Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How Long Does A 3D Printer Take To Print


Smart Home Devices
How Long Does A 3D Printer Take To Print
Published: January 8, 2024
Learn how long it takes for a 3D printer to complete a print and optimize your smart home devices for efficient use. Discover the printing time for different types of 3D models and enhance your smart home experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
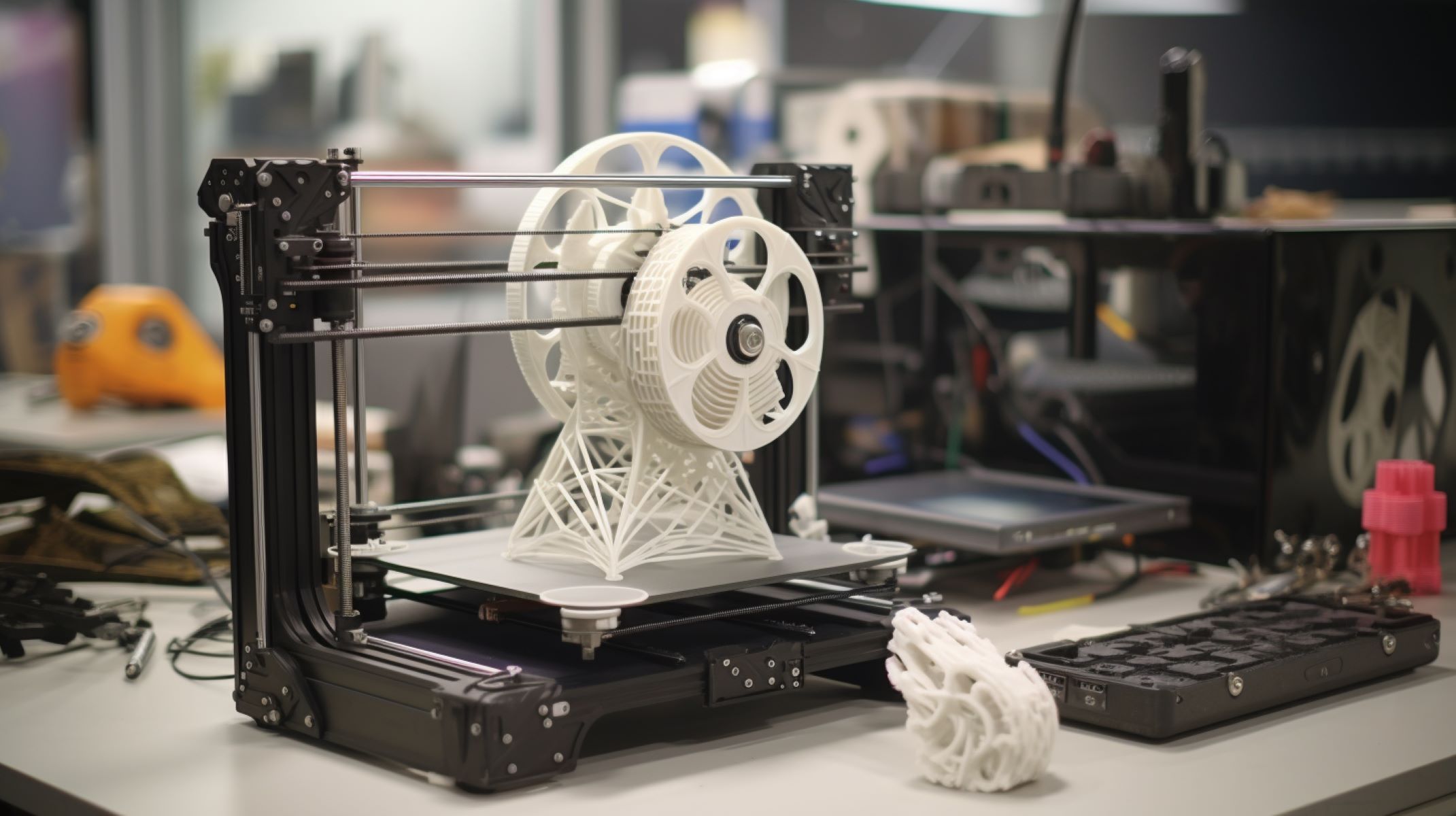
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing! Whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional designer, or an enthusiast exploring the endless possibilities of this technology, one of the most common questions that arise is, “How long does a 3D printer take to print?” The answer to this question is multifaceted, as several factors come into play when determining the printing time for a 3D object. In this article, we’ll delve into the various elements that influence 3D printing duration, explore the different types of 3D printers and their printing speeds, examine the impact of printing materials, and provide valuable tips for optimizing 3D printing time.
Understanding the intricacies of 3D printing time can significantly enhance your overall printing experience, enabling you to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and achieve impressive results. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey through the realm of 3D printing time and uncover the essential insights that will elevate your understanding of this innovative technology.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D printing time is influenced by factors like layer height, infill density, and printer technology. Understanding these elements helps optimize printing duration for efficient and successful 3D prints.
- Different types of 3D printers, such as FDM, SLA, and SLS, offer varying printing speeds and capabilities. Selecting the right printer based on project requirements is crucial for achieving desired printing speed and quality.
Factors Affecting 3D Printing Time
Several key factors influence the duration of a 3D printing process, each playing a crucial role in determining the overall printing time. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the printing process and achieving efficient results. Let’s explore the primary elements that impact 3D printing time:
- Layer Height: The layer height, or layer thickness, directly affects the printing time. A smaller layer height results in finer details but increases the number of layers required to build the object, thus extending the printing duration.
- Infill Density: The infill density refers to the internal structure of the printed object. Higher infill densities lead to a longer printing time, as more material is used to fill the interior of the object.
- Print Speed: The speed at which the printer’s extruder moves during printing significantly impacts the overall printing time. Slower print speeds may result in higher quality but extend the duration, while faster speeds can reduce printing time but may compromise on detail and surface finish.
- Complexity of Design: The complexity of the 3D model being printed directly affects the printing time. Objects with intricate details, overhangs, and intricate geometries may require additional support structures and slower printing speeds, thereby increasing the overall printing duration.
- Printer Technology: Different 3D printing technologies, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), have varying printing speeds and capabilities. The specific technology used can significantly impact the printing time.
- Printer Settings: Various settings within the 3D printer’s software, such as layer cooling, retraction settings, and print acceleration, can influence the printing time and the quality of the final print.
By considering and optimizing these factors, you can effectively manage and reduce the printing time while maintaining the desired print quality. Understanding the interplay of these elements is crucial for achieving efficient and successful 3D prints.
Types of 3D Printers and Their Printing Speed
3D printers come in various types, each employing distinct technologies that influence their printing speed and capabilities. Understanding the different types of 3D printers is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on your specific printing requirements. Let’s explore the common types of 3D printers and their associated printing speeds:
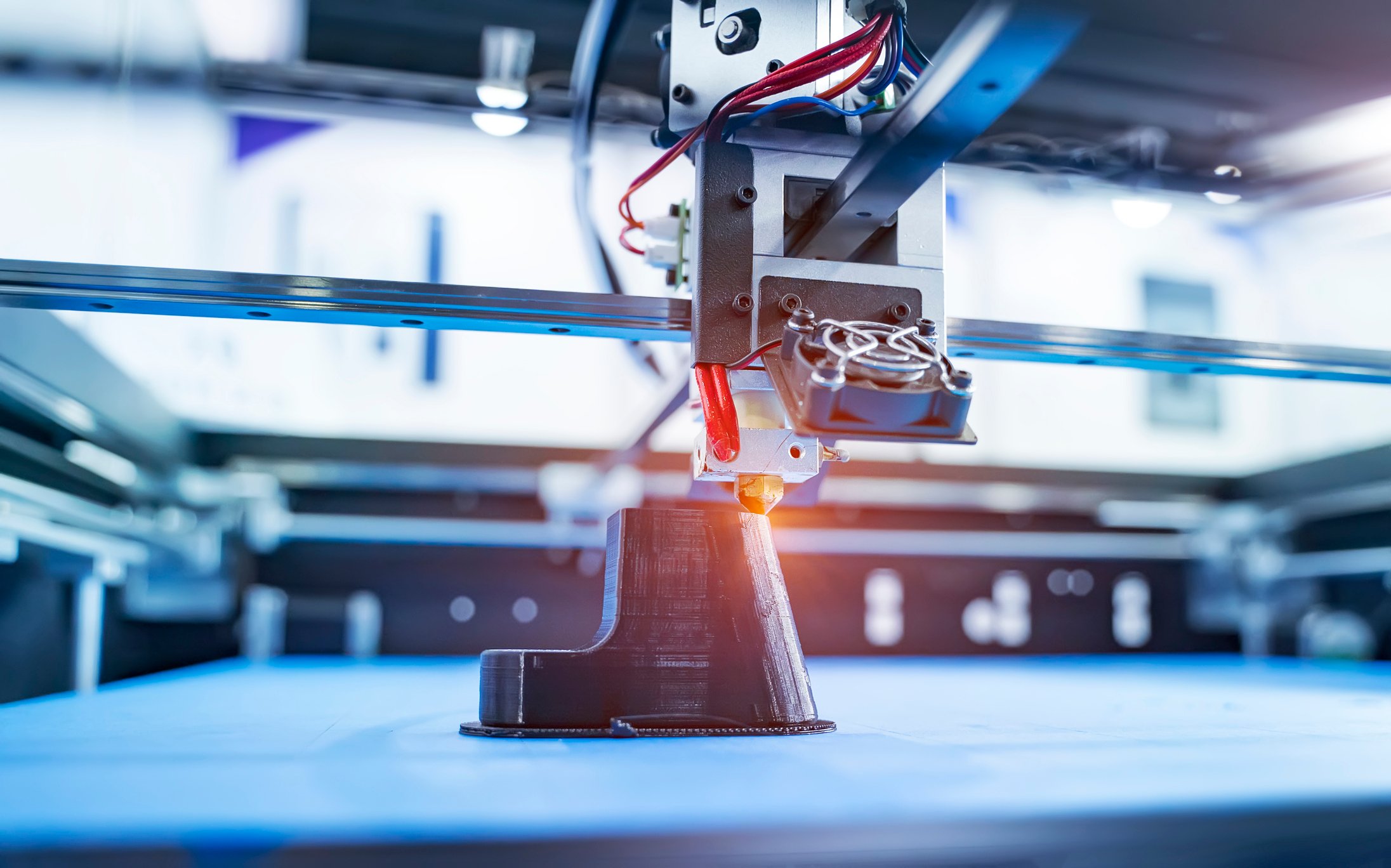
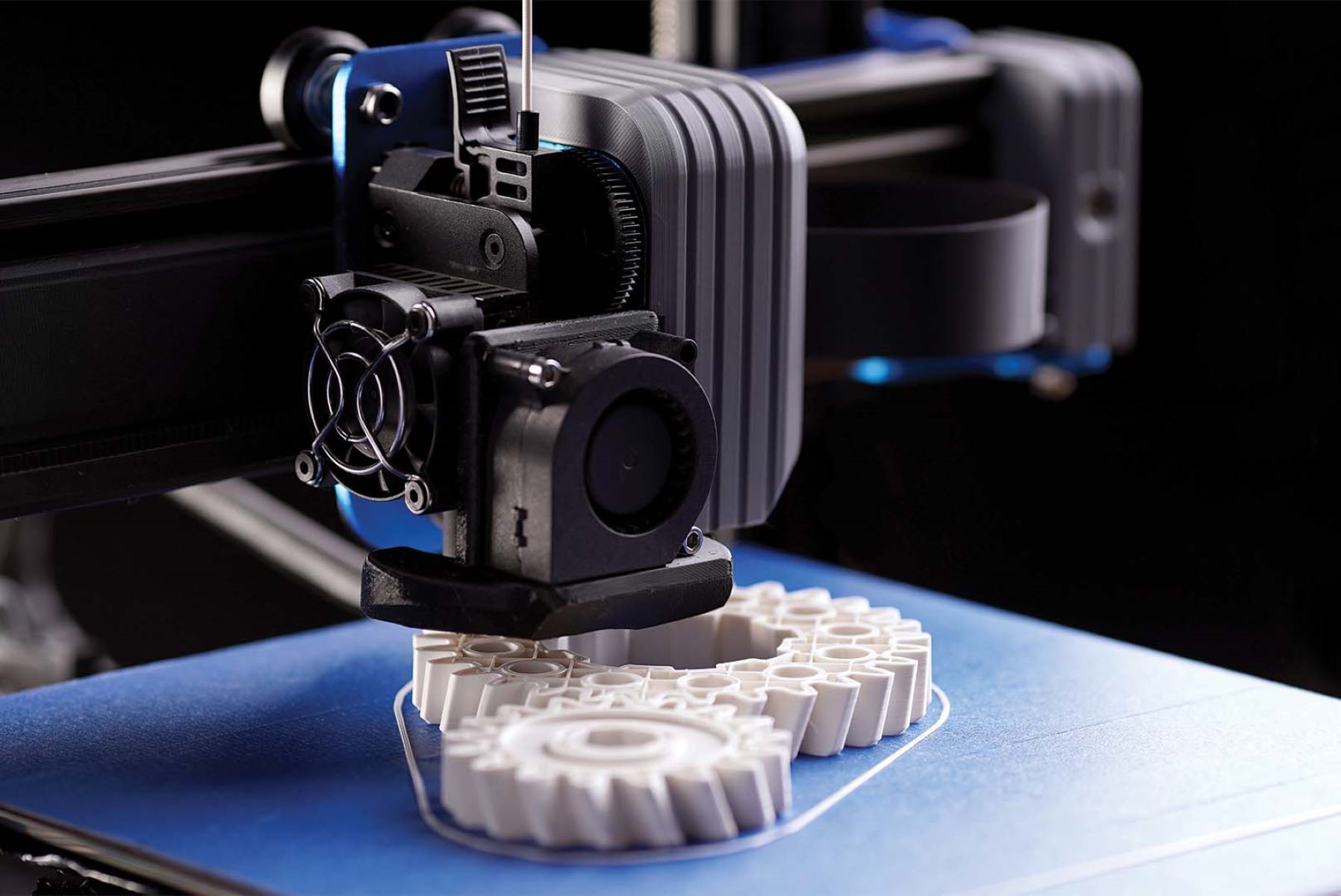
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Printers: FDM printers are widely used and known for their accessibility and affordability. These printers extrude thermoplastic filaments to create 3D objects layer by layer. While FDM printers are generally slower compared to other technologies, advancements in FDM printer designs and extrusion systems have led to improved printing speeds.
- Stereolithography (SLA) Printers: SLA printers utilize a process that involves curing liquid resin with a UV laser to build 3D objects. SLA printers are capable of achieving high levels of detail and precision at relatively faster printing speeds compared to FDM printers, making them suitable for applications requiring intricate designs and fine surface finishes.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Printers: SLS printers use a laser to sinter powdered material, such as nylon or polyamide, to create 3D objects. While SLS printers are known for their ability to produce robust and functional parts, they typically operate at slower printing speeds due to the intricacies of the sintering process.
- Binder Jetting Printers: Binder jetting printers deposit a binding agent onto a powder bed to solidify the material and create 3D objects. While binder jetting offers the advantage of printing multiple objects simultaneously, the printing speed may vary based on the size and complexity of the objects being printed.
It’s important to note that advancements in 3D printing technology continue to drive improvements in printing speeds across all types of printers. Additionally, factors such as the specific model of the printer, the quality of components, and the sophistication of the printing mechanism can also influence the overall printing speed.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each 3D printing technology, you can make informed decisions when selecting a printer that aligns with your project requirements and desired printing speed.
The time it takes for a 3D printer to complete a print job depends on the size, complexity, and quality settings of the object being printed. Smaller and simpler objects may take a few hours, while larger and more complex objects can take several days to complete.
Printing Materials and Their Impact on Printing Time
The choice of printing materials significantly influences the printing time and the overall performance of 3D printing processes. Understanding the characteristics of different materials and their impact on printing time is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on the specific requirements of your 3D printing projects. Let’s explore the common printing materials and their influence on printing time:
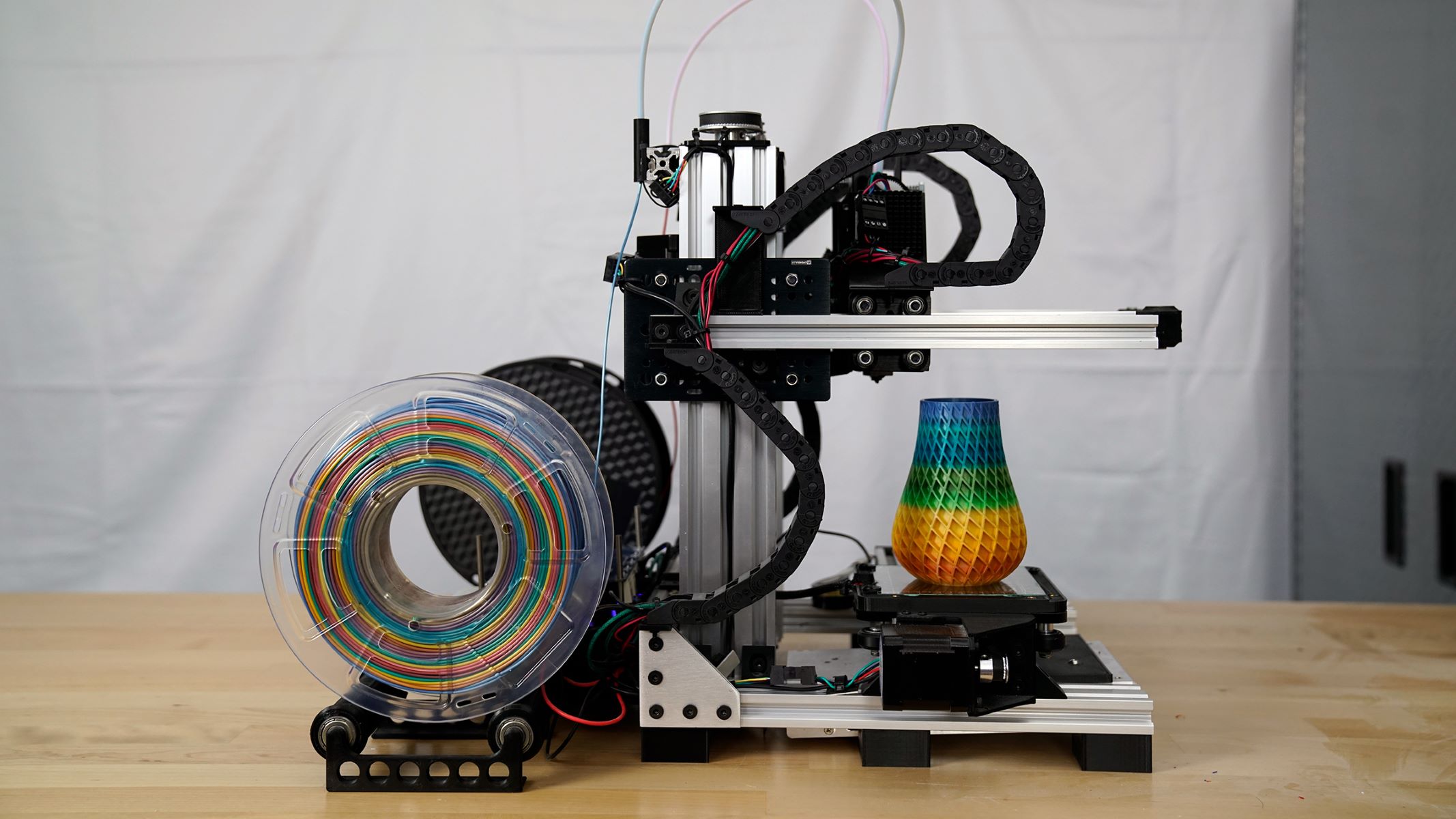
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is a popular thermoplastic material known for its ease of use and environmental friendliness. It typically requires lower printing temperatures and exhibits minimal warping, making it ideal for quick and efficient 3D printing. Objects printed with PLA generally have shorter printing times compared to other materials.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a durable and impact-resistant material commonly used in 3D printing. While ABS may require higher printing temperatures and enhanced bed adhesion, it offers faster cooling times, enabling quicker solidification of printed layers and reducing overall printing durations.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG combines the strength of ABS with the ease of printing associated with PLA. Its moderate printing temperatures and minimal shrinkage contribute to efficient printing, resulting in relatively shorter printing times for PETG-based projects.
- Nylon: Nylon is valued for its strength, flexibility, and impact resistance. While nylon printing may require slower print speeds to ensure proper adhesion and layer bonding, the material’s favorable cooling properties can contribute to efficient printing times for intricate and durable objects.
- Resin (for SLA and DLP Printing): Resin materials used in SLA and DLP printing processes offer exceptional detail and surface finish. The printing times for resin-based projects may vary based on the specific resin composition, layer curing requirements, and the complexity of the printed designs.
It’s important to consider the unique properties of each printing material and their compatibility with your 3D printer when aiming to optimize printing times. Additionally, advancements in material formulations and 3D printing technologies continue to drive improvements in printing speeds and efficiency across a wide range of materials.
By selecting the most suitable printing material for your projects and optimizing the printing parameters, you can effectively manage printing times while achieving exceptional results tailored to your specific application needs.
Tips for Speeding Up 3D Printing
Optimizing the 3D printing process for efficiency and speed is a common goal for creators and manufacturers seeking to streamline their production workflows. By implementing strategic techniques and leveraging the capabilities of 3D printing technology, it’s possible to significantly reduce printing times without compromising on quality. Here are valuable tips for speeding up 3D printing:
- Optimize Layer Height and Infill Density: Adjusting the layer height and infill density based on the specific requirements of your project can help reduce printing times. While finer details may necessitate lower layer heights, utilizing lower infill densities for non-structural components can expedite the printing process.
- Utilize High-Performance Nozzles: Upgrading to high-performance nozzles, such as hardened steel or ruby nozzles, can enhance the printing speed and durability, allowing for increased extrusion rates and compatibility with a broader range of printing materials.
- Employ Parallel Printing: When producing multiple identical objects or smaller components, leveraging the capability of your 3D printer to simultaneously print multiple items can significantly reduce the overall printing time, maximizing efficiency and throughput.
- Implement Print Cooling Strategies: Efficient cooling mechanisms, such as active cooling fans and optimized print cooling settings, can expedite the solidification of printed layers, enabling faster print speeds while maintaining print quality.
- Opt for High-Speed Printing Modes: Many modern 3D printers offer high-speed printing modes or settings that prioritize faster print speeds over finer details. Utilizing these modes for non-critical components can effectively reduce printing times.
- Explore Hybrid Printing Approaches: Hybrid printing, which combines multiple 3D printing technologies or materials in a single print, can optimize the printing process by leveraging the strengths of each technology while minimizing overall printing durations.
- Utilize Advanced Slicing Software: Leveraging advanced slicing software with optimized algorithms and customizable settings can fine-tune the printing process, minimizing unnecessary movements and optimizing toolpaths for accelerated printing.
By incorporating these tips into your 3D printing practices, you can harness the full potential of your 3D printer and achieve remarkable efficiency gains. It’s essential to experiment with these strategies while considering the specific requirements of your projects and balancing printing speed with the desired quality of the final prints.
Read more: How To Remove Print From A 3D Printer
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the factors influencing 3D printing time, the diverse landscape of 3D printing technologies, materials, and optimization strategies offers a wealth of opportunities for creators and innovators. Understanding the interplay of these elements is paramount for achieving efficient and successful 3D printing outcomes while balancing printing speed with quality.
By comprehending the impact of factors such as layer height, infill density, print speed, complexity of design, printer technology, and materials, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their 3D printing processes. The evolution of 3D printing technology continues to drive advancements in printing speeds, material capabilities, and software solutions, empowering users to elevate their creative and manufacturing endeavors.
Furthermore, the integration of strategic tips, including optimizing printing parameters, leveraging high-performance components, and exploring innovative printing approaches, equips practitioners with the tools to expedite their production workflows without compromising on the integrity of their prints.
As the realm of 3D printing continues to expand and evolve, the quest for efficient and rapid printing remains a focal point for enthusiasts and industry professionals alike. Embracing the dynamic nature of 3D printing and harnessing its potential for accelerated innovation and production underscores the transformative impact of this revolutionary technology.
With a deepened understanding of the intricate factors influencing 3D printing time and the implementation of strategic measures, individuals and businesses can embark on a journey of unparalleled creativity, efficiency, and productivity, shaping the future of manufacturing and design with each meticulously crafted layer.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Does A 3D Printer Take To Print
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Long Does A 3D Printer Take To Print”