Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How Long Does 3D Printer Filament Last


Smart Home Devices
How Long Does 3D Printer Filament Last
Modified: January 24, 2024
Discover the longevity of 3D printer filament for smart home devices. Learn how to maximize the lifespan of your filament for optimal printing results.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Read more: How To Make 3D Printer Filament
Introduction
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create objects, from simple prototypes to intricate designs. One crucial component of the 3D printing process is the filament, which serves as the raw material for producing the final printed product. Understanding the lifespan of 3D printer filament is essential for achieving consistent print quality and avoiding potential issues that may arise from using degraded filament.
In this article, we will explore the factors that affect the lifespan of 3D printer filament, including storage and handling practices, print settings, and usage. By gaining insights into these factors, you can effectively prolong the lifespan of your filament and optimize your 3D printing experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage and handling, including moisture control and temperature regulation, are crucial for preserving 3D printer filament quality and longevity. Adhering to these practices ensures consistent print performance and minimizes degradation risks.
- Optimizing print settings and usage practices, such as extruder temperature and print speed, significantly extends the lifespan of 3D printer filament. By fine-tuning these parameters, users can achieve durable prints and maximize filament longevity.
Factors Affecting Filament Lifespan
Several factors play a significant role in determining the lifespan of 3D printer filament. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining the quality and integrity of the filament throughout its usage.
1. Material Composition: The type of material used in the filament heavily influences its lifespan. For instance, PLA (Polylactic Acid) filament tends to have a shorter lifespan compared to ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) due to its biodegradable nature. Specialty filaments, such as PETG and TPU, also have varying lifespans based on their unique properties.
2. Environmental Conditions: Exposure to moisture, humidity, and UV light can significantly impact the longevity of 3D printer filament. Moisture absorption can lead to filament degradation and affect print quality, especially with hygroscopic materials like nylon. Storing filament in a dry and cool environment is essential for preserving its integrity.
3. Print Frequency: The frequency of 3D printing activities can affect the lifespan of filament. Continuous and high-volume printing may lead to faster depletion of filament compared to occasional or moderate usage. Additionally, prolonged exposure to heat during printing can contribute to filament degradation.
4. Filament Quality: The overall quality of the filament, including its diameter consistency, manufacturing standards, and purity, directly impacts its lifespan. High-quality filaments are less prone to premature degradation and are more reliable for long-term usage.
5. Printer Maintenance: The condition of the 3D printer and its components, such as the extruder and hotend, can influence the wear and tear on the filament during the printing process. Regular maintenance and proper calibration can contribute to extending the lifespan of the filament.
By considering these factors, users can make informed decisions regarding filament selection, storage practices, and printing routines to maximize the lifespan of their 3D printer filament.
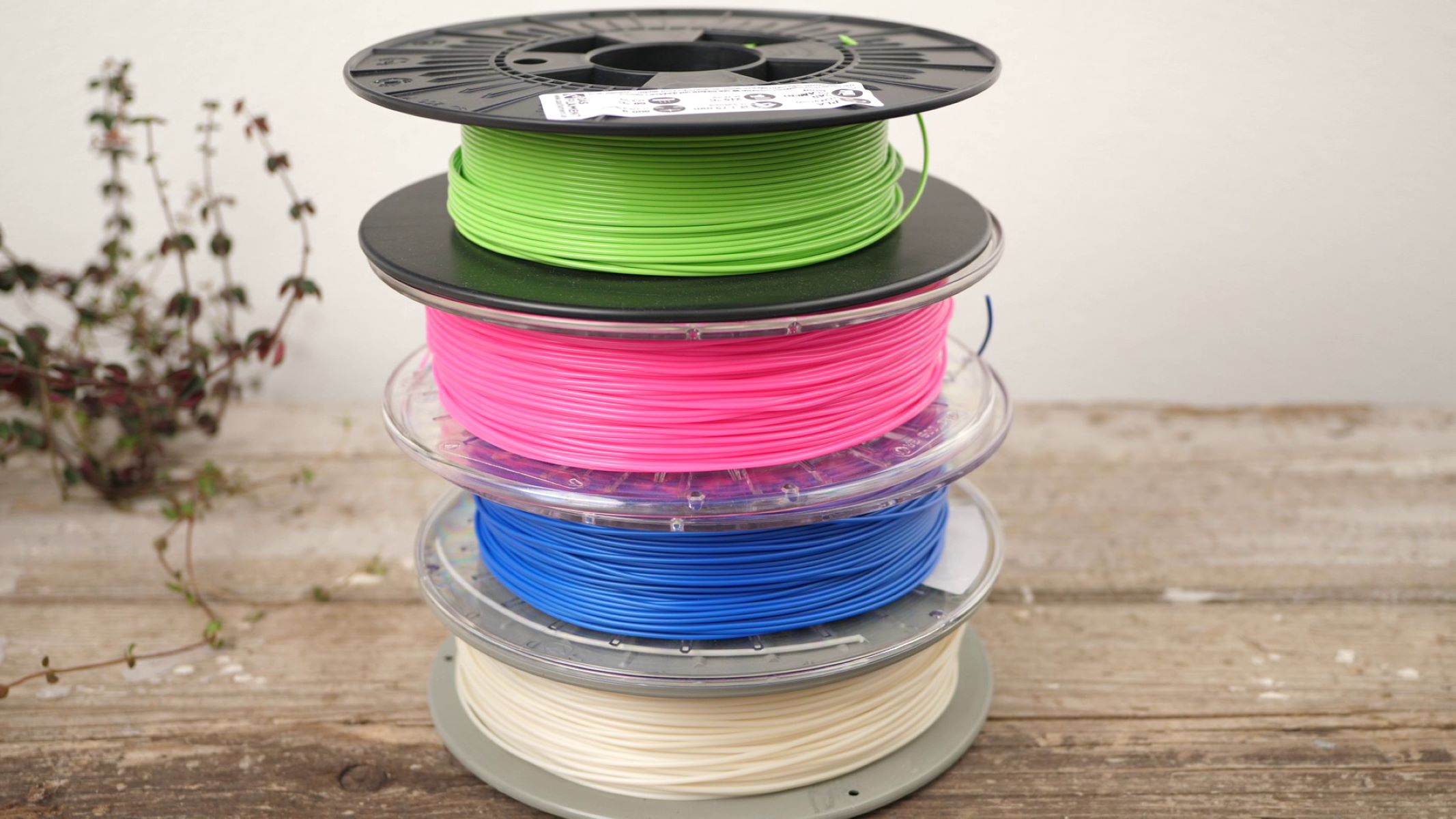
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling are paramount for preserving the quality and longevity of 3D printer filament. The following best practices can significantly impact the lifespan of filament:
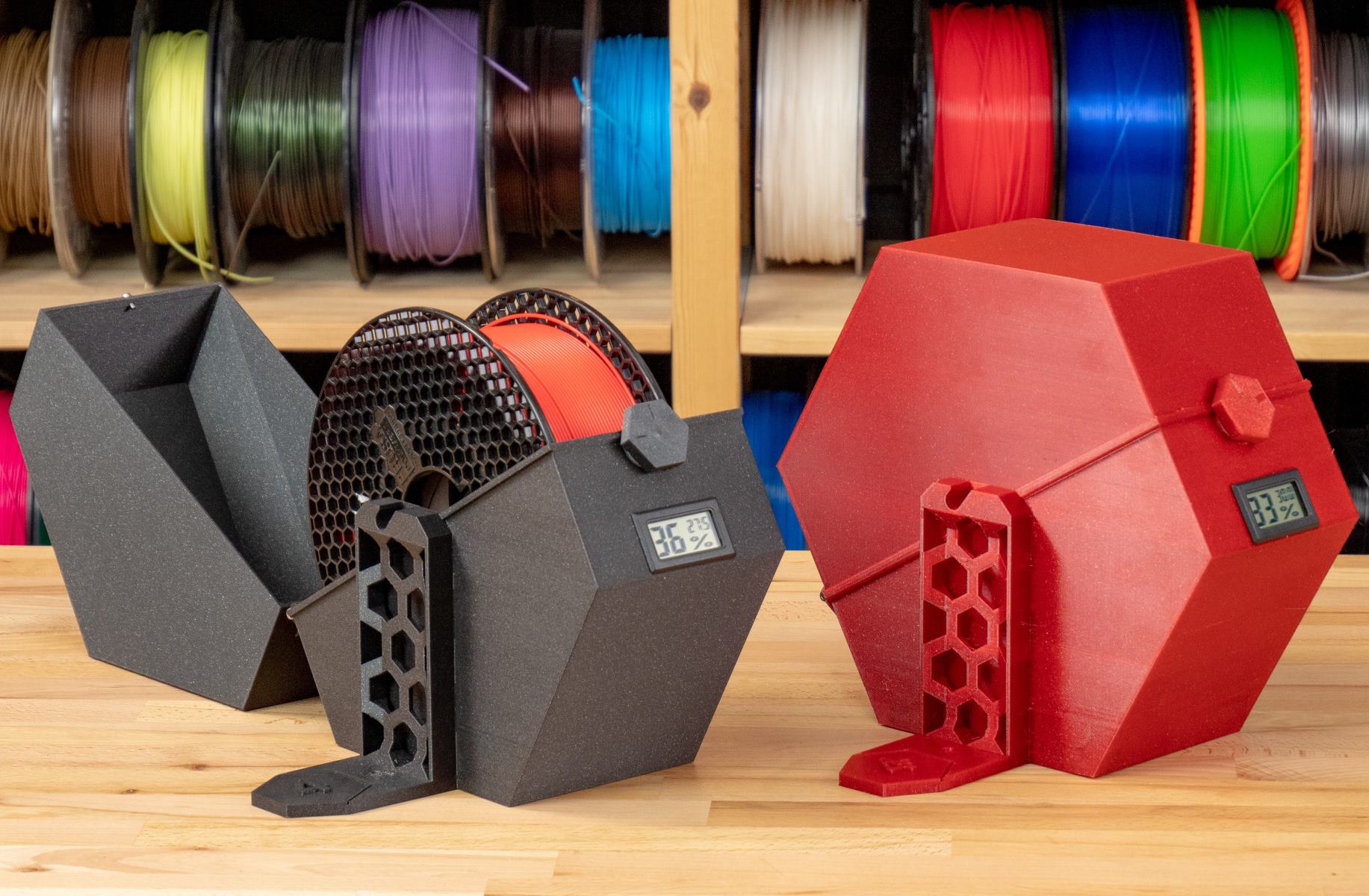
- Moisture Control: Moisture is a common adversary of filament integrity. Hygroscopic materials, including nylon and certain types of ABS, are particularly susceptible to moisture absorption, leading to filament degradation and print quality issues. To mitigate this, storing filament in airtight containers or vacuum-sealed bags with desiccants can effectively prevent moisture infiltration.
- Temperature Regulation: Extreme temperatures can adversely affect filament properties. Storing filament in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight and heat sources is essential for maintaining its structural integrity. Additionally, avoiding rapid temperature fluctuations is crucial for preventing condensation and moisture buildup within the filament spool.
- UV Protection: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can degrade certain filament materials, such as PLA. Storing filament in opaque or UV-resistant containers and keeping it away from direct sunlight helps preserve its composition and prevent premature degradation.
- Spool Management: Proper spool handling during storage and printing is essential for preventing tangles, twists, and filament entanglement. Utilizing spool holders or wall-mounted spool racks can maintain the integrity of the filament and facilitate smooth feeding during printing.
By adhering to these storage and handling guidelines, users can safeguard their 3D printer filament from environmental factors that may compromise its quality and longevity. Implementing these practices is instrumental in ensuring consistent print performance and minimizing the risk of filament degradation.
Print Settings and Usage
Optimizing print settings and adopting appropriate usage practices are pivotal for extending the lifespan of 3D printer filament and achieving high-quality prints. The following considerations can significantly impact filament longevity and overall printing performance:
- Extruder Temperature: Adhering to the recommended extrusion temperatures specified by filament manufacturers is essential for preventing overheating and thermal degradation. Excessive temperatures can accelerate filament wear and compromise its structural integrity, leading to inconsistent printing results and potential clogging.
- Print Speed and Layer Height: Balancing print speed and layer height is crucial for minimizing mechanical stress on the filament during the printing process. Higher print speeds and excessively low layer heights can exert excessive strain on the filament, potentially shortening its lifespan. Optimizing these parameters based on filament type and printer capabilities is essential for achieving durable and high-quality prints.
- Retraction Settings: Proper retraction settings, including retraction distance and speed, play a vital role in preventing filament oozing and stringing. Fine-tuning retraction parameters can minimize unnecessary filament stress and abrasion, contributing to prolonged filament lifespan and improved print quality.
- Print Cooling: Effective print cooling mechanisms, such as cooling fans and ducts, are essential for maintaining optimal print quality and preventing filament overheating. Proper cooling minimizes warping and ensures consistent layer adhesion, thereby enhancing the longevity of the filament and the structural integrity of the printed objects.
- Print Infill and Supports: Adjusting infill density and support structures based on print requirements can reduce filament consumption and mechanical strain during printing. Implementing suitable infill patterns and support settings optimizes filament usage while preserving print quality, ultimately contributing to prolonged filament lifespan.
By meticulously configuring print settings and employing prudent usage practices, users can mitigate potential sources of filament wear and degradation, thereby prolonging the lifespan of their 3D printer filament and achieving superior print outcomes.
Store 3D printer filament in a cool, dry place to extend its shelf life. Keep it sealed in its original packaging or airtight container to prevent moisture absorption.
Read more: How To Store 3D Printer Filament
Signs of Filament Degradation
Recognizing the signs of filament degradation is crucial for identifying potential issues early on and preventing compromised print quality. The following indicators may signify filament degradation and necessitate corrective actions:
- Brittleness: Filament that has become brittle and prone to snapping or fracturing indicates potential degradation, often attributed to moisture absorption or prolonged exposure to environmental stressors. Increased brittleness compromises print reliability and may lead to print failures.
- Color Irregularities: Discoloration, yellowing, or darkening of filament, particularly in areas exposed to heat or UV light, can signify thermal degradation or material breakdown. Such irregularities may affect print aesthetics and mechanical properties.
- Inconsistent Extrusion: Irregular extrusion patterns, including under-extrusion, inconsistent flow, or nozzle clogging, may indicate filament degradation or contamination. These issues can result in print defects and necessitate troubleshooting to identify the underlying cause.
- Print Quality Deterioration: Reduced print adhesion, layer separation, or surface imperfections in printed objects can be indicative of filament degradation affecting print consistency and structural integrity. Monitoring print quality is essential for detecting subtle signs of filament wear.
- Unusual Odors: The emission of unusual or pungent odors during printing, particularly when using certain filament types, may signal thermal degradation or the release of volatile compounds. Unpleasant odors warrant investigation and potential reassessment of filament usage.
By remaining attentive to these signs, users can promptly address filament degradation issues, implement corrective measures, and optimize their printing processes to maintain filament integrity and uphold print quality standards.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors influencing the lifespan of 3D printer filament is essential for maximizing its longevity and ensuring consistent print quality. By considering the material composition, environmental conditions, print frequency, filament quality, and printer maintenance, users can make informed decisions to prolong the lifespan of their filament and optimize their 3D printing experiences.
Implementing proper storage and handling practices, including moisture control, temperature regulation, UV protection, and spool management, is instrumental in safeguarding filament integrity and mitigating potential degradation risks. By prioritizing these practices, users can preserve the quality of their filament and minimize the impact of environmental stressors.
Optimizing print settings, such as extruder temperature, print speed, retraction parameters, print cooling, and support structures, contributes to reducing filament wear and maintaining print consistency. Adhering to prudent usage practices is pivotal for extending filament lifespan and achieving superior print outcomes.
Recognizing the signs of filament degradation, including brittleness, color irregularities, inconsistent extrusion, print quality deterioration, and unusual odors, empowers users to identify and address potential issues promptly, thereby sustaining filament integrity and print reliability.
In conclusion, by integrating these insights into their 3D printing workflows, users can effectively prolong the lifespan of 3D printer filament, optimize print quality, and elevate their overall printing experiences. Embracing proactive filament management practices and continuous vigilance are paramount for sustaining filament integrity and unlocking the full potential of 3D printing technology.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Does 3D Printer Filament Last
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Long Does 3D Printer Filament Last”