Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is A Digital Blueprint


Architecture & Design
What Is A Digital Blueprint
Modified: January 24, 2024
Learn what a digital blueprint is and how it can transform the architecture design process. Enhance efficiency and streamline workflows with this innovative technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of digital blueprints, where architecture and design meet the power of technology. In this fast-paced era, the traditional methods of creating and sharing architectural plans have been revolutionized by the emergence of digital blueprints. But what exactly is a digital blueprint, and why is it so important in the world of architecture and design?
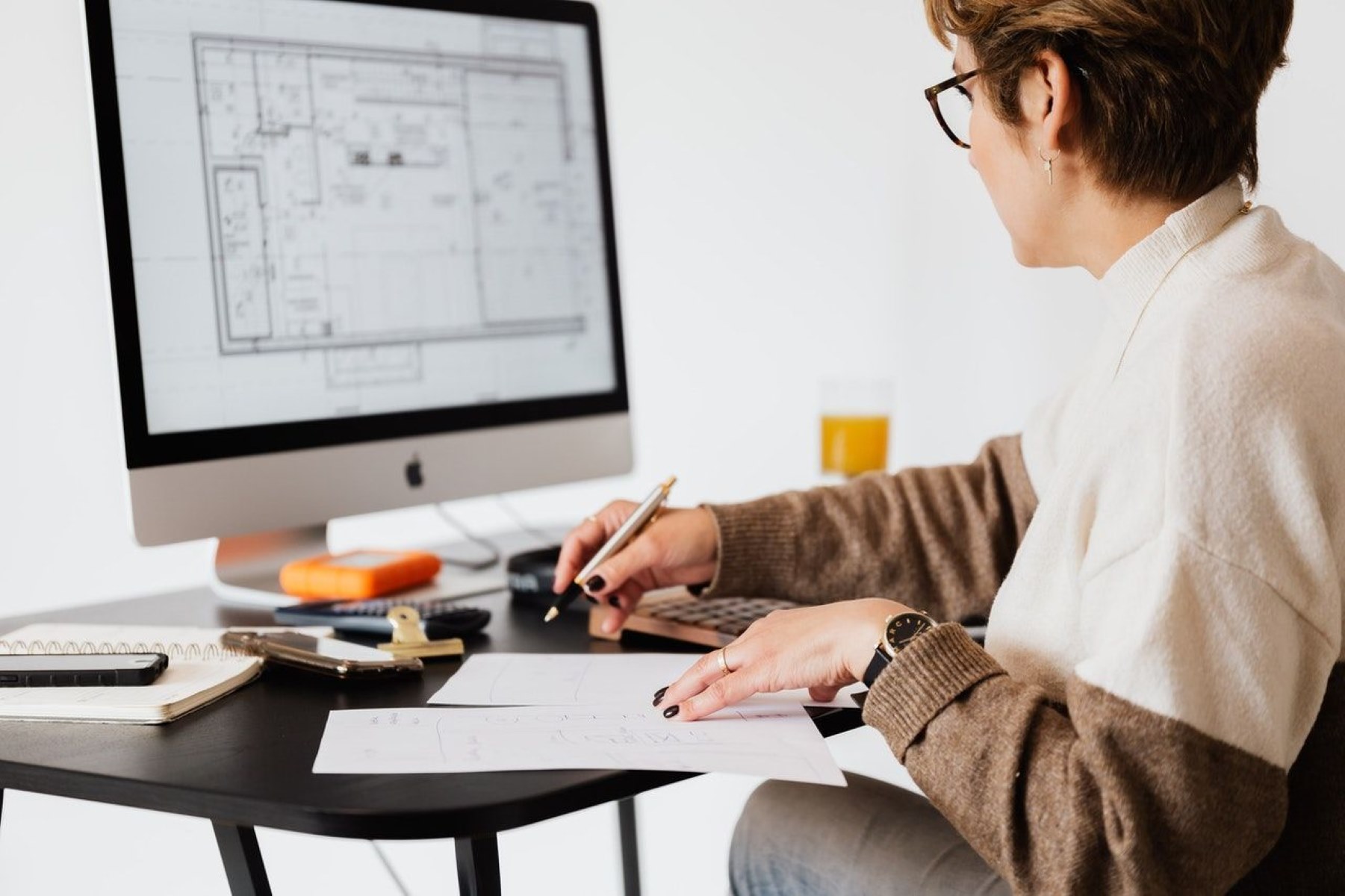
A digital blueprint is a detailed and comprehensive electronic representation of architectural plans and designs. It is typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software and encompasses all the necessary information to construct a building or structure. It includes detailed drawings, measurements, annotations, and specifications that guide the construction process.
The importance of digital blueprints cannot be overstated in today’s architectural landscape. They enable architects, designers, and construction professionals to collaborate seamlessly, streamline the building process, and enhance project efficiency. With a digital blueprint, stakeholders have a precise visual representation of the structure, allowing them to make informed decisions and avoid potential conflicts or errors.
One of the key benefits of using digital blueprints is their versatility. Unlike traditional paper blueprints, digital blueprints can be easily accessed, shared, modified, and stored digitally. This eliminates the need for physical storage space and the risk of losing or damaging important documents. It also enables multiple team members to work simultaneously on the same project, promoting collaboration and productivity.
Moreover, digital blueprints offer enhanced accuracy and precision. With their advanced CAD capabilities, architects and designers can create detailed 3D models and simulations, allowing them to better visualize the final structure and identify any design flaws or conflicts early in the process. This can result in significant time and cost savings, as issues can be addressed and resolved before construction begins.
Key Takeaways:
- Digital blueprints revolutionize architecture by enhancing collaboration, accuracy, and efficiency. They offer improved visualization, seamless sharing, and cost savings, shaping a sustainable future for construction projects.
- Despite challenges, digital blueprints empower architects with advanced tools for precise design, seamless collaboration, and sustainable practices. Embracing digital blueprints paves the way for innovation and excellence in architecture and design.
Read more: What Is Blueprint App
Definition of Digital Blueprint
A digital blueprint is a digital representation of architectural plans and designs that provides a comprehensive and detailed overview of a construction project. It serves as a visual guide, incorporating precise measurements, annotations, and specifications that are essential for constructing a building or structure.
Unlike traditional paper blueprints, which are static and limited in scope, digital blueprints can be created and accessed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This allows architects and designers to leverage the power of technology to create dynamic and interactive representations of their designs.
Digital blueprints are typically created by architects and designers using specialized CAD software. These programs provide a wide range of tools and functionalities to create detailed 2D and 3D representations of the structure. With CAD software, professionals can easily manipulate and modify their designs, test different scenarios, and generate accurate measurements and specifications.
Furthermore, digital blueprints offer the advantage of being easily sharable and accessible. They can be stored and transmitted electronically, eliminating the need for physical copies or storage space. This enables seamless collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and contractors, as they can access the digital blueprint from anywhere at any time.
In addition to their visual representation, digital blueprints often include annotations and notes that provide additional information about the design. This can include details about materials, construction techniques, and specific instructions for the builders. By including this information, digital blueprints offer a more comprehensive understanding of the project, ensuring that all parties involved are on the same page.
Overall, digital blueprints have revolutionized the architectural and construction industry. They provide a more efficient, accurate, and collaborative approach to designing and constructing buildings. With their digital nature and advanced functionalities, they offer numerous advantages over traditional paper blueprints, ultimately improving the quality and success of construction projects.
Importance of Digital Blueprints
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the use of digital blueprints has become increasingly important in the field of architecture and design. Here are some key reasons why digital blueprints are crucial in modern construction projects:
- Accuracy and Precision: Digital blueprints leverage computer-aided design (CAD) software, allowing architects and designers to create highly accurate and precise representations of their designs. With advanced measurement tools and simulation capabilities, professionals can identify and address potential issues before construction begins, ultimately improving the quality and efficiency of the project.
- Collaboration and Communication: Digital blueprints enable seamless collaboration among stakeholders, including architects, designers, engineers, and construction teams. Through the use of digital platforms and cloud-based storage, all team members can access and share the blueprint in real-time. This enhances communication, reduces errors, and ensures that everyone involved is working from the same up-to-date information.
- Efficiency and Time Savings: The use of digital blueprints streamlines the design and construction process, leading to significant time savings. With the ability to make changes and revisions easily, architects and designers can quickly respond to client feedback and adapt the design accordingly. This agility enhances project efficiency and helps meet tight deadlines.
- Cost Reduction: Digital blueprints can contribute to cost savings in various ways. First, the virtual nature of digital blueprints eliminates the need for costly printing, storage, and transportation of physical copies. Second, the ability to detect potential design issues and conflicts early on helps prevent costly rework during the construction phase. By addressing these issues beforehand, construction delays and cost overruns can be minimized.
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits: Digital blueprints align with the global push for sustainable practices in the construction industry. By reducing paper waste and promoting digital workflows, the use of digital blueprints minimizes the environmental impact associated with traditional paper-based processes.
In summary, digital blueprints offer numerous benefits in terms of accuracy, collaboration, efficiency, cost savings, and sustainability. By adopting digital blueprints, architects, designers, and construction professionals can optimize their workflows, enhance project outcomes, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of architecture and design.
Benefits of Using Digital Blueprints
The adoption of digital blueprints in the field of architecture and design brings forth a multitude of benefits that revolutionize the way construction projects are executed. Here are some key advantages of using digital blueprints:
- Enhanced Visualization: Digital blueprints allow architects and designers to create detailed 2D and 3D visualizations of their designs. This enables stakeholders to have a realistic and immersive understanding of the final structure, facilitating better decision-making and avoiding design conflicts.
- Improved Collaboration: With digital blueprints, collaboration between architects, designers, engineers, and contractors becomes streamlined and efficient. Team members can view and work on the same blueprint simultaneously, making it easier to communicate and share ideas. This promotes effective collaboration, reduces miscommunication, and fosters a more cohesive and integrated project team.
- Efficiency in Design Modifications: Digital blueprints can be edited and revised with ease, allowing quick and efficient design modifications. Changes can be made digitally, eliminating the need for manual tracing or reprinting of traditional paper blueprints. This flexibility reduces the time and costs associated with design revisions and ensures that the latest version of the blueprint is always accessible to stakeholders.
- Increased Accuracy and Precision: Digital blueprints offer advanced measurement and annotation tools, ensuring greater accuracy and precision in designs. Detailed measurements and annotations aid in making informed decisions, avoiding mistakes, and facilitating construction processes. This leads to improved quality control and minimizes errors during the construction phase.
- Accessibility and Portability: Digital blueprints can be easily accessed and shared digitally, making them highly portable. Stakeholders can view the blueprint from anywhere, using mobile devices or computers, eliminating the need for physical copies. This accessibility enables remote collaboration and facilitates real-time decision-making, saving time and resources.
- Seamless Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM): Digital blueprints can be integrated with Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, allowing for a holistic approach to construction projects. When combined with BIM, digital blueprints enable the visualization of design elements, structural systems, and even project schedules, enhancing project coordination, and reducing conflicts and delays.
- Reduction in Environmental Impact: Digital blueprints contribute to a more sustainable approach to the construction industry. By eliminating the need for excessive paper usage and reducing waste, they have a positive environmental impact. Additionally, the digital nature of these blueprints promotes digital collaboration, reducing the carbon footprint associated with physical meetings and travel.
By embracing digital blueprints, the architectural and design community can unlock numerous benefits, including improved visualization, enhanced collaboration, increased efficiency, higher accuracy, better accessibility, and reduced environmental impact. These advantages empower professionals to deliver successful construction projects while embracing technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Types of Digital Blueprints
Digital blueprints come in various forms, each designed to serve specific purposes and cater to different stages of the construction process. Here are some common types of digital blueprints:
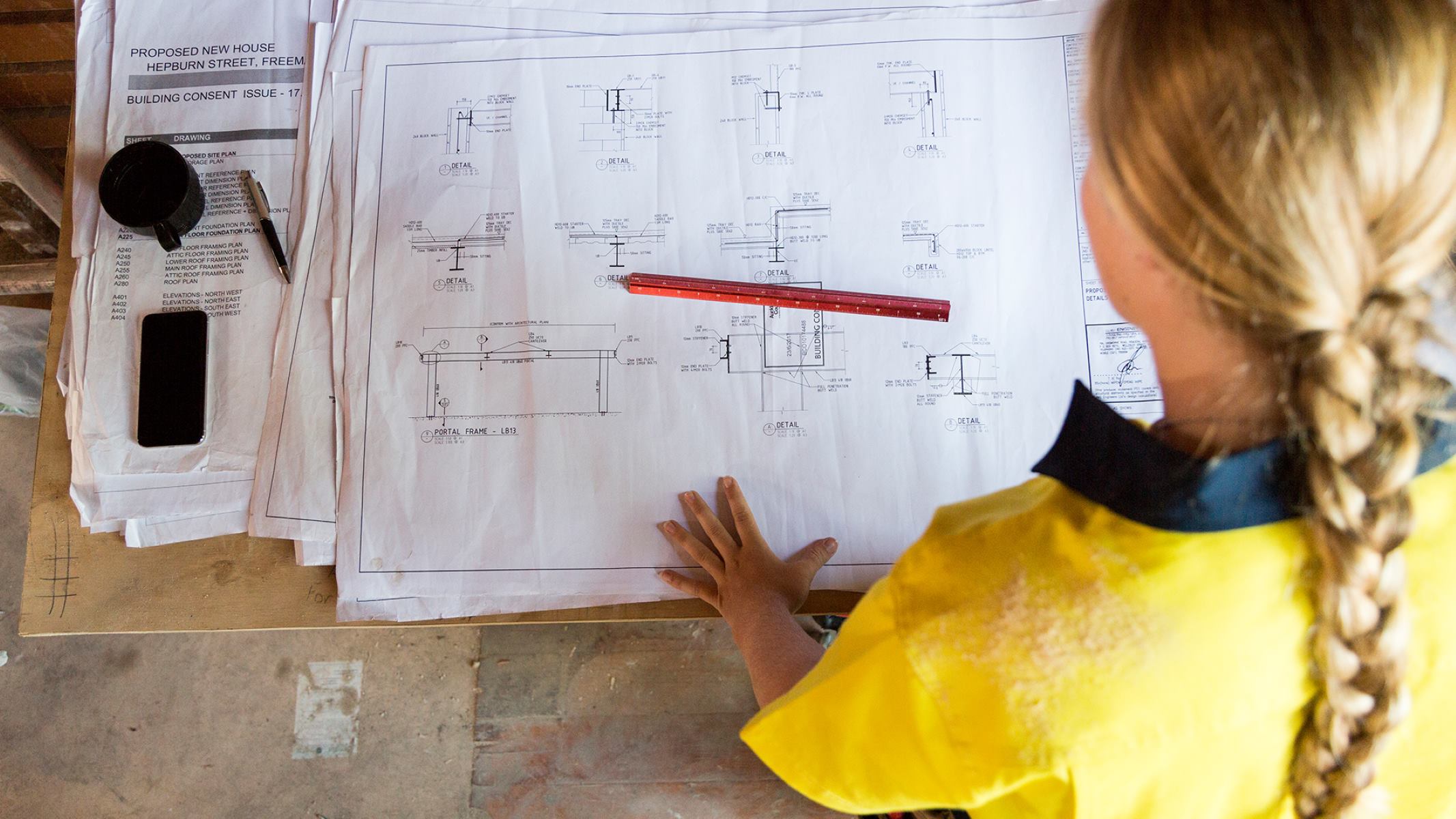
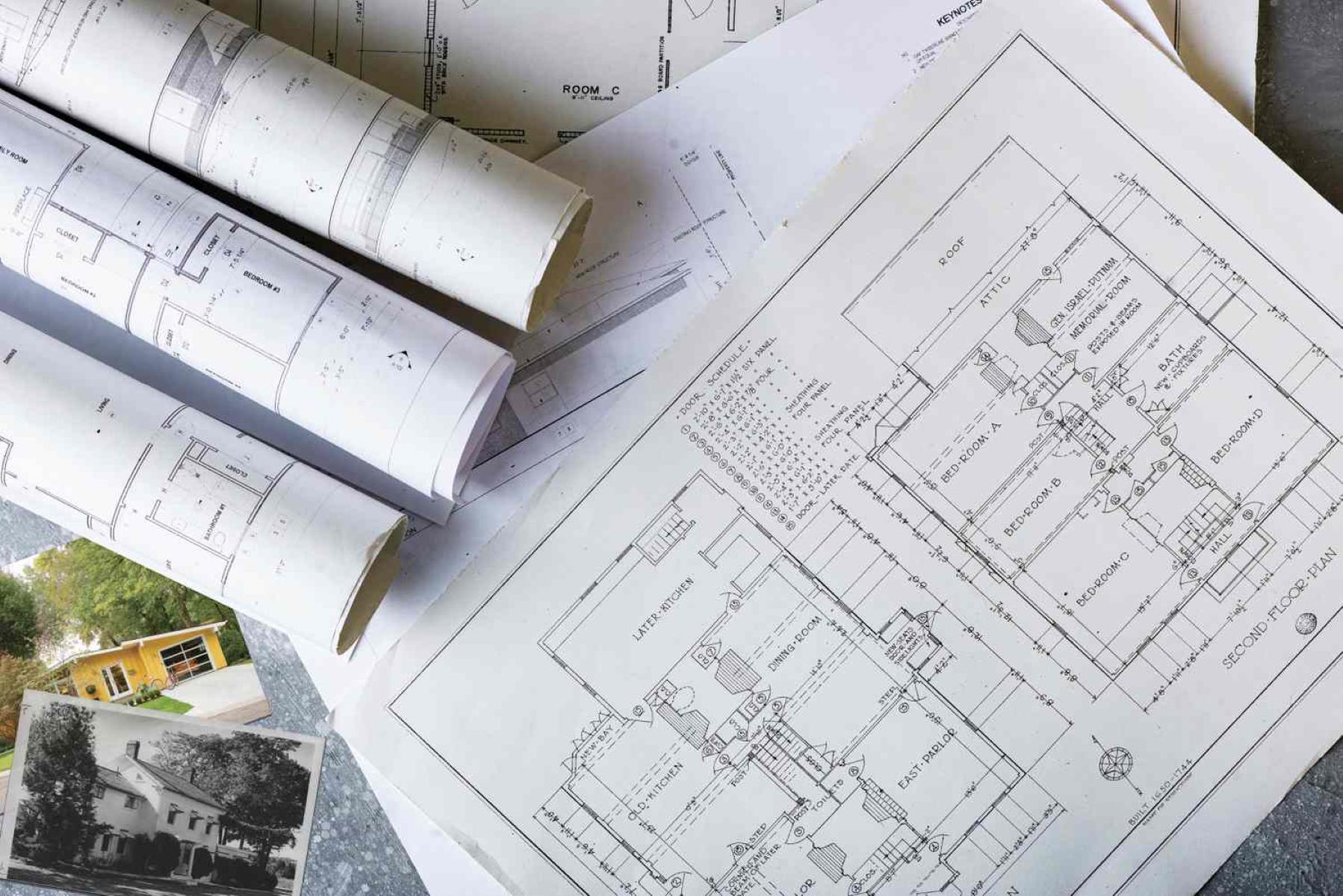
- Architectural Blueprints: Architectural blueprints form the foundation of any construction project. These blueprints provide a comprehensive representation of the building’s layout, including floor plans, elevations, sections, and details. Architectural blueprints focus on the overall design and spatial layout of the structure, providing essential information for construction teams.
- Structural Blueprints: Structural blueprints focus on the structural elements of a building, such as beams, columns, and foundations. These blueprints outline the dimensions, materials, and connections required for the structure’s stability and strength. Structural blueprints are crucial for ensuring that the building can withstand the intended loads and forces.
- Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Blueprints: MEP blueprints cover the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems of a building. These blueprints detail the layout and specifications of HVAC systems, electrical wiring, lighting, plumbing fixtures, and other related components. MEP blueprints ensure that these systems align with the overall design and code requirements.
- Construction Sequence Blueprints: Construction sequence blueprints illustrate the order and steps required to construct the building. These blueprints depict the chronological sequence of construction activities, including foundation work, framing, installation of MEP systems, and finishing touches. Construction sequence blueprints help contractors and project managers visualize and plan the construction process.
- As-Built Blueprints: As-Built blueprints document any modifications or changes made to the original design during the construction process. These blueprints reflect the final layout and configurations of the completed structure. As-Built blueprints are essential for facility management and future renovations, as they provide an accurate representation of the as-built conditions.
- Interior Design Blueprints: Interior design blueprints focus on the aesthetics and functionality of the interior spaces. These blueprints include detailed plans for room layouts, furniture placement, finishes, and lighting design. Interior design blueprints help designers and contractors visualize and execute the desired interior design concept.
- Landscape Blueprints: Landscape blueprints outline the design and layout of outdoor spaces surrounding the building. These blueprints include elements such as gardens, pathways, irrigation systems, and hardscapes. Landscape blueprints are crucial for creating harmonious outdoor environments that complement the building’s design.
These are just a few examples of the various types of digital blueprints used in the construction industry. Each type plays a crucial role in the overall design, construction, and functionality of a building. By utilizing the appropriate digital blueprint, architects, designers, and construction professionals can effectively communicate their vision, ensure coordination among various systems, and deliver successful construction projects.
A digital blueprint is a detailed plan or design for a digital product or solution, outlining its structure, functionality, and user experience. It serves as a roadmap for development and helps ensure the successful execution of a project.
Read more: What Is A Blueprint Of A House
Creating a Digital Blueprint
To create a digital blueprint, architects and designers follow a series of steps using specialized computer-aided design (CAD) software. Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Gather Project Information: Start by gathering all relevant project information, including client requirements, site surveys, building codes, and regulations. This lays the foundation for the design and ensures that the blueprint meets all necessary criteria.
- Conceptual Design: Begin the design process by creating a conceptual layout of the building. This involves sketching out preliminary floor plans and elevations to explore different design options and spatial relationships. This stage allows for creativity and experimentation with various design ideas.
- Refine the Design: Once a conceptual design is chosen, refine it by incorporating detailed dimensions, materials, and design elements. This stage involves creating more accurate and precise drawings, including floor plans, sections, and 3D models. CAD software provides tools to manipulate and modify the design rapidly.
- Annotate and Label: Annotate the digital blueprint with relevant information such as dimensions, materials, and construction techniques. These annotations provide additional clarity to the construction team and ensure accurate interpretation of the design.
- Collaboration and Review: Share the digital blueprint with stakeholders, including clients, engineers, and contractors, for feedback and collaboration. Use collaborative tools within the CAD software or online platforms to facilitate real-time communication and track revisions, ensuring that everyone is working from the most up-to-date version of the blueprint.
- Integration of Systems: If applicable, incorporate MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems into the digital blueprint. Coordinate with MEP professionals to ensure that the systems are properly integrated into the design, considering factors such as functionality, efficiency, and code compliance.
- Finalize and Document: Once all necessary revisions and adjustments are made, finalize the digital blueprint and prepare the necessary documentation. This includes generating 2D drawings, 3D models, sections, and any other required documentation for the construction team.
- Manage Changes: As the construction progresses, document any changes or modifications made to the design. Update the digital blueprint to reflect these changes, ensuring that the as-built blueprint is accurate and up to date.
It is important to note that the creation of a digital blueprint is an iterative process that involves collaboration, review, and continuous refinement. By utilizing the capabilities of CAD software and incorporating input from stakeholders, architects and designers can create precise, detailed, and highly functional digital blueprints that serve as a solid foundation for successful construction projects.
Best Practices for Using Digital Blueprints
Using digital blueprints effectively is crucial for maximizing the benefits they offer. Here are some best practices to consider when working with digital blueprints:
- Standardize File Naming and Organization: Develop a consistent file naming and organization system to ensure easy retrieval and management of digital blueprints. Create folders and subfolders for different project phases, and use descriptive names that reflect the content of each file.
- Apply Layer Management: Utilize layer management functionality within the CAD software to organize and control the visibility of different elements within the digital blueprint. This allows for greater clarity and control when working with complex designs.
- Regularly Save and Backup: Save your digital blueprints frequently to avoid the loss of valuable work. Additionally, implement a robust backup system to protect against data loss or corruption. Cloud storage or external hard drives are reliable options for keeping backups.
- Ensure Compatibility: When collaborating with multiple stakeholders, ensure that the digital blueprint file format is compatible with the software they are using. Communicate and confirm the chosen file formats and software versions to ensure seamless collaboration and avoid compatibility issues.
- Include Clear Annotations and Descriptions: Provide clear and concise annotations and descriptions within the digital blueprint to communicate important information to contractors and other professionals. This can include measurements, materials, building codes, and any specific instructions that need to be followed during construction.
- Regularly Review and Update: Conduct regular reviews and updates of the digital blueprints throughout the construction process. This helps to identify any discrepancies or required modifications, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to accurate and up-to-date information.
- Track and Communicate Changes: Maintain a detailed record of any changes, revisions, or modifications made to the digital blueprints. Implement a change management process to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of and understand the updated versions. This helps to minimize confusion and ensures that everyone is working from the most current blueprint.
- Train and Provide Support: Provide proper training and support to team members who will be working with digital blueprints. Familiarize them with the CAD software, design standards, and any specific guidelines or protocols related to the project. This ensures that everyone is equipped with the necessary skills to work effectively with digital blueprints.
- Consider Security Measures: Protect the digital blueprints from unauthorized access or modifications by implementing appropriate security measures. Use encryption, passwords, and restricted access controls to safeguard sensitive project information.
- Document As-Built Changes: Document and update the digital blueprints to reflect any changes made to the design during the construction process. This ensures that the as-built blueprint accurately represents the final structure and serves as a valuable reference for future renovations or maintenance.
By adhering to these best practices, architects, designers, and construction professionals can effectively utilize digital blueprints, enhance collaboration, improve efficiency, and achieve successful project outcomes.
Challenges of Implementing Digital Blueprints
While the adoption of digital blueprints brings numerous benefits to the architectural and construction industry, there are also some challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some common challenges of implementing digital blueprints:
- Technical Skills and Training: Working with digital blueprints requires proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and related technical skills. Professionals need to be trained and familiarized with the software and its functionalities. This can pose a learning curve for individuals who are transitioning from traditional paper-based methods to digital workflows.
- Hardware and Software Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between different CAD software versions and hardware configurations can be a challenge, especially when collaborating with multiple stakeholders. Differences in software versions may result in compatibility issues, requiring additional time and effort to resolve.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: Protecting the confidentiality and security of digital blueprints becomes critical. Adequate measures need to be put in place to safeguard sensitive project information from unauthorized access or data breaches. Encryption, secure file sharing, and access controls are essential to maintain the integrity and privacy of the digital blueprints.
- Version Control and Document Management: Keeping track of multiple versions of digital blueprints can be challenging without proper version control and document management. It is essential to establish structured processes for tracking revisions, managing change requests, and ensuring that all stakeholders are working with the latest version of the blueprint.
- Collaboration and Communication: Collaborating with various stakeholders, such as architects, designers, engineers, and contractors, can present challenges when using digital blueprints. Clear communication channels and collaboration platforms need to be established to facilitate effective communication and real-time collaboration among team members.
- File Size and Storage: Digital blueprints can be large in file size, especially when dealing with complex projects that involve 3D models and detailed documentation. Adequate storage and efficient file-sharing systems are necessary to ensure that all team members can access and work with the digital blueprints without delays or performance issues.
- Skill and Knowledge Gaps: There may be skill and knowledge gaps among construction professionals in effectively working with digital blueprints. Ongoing training and professional development programs are necessary to bridge these gaps and ensure that all team members are proficient in utilizing digital blueprints to their full potential.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing digital blueprints may face resistance from those accustomed to traditional paper-based methods. Some individuals may be hesitant to adapt to new technologies and workflows. It is essential to provide proper training, address concerns, and emphasize the benefits of digital blueprints to gain buy-in from all stakeholders.
- Cost Considerations: Implementing digital blueprints may require investment in hardware, software licenses, and training programs. The initial costs associated with transitioning to digital workflows can be a challenge for some organizations. However, it is important to consider the long-term cost savings and increased efficiency that digital blueprints offer.
By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can successfully implement digital blueprints, capitalize on their benefits, and overcome any potential obstacles that may arise during the transition to digital workflows.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital blueprints have revolutionized the field of architecture and design, offering numerous advantages over traditional paper-based methods. The shift towards digital workflows has transformed the way construction projects are executed, promoting improved collaboration, efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability.
Digital blueprints provide enhanced visualization, allowing stakeholders to better understand the design and make informed decisions. Their digital nature enables easy sharing and access, facilitating seamless collaboration among team members and reducing errors and miscommunication.
The use of digital blueprints also brings significant time and cost savings. Design modifications can be made quickly and effectively, minimizing the need for manual revisions or reprints. Additionally, the precision and accuracy of digital blueprints help prevent issues and conflicts during construction, resulting in reduced rework and potential cost overruns.
While implementing digital blueprints may come with its challenges, such as technical skills, compatibility, and data security, these obstacles can be overcome with proper training, standardized processes, and effective communication strategies.
In the fast-paced digital era, the adoption of digital blueprints is essential for architects, designers, and construction professionals to stay competitive, deliver successful projects, and embrace sustainable practices. By leveraging the power of computer-aided design (CAD) software and embracing collaboration and innovation, the industry can unlock the full potential of digital blueprints and transform the way buildings and structures are designed and constructed.
As technology continues to advance, the future of digital blueprints looks promising. With advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence, digital blueprints will continue to evolve and offer even more immersive and intelligent tools to enhance the architectural and construction process.
Embracing digital blueprints is not just about embracing technology; it’s about embracing the future of architecture and design. It’s about embracing efficient workflows, precise communication, and sustainable practices. By embracing digital blueprints, the industry can pave the way for innovation and excellence in the built environment, shaping a brighter and more sustainable future for the world of architecture and design.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Digital Blueprint
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is A Digital Blueprint”