Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is 3D Modeling?

Architecture & Design
What Is 3D Modeling?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the world of 3D modeling in architecture and design. From concept development to final renderings, learn how this technology revolutionizes the way structures are visualized and created.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
3D modeling is an integral part of today’s digital world, revolutionizing various industries and enhancing the way we visualize and interact with objects and environments. It is a powerful technique that enables the creation of three-dimensional virtual representations of real-world objects, spaces, or characters.
With the advancement of technology and the wide availability of 3D modeling software, this technique has become more accessible and widely used across numerous fields. From architecture and product design to gaming and filmmaking, 3D modeling has transformed the way we conceptualize, design, and communicate our ideas.
In this article, we will explore the world of 3D modeling, diving into its definition, applications, process, techniques, advantages, limitations, and popular software. So let’s embark on a journey into the fascinating realm of 3D modeling and discover its immense potential.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D modeling revolutionizes industries by creating immersive virtual representations, enhancing communication, and enabling better decision-making across architecture, product design, gaming, engineering, healthcare, and entertainment.
- While 3D modeling offers visual realism, improved communication, and design iteration, it also presents challenges such as a learning curve, hardware requirements, time intensity, and limitations in physical accuracy.
Definition of 3D Modeling
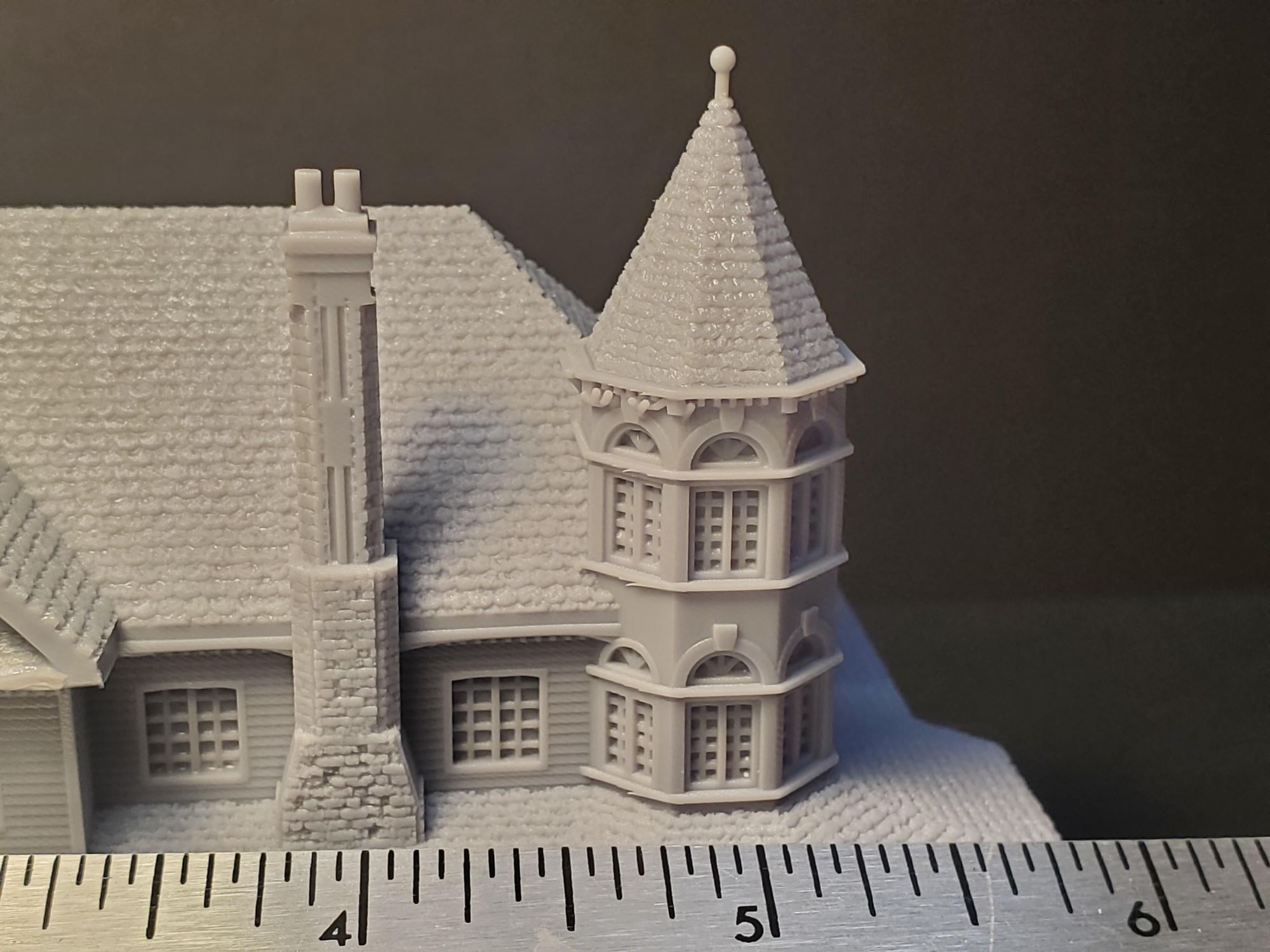
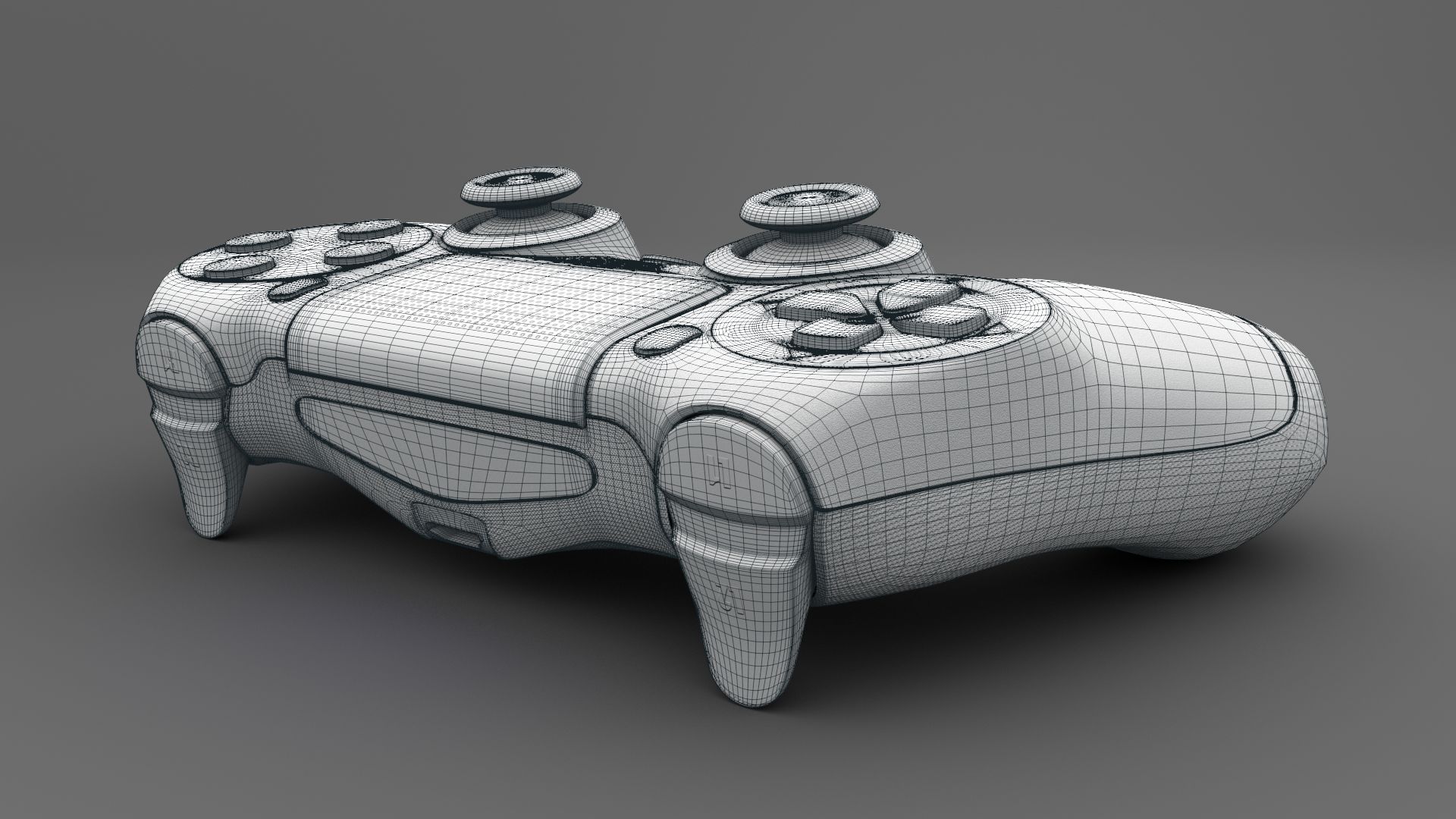
3D modeling is the process of creating a virtual representation of a three-dimensional object or environment using specialized software. It involves using geometric data to define the shape, texture, color, and other visual aspects of the object. The result is a digital model that can be manipulated, viewed from different angles, and used in various applications.
One of the key features of 3D modeling is its ability to create realistic and lifelike representations. By incorporating detailed textures, lighting effects, and accurate proportions, 3D models can closely mimic real-world objects or environments, providing a highly immersive and interactive experience.
3D models are typically created using a combination of geometric primitives such as cubes, spheres, and cylinders, which are then manipulated and transformed using various tools and techniques. These models can range from simple objects to complex structures, characters, or even entire virtual worlds.
The process of 3D modeling involves several steps, including conceptualization, designing, sculpting, texturing, and rendering. It requires a blend of technical skills, artistic creativity, and attention to detail to produce high-quality and visually appealing models.
3D modeling finds applications in a wide range of industries. In architecture and product design, it is used to create realistic representations of buildings, interiors, and products before they are constructed. In the gaming and animation industry, 3D models serve as the foundation for creating virtual characters, environments, and special effects. Even in fields such as medicine and engineering, 3D models play a crucial role in visualizing complex structures and systems.
With the rapid advancements in technology, 3D modeling has evolved beyond static representations. With the introduction of virtual reality and augmented reality, 3D models can now be experienced in an immersive and interactive manner, allowing users to explore virtual environments in real-time.
In summary, 3D modeling is the art and science of creating virtual representations of objects and environments. It combines technical expertise with artistic creativity to produce visually stunning and interactive models that have transformed various industries and opened up new possibilities for design, visualization, and communication.
Applications of 3D Modeling
The applications of 3D modeling are vast and span across multiple industries. Its versatility and ability to create realistic representations have made it an indispensable tool for various fields. Let’s explore some of the prominent applications of 3D modeling:
- Architecture and Interior Design: 3D modeling plays a crucial role in the architectural and interior design industries. It allows designers and architects to create detailed virtual representations of buildings, landscapes, and interiors, helping clients visualize the final product before construction begins. This enables better communication, improved design accuracy, and the ability to make informed decisions.
- Product Design and Manufacturing: 3D modeling is widely used in product design and manufacturing processes. It enables designers to create 3D prototypes, test functionality, and simulate real-world scenarios. This helps streamline the design process, reduce costs, and minimize errors before physical production begins.
- Gaming and Entertainment: 3D modeling forms the foundation of the gaming and entertainment industries. Game developers use 3D models to create lifelike characters, virtual environments, and special effects. Additionally, the film and animation industries rely heavily on 3D modeling for creating realistic and immersive visual experiences.
- Engineering and Manufacturing: In engineering and manufacturing, 3D modeling is pivotal for designing and prototyping. It allows engineers to create detailed models of mechanical components and structures, perform simulations, and analyze performance. This leads to better design optimization, improved manufacturing processes, and reduced development costs.
- Medical and Healthcare: 3D modeling has revolutionized the medical and healthcare fields. It enables the creation of anatomically accurate models for surgical planning, medical education, and implant design. Surgeons can use 3D models to practice complex procedures and improve patient outcomes.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: With the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), 3D modeling has become essential for creating immersive and interactive experiences. It allows users to explore virtual worlds, interact with virtual objects, and enhance real-world environments with digital overlays.
These are just a few examples of the numerous applications of 3D modeling. From advertising and marketing to archaeology and education, 3D modeling has found its way into almost every aspect of our modern lives. Its ability to visualize ideas and concepts in a realistic and interactive manner has transformed industries and opened up new realms of possibilities.
Process of 3D Modeling
The process of 3D modeling involves several steps that artists and designers follow to create detailed and realistic virtual representations. While each artist may have their own unique approach, the general process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Conceptualization: The first step in 3D modeling is conceptualization. This involves brainstorming and developing an idea or concept for the model. Artists may sketch rough drawings or create mood boards to visualize their thoughts and gather references for the design elements.
- Modeling: Once the concept is established, the actual modeling process begins. Artists use specialized 3D modeling software to craft the digital mesh that defines the shape and structure of the object. This is done by creating and manipulating geometric primitives and polygons to form the basic shape.
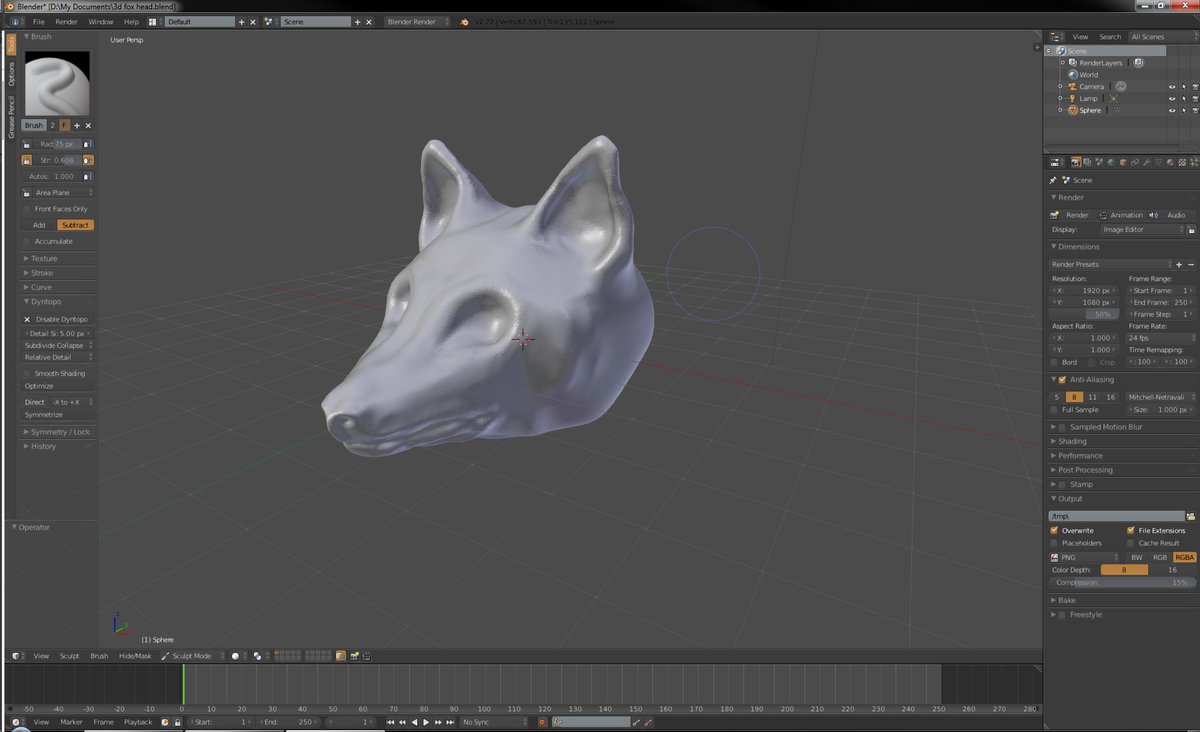
- Sculpting: After the basic structure is created, artists can refine and sculpt the 3D model to add more details and organic shapes. This can be done by using sculpting tools that simulate traditional sculpting techniques such as pushing, pulling, smoothing, and carving. This step helps add realism and intricate details to the model.
- Texturing: Texturing involves applying and mapping 2D images, called textures, onto the surfaces of the 3D model. This helps add color, patterns, and realistic materials to the model. Artists can either create their own textures or use pre-existing ones to achieve the desired look and feel.
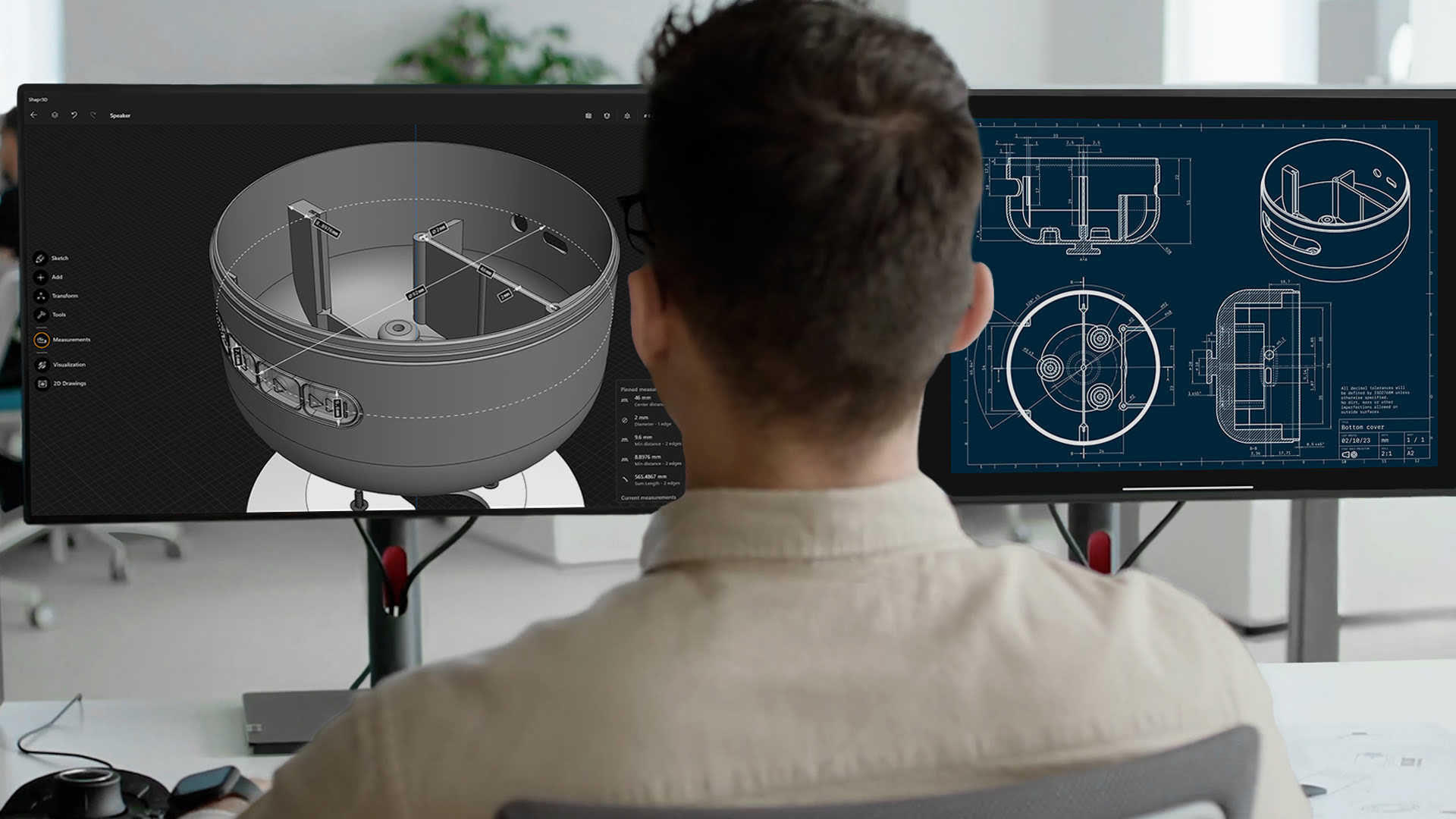
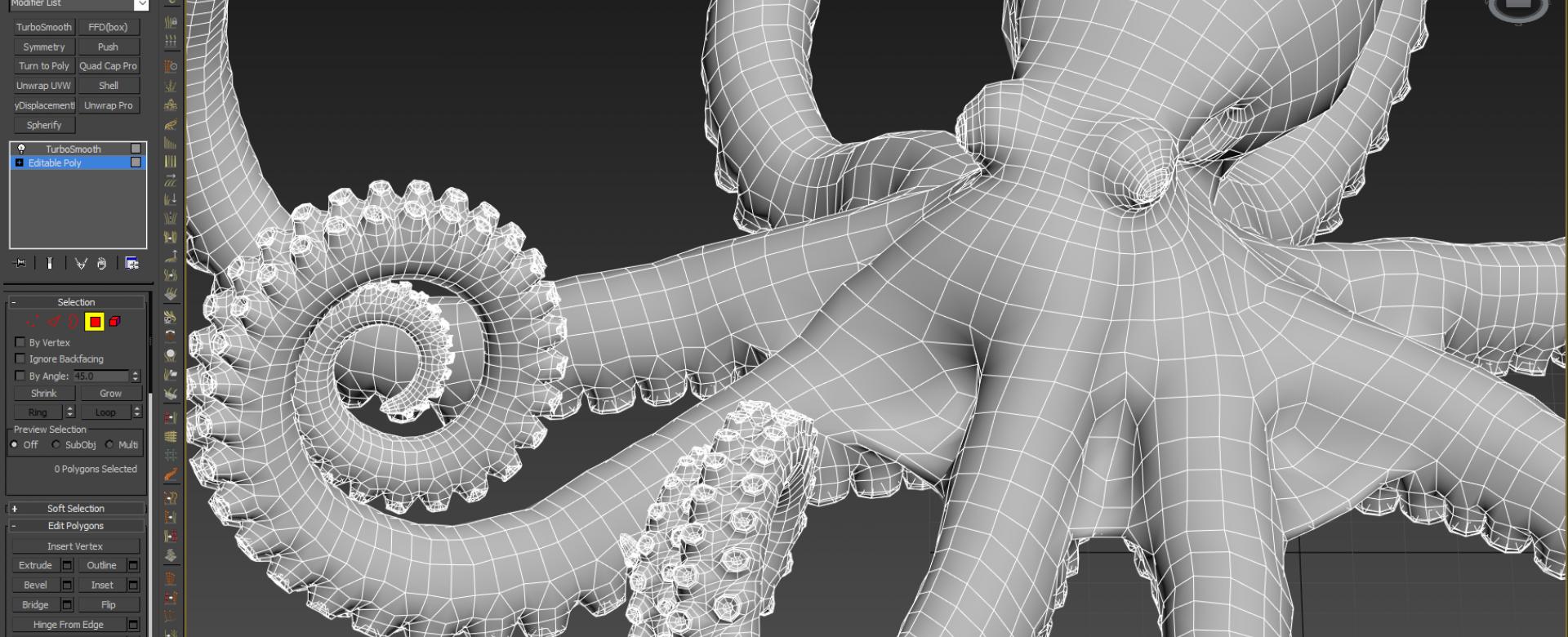
- UV Mapping: UV mapping is the process of unwrapping the 3D model’s surface and creating 2D flat representations, known as UV maps. This allows artists to paint textures and apply images accurately onto the model’s surface. UV mapping ensures the textures appear correctly and consistently across the model.
- Lighting and Rendering: Lighting plays a crucial role in creating realistic and visually appealing 3D models. Artists set up virtual lights within the software to simulate different lighting conditions. They can also adjust the intensity, color, and shadows to enhance the overall appearance of the model. Once the lighting is set, the model is rendered, which is the process of converting the 3D model into a final, 2D image or animation.
- Post-Processing: After rendering, the final image or animation may undergo post-processing to enhance its quality. This can include adjusting the colors, contrast, and adding special effects or filters. Post-processing helps achieve the desired final look and polish the model for presentation or integration into other projects.
While this is a general overview of the 3D modeling process, it’s important to note that the complexity and specific steps can vary depending on the software, purpose, and complexity of the project. With practice and experience, artists can refine their process and develop their own techniques to create stunning 3D models.
Types of 3D Modeling Techniques
3D modeling techniques can vary depending on the desired outcome, the complexity of the object, and the artist’s preferred approach. Here are some of the commonly used 3D modeling techniques:
- Polygonal Modeling: Polygonal modeling is one of the most widely used techniques in 3D modeling. It involves creating a 3D model by connecting various polygons, primarily triangles or quads, to form the object’s shape. Artists manipulate individual vertices, edges, and faces to define the geometry and structure of the model. This technique allows for precise control over the shape and enables artists to create detailed models efficiently.
- NURBS Modeling: NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline) modeling is based on mathematical representations of curves and surfaces. It allows for the creation of smooth and organic shapes by manipulating control points and curves. Unlike polygonal modeling, NURBS modeling uses mathematical calculations to define the model’s shape, resulting in more accurate curves and surfaces. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive design and industrial product design.
- Subdivision Surface Modeling: Subdivision surface modeling, also known as Sub-D modeling, starts with a simple base mesh and iteratively subdivides it to create a more detailed and smooth surface. Artists refine the model by adding more subdivisions and adjusting the control points to achieve the desired level of detail. Sub-D modeling is often used in character modeling and organic objects, as it allows for smooth contours and fine details.
- Sculpting: Sculpting is a technique that simulates traditional sculpting in a digital environment. Artists use sculpting tools to manipulate the digital model as if they were molding clay in real life. This technique is particularly useful for creating intricate details, organic shapes, and character modeling. Sculpting software provides various brushes, textures, and pressure-sensitive controls to mimic the tactile experience of traditional sculpting.
- Procedural Modeling: Procedural modeling is a technique that relies on algorithms and mathematical formulas to generate complex models automatically. Artists define rules and parameters, such as fractals, noise patterns, or mathematical functions, to dictate the shape and characteristics of the model. This technique is commonly used in generating terrain, foliage, and architectural elements where repetitive patterns or natural variations are required.
These are just a few examples of the different techniques employed in 3D modeling. Moreover, many artists combine multiple techniques creatively to achieve unique and desired results. The choice of technique depends on the specific requirements of the project, the artist’s skillset, and the desired style or outcome. By mastering these techniques, artists can unleash their creativity and bring their imagination to life in the digital realm.
When starting out with 3D modeling, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the basic tools and functions of the software you are using. Take the time to practice and experiment with different techniques to build your skills.
Read more: What Are Polygons In 3D Modeling
Advantages of 3D Modeling
3D modeling has numerous advantages that have revolutionized various industries and transformed the way we design, communicate, and interact with virtual objects and environments. Here are some of the key advantages of 3D modeling:
- Visual Realism: 3D models can closely mimic real-world objects and environments, providing a high level of visual realism. Detailed textures, accurate proportions, and realistic lighting effects make 3D models appear lifelike and immersive, allowing for better visualization and understanding of the final product or concept.
- Improved Communication: 3D models facilitate better communication and collaboration among designers, clients, and stakeholders. With a visually rich and interactive representation, it becomes easier to convey design ideas, demonstrate functionality, and address potential issues or modifications. This leads to greater clarity and alignment in project requirements and expectations.
- Design Iteration and Exploration: 3D modeling allows for quick and flexible design iteration. Designers can easily modify and experiment with different shapes, sizes, and materials, enabling exploration of multiple design options. This iterative process helps refine and optimize the design, resulting in more innovative and efficient solutions.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: In traditional design processes, physical prototypes and mock-ups can be time-consuming and costly. 3D modeling eliminates the need for physical prototypes by providing a virtual representation that can be visualized, tested, and refined before manufacturing. This reduces costs, accelerates the design process, and minimizes errors and rework.
- Flexibility and Customization: 3D modeling allows for customization and adaptability to specific project requirements. Designs can be easily modified, scaled, or personalized to meet the client’s preferences and needs. With parametric modeling techniques, designers can create parametric models that can be adjusted dynamically, enabling design variations without starting from scratch.
- Simulations and Analysis: 3D models enable simulations and analysis of real-world scenarios, contributing to better decision-making. Engineers can simulate physical properties, test structural integrity, analyze fluid dynamics, and perform virtual simulations to evaluate performance, identify potential issues, and optimize designs. This empowers designers to create more robust and efficient solutions.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality Integration: 3D models seamlessly integrate with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, expanding their potential applications. VR allows users to immerse themselves in virtual environments and interact with 3D models in a realistic and interactive manner, while AR overlays virtual elements onto the real world, enhancing visualization and providing contextual information.
These advantages of 3D modeling have significantly impacted industries such as architecture, product design, entertainment, engineering, and healthcare. The ability to create realistic and dynamic virtual representations has opened up new possibilities for innovation, visualization, and efficient design processes.
Limitations of 3D Modeling
While 3D modeling offers numerous benefits, it also has certain limitations that should be taken into consideration. Here are some of the key limitations of 3D modeling:
- Initial Learning Curve: Mastering the technical skills and software required for 3D modeling can be challenging and time-consuming. It often requires training and practice to become proficient in the various tools, techniques, and software platforms available. This initial learning curve may deter some individuals from fully utilizing 3D modeling in their work.
- Hardware and Software Requirements: 3D modeling typically requires powerful hardware and software to handle the complex calculations and rendering processes involved. High-performance computers with sufficient processing power and memory are necessary to work with large and complex 3D models. Additionally, professional-grade 3D modeling software can be expensive, further limiting accessibility for some users.
- Time and Resource Intensive: Creating detailed and high-quality 3D models can be a time-consuming process. It requires attention to detail, precise adjustments, and numerous iterations to achieve the desired outcome. Additionally, rendering complex scenes or animations can require significant computing resources, leading to longer processing times.
- Limitations in Physical Accuracy: While 3D models can be visually realistic, they may not always accurately represent physical properties and behaviors. Simulating complex physical phenomena, such as fluid dynamics or real-time physics, may require specialized software and expertise. This can result in limitations when attempting to create highly realistic and physically accurate models.
- Complexity of Model Management: Managing and organizing a large number of 3D models, textures, and related assets can be challenging. Without proper file organization and version control, locating specific models or making changes to a project can become difficult. Additionally, the file sizes of 3D models can be substantial, requiring efficient storage and management systems.
- Limitations in Surface Detail: The level of surface detail achievable in 3D models may be limited by hardware capabilities, rendering algorithms, and file sizes. Achieving extremely fine details or intricate textures can increase file sizes significantly and require more computational resources. This can impact real-time applications or constrain the level of realism in certain scenarios.
- Human Artistic Interpretation: 3D modeling, like any form of art, relies on the artistic interpretation of the creator. While technology has advanced, creating truly realistic and natural-looking models can still be challenging. Artists need to translate their artistic vision and creativity into the constraints of digital tools, which can sometimes result in a slightly stylized or less organic appearance.
Understanding these limitations helps users better navigate the world of 3D modeling and make informed decisions regarding their application and usage. Despite these limitations, the advancements in 3D modeling technology continue to push the boundaries, offering more accessible and powerful tools for artists and designers to create captivating and realistic virtual creations.
Popular Software for 3D Modeling
There are several popular software options available for 3D modeling, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Here are some of the most widely used software for 3D modeling:
- Autodesk Maya: Autodesk Maya is a comprehensive 3D modeling and animation software used in various industries, including film, television, gaming, and visual effects. It offers a robust set of tools for modeling, texturing, rigging, and animation, making it a popular choice for creating complex character models and dynamic simulations.
- Blender: Blender is a powerful open-source 3D modeling software that is free to use. It is known for its versatility and extensive feature set, including modeling, animation, sculpting, rigging, and rendering. Blender has a strong community of users and developers, resulting in regular updates, add-ons, and tutorials.
- Autodesk 3ds Max: Autodesk 3ds Max is widely used in the gaming industry and architectural visualization for its robust modeling and rendering capabilities. It offers a wide range of tools for creating detailed 3D models, animations, and visual effects. It also supports third-party plugins, expanding its functionality.
- Cinema 4D: Cinema 4D is a popular 3D modeling and animation software known for its ease of use and intuitive interface. It offers a wide range of features, including modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering. Cinema 4D is commonly used in motion graphics, product visualization, and visual effects.
- ZBrush: ZBrush is a digital sculpting software widely used for creating highly detailed and organic models. It provides powerful sculpting tools that allow artists to sculpt intricate details and shapes with fine control. ZBrush is commonly used in character modeling, creature design, and digital sculpting for 3D printing.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a parametric 3D modeling software specifically designed for engineering and product design. It focuses on creating precise and mechanical models that can be used for product prototyping and manufacturing processes. SolidWorks offers a wide range of tools for creating complex assemblies, performing simulations, and generating engineering drawings.
These are just a few examples of popular software options for 3D modeling. Other notable mentions include Houdini, SketchUp, Rhino, and Substance Designer. The choice of software depends on various factors such as the specific requirements of the project, the artist’s skillset, budget constraints, and industry standards. Exploring different software options and understanding their strengths and weaknesses can help users find the most suitable tool for their 3D modeling needs.
Conclusion
3D modeling has emerged as a powerful tool that has revolutionized various industries and transformed the way we visualize, design, and interact with virtual objects and environments. It enables the creation of realistic and immersive digital representations, allowing for better communication, enhanced visualization, and improved decision-making.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of 3D modeling, its applications, the process involved, different techniques used, as well as the advantages and limitations associated with this technique. We have also highlighted some of the popular software options available for 3D modeling.
Undoubtedly, 3D modeling has proven to be an invaluable asset in industries such as architecture, product design, gaming, engineering, healthcare, and entertainment. It has streamlined the design process, reduced costs, and allowed for greater creativity and flexibility.
However, it is important to acknowledge that 3D modeling is not without its limitations. The initial learning curve, hardware requirements, time-intensive nature, and limitations in physical accuracy are factors that should be considered. Additionally, managing large-scale projects and achieving a high level of surface detail can pose challenges.
Nevertheless, the advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of 3D modeling, making it more accessible, efficient, and powerful than ever before. With the integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), the possibilities for immersive and interactive experiences have expanded further.
In conclusion, 3D modeling has transformed industries and opened up new avenues for creativity, design, and communication. Its ability to create realistic virtual representations has revolutionized the way we conceptualize and bring ideas to life. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments in the world of 3D modeling, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and fueling innovation across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is 3D Modeling?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is 3D Modeling?”