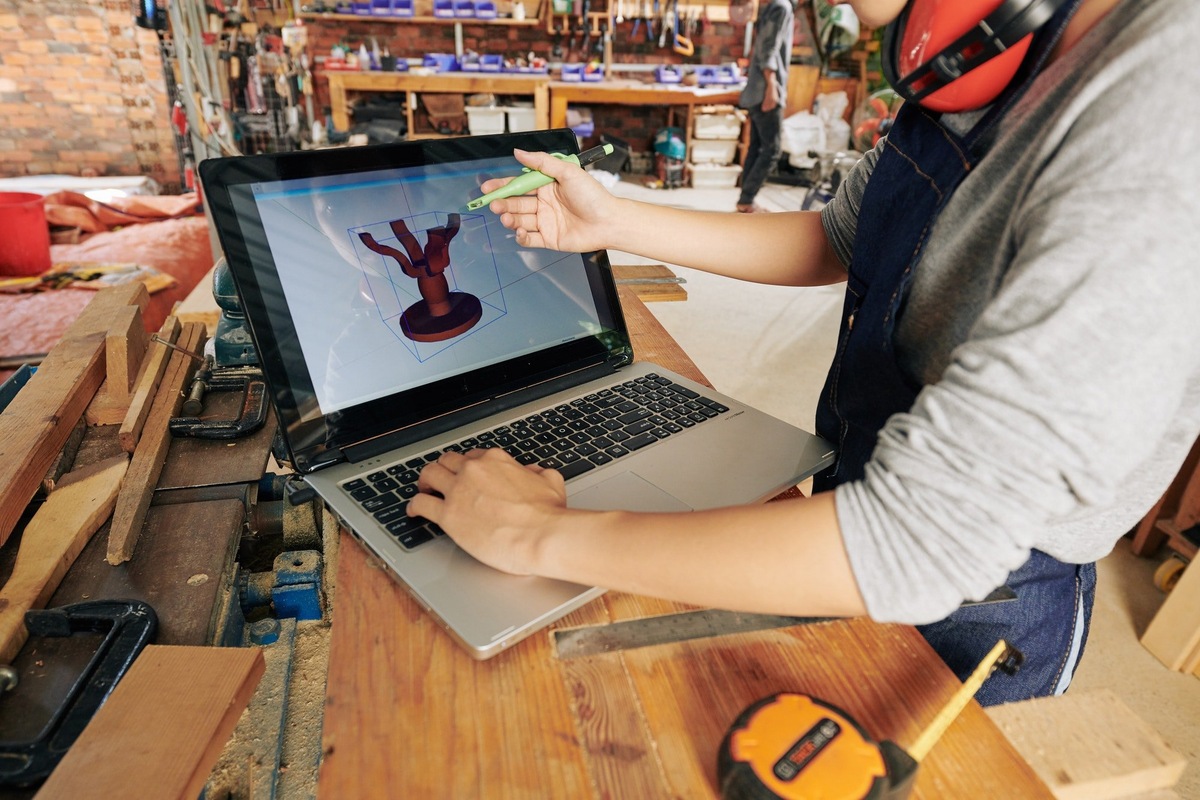
3D modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects, scenes, or characters using specialized software. Unlike traditional 2D drawing techniques, 3D modeling allows designers to create virtual models that can be manipulated, viewed from different angles, and even animated.
Using 3D modeling software, designers can build objects by shaping individual elements such as vertices, edges, and faces. These elements are combined to create complex geometries, which can be further refined with textures, colors, and materials. The end result is a lifelike representation that closely resembles the real world.
There are two primary methods of 3D modeling: procedural modeling and sculpting. Procedural modeling involves creating objects using mathematical algorithms and predefined rules. This method is often used in architectural design and industrial modeling, where precision and accuracy are essential. Sculpting, on the other hand, is a more organic approach that mimics the physical act of sculpting clay or carving materials. It allows artists to manipulate digital objects freely, adding details and refining shapes in a more artistic and intuitive way.
3D modeling is not limited to inanimate objects – it also plays a crucial role in character animation for films, video games, and virtual reality experiences. Using skeletal rigs and animation controls, artists can bring digital characters to life by manipulating their movements, expressions, and interactions with the virtual environment.
In summary, 3D modeling is a versatile and powerful technique that enables the creation of intricate virtual models, ranging from architectural designs to animated characters. It revolutionizes the way we visualize, design, and communicate ideas in various industries, making it an essential skill for professionals in the fields of architecture, design, animation, and gaming.
The importance of 3D modeling in various industries
3D modeling has become increasingly important in a wide range of industries due to its ability to enhance visualization, streamline design processes, and improve communication. Let’s explore some of the key industries where 3D modeling plays a crucial role:
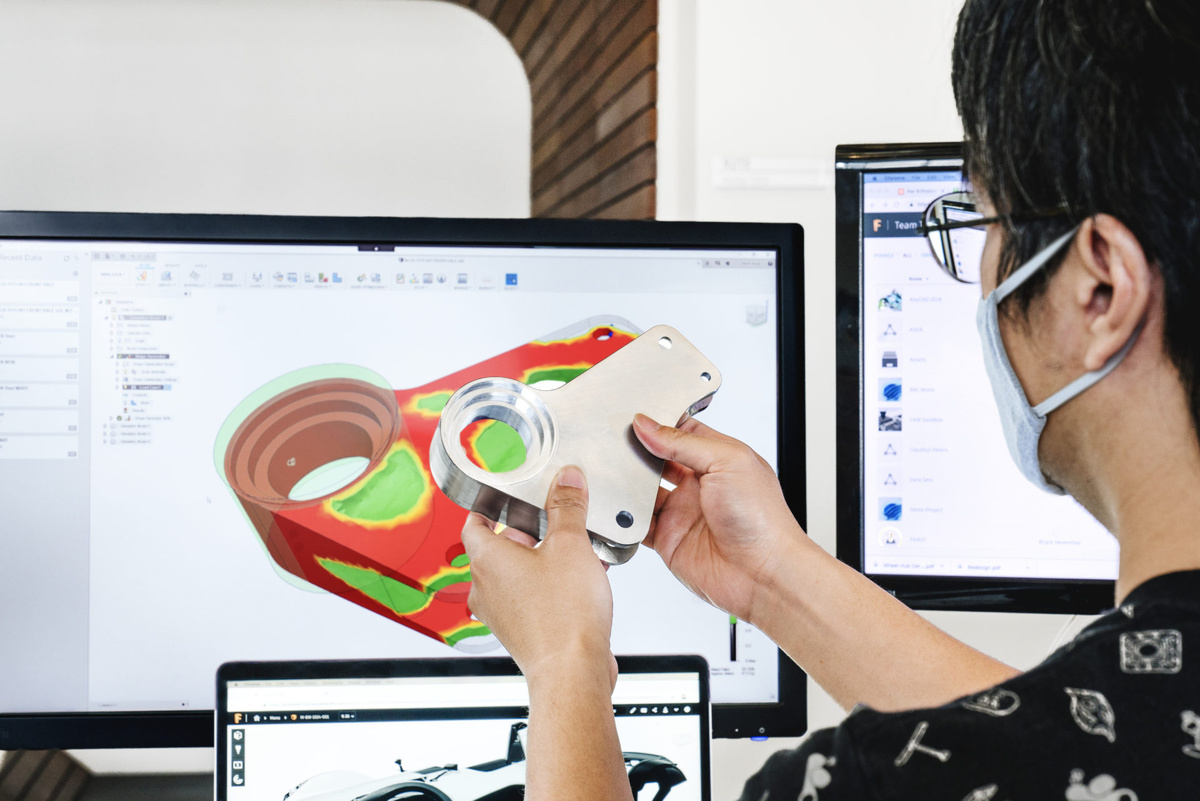
- Architecture and Construction: 3D modeling allows architects and designers to create detailed virtual models of buildings and structures. This enables them to visualize the final project, assess its aesthetic appeal, and identify any design flaws or conflicts before construction begins. It also aids in communication with clients, contractors, and other stakeholders by providing a realistic representation of the proposed design.
- Manufacturing and Product Design: 3D modeling plays a vital role in the manufacturing industry by facilitating the design and development of products. With 3D models, designers can test and iterate their designs, evaluate their functionality, and optimize manufacturing processes. It also enables the creation of photorealistic product renderings for marketing and advertising purposes.
- Entertainment and Media: 3D modeling is widely used in the entertainment industry, including films, television shows, and video games. It allows artists to create realistic and visually stunning environments, characters, and special effects. Furthermore, 3D models can be animated and rigged for lifelike movements and interactions, bringing stories and concepts to life in a captivating way.
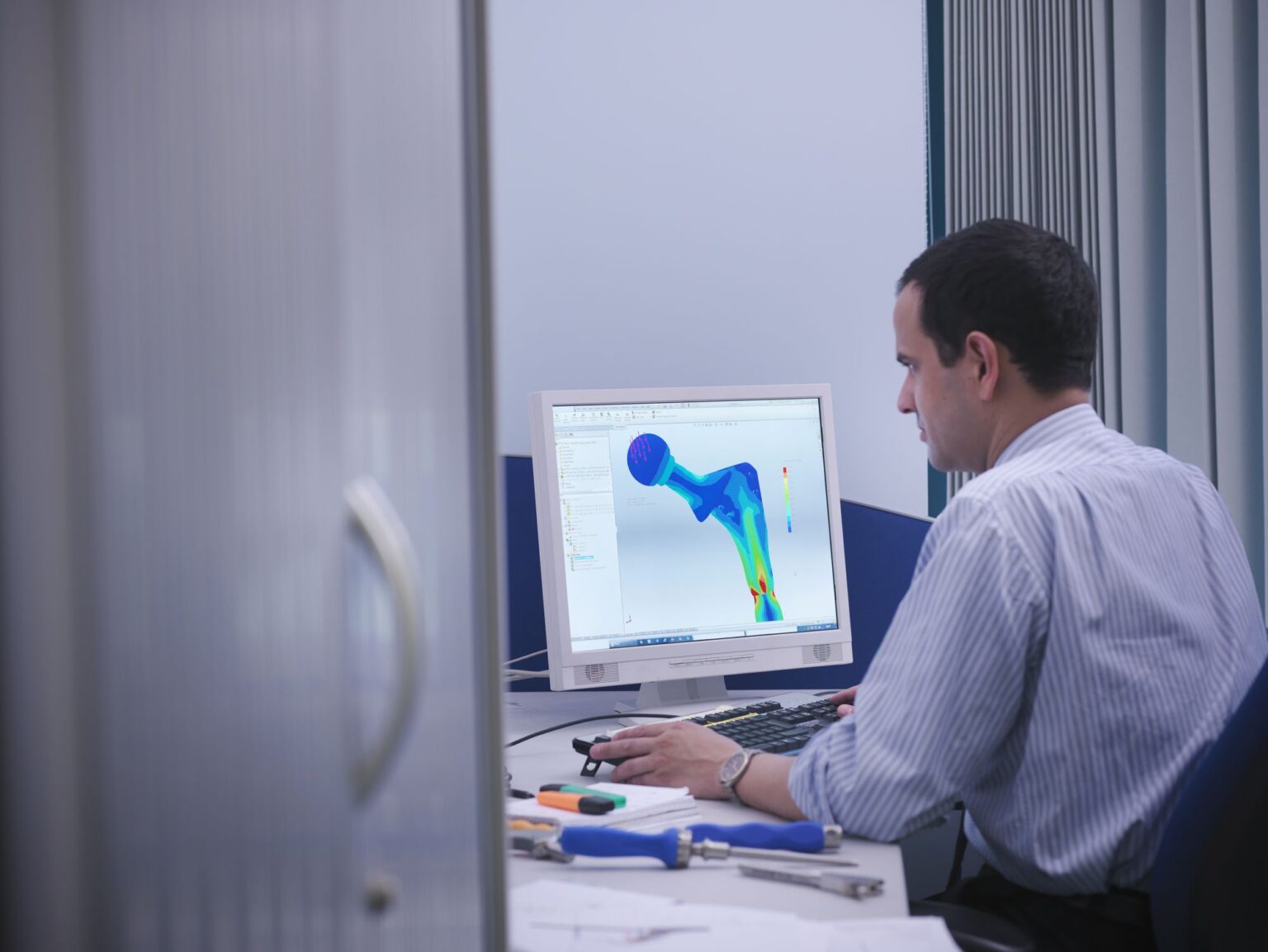
- Medical and Healthcare: 3D modeling has revolutionized the medical field by enabling the creation of detailed patient-specific anatomical models. These models can be used for surgical planning, medical education, and the customization of medical devices. 3D printing, in conjunction with 3D modeling, has also opened up new possibilities for creating patient-specific implants and prosthetics.
- Gaming and Virtual Reality: The gaming industry heavily relies on 3D modeling for creating immersive and realistic game worlds, characters, and assets. With the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), 3D modeling has become even more crucial for creating engaging and interactive virtual experiences.
Overall, 3D modeling is an essential tool in various industries, enabling professionals to visualize designs, improve collaboration, and enhance the overall quality of their work. Its impact spans from architecture and manufacturing to entertainment and healthcare, contributing to innovation and efficiency in countless applications.
Different types of 3D modeling techniques
3D modeling encompasses a variety of techniques, each suited for different purposes and industries. Let’s explore some of the key types of 3D modeling techniques:
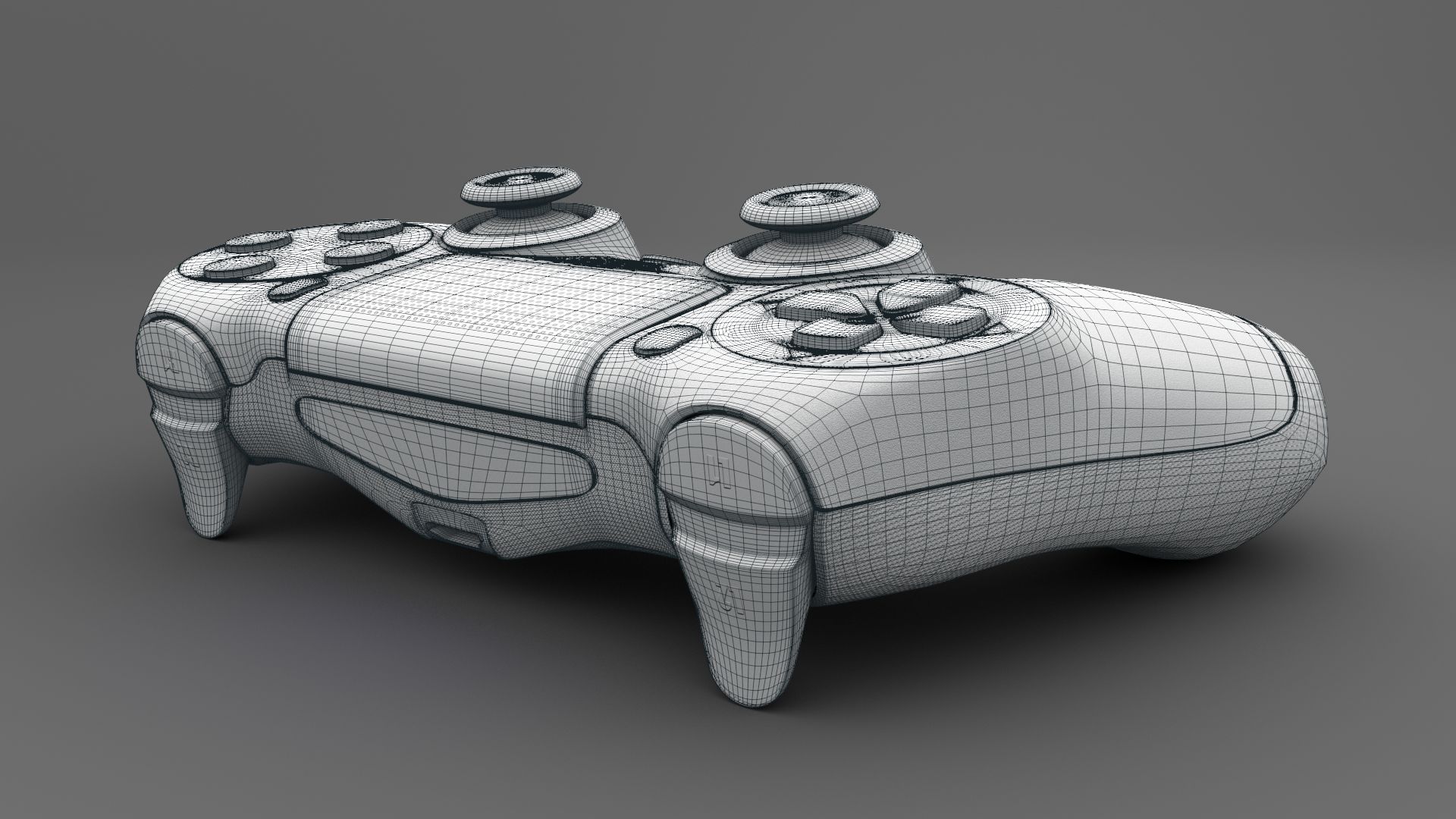
- Polygonal Modeling: This is the most common and widely-used form of 3D modeling. It involves creating objects by manipulating individual polygons (usually triangles or quadrilaterals), which are connected to form the surface of the model. Polygonal modeling allows for precise control over geometry and is commonly used in architectural design, product prototyping, and character modeling.
- NURBS Modeling: NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modeling is a mathematical approach that uses curves and surfaces to define the shape of objects. It is particularly useful for creating smooth and organic forms, such as car bodies or furniture. NURBS modeling provides greater flexibility in manipulating shapes and allows for precise control over curves and surfaces.
- Sculpting: Sculpting is a technique that mimics the physical act of sculpting. Artists use specialized software to sculpt virtual clay or other malleable materials, allowing for the creation of highly detailed and organic models. Sculpting is commonly used in character modeling, creature design, and digital sculpting for film and video games.
- Procedural Modeling: Procedural modeling involves using mathematical algorithms and predefined rules to generate complex and intricate models. This technique is often used in architectural design, where repetitive patterns, such as cityscapes or buildings with regular shapes, need to be created quickly and efficiently. Procedural modeling allows for the creation and modification of objects based on parameters and rules, offering great flexibility and automation.
- Voxel Modeling: Voxel modeling, also known as volumetric modeling, uses voxels (3D pixels) to create objects. It allows for the creation of highly detailed and precise models, especially suited for organic and complex structures. Voxel modeling is commonly used in medical imaging, scientific visualization, and digital representation of natural phenomena.
These are just a few examples of the different 3D modeling techniques available. The choice of technique depends on the desired outcome, the complexity of the object or scene being modeled, and the specific requirements of the industry or project. By mastering these techniques, artists and designers can effectively bring their creative vision to life in the digital realm.
Challenges faced in 3D modeling
While 3D modeling is an incredibly powerful and versatile technique, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Let’s explore some of the common challenges faced by professionals in the field:
- Complexity: 3D modeling involves dealing with intricate geometries and complex shapes. Creating realistic and visually appealing models requires a deep understanding of form, anatomy, and composition. It can be challenging to accurately capture every detail and ensure that the final result looks natural and convincing.
- Technical Skills: Mastering 3D modeling software requires a significant investment of time and effort. Artists and designers need to be proficient in the tools and techniques specific to the software they use. Learning about polygons, NURBS, texture mapping, lighting, and rendering are just a few of the technical skills that need to be acquired.
- Time and Patience: 3D modeling is a highly meticulous and time-consuming process. Creating intricate models with realistic details can take days, weeks, or even months. It requires patience and a willingness to iterate and refine the work until it reaches the desired level of quality.
- Hardware and Software Limitations: Working with 3D modeling software can be hardware-intensive, requiring powerful computers with sufficient RAM and processing power. Rendering complex scenes or animations can be time-consuming and may require specialized rendering software or cloud-based rendering services.
- Problem-solving: The process of 3D modeling often involves encountering and overcoming various technical and creative challenges. Artists and designers need to constantly problem-solve and find solutions to achieve the desired outcome. This requires a combination of technical expertise, creative thinking, and a willingness to explore new techniques and approaches.
Despite these challenges, the rewards of 3D modeling are immense. With dedication, practice, and a passion for the craft, professionals can overcome these hurdles and create stunning and impactful 3D models that bring their visions to life.
When starting 3D modeling, focus on learning the basic tools and techniques first before moving on to more complex tasks. Practice regularly to improve your skills and don’t be afraid to seek out tutorials and resources to help you along the way.
Required skills and knowledge for 3D modeling
Mastering the art of 3D modeling requires a combination of technical skills, artistic abilities, and industry knowledge. Here are some of the key skills and knowledge areas that are essential for success in the field:
- Understanding of Form and Composition: A solid understanding of form, anatomy, and composition is crucial for creating visually appealing and realistic 3D models. Artists and designers need to study real-world objects, observe how light interacts with different materials, and understand the principles of composition and visual storytelling.
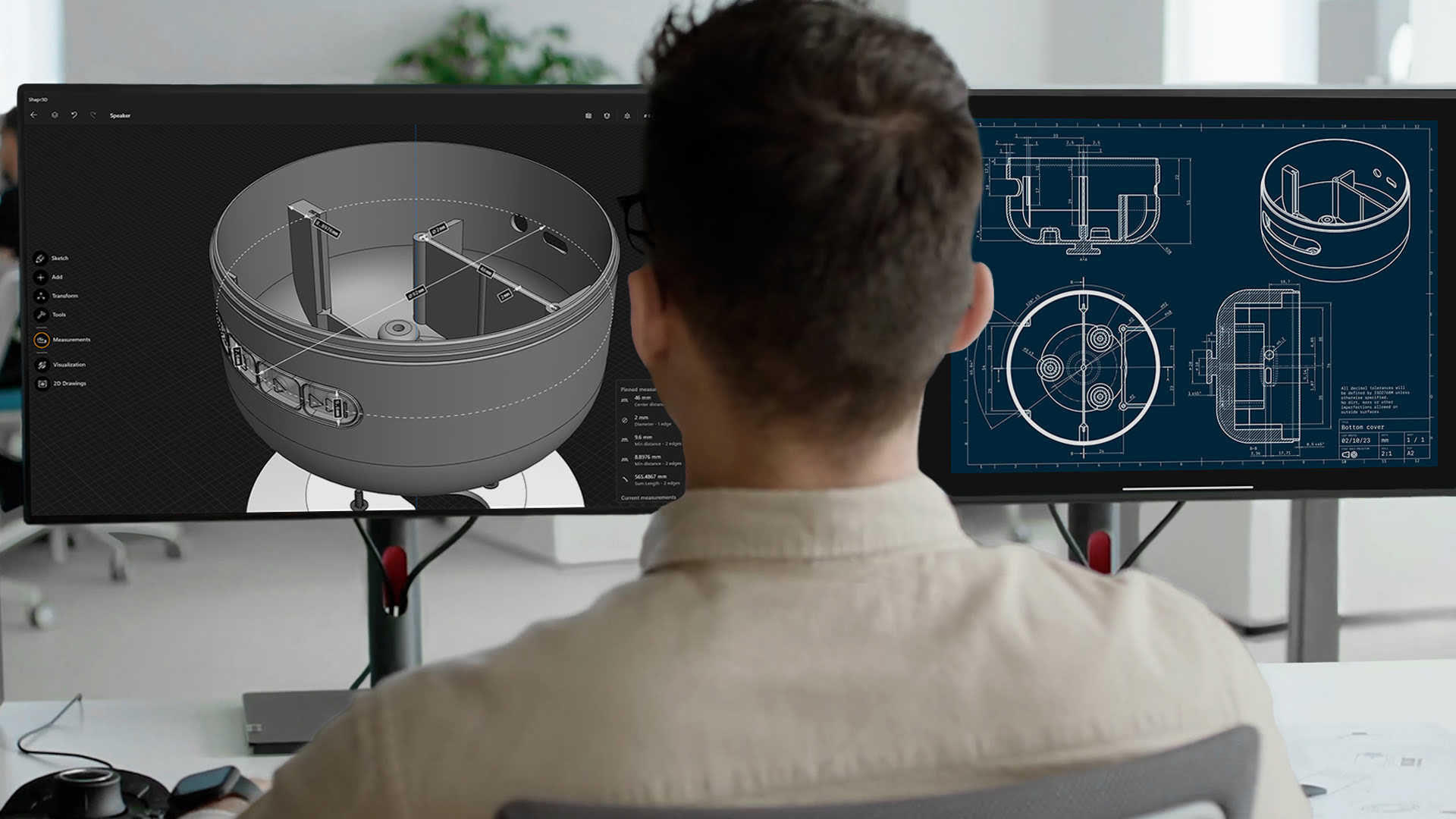
- Proficiency in 3D Modeling Software: A strong command of 3D modeling software is necessary to bring ideas to life. Artists should be proficient in popular software such as Autodesk Maya, 3ds Max, Blender, or ZBrush. Familiarity with the software’s tools, interface, and workflows will significantly enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Knowledge of Polygonal and NURBS Modeling: Understanding the fundamentals of polygonal and NURBS modeling is essential for creating accurate and detailed 3D models. Artists should be well-versed in concepts such as topology, edge flow, subdivision modeling, and surface manipulation.
- Texturing and UV Mapping: Artists need to understand the process of applying textures and materials to 3D models. This includes UV mapping, the process of unwrapping a 3D model’s surface into a 2D space, and applying textures and materials in a way that appears seamless and realistic.
- Lighting and Rendering: Knowledge of lighting principles and rendering techniques is crucial for giving 3D models a realistic appearance. Artists should understand how different lighting setups affect the mood and perception of a scene and be able to optimize render settings to achieve desirable results.
- Problem-solving and Attention to Detail: 3D modeling often involves encountering and solving technical challenges. Artists should have sharp problem-solving skills and a keen eye for detail. This includes the ability to troubleshoot issues, optimize models for performance, and fine-tune the details to achieve realism.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptability: The field of 3D modeling is constantly evolving, with new software, techniques, and trends emerging regularly. Artists and designers need to stay updated with the latest advancements, techniques, and industry standards. This requires a mindset of continuous learning, adaptability, and a willingness to explore new tools and workflows.
Developing these skills and knowledge areas requires practice, dedication, and a passion for 3D modeling. By honing these abilities, artists can bring their imagination to life and create stunning and impactful 3D models that captivate audiences.
Tools and software used for 3D modeling
In the world of 3D modeling, there is a wide range of tools and software available to help artists and designers bring their creative visions to life. These tools offer a variety of features and functionalities that cater to different needs and skill levels. Let’s explore some popular software used for 3D modeling:
- Autodesk Maya: Autodesk Maya is one of the most widely used and powerful 3D modeling software in the industry. It offers a comprehensive range of tools for modeling, animation, simulation, and rendering. Maya is favored by professionals in film, television, and game development industries for its versatility and extensive feature set.
- Blender: Blender is an open-source 3D modeling software that is free to use. It has a robust set of features and is suitable for both beginners and experienced artists. Blender offers many modeling tools, including polygonal modeling, sculpting, and advanced UV mapping capabilities. It is well-regarded for its active community and regular updates.
- Autodesk 3ds Max: 3ds Max is another popular 3D modeling and rendering software from Autodesk. It is widely used in architectural visualization, game development, and product design. 3ds Max offers a wide range of modeling tools and advanced features, such as particle systems and cloth simulation, making it a comprehensive solution for 3D modeling and visualization.
- ZBrush: ZBrush is renowned for its digital sculpting capabilities. It allows artists to sculpt highly detailed and organic models with unparalleled precision. ZBrush’s unique sculpting brushes and intuitive interface make it a preferred choice for character artists, creature designers, and digital sculptors.
- Cinema 4D: Cinema 4D is a popular choice among motion graphics artists and visual effects professionals. It offers a wide range of modeling, animation, and rendering tools and is known for its ease of use and intuitive workflow. Cinema 4D is widely used in industries such as advertising, broadcast, and architecture.
These are just a few examples of the tools and software available for 3D modeling. Other notable mentions include Houdini, Modo, Substance Designer, and SketchUp. The choice of software often depends on the specific needs of the artist, the industry requirements, and personal preferences.
In addition to these software packages, 3D modeling often involves the use of supporting tools such as digital sculpting tablets, 3D scanners, and render farms for efficient processing of complex scenes and animations.
It is worth noting that regardless of the software used, the key to becoming proficient in 3D modeling lies in practicing regularly, experimenting with different techniques, and constantly learning and refining your skills.
Examples of 3D modeling in real-world applications
3D modeling has revolutionized various industries by providing a powerful tool for visualizing ideas and creating realistic virtual representations. Let’s explore some examples of how 3D modeling is applied in real-world applications:
- Architectural Visualization: 3D modeling is extensively used in architecture to create visually stunning and accurate representations of buildings and structures. Architects can use 3D models to showcase their designs to clients, allowing them to immerse themselves in the proposed spaces and make more informed decisions before construction begins.
- Product Design and Prototyping: 3D modeling is a vital part of product design and prototyping. Designers can create detailed virtual models of products, iterate on designs, and even simulate their functionality before physical prototypes are produced. This enables faster and more efficient product development cycles.
- Entertainment and Media: The entertainment industry heavily relies on 3D modeling for creating visually striking and awe-inspiring experiences. From movie special effects and animated characters to video game environments and virtual reality worlds, 3D modeling brings imagination to life and enhances storytelling.
- Medical Visualization: In the medical field, 3D modeling plays a crucial role in visualizing complex structures, such as organs, bones, and tumors, for diagnostic and educational purposes. Surgeons can use 3D models to plan and simulate surgeries, improving accuracy and patient outcomes.
- Engineering and Manufacturing: 3D modeling is used in engineering and manufacturing industries for creating precise and detailed models of mechanical parts, machinery, and industrial equipment. It aids in product development, assembly line optimization, and quality control.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: The rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences relies heavily on 3D modeling. 3D models serve as the foundation for creating immersive virtual environments and digital overlays in the real world.
These examples represent just a fraction of the many applications of 3D modeling in various industries. The versatility and potential of 3D modeling are vast, and its impact continues to expand as technology advances.
Overall, 3D modeling enables professionals to visualize concepts, communicate ideas effectively, streamline design processes, and push the boundaries of creativity in numerous fields.
Conclusion
3D modeling is a powerful and transformative technology that has revolutionized industries ranging from architecture to entertainment. It allows professionals to create detailed and realistic virtual representations of objects, spaces, and characters, bringing ideas to life in a visually captivating manner.
While mastering 3D modeling can be challenging and requires a combination of technical skills and artistic abilities, the rewards are immense. By honing their skills in software such as Autodesk Maya, Blender, or ZBrush, artists and designers can create stunning and impactful 3D models that captivate audiences and enhance the communication of ideas.
From architectural visualization and product design to entertainment and healthcare, 3D modeling plays a crucial role in various industries. It enables professionals to visualize designs, streamline workflows, and improve collaboration with clients and stakeholders.
Moreover, the continual advancement of technology, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, further expands the possibilities of 3D modeling, allowing for immersive and interactive experiences that were once unimaginable.
In conclusion, the art of 3D modeling is a complex and dynamic field that offers endless opportunities for creativity and innovation. By embracing the required skills, leveraging the right tools and software, and staying updated with the latest trends, professionals in 3D modeling can continue pushing the boundaries of what is possible and revolutionize industries across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Hard Is 3D Modeling
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Hard Is 3D Modeling”