Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Represent Stairs On A Floor Plan

Architecture & Design
How To Represent Stairs On A Floor Plan
Modified: May 6, 2024
Learn how to effectively represent stairs on a floor plan with our comprehensive guide. Enhance your architecture and design skills today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to designing and understanding architectural floor plans, every detail matters. One crucial element that needs to be accurately represented is the staircase. Stairs are not just functional components; they also add visual interest and flow to a building’s design. Properly representing stairs on a floor plan is essential for both architects and builders to ensure accurate construction and efficient use of space.
In this article, we will explore the importance of representing stairs on a floor plan and provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to do it effectively. We will discuss the basics of stair representation, including identifying stair locations, drawing staircase outlines, indicating stair direction, and adding stair dimensions. We will also cover stair symbols and conventions, as well as the proper labeling of stair sections.
Whether you’re an architect, interior designer, or someone who simply wants to understand floor plans better, this article will equip you with the necessary knowledge to effectively represent stairs in architectural drawings.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets to perfectly representing stairs on a floor plan.
Key Takeaways:
- Accurate representation of stairs on architectural floor plans is crucial for functionality, space planning, structural integrity, effective communication, and aesthetic appeal, ensuring seamless integration into the overall design.
- Key considerations for representing stairs include identifying their location, drawing accurate outlines, indicating direction, adding dimensions, and utilizing standardized symbols and labels to facilitate clear communication and construction accuracy.
Read more: What Is A Floor Plan
Understanding Floor Plans
Before we delve into representing stairs on a floor plan, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of what floor plans are and how they are used in the architectural design process.
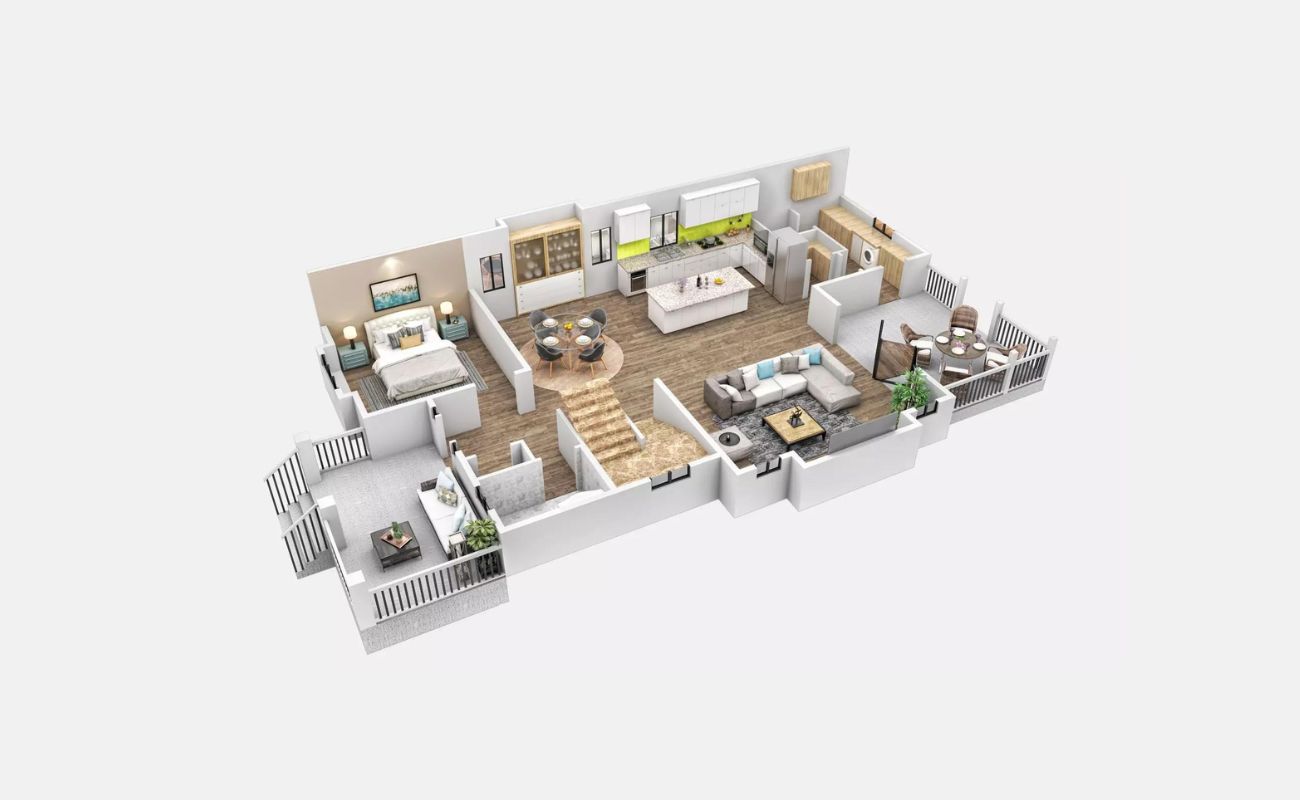
A floor plan is a scaled diagram that illustrates the layout of a building or a specific floor of a building. It provides a bird’s eye view of the space, showing the arrangement of rooms, walls, windows, doors, and other architectural elements. Floor plans are used by architects, designers, and builders as a primary tool for visualizing and communicating the design intent of a space.
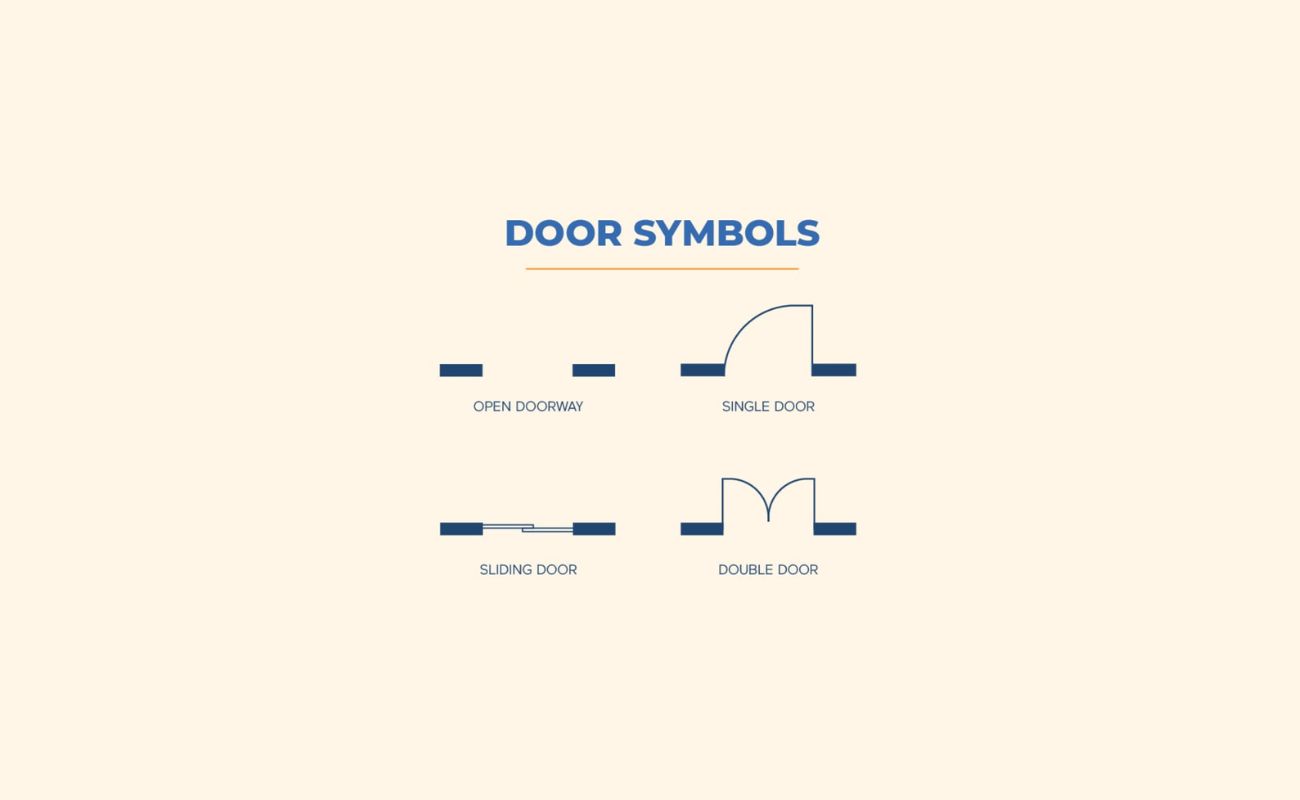
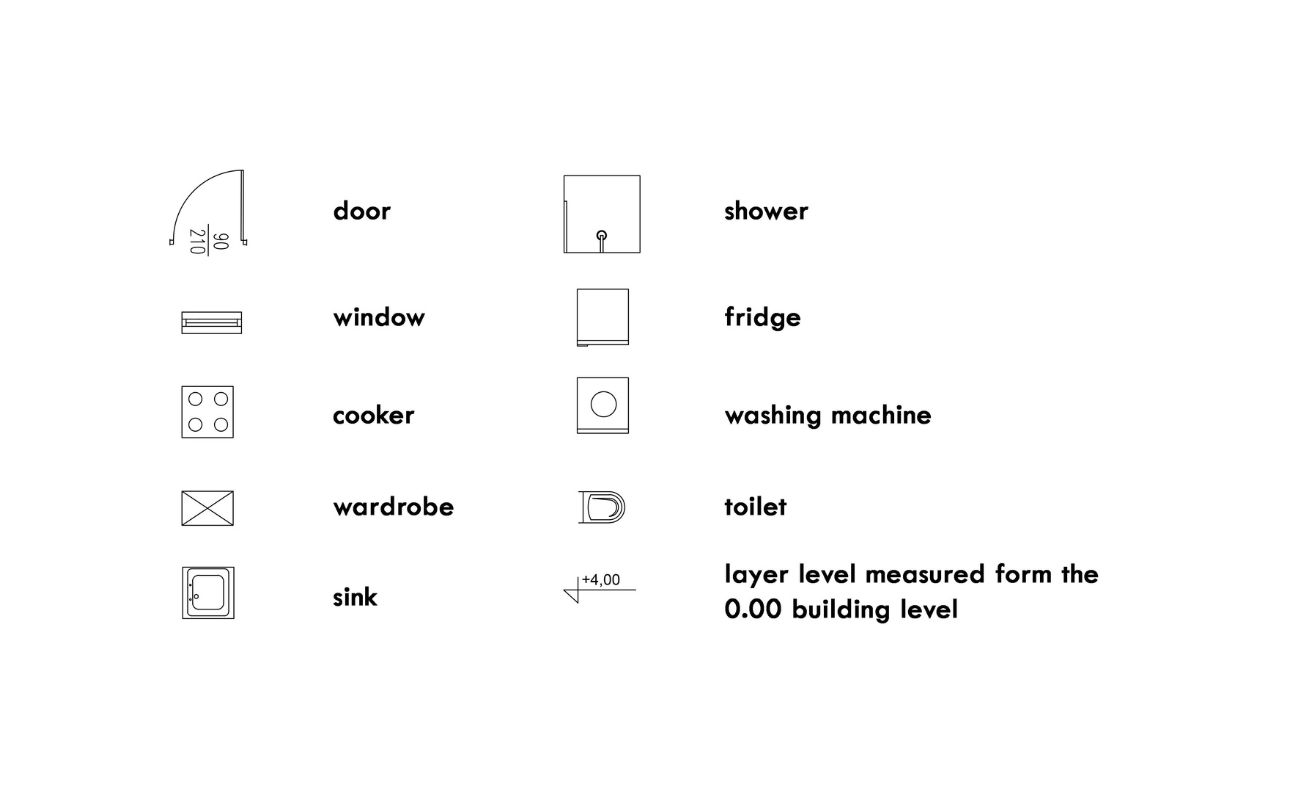
Each element in a floor plan is represented using symbols and conventions to convey specific information. This includes walls, windows, doors, furniture, and of course, stairs. Understanding floor plan symbols is crucial to effectively interpret and communicate architectural designs.
In terms of scale, floor plans can be drawn to various levels of detail. From a bird’s eye view, the floor plan may show the overall layout and division of spaces. In more detailed floor plans, dimensions, materials, and other annotations may be included to provide a comprehensive understanding of the design.
Now that we have a basic understanding of floor plans, let’s move on to the importance of representing stairs accurately on these plans.
Importance of Representing Stairs
Representing stairs accurately on a floor plan is crucial for several reasons. Let’s explore the importance of properly representing stairs in architectural drawings:
- Functionality: Stairs are essential for navigating different levels within a building. Representing stairs on a floor plan ensures that they are incorporated into the design in a practical and functional manner, allowing for easy movement between floors. It also helps architects and builders determine the appropriate size, placement, and configuration of stairs to meet safety regulations and building codes.
- Space Planning: Stairs take up valuable space within a building. By accurately representing stairs on a floor plan, architects can plan and optimize the use of space efficiently. They can determine the best location for stairs, taking into consideration factors such as traffic flow, aesthetics, and the overall layout of the building.
- Structural Considerations: Stairs are not only functional but also play a role in the structural integrity of a building. By representing stairs accurately, architects can properly incorporate them into the structural design. This ensures that the stairs are adequately supported and can bear the weight of people using them.
- Communication: Floor plans serve as a crucial communication tool between architects, designers, builders, and clients. Accurately representing stairs allows everyone involved in the construction process to have a clear understanding of the design intent and layout. It facilitates effective communication and minimizes mistakes or misunderstandings during the construction phase.
- Aesthetics: Stairs can be a visually striking element in architectural designs. Proper representation of stairs on a floor plan ensures that their aesthetic qualities are considered in the overall design. It allows architects and designers to incorporate unique design features, materials, and lighting to enhance the visual appeal of the stairs.
In summary, representing stairs accurately on a floor plan is vital for functionality, space planning, structural considerations, effective communication, and aesthetics. It ensures that stairs are seamlessly integrated into the design, optimizing both practicality and visual appeal.
Basics of Stair Representation
Now that we understand the importance of representing stairs on a floor plan, let’s dive into the basics of stair representation. Properly representing stairs involves several key steps, from identifying their location to indicating their direction and dimensions.
Identifying Stair Location: The first step in representing stairs is identifying their location within the floor plan. This can be done by analyzing the overall layout and considering factors such as ease of access, traffic flow, and the desired relationship between different spaces. Stairs are typically located near entrances, in central areas, or in designated stairwells.
Drawing Staircase Outline: Once the location of the stairs is determined, the next step is to draw the outline of the staircase on the floor plan. This includes representing the shape, size, and position of the stairs. Stair outlines are typically represented as a series of straight lines and angles, indicating the rise, run, and landing of each step.
Indicating Stair Direction: Stair direction refers to the orientation in which the stairs ascend or descend. It is crucial to indicate stair direction accurately to ensure the proper flow and functionality of the space. Stair direction can be represented using arrows or by labeling the start and end points of the stairs.
Adding Stair Dimensions: Including stair dimensions on the floor plan is essential for both construction purposes and spatial planning. Stair dimensions typically include the total height (rise) and total horizontal length (run) of the staircase. Additionally, the dimensions of each individual step, known as the tread and riser dimensions, are also important to indicate.
Indicating Stair Type: There are various types of stairs, including straight stairs, L-shaped stairs, U-shaped stairs, spiral stairs, and more. It is crucial to indicate the type of stairs being represented on the floor plan so that builders and contractors can accurately construct them according to the design intent.
By following these basic guidelines for stair representation, architects and designers can effectively communicate the design intent and ensure that the stairs are constructed accurately and functionally.
Identifying Stair Location
When representing stairs on a floor plan, it is crucial to accurately identify their location. The placement of stairs has an impact on the overall functionality and flow of the space, as well as the aesthetic appeal of the design. Here are some considerations for identifying the stair location:
Accessibility: The first consideration when determining the location of stairs is accessibility. Stairs should be conveniently located to provide easy and efficient access between different levels of the building. They should be easily accessible from main entrances and common areas to ensure a smooth flow of traffic.
Traffic Flow: Analyzing the traffic flow within the space is essential. Consider the natural path that people are likely to take when moving through the building. Stairs should be placed in a way that minimizes congestion and allows for a seamless transition between floors.
Relationship Between Spaces: The relationship between different spaces within the building should also be considered when determining stair location. Stairs should ideally connect areas that have a logical connection or purpose. For example, in a multi-level office building, stairs may be located near communal areas or close to the entrance and main lobby.
Building Codes and Regulations: It is crucial to comply with building codes and regulations when determining the location of stairs. Local building codes may specify requirements for the placement of stairs, such as minimum width, headroom clearance, and the maximum number of steps before requiring a landing. These regulations ensure the safety and accessibility of the staircase for occupants.
Aesthetics: The visual impact of the stair location should also be taken into account. Stairs can be a focal point of the design, so their placement should contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of the space. Consider how the stairs will interact with other architectural elements and how they can enhance the visual flow and character of the building.
By carefully considering accessibility, traffic flow, spatial relationships, building codes, and aesthetics, architects and designers can identify the ideal location for stairs. This ensures that the stairs are functional, safe, and contribute to the overall design vision of the building.
Read more: How To Dimension A Floor Plan
Drawing Staircase Outline
Once the location of the stairs is identified, the next step in representing stairs on a floor plan is to draw the outline of the staircase. This involves accurately representing the shape, size, and position of the stairs. Here are some guidelines for drawing a staircase outline:
Start and End Points: Begin by marking the start and end points of the staircase. These points indicate where the staircase begins and where it ends. They play a crucial role in indicating the direction and flow of the stairs.
Straight or Curved: Determine if the stairs will be straight or curved. Straight stairs are the most common type and consist of a series of straight steps. Curved stairs, on the other hand, have a more flowing design and follow a curved path. The choice of straight or curved stairs depends on the design intent and available space.
Rise and Run: The rise and run of a staircase refer to the vertical and horizontal dimensions of each step. The rise is the height between each step, while the run is the depth or length of each step. Determine the desired rise and run for the staircase and ensure that it complies with local building codes and regulations.
Landings: Landings are flat platforms or resting areas within a staircase. They provide a space for users to pause and change direction if necessary. If the staircase includes more than one flight of steps or changes direction, include landings in the outline to indicate their presence.
Width: Consider the width of the staircase. The width should be sufficient to allow comfortable passage for users. It should comply with local building codes to ensure safety and accessibility. Include the width of the stairs in the outline to provide accurate information to builders and contractors.
Dimensions: Including dimensions in the staircase outline is important for construction purposes. Add measurements for the rise, run, width, and landings to ensure that the stairs are constructed accurately according to the design intent.
By following these guidelines and accurately drawing the outline of the staircase, architects and designers can effectively communicate the design to builders and ensure that the stairs are constructed to meet functional and aesthetic requirements.
Indicating Stair Direction
Indicating the direction of the stairs is an important aspect of representing them accurately on a floor plan. The direction conveys how the stairs ascend or descend within the building and affects the overall flow and functionality of the space. Here are some methods for indicating stair direction:
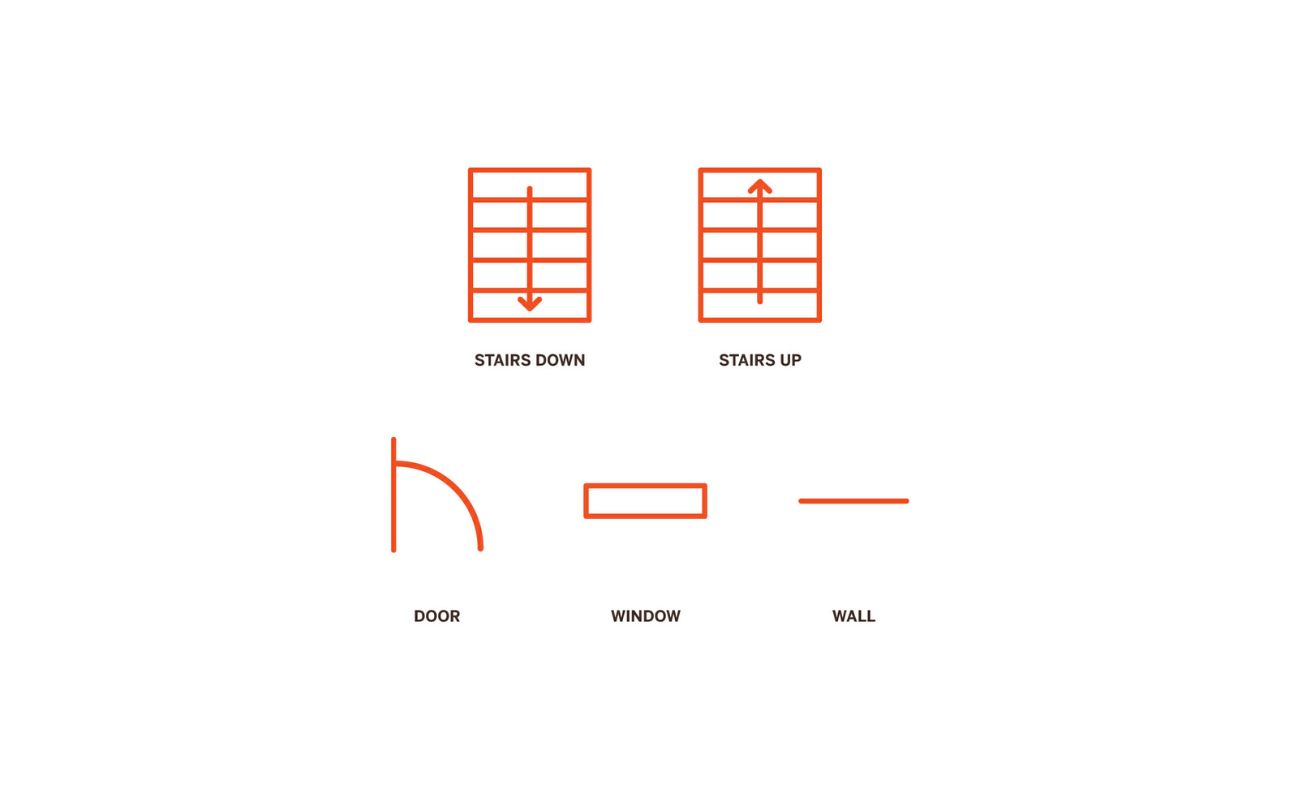
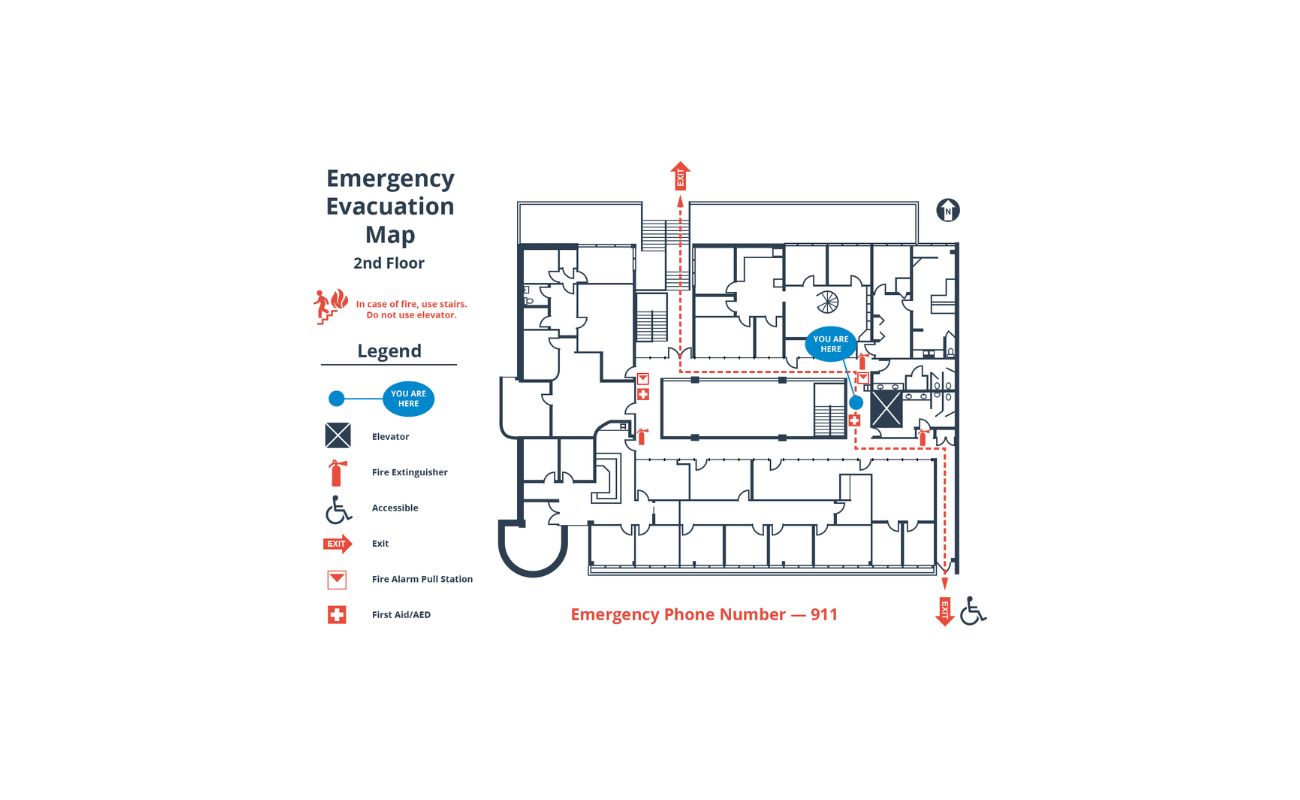
Arrows: One straightforward way to indicate stair direction is by using arrows. Arrows can be placed on the floor plan to show the direction in which the stairs ascend or descend. Use a single arrow for a straight flight of stairs or multiple arrows for stairs with landings or changes in direction.
Start and End Points: Another method is to label the start and end points of the stairs. This can be done using letters or numbers to indicate the beginning and end of the staircase. For example, you can label the start point of the stairs as “A” and the end point as “B” to show the direction of movement.
Text Annotations: Text annotations can complement the arrows or labels to provide additional clarity. You can add text next to the arrows or labels specifying “Up” and “Down” to explicitly indicate the direction of the stairs.
Orientation Labels: Orientation labels can be used in combination with arrows or labels to provide further information. For example, the floor plan could include a compass rose or directional labels such as “North,” “South,” “East,” and “West” to indicate the orientation of the stairs in relation to the overall floor plan.
Graphic Symbols: In some cases, graphic symbols may be used to represent the direction of the stairs. These symbols can vary depending on the design style or specific conventions used in the architectural industry. Consult the relevant graphics standards or conventions to determine the appropriate symbol to represent stair direction.
By utilizing these methods to indicate stair direction on a floor plan, architects and designers can effectively communicate the intended flow and movement of users between different levels of the building. This ensures that the stairs are correctly understood and incorporated into the construction process.
When representing stairs on a floor plan, use a symbol with a straight line for the stairs and indicate the direction of travel with arrows. Include the total rise and run measurements for clarity.
Adding Stair Dimensions
In addition to accurately representing the shape, size, and direction of stairs on a floor plan, it is crucial to include stair dimensions. Stair dimensions provide critical information for both construction purposes and spatial planning. Here are some key dimensions to consider when adding stair dimensions:
Total Height (Rise): The total height, also known as the rise, represents the vertical distance between the starting point and the ending point of the stairs. This measurement is essential for determining the overall height of the staircase and ensuring that it complies with building codes and safety regulations.
Total Horizontal Length (Run): The total horizontal length, also known as the run, represents the horizontal distance covered by the complete set of stairs. It is important for understanding the overall footprint of the staircase and ensuring that it fits within the available space.
Individual Step Dimensions: Each step within the staircase has its own dimensions that need to be indicated. This includes the tread, which is the horizontal surface of the step that is stepped on, and the riser, which is the vertical height between each step. Indicating these dimensions helps ensure the comfort and safety of users when ascending or descending the stairs.
Landings: If the staircase includes landings, it is important to include their dimensions as well. Landings provide resting areas and transition points within the staircase. Include the width and length of the landing to accurately represent its size and facilitate construction.
Clearances: Consider any clearances required around the stairs, such as headroom clearance. Headroom clearance refers to the vertical space above the stairs, ensuring that users can comfortably pass beneath any obstacles or obstructions. Include these clearances in the dimensions to ensure compliance with building codes.
Adding stair dimensions on the floor plan provides all the necessary information for builders and contractors to accurately construct the staircase. It also helps architects and designers plan the overall layout and spatial organization of the building, ensuring that the stairs seamlessly integrate with the surrounding spaces.
By including comprehensive stair dimensions on the floor plan, architects can ensure that the staircase is not only aesthetically pleasing but also up to code and functional for everyday use.
Indicating Stair Type
When representing stairs on a floor plan, it’s important to indicate the type of stairs being used in the design. There are various types of stairs, each with its own characteristics and considerations. Indicating the stair type on the floor plan helps communicate the intended design and construction details to builders and contractors. Here are some common stair types and methods for indicating them:
Straight Stairs: Straight stairs are the most common and straightforward type of stairs. They are characterized by a straight flight of steps that ascend or descend in a linear fashion. To indicate straight stairs on the floor plan, simply draw a continuous line representing the series of steps with a clear start and end point.
L-Shaped Stairs: L-shaped stairs consist of a straight flight of steps that make a 90-degree turn midway. This type of stairs is commonly used when space is limited or when there is a need to change the direction of the staircase. To indicate L-shaped stairs on the floor plan, draw the straight flight of steps with a landing at the turn point.
U-Shaped Stairs: U-shaped stairs are similar to L-shaped stairs but with an additional flight of steps that create a complete U-shape. This type of stairs is often used in larger spaces or as a prominent architectural feature. Indicate U-shaped stairs on the floor plan by drawing the two flights of steps with a landing at the turn point.
Spiral Stairs: Spiral stairs are designed in a circular or helical shape, featuring a central column and steps that radiate around it. They are often used in tight spaces or as a design statement. To indicate spiral stairs on the floor plan, use a recognizable spiral symbol or a curved line representing the spiral shape.
Circular Stairs: Circular stairs are similar to spiral stairs but with a larger radius and a more gentle curve. They create a circular or semi-circular shape and can be used as a grand architectural feature. Indicate circular stairs on the floor plan by drawing a curved line representing the circular shape of the stairs.
By including these stair types and symbols on the floor plan, architects and designers can effectively convey the intended design and configuration of the staircase. This helps builders and contractors accurately construct the stairs, ensuring that they meet both the functional and aesthetic requirements of the space.
Read more: How To Choose A Floor Plan
Stair Symbols and Conventions
When representing stairs on a floor plan, it’s common to use symbols and conventions to provide a standardized representation. Stair symbols help convey important information about the staircase to builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. Here are some commonly used stair symbols and conventions:
Straight Stairs: Straight stairs are typically represented by a simple straight line with vertical tick marks indicating the position of each step. The direction of the stairs can be indicated with arrows or labels such as “Up” and “Down.”
L-Shaped Stairs: L-shaped stairs are represented with a straight line for the first flight of steps, followed by a right-angle turn and another straight line for the second flight. A landing symbol can be used to indicate the turn in the stairs.
U-Shaped Stairs: U-shaped stairs are represented with two parallel straight lines for the main flights of steps and two curved lines connecting them to indicate the curves of the U shape. Landings are indicated at the turn points with appropriate symbols.
Spiral Stairs: Spiral stairs can be represented by a spiral symbol, usually with an arrow indicating the direction of movement. The number of steps can be indicated inside the spiral symbol, and dimensions such as the diameter of the spiral can also be included.
Circular Stairs: Circular stairs are often represented using a large circle or semi-circle symbol, with tick marks or dashed lines indicating the position of each step. Arcs or curves can be added to the symbol to represent the shape of the stairs.
Dimensioning: It’s important to include dimensions for the rise (vertical height of each step), run (horizontal depth of each step), and any landings on the floor plan. Use distinct symbols or conventions to represent these dimensions, such as arrows with labeled dimensions.
In addition to these symbols, it’s important to follow industry-standard conventions and utilize symbols that are widely recognized. Different regions or organizations may have slight variations in symbols, so consulting specific local building codes and graphics standards is essential for accurate representation.
By using standard stair symbols and conventions, architects and designers can effectively communicate the design details of the staircase, ensuring clarity and consistency throughout the construction process.
Labeling Stair Sections
In addition to accurately representing the shape and dimensions of stairs on a floor plan, it is essential to label different sections of the staircase. Labeling stair sections helps clarify the various parts of the stairs and provides additional information for builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. Here are some key sections of stairs that should be labeled:
Flight: The flight refers to a continuous series of steps between landings or floors. It is important to label each flight of stairs to indicate the number of steps and the direction of movement. This helps distinguish the different sections of the stairs and makes it easier to follow the flow of the staircase.
Landing: Landings are flat platforms or resting areas within a staircase. They provide a space for users to pause, change direction, or transition between different flights of stairs. Labeling the landings on the floor plan helps identify their location and facilitates accurate construction.
Nosing: The nosing is the front edge of each step that extends beyond the tread. It is often labeled to indicate the overhang or beveled portion of the step. Labeling the nosing helps ensure that the design and construction accurately reflect the intended dimensions and aesthetics of the staircase.
Handrail: The handrail is an important safety feature of stairs, providing support and stability for users. It is crucial to label the handrail on the floor plan to indicate its position, height, and any specific design details. This ensures that the handrail is correctly installed and compliant with building codes.
Balusters: Balusters are the vertical posts or spindles that support the handrail along the staircase. They play a vital role in both the function and aesthetics of the staircase. Labeling the balusters on the floor plan helps ensure the proper placement and spacing, creating a safe and visually pleasing stair design.
Newel Post: The newel post is a larger, more decorative post that is often found at the beginning and end of a handrail. It provides structural support and serves as a prominent design element. Labeling the newel post on the floor plan helps indicate its position and any specific design details or dimensions.
By clearly labeling these different sections of the staircase on the floor plan, architects and designers can effectively communicate the design intent and provide comprehensive information for builders and contractors. This ensures that the staircase is constructed accurately and in accordance with the desired design and safety standards.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When representing stairs on a floor plan, there are common mistakes that should be avoided to ensure accurate and clear communication of the design intent. By being aware of these mistakes, architects and designers can prevent errors and potential issues during the construction process. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Inaccurate Dimensions: One of the most critical mistakes is providing inaccurate dimensions for the stairs. Incorrect rise and run measurements can lead to uneven step heights or a steep or uncomfortable staircase. Always double-check and verify the dimensions before including them on the floor plan.
Omission of Stair Labels: It is important to label each section of the stairs, such as flights, landings, nosing, handrails, and balusters. Omitting these labels can lead to confusion and misinterpretation during the construction phase. Ensure that all relevant sections and features of the staircase are clearly labeled on the floor plan.
Ignoring Building Codes: Building codes dictate various requirements for stairs, including minimum width, headroom clearance, maximum riser height, and more. Ignoring these codes can result in safety hazards or non-compliance during inspections. Always consult and adhere to the local building codes to ensure the stairs meet all necessary regulations.
Inadequate Space Planning: Inadequate space planning can lead to cramped or inefficient staircases. Insufficient clearances, narrow widths, or inadequate landing sizes can compromise the usability and safety of the stairs. Properly plan the space requirements for the stairs, considering traffic flow, ease of use, and compliance with accessibility standards.
Unsuitable Stair Type: Choosing the wrong type of stairs for a space can lead to functional and visual issues. Consider the available space, design aesthetic, and user needs when selecting the appropriate stair type. The stairs should fit well within the overall architecture and accommodate the desired flow of movement between levels.
Poor Graphic Representation: Clear and consistent graphic representation of stairs is essential for effective communication. Using unclear symbols, inconsistent labeling, or inadequate line work can cause confusion and misinterpretation of the design. Use standardized symbols and graphic conventions to ensure clarity and consistency throughout the floor plan.
Lack of Coordination with Other Elements: Stairs are an integral part of the overall architectural design. Failing to coordinate the staircase with other elements such as doors, walls, windows, and furniture can lead to conflicts and functional issues. Ensure that the stair representation on the floor plan aligns properly with the other design elements.
By avoiding these common mistakes, architects and designers can accurately communicate their design intentions, facilitate smooth construction, and ensure the creation of safe and aesthetically pleasing staircases.
Conclusion
Representing stairs on a floor plan is a crucial aspect of architectural design. Accurate representation of stairs ensures both functionality and aesthetics, allowing for smooth movement between levels and enhancing the overall design of a building. By following the guidelines and best practices discussed in this article, architects and designers can effectively communicate the design intent of the stairs and facilitate their construction.
We started by understanding the importance of representing stairs on a floor plan, acknowledging their functionality, space planning, structural considerations, communication value, and aesthetic impact. Recognizing these factors underscores the significance of accurately representing stairs in architectural drawings.
We then delved into the basics of stair representation, including identifying stair locations, drawing staircase outlines, indicating stair direction, and adding stair dimensions. Each step in the process contributes to the clarity and accuracy of the floor plan, enabling builders and contractors to construct the staircase according to the design intent and ensuring a safe and functional end result.
We also explored the use of stair symbols and conventions, as well as the labeling of different stair sections. Properly utilizing symbols and labels helps facilitate clear communication and understanding between stakeholders involved in the construction process, avoiding potential errors and enhancing collaboration.
Lastly, we highlighted common mistakes to avoid, such as inaccurate dimensions, omission of labels, non-compliance with building codes, inadequate space planning, unsuitable stair types, poor graphic representation, and lack of coordination. Awareness of these mistakes empowers architects and designers to address potential pitfalls and deliver accurate, well-designed staircases and floor plans.
In conclusion, representing stairs on a floor plan requires attention to detail, knowledge of industry conventions, and adherence to building codes. By following the guidelines, avoiding common mistakes, and applying creativity, architects can effectively communicate their design vision and contribute to the creation of functional, safe, and visually appealing staircases within architectural projects.
After mastering how to depict stairs on floor plans, you might wonder about the broader aspects of these architectural blueprints. Diving deeper, our next piece demystifies what a floor plan is, covering its functions, benefits, and key components. Whether you're a budding architect or a curious homeowner, understanding floor plans will surely refine your knowledge of space planning and design. Don't miss out on enhancing your skills further!
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Represent Stairs On A Floor Plan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.





0 thoughts on “How To Represent Stairs On A Floor Plan”