Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is CAD In 3D Printing


Architecture & Design
What Is CAD In 3D Printing
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn about CAD in 3D printing and its application in architecture and design. Explore the benefits of using CAD software in creating innovative and precise models for your projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
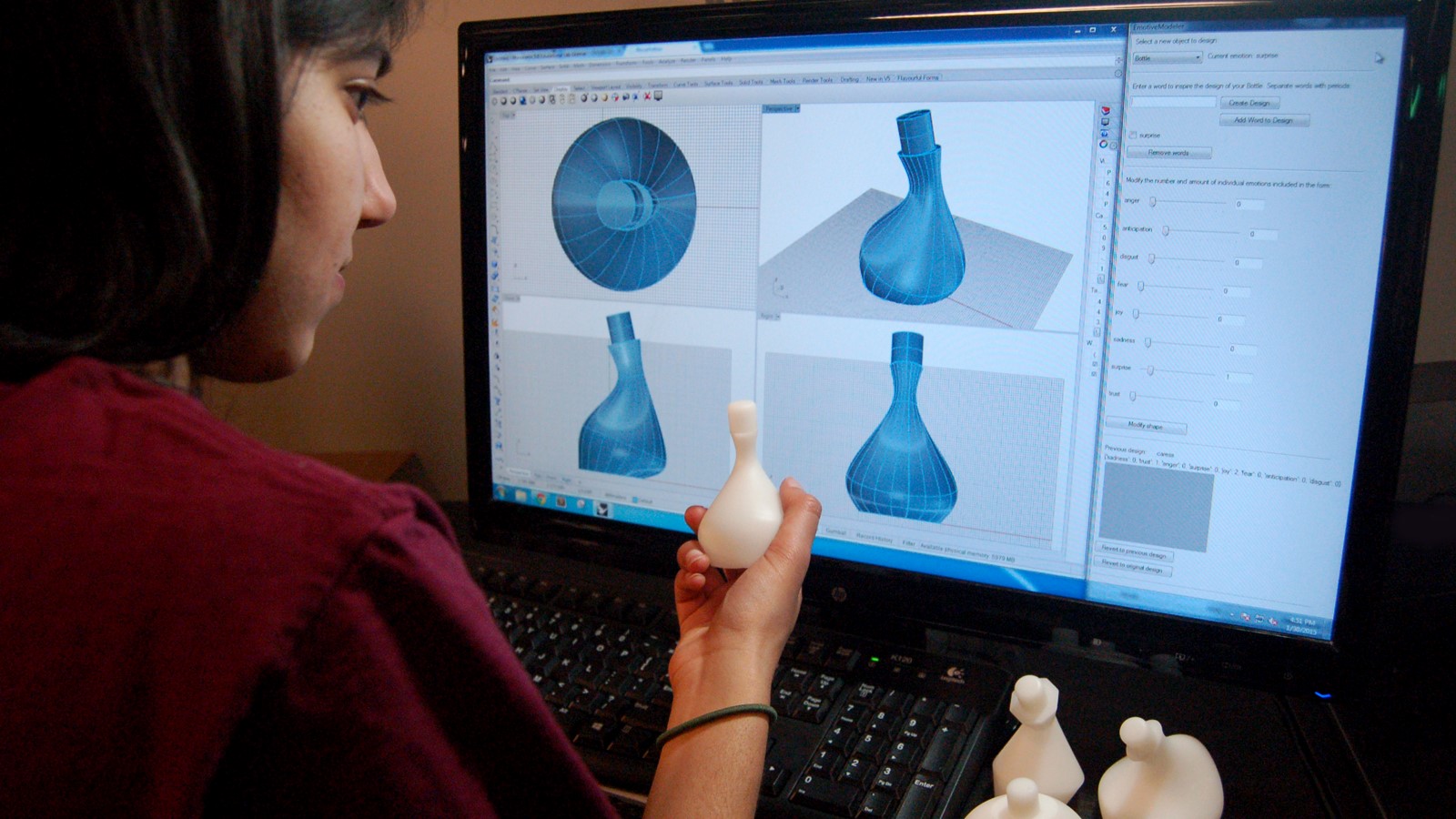
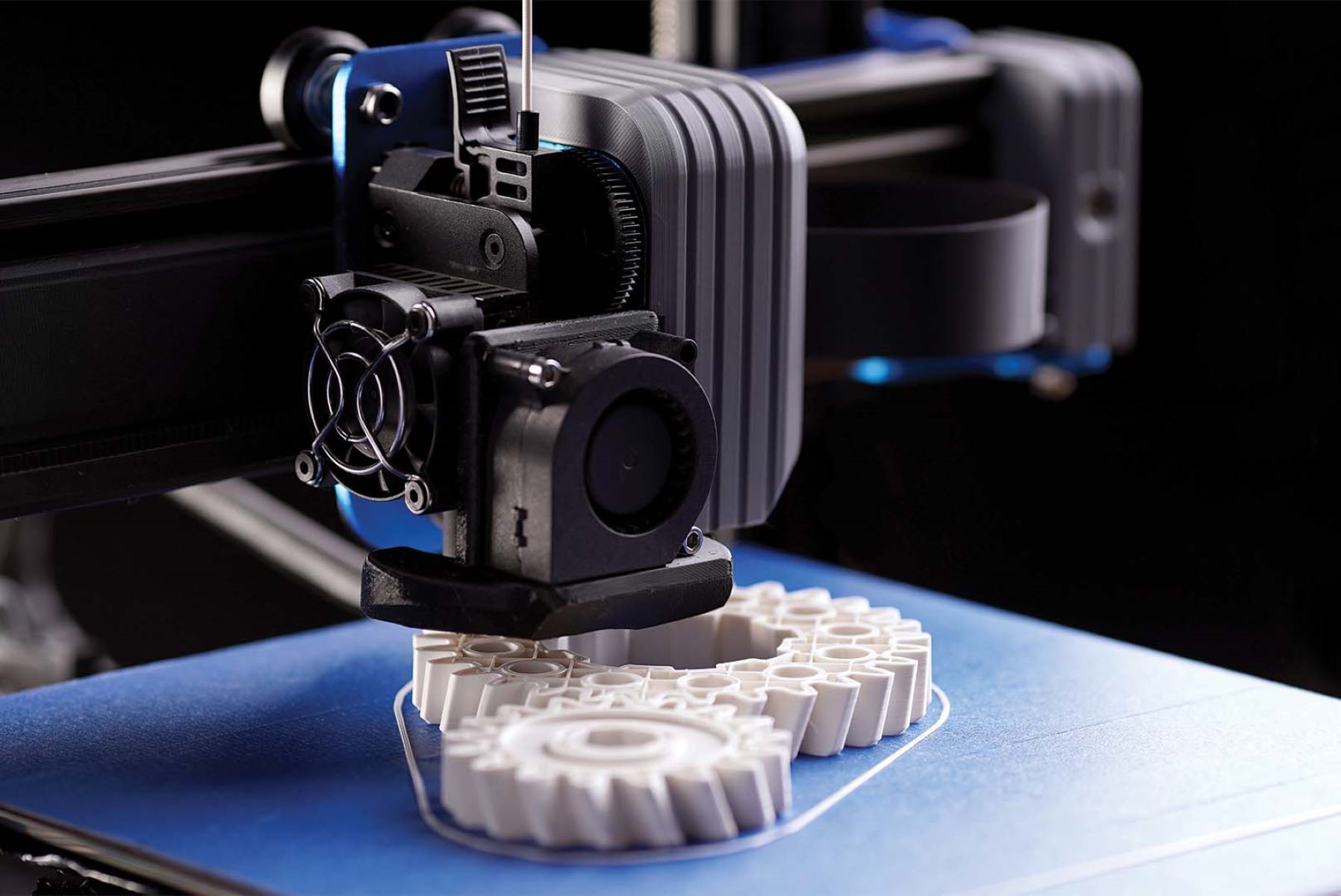
In the world of 3D printing, precision and accuracy are key. Designing intricate and complex objects requires a powerful tool that can bring imagination to life. This is where Computer-Aided Design (CAD) comes into the picture. CAD is a fundamental part of the 3D printing process, revolutionizing the way objects are designed and manufactured.
CAD is a software technology used by architects, engineers, and designers to create detailed, digital representations of objects. It enables them to visualize and manipulate their designs before they are physically brought to life through 3D printing.
In this article, we will explore the concept of CAD in the context of 3D printing. We will delve into its definition, its role in the 3D printing process, the benefits of using CAD in 3D printing, common CAD software used in the industry, and key terminology associated with CAD in 3D printing.
So, whether you are a 3D printing enthusiast, a professional designer, or simply curious about the technology, let us embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating world of CAD and its impact on 3D printing.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD is the backbone of 3D printing, enabling precise design creation, visualization, customization, and time/cost savings. Its collaborative features streamline the workflow, propelling innovation in the industry.
- Popular CAD software options for 3D printing, like AutoCAD and SolidWorks, offer diverse capabilities to unleash creativity. Understanding common CAD terminology enhances communication and navigation within the software.
Read more: What Is 3D CAD
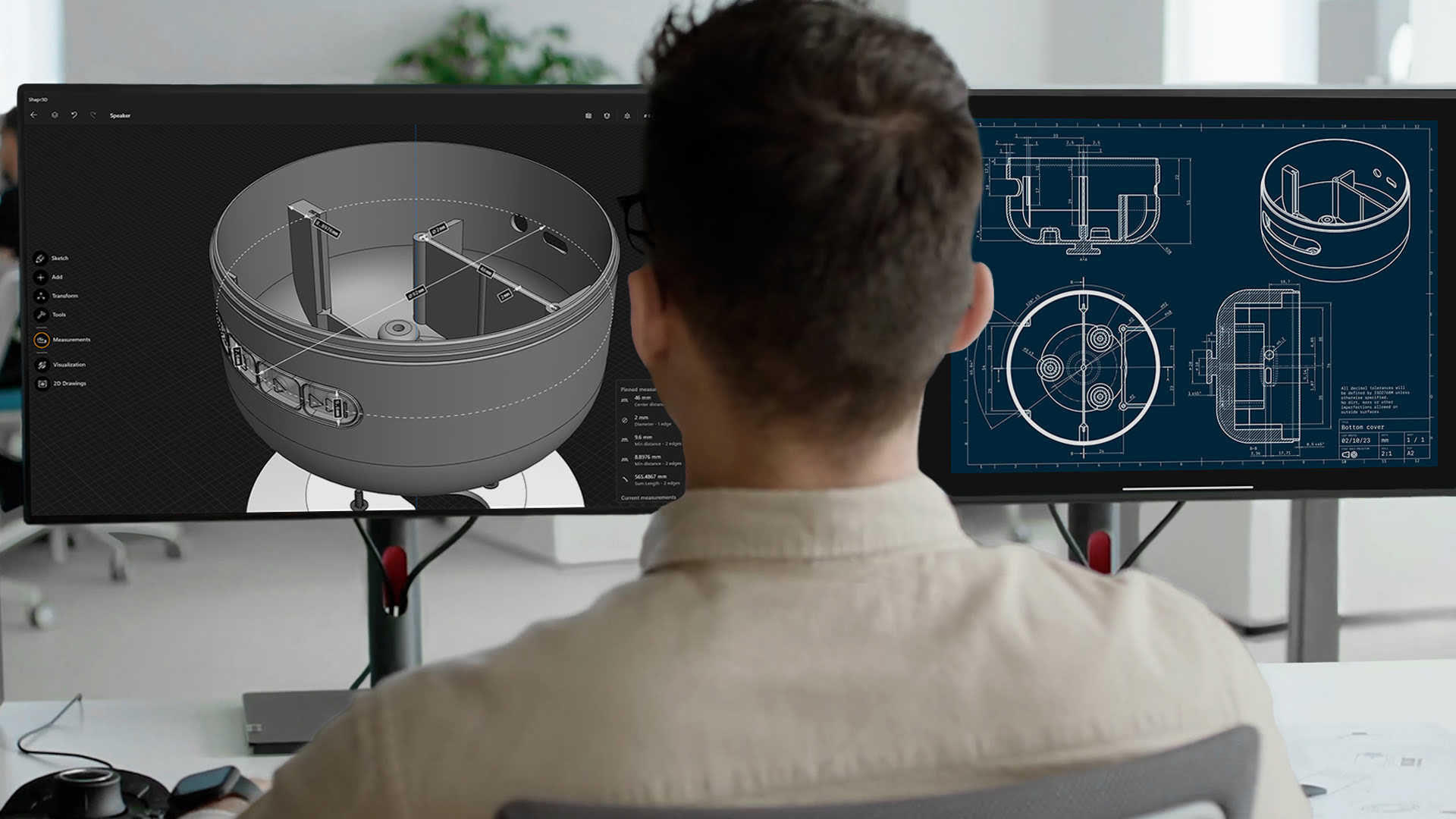
What is CAD?
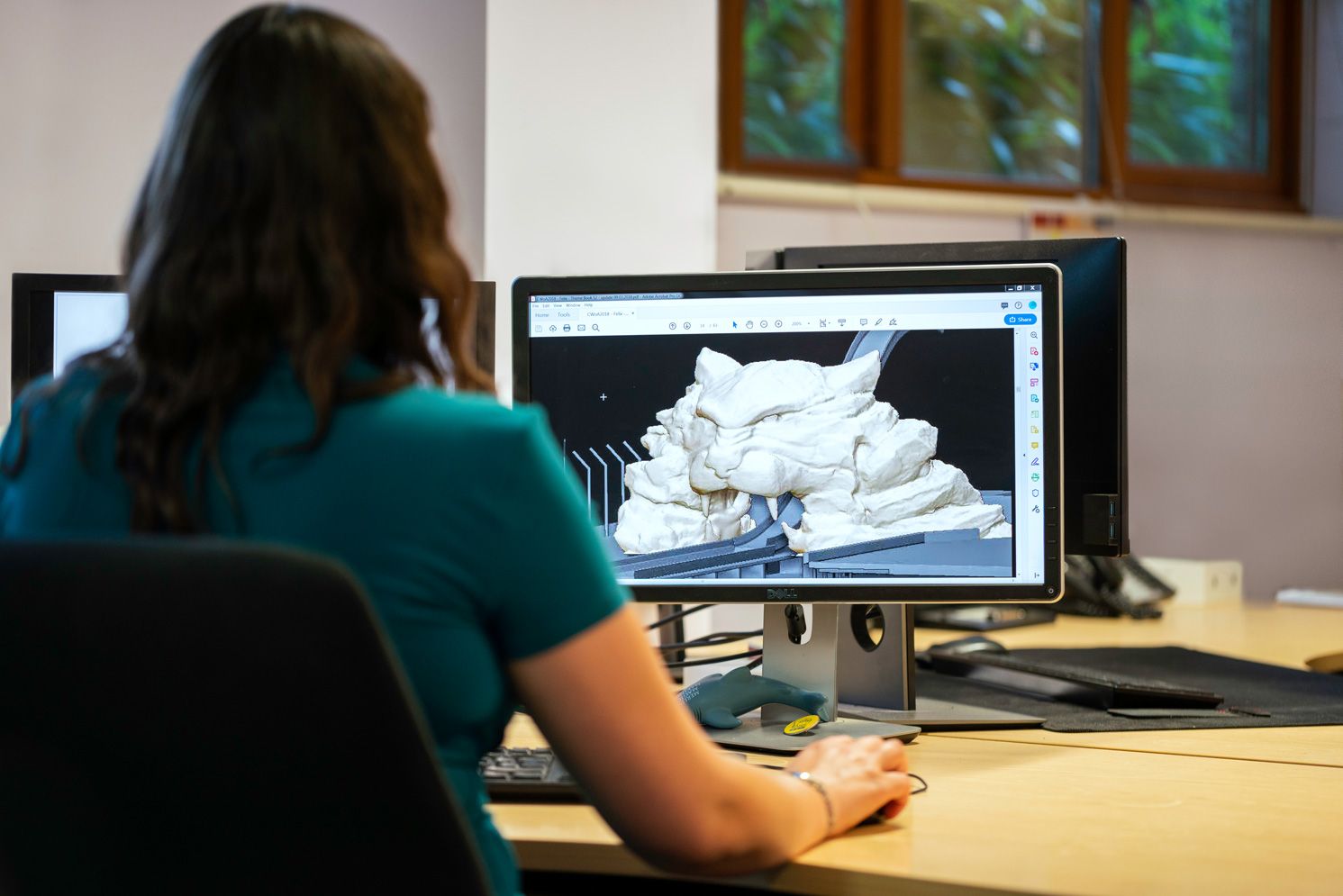
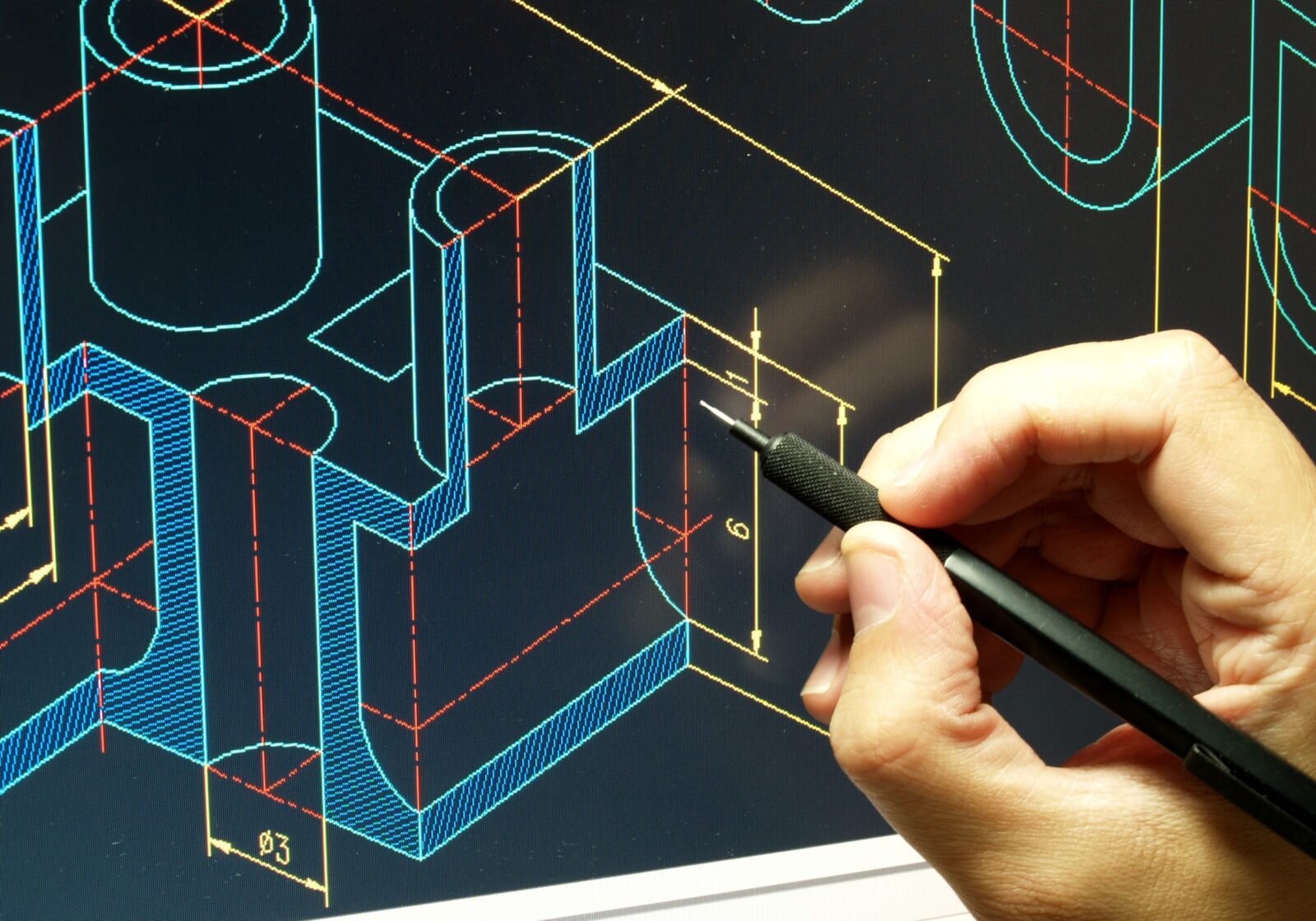
CAD, short for Computer-Aided Design, is a technology that enables designers to create digital representations of objects with precise measurements and specifications. It replaces traditional manual methods of drafting and designing, offering a more efficient and accurate approach to the creative process.
Using CAD software, designers can construct virtual models of their designs, incorporating various geometric shapes, textures, and dimensions. These models can be manipulated and visualized from multiple angles, providing a comprehensive view of the final product.
CAD software offers a wide range of tools and features that empower designers to explore their creativity and transform their ideas into tangible designs. From simple 2D drawings to complex 3D models, CAD software allows designers to create designs with intricate details, intricate geometries, and precise measurements.
With CAD, designers can make changes and modifications to their designs effortlessly. They can experiment with different materials, colors, and textures, allowing for quick iterations and improvements. This flexibility and agility are crucial in the context of 3D printing, as it enables designers to adapt their designs to the specific requirements and constraints of the printing process.
Moreover, CAD software facilitates collaboration and communication among designers, engineers, and stakeholders. Multiple users can work on the same design simultaneously, making real-time changes and sharing feedback. This collaborative approach streamlines the design process, reduces errors, and enhances overall productivity.
Overall, CAD serves as the foundation for the 3D printing process. It empowers designers to bring their ideas to life, unleashing their creativity and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
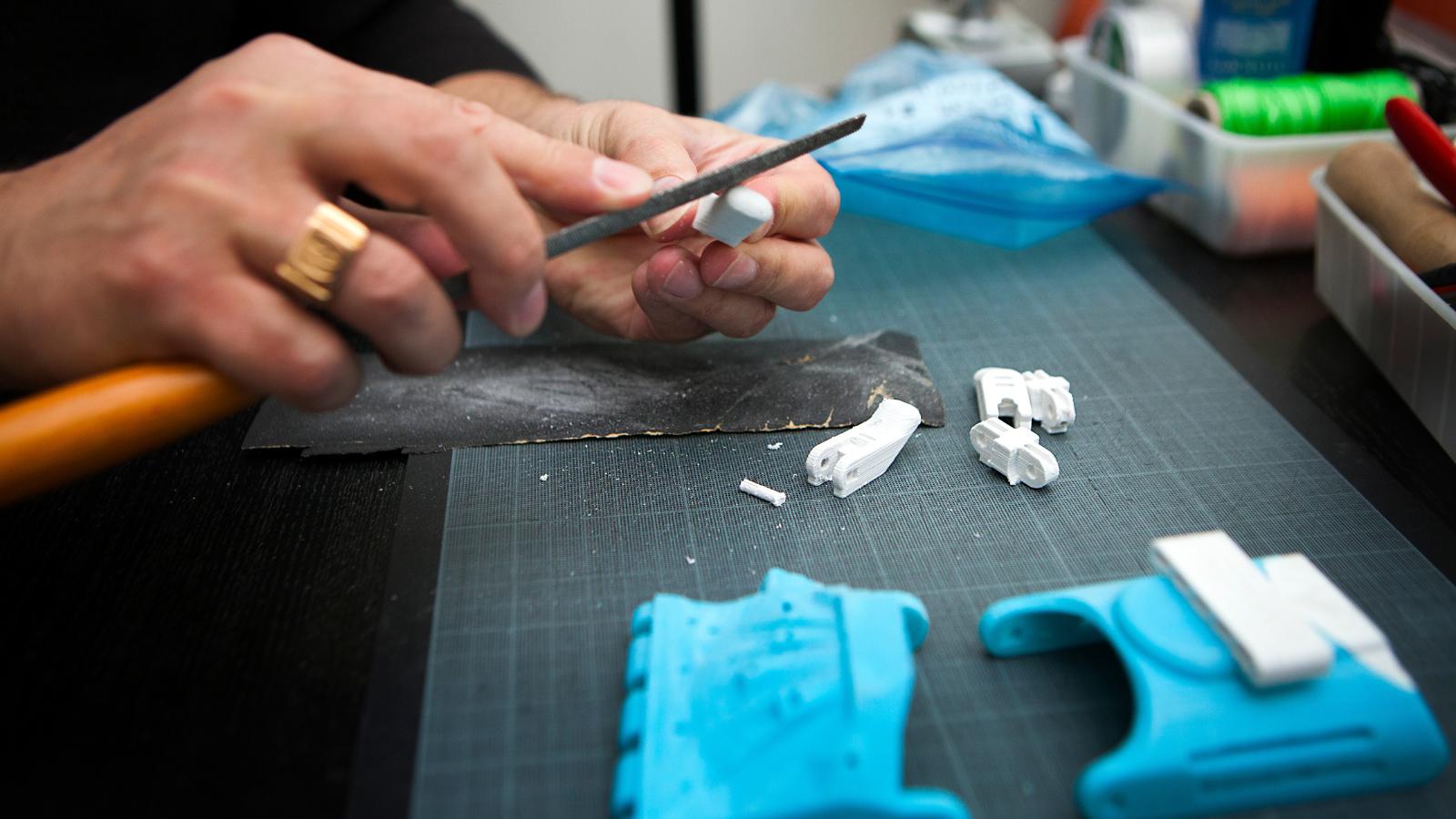
Role of CAD in 3D Printing
CAD plays a crucial role in the 3D printing process, acting as the bridge between the designer’s vision and the physical creation of the object. Here are some key ways in which CAD enhances the 3D printing workflow:
- Design Creation: CAD allows designers to create intricate and complex designs with precision and accuracy. It provides a digital canvas where designers can unleash their creativity and experiment with various geometries, shapes, and dimensions.
- Visualization: CAD software provides a visual representation of the design, allowing designers to see how the final object will look before it is printed. This visualization capability helps designers identify design flaws, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the final object meets their expectations.
- Design Optimization: CAD enables designers to optimize their designs for 3D printing. They can analyze the design and identify areas that may require support structures, improve printability, and enhance structural integrity. By iteratively refining their designs using CAD, designers can create objects that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functionally sound.
- Customization: 3D printing offers unparalleled customization possibilities, and CAD is the tool that brings this customization to life. With CAD, designers can easily modify designs to meet specific requirements, such as incorporating personalized elements or adapting the design to fit a particular purpose or user.
- Time and Cost Savings: CAD streamlines the design process, enabling faster iterations and reducing the need for physical prototypes. This not only saves time but also reduces costs associated with material wastage and iterative testing.
- Design Documentation: CAD software allows designers to keep a detailed record of their designs, including dimensions, materials, and other specifications. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future reference and enables easy replication or modification of designs.
Overall, CAD serves as the backbone of the 3D printing workflow, propelling the transformation of ideas into physical objects. Its capabilities in design creation, optimization, customization, and documentation empower designers to push the boundaries of innovation in the 3D printing industry.
Benefits of using CAD in 3D Printing
The integration of CAD software into the 3D printing process offers numerous benefits that revolutionize the way objects are designed and manufactured. Here are some of the key advantages of using CAD in 3D printing:
- Precision and Accuracy: CAD software allows designers to create highly precise and accurate designs, ensuring that the final printed object matches the intended specifications.
- Time and Cost Savings: CAD enables faster design iterations and reduces the need for physical prototypes, resulting in significant time and cost savings. It also minimizes material wastage by allowing designers to optimize designs for printability.
- Design Visualization: CAD provides a visual representation of the design before it is printed, allowing designers to identify potential design flaws and make necessary adjustments. This visualization capability helps ensure that the final printed object meets the desired aesthetic and functional requirements.
- Design Customization: With CAD, designers can easily customize their designs to meet specific requirements. This flexibility allows for personalized elements, customization for different users, and adaptation of designs to suit particular purposes.
- Design Optimization for 3D Printing: CAD software enables designers to optimize their designs for 3D printing, taking into account factors such as support structures, printability, and structural integrity. This optimization helps to achieve the best possible print quality and functionality of the object.
- Collaborative Workflow: CAD software facilitates collaboration among designers, engineers, and stakeholders. Multiple users can work on the same design simultaneously, making real-time changes and sharing feedback, which improves overall productivity and eliminates communication barriers.
- Documentation and Version Control: CAD allows designers to keep a comprehensive record of their designs, including dimensions, materials, and other specifications. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future reference and ensures consistency in design versions.
- Complex Geometry and Intricate Details: CAD software enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate details that would be challenging to achieve using traditional design methods. This capability expands the design possibilities in 3D printing and opens up new avenues for innovation.
In summary, CAD empowers designers to create highly accurate and customized designs, optimize them for 3D printing, and streamline the design workflow. The integration of CAD in 3D printing brings significant advantages in terms of precision, time and cost savings, collaboration, customization, and design complexity, propelling the industry to new heights of creativity and efficiency.
When designing for 3D printing, always use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create precise and accurate 3D models. This will ensure that your designs are suitable for 3D printing and will result in high-quality prints.
CAD Software for 3D Printing
When it comes to 3D printing, there is no shortage of CAD software options available. These software tools provide designers with powerful capabilities to create, modify, and optimize designs for the 3D printing process. Here are some popular CAD software options specifically tailored for 3D printing:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is a well-known CAD software that offers a comprehensive set of tools for 2D and 3D design. It provides features specifically designed for 3D printing, allowing designers to create precise models and generate 3D printable files.
- Fusion 360: Fusion 360, developed by Autodesk, is a cloud-based CAD software that combines mechanical, industrial, and 3D design. It provides an integrated platform for designing, manufacturing, and 3D printing, making it a popular choice among professionals and hobbyists alike.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a widely used CAD software that offers powerful 3D modeling capabilities. It provides advanced tools for designing complex objects and optimizing designs for 3D printing, making it a preferred choice for engineering and industrial applications.
- Tinkercad: Tinkercad is a beginner-friendly CAD software that offers a simple and intuitive interface. It is widely used by educators and hobbyists to introduce 3D modeling concepts and create basic designs for 3D printing.
- SketchUp: SketchUp is a versatile CAD software that offers both a free and a professional version. It provides a user-friendly interface and a wide range of tools for 3D modeling, making it suitable for architects, designers, and hobbyists.
- Onshape: Onshape is a collaborative cloud-based CAD software that allows multiple users to work on the same design simultaneously. It offers robust 3D modeling capabilities and seamless integration with 3D printing workflows.
- FreeCAD: FreeCAD is an open-source parametric CAD software that allows designers to create complex 3D designs. It offers a range of features suitable for 3D printing, such as generating 3D printable files and analyzing designs for printability.
These are just a few examples of CAD software options available for 3D printing. Each software has its own strengths and focuses, catering to different user requirements and skill levels. It’s important for designers to explore and experiment with different CAD software to find the one that best suits their needs and preferences.
Whether you’re a professional designer, an enthusiast, or someone curious about 3D printing, these CAD software options provide the necessary tools and features to bring your designs to life through the exciting world of 3D printing.
Read more: What Does CAD Stand For In 3D Printing
Common CAD Terminology in 3D Printing
When diving into the world of CAD for 3D printing, it’s helpful to familiarize yourself with some common terminology. Understanding these terms will enable you to navigate through the software and communicate effectively with others in the industry. Here are some key CAD terminology frequently used in the context of 3D printing:
- Model: A digital representation of an object created using CAD software. It includes the geometric shape, dimensions, and other properties of the design.
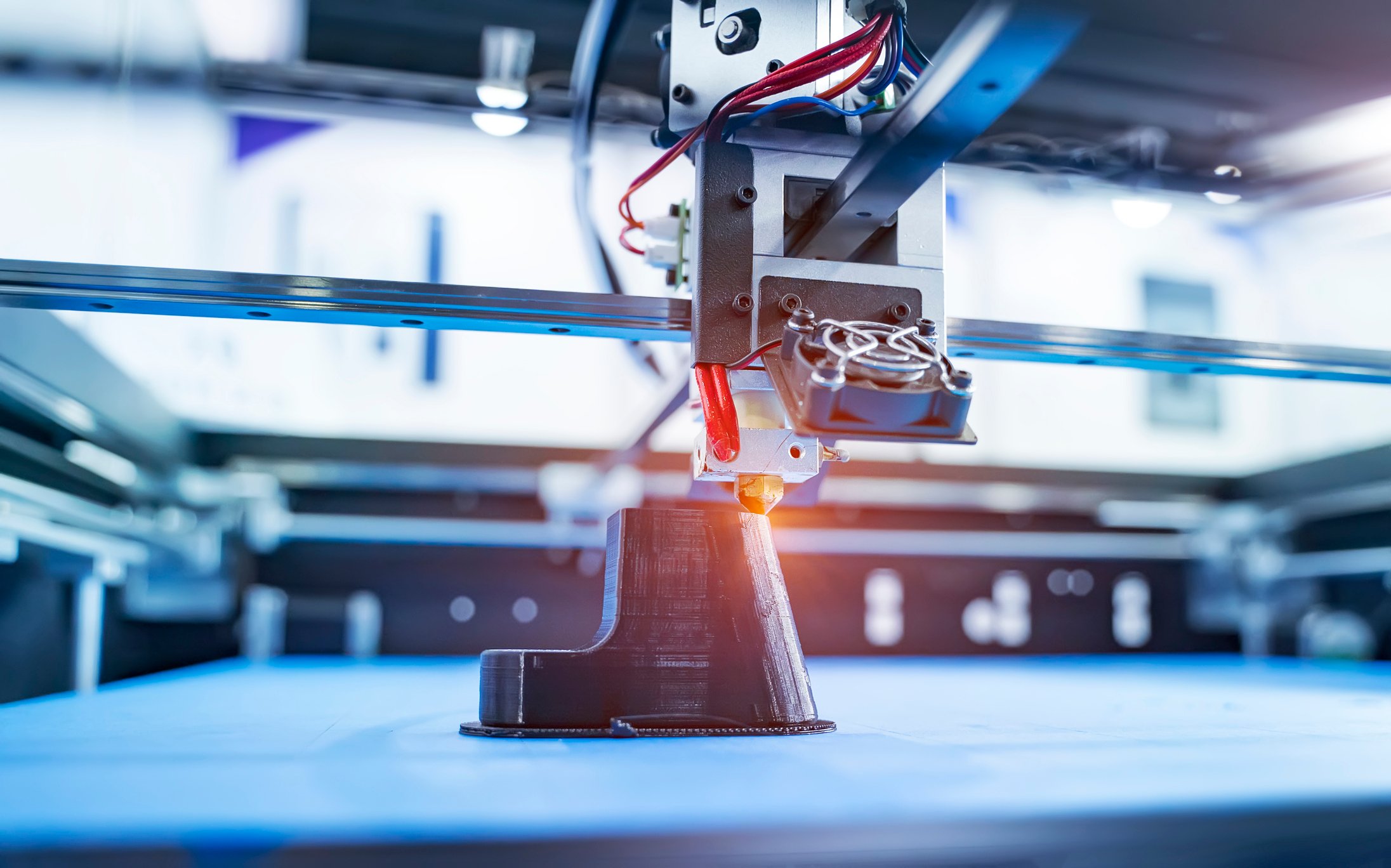
- Extrusion: The process of creating a 3D object by adding material layer by layer. In CAD software, it involves creating a 2D profile and extruding it to give it depth and form.
- Boolean Operations: Operations used to combine or subtract one or more 3D shapes to create complex forms. Common boolean operations include union, difference, and intersection.
- Fillet/Chamfer: Filleting refers to rounding off sharp edges or corners of a design, while chamfering involves creating an angled edge or bevel.
- Support Structures: Temporary structures generated by CAD software to support overhangs and bridges in a 3D print. They are designed to be easily removed after printing.
- Infill: The pattern or density of material used to fill the internal structure of a 3D printed object. In CAD software, infill can be adjusted to balance structural integrity with material usage.
- Layer Height: The thickness of each layer in a 3D printed object. It is defined in the CAD software and affects the level of detail and print time.
- File Format: The standardized format in which CAD files are saved. Common file formats for 3D printing include STL (Standard Triangle Language) and OBJ (Object).
- Scaling: Adjusting the size of a design in CAD software. Scaling is used to make objects larger or smaller without affecting their proportions.
- G-code: A numerical control language used to control 3D printers. It contains instructions for the movement and extrusion of the printer’s nozzle based on the CAD design.
These are just a few examples of the many terminology used in CAD for 3D printing. As you explore the software and engage in the 3D printing community, you will come across more specialized terms and techniques. Continual learning and staying up-to-date with industry advancements will significantly enhance your CAD skills and maximize your potential as a 3D printing enthusiast or professional.
Conclusion
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, has become an essential component of the 3D printing process. It empowers designers to create intricate and precise digital models, optimize designs for printability, and visualize the final product before it is physically produced. CAD software offers a wide range of tools and features that enhance the creativity, efficiency, and collaboration of designers in the 3D printing industry.
By utilizing CAD software, designers can achieve unparalleled precision, customize designs to meet specific requirements, and optimize designs for 3D printing. This enables faster iterations, reduces costs, and wastage, and allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate details that would be difficult to achieve using traditional design methods.
Furthermore, CAD software facilitates collaboration and communication among designers, engineers, and stakeholders. It allows for real-time changes, feedback sharing, and simultaneous work on the same design, eliminating communication barriers and improving productivity.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and significance of CAD in 3D printing, the role it plays in the design process, the benefits it offers, common CAD software options, and key terminology associated with CAD in 3D printing.
As the field of 3D printing continues to advance, CAD will continue to serve as a critical tool in driving innovation and transforming ideas into physical objects. Whether you are a professional designer, an enthusiast, or simply interested in the fascinating world of 3D printing, understanding and harnessing the power of CAD will unlock new possibilities and propel you towards creating unique and remarkable designs.
So, embrace the world of CAD in 3D printing, explore the software options available, and let your imagination soar as you bring your digital designs to life through the extraordinary process of 3D printing.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is CAD In 3D Printing
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is CAD In 3D Printing”