Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is The Purpose Of The 2D Drawings In CAD?


Architecture & Design
What Is The Purpose Of The 2D Drawings In CAD?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn the importance of 2D drawings in CAD for architecture design and how they serve as a vital tool for precise measurements and visualization.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), where architects, engineers, and designers use sophisticated software to create and visualize complex designs. CAD has revolutionized the design process, allowing for faster and more precise creations that were once only possible through traditional drawing methods.
One of the fundamental aspects of CAD is the use of 2D drawings. While CAD software is capable of creating stunning 3D models and renderings, 2D drawings still play a vital role in the design process. In this article, we will explore the purpose and importance of 2D drawings in CAD.
But first, what exactly is CAD? CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, refers to the use of specialized software to create, modify, and analyze designs. It allows designers to digitally represent their ideas and concepts, transforming them into detailed visualizations or even physical prototypes. CAD software provides a range of powerful tools and features that enable designers to create intricate and accurate designs, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and productivity in the design process.
Now that we have a basic understanding of CAD, let’s delve into the role of 2D drawings in this digital design realm. 2D drawings in CAD are two-dimensional representations of objects, created using a combination of lines, shapes, and dimensions. They provide a clear and concise depiction of a design, allowing designers to communicate their ideas effectively to clients, colleagues, and manufacturers.
While 3D models and renderings offer a realistic and immersive view of a design, 2D drawings have their own unique advantages. They simplify complex designs into easily understandable plans, elevations, sections, and details. These drawings serve as a visual language that bridges the gap between the designer and other stakeholders involved in the project.
Throughout the design process, 2D drawings serve as a reference point for designers, aiding in decision-making and problem-solving. They provide accurate measurements, annotations, and specifications, allowing for precise communication of design intent. Whether it’s the placement of structural elements, the distribution of electrical wiring, or the positioning of plumbing fixtures, 2D drawings provide the necessary information for construction and fabrication.
In the next section, we will explore the different types of 2D drawings commonly used in CAD and their specific purposes.
Key Takeaways:
- 2D drawings in CAD serve as a universal language, simplifying complex designs for effective communication with clients, colleagues, and manufacturers. They provide clear, concise representations of design intent, aiding in decision-making and problem-solving.
- While 2D drawings have limitations, such as a lack of realism and difficulty in representing complex forms, they remain vital in the design process. Designers can leverage other tools, like 3D models, to complement and augment the information provided by 2D drawings.
Read more: What Are CAD Drawings
Definition of CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
Computer-Aided Design, commonly known as CAD, is a broad term that encompasses the use of specialized software tools to create, modify, and analyze designs in a digital environment. It is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the field of architecture, engineering, and design, allowing professionals to create, visualize, and communicate complex ideas with precision and efficiency.
CAD software provides a wide range of features and tools that enable designers to generate accurate and detailed representations of their designs. These software packages offer intuitive user interfaces, allowing designers to easily create, manipulate, and modify 2D and 3D models. With CAD, designers can explore multiple design options, assess their feasibility, and make informed decisions before committing to the final design.
One of the key advantages of CAD is its ability to create designs that are not limited by the constraints of traditional drawing methods. With CAD, designers can easily create intricate and complex designs that would be time-consuming or even impossible to achieve manually. CAD software allows for precise measurements, accurate calculations, and seamless integration of various design elements, resulting in enhanced accuracy and efficiency.
Moreover, CAD enables designers to easily make changes and updates to their designs. In traditional drafting, making changes to a drawing often required starting from scratch or relying on manual edits that often resulted in errors. CAD eliminates these limitations by providing advanced editing tools that allow for easy modifications to design elements. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors and inconsistencies in the final design.
CAD also facilitates collaboration among design teams and stakeholders. Designs can be shared, reviewed, and modified in real-time, allowing for efficient communication and seamless coordination among team members. This level of collaboration streamlines the design process and ensures that all members of the team are working towards the same goal.
Overall, CAD has transformed the way professionals in various fields approach design. It has become an indispensable tool for architects, engineers, and designers, enabling them to create detailed and precise designs while improving efficiency and productivity. As technology continues to advance, CAD software will continue to evolve, providing even more powerful tools and features to shape the future of design.
Overview of 2D Drawings in CAD
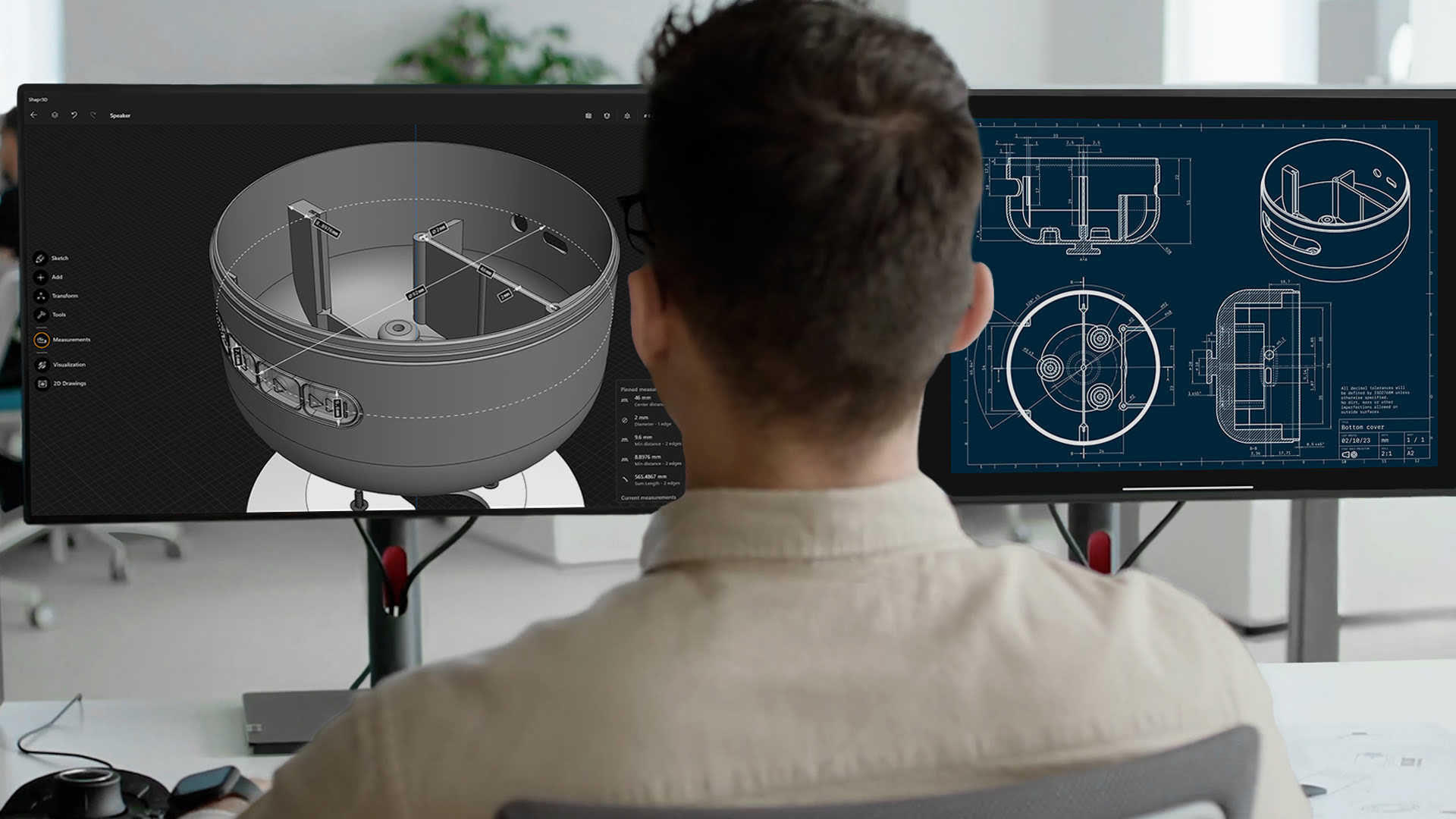
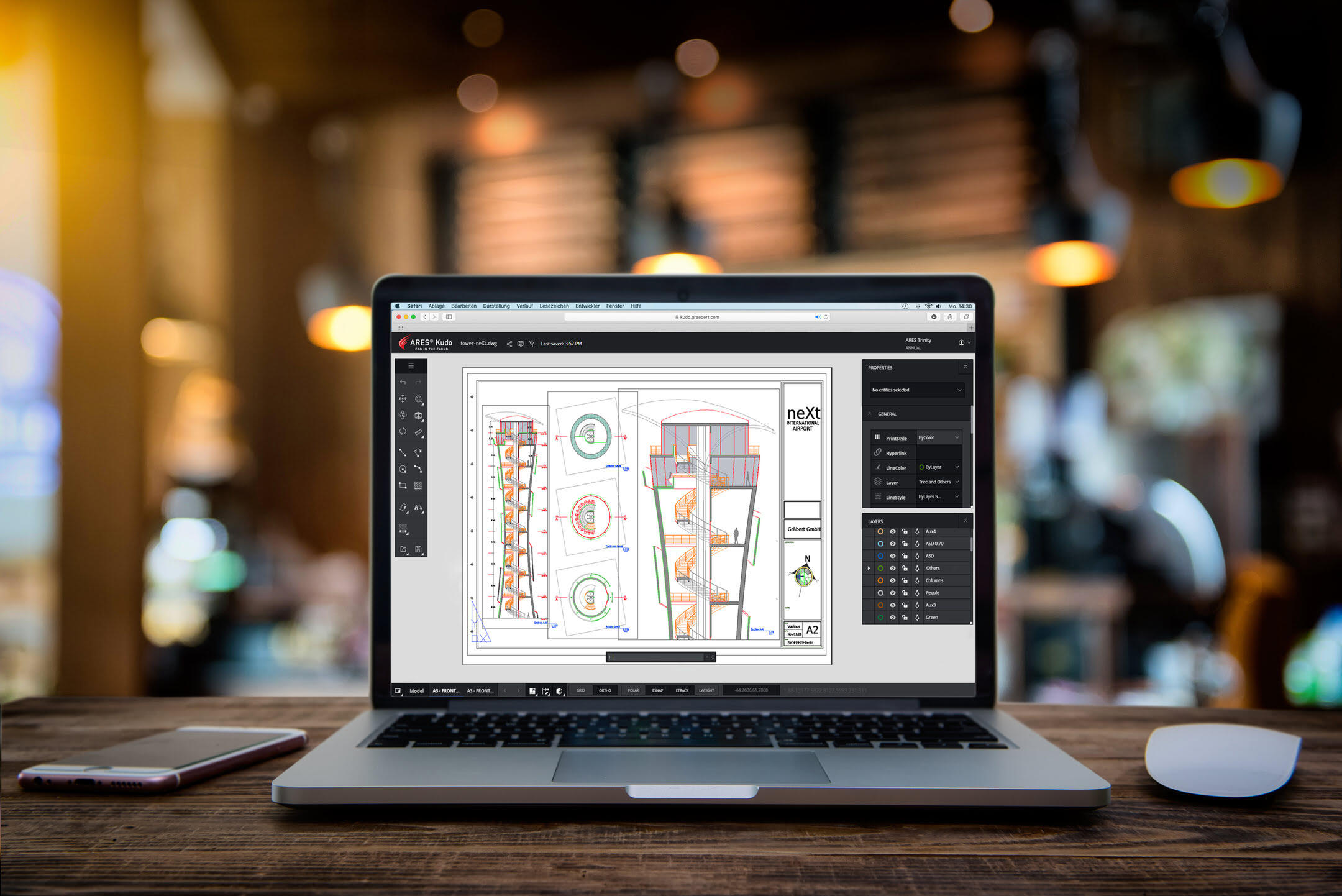
In the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), 2D drawings play a crucial role in the design process. While CAD software offers the capability to create stunning 3D models and visualizations, 2D drawings remain an integral part of the design workflow. These drawings serve as a bridge between the digital design environment and the physical world, providing a clear and concise representation of the design intent.
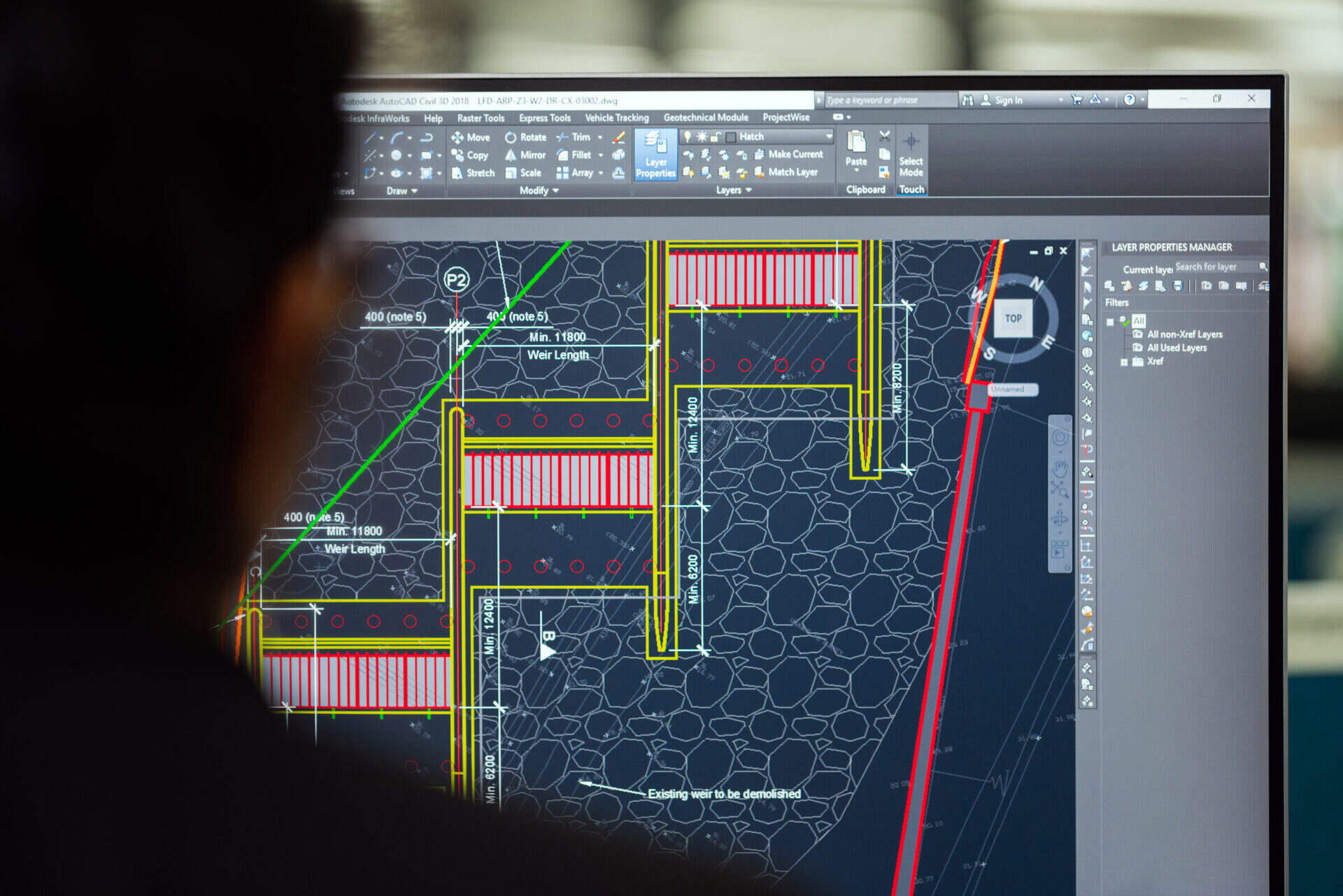
2D drawings in CAD are two-dimensional representations of objects or designs. They are created using lines, shapes, and dimensions to communicate the size, shape, and details of a design. These drawings are typically created in plan, elevation, section, and detail views, allowing designers to depict different aspects of the design accurately.
One of the key advantages of using 2D drawings in CAD is their simplicity and clarity. 2D drawings simplify complex designs into easily understandable representations, allowing designers to communicate their ideas effectively to clients, colleagues, and manufacturers. They provide a bird’s-eye view of the design, helping stakeholders visualize the layout, arrangement, and functionality of different components.
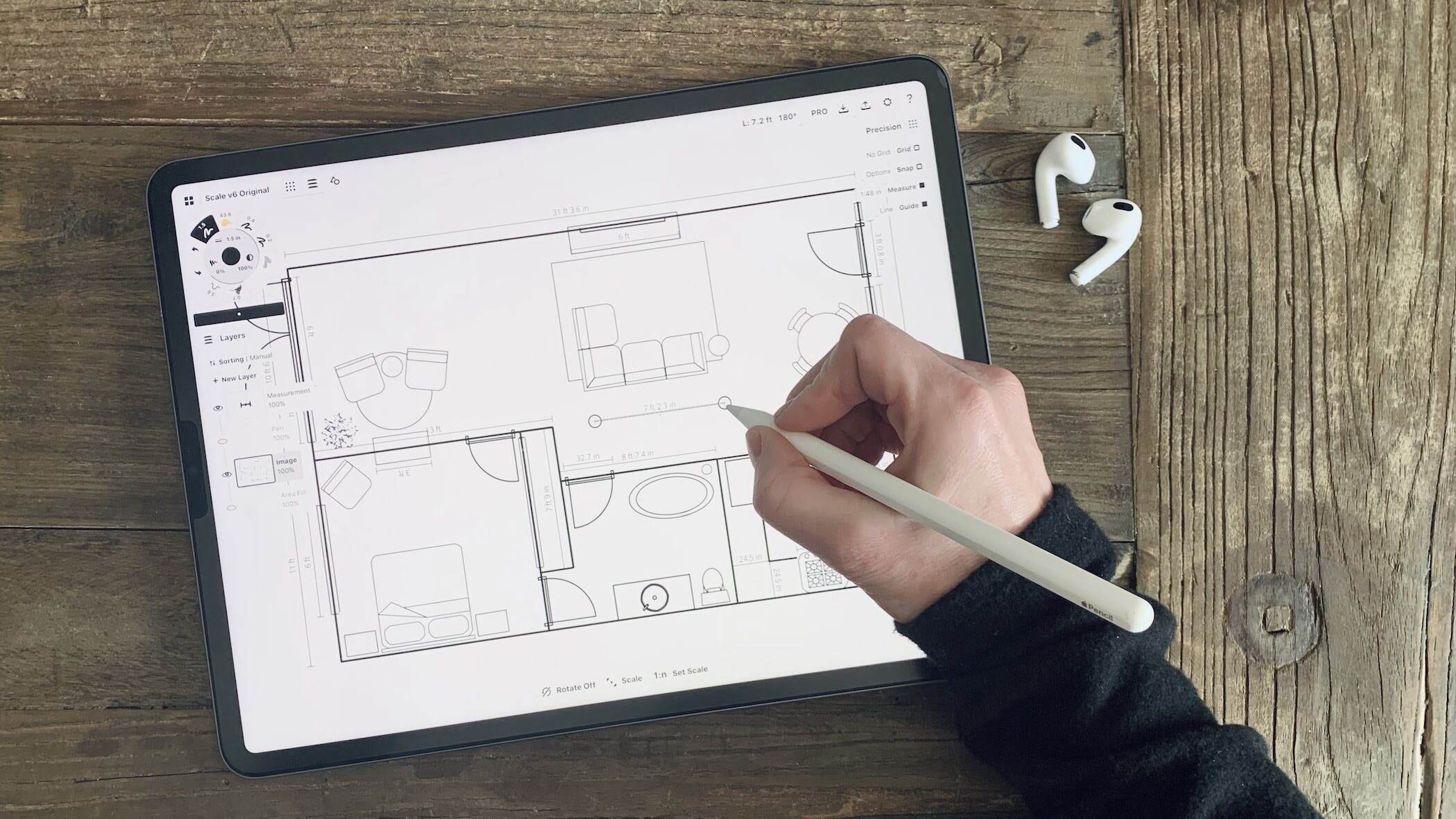
Another benefit of 2D drawings is that they allow for precise measurements and annotations. Designers can include dimensions, labels, and notes on the drawings, providing crucial information about the design intent and requirements. These annotations help manufacturers understand the specifications, materials, and assembly methods, ensuring accurate production and construction.
In addition, 2D drawings are essential for the documentation and record-keeping purposes. They serve as a visual record of the design process, allowing designers to refer back to previous iterations or revisions. This ensures consistency and traceability in the design and construction process, reducing errors and rework.
Furthermore, 2D drawings in CAD enable designers to create fabrication drawings. These drawings provide detailed information about the manufacturing processes and requirements, including tolerances, materials, finishes, and assembly instructions. Fabricators use these drawings to create components or parts with precision, ensuring that they fit together as intended.
Overall, 2D drawings in CAD are vital tools for design communication, documentation, and fabrication. They streamline the design process, provide accurate information, and allow for effective collaboration among different stakeholders. While 3D models and renderings offer a realistic representation of the design, 2D drawings provide essential information that is needed for construction, manufacturing, and communication.
Importance of 2D Drawings in CAD
2D drawings play a significant role in the CAD design process and are essential for several reasons. Here are some key reasons why 2D drawings are important in CAD:
1. Clear Communication: 2D drawings provide a clear and concise representation of a design. They serve as a universal language that allows designers to communicate their ideas effectively to clients, colleagues, and manufacturers. These drawings simplify complex designs, making them easily understandable for all stakeholders involved in the project.
2. Design Documentation: 2D drawings serve as an important documentation tool. They capture the design intent, specifications, and dimensions, ensuring accurate documentation of the design. These drawings help in maintaining a record of the design process, facilitating design revisions, and providing a reference for future projects.
3. Design Visualization: 2D drawings provide a visual representation of the design. They help stakeholders visualize the layout, arrangement, and functionality of different design components. These drawings give a comprehensive overview of the design, aiding in the decision-making process and ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
4. Design Analysis: 2D drawings play a crucial role in design analysis. They allow designers to assess the structural integrity, dimensions, and feasibility of a design. These drawings can be used to perform calculations, simulations, and analysis, helping designers identify potential issues and make necessary modifications before moving to the 3D modeling or manufacturing stage.
5. Construction and Fabrication: 2D drawings are vital for construction and fabrication purposes. Contractors, builders, and fabricators rely on these drawings to understand the design requirements and specifications. These drawings provide accurate measurements, annotations, and details that guide the construction and fabrication process, ensuring that the end product matches the design intent.
6. Cost and Time Efficiency: By using 2D drawings in CAD, designers can save time and effort. These drawings provide a detailed plan that can be easily shared with stakeholders, eliminating the need for multiple meetings and explanations. 2D drawings also help in identifying potential issues early on, reducing costly rework and delays during the construction or fabrication phase.
Overall, the importance of 2D drawings in CAD cannot be overstated. They are crucial for effective communication, design documentation, visualization, analysis, and construction. 2D drawings provide the necessary information for successful implementation of a design, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and client satisfaction.
Understanding Different Types of 2D Drawings
In the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), different types of 2D drawings are used to convey specific information about a design. Each type of drawing serves a unique purpose and provides a different perspective or view of the design. Here are some of the most common types of 2D drawings used in CAD:
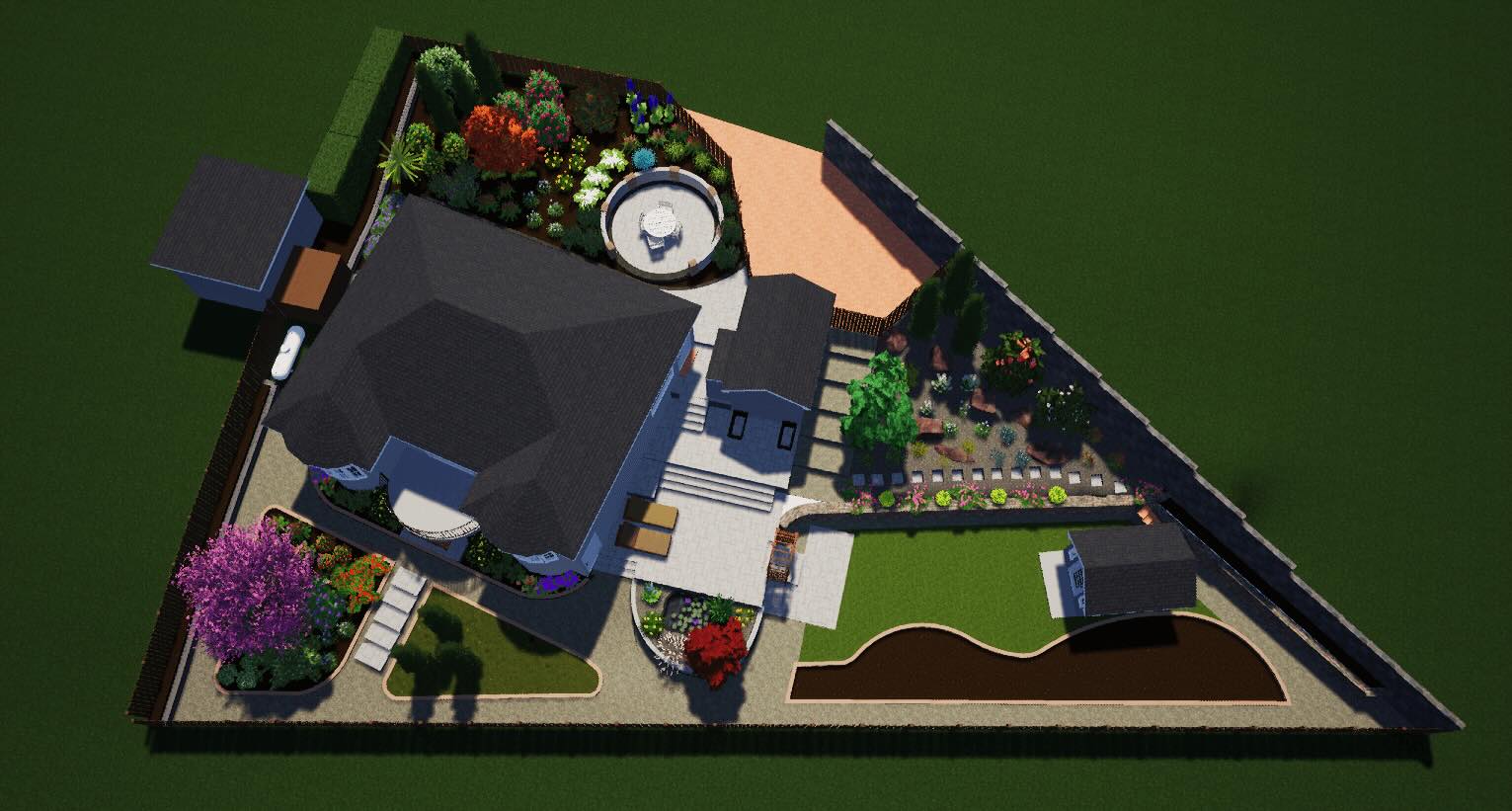
1. Plan Drawings: Plan drawings, also known as floor plans, provide a bird’s-eye view of a design. They illustrate the layout of a space, including walls, doors, windows, and furniture. Plan drawings are commonly used in architecture and interior design to communicate the overall arrangement and flow of a building or space.
2. Elevation Drawings: Elevation drawings depict the vertical surfaces of a design. They provide a view of the design from a specific direction, showing the height, shape, and details of walls, facades, and elements such as windows, doors, and architectural features. Elevation drawings are essential in architecture and construction to visualize the appearance and proportions of a building’s exterior.
3. Section Drawings: Section drawings cut through a design to reveal its internal structure and spatial relationships. They provide a cross-sectional view of a design, showing the arrangement of elements such as floors, walls, ceilings, and structural components. Section drawings are important for understanding the spatial organization and construction details of a design.
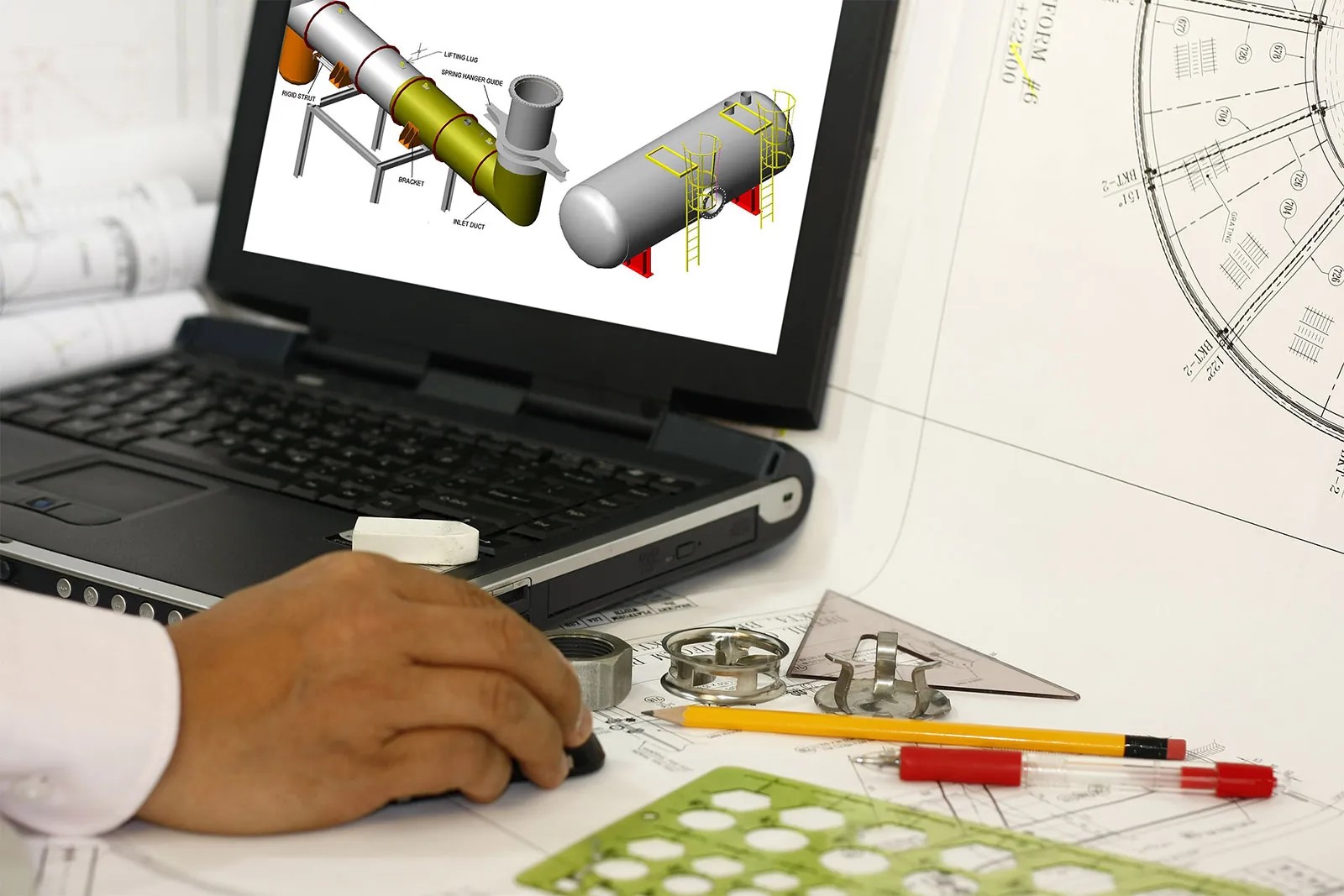
4. Detail Drawings: Detail drawings zoom in on specific areas or components of a design to provide a more detailed view. They showcase the construction and mechanical details of elements such as joints, connections, and assemblies. Detail drawings are commonly used in engineering and manufacturing to provide instructions and guidance for fabricating or constructing complex parts.
5. Assembly Drawings: Assembly drawings show how different components of a design fit together to form a larger entity. They depict the arrangement, orientation, and connections of individual parts, allowing for the assembly and construction of the final product. Assembly drawings are instrumental in manufacturing and fabrication to ensure proper assembly and functionality.
6. Schematic Diagrams: Schematic diagrams are simplified 2D drawings used in electrical and mechanical design. They illustrate the connections, relationships, and flow of components in a system. Schematic diagrams use symbols and labels to represent various elements, such as electrical circuits, piping systems, or mechanical systems, aiding in design, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
These are just a few examples of the different types of 2D drawings used in CAD. Each type of drawing provides specific information and serves a unique purpose in the design process. By utilizing a combination of these drawings, designers can effectively communicate their design intent, provide accurate measurements, and guide the construction or fabrication process.
2D drawings in CAD are used to communicate the design intent and specifications to manufacturers, contractors, and other stakeholders. They provide detailed information about dimensions, tolerances, materials, and assembly instructions.
Read more: How To Make A 2D Floor Plan In Sketchup
Role of 2D Drawings in Design Process
2D drawings play a crucial role throughout the design process, serving as a foundation and guide for the creation and realization of a design. They provide essential information and serve multiple purposes that aid in the design, communication, and implementation of a project. Here are the key roles that 2D drawings play in the design process:
1. Conceptualization: 2D drawings are often the first step in the design process. Designers use sketches and rough drawings to explore and visualize their ideas. These initial 2D drawings help in conceptualizing the design, capturing the essence of the project, and laying the groundwork for further development.
2. Design Development: As the design progresses, 2D drawings serve as a platform for refining and developing the concept. Designers create detailed 2D drawings that incorporate accurate dimensions, scale, and annotations to convey the design intent. These drawings act as a roadmap, guiding further design decisions and detailing.
3. Communication: 2D drawings are a powerful communication tool. They allow designers to effectively express their ideas to clients, colleagues, contractors, and fabricators. These drawings convey the design intent, allowing stakeholders to visualize the proposed design and provide feedback in a clear and understandable manner. 2D drawings facilitate effective collaboration and ensure all parties are on the same page.
4. Decision Making: 2D drawings assist in making important decisions during the design process. Designers use these drawings to analyze the feasibility, proportions, and functionality of the design. They help identify design flaws or potential issues that may require adjustment or modification before the design progresses further. 2D drawings enable designers to make informed decisions and improve the overall quality of the design.
5. Construction and Fabrication: 2D drawings provide the necessary information for construction and fabrication. Contractors and fabricators rely on comprehensive 2D drawings to understand the design requirements, dimensions, and specifications. These drawings guide them in the construction and fabrication process, ensuring that the end result matches the original design intent.
6. Documentation and Record-Keeping: 2D drawings act as important documentation tools throughout the design process. They serve as a visual record of the design decisions, revisions, and modifications. These drawings become part of the project documentation, allowing designers to refer back to them in future projects, ensuring consistency, and maintaining a comprehensive design history.
Overall, 2D drawings play a fundamental role in the design process by facilitating conceptualization, communication, decision-making, and implementation. They serve as a vital link between the designer’s vision and the realization of the project, providing a tangible representation of the design intent.
Benefits of Using 2D Drawings in CAD
2D drawings in CAD offer several benefits that contribute to the efficiency, accuracy, and communication of the design process. Here are some key advantages of using 2D drawings in CAD:
1. Clarity and Precision: 2D drawings provide a clear and precise representation of a design. They simplify complex designs, making them easily understandable and accessible to clients, colleagues, and manufacturers. Using lines, shapes, and dimensions, designers can accurately convey the size, shape, and details of the design, ensuring accurate interpretation and implementation.
2. Communication and Collaboration: 2D drawings serve as a common language that enables effective communication and collaboration among different stakeholders. They help designers effectively convey their design intent to clients, contractors, and fabricators. These drawings act as a visual reference, facilitating discussions, feedback, and input from all parties involved, leading to better decision-making and ultimately, a successful project.
3. Design Analysis and Evaluation: 2D drawings are instrumental in analyzing and evaluating the design. Designers can use these drawings to assess various aspects, such as dimensions, proportions, and relationships between different components. They provide a platform for making informed design decisions, identifying potential issues, and refining the design before moving to the next phase.
4. Reusability and Documentation: 2D drawings have long-term value beyond the initial design phase. They serve as documentation that records the design intent, dimensions, and specifications. These drawings can be reused or referenced for future projects, ensuring consistency, eliminating duplication of effort, and saving time and resources in subsequent designs.
5. Precision in Manufacturing: 2D drawings provide accurate and detailed information that guides the manufacturing process. Fabricators and manufacturers rely on these drawings to understand the design requirements, materials, dimensions, and assembly methods. With precise measurements and annotations, 2D drawings ensure that the manufactured components or products align with the original design’s specifications.
6. Cost and Time Efficiency: Using 2D drawings in CAD can lead to cost and time savings. These drawings provide a comprehensive plan and specific details that can be easily communicated to contractors and fabricators. They minimize errors, avoid rework, and expedite the construction or manufacturing process, resulting in reduced costs and faster project completion.
Overall, the benefits of using 2D drawings in CAD contribute to improved communication, better decision-making, precise manufacturing, and streamlined project workflow. These drawings serve as a foundation for design collaboration, ensuring that the design intent is accurately translated from concept to realization.
Limitations of 2D Drawings in CAD
While 2D drawings in CAD offer numerous benefits, they also have certain limitations that designers and stakeholders should be aware of. Understanding these limitations is crucial for leveraging the full potential of 2D drawings in the design process. Here are some of the limitations of 2D drawings in CAD:
1. Lack of Realism: 2D drawings, by nature, lack the realistic representation of a design that can be achieved with 3D models or renderings. They do not provide a fully immersive view of the design and may not effectively convey the three-dimensional aspects of the project. This limitation can make it challenging to visualize the actual appearance or experience of the design.
2. Limited Spatial Understanding: 2D drawings, particularly floor plans and elevations, may not fully capture the spatial relationships between different elements within a design. While they provide a bird’s-eye or frontal view, they may not adequately represent the depth, scale, or volume of the design. This limitation could potentially result in misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the design intent.
3. Difficulty in Representing Complex Forms: 2D drawings may struggle to represent complex geometries or intricate design details. The limitations of flat surfaces and simple lines may make it challenging to accurately portray complex curves, organic shapes, or surface textures. This could make it difficult for stakeholders to fully appreciate the intricacies of the design.
4. Limited Dimensional Information: While 2D drawings provide dimensions and measurements, they may not fully convey all the necessary information about a design. Certain design elements may require additional annotations or descriptions to communicate their intended functionality or purpose. Designers need to be mindful of providing comprehensive supplementary information alongside the 2D drawings.
5. Difficulty in Visualizing Assembly or Disassembly: 2D drawings can sometimes struggle to effectively communicate the assembly or disassembly process of a complex design. It may be challenging to convey the order, sequence, or dynamics involved in the construction or disassembly of the components. Additional written instructions or exploded views may be necessary to supplement the 2D drawings.
6. Limited Interactivity: 2D drawings are static representations of a design and lack the interactive and dynamic nature of 3D models or virtual reality simulations. Stakeholders cannot interact directly with the design or explore it from different angles. This limitation may hinder the ability to fully grasp the spatial relationships and functional aspects of the design.
Despite these limitations, 2D drawings remain an integral part of the design process. By understanding these limitations, designers can mitigate their impact and leverage other tools, such as 3D models or renderings, to complement and augment the information provided by 2D drawings.
Conclusion
2D drawings in CAD are a critical component of the design process, offering a range of benefits for designers, stakeholders, and manufacturers. While they have their limitations, 2D drawings serve as a foundation for effective communication, precise documentation, and efficient implementation of a design.
Throughout this article, we explored the various roles and importance of 2D drawings in CAD. These drawings allow designers to convey their design intent, visualize the layout and proportions, and provide accurate specifications to clients, colleagues, contractors, and fabricators. They serve as a common language that facilitates collaboration and decision-making throughout the design process.
Different types of 2D drawings, such as plan drawings, elevation drawings, section drawings, detail drawings, assembly drawings, and schematic diagrams, fulfill specific purposes and convey valuable information. Designers utilize these drawings to conceptualize their ideas, analyze the design, evaluate feasibility, guide construction or fabrication, and document the design process.
While 2D drawings have their limitations, such as a lack of realism and difficulties in representing complex forms, they still play an integral role in the design workflow. Designers can overcome these limitations by leveraging other tools like 3D models or renderings to complement and augment the information presented by 2D drawings.
In conclusion, 2D drawings in CAD provide a practical and effective means of communicating design ideas, documenting the design process, and guiding the implementation of a project. By utilizing these drawings effectively, designers can ensure precise and accurate interpretation of their designs, leading to successful outcomes and satisfied stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Purpose Of The 2D Drawings In CAD?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is The Purpose Of The 2D Drawings In CAD?”