Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Do A CAD Drawing

Architecture & Design
How To Do A CAD Drawing
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how to create an architecture design CAD drawing with our step-by-step guide. Get expert tips and techniques for precise and professional results.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
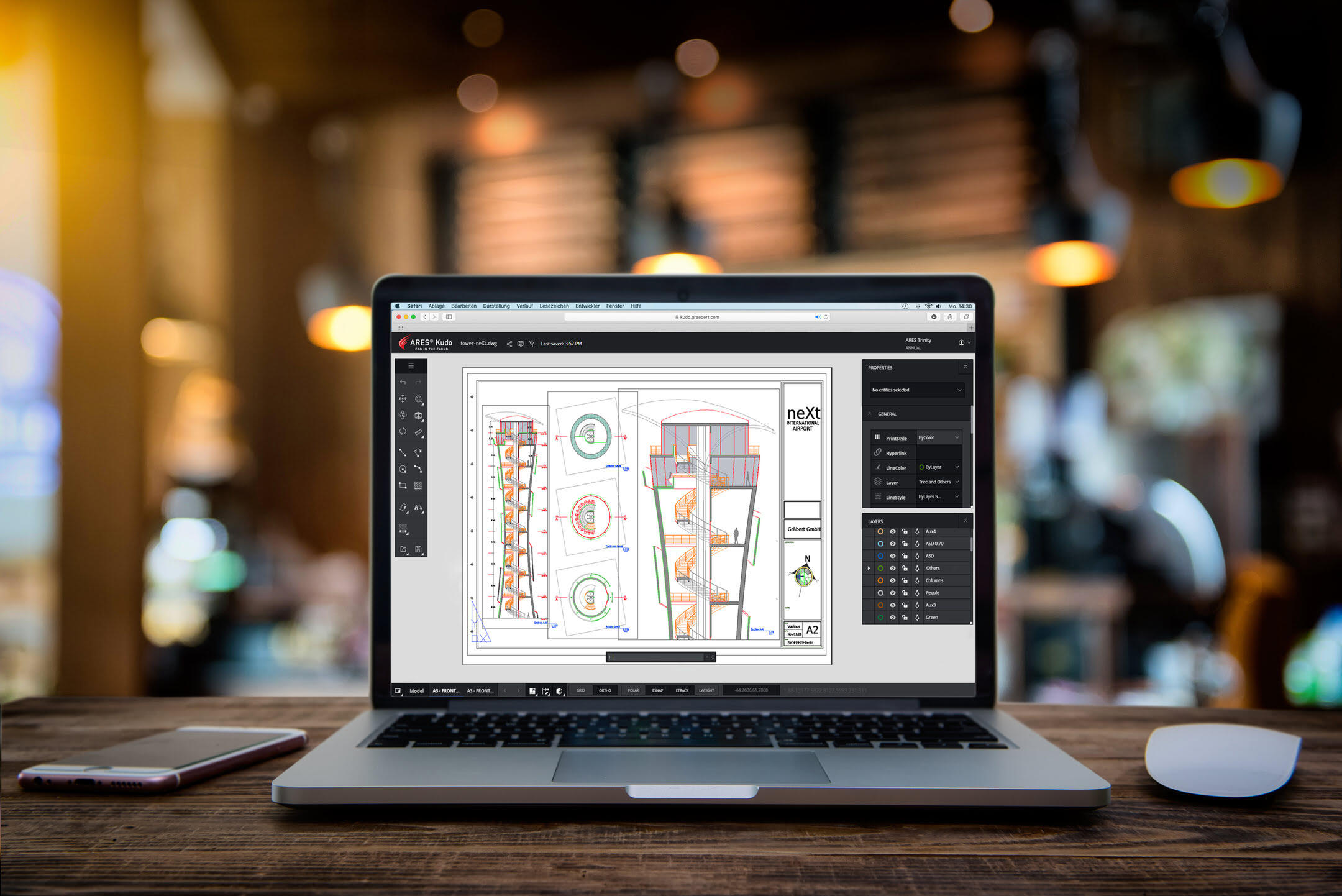
Computer-Aided Design, or CAD, has revolutionized the way we design and create architectural structures, industrial products, and various other objects. It has become an integral part of the architecture, engineering, and manufacturing industries, allowing designers and engineers to create intricate and precise drawings with ease.
In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD drawing and explore the basic tools, techniques, and software required to create visually appealing and accurate designs. Whether you are a beginner looking to learn the fundamentals or an experienced professional seeking to enhance your skills, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of CAD drawing.
But first, let’s define CAD drawing. CAD drawing refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, and optimize digital representations of physical objects. It allows designers to visualize their ideas in a virtual environment, making it easier to manipulate and refine their designs before bringing them to life.
The importance of CAD drawing cannot be overstated. It offers numerous advantages over traditional manual drafting, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. With CAD, designers can easily make changes, experiment with different design options, and collaborate with others in real-time.
Now, let’s start exploring the world of CAD drawing by understanding the basic tools and software required for this process. By familiarizing ourselves with the essential elements of CAD drawing, we can lay a solid foundation for creating stunning designs.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD drawing revolutionizes design by enabling precise digital representations of physical objects, enhancing productivity, and improving collaboration in architecture, engineering, and manufacturing industries.
- Mastering CAD drawing techniques and tools unleashes creativity, attention to detail, and deep understanding of design principles, leading to captivating and engaging visual representations that resonate with viewers.
Read more: What Are CAD Drawings
Defining CAD Drawing
CAD drawing, as mentioned earlier, is the process of using computer software to create and modify digital representations of physical objects. It involves the use of specialized tools and techniques to design and visualize objects in a virtual environment.
With CAD drawing, designers can create detailed 2D and 3D models of their designs, allowing them to explore various perspectives and dimensions. These models can be used for a wide range of purposes, including architectural planning, product design, mechanical engineering, and more.
One of the key features of CAD drawing is its precision and accuracy. Unlike manual drafting, which is prone to human error, CAD software ensures that measurements and dimensions are consistent and precise. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors in the final product.
Another important aspect of CAD drawing is its ability to facilitate collaboration and communication. Designers can easily share their CAD files with colleagues or clients, enabling them to provide feedback and suggestions. This streamlined workflow improves efficiency and minimizes miscommunication.
CAD drawing also offers a range of advanced features and tools that go beyond traditional manual drafting. These include the ability to simulate real-world conditions, such as lighting and material properties, to create more realistic and immersive designs. Additionally, CAD software allows for parametric modeling, which means that changes made to one part of the design automatically update all related components, saving time and effort.
Overall, CAD drawing is essential in modern design processes for its versatility, accuracy, and efficiency. It has transformed the way we create and visualize designs, providing a powerful tool for designers, engineers, and architects to bring their ideas to life.
The Importance of CAD Drawing
CAD drawing plays a crucial role in various industries, from architecture and engineering to manufacturing and construction. Its importance lies in its ability to streamline the design process, improve accuracy, and enhance collaboration. Let’s explore some of the key reasons why CAD drawing is so important in today’s professional landscape.
1. Efficiency and Productivity: CAD software offers a wide range of powerful tools and features that significantly speed up the design process. Designers can quickly create, modify, and replicate objects, eliminating the tedious and time-consuming tasks associated with manual drafting. This increased efficiency translates into higher productivity, allowing designers to create more in less time.
2. Accuracy and Precision: CAD drawing eliminates human errors often found in manual drafting. The software ensures precise measurements, angles, and dimensions, resulting in accurate representations of designs. This level of precision is invaluable in industries where even the slightest measurement discrepancy can have significant implications.
3. Visualization and Exploration: CAD drawing enables designers to visualize their ideas in both 2D and 3D formats. This allows for better exploration of design concepts and helps designers identify potential flaws or improvements before the manufacturing or construction phase. By creating realistic renderings and virtual walkthroughs, CAD drawing provides a comprehensive understanding of the final product.
4. Design Analysis and Optimization: CAD software provides powerful analysis tools that allow designers to simulate real-world conditions and test their designs for functionality, stability, and performance. By running simulations, designers can identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments early in the process, saving both time and resources in the long run.
5. Collaboration and Communication: CAD software facilitates seamless collaboration among designers, engineers, and stakeholders. Multiple team members can work simultaneously on a design, making real-time changes and sharing feedback. This enhances communication, reduces errors, and ensures that everyone is working with the latest version of the design, leading to better project outcomes.
6. Flexibility and Iteration: CAD drawing enables designers to easily iterate and experiment with different design options. Changes can be made quickly, and different variations can be explored without starting from scratch. This flexibility encourages innovation and allows designers to push the boundaries of creativity.
With these advantages, it is clear that CAD drawing has become an indispensable tool in modern design industries. Its ability to improve efficiency, accuracy, visualization, and collaboration has revolutionized the way we create and innovate.
Basic Tools and Software
When it comes to CAD drawing, having the right tools and software is essential to create professional and accurate designs. Let’s explore some of the basic tools and software commonly used in CAD drawing.
1. CAD Software: The foundation of CAD drawing is the CAD software itself. There are various CAD software available in the market, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some popular CAD software options include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Rhino, and Fusion 360. These software provide a user-friendly interface, powerful design tools, and extensive libraries of pre-built objects.
2. Drawing and Editing Tools: CAD software comes equipped with a range of drawing and editing tools to create geometric shapes, lines, arcs, and curves. These tools allow designers to precisely define the dimensions and angles of each element. Additionally, CAD software offers editing tools such as trim, extend, fillet, and chamfer to manipulate and refine the shapes.
3. Measurement Tools: Accurate measurements are crucial in CAD drawing. CAD software provides measurement tools that allow designers to measure distances, angles, and areas within the design. These tools ensure that the dimensions of the objects are precise and consistent throughout the design process.
4. Layers: CAD software uses a layer-based system to organize and manage different elements within a design. Layers allow designers to group and organize objects logically. For example, architectural plans may have separate layers for walls, doors, windows, and electrical elements. This layer organization makes it easier to manipulate and edit specific parts of the design without affecting others.
5. Snap and Grid: Snap and grid settings help designers align and position objects accurately. The snap feature enables objects to snap to specific points on the grid or other objects, ensuring precise alignment. The grid provides a visual reference for creating and positioning objects in a consistent manner.
6. File Management: CAD software includes file management features that allow designers to save, organize, and retrieve their drawings efficiently. These features typically include options to save different versions, create backups, and collaborate with others by sharing files.
7. 3D Viewing and Rendering: Many CAD software offer advanced 3D viewing and rendering capabilities. Designers can navigate and explore the design in 3D, allowing them to visualize the object from different angles. Rendering tools allow designers to add textures, materials, lighting, and shadows to create realistic visualizations of the final product.
8. Exporting and Sharing: CAD software allows designers to export their drawings in various file formats such as .DWG, .DXF, or .PDF. These formats ensure that the drawings can be easily shared with clients, manufacturers, or other stakeholders who may not have access to the CAD software itself.
These basic tools and software form the foundation of CAD drawing. Familiarizing yourself with these tools and mastering the software’s features will greatly enhance your ability to create accurate and visually stunning designs.
Understanding CAD Layers
When working with CAD drawing, understanding layers is essential for organizing and managing the different elements of your design. Layers are like transparent sheets that stack on top of each other, allowing you to group and organize specific objects or elements within your drawing. Let’s dive deeper into understanding CAD layers and how they can enhance your design workflow.
1. Logical Organization: Layers provide a logical way to organize your design elements. Rather than having all objects in a single layer, you can separate them into different layers based on their categories or functionalities. For example, in an architectural drawing, you may have separate layers for walls, windows, doors, electrical components, and furniture. This organization makes it easier to edit or manipulate specific elements without affecting others.
2. Hierarchy and Visibility: Layers allow you to control the visibility and hierarchy of your design elements. You can toggle the visibility of individual layers, making it easier to focus on specific parts of your design while uncluttering the workspace. Additionally, layers can be arranged in a hierarchical structure, creating a parent-child relationship. This hierarchy determines the order in which the layers are displayed and can help in managing complex drawings.
3. Editing Efficiency: With layers, you can make changes to specific objects or elements without affecting the rest of the design. For example, if you need to modify the windows in an architectural drawing, you can simply select the window layer and make the necessary changes. This eliminates the need to select or edit each window individually, saving time and effort.
4. Organization by Drawing Phases: Layers can also be used to organize elements based on different phases of the design process. For example, in a building construction project, you can have layers for the initial design phase, the structural phase, the mechanical phase, and so on. This allows you to easily turn on or off specific layers depending on the stage of the project, making it easier to manage and review the design as it progresses.
5. Collaboration and Flexibility: Layers are also beneficial when collaborating with team members or stakeholders. Each person can work on different layers, making changes and additions without interfering with others’ work. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone can work simultaneously on the design, improving productivity and enhancing communication.
Understanding how to effectively use layers is crucial for efficient and organized CAD drawing. It allows you to manage complex projects, streamline your workflow, and enhance collaboration. By utilizing layers, you can create cohesive and visually appealing designs while maintaining flexibility and efficiency throughout the design process.
Read more: How To Print A CAD Drawing
Setting up the Drawing Workspace
Before you start creating your CAD drawing, it’s important to set up your drawing workspace to ensure a smooth and efficient workflow. The workspace refers to the layout and arrangement of tools, menus, and panels within the CAD software. By customizing your workspace to suit your needs, you can optimize productivity and navigate through your drawing with ease. Let’s explore some key aspects of setting up the drawing workspace.
1. User Interface: Familiarize yourself with the user interface of the CAD software you are using. Typically, the interface consists of a menu bar, toolbar, drawing area, properties panel, and command prompt. Arrange these elements based on your preference and working style. You may want to have commonly used tools readily accessible on your toolbar for quick access.
2. Customize Tool Palettes: Most CAD software allows you to customize tool palettes, which are panels that contain various tools and commands. Organize your commonly used tools into separate palettes based on their functionalities. This way, you can easily access specific tools without having to navigate through multiple menus.
3. Arrange Panels and Windows: CAD software often comes with various panels and windows that provide additional functionalities and information. Arrange these panels in a way that suits your workflow. For example, you may want to have a Properties panel and Layers panel visible at all times for easy access to object properties and layer management.
4. Create Workspaces: Some CAD software allows you to create and save multiple workspaces. Workspaces are a set of customized interface settings. You can create different workspaces for different types of projects or tasks. For instance, you can have a workspace specifically for architectural drawings and another for mechanical designs. This allows you to switch between workspaces quickly and have your preferred tools and settings readily available for different projects.
5. Shortcuts and Keyboard Commands: Take advantage of keyboard shortcuts and customizable commands provided by the CAD software. Familiarize yourself with commonly used shortcuts to work more efficiently. You can also create your own custom shortcuts for frequently used commands, further enhancing your productivity.
6. Workspace Preservation: Many CAD software allow you to save your workspace settings, ensuring that you can restore them if they get accidentally reset. This feature is especially useful when switching between computers or in case of any unexpected changes to your settings.
Setting up the drawing workspace according to your preferences and working style can greatly improve your efficiency and productivity while working on CAD drawings. Experiment with different settings and layouts until you find the setup that suits you best. By customizing your workspace, you can focus more on the creative process and less on navigating through menus and panels, ultimately enhancing your drawing experience.
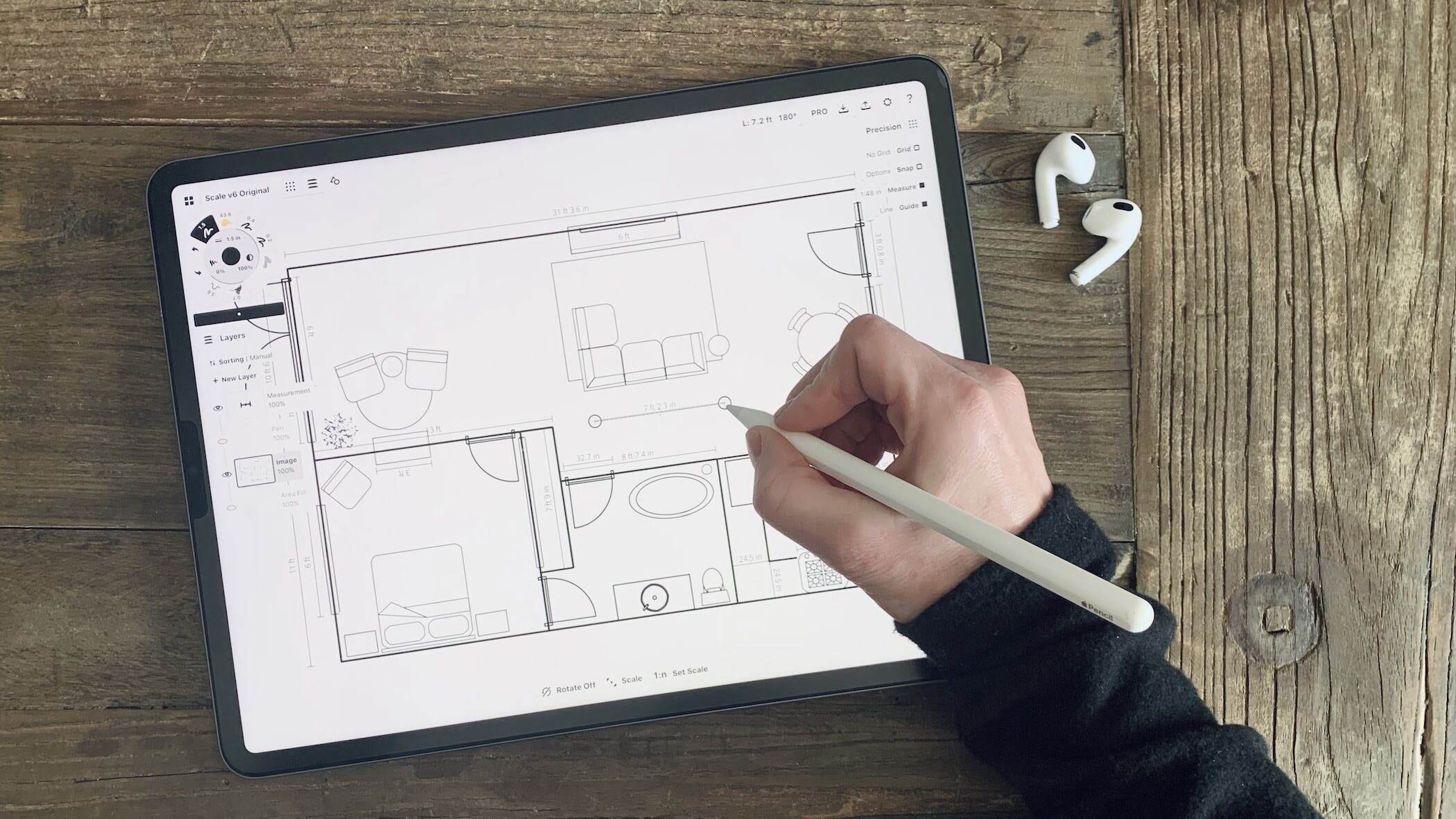
Drawing and Editing Geometric Shapes
When working with CAD drawing, the ability to create and edit geometric shapes is fundamental. Whether you’re designing a building plan, mechanical component, or product prototype, understanding how to draw and manipulate shapes accurately is crucial. Let’s explore the process of drawing and editing geometric shapes in CAD.
1. Line Tool: The line tool allows you to draw straight lines between specified points. Simply select the line tool, click on the starting point, and then click on the ending point to create a line. You can specify the length and angle of the line if desired. To edit a line, select it and use the editing tools provided by the CAD software, such as lengthening, shortening, or rotating.
2. Circle and Arc Tools: The circle tool is used to draw perfect circles. Specify the center point and the radius, and the software will create a circle accordingly. Arc tools allow you to draw circular arcs by specifying the center point, radius, and start and end angles. These tools are perfect for creating curved geometries such as rounded corners or circular elements.
3. Polygon and Rectangle Tools: The polygon and rectangle tools allow you to quickly create regular shapes. With the polygon tool, specify the number of sides or radius to create a polygon. The rectangle tool allows you to draw rectangles or squares by specifying the length and width. These tools are ideal for creating simple shapes and geometries.
4. Bezier and Spline Curves: More complex curves can be created using Bezier curves or splines. These tools allow you to create smooth, flowing curves by defining control points. Bezier curves give you more control over the shape, while splines create a smoother curve based on a series of points. These tools are commonly used in industrial design and complex architectural projects.
5. Modifying Shapes: CAD software provides a wide range of tools to modify and edit geometric shapes. You can easily resize, stretch, mirror, or rotate shapes to match your design requirements. Additionally, CAD software often includes operations such as filleting (adding rounded edges), chamfering (creating beveled corners), and trimming (removing unnecessary parts of shapes).
6. Snapping to Points and Objects: CAD software offers a feature called “snapping,” which helps you draw and align shapes accurately. Snapping allows you to snap to specific points, such as endpoints, midpoints, or intersections. You can also snap objects to each other, ensuring precise alignment and connections between shapes.
7. Parametric Modeling: Some CAD software incorporates parametric modeling, where you can define specific dimensions and constraints for your shapes. This allows you to easily modify shapes by changing the numerical parameters, which automatically updates the entire design. Parametric modeling offers flexibility and efficiency in the design process.
By utilizing the drawing and editing tools provided by CAD software, you can create precise and complex geometries with ease. Experiment with different tools and techniques to enhance your skills and expand your design capabilities. The ability to confidently draw and manipulate geometric shapes is a crucial skill that will significantly contribute to your success in CAD drawing.
Adding Dimensions and Annotations
Adding dimensions and annotations to your CAD drawing is essential for communicating design specifications and providing clarity to the viewers. Whether you’re creating architectural plans, mechanical drawings, or product designs, accurate and comprehensive dimensioning is crucial. Let’s explore the process of adding dimensions and annotations in CAD.
1. Linear Dimensions: Linear dimensions are used to indicate the measurements of straight lines or distances between two points. To add a linear dimension, select the dimension tool and click on the starting and ending points of the line you want to dimension. CAD software typically allows you to customize dimension styles, including text size, arrow style, and units of measurement.
2. Angular Dimensions: Angular dimensions are used to indicate the angle between two lines or the angle of a curved element. To add an angular dimension, select the dimension tool and click on the lines or points that define the angle. The dimension value and the angle symbol will be displayed adjacent to the angle. Similar to linear dimensions, you can customize the style of angular dimensions to fit your design requirements.
3. Radial and Diameter Dimensions: Radial dimensions are used to measure the radius of circular or arc-shaped elements, while diameter dimensions indicate the diameter of a circle. Select the appropriate dimension tool and click on the circle or arc to add the dimension. Adjust the position and style of the dimension as needed to ensure clarity and readability.
4. Text Annotations: In addition to dimensions, text annotations are commonly used to provide additional information and clarify specific details in the drawing. You can add text annotations using the CAD software’s text tool. Simply click in the desired location, enter the text, and customize the font, size, and style to match your design requirements. Text annotations can be used to label elements, provide instructions, or include informational notes.
5. Leaders and Callouts: When adding annotations, it’s often helpful to use leaders and callouts to point to specific elements in the drawing. Leaders are lines with an arrow or dot at one end, indicating the specific item being referred to. Callouts are boxes or bubbles attached to the leader line, containing the annotation text. Leaders and callouts help to visually connect the annotation to the relevant part of the drawing, improving clarity and understanding.
6. Dimension Styles and Standards: CAD software often allows you to create and save dimension styles and standards for consistency across your drawings. You can define default settings for text size, arrow types, and units of measurement. By using standard dimension styles, you can maintain consistency throughout your drawings and ensure that the dimensions adhere to industry standards.
Adding dimensions and annotations in your CAD drawing is crucial for conveying accurate information and ensuring a clear understanding of the design. As you work on your drawings, pay attention to the placement, style, and readability of dimensions and annotations. Remember to adhere to established standards and use proper conventions to enhance the clarity and professionalism of your CAD drawings.
When doing a CAD drawing, start by creating a rough sketch to plan out the design and dimensions before moving on to the detailed drawing in the software.
Creating and Editing Objects
Creating and editing objects is a fundamental aspect of CAD drawing. Whether you’re designing architectural layouts, engineering components, or intricate product models, having the ability to create and modify objects accurately is essential. Let’s explore the process of creating and editing objects in CAD.
1. Creating Basic Objects: CAD software provides a range of tools to create basic objects such as lines, circles, rectangles, and polygons. Simply select the desired tool, specify the required parameters (e.g., length, radius, or number of sides), and click in the design area to create the object. These basic objects serve as building blocks for more intricate designs.
2. Modifying Objects: CAD software offers a wide range of tools to modify and edit objects. You can resize objects, stretch or extend them, rotate them to specific angles, or mirror them to create symmetrical designs. Additionally, CAD software often includes operations such as filleting (adding rounded edges), chamfering (creating beveled corners), and trimming (removing unnecessary parts of objects) to refine and manipulate shapes as needed.
3. Parametric Modeling: Some CAD software incorporates parametric modeling capabilities. Parametric modeling allows you to define specific dimensions and constraints for objects. You can set parameters such as length, width, and height and modify them at any time to automatically update the entire design. Parametric modeling offers flexibility and efficiency by allowing you to make design changes easily without manually adjusting each object.
4. Using Construction Lines and Reference Geometry: Construction lines and reference geometry are useful tools in creating and aligning objects accurately. Construction lines act as temporary guidelines to help you create precise shapes and alignments. Reference geometry, such as points, axes, or planes, can be used as a reference to create or align objects. These tools assist in creating designs with precision and maintaining consistency throughout the drawing.
5. Cloning and Arrays: CAD software often includes features that allow you to clone or create arrays of objects. Cloning tools enable you to duplicate objects with ease, providing efficient workflows for elements that repeat throughout the design. Array tools create multiple copies of objects arranged in a pattern, such as a straight line, circular arrangement, or rectangular grid. These features save time and effort when working with repetitive elements in your design.
6. Grouping and Associating Objects: CAD software enables you to group objects to organize and manage them collectively. Grouping objects is especially useful when you need to move, copy, or edit multiple components at once. Additionally, you can associate objects, which establishes relationships between them. For example, associating a window object with a wall ensures that any changes to the wall automatically update the associated window.
Creating and editing objects in CAD requires a good understanding of the tools and techniques provided by the software. By utilizing the various creation and modification tools available, you can bring your design ideas to life and make precise adjustments as needed. Experiment with different tools and explore the capabilities of your CAD software to refine your object creation and editing skills.
Read more: How To Read A CAD Drawing
Working with CAD Blocks
In CAD drawing, blocks are a powerful tool for organizing and reusing design elements. Blocks can be thought of as reusable objects or symbols that you can insert into your drawings. They allow you to streamline your workflow, maintain consistency, and save time by avoiding the need to recreate frequently used elements. Let’s explore how to work with CAD blocks effectively.
1. Creating Blocks: To create a block, select the objects you want to include in the block, then use the “Create Block” command in the CAD software. Give the block a name and specify any relevant settings, such as insertion point and scale. Once created, the block becomes a single entity that can be easily copied and placed throughout your drawing.
2. Inserting Blocks: To insert a block into your drawing, use the “Insert” or “Insert Block” command. This allows you to browse your block library and select the desired block to be placed in your drawing. You can also specify the insertion point, scale, and rotation angle of the block during insertion. Once inserted, the block can be easily manipulated and modified.
3. Editing Blocks: Editing blocks is a powerful feature in CAD software. When you edit a block, any modifications made to the block will affect all instances of that block in the drawing. To edit a block, use the “Edit Block” or “Block Editor” command. This opens a special editing mode where you can modify the individual objects within the block. Once you exit the block editor, all instances of the block will reflect the changes you made.
4. Attribute Blocks: Attribute blocks are a special type of block that contain customizable attributes. Attributes are like placeholders for information that can be filled in during or after block insertion. Common examples include part numbers, descriptions, and quantities. Attribute blocks are especially useful for creating parts lists, bills of materials, or title blocks in your drawing.
5. Managing Block Libraries: CAD software often allows you to create and manage block libraries, which are collections of blocks you have created or downloaded. Creating libraries helps organize and categorize your blocks for easy access. You can organize blocks based on their type, project, or any other criteria that make sense for your workflow. This makes it quicker and easier to find and insert the blocks you need.
6. Updating Blocks: If you make changes to a block in your block library, you can update all instances of that block within your drawing by using the “Update Block” or “Refresh Block” command. This ensures consistency throughout the drawing and saves you from manually updating each instance of the block.
Working with CAD blocks offers many advantages, including increased efficiency, improved consistency, and simplified editing. By utilizing the power of blocks, you can streamline your workflow, save time, and maintain a cohesive and professional design. Experiment with creating and managing blocks to discover how they can enhance your CAD drawing process.
Applying Colors and Textures
One of the key aspects of CAD drawing is applying colors and textures to your designs. Adding visual elements such as colors and textures brings life and realism to your drawings. Whether you’re working on architectural renderings, product designs, or mechanical engineering models, applying colors and textures can greatly enhance the visual impact of your design. Let’s explore how to effectively apply colors and textures in CAD drawing.
1. Color Selection: When choosing colors for your CAD drawing, consider the purpose and context of the design. Colors can evoke certain emotions, convey messages, or differentiate elements within the design. For architectural plans, you may use different colors to represent different materials or functional areas. In product design, colors can reflect brand identity or enhance usability. Use a color palette that not only captures the aesthetics but also serves the intended purpose of the design.
2. Applying Solid Colors: Most CAD software allows you to apply solid colors to objects or surfaces. Use the software’s fill or hatch tools to select a color and apply it to the desired area. This is particularly useful when you want to differentiate between different parts or highlight specific elements in your design. Solid colors can be used to represent materials, finishes, or simply to add visual interest.
3. Textures and Patterns: CAD software also provides options to apply textures and patterns to surfaces within your design. Textures help simulate the appearance of real-world materials such as wood, stone, or fabric. Patterns can be used to create visual interest or indicate specific design elements. Libraries of predefined textures and patterns are often available in CAD software, but you can also import your own custom textures or patterns.
4. Materials and Shading: In addition to colors and textures, CAD software allows you to apply materials to objects or surfaces. Materials include properties such as reflectivity, transparency, and shininess, which contribute to the realism of your design. Applying materials helps visualize how light interacts with different surfaces, giving depth and dimension to your drawing. You can assign materials from predefined libraries or create custom material properties as per your requirements.
5. Lighting and Shadows: Lighting plays a crucial role in creating realistic and visually appealing CAD renderings. CAD software often provides tools to add directional lights, ambient lighting, or even simulate realistic outdoor lighting conditions. Properly placed and adjusted lighting can dramatically enhance the appearance of your design, highlighting key features and creating realistic shadows and reflections.
6. Rendering and Visualization: Once you have applied colors, textures, materials, and lighting, you can use the rendering capabilities of your CAD software to create stunning visualizations of your design. Renderings add a level of realism that showcases the design in its full glory. Depending on the complexity of your design and the capabilities of your software, you can choose between real-time renderings or higher-quality, photorealistic renderings.
By skillfully applying colors, textures, and other visual elements, you can elevate the appearance of your CAD drawings and breathe life into your designs. Experiment with different color schemes, materials, and lighting techniques to create visually stunning and accurate representations of your ideas. Remember, the goal is not only to create functional designs but also to communicate your vision effectively through captivating visuals.
Adding Lighting and Shadows
Adding lighting and shadows is an essential step in enhancing the realism and visual appeal of your CAD designs. Whether you’re working on architectural renderings, product visualizations, or mechanical simulations, effectively incorporating lighting and shadows can greatly impact the perception and understanding of your design. Let’s explore how to add lighting and shadows to your CAD drawings.
1. Understanding Light Sources: Begin by understanding the different types of light sources and their characteristics. CAD software typically offers options for point lights, directional lights, and ambient lights. Point lights emit light in all directions from a single point, while directional lights simulate the effect of light coming from a specific direction. Ambient lights provide overall illumination without a specific source. By understanding the properties of each light and their effects on the design, you can create realistic lighting scenarios.
2. Adjusting Light Intensity and Color: Experiment with adjusting the intensity and color of your light sources to achieve the desired effect. Brighter lights create more pronounced highlights and shadows, while dimmer lights produce a softer and more diffused lighting. You can also modify the color of the light to create specific moods or to mimic real-world lighting conditions, such as warm sunlight or cool fluorescent lighting.
3. Casting Shadows: Shadows play a crucial role in creating depth and realism in your CAD drawings. Enable the shadow casting feature in your CAD software and adjust the settings accordingly. Consider the position and orientation of your light sources to determine the placement and size of the shadows. Shadows can help visually anchor objects to the ground, indicate the form and depth of objects, and contribute to the overall ambiance of the design.
4. Softening Shadows: Depending on your software and the desired effect, you can control the softness or hardness of the shadows. Softer shadows have less defined edges, creating a diffused effect, while sharper shadows have more defined and crisp edges. Experimenting with the shadow settings allows you to achieve the desired balance between realism and artistic style.
5. Shadows and Material Properties: Consider the material properties of your objects when adding shadows. Different materials have varying degrees of reflectivity and transparency, which affect the appearance of shadows. Shadows can appear differently on opaque, transparent, or reflective surfaces. Pay attention to the interaction between light, shadows, and materials to achieve a cohesive and accurate representation of your design.
6. Rendering and Visualization: Once you have set up the lighting and shadows, you can utilize the rendering capabilities of your CAD software to create high-quality visualizations. Renderings add a level of realism by simulating how light interacts with different materials, creating more accurate reflections and shadows. Depending on your requirements, you can choose between real-time renderings or higher-quality, photorealistic renderings to showcase your design.
By skillfully incorporating lighting and shadows into your CAD drawings, you can elevate the visual impact and realism of your designs. Experiment with different lighting setups, adjust shadow settings, and pay attention to material properties to create captivating and visually stunning representations of your ideas. Remember, the goal is not only to create accurate designs but to evoke emotions and effectively communicate your vision through the interplay of light and shadow.
Setting up Views and Perspectives
Setting up views and perspectives is a crucial step in CAD drawing that allows you to showcase your design from different angles and optimize the visual representation of your project. By carefully selecting viewpoints, adjusting camera settings, and choosing the right perspective, you can effectively communicate the design intent and highlight key features of your CAD drawings. Let’s explore how to set up views and perspectives in CAD drawing.
1. Selecting Viewpoints: Start by considering the purpose and focus of your CAD drawing. Identify the key elements or aspects of the design that you want to highlight. From there, choose the appropriate viewpoints that showcase those features effectively. This may involve selecting multiple viewpoints to capture various angles, sections, or elevations of the design.
2. Adjusting Camera Settings: CAD software typically allows you to adjust camera settings, such as field of view, depth of field, and focal length. The field of view determines how much of the scene is visible within the frame. Depth of field controls the focus and blurriness of elements in the foreground and background. Focal length affects the perceived perspective and distortion. Experiment with different camera settings to achieve the desired visual impact and clarity in your CAD drawings.
3. Exploring 2D and 3D Views: CAD software provides options for both 2D and 3D views. In 2D views, such as elevations, plans, or sections, the design is represented without depth. 3D views, on the other hand, provide a more realistic representation with depth and perspective. Consider when to use each view type based on the purpose and audience of your CAD drawing. 2D views may be suitable for technical documentation, while 3D views may be more effective for presentations or marketing materials.
4. Showcasing Details and Views: Depending on the complexity of your design, it may be helpful to showcase specific details or views in separate sections of your CAD drawing. This can be achieved by cropping or enlarging sections of your design to highlight specific areas of interest. By zooming in or focusing on certain elements, you can effectively communicate intricate details or specific design nuances to your audience.
5. Utilizing Perspective Views: Perspective views create a sense of depth and realism in your CAD drawings. By adjusting the perspective, you can mimic the way human eyes perceive the world. Perspective views are particularly useful when showcasing architectural designs, interiors, or product visualizations, as they can help viewers better understand the look and feel of the design.
6. Viewpoint Annotations: Consider adding annotations to your CAD drawings to provide additional information about the different viewpoints. Annotations can include labels, arrows, or callouts to highlight specific features or aspects of the design. This helps guide the viewer’s attention and ensures a clear understanding of the design intent.
By carefully setting up views and perspectives in your CAD drawings, you can effectively communicate your design concepts and highlight key features. Experiment with different viewpoints, camera settings, and annotation techniques to create visually appealing and informative drawings. Remember to consider the purpose, audience, and context of your design to determine the most effective ways to present your work.
Read more: How To Draw An Arrow In CAD
Rendering and Exporting the CAD Drawing
Rendering and exporting your CAD drawing is the final step in the design process, allowing you to create high-quality visual representations of your design and share them with others. Rendering enhances the realism and aesthetics of the CAD drawing, while exporting enables you to save and distribute the final output in various file formats. Let’s explore the process of rendering and exporting CAD drawings.
1. Choosing the Rendering Method: CAD software offers different rendering methods, ranging from real-time rendering to more advanced photorealistic rendering. Real-time rendering provides immediate feedback and allows for quick visualization of the design in different lighting conditions. Photorealistic rendering, on the other hand, simulates the effects of light, shading, and materials to create highly realistic representations of the design. Select the rendering method that best suits your project goals and software capabilities.
2. Setting up Materials and Lighting: Before rendering, ensure that you have properly applied materials and set up lighting in your CAD drawing. Assign materials to objects, specify their properties such as reflectivity and transparency, and adjust lighting sources and settings to achieve the desired effect. These adjustments greatly enhance the realism and visual quality of the final rendering.
3. Adjusting Render Settings: CAD software typically provides various settings to control the quality, resolution, and output format of the rendering. Adjust these settings based on your requirements and available resources. Higher quality renderings typically require more processing power and time to generate. Experiment with different settings to find the balance between visual fidelity and the time required for rendering.
4. Rendering the CAD Drawing: Once you have set up materials, lighting, and rendering settings, initiate the rendering process. Depending on the complexity of your design and the rendering method selected, this may take some time. Consider letting the rendering run overnight or during non-working hours for large-scale or time-intensive projects. Monitor the progress to ensure a successful completion and to address any issues that may arise during the rendering process.
5. Reviewing and Tweaking the Rendering: After the rendering is complete, review the output and check for any visual discrepancies or errors. Assess the overall quality, lighting, material representation, and accuracy of the rendering. If necessary, make adjustments to objects, materials, lighting, or rendering settings to achieve the desired result. Iteratively review and tweak the rendering until you are satisfied with the visual representation of your design.
6. Exporting the CAD Drawing: Once you are satisfied with the rendered image, it’s time to export the CAD drawing. CAD software supports a variety of file formats for export, including popular formats such as JPEG, PNG, or PDF. Select the appropriate file format based on the intended use of the exported drawing. Consider the resolution, compatibility, and file size requirements when choosing the export settings.
By rendering and exporting your CAD drawing, you transform a digital design into visually stunning representations that can be shared with clients, colleagues, or stakeholders. The rendering process enhances the realism and aesthetics of your design, while exporting allows for easy distribution and presentation. Taking the time to refine and optimize the rendering and export settings ensures that your final output accurately reflects your design vision and effectively communicates your ideas.
Conclusion
CAD drawing has become an indispensable tool in the fields of architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and design. It allows designers to create intricate and precise digital representations of physical objects, revolutionizing the way we visualize and bring ideas to life. Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of CAD drawing, from understanding its definition to mastering the essential techniques and tools.
By delving into topics such as drawing and editing geometric shapes, adding dimensions and annotations, working with CAD blocks, applying colors and textures, setting up views and perspectives, and adding lighting and shadows, we have gained a comprehensive understanding of the process. We have also learned about the importance of setting up the drawing workspace, rendering and exporting CAD drawings, and how each of these elements contributes to the overall design workflow.
Throughout this journey, we’ve recognized the significance of accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration in CAD drawing. With the right tools, software, and techniques, designers can create visually appealing and precise designs while improving productivity and enhancing communication with team members and stakeholders.
It is important to remember that CAD drawing is an art as much as it is a skill. It requires creativity, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of design principles. By harnessing the power of CAD tools and incorporating human-like touches into our designs, we can create captivating and engaging visual representations that resonate with viewers.
In conclusion, CAD drawing has revolutionized the design process, enabling us to create intricate and accurate representations of physical objects. By mastering the techniques, tools, and software discussed in this article, you can unleash your creativity and take your CAD drawing skills to the next level. Whether you are a beginner looking to learn the fundamentals or an experienced professional seeking to enhance your expertise, continuous learning and practice in CAD drawing will undoubtedly open up new opportunities for innovation and excellence in your design journey.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Do A CAD Drawing
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “How To Do A CAD Drawing”