Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How Does A Tiny House Fit Into Sustainable Design


Architecture & Design
How Does A Tiny House Fit Into Sustainable Design
Modified: March 24, 2024
Discover how a tiny house seamlessly integrates into sustainable design principles, with a focus on architecture and design.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of tiny houses, where small living spaces are making a big impact on sustainable design. In recent years, the popularity of tiny houses has grown exponentially as people seek more environmentally-friendly and minimalistic lifestyles.
A tiny house is typically defined as a dwelling that is smaller than traditional homes, often ranging from 100 to 400 square feet. Despite their size, these homes are designed to maximize space efficiency and functionality, utilizing every nook and cranny to create a comfortable and livable environment.
But what sets tiny houses apart from their larger counterparts goes beyond just their size. They embody the principles of sustainable design, which aim to minimize environmental impact and create more sustainable living solutions.
In this article, we will explore how tiny houses fit into the realm of sustainable design. We will delve into the specific strategies and principles used in tiny house construction that contribute to a more environmentally-friendly and resource-efficient lifestyle. From energy efficiency to waste reduction, water conservation to utilizing renewable energy sources, tiny houses offer a multitude of sustainable benefits.
So, whether you’re intrigued by the idea of downsizing or simply want to learn more about sustainable design, join us as we take a closer look at the world of tiny houses and how they align with the principles of sustainability.
Key Takeaways:
- Tiny houses showcase sustainable living through efficient design, renewable energy, and minimalistic lifestyles, inspiring a greener future for housing and promoting environmental stewardship.
- Despite challenges like limited space and zoning regulations, tiny houses offer affordable, eco-friendly living options that foster community, innovation, and a smaller ecological footprint.
Read more: How Does Plumbing Work In A Tiny House
What is a Tiny House?
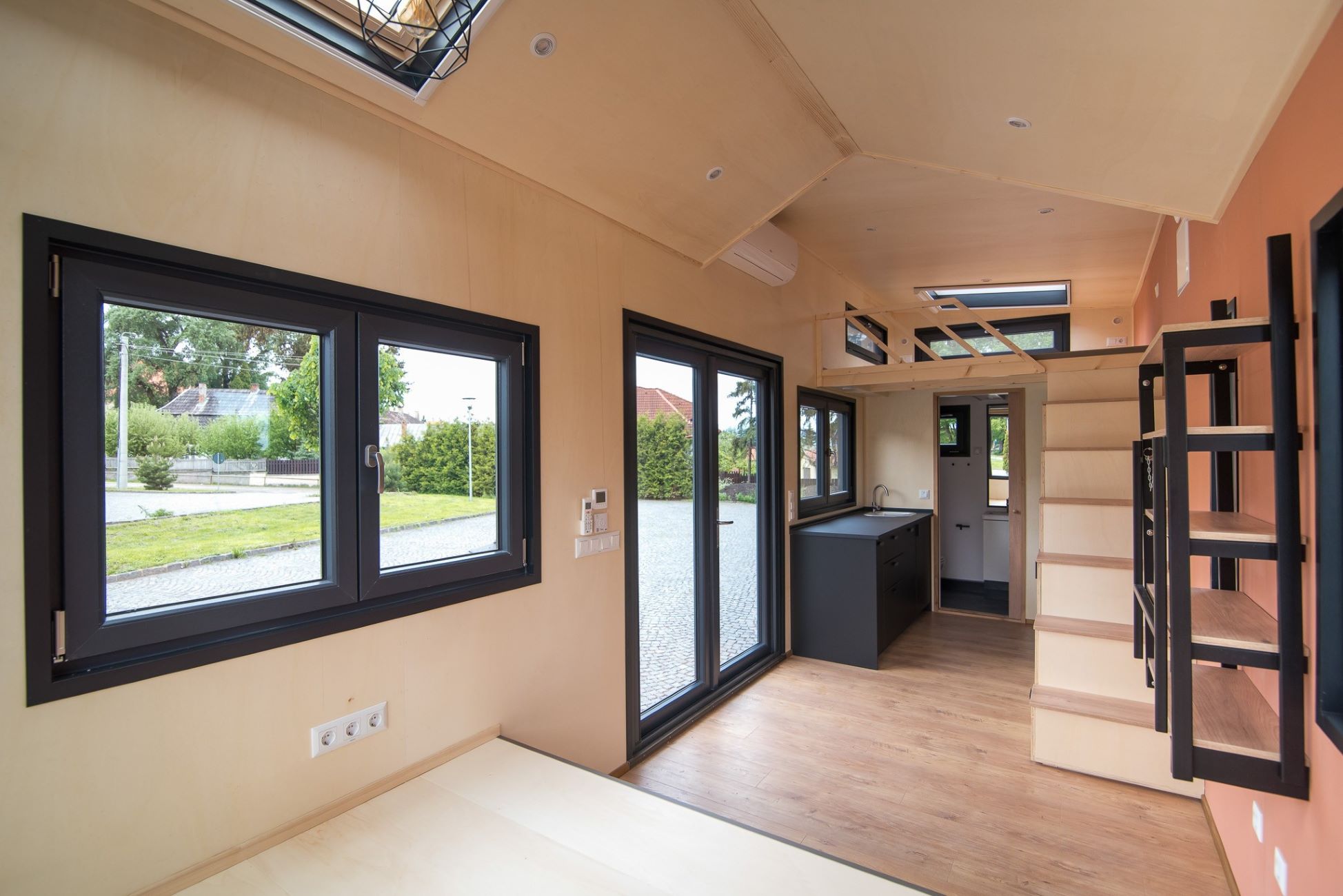
A tiny house is a minimalist and compact living space that has gained popularity in recent years. These homes are typically between 100 to 400 square feet in size, offering a cozy and functional living environment. While the size may be small, the design and utilization of space in tiny houses are anything but cramped.
One of the defining characteristics of a tiny house is its focus on efficient and thoughtful design. Every square inch is carefully planned and utilized to create a harmonious and livable space. From multi-purpose furniture and built-in storage to creative use of vertical space, tiny houses are a testament to ingenuity and maximizing functionality.
Moreover, tiny houses embrace a more minimalist lifestyle, encouraging individuals to downsize and prioritize experiences and connections over material possessions. Many people are drawn to the idea of simplifying their lives and living more sustainably by reducing their ecological footprint.
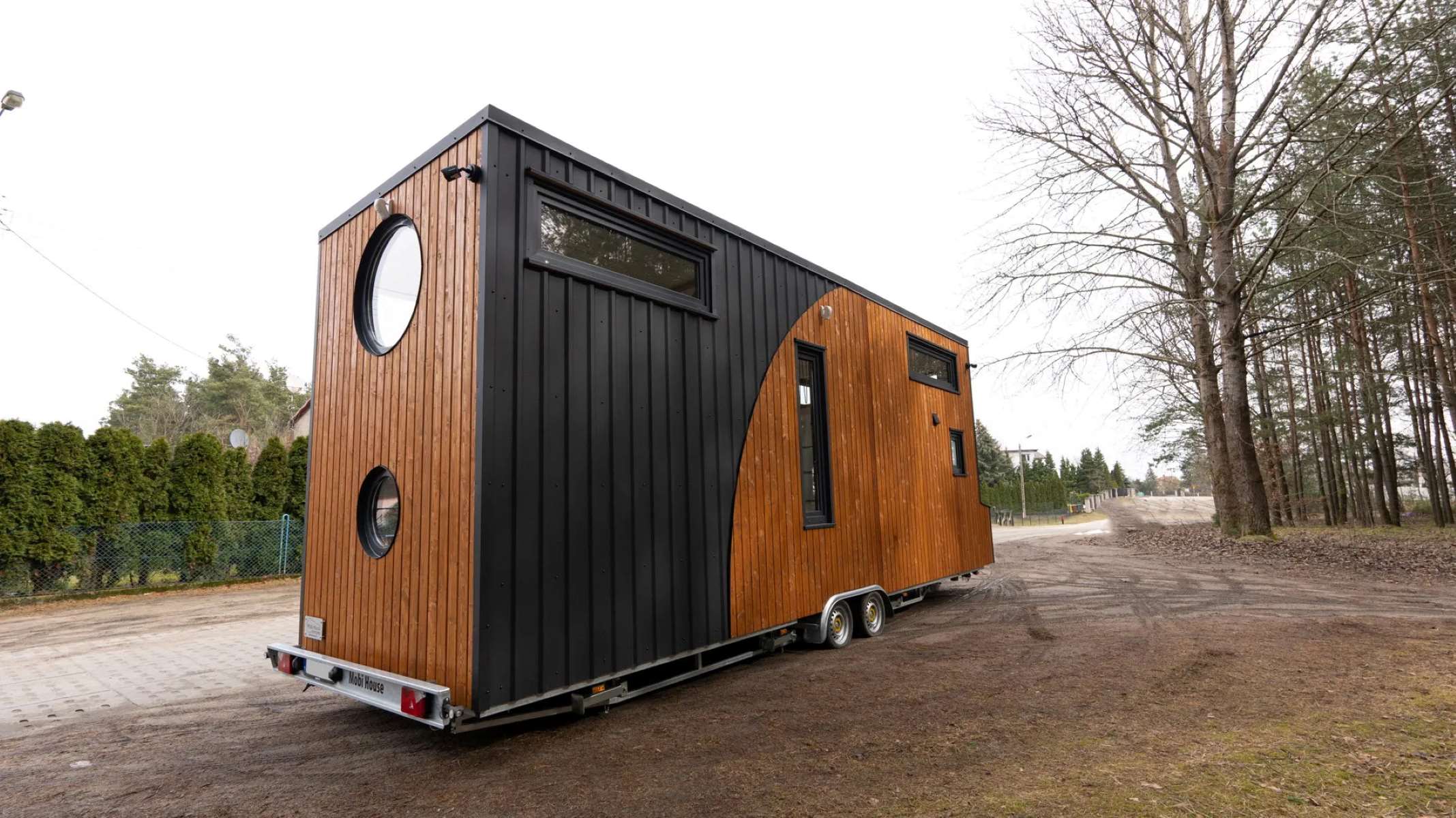
Despite their small size, tiny houses are built to meet the same requirements and codes as traditional homes, ensuring their safety and durability. They can be built on foundations or on wheels, depending on individual preferences and local regulations.
In addition to their compact design and sustainability benefits, tiny houses offer the potential for financial freedom. With lower mortgage and utility costs, individuals and families can significantly reduce their expenses and focus on other aspects of life, such as travel, hobbies, and personal fulfillment.
Overall, tiny houses represent a new way of thinking about housing. They challenge the conventional notion of what a home should be and offer a viable alternative for those seeking simplicity, sustainability, and a unique living experience.
The Principles of Sustainable Design
Sustainable design is a holistic approach that seeks to minimize the negative impact on the environment while maximizing the use of resources and promoting social equity. It encompasses various principles that guide the design and construction of buildings, including tiny houses.
1. Energy Efficiency: One of the key principles of sustainable design is reducing energy consumption. This involves incorporating energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and passive solar design techniques to minimize the need for heating and cooling.
2. Renewable Energy Sources: Another important aspect of sustainable design is the utilization of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to power the home. By harnessing clean and renewable energy, tiny houses can operate off the grid or significantly reduce their reliance on non-renewable sources.
3. Water Conservation and Management: Sustainable design promotes water efficiency through the use of low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and gray water recycling. These measures help conserve water resources and reduce strain on municipal water supplies.
4. Sustainable Materials: Choosing eco-friendly and sustainable materials is essential in sustainable design. In the construction of tiny houses, materials like reclaimed wood, bamboo, or recycled materials can be used to minimize environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity.
5. Waste Reduction and Recycling: Sustainable design emphasizes the reduction of waste generated during construction and occupancy. By incorporating recycling systems, composting toilets, and designing for adaptability and future reuse, tiny houses can minimize waste and promote a circular economy.
6. Efficient Use of Space: Tiny houses embody the principle of utilizing space efficiently. By optimizing floor plans, incorporating smart storage solutions, and multi-purpose furniture, individuals can make the most out of limited square footage and reduce the need for excessive consumption.
7. Site Design: Sustainable design takes into consideration the site’s natural features, such as sun exposure and wind patterns, to maximize energy efficiency. It also prioritizes green spaces, native plantings, and responsible stormwater management to minimize environmental impact.
By embracing these principles, tiny houses align with the values of sustainable design. They provide a template for a more conscientious and environmentally-friendly way of living, showcasing that small spaces can have a big impact.
Minimizing Environmental Impact through Tiny House Design
One of the key advantages of tiny house living is its ability to minimize environmental impact. The design and construction of tiny houses prioritize sustainability and resource efficiency, making them an eco-friendly housing option. Here are some ways in which tiny house design minimizes environmental impact:
1. Reduced Energy Consumption: The small size of tiny houses means that less energy is needed to heat, cool, and power the space. Well-insulated walls, energy-efficient appliances, and the use of natural lighting techniques help reduce energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Smaller Carbon Footprint: Tiny houses have a significantly smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional homes. The construction materials required are minimal, resulting in fewer energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Additionally, their reduced energy consumption further contributes to a smaller carbon footprint.
3. Sustainable Materials: Tiny house builders often prioritize the use of sustainable and recycled materials. From reclaimed wood flooring to repurposed fixtures and furniture, these materials help reduce the extraction of new resources and minimize waste.
4. Water Conservation: Tiny houses are designed to be water-efficient. Installing low-flow fixtures and utilizing rainwater harvesting systems help minimize water usage. Additionally, composting toilets or greywater recycling systems can be implemented to further reduce water waste.
5. Durable and Long-lasting Construction: Tiny houses are typically constructed with durability in mind. By implementing high-quality materials and construction techniques, these homes can have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent renovations or rebuilds that contribute to waste and environmental impact.
6. Off-grid Capabilities: Many tiny houses are designed to be off-grid or have the ability to operate independently from utilities. Utilizing renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines and incorporating storage systems allows for self-sufficiency and a reduced reliance on centralized energy grids.
7. Minimal Land Use: The small footprint of tiny houses requires less land compared to traditional homes, which reduces the amount of natural land being developed. This preservation of natural surroundings helps promote biodiversity and protect ecosystems.
By incorporating these sustainable design principles, tiny houses offer an environmentally-friendly solution to housing. They showcase that even with limited space, it is possible to live comfortably while still minimizing our impact on the planet.
Energy Efficiency in Tiny House Construction
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of sustainable design, and it plays a significant role in the construction and operation of tiny houses. Despite their small size, there are several strategies and techniques that contribute to the energy efficiency of these homes:
1. Insulation: Proper insulation is essential in tiny house construction to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. By using high-quality insulation materials, such as spray foam or rigid foam boards, tiny houses can minimize heat transfer and reduce the need for excessive heating or cooling.
2. Passive Solar Design: Passive solar design is a technique that takes advantage of the sun’s energy to heat and cool a building naturally. Through careful orientation and placement of windows, as well as the use of thermal mass, tiny houses can maximize solar gain in the winter and minimize it in the summer, reducing the reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems.
3. Efficient Appliances: Choosing energy-efficient appliances, such as ENERGY STAR-rated refrigerators and LED lighting fixtures, can significantly reduce energy consumption in tiny houses. These appliances are specifically designed to operate more efficiently, consuming less energy while still providing the necessary functionalities.
4. Natural Lighting: Maximizing natural lighting not only creates a bright and welcoming space but also reduces the need for artificial lighting during the day. By incorporating large windows, skylights, and light tubes, tiny houses can optimize daylighting and reduce energy consumption.
5. Ventilation and Airflow: Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining indoor air quality and preventing moisture buildup. In tiny houses, efficient ventilation systems, such as mechanical ventilation with heat recovery, can help reduce the reliance on air conditioning to maintain comfortable and healthy living conditions.
6. Energy Monitoring and Control Systems: Installing energy monitoring systems allows occupants to track their energy consumption and make informed decisions regarding their energy usage. Smart thermostats and energy management systems further optimize energy efficiency by automating heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and user preferences.
7. Off-Grid Solutions: Many tiny houses are designed with off-grid capabilities, allowing them to operate independently from the traditional power grid. Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or small wind turbines, along with battery storage systems, provides a sustainable and self-sufficient energy solution.
Implementing these energy-efficient strategies in tiny house construction not only reduces environmental impact but also contributes to long-term energy and cost savings for homeowners. By embracing energy efficiency, tiny houses offer a sustainable housing option that aligns with the principles of sustainable design.
Read more: How To Design A Sustainable House
Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in sustainable design, and tiny houses are no exception. These compact homes offer the perfect platform to harness renewable energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Here are some ways in which tiny house owners can utilize renewable energy sources:
1. Solar Power: Solar energy is one of the most popular forms of renewable energy for tiny houses. By installing solar panels on the roof or in an optimal location, homeowners can generate their electricity from the sun. Solar energy is clean, abundant, and readily available, making it a sustainable and cost-effective choice.
2. Wind Power: In certain locations, wind power can be a viable option for tiny house owners. Small wind turbines can be installed to generate electricity from the power of the wind. However, it’s important to consider local regulations, wind patterns, and the availability of suitable space before installing wind turbines.
3. Micro-hydro Power: If you have a water source, such as a stream or a small river nearby, micro-hydro power can be an option for generating electricity in your tiny house. Water turbines can convert the flow of water into energy, providing a renewable and continuous power source.
4. Biomass Energy: Biomass energy involves the use of organic materials, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, to generate heat and electricity. Tiny house owners can install biomass heaters or stoves that burn these materials, providing a renewable and sustainable source of heating.
5. Hybrid Systems: Some tiny house owners may choose to combine different renewable energy sources to create hybrid systems. For example, a combination of solar panels and wind turbines can provide a more reliable and continuous power supply, especially in areas with varying weather conditions.
When incorporating renewable energy sources into a tiny house, it’s important to consider factors such as the availability of sunlight, wind patterns, and the energy needs of the occupants. It’s also wise to invest in energy storage systems, such as batteries or hydrogen fuel cells, to store excess energy for times when the renewable source is not producing enough power.
Utilizing renewable energy sources not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle. By generating clean and renewable energy, tiny house owners can minimize their environmental impact and enjoy the benefits of a self-sufficient and off-grid lifestyle.
Water Conservation and Management
Water conservation is a critical aspect of sustainable living, and tiny houses provide an excellent opportunity to implement water-saving strategies. With limited space and resources, it is essential for tiny house owners to prioritize water conservation and management. Here are some ways in which water conservation can be achieved in tiny houses:
1. Low-Flow Fixtures: Installing low-flow faucets, showerheads, and toilets in a tiny house can significantly reduce water usage. These fixtures are designed to maintain adequate water pressure while using less water, helping to conserve water without sacrificing functionality.
2. Rainwater Harvesting: Capturing and storing rainwater can help supplement water needs in a tiny house. Installing rain barrels or larger underground cisterns allows homeowners to collect rainwater from the roof and use it for non-potable water needs such as gardening, cleaning, or flushing toilets.
3. Graywater Recycling: Graywater is water that has been used in sinks, showers, and laundry and can be recycled for secondary uses. Installing a graywater recycling system in a tiny house allows homeowners to reuse water for irrigation, toilet flushing, or other non-potable purposes. It not only reduces water consumption but also minimizes the strain on the wastewater system.
4. Water-Efficient Appliances: Choosing water-efficient appliances, such as ENERGY STAR-rated dishwashers and washing machines, can help minimize water usage in a tiny house. These appliances are designed to use less water while still providing efficient performance.
5. Smart Water Management: Utilizing smart water management systems helps monitor and control water usage in a tiny house. These systems can provide real-time data on water consumption, detect leaks, and automate irrigation, ensuring efficient water usage and minimal wastage.
6. Sensible Landscaping: Designing a water-wise landscape around a tiny house can contribute to water conservation. Opting for native and drought-resistant plant species, implementing mulching techniques, and utilizing drip irrigation systems can help reduce the need for excessive watering.
7. Efficient Plumbing Design: Planning the plumbing system in a tiny house with efficiency in mind can help minimize water waste. By shortening pipe runs, insulating hot water pipes, and avoiding long waits for hot water, homeowners can reduce water and energy waste.
It’s important for tiny house owners to be mindful of their water usage and make conscious efforts to conserve this essential resource. By implementing water-saving strategies, tiny houses can demonstrate sustainable living practices and contribute to a more environmentally-friendly lifestyle.
When designing a tiny house for sustainability, focus on energy efficiency by using high-quality insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and incorporating passive solar design principles to maximize natural light and heat.
Sustainable Materials and Construction Techniques
When it comes to sustainable design, the choice of materials and construction techniques plays a crucial role in reducing environmental impact. In the construction of tiny houses, using sustainable materials and adopting eco-friendly construction techniques are essential. Here are some key considerations:
1. Reclaimed and Recycled Materials: Using reclaimed or recycled building materials is an excellent way to reduce the demand for new resources. Reclaimed wood from old buildings, salvaged fixtures, and recycled insulation materials can be incorporated into the construction of tiny houses, adding character while minimizing environmental impact.
2. Eco-Friendly Insulation: Insulation is vital for energy efficiency in tiny houses. Opting for eco-friendly insulation materials, such as cellulose insulation made from recycled paper or recycled denim, can provide effective insulation while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals often found in traditional insulations.
3. Sustainable Timber: If new wood is needed, choosing sustainable timber from responsibly managed forests or using alternatives like bamboo, which is a rapidly renewable resource, can help reduce deforestation and promote sustainable forestry practices.
4. Non-Toxic Finishes: Many conventional construction materials and finishes contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can negatively impact indoor air quality. Opting for low or zero VOC paints, stains, and finishes ensures a healthier living environment for tiny house occupants.
5. Prefabricated and Modular Construction: Prefabricated or modular construction allows for reduced waste generation during the building process. Precise measurements and off-site fabrication of components minimize on-site construction waste and optimize material usage.
6. Design for Deconstruction: Designing tiny houses with the ability to be disassembled and materials easily reclaimed is important for sustainable construction. By incorporating methods that enable easy disassembly and salvage, future renovations or relocations become more efficient and reduce waste.
7. Passive Design Strategies: Passive design techniques rely on the natural environment to help regulate temperature and lighting in a building. Orienting the tiny house to maximize solar gain, incorporating shading devices, and optimizing natural ventilation can reduce the need for energy-intensive heating, cooling, and artificial lighting.
By selecting sustainable materials and implementing eco-friendly construction techniques, tiny houses can serve as exemplars of environmentally-conscious design and promote a more sustainable way of living.
Waste Reduction and Recycling in Tiny Houses
Waste reduction and recycling are fundamental components of sustainable living, and tiny houses offer a unique platform to practice these principles. Due to their small size and minimalist lifestyle, tiny houses naturally encourage a more conscious approach to waste management. Here are some ways in which waste reduction and recycling can be incorporated into tiny house living:
1. Minimalist Approach: The core philosophy of a tiny house revolves around simplifying and downsizing. By adopting a minimalist lifestyle, occupants are encouraged to reduce their consumption habits and only acquire what they truly need. This mindset inherently reduces waste generation.
2. Composting: Composting is an effective way to recycle organic waste and produce nutrient-rich soil for gardening. Tiny house owners can implement composting systems, such as worm bins or compost tumblers, to compost food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials, turning them into valuable nutrients for plants.
3. Recycling Systems: Setting up a well-organized recycling system is essential in a tiny house. Tiny house owners should have designated bins or containers to sort and collect recyclable materials such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal. These materials can then be taken to recycling centers or appropriate facilities to be processed and reused.
4. Upcycling and Repurposing: Embracing a creative mindset, tiny house owners can find ways to upcycle and repurpose materials. Furniture or decor items can be made from salvaged or reclaimed materials, giving them a new life and reducing the need for new purchases.
5. Responsible Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of waste is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Tiny house owners should familiarize themselves with local waste disposal regulations and ensure that waste is disposed of correctly to prevent pollution and harm to the environment.
6. Designing for Recycling: In the construction of a tiny house, it’s important to consider the recyclability of materials used. Design elements should be chosen with future recycling in mind, such as using materials that can be easily separated and recycled at the end of the life cycle.
7. Participating in Community Recycling Programs: Tiny house communities may have access to shared recycling programs or facilities. By actively participating in these community programs, tiny house owners can contribute to greater recycling efforts and make a positive impact on the environment.
By prioritizing waste reduction and recycling, tiny house owners can significantly minimize their environmental footprint. These practices align with the ethos of sustainable living and promote a circular economy where resources are conserved and reused, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Read more: How To Build A Foundation For A Tiny House
The Importance of Location and Site Design
When it comes to sustainable living in tiny houses, the location and site design play a crucial role in maximizing environmental benefits and minimizing the ecological footprint. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of location and site design for tiny houses:
1. Access to Resources: Choosing a location that provides easy access to essential resources is important for sustainable living. Proximity to local markets, community gardens, public transportation, and basic amenities can minimize the need for long commutes and reduce reliance on private vehicles, promoting a more sustainable and efficient lifestyle.
2. Renewable Energy Potential: Evaluating the location for its renewable energy potential is crucial for off-grid tiny houses seeking self-sufficiency. An area with ample sunlight or strong wind patterns can greatly benefit the integration of solar panels or wind turbines, maximizing the renewable energy generation and reducing dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
3. Weather Considerations: Understanding the local climate and weather patterns is essential for efficient heating and cooling in tiny houses. Orienting the house to maximize solar gain or incorporating shading elements to reduce heat gain in warmer climates can significantly impact energy consumption and comfort levels within the tiny house.
4. Water Management: The location should be selected with water management in mind. Choosing a site that allows for water catchment, such as collecting rainwater in barrels or implementing greywater recycling systems, can reduce the strain on municipal water supply and promote sustainable water usage within the tiny house.
5. Natural Surroundings: A well-designed site integrates and preserves the natural surroundings. Strategically positioned windows and landscaping can harness natural lighting, enhance ventilation, and blend the tiny house with the surrounding environment. This not only creates a pleasant living atmosphere but also promotes biodiversity and respects the natural ecosystem.
6. Sustainable Landscaping: Designing the landscape around the tiny house with sustainability in mind adds aesthetic appeal while minimizing environmental impact. Utilizing native plants, employing water-efficient irrigation methods, and avoiding chemical pesticides and fertilizers contribute to a healthy and sustainable outdoor environment.
7. Zoning and Regulations: Understanding local zoning and building regulations is vital for the successful placement of a tiny house. Being aware of zoning restrictions, codes, and permit requirements ensures compliance with the law and allows for smoother construction and habitation of the tiny house.
Choosing the right location and implementing thoughtful site design are crucial elements in the sustainable living journey of tiny house owners. By carefully considering factors such as resource accessibility, renewable energy potential, water management, and integration with the natural surroundings, individuals can create a harmonious and eco-friendly living space that aligns with the principles of sustainable design.
Community and Societal Benefits of Tiny Houses
While tiny houses provide individuals and families with a unique and sustainable living experience, they also offer a range of community and societal benefits. Here are some key ways in which tiny houses contribute to the greater community:
1. Affordability and Housing Accessibility: Tiny houses offer an affordable housing option, allowing individuals and families to attain homeownership without the burden of a large mortgage. This accessibility to affordable housing can help address the housing crisis by providing alternative housing options for those with limited financial resources.
2. Minimal Ecological Footprint: Tiny houses have a significantly smaller ecological footprint compared to traditional homes. Their reduced size, energy efficiency, and use of sustainable materials contribute to lower energy consumption, reduced waste generation, and a smaller carbon footprint. This sustainable living approach can inspire others and promote environmentally-conscious behavior in the community.
3. Stronger Sense of Community: Tiny house communities foster a strong sense of community and connection among residents. With shared common spaces and a focus on communal living, tiny house communities often encourage social interactions, collaboration, and mutual support. This sense of community can help combat social isolation and improve overall well-being.
4. Reduced Infrastructure Demand: Tiny houses require fewer resources and put less strain on infrastructure compared to larger homes. With smaller square footage, the demand for utilities, such as water, electricity, and sewage, is significantly reduced. This can alleviate pressure on local infrastructure systems and contribute to more sustainable and resilient communities.
5. Mobility and Flexibility: Tiny houses on wheels provide the opportunity for mobility and flexibility. This allows individuals to easily relocate and adapt to changing circumstances, whether it be for employment opportunities, closer proximity to family, or exploring different communities. This mobility can foster a sense of adventure and encourage new experiences.
6. Inspiration for Sustainable Living: By showcasing sustainable living practices, tiny houses often inspire others to adopt a more sustainable lifestyle. Whether it’s through energy-efficient design, minimalism, or eco-friendly practices, tiny house owners serve as role models for environmentally-conscious behavior and encourage others to rethink their own consumption patterns.
7. Creativity and Innovation: The design and construction of tiny houses often require creative problem-solving. This fosters a culture of innovation and experimentation, as owners find unique and efficient ways to optimize limited space and resources. These innovative approaches can ripple into the broader community, inspiring creativity across various aspects of life.
Tiny houses offer not only an alternative housing solution but also the potential to transform communities and promote sustainable living practices. By emphasizing affordability, environmental consciousness, and a sense of community, tiny houses contribute to a more inclusive, resilient, and environmentally-friendly society.
Challenges and Considerations in Sustainable Tiny House Living
While sustainable tiny house living offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind. Understanding these factors is crucial for a successful and fulfilling experience. Here are some key challenges and considerations in sustainable tiny house living:
1. Limited Space: The most obvious challenge of tiny house living is the limited space. It requires careful planning and organization to maximize functionality and storage. Individuals must be willing to downsize and prioritize possessions, which can be a significant adjustment for some.
2. Zoning and Regulations: Tiny houses often face zoning and regulatory challenges. Many areas have restrictions on minimum square footage, parking requirements, and where tiny houses can be located. It’s important to do thorough research to ensure compliance with local regulations before moving forward with a tiny house project.
3. Land and Site Acquisition: Finding suitable land for a tiny house can be a challenge, especially in densely-populated areas or areas with high land prices. Navigating land acquisition, leases, or joining a tiny house community are all potential options, each with their own considerations and requirements.
4. Utilities and Off-Grid Living: Sustainable tiny houses often strive for energy efficiency and off-grid capabilities. Managing off-grid systems, such as solar panels or rainwater collection, may require additional technical knowledge and maintenance. It’s important to assess the availability of utilities, such as water and sewage, before committing to a particular location.
5. Cost Considerations: While tiny houses are generally more affordable than traditional homes, there are still costs associated with construction, permits, land, and ongoing maintenance. It’s essential to carefully budget and consider the long-term financial implications of tiny house living, including potential future expenses and lifestyle changes.
6. Social Considerations: Living in a tiny house may raise questions from family, friends, and society at large. It can challenge societal norms and may require explaining and educating others about the benefits and values of sustainable tiny house living. Community acceptance and integration can vary, and it’s important to consider the social aspect of living in a non-traditional dwelling.
7. Future Needs and Life Changes: Tiny house living requires adaptability as future needs and circumstances may change. Consideration should be given to potential life changes, such as the addition of children, caring for aging family members, or career changes that may necessitate a different living arrangement.
While these challenges and considerations are important to keep in mind, they can be overcome with careful planning, research, and a commitment to sustainable living. By approaching tiny house living with a realistic understanding of these factors, individuals can navigate the challenges and create a fulfilling and sustainable lifestyle that aligns with their values and goals.
Conclusion
Tiny houses offer a unique and sustainable approach to housing that aligns with the principles of sustainable design. These compact living spaces maximize functionality and minimize environmental impact through efficient design, energy efficiency measures, and thoughtful material choices.
From their small size and minimalistic design to their use of renewable energy sources and water conservation systems, tiny houses exemplify the importance of sustainability in the realm of architecture and housing. They provide an opportunity for individuals and families to live more consciously, reducing their ecological footprint while enjoying a simpler and more affordable lifestyle.
By prioritizing energy efficiency, utilizing renewable energy sources, and incorporating water conservation systems, tiny houses contribute to a greener future. They showcase the potential of sustainable living, inspiring others to rethink their own consumption habits and embrace a more environmentally-friendly lifestyle.
However, sustainable tiny house living also comes with certain challenges and considerations. Limited space, zoning regulations, land acquisition, and social acceptance are factors that need to be carefully considered and navigated. By facing these challenges head-on and finding creative solutions, individuals can overcome obstacles and fully embrace the benefits of tiny house living.
In conclusion, tiny houses represent more than just a minimalistic and compact living space. They embody the principles of sustainable design and offer an alternative approach to housing that promotes resource efficiency, environmental stewardship, and community connectivity. By embracing sustainable features and living practices, tiny houses demonstrate that small can indeed be mighty in terms of the positive impact they can have on the planet and our collective well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Tiny House Fit Into Sustainable Design
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does A Tiny House Fit Into Sustainable Design”