

Articles
How Long Can You Run Electrical Wire
Modified: October 31, 2024
Discover how long electrical wire can be run in this informative article. Learn about important factors to consider when planning your electrical installations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
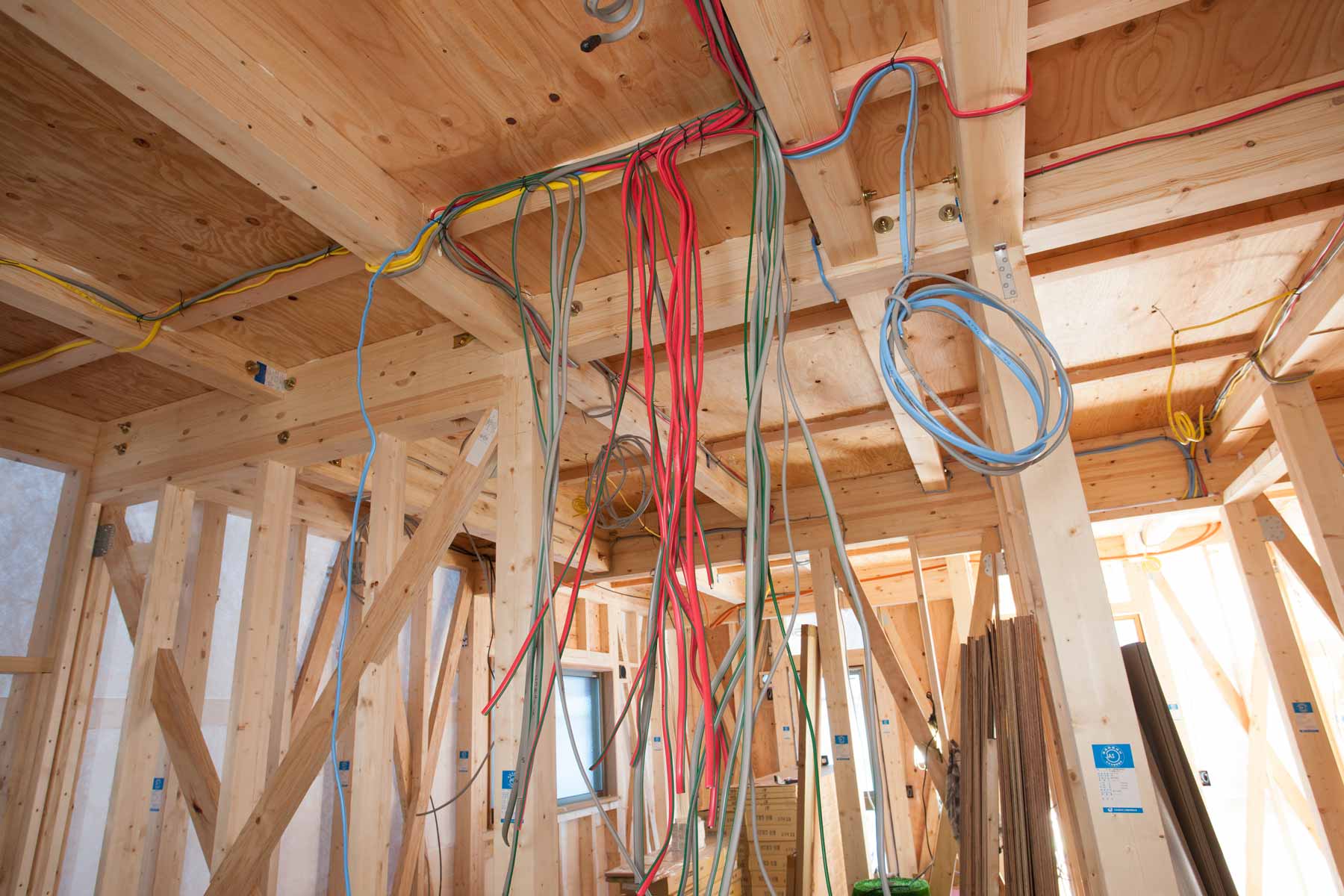
Welcome to the world of electrical wiring! If you’ve ever wondered how long you can run electrical wire, you’re in the right place. Determining the maximum distance for running electrical wire is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system. Whether you’re a homeowner embarking on a DIY project or a professional electrician, understanding the factors that affect wire length and complying with the relevant codes are essential.
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s take a moment to understand the importance of wire length. Electrical wire is responsible for carrying electricity from the source to various fixtures and outlets in a building. The length of the wire can directly impact its performance, voltage drop, and overall electrical system efficiency. Running wire over long distances without proper consideration can lead to voltage drop, increased electrical resistance, and potential safety hazards.
Now, let’s explore the factors that affect the permissible wire length in an electrical system.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the factors affecting wire length and complying with codes is crucial for a safe and efficient electrical system. Consider voltage drop, ampacity rating, wire gauge, environmental conditions, and conduit size when planning your wiring.
- Adhering to best practices such as proper wire routing, securing the wire, labeling, and hiring professional electricians ensures a reliable and hazard-free electrical installation. Prioritize safety and follow industry standards for a well-designed system.
Read more: How To Run Electrical Wire In A House
Factors Affecting Wire Length
Several factors come into play when determining how long you can run electrical wire. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Let’s explore them in detail:
- Voltage Drop: Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage as electricity flows through a wire. As the length of the wire increases, so does the voltage drop. Excessive voltage drop can lead to dimming lights, decreased performance of electrical appliances, and even damage to sensitive equipment. It is important to consider the maximum acceptable voltage drop for your specific application.
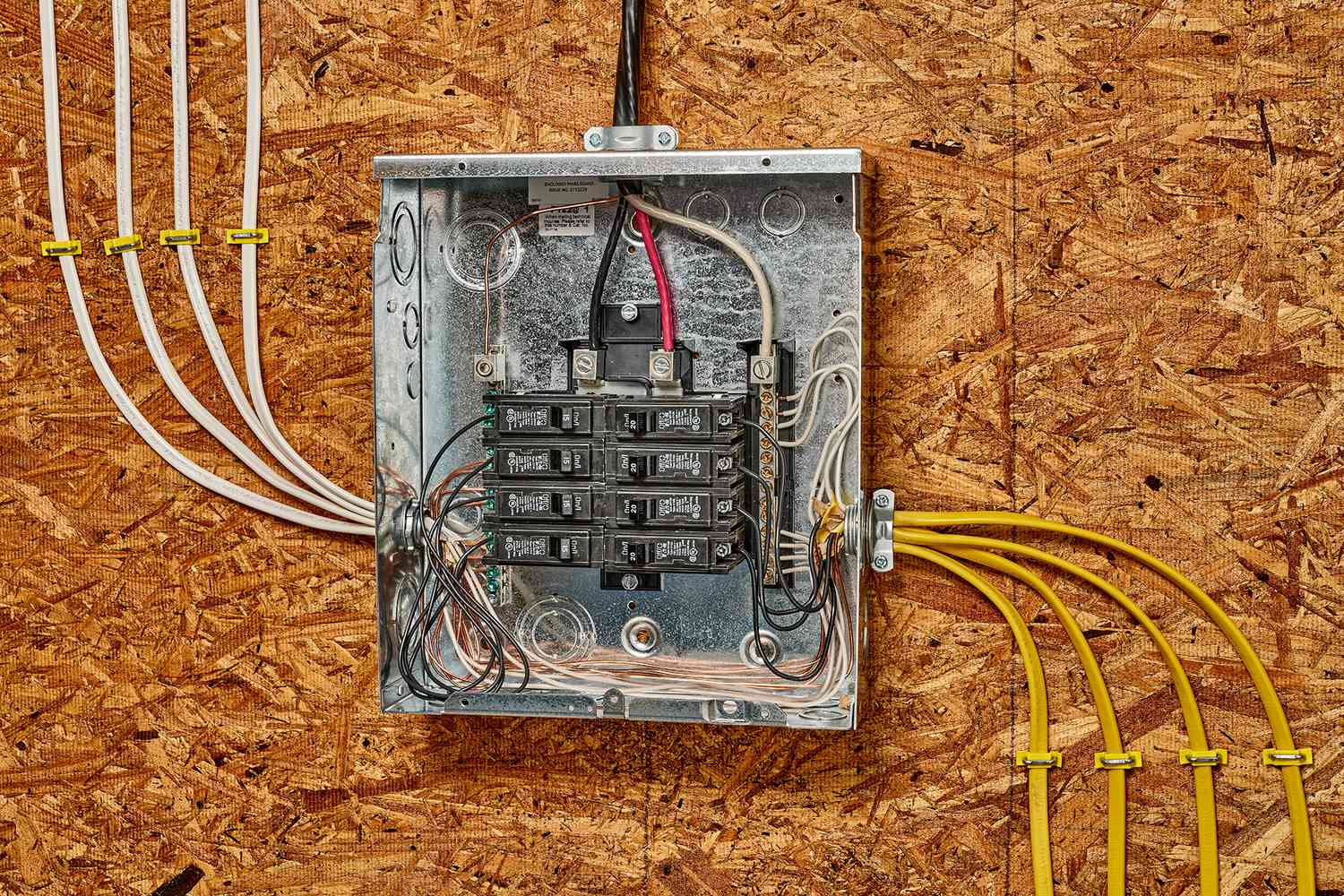
- Ampacity Rating: Ampacity rating is the maximum amount of current that a wire can safely carry. Each wire size and type has a specific ampacity rating, which is determined by factors such as material, insulation type, and wire diameter. Exceeding the ampacity rating can cause overheating, insulation damage, and even fires. It’s crucial to select the appropriate wire size based on the expected load and the environment in which it will be installed.
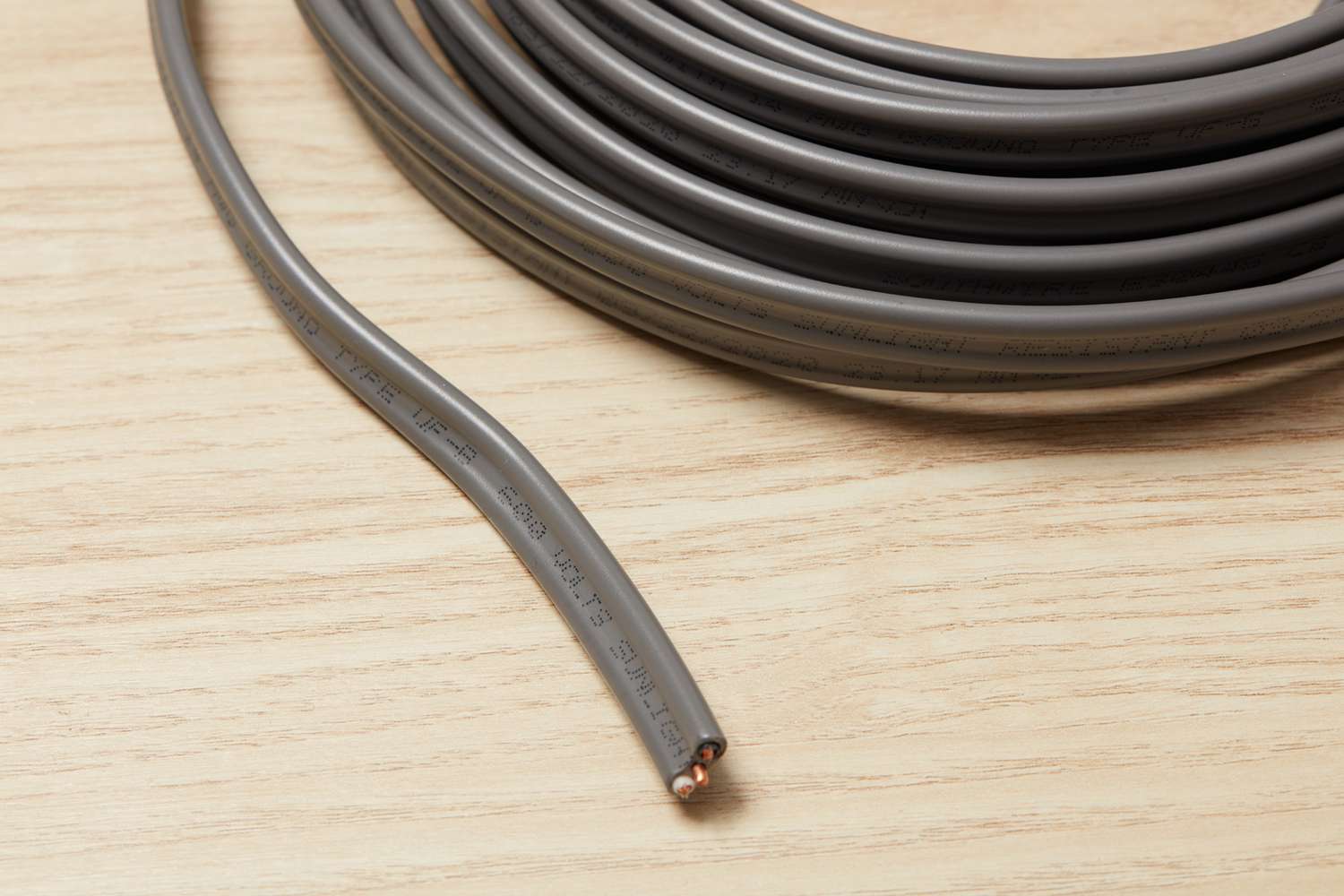
- Wire Gauge: The gauge of the wire refers to its diameter or thickness. Smaller gauge numbers indicate thicker wires, capable of carrying higher currents over longer distances. Choosing the right wire gauge based on the expected load and distance is critical for minimizing voltage drop and ensuring the safe operation of the electrical system.
- Environmental Factors: The environment in which the wire is installed plays a significant role in determining its maximum permissible length. Factors such as temperature, moisture, and exposure to chemicals or sunlight can affect the wire’s insulation, conductivity, and overall performance. It’s essential to choose wires with appropriate insulation ratings and consider any special environmental considerations when calculating wire length.
- Conduit Size: If the wire is installed within a conduit or raceway, the size of the conduit can limit the maximum permissible wire length. Conduit size restrictions are determined by factors such as wire diameter, number of conductors, and ease of installation. Ensuring proper conduit sizing is crucial for preventing wire damage, reducing friction, and facilitating future maintenance and upgrades.
These factors interplay with each other and have a cumulative effect on determining the maximum permissible wire length in any given application. It’s important to consider all of these factors when planning and installing electrical wiring to ensure a safe and efficient electrical system.
Wire Length Limitations by Code
Building codes and regulations govern the installation of electrical wiring to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. These codes set limits on wire length to prevent potential hazards and maintain the integrity of the electrical system. Let’s take a look at the two primary sources of wire length limitations:
- National Electrical Code (NEC) Guidelines: The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a comprehensive standard published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). It provides guidelines and regulations for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment. The NEC contains specific rules regarding wire length limitations based on factors such as the type of wire, voltage, and application. These guidelines are regularly updated to incorporate technological advancements and enhance safety practices.
- Local Building Codes: In addition to the NEC, local jurisdictions may have their own set of building codes and regulations that dictate wire length limitations. These codes often adopt or modify the NEC guidelines to address specific regional considerations. It’s essential to consult local building authorities and obtain necessary permits to ensure compliance with the applicable codes. Failure to comply with local codes can result in penalties, invalidate insurance coverage, and pose safety risks.
Both the NEC guidelines and local building codes aim to promote uniformity, safety, and best practices in electrical wiring installations. They provide essential guidelines for determining factors such as wire type, wire gauge, conduit size, and maximum permissible wire length. Adhering to these codes ensures that the electrical system is designed and installed correctly, reducing the risk of electrical accidents, fires, and other hazards.
As an individual or professional undertaking an electrical project, it is crucial to research and familiarize yourself with the applicable codes and regulations in your area. Understanding and adhering to these codes not only ensures safety but also protects the value and functionality of your property.
When running electrical wire, always make sure to use the correct gauge for the distance and load. Consult local building codes for specific requirements.
Wire Length Calculation Methods
Calculating the permissible length for running electrical wire requires consideration of various factors to maintain safety and the desired level of electrical performance. Several methods can be used to determine wire length, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Let’s discuss three commonly used calculation methods:
- Voltage Drop Calculation: Voltage drop calculation involves estimating the voltage drop that will occur over the desired wire length. This method considers factors such as wire gauge, wire material, current load, and acceptable voltage drop. By using Ohm’s Law and voltage drop formulas, you can calculate the maximum permissible wire length for a given voltage drop level. This ensures that electrical devices receive the required voltage to operate efficiently.
- Maximum Ampacity Calculation: Maximum ampacity calculation is used to determine the maximum current-carrying capacity that the chosen wire gauge and type can handle. This calculation considers factors such as wire gauge, insulation rating, ambient temperature, and conductor material. By examining the ampacity ratings from industry standards and referencing the NEC guidelines, you can determine the maximum current that can flow through the wire. This, in turn, helps establish the maximum permissible wire length based on the expected load.
- Conduit Fill Calculation: Conduit fill calculation is relevant when running wires through conduit or raceway systems. It involves determining the maximum number and size of wires that can be safely placed in the conduit without exceeding its fill capacity. This calculation takes into account the diameter of the conduit, the wire size, the number of conductors, and any spacing requirements specified by codes or manufacturer guidelines. By accurately calculating conduit fill, you can avoid overcrowding, reduce friction, and ensure ease of future maintenance.
These calculation methods are invaluable tools for designing and installing electrical systems that meet safety requirements and provide optimal performance. They enable you to determine the appropriate wire length based on factors such as voltage drop, ampacity, and conduit capacity. It’s essential to carefully execute these calculations or consult with a qualified electrician to ensure accurate results and compliance with codes and regulations.
Best Practices for Running Electrical Wire
When it comes to running electrical wire, following best practices is essential to ensure a safe and properly functioning electrical system. Here are some key practices to keep in mind:
- Proper Wire Routing: Ensure that wires are routed in a neat and organized manner, avoiding sharp bends, kinks, or tight loops. Proper routing helps prevent damage to the wire insulation and minimizes the risk of electrical shorts or faults.
- Securing the Wire: Use appropriate methods to secure the wire along its route, such as cable clips, staple guns, or conduit straps. Keeping the wire securely in place protects it from accidental damage and reduces the risk of tripping or entanglement.
- Labeling and Documentation: Properly label and document all electrical wirings, including junction boxes, breakers, and switches. Clear labeling ensures easy identification and troubleshooting in the future, saving time and effort. It also enhances safety by minimizing the risk of incorrect connections or mismatches during repairs or additions.
- Hiring a Professional Electrician: While DIY electrical projects can be tempting, it’s always advisable to consult or hire a professional electrician for complex installations or modifications. Electricians have the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to ensure compliance with codes, identify potential hazards, and execute the work safely and effectively.
Remember, electrical work can be hazardous, and mistakes can have severe consequences. If you’re unsure about any aspect of an electrical project, it’s better to seek professional assistance rather than compromise safety or risk damage to your property.
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure that your electrical wiring is properly installed, labeled, and secured, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and providing a reliable and efficient electrical system for your home or business.
Read more: How To Run Outdoor Electrical Wire
Conclusion
Running electrical wire requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a safe and efficient electrical system. Understanding the factors that affect wire length, complying with relevant codes and regulations, and following best practices are crucial for a successful installation. By adhering to these guidelines, you can minimize the risk of electrical hazards, voltage drop, and performance issues.
Factors such as voltage drop, ampacity rating, wire gauge, environmental conditions, and conduit size all play a role in determining the permissible wire length. Proper calculation methods, including voltage drop calculation, maximum ampacity calculation, and conduit fill calculation, help determine the appropriate wire length for a given application.
Compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines and local building codes is essential for ensuring the safety and legality of your electrical wiring. These codes provide specific requirements and limitations for wire length, offering guidance on wire type, gauge, and installation practices.
Following best practices such as proper wire routing, securing the wire, labeling and documentation, and knowing when to hire a professional electrician are essential for a successful electrical installation. These practices promote organization, safety, and ease of troubleshooting, enhancing the overall functionality of the electrical system.
In conclusion, running electrical wire involves careful planning, compliance with codes, and adherence to best practices. It is a task that should not be taken lightly, as it directly impacts the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, prioritizing safety and following industry standards will ensure a well-designed and reliable electrical infrastructure.
Now that you've got the scoop on running electrical wire lengths, why not tackle a specific project? If extending power to your garage sounds like the next step, you won’t want to miss our guide on how to run overhead electrical wire to your garage. This piece is packed with practical tips to safely and efficiently power up your workspace or storage area. So, grab your tools and let's get that garage powered up!
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Can You Run Electrical Wire
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Long Can You Run Electrical Wire”