Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How Small Can A 3D Printer Print


Smart Home Devices
How Small Can A 3D Printer Print
Published: January 20, 2024
Discover the capabilities of 3D printing technology for creating small objects and smart home devices. Learn how small a 3D printer can accurately print. Explore the possibilities for precision manufacturing in your own home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing, where the boundaries of creativity and innovation are continually being pushed. One of the most intriguing aspects of 3D printing is the ability to create intricate and detailed objects with astonishing precision. As technology advances, the question arises: How small can a 3D printer print?
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of 3D printing, exploring the factors that influence the minimum print size and uncovering the incredible potential of small-scale 3D printing. From understanding the underlying principles to discovering the real-world applications, we will embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of miniature 3D printing.
So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to explore the captivating realm of small-scale 3D printing, where precision meets creativity in the most extraordinary ways.
Key Takeaways:
- Small-scale 3D printing allows for creating incredibly detailed and intricate objects, from tiny mechanical components to personalized jewelry, revolutionizing industries and sparking creativity.
- The precision and customization offered by small 3D printing have led to groundbreaking advancements in healthcare, robotics, and art, shaping the future of innovation and creativity.
Read more: How To Remove Print From A 3D Printer
Understanding 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary process that involves creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. This groundbreaking technology has gained widespread attention for its ability to transform digital designs into physical objects with remarkable precision and complexity.
At the core of 3D printing is the concept of layer-by-layer construction. The process begins with a digital 3D model, which is sliced into thin horizontal cross-sections using specialized software. These slices serve as a blueprint for the 3D printer, dictating the precise paths for the deposition of material.
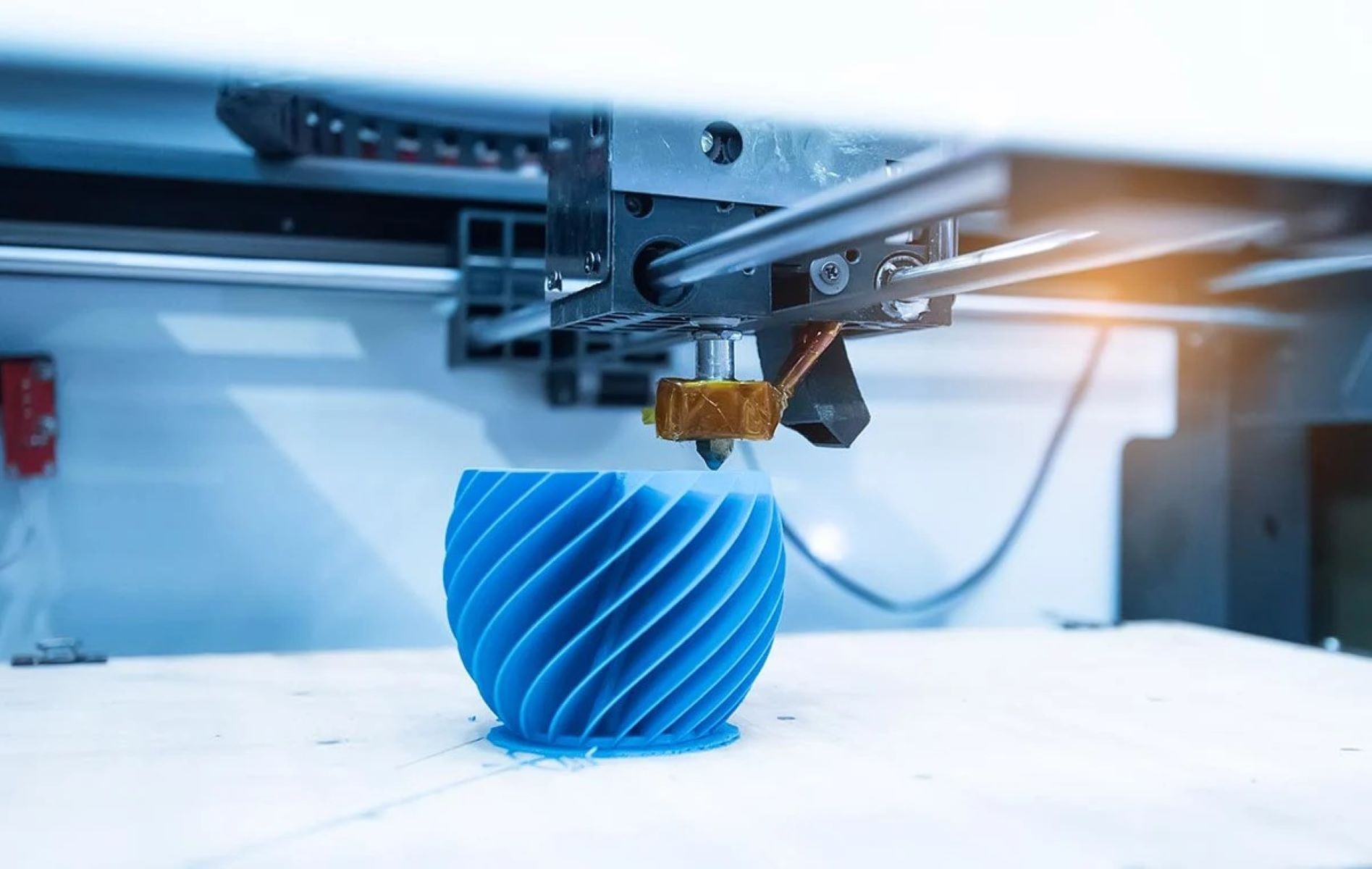
As the 3D printer springs into action, it meticulously deposits material layer by layer, gradually building up the object according to the predefined design. This additive approach sets 3D printing apart from traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, where material is carved away from a solid block to create the desired shape.
3D printing encompasses a diverse range of technologies and materials, including plastic filaments, resins, metals, ceramics, and even edible substances. Each material offers unique properties and characteristics, allowing for the creation of objects with varying degrees of strength, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal.
From rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing to artistic expression and medical advancements, 3D printing has permeated numerous industries, unlocking new possibilities and pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved. The versatility and precision of 3D printing have sparked a wave of innovation, inspiring designers, engineers, and creators to explore uncharted territories and bring their imaginations to life.
With a solid understanding of the fundamental principles of 3D printing, we can now delve into the factors that influence the minimum print size, shedding light on the remarkable intricacies of small-scale 3D printing.
Factors Affecting Minimum Print Size
When it comes to determining the minimum print size achievable with a 3D printer, several factors come into play, each exerting a significant influence on the precision and intricacy of the final output. Understanding these factors is crucial for unlocking the full potential of small-scale 3D printing.
- Printer Resolution: The resolution of a 3D printer, often measured in microns, directly impacts the level of detail it can achieve. A lower resolution allows for finer layers to be deposited, resulting in smoother surfaces and sharper edges. High-resolution printers are capable of producing incredibly small features with exceptional precision.
- Nozzle Size: The size of the printer’s nozzle dictates the diameter of the material extruded during the printing process. Smaller nozzles enable finer control over the deposition of material, making it possible to create intricate details and delicate structures.
- Layer Height: The layer height, or the thickness of each deposited layer, plays a crucial role in determining the minimum achievable print size. Smaller layer heights result in finer details but may require more time to print due to the increased number of layers.
- Material Properties: The physical properties of the printing material, such as its viscosity, flow characteristics, and curing behavior, can impact the level of detail that can be achieved. Materials with high flowability and precise curing mechanisms are well-suited for small-scale printing.
- Support Structures: In complex designs, support structures may be necessary to prevent overhangs and ensure the stability of the printed object. The ability to create and remove intricate support structures without damaging the final print is essential for achieving small-scale intricacy.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Proper calibration of the 3D printer, regular maintenance of its components, and meticulous fine-tuning of printing parameters are essential for achieving consistent and precise small-scale prints.
By carefully considering and optimizing these factors, 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals can unlock the full potential of their printers, pushing the boundaries of small-scale fabrication and ushering in a new era of precision and intricacy.
When choosing a 3D printer, look for one with a smaller nozzle size, typically around 0.4mm or smaller. This will allow for finer details and smaller prints. Keep in mind that the smaller the print, the longer it will take to complete.
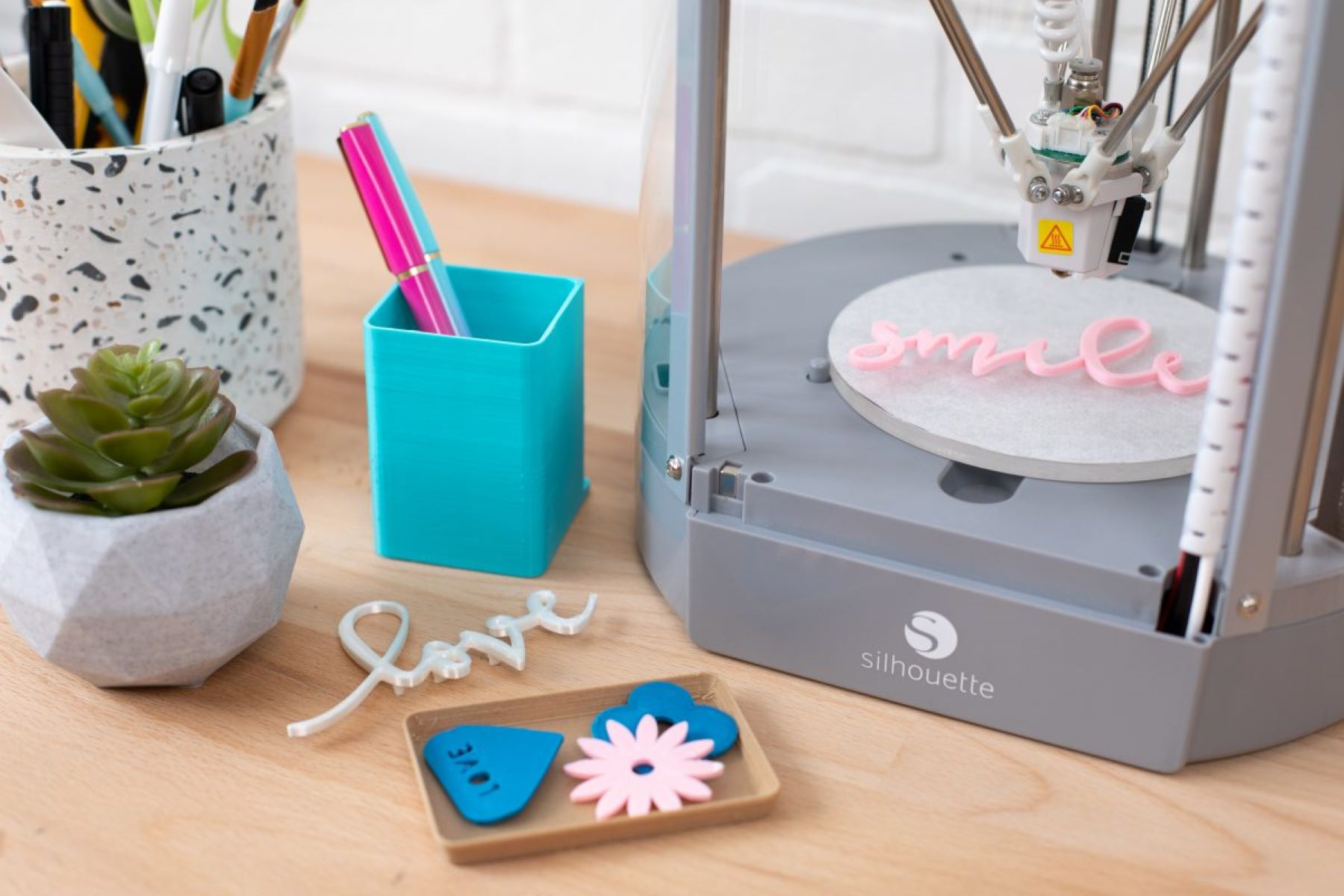
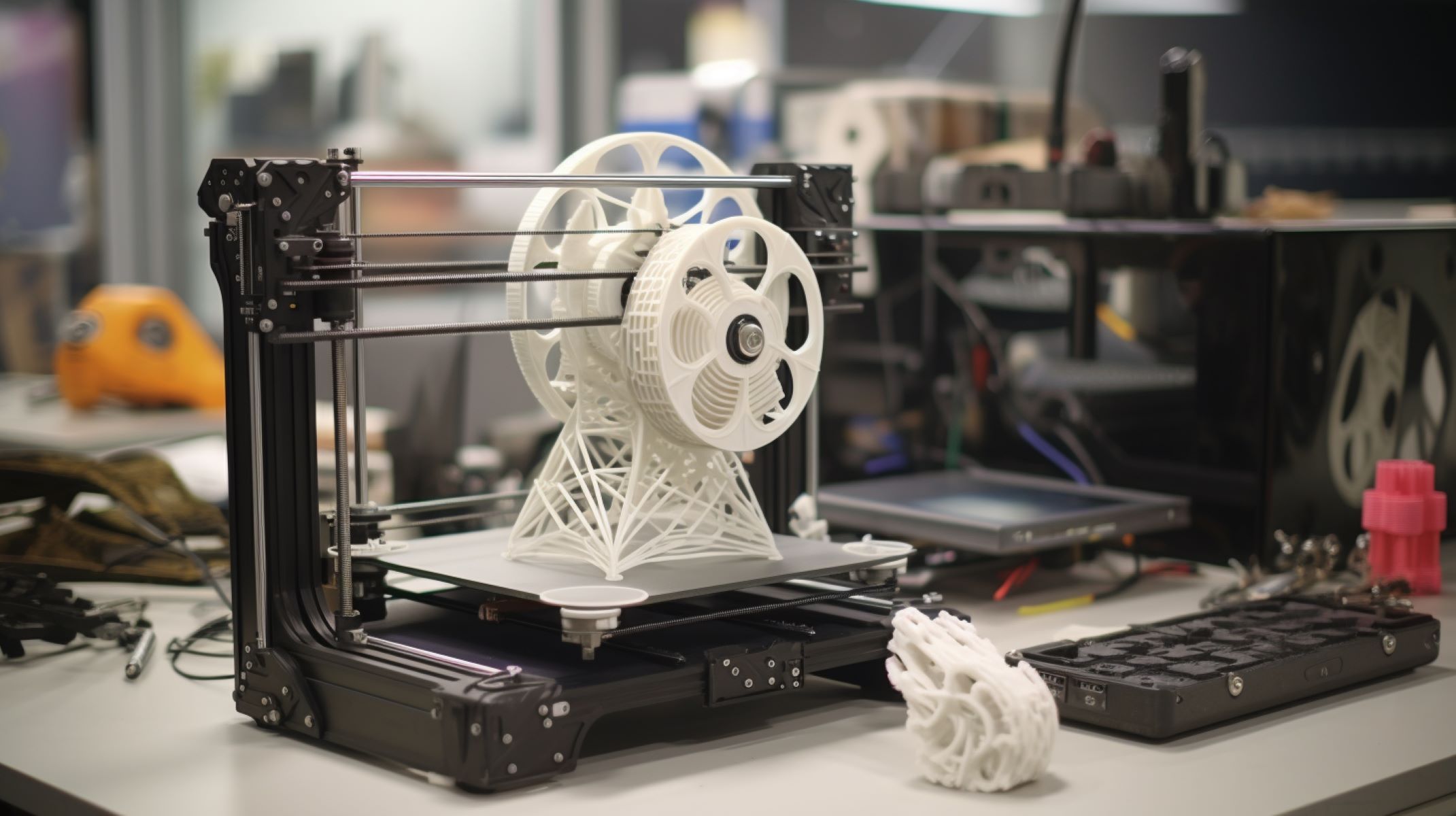
The Smallest Objects 3D Printers Can Create
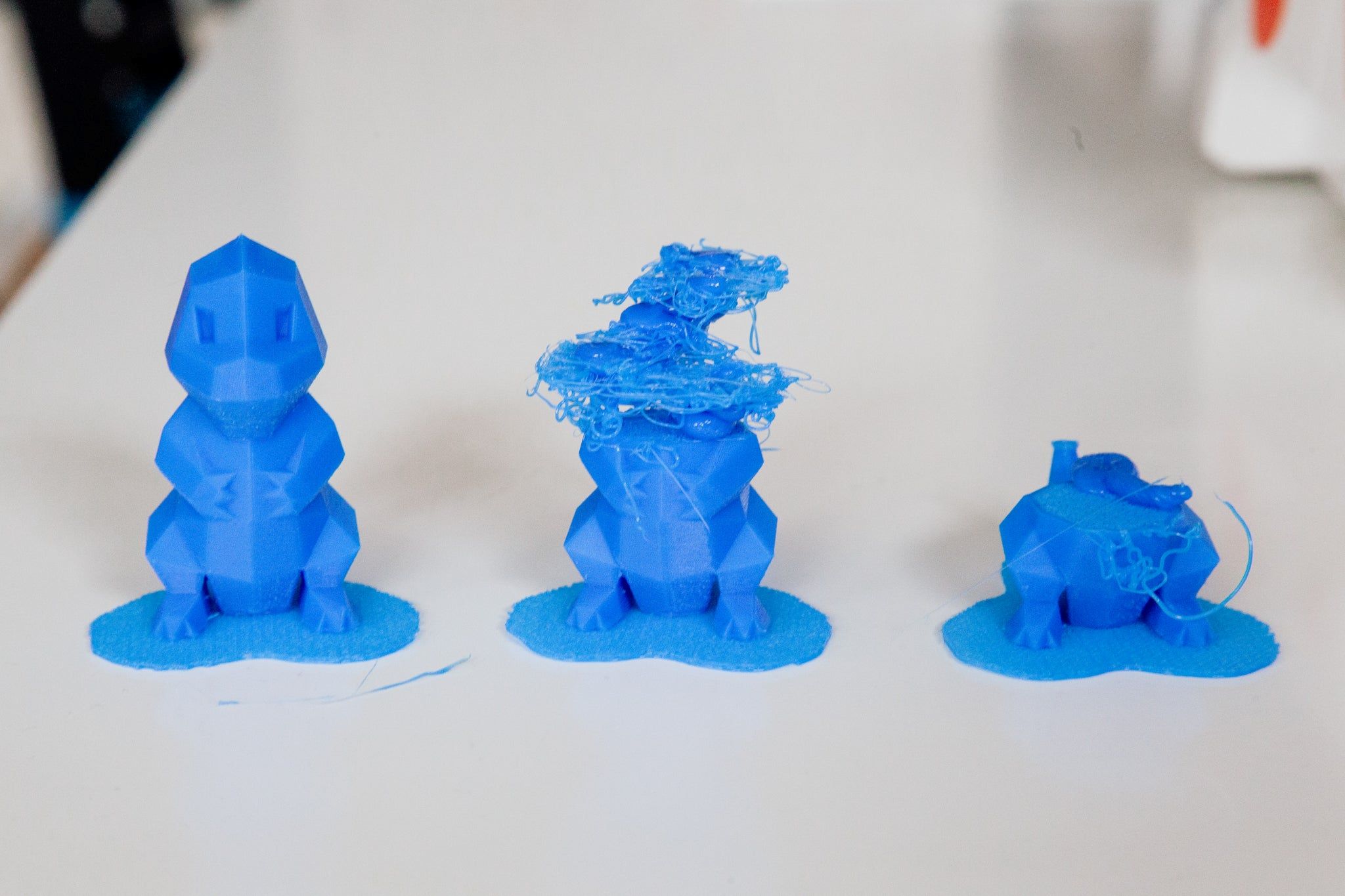
The capabilities of 3D printers have evolved significantly, enabling the creation of incredibly small and intricate objects with astonishing precision. While the achievable minimum print size varies across different 3D printing technologies and models, the boundaries of small-scale printing continue to be redefined as advancements propel the industry forward.
Microscopic details, intricate patterns, and delicate structures are within the grasp of modern 3D printers, thanks to their exceptional precision and fine control. From tiny mechanical components and jewelry to intricate figurines and architectural models, the range of small-scale objects that 3D printers can create is truly remarkable.
One notable application of small-scale 3D printing is the production of microfluidic devices. These intricate systems, often featuring channels and chambers at the micrometer scale, are utilized in various fields, including biomedical research, chemical analysis, and environmental monitoring. 3D printing enables the precise fabrication of these complex microfluidic structures, offering researchers and scientists unprecedented control over fluid manipulation at the microscale.
In the realm of electronics, 3D printers are capable of producing miniature circuitry and components with exceptional detail and accuracy. This opens doors to rapid prototyping of custom electronics and the creation of compact, intricately designed devices that were previously challenging to manufacture using traditional methods.
The jewelry industry has also embraced small-scale 3D printing, leveraging its capabilities to craft exquisitely detailed and intricate pieces. From ornate filigree designs to personalized pendants and earrings, 3D printers offer jewelry designers the freedom to bring their most intricate visions to life with unparalleled precision.
Furthermore, the field of microscale modeling and miniatures has witnessed a renaissance, with 3D printing enabling the creation of incredibly detailed architectural models, tabletop gaming miniatures, and figurines with intricate features and textures that were once painstakingly crafted by hand.
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, the boundaries of small-scale fabrication are continually being pushed, opening up new possibilities for creating intricate, detailed objects that were once deemed unattainable. The ability to produce small-scale objects with exceptional precision has not only revolutionized traditional manufacturing processes but has also sparked a wave of creativity and innovation across various industries.
Applications of Small 3D Printing
The capabilities of small-scale 3D printing have permeated numerous industries, unlocking a myriad of applications that harness the precision and intricacy offered by this transformative technology. From healthcare and electronics to art and engineering, small 3D printing has paved the way for innovative solutions and groundbreaking advancements across diverse domains.
Medical Advancements: In the realm of medicine, small-scale 3D printing has revolutionized the production of patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments. With the ability to create intricately detailed and customized medical devices, 3D printing has empowered healthcare professionals to offer personalized treatment solutions, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Microscale Robotics: Small 3D printing has played a pivotal role in the development of microscale robots and devices with intricate features. These miniature marvels find applications in fields such as targeted drug delivery, minimally invasive surgery, and precise manipulation of tiny components, offering unprecedented control at the microscale.
Jewelry and Fashion: The jewelry and fashion industries have embraced small-scale 3D printing to craft intricate, personalized accessories and ornate designs that were once challenging to produce using traditional methods. From bespoke jewelry pieces to avant-garde fashion accessories, 3D printing has unleashed a wave of creativity and customization in these artistic domains.
Electronics and Miniature Devices: Small 3D printing has empowered engineers and innovators to prototype and manufacture miniature electronic components, intricate circuitry, and compact devices with exceptional precision. This capability has led to advancements in miniaturization, enabling the development of compact, high-performance electronics for diverse applications.
Microfluidics and Biomedical Research: The precision offered by small-scale 3D printing has propelled the field of microfluidics, enabling the creation of intricate systems for precise fluid manipulation at the microscale. These microfluidic devices find applications in biomedical research, diagnostics, and drug development, offering researchers unprecedented control over complex fluidic processes.
Miniature Modeling and Art: Small 3D printing has redefined the art of miniature modeling, allowing artists and hobbyists to create intricately detailed architectural models, dioramas, and figurines with unparalleled precision. This has sparked a renaissance in miniature art, enabling the realization of intricate, lifelike scenes and sculptures.
These applications represent just a glimpse of the transformative potential of small-scale 3D printing. As the technology continues to advance, its impact across diverse industries is poised to grow, driving innovation, customization, and precision in ways previously unimaginable.
Conclusion
The realm of small-scale 3D printing is a testament to the remarkable convergence of precision, creativity, and technological innovation. As we’ve journeyed through the intricacies of 3D printing, exploring its underlying principles, the factors influencing minimum print size, and the diverse applications of small-scale fabrication, one thing becomes abundantly clear: the potential of 3D printing knows no bounds.
From the creation of microscale devices that revolutionize healthcare and robotics to the intricate detailing of jewelry and miniature art, small 3D printing has ushered in a new era of precision and customization. The ability to produce objects with microscopic intricacy has not only transformed traditional manufacturing processes but has also sparked a wave of creativity and innovation across diverse industries.
As technology continues to advance, the boundaries of small-scale 3D printing will undoubtedly be pushed further, unlocking new frontiers in precision engineering, personalized healthcare solutions, and artistic expression. The fusion of advanced materials, high-resolution printing, and intricate design capabilities is poised to redefine what is achievable on the small scale, inspiring a new wave of creativity and ingenuity.
As we look to the future, the potential applications of small 3D printing are as vast as the imagination itself. Whether it’s the creation of bespoke medical implants, the development of microscale robots, or the crafting of exquisitely detailed jewelry, small-scale 3D printing stands at the forefront of innovation, offering unparalleled precision and customization.
So, as we marvel at the intricacy of small 3D-printed objects and the transformative impact they have across industries, let us embrace the boundless potential of this technology. Small-scale 3D printing is not just about creating tiny objects; it’s about unlocking the power of precision, customization, and innovation in ways that were once unimaginable.
As we continue to explore the frontiers of small-scale 3D printing, let us remember that the smallest creations can often have the most significant impact, shaping the future of manufacturing, healthcare, art, and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Small Can A 3D Printer Print
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Small Can A 3D Printer Print”