
Articles
How To Ground An Electrical Box
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the best articles about how to ground an electrical box, including step-by-step instructions and expert tips. Upgrade your electrical safety knowledge today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
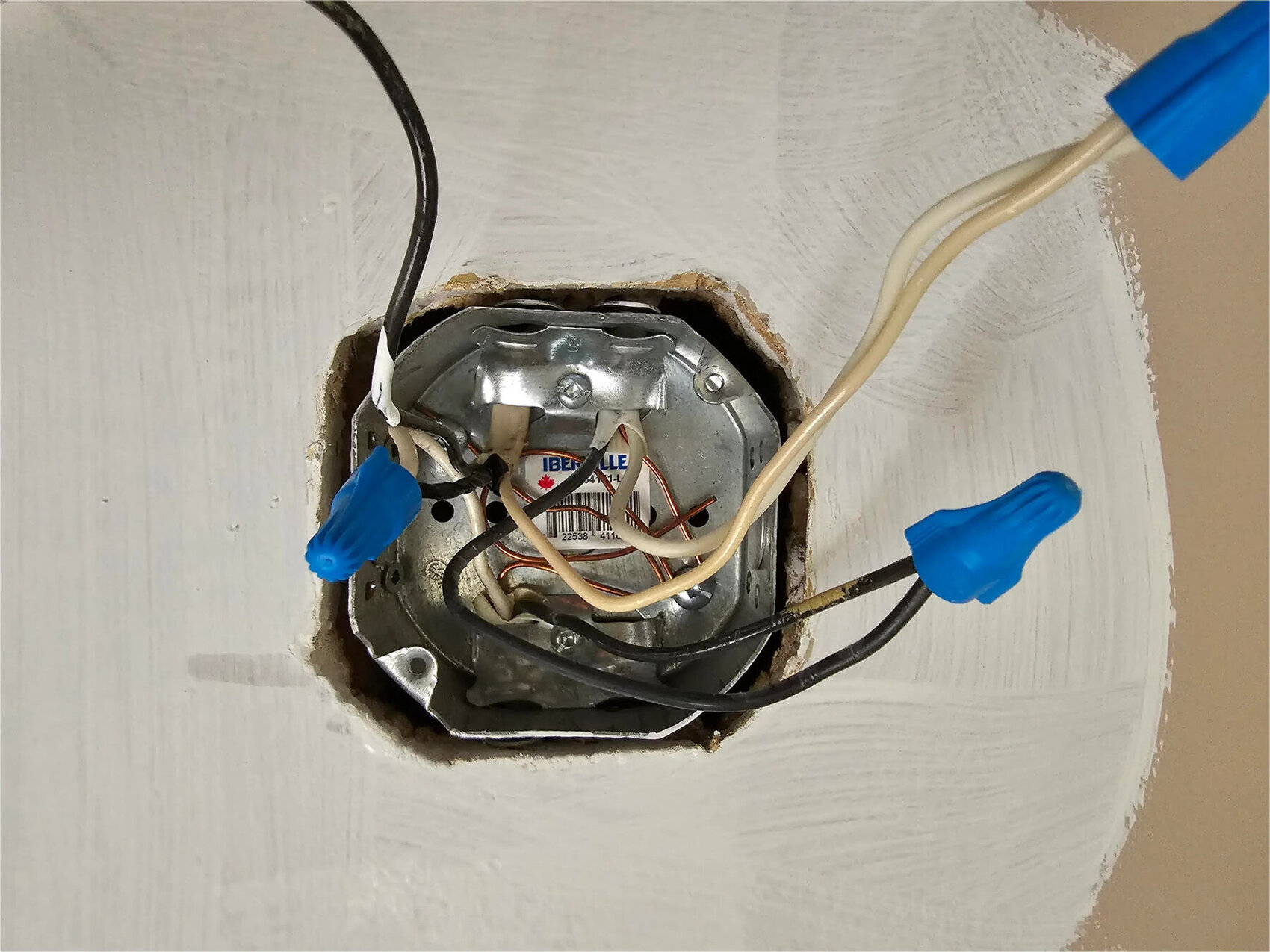
The proper grounding of electrical boxes is an essential aspect of electrical installations. Grounding ensures the safety of both the systems and the individuals using them. When an electrical box is not properly grounded, it can pose several risks, such as electrical shocks, fires, and damage to appliances and equipment. In this article, we will guide you on how to correctly ground an electrical box, ensuring the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
Understanding the importance of grounding is crucial in maintaining the integrity of your electrical system. Grounding provides a path for electrical current to flow to the ground in the event of a fault or surge, preventing it from causing damage to appliances or posing a risk to human life. It helps to stabilize voltage levels, protects against electrical faults, and provides a reference point for voltage measurements. Without proper grounding, electrical systems are more susceptible to malfunctioning and can put people and property at risk.
Before we begin, ensure that you have the proper tools and materials ready for the grounding process. Here is a list of essential items you will need:
- Grounding wire
- Wire stripper
- Screwdriver
- Grounding clamp
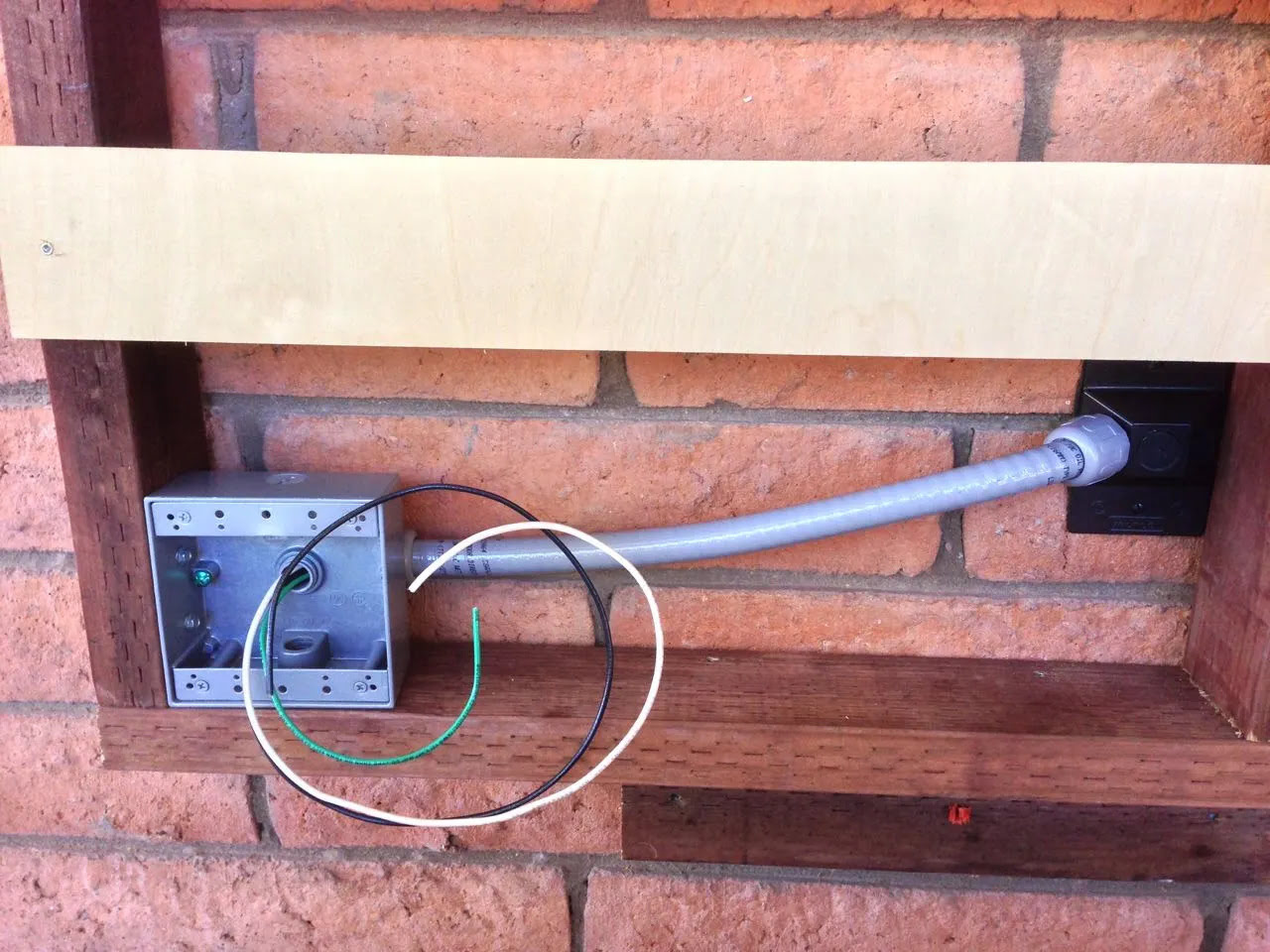
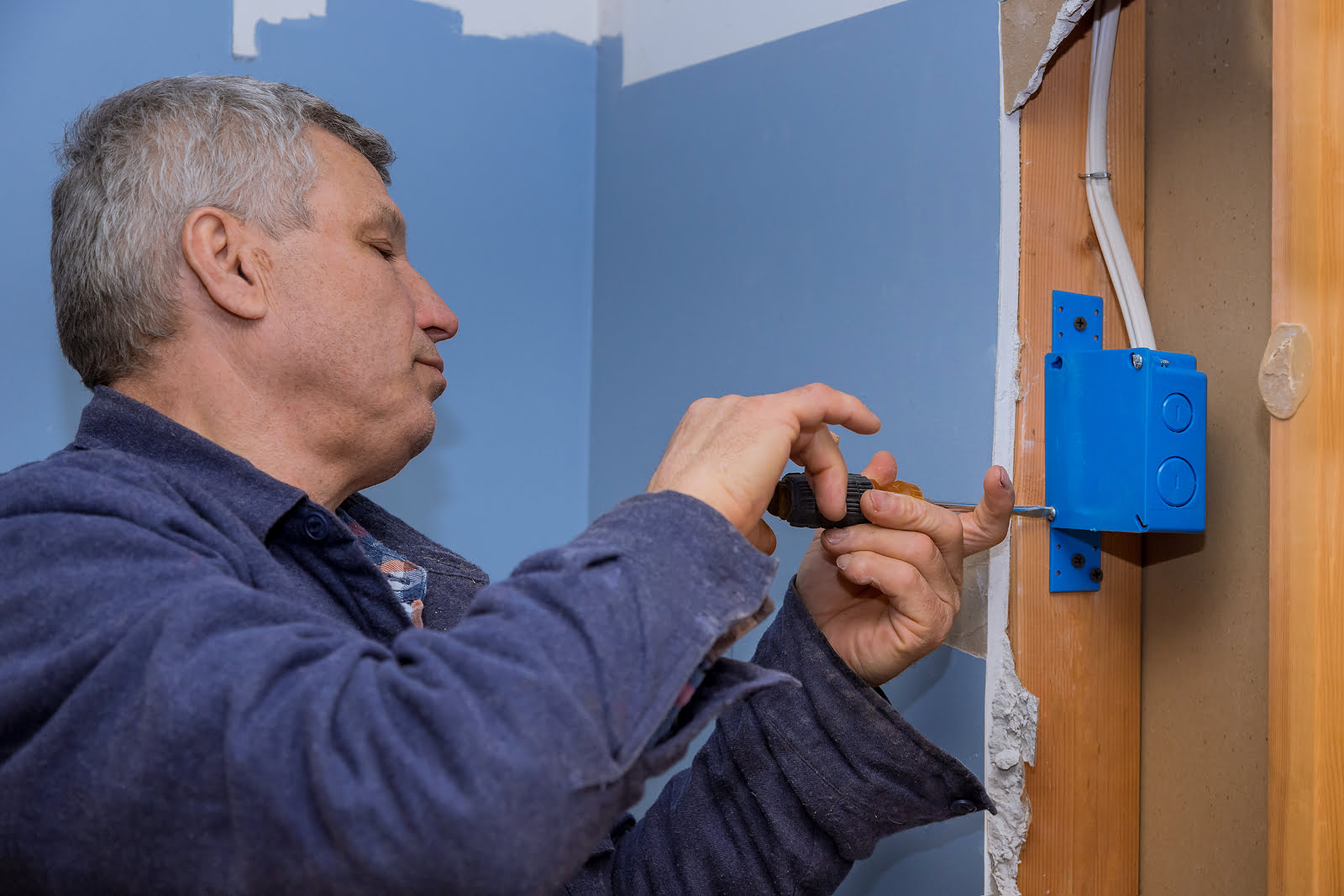
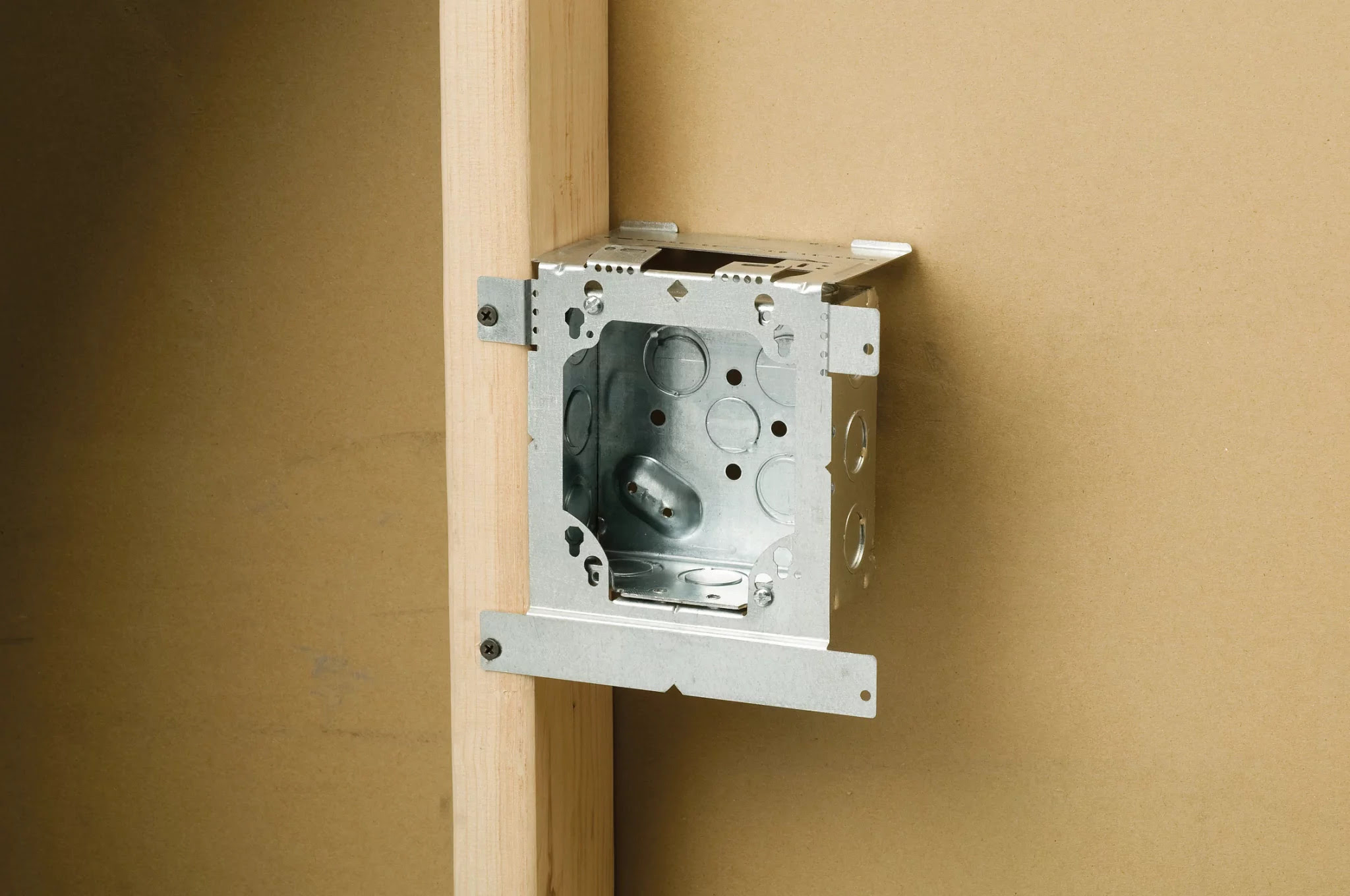
- Junction box
- Grounding screw
Now that you have your tools and materials ready, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of grounding an electrical box:
Key Takeaways:
- Proper grounding of electrical boxes is crucial for safety, protecting against shocks, fires, and equipment damage. Following the step-by-step guide and avoiding common mistakes ensures an effective and secure grounding installation.
- Understanding the importance of grounding, having the right tools, and testing the ground connection are essential for maintaining a safe and functional electrical system. Regular testing and adherence to local electrical codes ensure ongoing safety and reliability.
Read more: How To Ground Plastic Electrical Box
Understanding the Importance of Grounding
Grounding is a vital aspect of any electrical system. It serves as a safeguard that protects against electrical malfunctions and ensures the safety of people and property. Here are some key reasons why grounding is crucial:
- Protection against electrical shocks: Grounding helps to prevent electrical shocks by providing a low-impedance path for fault currents to flow into the ground. In the event of a fault, such as a short circuit or ground fault, the excess electrical current will follow the path of least resistance and flow safely into the ground, rather than passing through appliances or individuals.
- Protection against electrical fires: Proper grounding significantly reduces the risk of electrical fires. By establishing a connection to the ground, grounding helps to dissipate excess electrical energy and prevents it from overheating electrical equipment or igniting flammable materials. It also helps to stabilize voltage levels and minimize voltage surges that could potentially cause a fire.
- Equipment and appliance protection: Grounding helps to protect electrical equipment and appliances from damage. When a fault occurs, the grounding pathway allows the excess current to flow away from sensitive components and back into the ground. This protects the equipment from potential damage caused by a sudden increase in electrical current.
- Easier fault detection: Grounding provides a reference point for voltage measurements, making it easier to detect faults in the electrical system. By measuring the voltage between the ground and different points in the system, it is possible to identify abnormalities such as voltage imbalances or the presence of stray currents. This allows for timely troubleshooting and maintenance, preventing potential hazards.
- Compliance with electrical codes and regulations: Proper grounding is a requirement in electrical codes and regulations for residential, commercial, and industrial installations. Adhering to these standards ensures that the electrical system meets safety guidelines and regulations set by local authorities. Neglecting to properly ground an electrical box could result in violations and potential legal consequences.
By understanding the importance of grounding, you can ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical system. The next step is to properly ground an electrical box, which we will cover in the following sections.
Tools and Materials Required
Before you begin the process of grounding an electrical box, it’s important to have the necessary tools and materials ready. Having everything prepared will make the process smoother and more efficient. Here is a list of the essential items that you will need:
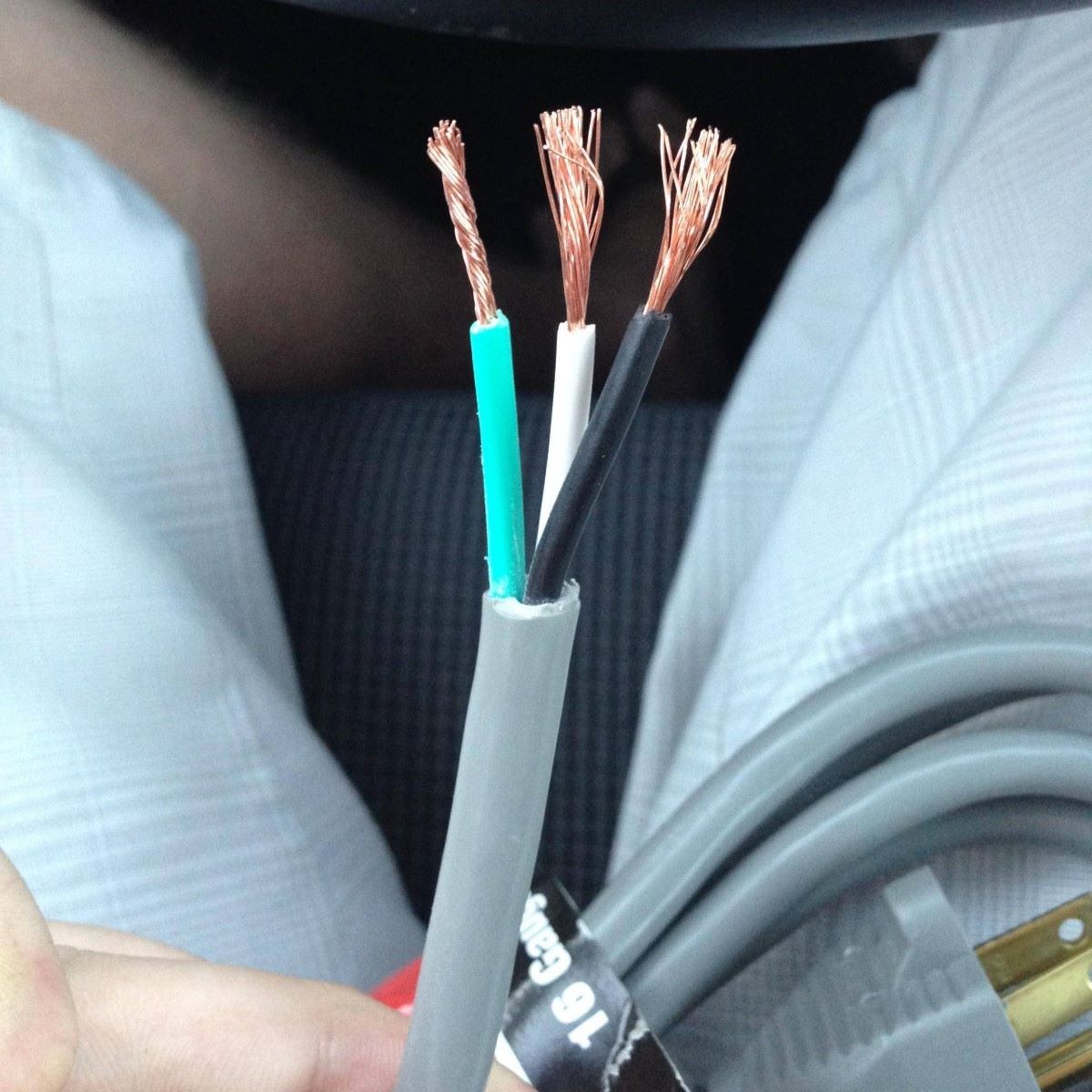
- Grounding wire: This is a copper wire with a green insulation coating. The gauge of the wire will depend on the electrical load and the specific requirements of your electrical system.
- Wire stripper: A wire stripper is used to remove the insulation from the grounding wire. It has different sized holes to accommodate various wire gauges and a cutting edge to remove the insulation without damaging the wire itself.
- Screwdriver: You will need a screwdriver to secure the grounding wire to the electrical boxes and other components. Make sure to have both flathead and Phillips head screwdrivers on hand, as different screws may require different types of screwdriver heads.
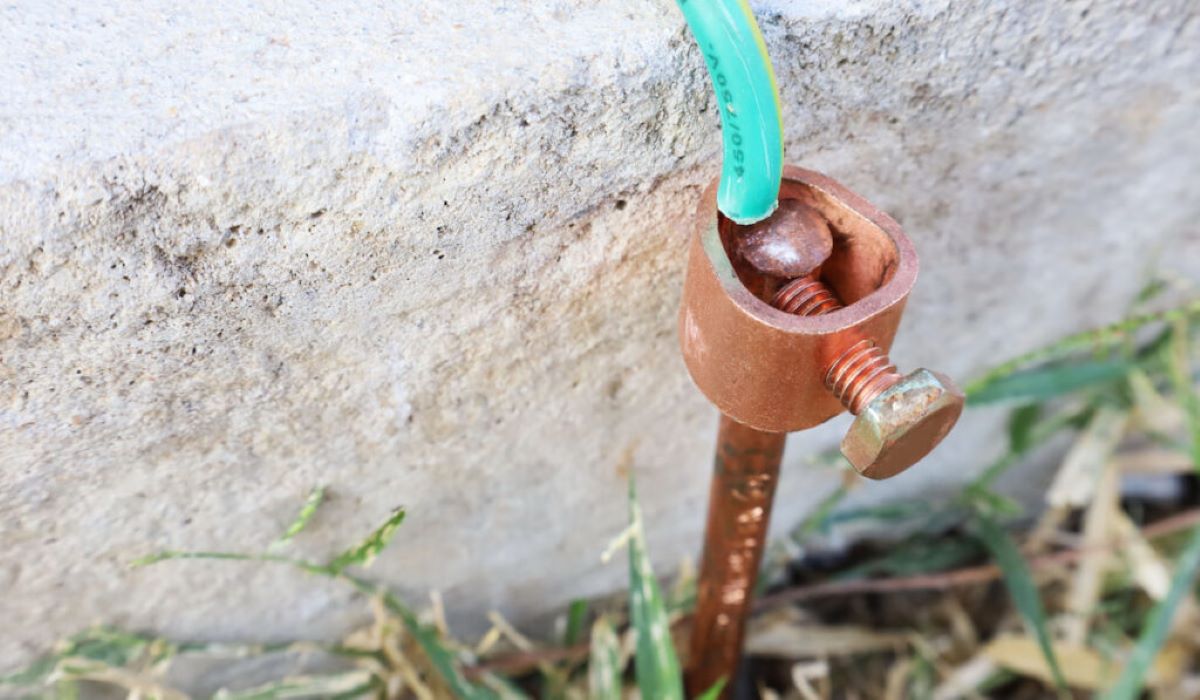
- Grounding clamp: A grounding clamp is used to secure the grounding wire to the electrical box. It ensures a solid connection between the wire and the box to establish the grounding pathway.
- Junction box: In some cases, you may need to install a junction box to accommodate additional wires or connections. Junction boxes provide a safe enclosure for electrical connections and can be surface-mounted or recessed, depending on your specific installation requirements.
- Grounding screw: A grounding screw is used to attach the grounding wire to the electrical box. It is typically a green screw and is specifically designed for grounding purposes.
Make sure to gather all the necessary tools and materials before you start the grounding process. This will ensure that you have everything you need to complete the task efficiently and effectively. Additionally, always prioritize safety by wearing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, while working with electrical components.
Now that you have all the required tools and materials ready, we can move on to the step-by-step guide on grounding an electrical box.
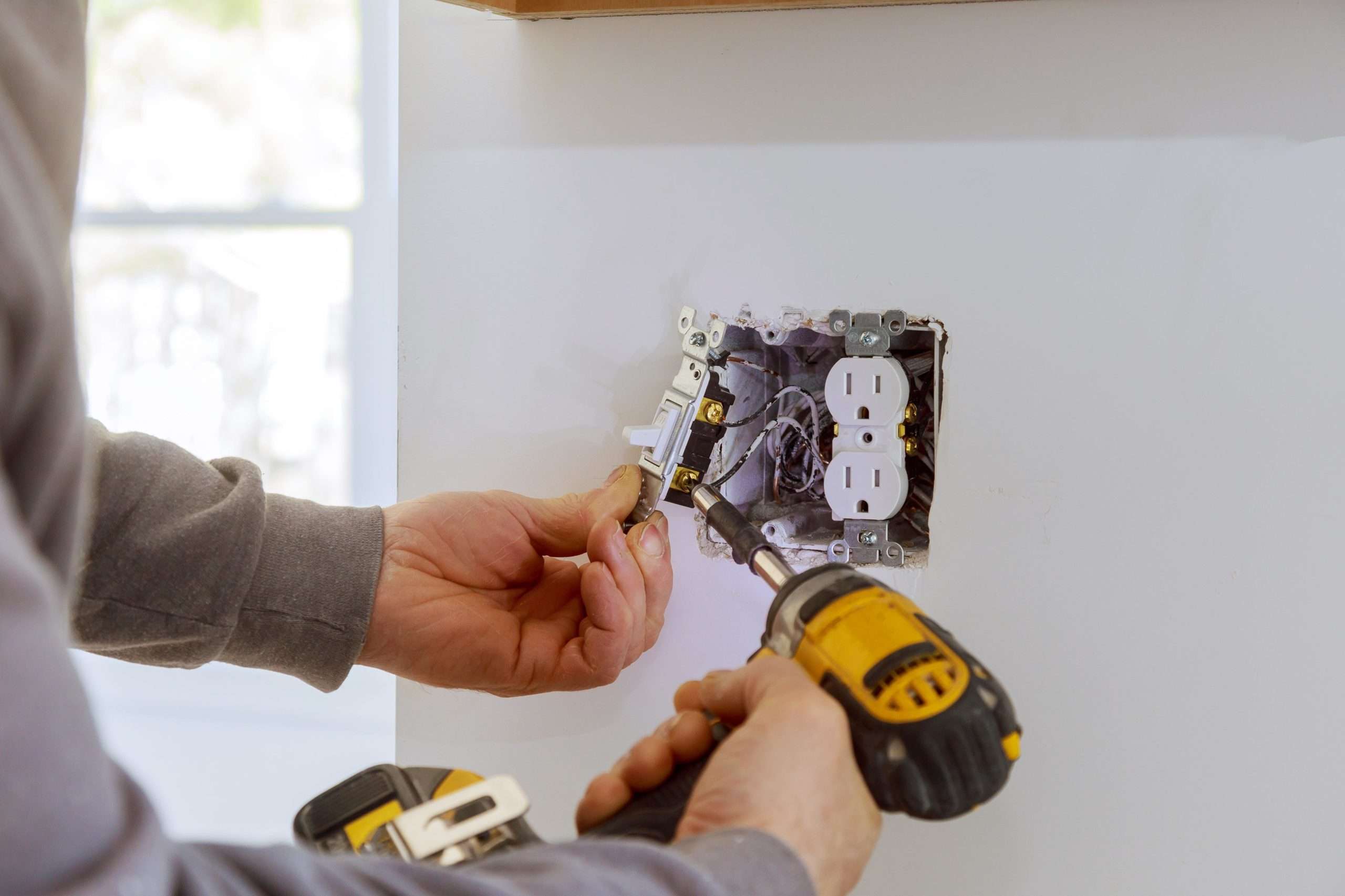
Step-by-Step Guide on Grounding an Electrical Box
Gounding an electrical box is a relatively simple process that involves connecting the grounding wire to the box itself. Follow these steps to ground an electrical box effectively:
- Turn off the power: Before starting any electrical work, it’s crucial to turn off the power supply to the area where you’ll be working. Locate the circuit breaker that controls the power to the electrical box and switch it off. Use a voltage tester to double-check that there is no electrical current flowing to the box.
- Select the grounding wire: Choose the appropriate gauge of the grounding wire based on the electrical load and the specific requirements of your electrical system. The grounding wire should be copper and have a green insulation coating.
- Strip the insulation: Using a wire stripper, carefully remove around 3/4 inch of insulation from the end of the grounding wire. Make sure not to damage the wire while stripping off the insulation.
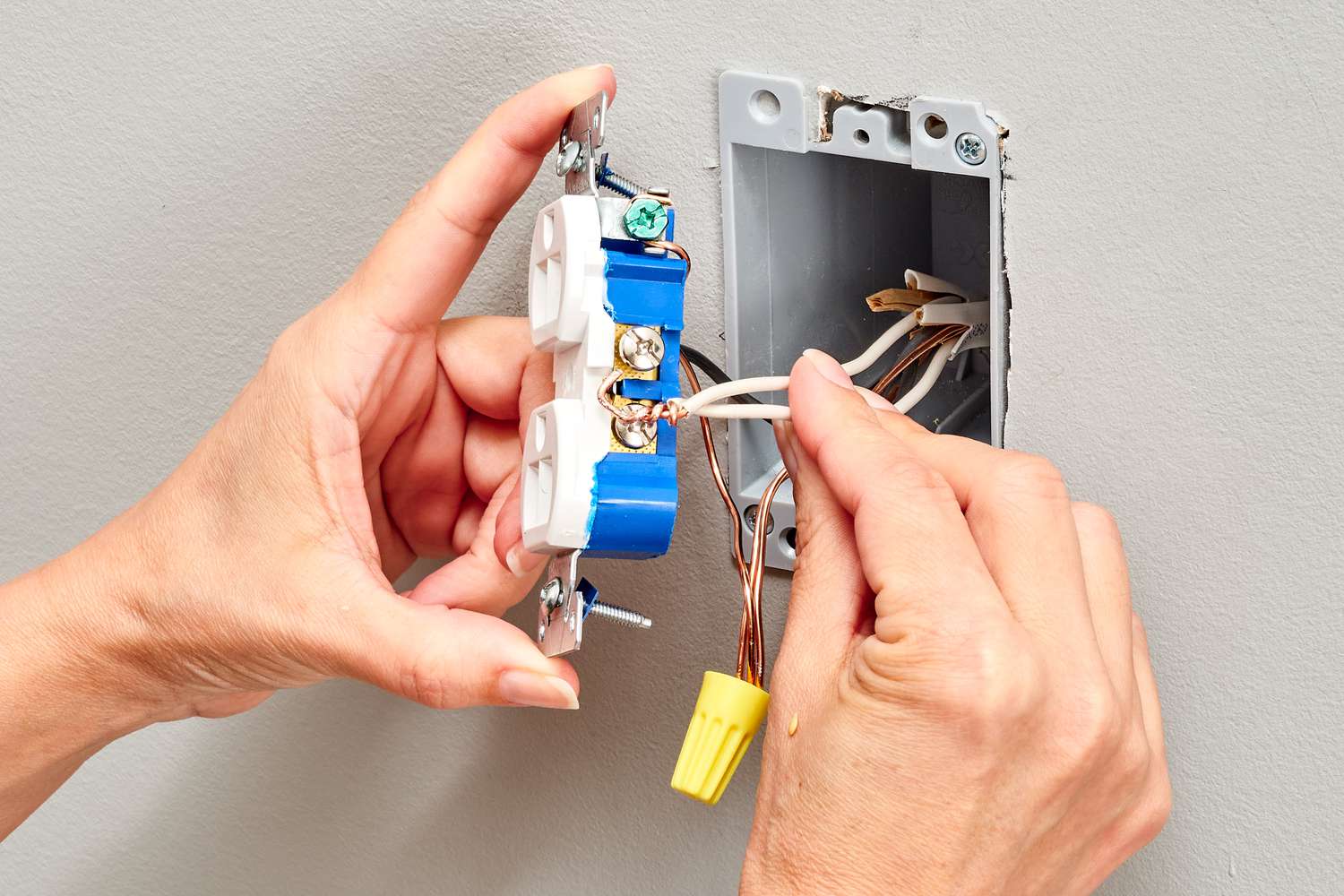
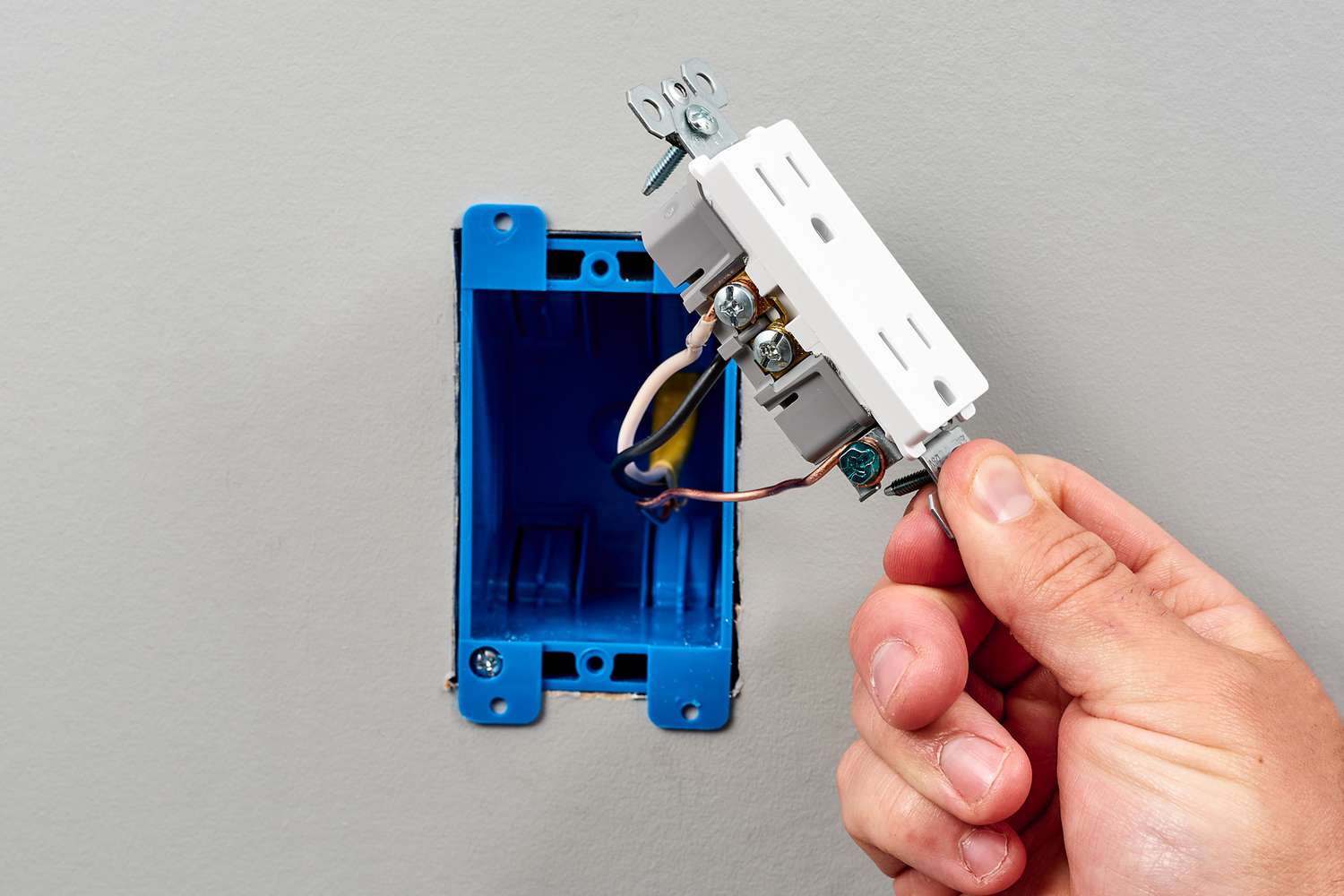
- Attach the grounding wire: Place the stripped end of the grounding wire around the grounding screw located inside the electrical box. Use a screwdriver to tighten the grounding screw, securing the wire in place.
- Secure the grounding wire to the box: Attach a grounding clamp to the grounding wire, ensuring a tight and secure connection. Fasten the grounding clamp to the electrical box, ensuring that it is securely in place.
- Check for proper grounding: Once you have completed the grounding process, it’s essential to test the ground connection. Use a continuity tester or a multimeter set to the continuity mode to ensure that there is a proper electrical connection between the grounding wire and the electrical box.
Following these steps will help you properly ground an electrical box, ensuring the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
When grounding an electrical box, make sure to use a grounding screw or clip to secure the grounding wire to the box. This will help prevent electrical shock and ensure the safety of the electrical system.
Testing the Ground Connection
After grounding an electrical box, it is crucial to test the ground connection to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Testing the ground connection will verify that there is a proper electrical pathway for fault currents to flow into the ground. Follow these steps to test the ground connection:
- Turn off the power: Before conducting any tests, ensure that the power to the electrical circuit is switched off at the circuit breaker to prevent any electrical accidents.
- Prepare the multimeter or continuity tester: If you are using a multimeter, set it to the resistance or continuity mode. For a continuity tester, simply turn it on.
- Probe the grounding wire: Place one probe from the multimeter or continuity tester onto the grounding wire that is connected to the electrical box.
- Probe the ground: With the other probe, touch a metal surface or a grounding point near the electrical box. This could be a metal pipe, grounding rod, or another known grounding point.
- Check for continuity: If the multimeter displays a resistance reading close to zero ohms or if the continuity tester signals a circuit by beeping or lighting up, it means that there is a good ground connection. This indicates that the fault current will flow properly into the ground in case of a fault.
- Recheck connections: If the continuity test indicates an open circuit or a high resistance reading, double-check all the connections made during the grounding process. Ensure that the grounding wire is securely attached to both the electrical box and the grounding point, and that all clamps and screws are tightened properly.
Regularly testing the ground connection is critical to maintain the safety and effectiveness of your electrical system. It is recommended to conduct these tests periodically or after any significant electrical work or modifications. If you encounter any issues with the ground connection, it is advisable to consult a licensed electrician to rectify the problem.
By following these steps and conducting regular ground connection tests, you can have peace of mind knowing that your electrical system is properly grounded and safe.
Read more: How To Tell If Electrical Box Is Grounded
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When grounding an electrical box, it is important to avoid common mistakes that can compromise the effectiveness of the grounding system. By being aware of these mistakes, you can ensure a proper and safe grounding installation. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Inadequate wire size: Using an inadequate gauge of grounding wire can result in an ineffective grounding system. Make sure to choose the appropriate wire size based on the electrical load and the requirements of your electrical system.
- Improper wire stripping: Carefully stripping the insulation from the grounding wire is crucial to ensure a good electrical connection. Avoid damaging the wire while stripping off the insulation, as it could lead to poor conductivity and may even pose a safety risk.
- Incorrect attachment of the grounding wire: It is important to securely attach the grounding wire to both the electrical box and the grounding point. Ensure that the grounding wire is tightly connected to the grounding screw and that the grounding clamp is properly fastened to the electrical box.
- Failing to turn off the power: Always remember to turn off the power to the electrical circuit before starting any grounding work. Failing to do so can lead to electrical shocks or damage to equipment.
- Not testing the ground connection: After completing the grounding installation, it is vital to test the ground connection using a continuity tester or a multimeter. Neglecting to do this can leave you unaware of any potential issues with the ground connection.
- Ignoring local electrical codes and regulations: Each region has its own electrical codes and regulations that must be followed during grounding installations. Failing to adhere to these codes and regulations can result in safety hazards and may lead to legal consequences.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following proper grounding techniques, you can ensure a safe and effective grounding system for your electrical boxes. If you are unsure about any steps of the grounding process or encounter any difficulties, it is recommended to seek assistance from a licensed electrician. They can provide expert guidance and ensure that the grounding is done properly.
Now that you are aware of the common mistakes to avoid, you can proceed with your grounding project confidently, knowing that you are taking all the necessary precautions for a successful installation.
Conclusion
Proper grounding of electrical boxes is crucial for the safety and functionality of electrical systems. Grounding helps protect against electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage by providing a path for fault currents to flow into the ground. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can effectively ground an electrical box and ensure the integrity of your electrical system.
Understanding the importance of grounding and the potential risks of not properly grounding electrical boxes is vital. It is also essential to have the right tools and materials on hand before starting the grounding process. By gathering all the necessary equipment and wearing appropriate safety gear, you can ensure a smooth and secure installation.
Throughout the grounding process, it is important to avoid common mistakes, such as using inadequate wire sizes, improper wire stripping, and not testing the ground connection. These mistakes can compromise the effectiveness of the grounding system and pose safety hazards. Adhering to local electrical codes and regulations is equally important to ensure compliance and avoid any legal consequences.
Regular testing of the ground connection is recommended to ensure a proper and effective grounding system. By periodically checking the connectivity of the grounding wire, you can identify any issues and address them promptly, ensuring the ongoing safety of your electrical system.
In conclusion, grounding an electrical box is a fundamental aspect of electrical installations. It promotes safety, protects against hazards, and helps maintain the functionality of electrical systems. By following the guidelines provided in this article, you can confidently ground your electrical boxes, ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Ground An Electrical Box
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Ground An Electrical Box”