Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is Blueprint In Construction


Architecture & Design
What Is Blueprint In Construction
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn all about blueprint in construction and its importance in architectural design. Find out how blueprints serve as crucial guides in the construction process.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to the construction industry, precision and accuracy are of utmost importance. Every detail, measurement, and design element must be carefully planned and executed to ensure a successful project. This is where blueprints come into play.
Blueprints are an essential part of the construction process. They serve as a visual representation of the project, providing all the necessary information for contractors, architects, and engineers to bring a concept to life. In this article, we will explore what blueprints are, their importance in construction, how to read and understand them, and the various types of blueprints commonly used in the industry.
Blueprints, also known as construction plans or working drawings, are a detailed set of documents that outline the specifications, measurements, and instructions for a construction project. They are created by architects, engineers, or drafters and act as a roadmap for the construction team.
Before the digital age, blueprints were created using a chemical process known as the blueprinting process, which involved coating a paper with light-sensitive chemicals and exposing it to a drawing. Nowadays, blueprints are mostly created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, providing more accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility in the design process.
The significance of blueprints in construction cannot be overstated. They act as a crucial link between the design phase and the actual construction, merging creativity with technical details. Blueprints serve as a communication tool, allowing everyone involved in the project, from contractors to subcontractors, to have a clear understanding of the final vision.
Moreover, blueprints ensure that all aspects of a project are well-coordinated and organized. They provide information about structural elements, electrical layouts, plumbing systems, HVAC systems, and other critical components. By having a detailed blueprint, potential clashes or conflicts can be identified and resolved before construction begins, saving time, money, and potential headaches down the line.
Reading and understanding blueprints is a skill that requires a thorough knowledge of architectural and engineering symbols, scales, and techniques. It takes years of experience and training to become proficient in blueprint interpretation. However, having a basic understanding of blueprints can benefit various stakeholders involved in the construction process, from contractors and foremen to project managers and inspectors.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the components of a construction blueprint, explore different types of blueprints, understand the process of creating a blueprint, and familiarize ourselves with the symbols and abbreviations commonly used in blueprints.
Key Takeaways:
- Blueprints are the backbone of construction, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and coordination. Understanding their components, creation process, and potential pitfalls is crucial for successful project execution.
- Effective blueprint interpretation requires attention to detail, collaboration, and compliance with building codes. Avoiding common mistakes and staying updated with the latest tools and software are essential for accurate implementation.
Read more: How To Read Construction Blueprints
Definition of Blueprint in Construction
A blueprint in construction refers to a detailed technical drawing or set of drawings that serve as a guide for the construction process. It is a visual representation of the proposed structure, illustrating the design, dimensions, and specifications of the project. Blueprints provide critical information to contractors, architects, engineers, and other professionals involved in the construction process.
The term “blueprint” originated from the blueprinting process that was used to create copies of the original drawings. Originally, blueprints were created by coating paper with light-sensitive chemicals and exposing them to a drawing, resulting in a white or blue image on a blue background. However, with advancements in technology, blueprints are now created digitally using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, and the term “blueprint” is still used to describe these technical drawings.
Blueprints in construction are created during the design phase of a project. Architects, engineers, or drafters use their expertise to translate the conceptual design into a tangible plan that can be implemented during construction. The blueprint includes dimensions, materials, structural details, plumbing and electrical layouts, and any other relevant information necessary to construct the building.
Blueprints are essential for a variety of reasons. They act as a communication tool, allowing different professionals involved in the construction process to understand and interpret the design intent accurately. Contractors rely on blueprints to estimate costs, materials, and labor requirements. Subcontractors use them to understand their scope of work and coordinate with other trades. Inspectors refer to blueprints to ensure that the construction complies with building codes and regulations.
Overall, blueprints form the foundation of any construction project. They provide precise instructions and details that guide the construction team throughout the entire process. From the initial design to the actual construction, the blueprint serves as a blueprint for success, ensuring that all stakeholders involved have a clear understanding of the project’s objectives and specifications.
Importance of Blueprints in Construction
Blueprints play a crucial role in the construction industry, serving as a vital tool for ensuring accuracy, coordination, and successful project completion. Here are some key reasons why blueprints are of utmost importance in construction:
- Communication and Visualization: Blueprints provide a visual representation of the project, allowing all stakeholders to understand the design intent and construction requirements. They serve as a common language for architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Accuracy and Precision: Blueprints provide precise measurements, dimensions, and specifications. They help in accurately estimating materials, costs, and labor requirements. By following the detailed instructions in the blueprint, construction teams can ensure that the project is executed with precision and to the highest quality standards.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Blueprints facilitate coordination between different trades and disciplines involved in the construction process. For example, electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems can be accurately planned and integrated within the overall design. This coordination ensures seamless execution and minimizes conflicts or rework during construction.
- Compliance with Codes and Regulations: Blueprints provide valuable information that helps ensure the project complies with building codes, zoning regulations, and safety standards. Inspectors refer to blueprints to verify that the construction aligns with the approved plans and meets all legal requirements.
- Problem Identification and Mitigation: Blueprints allow potential issues, clashes, or conflicts to be identified and addressed early in the construction process. For example, structural elements, utility layouts, or access points can be verified and optimized before construction begins. This results in a smoother construction process and minimizes delays or costly changes during the project.
- Documentation and Reference: Blueprints serve as a documented record of the construction project, providing a historical reference that can be used for future maintenance, renovations, or repairs. As-built drawings, which document any changes made during construction, can be created based on the original blueprints.
- Professionalism and Client Satisfaction: By using blueprints, construction professionals demonstrate a high level of expertise, professionalism, and attention to detail. Clear and accurate blueprints lead to efficient and successful construction projects, resulting in increased client satisfaction.
In summary, blueprints are an indispensable part of the construction process. They ensure effective communication, accuracy, coordination, and compliance with regulations. By following the guidance provided in blueprints, construction projects can be executed efficiently, meeting client expectations and delivering high-quality results.
Components of a Construction Blueprint
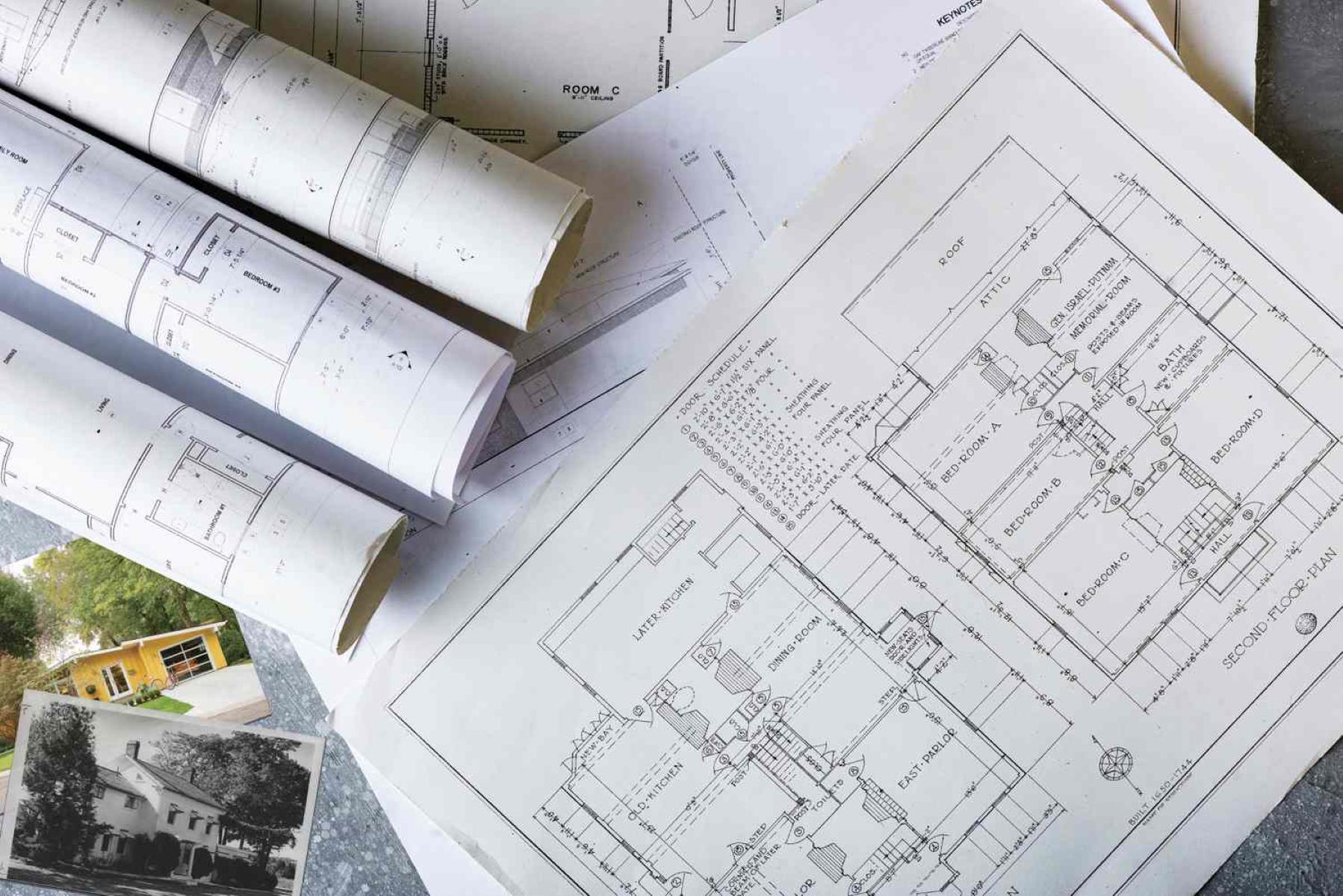
A construction blueprint is a comprehensive set of drawings and documents that provide detailed information about a construction project. These blueprints serve as the foundation for the entire construction process. Let’s explore the key components typically included in a construction blueprint:
- Architectural Drawings: Architectural drawings are a vital component of a construction blueprint. They showcase the design and layout of the building, including floor plans, elevation drawings, and sections. These drawings provide a visual representation of the project, illustrating the placement of walls, doors, windows, and other architectural features.
- Structural Drawings: Structural drawings focus on the structural components of the building, such as foundations, beams, columns, and load-bearing walls. They provide details about the construction methods, materials, and sizes required to ensure the structural integrity of the building. These drawings are crucial for the safe and stable construction of the project.
- Mechanical Drawings: Mechanical drawings encompass the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems of the building. They include information about the ductwork, air distribution, and equipment placement. Mechanical drawings ensure the optimal functioning and comfort of the building’s indoor environment.
- Electrical Drawings: Electrical drawings illustrate the electrical systems of the building. They include details about power distribution, lighting fixtures, and outlet placement. These drawings guide electricians in installing the necessary wiring and components to provide electricity throughout the building.
- Plumbing Drawings: Plumbing drawings provide information about the plumbing systems in the building, including pipes, drains, fixtures, and water supply. They illustrate the layout and connections of the plumbing infrastructure, ensuring the proper functioning of water supply and waste removal within the building.
- Finish Schedules: Finish schedules specify the materials, finishes, and colors to be used throughout the building. This includes flooring materials, paint colors, door styles, and other finishes. Finish schedules ensure consistency and coordination in the selection and implementation of the building’s aesthetics.
- Specifications: Specifications are written documents that accompany the drawings and provide detailed instructions regarding the construction materials, methods, and standards. They outline the quality requirements, performance criteria, and installation techniques necessary for the project. Specifications help ensure consistency and adherence to industry standards.
- Notes and General Information: Blueprints often include notes and general information that provide additional details and instructions. These may include explanations of symbols and abbreviations used in the drawings, project notes, or contractor-specific instructions. These notes help clarify any ambiguities and guide the construction team during the project.
These components collectively form a comprehensive construction blueprint. Each component plays a vital role in providing specific information about the design, structure, systems, and finishes of the building. By carefully reviewing and understanding all the components, construction professionals can effectively implement and execute the construction project.
Reading and Understanding Blueprints
Reading and understanding blueprints is a crucial skill for anyone involved in the construction industry. While it can be complex and requires practice, having a solid understanding of blueprint reading is essential for ensuring accurate interpretation and successful project execution. Here are some key steps to effectively read and understand blueprints:
- Start with the Title Block: The title block is usually located in the bottom right-hand corner of the blueprint and contains important information about the project, such as the project name, address, sheet number, scale used, and date of creation. Familiarize yourself with this information as it provides context for the rest of the blueprint.
- Understand the Scales: Blueprints use scales to represent real-world dimensions. Typically, there will be multiple scales used throughout the blueprint. Pay close attention to the scale indicated in the title block and ensure you are working within the correct scale when taking measurements or referring to dimensions.
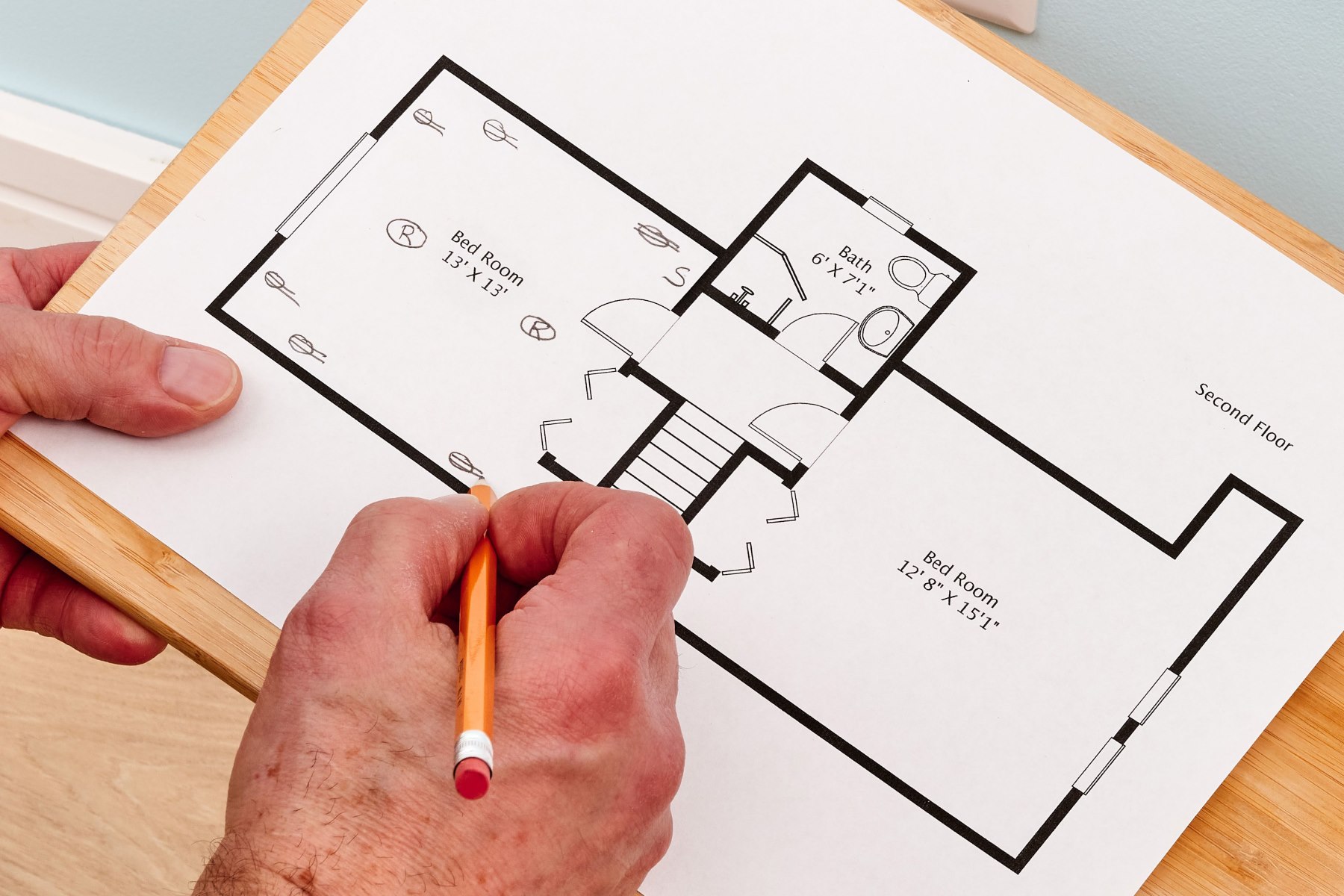
- Study the Floor Plans: The floor plans provide a bird’s-eye view of each level of the building. Familiarize yourself with the symbols, lines, and measurements used to depict walls, doors, windows, and other architectural features. Pay attention to room labels, dimensions, and any special notations provided.
- Examine the Sections and Elevations: Sections and elevations provide a more detailed view of specific areas of the building. They show vertical slices or exterior views of the structure, highlighting important structural elements, heights, and relationships between different components.
- Analyze the Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing Drawings: Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing drawings focus on specific building systems. Take the time to understand the symbols, legends, and connections shown in these drawings. Pay attention to the locations of equipment, fixtures, and any relevant notes or specifications.
- Review the Specifications: Specifications provide written instructions and details about the materials, finishes, and construction methods for various components of the project. Read the specifications carefully to understand the requirements and standards to be followed during construction.
- Refer to the Legend and Abbreviations: Blueprints often include a legend that explains the meanings of symbols, abbreviations, and notations used in the drawings. Familiarize yourself with the legend and regularly refer to it to ensure you understand the various symbols and abbreviations used throughout the blueprint.
- Practice and Seek Guidance: Blueprint reading is a skill that improves with practice. Start with simpler blueprints and gradually work your way up to more complex ones. Seek guidance from experienced professionals or take courses to enhance your understanding. Also, don’t hesitate to ask questions or consult with the project team if you come across anything unclear or challenging.
By following these steps and regularly practicing blueprint reading, you can develop the skills needed to accurately interpret and understand construction blueprints. This will enable you to effectively communicate, plan, and execute construction projects with precision and confidence.
Read more: What Is Blueprint App
Types of Blueprints in Construction
In the construction industry, there are various types of blueprints that serve different purposes throughout the project lifecycle. Different types of blueprints provide specific information related to the design, structure, systems, and finishes of the building. Here are some common types of blueprints used in construction:
- Architectural Blueprints: Architectural blueprints focus on the design and layout of the building. They include floor plans, elevation drawings, and sections, illustrating the placement of walls, doors, windows, and other architectural features. These blueprints serve as a visual guide for construction teams to understand the design intent and construct the building accordingly.
- Structural Blueprints: Structural blueprints provide detailed information about the structural components of the building. They include foundation plans, framing plans, and structural details. These blueprints highlight the load-bearing walls, columns, beams, and other structural elements that are essential for the stability and integrity of the building.
- Mechanical Blueprints: Mechanical blueprints focus on the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems of the building. They include details about ductwork, equipment placement, air distribution, and other mechanical components. These blueprints ensure that the mechanical systems are well-coordinated and integrated into the overall design of the building.
- Electrical Blueprints: Electrical blueprints provide information about the electrical systems of the building. They include the layout of electrical panels, wiring diagrams, lighting plans, and outlet placements. These blueprints guide electricians in installing the necessary wiring and components to provide electricity throughout the building.
- Plumbing Blueprints: Plumbing blueprints focus on the plumbing systems of the building, including water supply, drainage, and fixture locations. They illustrate the layout and connections of pipes, valves, and other plumbing fixtures. These blueprints ensure that the plumbing infrastructure is well-coordinated and properly installed.
- Fire Protection Blueprints: Fire protection blueprints provide details about fire sprinkler systems, fire alarms, and other fire protection measures in the building. They include the locations of sprinkler heads, alarm control panels, and emergency exits. These blueprints are crucial for ensuring the safety and compliance of the building with fire codes and regulations.
- Landscape Blueprints: Landscape blueprints focus on the design and layout of the outdoor spaces surrounding the building. They include details about planting layouts, hardscape features, irrigation systems, and lighting. These blueprints ensure that the landscaping elements are integrated into the overall design, enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of the outdoor areas.
- Interior Design Blueprints: Interior design blueprints focus on the finishes and aesthetics of the building’s interior spaces. They include details about flooring materials, wall treatments, ceiling design, and other interior elements. These blueprints ensure that the interior spaces are designed and constructed according to the specified finishes and design intent.
These are just a few examples of the types of blueprints used in construction. Depending on the complexity and requirements of the project, additional types of blueprints may be included, such as civil blueprints, landscape lighting blueprints, or specialized systems blueprints.
Each type of blueprint serves a specific purpose in guiding the construction process, ensuring coordination between different trades, and meeting the design intent and building codes. Construction professionals need to understand these blueprints to accurately interpret and execute the project in a coordinated and efficient manner.
When creating a blueprint for construction, ensure all necessary details are included such as dimensions, materials, and structural elements to provide a clear and comprehensive guide for the construction process.
The Process of Creating a Blueprint
The creation of a blueprint is a meticulous process that requires careful planning, coordination, and expertise from architects, engineers, and drafters. The following steps outline the typical process of creating a blueprint for a construction project:
- Initial Design and Conceptualization: The process begins with the initial design and conceptualization of the building. Architects work closely with clients to understand their needs, preferences, and functional requirements. Through meetings, discussions, and sketches, the architectural team develops a preliminary design concept for the project.
- Detailed Drawings and Specifications: Once the initial design is approved, the architectural team starts developing detailed drawings and specifications. These drawings provide a comprehensive representation of the building’s layout, elevations, dimensions, and architectural features. Specifications outline the materials, finishes, and construction methods to be used in the project.
- Structural Analysis and Engineering: Simultaneously, structural engineers analyze the architectural design to ensure its structural integrity and safety. They perform calculations, assess the loads on the structure, and determine the appropriate structural elements required. This analysis is critical in creating the structural components and details for the blueprint.
- Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing Design: Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems are essential for the functioning of a building. MEP engineers design the HVAC, electrical, plumbing, and fire protection systems, integrating them with the architectural and structural elements. This coordination ensures that the MEP systems are well-integrated and functional.
- Finalizing the Blueprint: After all the necessary design components have been completed, the architectural, structural, and MEP drawings are combined to create the final blueprint. The drawings are carefully reviewed and checked for accuracy, consistency, and coordination. Any necessary revisions or modifications are made at this stage to ensure the blueprint accurately represents the design intent.
- Approval and Distribution: Once the final blueprint is complete, it is submitted for review and approval by relevant stakeholders, such as the client, regulatory authorities, and other professionals involved in the project. After obtaining necessary approvals, the blueprint is distributed to the construction team, subcontractors, and other parties involved in the construction process.
- Construction Based on the Blueprint: The construction phase begins based on the information provided in the blueprint. Contractors, subcontractors, and the project team refer to the blueprint to understand the scope of work, materials required, and construction methods to be employed. The blueprint acts as a guide for the entire construction process, ensuring accurate implementation of the design.
- Updates and As-Built Drawings: During construction, changes or modifications may be required due to unforeseen circumstances or design adjustments. These changes are recorded and documented through as-built drawings, which depict the revisions made during the construction process. As-built drawings are used to create a record of the final state of the building, supplementing the original blueprint.
The process of creating a blueprint involves a close collaboration between architectural, structural, and MEP teams. Clear communication, coordination, and attention to detail are essential to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the blueprint. From initial design to the final construction, the blueprint plays a critical role in guiding the project and ensuring successful execution.
Blueprint Symbols and Abbreviations
Blueprints use various symbols and abbreviations to convey information quickly and effectively. These symbols and abbreviations act as a visual language that allows construction professionals to interpret the blueprint accurately. Here are some common blueprint symbols and abbreviations:
- Architectural Symbols: Architectural symbols represent different architectural features and elements. For example, a solid line with arrows indicates walls, while a dashed line represents hidden or obscured features. Other symbols include door swings, windows, staircases, and furniture layouts.
- Structural Symbols: Structural symbols represent various structural elements and details. These can include symbols for beams, columns, different types of foundations, and load-bearing walls. Structural symbols are used to convey the design and placement of these components within the building.
- Electrical Symbols: Electrical symbols depict different electrical components, such as outlets, light fixtures, switches, and circuitry. These symbols provide information about the electrical layout, wiring connections, and placement of electrical equipment.
- Mechanical Symbols: Mechanical symbols represent components of the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, such as ductwork, vents, fans, and equipment. These symbols show the layout and relationship between different mechanical elements within the building.
- Plumbing Symbols: Plumbing symbols illustrate the various plumbing and piping components within the building, including pipes, valves, fixtures, and fittings. These symbols indicate the layout and connections of the plumbing system, such as wastewater drainage, supply lines, and plumbing fixtures.
- Fire Protection Symbols: Fire protection symbols are used to represent fire safety features within the building, such as sprinklers, fire alarms, fire extinguishers, and emergency exits. These symbols ensure that the fire protection system and safety measures are accurately represented in the blueprint.
- Symbols for Materials and Finishes: Blueprints often include symbols or notations to indicate the specific materials and finishes to be used in different areas of the building. This can include symbols for flooring materials, wall finishes, ceiling designs, and paint colors.
- Abbreviations: Blueprints use abbreviations to save space and provide quick reference. Common abbreviations can include “Elev.” for elevation, “F.F.” for finished floor, “CMU” for concrete masonry unit, and “HVAC” for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. A legend or key is typically provided on the blueprint to explain the meaning of each abbreviation.
It’s important to note that different regions or industries may have variations in symbols and abbreviations used in blueprints. It’s crucial for construction professionals to familiarize themselves with the specific set of symbols and abbreviations used in their area of expertise or jurisdiction.
Understanding blueprint symbols and abbreviations is critical for accurately interpreting and executing the design depicted in the blueprint. High attention to detail and a good understanding of the specific symbols and abbreviations used in the particular project are necessary for the successful implementation of the construction process.
Tools and Software for Creating Blueprints
Creating blueprints has evolved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in technology. Today, architects, engineers, and drafters rely on a combination of tools and software to create accurate and detailed blueprints. Here are some common tools and software used in the process of creating blueprints:
- Computers and Design Software: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is the backbone of modern blueprint creation. CAD software allows professionals to create precise, scalable, and editable drawings digitally. Programs like AutoCAD, Revit, and ArchiCAD are widely used in the industry, offering comprehensive tools and functionalities for creating detailed blueprints.
- Drawing Tablets and Stylus: Drawing tablets, often used in conjunction with CAD software, provide a digital interface for creating freehand sketches and annotations directly on the computer screen. They offer more natural drawing capabilities and enhance the precision and speed of the blueprint creation process.
- Laser Measuring Devices: Laser measuring devices are used to accurately measure distances, lengths, and angles. They provide quick and precise measurements, reducing human error and ensuring accurate dimensions are incorporated into the blueprint.
- Blueprint Grid Paper: Blueprint grid paper is an essential tool for creating hand-drawn blueprints. These papers have a grid pattern, typically at a specific scale, making it easier to maintain proportion and accurate scaling while drawing by hand.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software: BIM software, such as Autodesk BIM 360 or Vectorworks, offers a 3D modeling approach to the blueprint creation process. BIM allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate and integrate their designs in a coordinated manner, resulting in more accurate and efficient construction.
- Color Coding and Highlighting Tools: Color coding and highlighting tools, such as colored pens or markers, are useful for emphasizing or distinguishing different elements on a blueprint. These tools help to draw attention to specific features, annotations, or revisions, making the blueprint easier to read and understand.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Software: VR and AR software enable professionals to immerse themselves in a virtual representation of the building, providing a realistic and interactive viewing experience. This technology can help architects and clients visualize the design, make informed decisions, and identify potential issues before construction begins.
- Scanners and Digitization Tools: Scanners and digitization tools, such as large-format scanners or document cameras, are used to convert physical drawings or blueprints into digital formats. This allows for easy storage, sharing, and editing of existing blueprints.
- Project Management Software: Project management software, such as Procore or Primavera P6, helps manage the entire blueprint creation process, including collaboration, document control, and task scheduling. These tools facilitate effective communication and streamline workflow among different project stakeholders.
The use of these tools and software has revolutionized the blueprint creation process, making it more efficient, accurate, and collaborative. While traditional paper-based methods still have their place, the adoption of digital tools and software has significantly enhanced the speed and quality of blueprint creation.
It’s important for professionals in the construction industry to stay updated with the latest tools and software advancements to enhance their blueprint creation processes and maintain a competitive edge in the industry.
Read more: What Is A Blueprint Of A House
Blueprints and Building Codes
Building codes are a set of regulations and standards established by local, regional, or national authorities to ensure the safety, health, and welfare of occupants in built environments. These codes dictate the minimum requirements for the design, construction, and occupancy of buildings. Blueprints play a vital role in complying with building codes and ensuring that the construction project meets the necessary regulatory standards. Here’s how blueprints and building codes are closely intertwined:
- Incorporating Code Compliance into Blueprints: Building codes set out specific requirements relating to structural integrity, fire safety, accessibility, energy efficiency, electrical systems, plumbing systems, and more. Architects, engineers, and drafters consult these codes when creating blueprints and integrate the necessary design elements to meet code compliance.
- Structural Requirements: Building codes specify minimum structural requirements to ensure the stability and strength of a building. These requirements dictate elements such as foundation design, load-bearing capacities, structural framing, and seismic resistance. Blueprints incorporate these requirements by illustrating the appropriate structural components and their placement.
- Fire and Life Safety: Building codes outline fire and life safety measures to protect occupants in the event of a fire or other emergencies. Blueprints indicate the placement and specifications of fire alarm systems, sprinkler systems, emergency exits, fire-rated walls, and other fire safety features to ensure compliance with the relevant codes.
- Accessibility: Building codes also address accessibility requirements to ensure buildings can be used by individuals with disabilities. Blueprints incorporate features such as ramps, accessible entrances, door widths, and accessible restrooms to comply with accessibility guidelines specified in the codes.
- Plumbing and Electrical Systems: Building codes include regulations for plumbing installations and electrical systems to ensure safety, functionality, and water conservation. Blueprints detail the design and placement of plumbing fixtures, piping, drainage systems, electrical outlets, and wiring to comply with the necessary codes and standards.
- Energy Efficiency: Building codes often contain provisions to promote energy efficiency and sustainability in construction. These codes address insulation, energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and renewable energy requirements. Blueprints incorporate energy-efficient design elements and specify materials and equipment that comply with the energy codes.
- Inspections and Compliance Verification: During the construction process, building inspectors review the blueprints to ensure compliance with the applicable building codes. Inspections are conducted at various stages of construction, including foundation, framing, electrical, plumbing, and final inspections, to verify that the construction aligns with the approved plans.
- Code Updates: Building codes are periodically updated to reflect new standards, technologies, and safety practices. Architects and designers must stay informed about these updates and ensure that their blueprints incorporate the latest code requirements. Failure to comply with the updated codes can lead to delays, additional costs, and even legal implications.
By aligning blueprints with building codes, construction professionals can ensure that the design and construction of a building are in accordance with the necessary regulations. This not only promotes the safety and well-being of occupants but also helps avoid potential penalties, legal issues, and future challenges during occupancy or inspections.
It’s crucial for architects, engineers, and other professionals involved in blueprint creation to have a thorough understanding of local building codes and stay updated with any revisions or amendments. Collaboration with code officials and regular communication during the design process helps ensure that blueprints align with the applicable building codes, resulting in a compliant and safe construction project.
Common Mistakes in Blueprint Interpretation
Blueprint interpretation is a critical skill in the construction industry, as errors or misinterpretations can lead to costly mistakes and delays. Understanding and avoiding common mistakes in blueprint interpretation are essential for accurate project execution. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Failure to Review All Relevant Drawings: Blueprints typically consist of multiple pages or sets, including architectural, structural, electrical, plumbing, and mechanical drawings. One common mistake is overlooking or neglecting to review all of these drawings thoroughly. Each set of drawings contains vital information that must be integrated and coordinated to ensure the overall construction accuracy.
- Misunderstanding Scale and Measurements: Blueprints use scales to represent real-world dimensions accurately. Misinterpreting or failing to understand the scale can result in incorrect measurements and spatial relationships. It is essential to verify the scale used and cross-check measurements to ensure accuracy and precision.
- Overlooking Symbols and Abbreviations: Blueprints use symbols and abbreviations to convey information efficiently. Ignoring or misinterpreting symbols and abbreviations can lead to misunderstandings. It’s crucial to regularly refer to the legend/key provided and familiarize yourself with the commonly used symbols and abbreviations specific to the project and industry.
- Disregarding Design Notes or Specifications: Design notes and specifications provide additional details and instructions that affect the construction process. Neglecting to carefully review and implement these notes can result in deviations from the design intent and compromise the structural integrity, functionality, or aesthetics of the building.
- Failure to Communicate with the Design Team: Effective communication between the construction team and the design team is vital for blueprint interpretation. Failing to clarify uncertainties or seek clarification from architects, engineers, or designers can lead to misunderstandings and inaccurate implementation of the blueprint. Regular communication helps resolve potential issues and ensures a seamless construction process.
- Neglecting Changes or Revisions: Blueprints may undergo changes or revisions during the construction process. Neglecting to review and incorporate these changes can lead to outdated information being followed, resulting in errors or discrepancies. It is crucial to stay updated with the latest revision or as-built drawings and make the necessary adjustments in the construction process.
- Lack of Attention to Detail: Blueprint interpretation requires a keen eye for detail. Failing to pay attention to small details, such as intricate symbols, dimensions, or annotations, can lead to errors in construction. Thoroughly reviewing blueprints and double-checking measurements and specifications are essential to maintain accuracy.
- Failure to Consider Building Codes and Regulations: Building codes and regulations have a significant impact on blueprint interpretation and construction. Neglecting to consider these codes and regulations can result in non-compliance and potential legal repercussions. It’s essential to ensure that the design and implementation align with the relevant building codes and regulations.
- Not Seeking Professional Help When Needed: Blueprint interpretation can be complex, especially for intricate or large-scale projects. Failing to seek professional help or consultation when faced with challenging aspects of the blueprint can lead to costly mistakes. Engaging with experienced architects, engineers, or experts in blueprint reading can provide valuable guidance and ensure accurate interpretation.
Avoiding these common mistakes requires attention to detail, ongoing communication, continuous learning, and a commitment to accuracy. By being diligent in blueprint interpretation and collaborating effectively with the project team, construction professionals can minimize errors and successfully execute construction projects.
Conclusion
Blueprints are an indispensable part of the construction industry, providing a visual representation of a building design and guiding the construction process. They play a vital role in ensuring accuracy, coordination, and compliance with building codes and regulations. Understanding and effectively interpreting blueprints is essential for architects, engineers, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process.
In this article, we explored various aspects of blueprints in construction. We discussed the definition of blueprints and their importance in the construction industry. We examined the components of a construction blueprint, including architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing drawings, as well as finish schedules and specifications.
We delved into the process of creating a blueprint, which involves initial design, detailed drawings, and collaboration between professionals. We also explored the range of tools and software used in blueprint creation, such as CAD software, laser measuring devices, and project management software.
Furthermore, we highlighted the significance of blueprint compliance with building codes, as they dictate minimum requirements for construction safety, structural integrity, fire protection, accessibility, and energy efficiency. We discussed how blueprints incorporate code compliance through design elements and specifications.
Additionally, we touched on common mistakes in blueprint interpretation, ranging from misinterpreting scales and symbols to disregarding design notes and failing to consider changes or revisions. Recognizing and avoiding these mistakes is crucial for accurate implementation and successful project execution.
In conclusion, blueprints serve as critical communication tools, guiding construction professionals in bringing a design concept to life. They ensure accuracy, coordination, compliance with building codes, and the realization of a safe and functional building. By understanding the components, processes, and potential pitfalls of blueprint interpretation, construction professionals can confidently navigate the complexities of construction projects, delivering successful outcomes in the built environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Blueprint In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Is Blueprint In Construction”