Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is 3D Printing Construction


Building & Construction
What Is 3D Printing Construction
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn about the innovative technology of 3D printing in construction, revolutionizing the building-construction industry with its cost-efficiency and geometric freedom.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Construction has always been a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, requiring extensive planning, skilled labor, and the use of traditional building materials. However, in recent years, a new technology called 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer in the field of construction. With its ability to create complex and customized structures with speed and precision, 3D printing is revolutionizing the way we build.
So, what exactly is 3D printing? Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing involves layering materials to create three-dimensional objects based on a digital design. This process offers numerous advantages over traditional construction methods, such as greater design freedom, reduced waste, and improved efficiency.
In the construction industry, 3D printing is being used to create entire buildings, as well as individual components such as walls, floors, and columns. By utilizing 3D printers capable of handling various construction materials, including concrete, plastic, and even metal, architects and engineers are able to construct structures that are stronger, more durable, and more efficient than ever before.
The benefits of 3D printing in construction are vast. Time and cost savings are among the most significant advantages. By automating the construction process and reducing the need for manual labor, 3D printing can significantly shorten project timelines and eliminate costly errors. Additionally, the precise nature of 3D printing allows for optimal material usage, minimizing waste and lowering overall construction costs.
Furthermore, 3D printing unlocks a world of design possibilities. Traditional construction methods often have limitations when it comes to intricate designs or unique shapes. With 3D printing, architects can let their creativity flow and bring their wildest design concepts to life. Complex geometries, curved structures, and intricate ornamentation can all be achieved using 3D printing technology.
However, as with any emerging technology, there are also challenges and limitations associated with 3D printing in construction. One major hurdle is the scalability and adaptability of the technology. While 3D printing has been successfully used to construct small-scale structures, such as houses or small office buildings, there are still limitations in terms of printing larger structures and integrating complex systems like plumbing and electrical work.
Another challenge is the need for specialized skills and knowledge to operate and maintain 3D printing equipment. As the technology is relatively new, there is a shortage of trained professionals who understand the intricacies of 3D printing in construction. This shortage may slow down the widespread adoption of 3D printing in the construction industry.
Despite these challenges, 3D printing is already being implemented in various construction projects around the world. From the construction of affordable housing to the creation of intricate architectural masterpieces, the potential applications of 3D printing in construction are diverse and exciting.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the benefits of 3D printing in construction, explore the current applications of the technology, and discuss its future possibilities and innovations. Through this exploration, we will gain a better understanding of how 3D printing is shaping the future of the construction industry.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D printing in construction offers cost savings, design freedom, and reduced waste. It revolutionizes the industry with faster timelines, intricate designs, and sustainable practices, shaping the future of building.
- Despite challenges, 3D printing showcases innovative applications in building construction, modular design, and architectural elements. Future possibilities include sustainable practices, multi-material printing, and space exploration, driving the industry towards efficiency and creativity.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects through the layering of materials. Unlike traditional manufacturing processes that involve subtractive methods, such as cutting or drilling, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer using a computer-controlled printer.
The process begins with a digital design of the object, created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This design is then sent to a 3D printer, which interprets the design and starts the printing process. The printer deposits thin layers of material, such as plastic, metal, or even concrete, onto a platform. These layers gradually build upon each other until the final object is complete.
3D printing offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. One of the biggest benefits is the level of customization it allows. With 3D printing, designers have the freedom to create objects with intricate geometries and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional methods.
Another advantage of 3D printing is the ability to reduce waste. Traditional manufacturing often involves cutting or molding materials, resulting in significant material waste. In contrast, 3D printing only uses the exact amount of material needed to create the object, minimizing waste and optimizing material usage.
Furthermore, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and iteration. Designers can quickly produce a physical model of their concept and make modifications as needed. This accelerated design process allows for quicker iterations and ultimately leads to faster product development timelines.
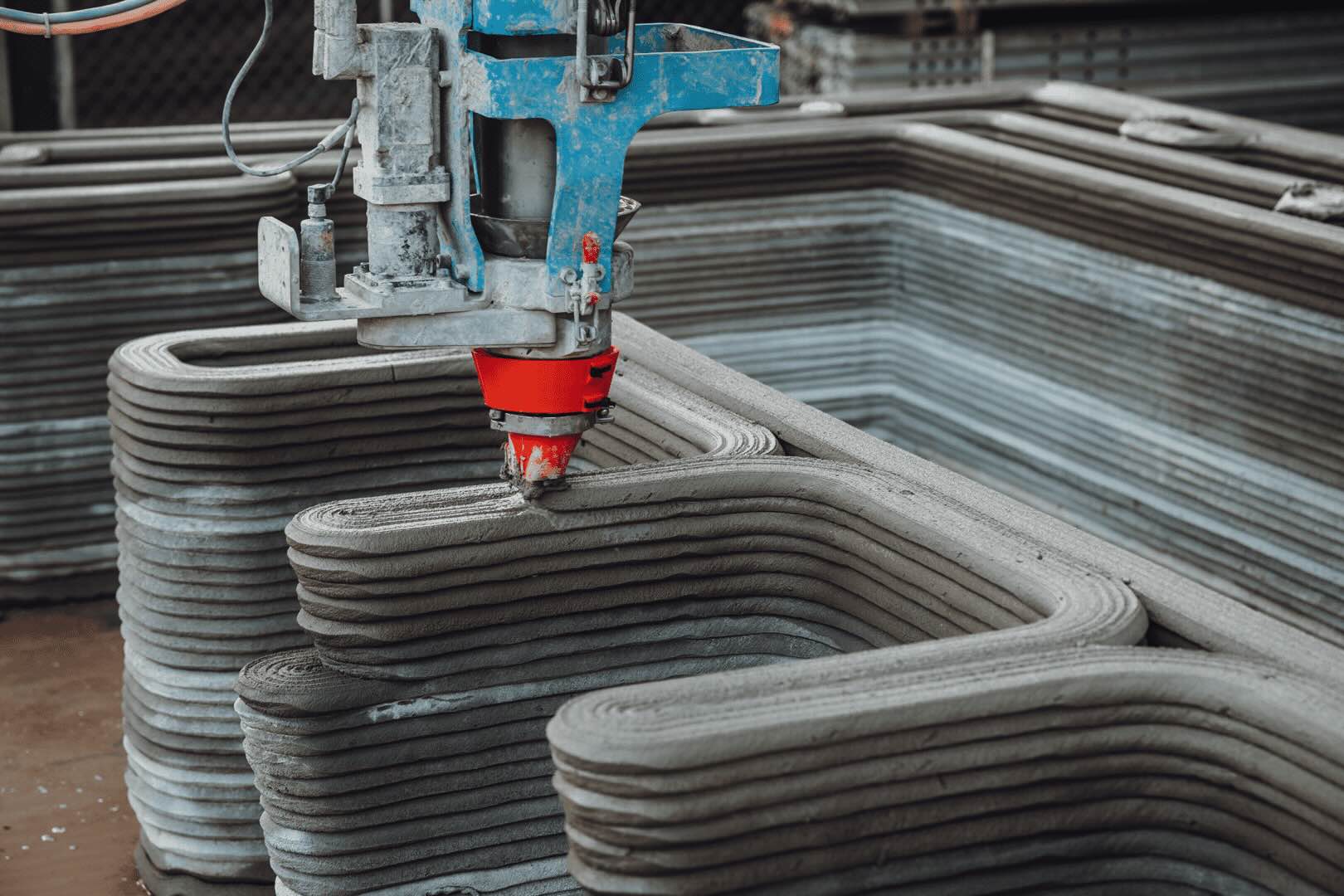
In recent years, 3D printing has expanded its capabilities into the realm of construction. Construction 3D printing, also known as 3D concrete printing, involves using specially designed 3D printers that can handle the challenges of working with construction materials like concrete.
The process of 3D concrete printing typically involves the precise deposition of layers of concrete in a pre-determined pattern, following a digital design. As each layer is deposited, it bonds with the previous layer, gradually building up the structure from the ground up.
3D printing in construction offers numerous benefits. The technology allows for the creation of complex architectural designs with ease, enabling architects and engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible in the built environment. It also enables the construction of structures that are more efficient, sustainable, and durable.
With its ability to automate and streamline the construction process, 3D printing can significantly reduce labor costs and construction timelines. The precise nature of 3D printing also ensures consistent quality and eliminates human error, resulting in higher construction standards.
As 3D printing continues to advance, it holds the potential to transform the construction industry. However, challenges such as scalability, regulatory hurdles, and material limitations still need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
Overall, 3D printing has already shown great promise in various industries, including healthcare, aerospace, and automotive. In the construction sector, the technology is poised to reshape the way buildings are designed and constructed, offering innovative solutions and pushing the boundaries of architectural possibilities.
3D Printing in Construction
3D printing is revolutionizing the construction industry by offering innovative solutions and transforming the way buildings are designed and constructed. With its ability to create complex structures with speed and precision, 3D printing is gaining traction as a viable alternative to traditional construction methods.
One of the key advantages of 3D printing in construction is the ability to automate and streamline the construction process. By utilizing 3D printers capable of handling construction materials like concrete, architects and engineers can create entire buildings or individual components with minimal human intervention. This automation not only reduces labor costs but also significantly shortens construction timelines.
Moreover, 3D printing technology allows for the creation of highly customized and intricate designs. Traditional construction methods often have limitations when it comes to complex geometries or unique shapes. With 3D printing, architects can realize their creative visions and construct buildings with unprecedented architectural freedom.
Another benefit of 3D printing in construction is the reduction of material waste. Traditional construction methods often involve cutting, shaping, and assembling materials, leading to significant waste generation. In contrast, 3D printing only uses the precise amount of material required to create the structure, minimizing waste and optimizing resource utilization.
Furthermore, 3D printed structures can be more efficient and sustainable. The layer-by-layer construction process enables the integration of features like hollow cavities and internal channels, resulting in lightweight yet sturdy structures. This lightweight nature can lead to energy savings in transportation and reduced environmental impact during construction.
In addition to these benefits, 3D printing offers the potential for cost savings. While the initial investment in 3D printing equipment may be significant, the long-term savings in labor and material costs can outweigh the upfront expenses. As the technology continues to develop and become more widely adopted, the cost of 3D printing equipment is also expected to decrease, making it more financially accessible.
However, it’s important to note that there are still challenges and limitations associated with 3D printing in construction. Scaling up the technology to construct larger buildings and achieving regulatory compliance remain areas of concern. Additionally, integrating complex building systems, such as plumbing and electrical work, into 3D printed structures is still a technological challenge that needs to be addressed.
Despite these challenges, numerous construction projects around the world have successfully implemented 3D printing technology. From the construction of affordable housing in developing countries to the creation of intricate architectural masterpieces, 3D printing is showcasing its potential and gaining recognition as a viable construction method.
The continued advancements in 3D printing technology, coupled with ongoing research and development efforts, are likely to overcome the current limitations and drive the widespread adoption of 3D printing in the construction industry. As the technology evolves, we can expect to see further innovations and applications that will transform the way we build and shape the world around us.
Benefits of 3D Printing Construction
3D printing in construction is unlocking a range of benefits that are revolutionizing the industry. From cost savings to design flexibility, this innovative technology offers numerous advantages over traditional construction methods. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of 3D printing in construction:
- Cost Savings: 3D printing can significantly reduce construction costs. By automating the construction process and minimizing labor, 3D printing eliminates the need for costly manual labor. Additionally, the precise nature of 3D printing reduces material waste, optimizing resource usage and reducing material costs.
- Time Efficiency: Compared to traditional construction methods, 3D printing offers faster construction timelines. The use of 3D printers automates the construction process, allowing for rapid and continuous printing. This leads to shorter project timelines, enabling buildings to be constructed in a fraction of the time compared to conventional methods.
- Design Freedom: 3D printing provides unparalleled design freedom and flexibility. Architects and designers can create complex and intricate structures that were once difficult or impossible to build using traditional construction methods. This allows for more innovative and customizable designs, giving architects the ability to bring their creative visions to life.
- Reduced Construction Waste: Traditional construction methods often generate a significant amount of waste. In contrast, 3D printing minimizes material waste by using only the exact amount of material needed for the construction process. This not only reduces costs but also contributes to a more sustainable construction industry by lowering environmental impact.
- Improved Quality and Precision: With 3D printing, the construction process becomes more precise and consistent. The layer-by-layer deposition ensures a high level of accuracy, resulting in structures with consistent quality. This eliminates human error and ensures that each element of the building meets the desired specifications.
- Enhanced Structural Performance: 3D printing technology allows for the creation of structurally optimized designs. By using computational algorithms, architects and engineers can design structures that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient. This results in buildings that can withstand various environmental conditions and offer improved performance.
- Customization and Personalization: 3D printing enables the customization and personalization of construction elements. It allows for the creation of unique shapes, patterns, and textures that cater to specific design preferences and functional requirements. This level of customization offers a higher level of client satisfaction and opens up new possibilities in architectural design.
- Sustainability: 3D printing in construction aligns with sustainable practices. It reduces material waste and can incorporate sustainable construction materials, such as recycled concrete or biodegradable compounds. Additionally, the lightweight nature of 3D printed structures can contribute to energy savings during transportation and reduced carbon emissions.
These are just a few of the many benefits that 3D printing brings to the construction industry. As the technology continues to advance and overcome current limitations, we can expect further improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. The future of construction is being reshaped by the potential of 3D printing, offering a glimpse into a more sustainable, customizable, and innovative built environment.
When using 3D printing for construction, ensure that the materials used are suitable for the specific project requirements, and that the printing process is carefully monitored to maintain structural integrity.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing Construction
While 3D printing construction holds immense potential, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption in the industry. Understanding these challenges is essential for realizing the full benefits of 3D printing technology. Let’s delve into some of the key challenges and limitations:
- Scalability: Scaling up 3D printing technology to construct larger buildings remains a significant challenge. While 3D printing has been successfully used to create small-scale structures, such as houses or office buildings, the technology still needs to overcome technical limitations when it comes to printing larger and taller structures.
- Integration of Complex Systems: Incorporating complex building systems, such as plumbing, electrical work, or HVAC systems, into 3D printed structures can be challenging. Integrating these systems seamlessly requires careful planning and coordination, as well as advancements in multi-material 3D printing capabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adapting existing building codes and regulations to accommodate 3D printed structures poses a challenge. The regulatory framework needs to be updated to ensure that 3D printed buildings meet safety and structural requirements. This process requires collaboration between regulatory bodies, architects, engineers, and industry stakeholders.
- Material Limitations: 3D printing construction is currently limited by the range of materials that can be used. While materials like concrete are commonly used, the development of suitable materials for 3D printing construction, including metals and composites, is still ongoing. Enhancing the range of construction-grade materials would open up more possibilities for 3D printing in the industry.
- Training and Expertise: There is a shortage of skilled professionals who understand the intricacies of 3D printing in construction. The technology is relatively new, and specialized training programs are needed to equip architects, engineers, and construction workers with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively operate and maintain 3D printing equipment.
- Cost and Affordability: While the cost of 3D printing equipment and materials has been decreasing over time, it still remains a significant investment for many construction companies. The upfront costs associated with adopting 3D printing technology can be a barrier, especially for smaller construction firms. However, as the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, it is expected that costs will continue to decrease.
- Perception and Acceptance: 3D printing construction is still a relatively unfamiliar concept to many professionals in the construction industry. Building trust and acceptance among architects, engineers, and clients is essential for wider adoption. Demonstrating the benefits and successful implementation of 3D printing technology through pilot projects and case studies can help overcome resistance and promote its acceptance.
Despite these challenges and limitations, progress is being made in overcoming these hurdles. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving scalability, material options, and the integration of complex systems. As the technology continues to evolve and gain acceptance, we can expect to see advancements that address these challenges and drive the widespread industrial adoption of 3D printing in construction.
While it may take time to overcome these limitations, the potential benefits of 3D printing in construction make it an exciting area of innovation and exploration. With continued collaboration, investment, and technological advancements, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry and shape the future of how we build.
Read more: What Is CAD In 3D Printing
Current Applications of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing technology is already making a significant impact in the construction industry, with a range of innovative applications and successful projects around the world. These applications showcase the potential of 3D printing to transform the way we build and construct structures. Here are some of the current applications of 3D printing in construction:
- Building Construction: One of the most notable applications of 3D printing in construction is the creation of entire buildings. 3D printing can be used to fabricate structural components, such as walls, floors, and even entire facades. Notable examples include the construction of a 3D printed office building in Dubai, a 3D printed residential building in Germany, and the world’s first 3D printed metal bridge in the Netherlands.
- Modular Construction: 3D printing is being utilized for modular construction, where pre-fabricated modules are 3D printed off-site and then assembled on-site. This approach allows for faster construction and improved efficiency. Modular 3D printed buildings can be easily customized, making them suitable for applications such as affordable housing or disaster relief solutions.
- Architectural Elements: 3D printing is being used to create intricate architectural elements, such as decorative facades, ornamental features, and sculptural pieces. The design freedom offered by 3D printing enables architects to experiment with complex and intricate designs that were once difficult or costly to achieve using traditional methods.
- Concrete Components: 3D concrete printing is a prominent application of 3D printing in construction. By using specially formulated concrete mixes and large-scale 3D printers, it is possible to print concrete walls, columns, and other structural elements. This approach offers enhanced structural performance, reduced material waste, and faster construction times compared to traditional concrete pouring methods.
- Prototyping and Design Iteration: 3D printing is extensively used for rapid prototyping and design iteration in the construction industry. Architects and engineers can quickly create physical models of designs, allowing for visualizing and assessing their concepts before moving to full-scale construction. This iterative design process leads to improved efficiency and better design outcomes.
- Repair and Retrofitting: 3D printing is being explored as a solution for repair and retrofitting of existing structures. By 3D printing components or custom parts, it is possible to replace damaged or deteriorated elements, improving the structural integrity and extending the lifespan of buildings. This approach offers cost-effective and precise solutions for maintenance and repair projects.
- Customized Building Elements: 3D printing enables the creation of customized building elements, such as unique façade panels, light fixtures, and furniture. These elements can be tailored to specific design preferences or functional requirements. The ability to provide personalized touches enhances the overall aesthetics and functionality of the built environment.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of 3D printing in construction. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations and applications across different sectors of the construction industry. From large-scale buildings to intricate design details, 3D printing is reshaping the way we approach construction and unlocking new possibilities for creativity and efficiency.
Future Possibilities and Innovations in 3D Printing Construction
The future of 3D printing in construction holds immense potential for further advancements and innovations. As the technology continues to evolve, new possibilities are emerging that have the potential to reshape the construction industry. Here are some of the future possibilities and innovations in 3D printing construction:
- Sustainable Construction: 3D printing can contribute to sustainable construction practices by using environmentally friendly materials and reducing construction waste. In the future, we can expect to see advancements in 3D printing technology that enable the use of biodegradable materials and recycled construction materials, leading to more sustainable and eco-friendly construction processes.
- Multi-Material Printing: Currently, most 3D printing construction focuses on a single material, such as concrete. However, future innovations may include the capability to 3D print structures using multiple materials in a single process. This would enable the integration of different properties, such as strength, insulation, and conductivity, into a single structure, expanding the possibilities for complex and high-performance buildings.
- On-Site 3D Printing: While many current applications of 3D printing in construction involve printing off-site and then transporting the components to the construction site, future advancements may enable on-site 3D printing. This would eliminate the need for transportation and allow for more flexible and customized construction processes directly at the project site, reducing cost and increasing efficiency.
- Additive Manufacturing and Robotics: The convergence of 3D printing and robotics holds promising possibilities for the future of construction. Combining 3D printing technology with robotic systems can enhance automation, precision, and productivity in construction processes. This can lead to the development of robotic arms or drones equipped with 3D printing capabilities, capable of constructing complex structures with speed and accuracy.
- Smart Structures: Integrated technologies and sensors can be incorporated into 3D printed structures, creating smart buildings. These structures can monitor their own health, adapt to environmental conditions, and optimize energy usage. We can expect to see advancements in embedding sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and other smart features into 3D printed structures, enabling a new level of interconnectivity and sustainability.
- Space Exploration and Extraterrestrial Construction: 3D printing technology is already being explored for its potential in constructing habitats on other planets. By using local resources, such as lunar or Martian regolith, 3D printing could enable the construction of habitats and infrastructure for future space missions. This innovative application could revolutionize space exploration, allowing for sustainable human habitation outside of Earth.
- Artificial Intelligence and Computational Design: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and computational design algorithms can enhance the capabilities of 3D printing in construction. AI can optimize designs, analyze structural performance, and improve printing processes. Computational design algorithms can generate optimized and efficient structures, taking into account various constraints and requirements.
These future possibilities and innovations in 3D printing construction represent a glimpse into the exciting developments ahead. Through ongoing research, collaboration, and technological advancements, 3D printing has the potential to transform the way we build and construct, offering sustainable, efficient, and innovative solutions for the construction industry.
Conclusion
3D printing in construction is ushering in a new era of innovation and transformation in the industry. This groundbreaking technology offers numerous advantages over traditional construction methods, ranging from cost savings and time efficiency to design flexibility and sustainability. While there are challenges and limitations to overcome, the potential benefits of 3D printing construction are immense.
With the ability to automate and streamline the construction process, 3D printing offers faster construction timelines and reduced labor costs. The design freedom provided by 3D printing allows architects and engineers to create intricate and customized structures, pushing the boundaries of architectural possibilities. This technology also enables the construction of more sustainable, efficient, and durable buildings through optimized material usage and lightweight designs.
Current applications of 3D printing in construction are already showcasing the capabilities of the technology. From the construction of entire buildings and modular structures to the creation of architectural elements and customized building components, 3D printing is demonstrating its potential across various sectors of the industry.
Looking to the future, continuous advancements in 3D printing technology hold immense promise. From sustainable construction practices and multi-material printing to on-site construction and the integration of robotics and AI, the possibilities for innovation are vast. Additionally, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize space exploration and enable extraterrestrial construction, pushing the boundaries of human habitation beyond Earth.
However, it is important to recognize that there are challenges and limitations associated with 3D printing construction. Scalability, integration of complex systems, regulatory compliance, material limitations, training, and cost are some areas that require further development and attention. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption of 3D printing in the construction industry.
In conclusion, 3D printing construction has the power to reshape the way we build and construct in the years to come. With its potential for cost savings, enhanced design possibilities, and sustainable practices, 3D printing is positioning itself as a disruptive force in the construction industry. As the technology continues to evolve and overcome its limitations, we can expect to witness a future where construction becomes more efficient, creative, and environmentally conscious.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is 3D Printing Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is 3D Printing Construction”