Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Does A BIM Modeler Do?

Building & Construction
What Does A BIM Modeler Do?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn what a BIM Modeler does in the building construction industry. Discover their responsibilities, skills, and the importance of BIM in the design process.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of building construction, where precision, efficiency, and collaboration are integral to successful project completion. In recent years, the industry has undergone a significant transformation with the adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology. BIM has revolutionized the way construction professionals plan, design, and construct buildings, enabling a streamlined and more efficient process.
But what exactly is BIM, and what role does a BIM modeler play in the construction process? In this article, we’ll explore the intricacies of BIM modeling and dive into the responsibilities, skills, and challenges faced by BIM modelers.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM modelers play a pivotal role in streamlining the design and construction process by creating, managing, and updating accurate 3D models, facilitating effective coordination, and enhancing visualization and communication.
- Despite challenges such as evolving technology and collaboration hurdles, skilled BIM modelers bring immense value to construction projects, ensuring improved accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration.
Read more: How To Upgrade A Revit Model On BIM 360
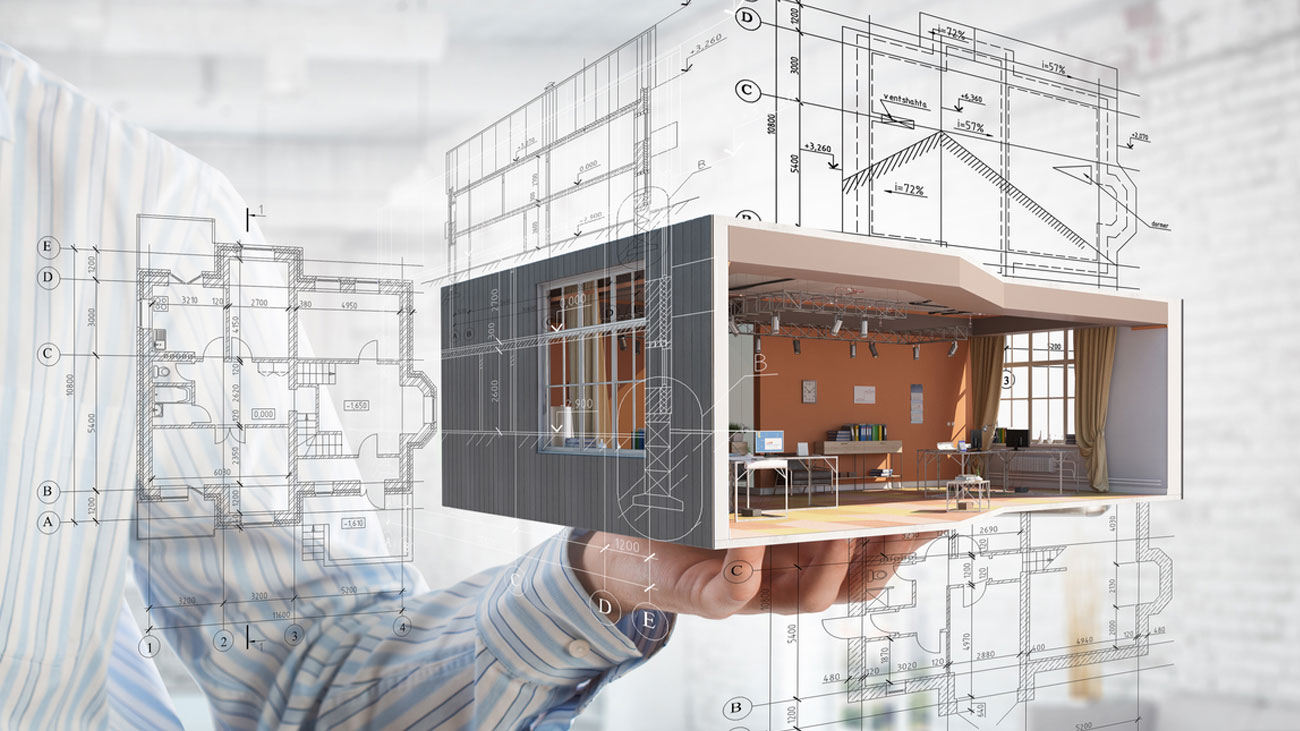
What is BIM?
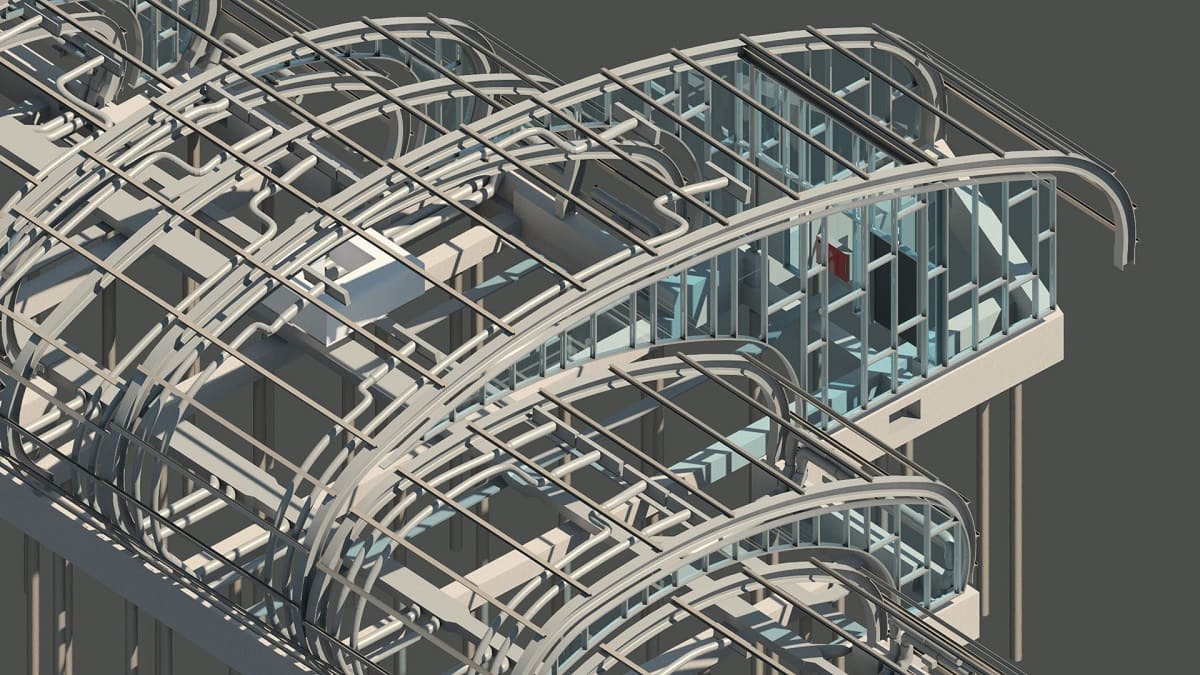
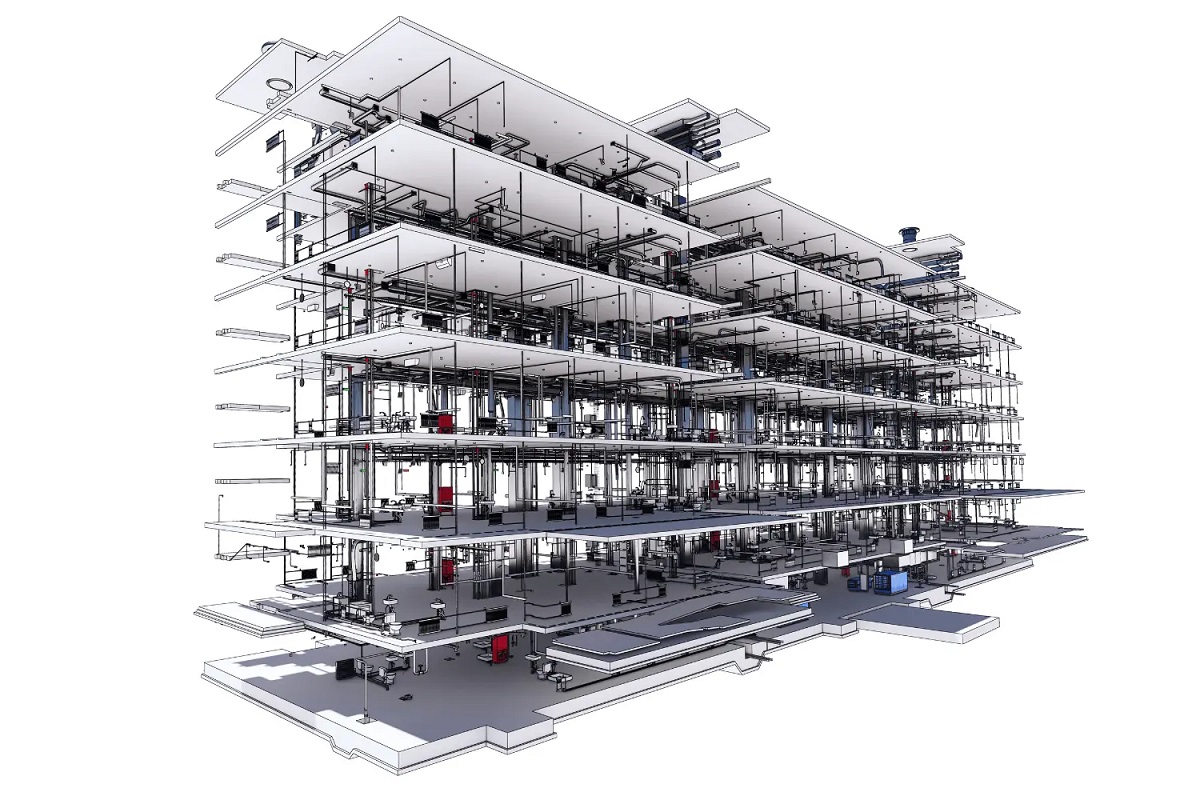
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. It is a collaborative process that involves the creation and management of data-rich 3D models that can be used throughout the entire lifecycle of a project, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
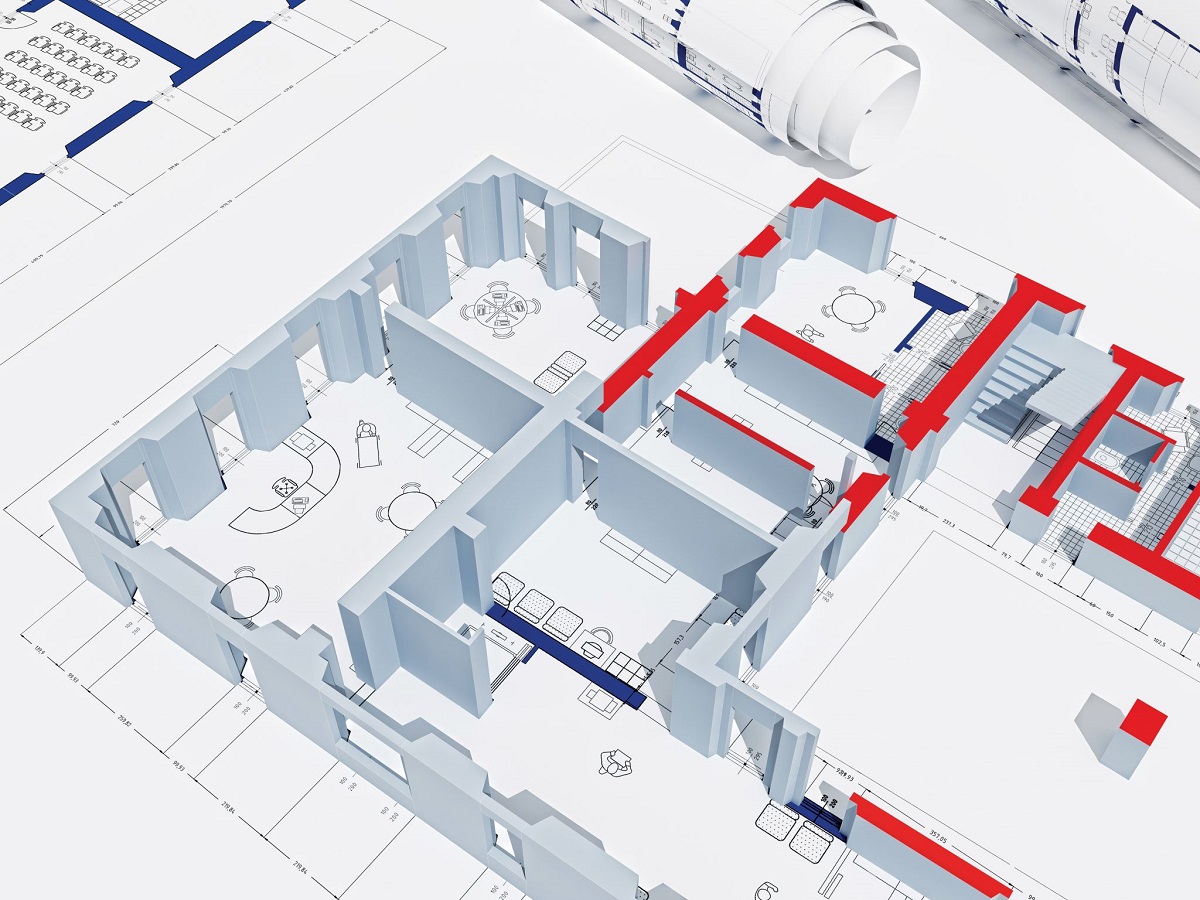
BIM goes beyond traditional 2D blueprints by adding an extra dimension of information. It allows architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to visualize and analyze the building’s components, systems, and spatial relationships. This holistic approach helps identify and resolve potential conflicts or issues before they arise on the construction site.
Role of a BIM Modeler
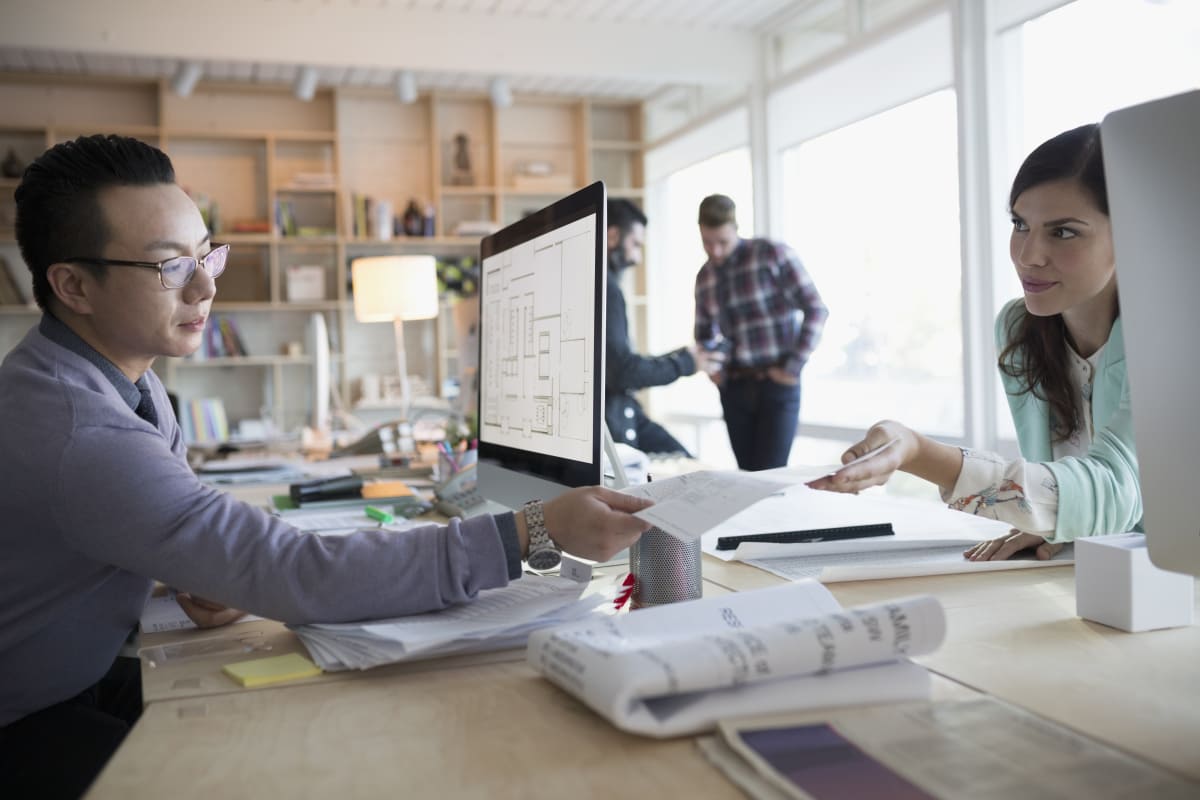
A BIM modeler is a key member of the design and construction team. They are responsible for creating, managing, and updating the digital models that form the foundation of the BIM process. BIM modelers work closely with architects, engineers, and contractors to ensure that the project is accurately represented in the virtual environment.
While the specific duties may vary depending on the project and organization, the core responsibility of a BIM modeler is to transform 2D drawings and specifications into detailed 3D models. These models incorporate information about the building’s geometry, materials, structural components, systems, and more.
The BIM modeler acts as a bridge between the design and construction teams, facilitating seamless communication and collaboration. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the virtual model accurately reflects the physical reality of the building, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and minimize costly errors and rework.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM modelers play a pivotal role in streamlining the design and construction process by creating, managing, and updating accurate 3D models, facilitating effective coordination, and enhancing visualization and communication.
- Despite challenges such as evolving technology and collaboration hurdles, skilled BIM modelers bring immense value to construction projects, ensuring improved accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration.
Read more: How To Upgrade A Revit Model On BIM 360
What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. It is a collaborative process that involves the creation and management of data-rich 3D models. These models contain information about the building’s geometry, materials, construction sequencing, and performance characteristics.
BIM goes beyond traditional 2D blueprints by adding an extra dimension of information. It allows architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to visualize and analyze the building’s components, systems, and spatial relationships. This holistic approach helps identify and resolve potential conflicts or issues before they arise on the construction site.
At its core, BIM is about improving communication, efficiency, and collaboration in the construction industry. By working in a shared digital environment, project stakeholders can better coordinate their efforts, reduce errors, and optimize the design and construction processes.
BIM encompasses various levels of detail (LOD) throughout the project lifecycle. In the early design stages, BIM models may be more conceptual in nature, providing a rough representation of the building. As the project progresses, the models evolve to contain more detailed information, including specific materials, equipment, and systems.
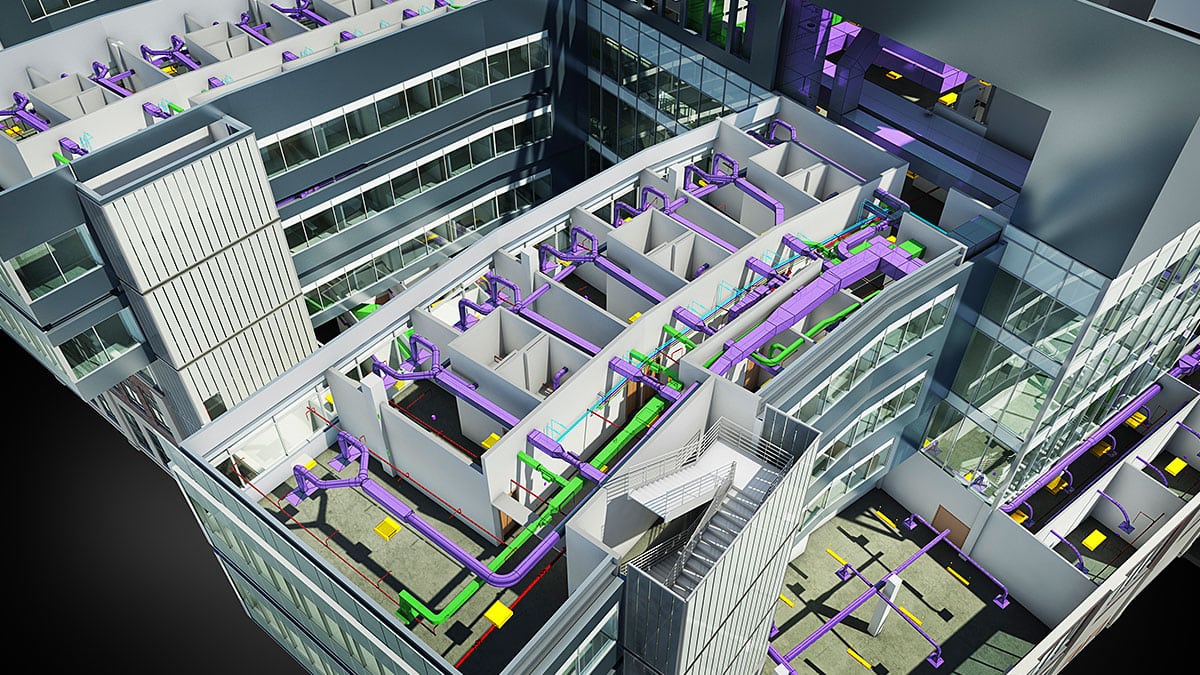
One of the key benefits of BIM is its ability to facilitate clash detection. Clash detection involves identifying potential conflicts or interferences among different building elements, such as structural components, HVAC systems, or plumbing. By running clash detection analyses on the BIM model, construction professionals can identify and resolve these issues early on, minimizing costly errors and rework.
BIM models are not only valuable during the design and construction phases but also throughout the building’s lifecycle. The data-rich models can be utilized for facility management, maintenance planning, and even demolition and renovation projects.
Overall, BIM has transformed the industry by enhancing collaboration, improving efficiency, and reducing risks. It has become an essential tool for construction professionals looking to streamline their processes, enhance project outcomes, and deliver high-quality buildings.
Role of a BIM Modeler
A BIM modeler is a vital member of the design and construction team, responsible for creating, managing, and updating the digital models that form the foundation of the BIM process. Their role revolves around transforming 2D drawings and specifications into detailed and accurate 3D models.
Collaboration is a key aspect of a BIM modeler’s role. They work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to ensure that the project’s digital representation aligns with the intended design and construction plans. By communicating and coordinating effectively with the team, the BIM modeler facilitates seamless integration of design and construction elements, minimizing errors and conflicts.
One of the primary responsibilities of a BIM modeler is to create and maintain an accurate BIM model. This involves translating architectural and engineering drawings into a 3D model using specialized software. The BIM modeler incorporates information about the building’s geometry, materials, components, systems, and other relevant details to create a comprehensive digital representation.
The BIM modeler ensures the accuracy of the model by continuously updating it as changes occur during the design and construction process. They incorporate design revisions, construction modifications, and as-built data into the BIM model, keeping it up to date. This enables stakeholders to have a real-time and accurate view of the building’s progress and helps identify any potential conflicts or issues.
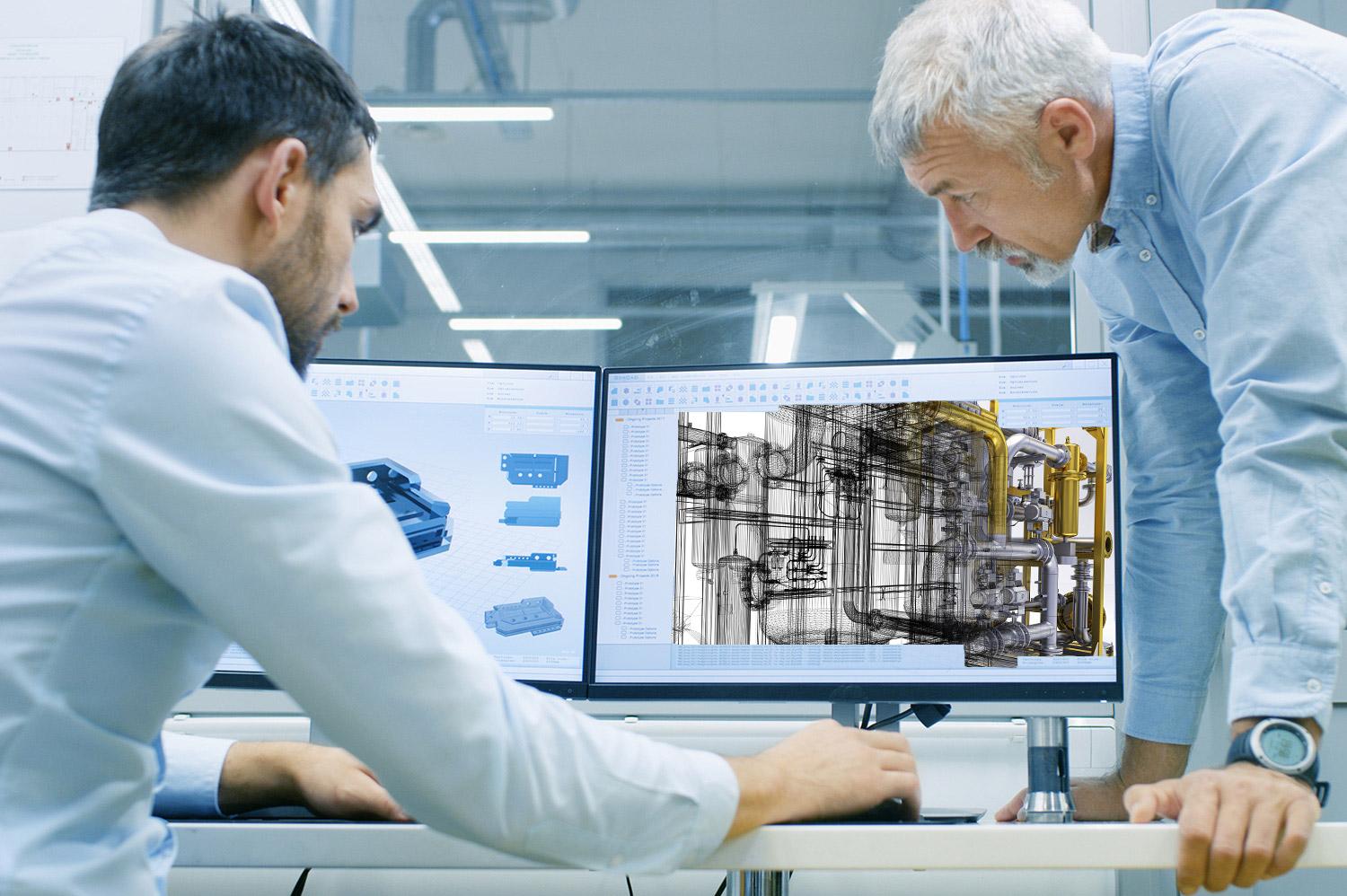
Beyond creating and updating the BIM model, a BIM modeler also plays a crucial role in clash detection and resolution. By conducting clash detection analyses on the model, they identify any clashes or interferences among various building elements, such as structural components, mechanical systems, electrical systems, and plumbing. The BIM modeler then collaborates with the different disciplines to resolve these clashes and optimize the design and construction processes.
Another important aspect of a BIM modeler’s role is to extract valuable information from the BIM model. They can generate reports, quantities, schedules, and other data that assist in cost estimating, material ordering, and project coordination. This information helps stakeholders make informed decisions, improve project efficiency, and streamline construction workflows.
Overall, a BIM modeler acts as a bridge between the design and construction teams, facilitating effective communication and collaboration. By creating and managing an accurate and up-to-date BIM model, they contribute to the success of the project by minimizing errors, improving coordination, and optimizing the overall construction process.
Read more: How To Archive A Revit Model In BIM 360
Responsibilities of a BIM Modeler
A BIM modeler plays a crucial role in the design and construction process, ensuring that the digital models accurately represent the physical building and facilitating effective collaboration between various stakeholders. Their responsibilities encompass a wide range of tasks, including:
- Creating 3D BIM models: The primary responsibility of a BIM modeler is to transform 2D design drawings and specifications into detailed 3D models. They use specialized software to accurately represent the building’s geometry, components, and systems.
- Updating BIM models: BIM models need to be continuously updated as design changes occur or as-built data becomes available. A BIM modeler ensures that the digital representation is up to date and reflects the current state of the project.
- Coordinating with design and construction teams: Effective communication and collaboration are essential for a BIM modeler. They work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to ensure that the BIM model aligns with the project’s goals and integrates various design disciplines seamlessly.
- Performing clash detection: Clash detection involves identifying conflicts or interferences between different building elements, such as structural components, mechanical systems, and electrical systems. A BIM modeler conducts clash detection analyses using the BIM model to identify and resolve these clashes before they become costly issues during construction.
- Generating schedules and quantities: BIM models contain valuable information that can be used to generate schedules, quantities, and reports. A BIM modeler can extract this data to assist with cost estimating, material ordering, and project planning.
- Facilitating collaboration and coordination: A BIM modeler acts as a central point of contact for design and construction teams, ensuring effective communication and coordination. They facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration and provide support in resolving design conflicts or coordination issues.
- Implementing BIM standards and protocols: BIM modelers adhere to industry standards and protocols to ensure consistency and interoperability among different software and models. They stay updated with the latest BIM trends, software advancements, and best practices.
- Providing technical support: BIM modelers may be responsible for providing technical support to the design and construction teams. They assist in troubleshooting software issues, resolving model conflicts, and providing training on BIM tools and processes.
- Continuously improving BIM workflows: BIM modelers contribute to the development and improvement of BIM workflows within their organization. They identify areas for enhancement, propose solutions, and implement efficient processes to optimize the use of BIM technology.
These responsibilities are critical in ensuring the successful implementation of BIM and enhancing the overall efficiency, collaboration, and accuracy of the design and construction process. A skilled BIM modeler is essential for leveraging the full potential of BIM technology in projects of all sizes and complexity.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Being a BIM modeler requires a combination of technical skills, industry knowledge, and attention to detail. While specific requirements may vary depending on the organization and project, there are several key skills and qualifications that are typically expected of a BIM modeler:
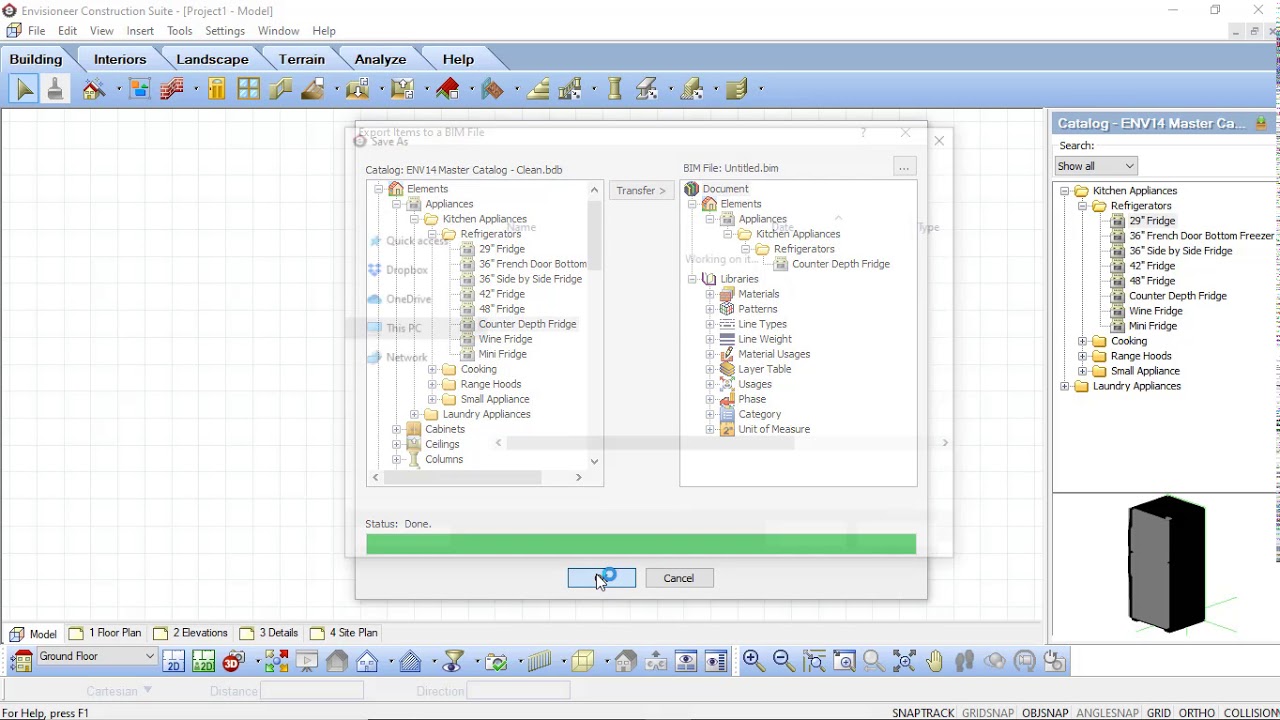
- Proficiency in BIM software: A strong command of BIM software is essential for a BIM modeler. They should be proficient in using software such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, or Bentley MicroStation, which are commonly used for BIM modeling. Knowledge of other related software, such as Navisworks for clash detection or AutoCAD for 2D drafting, is also beneficial.
- Knowledge of building design and construction: It is crucial for a BIM modeler to have a solid understanding of building design and construction principles. They should be familiar with architectural and engineering concepts, construction documentation, and building codes and regulations.
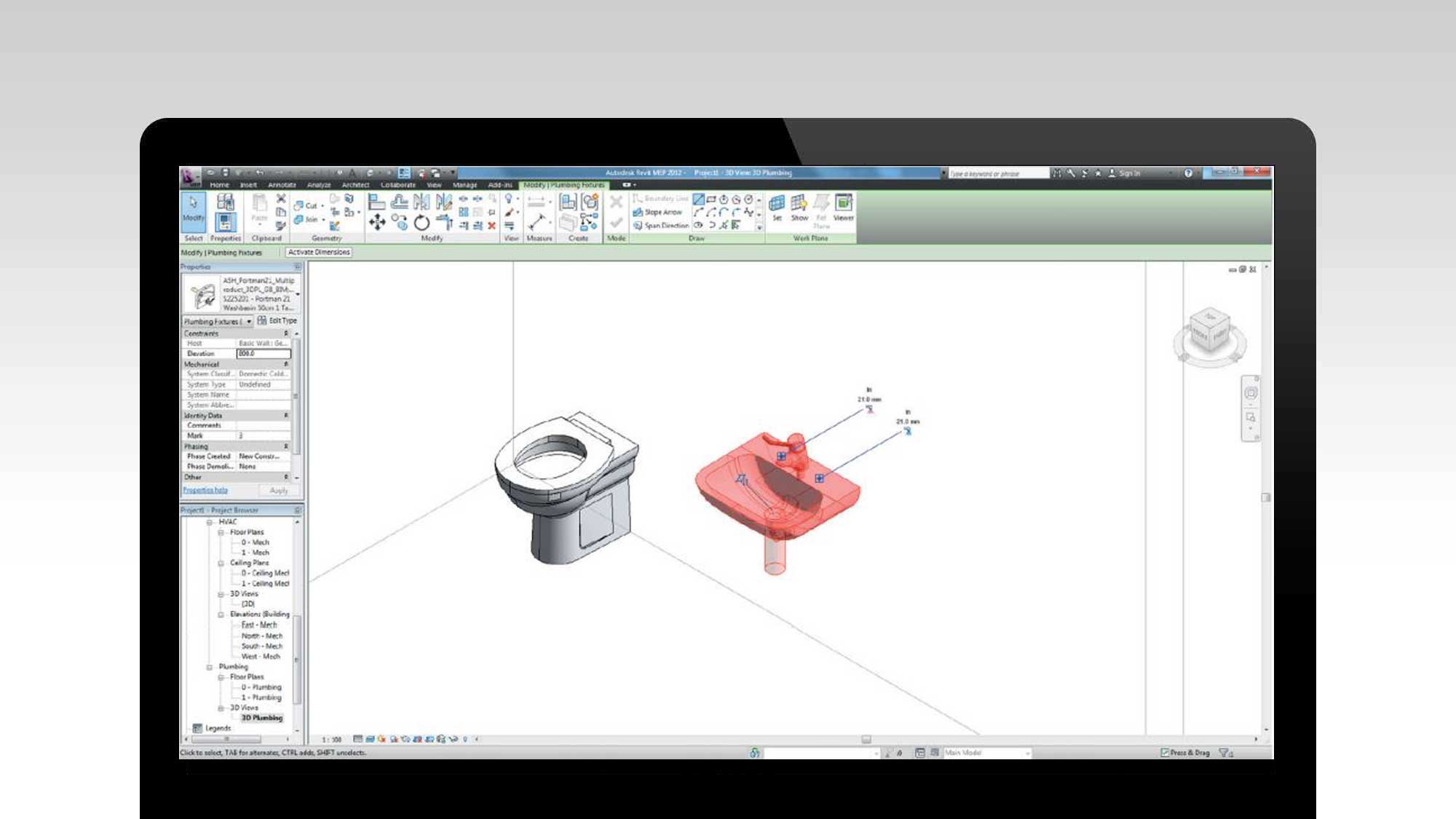
- 3D modeling skills: A BIM modeler should possess strong 3D modeling skills. They should be able to accurately interpret 2D drawings and translate them into a detailed 3D model using BIM software. Attention to detail, spatial awareness, and the ability to visualize the building components and systems are vital.
- Attention to detail: BIM modeling requires a high level of accuracy and attention to detail. A BIM modeler should be meticulous in their work, ensuring that the models are free of errors, inconsistencies, or clashes. They should have a keen eye for spotting potential issues and be able to resolve them effectively.
- Collaboration and communication skills: BIM modelers work closely with various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and project managers. Strong collaboration and communication skills are necessary to effectively coordinate with the team and ensure that the BIM model accurately reflects the design intent and construction requirements.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking: BIM modelers should possess problem-solving and critical thinking abilities. They should be able to analyze complex design challenges, identify clashes or conflicts, and propose effective solutions. Being able to think creatively and adapt to changing project requirements is crucial.
- Ability to work under pressure: Construction projects often have tight deadlines and require working under pressure. A BIM modeler should be able to handle stress and deliver accurate and timely models even in demanding situations.
- Continual learning: The field of BIM is constantly evolving, with new software updates and emerging technologies. A BIM modeler should have a passion for learning and be willing to stay updated with the latest industry trends and advancements. They should be proactive in enhancing their skills and knowledge through training, workshops, and certifications.
These skills and qualifications form the foundation of a successful BIM modeler. Having a strong blend of technical expertise, industry knowledge, and effective communication skills enables a BIM modeler to contribute effectively to the design and construction process and ensure the successful implementation of BIM technology.
A BIM modeler creates and manages digital 3D models of buildings and infrastructure. They should have a strong understanding of architecture, engineering, and construction principles, as well as proficiency in BIM software such as Revit or AutoCAD.
Tools and Software Proficiency
In the field of BIM modeling, proficiency in various tools and software is essential for effectively creating and managing BIM models. BIM modelers should have a strong command of the following tools and software:
- BIM software: BIM modelers should be proficient in using software specifically designed for BIM modeling, such as Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, or Bentley MicroStation. These software tools allow for the creation, visualization, and collaboration of 3D BIM models.
- Clash detection software: Clash detection is a vital aspect of BIM modeling, and having knowledge of clash detection software is beneficial. Tools like Autodesk Navisworks and Solibri Model Checker enable BIM modelers to detect clashes or interferences among various building elements and systems, helping to identify and resolve conflicts early on.
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is widely used for 2D drafting in the construction industry. BIM modelers should be proficient in AutoCAD to work with 2D drawings, import and export CAD files, and collaborate with stakeholders who use AutoCAD for their design work.
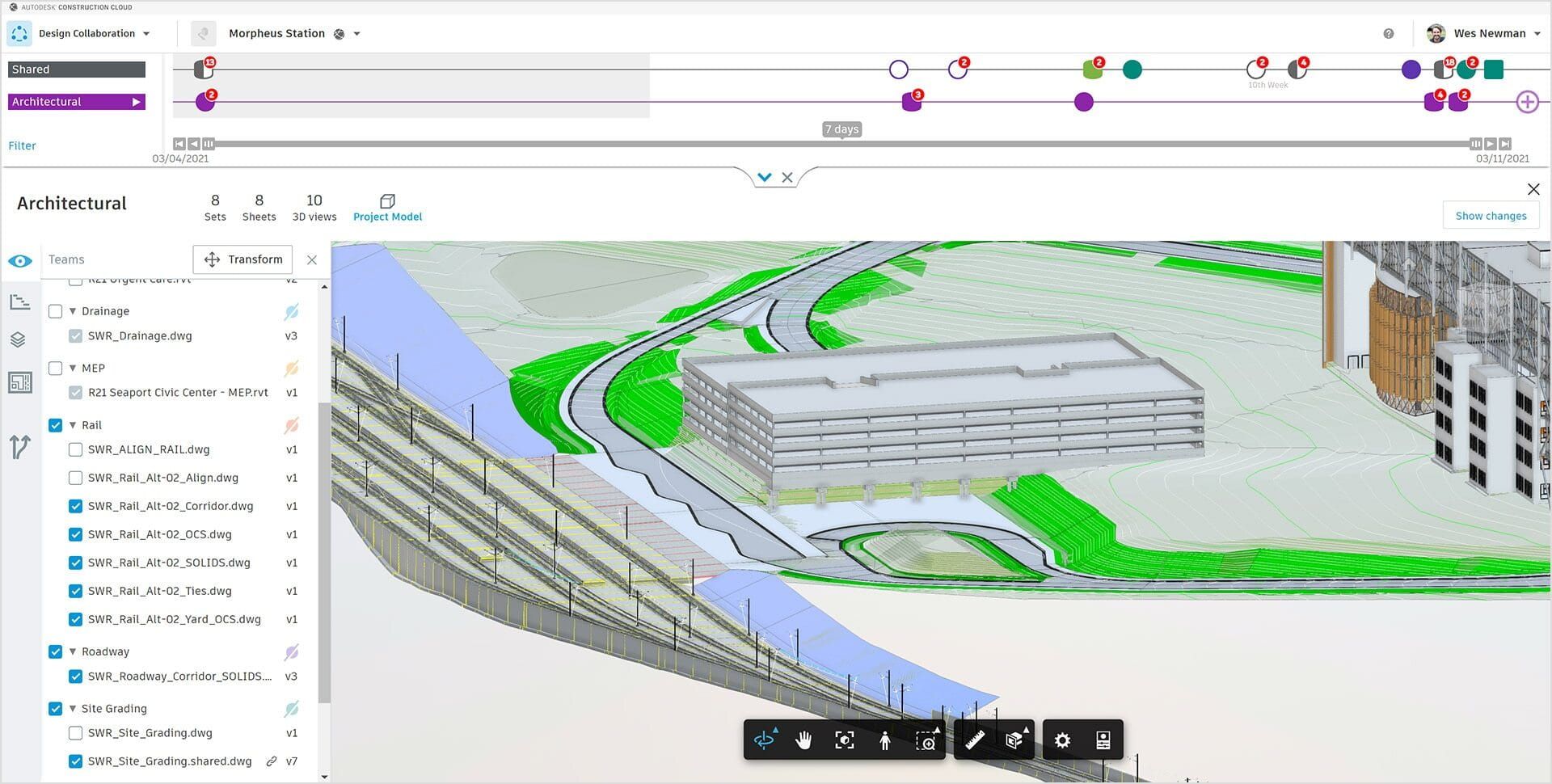
- BIM collaboration platforms: BIM modelers often collaborate with stakeholders who may be using different software tools. Familiarity with BIM collaboration platforms like BIM 360, Trimble Connect, or Aconex is beneficial, as these platforms enable seamless communication, coordination, and model sharing across the project team.
- Visualization tools: BIM modelers should have knowledge of visualization tools, such as Autodesk 3ds Max or Lumion. These tools allow for the creation of realistic visualizations and renderings from the BIM model, helping stakeholders better conceptualize the final appearance of the building.
- Data management software: BIM models are data-rich, and managing that data efficiently is crucial. Proficiency in data management software like Microsoft Excel, Autodesk BIM 360 Docs, or Aconex facilitates effective organization, analysis, and reporting of BIM-related information.
- Mobile applications: With the increasing adoption of mobile devices in the construction industry, familiarity with mobile applications that support BIM workflows can be advantageous. Tools like Autodesk BIM 360 Field or PlanGrid enable on-site access to BIM models, real-time collaboration, and seamless communication.
- Parametric modeling: Parametric modeling software, such as Grasshopper or Dynamo, can enhance the capabilities of BIM modeling. BIM modelers with knowledge of parametric modeling techniques can create complex designs, optimize building performance, and automate repetitive tasks.
Proficiency in these tools and software enables BIM modelers to effectively create, manage, collaborate on, and analyze BIM models. Keeping up with the latest updates in BIM software, understanding interoperability between different tools and platforms, and adapting to new software advancements are key factors in becoming a proficient BIM modeler in today’s evolving construction industry.
Typical Workflow of a BIM Modeler
A BIM modeler follows a structured workflow throughout the design and construction process to create, manage, and update BIM models. While the specific steps may vary depending on the project and organization, here is a typical workflow of a BIM modeler:
- Gathering project information: The BIM modeler starts by gathering project information, including architectural and engineering drawings, specifications, and other relevant documentation. They familiarize themselves with the project goals, design intent, and construction requirements.
- Creating the initial BIM model: Using specialized BIM software like Autodesk Revit or ArchiCAD, the BIM modeler begins by creating the initial 3D model. They translate the 2D drawings and specifications into a digital representation, incorporating the building’s geometry, materials, and major components.
- Refining the BIM model: The BIM modeler refines the initial model by adding more details and components as the design progresses. They incorporate structural elements, MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems, and other building systems into the model, ensuring accuracy and coordination among different disciplines.
- Collaborating with stakeholders: BIM modelers actively collaborate with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders throughout the workflow. They coordinate design changes, integrate feedback, and resolve clashes or conflicts that arise during coordination meetings or through clash detection software.
- Updating the BIM model: As the design evolves or as-built information becomes available, the BIM modeler updates the BIM model with the latest changes. They incorporate design revisions, construction modifications, and accurate field measurements to keep the model up to date.
- Performing clash detection: Using clash detection software like Autodesk Navisworks or Solibri Model Checker, the BIM modeler identifies clashes or interferences among various building elements and systems. They run clash detection analyses and collaborate with relevant disciplines to resolve clashes and optimize the design.
- Extracting data and generating reports: BIM models contain a wealth of information that can be utilized to generate schedules, quantities, and reports. BIM modelers extract this data and generate reports that assist in cost estimating, material ordering, and project coordination.
- Coordinating design changes: In collaboration with the design and construction teams, the BIM modeler coordinates and manages design changes. They update the BIM model accordingly and ensure that all stakeholders are kept informed of any modifications that may impact the overall project.
- Supporting construction activities: During the construction phase, the BIM modeler provides support to the construction team. They coordinate with contractors, review shop drawings, and provide guidance on the use of the BIM model for construction planning and sequencing.
- Maintaining the BIM model: Throughout the project’s lifecycle, the BIM modeler continually maintains the BIM model, incorporating as-built data, capturing changes, and updating the model with any modifications or renovations that occur post-construction.
This workflow ensures that the BIM model is accurate, up to date, and reflects the design intent. It allows for effective collaboration, clash detection, data extraction, and coordination among various project stakeholders, ultimately leading to enhanced project outcomes and improved construction efficiencies.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Collaboration with Other Professionals
Collaboration is a central aspect of BIM modeling, as it involves various professionals working together to achieve a common goal. BIM modelers play a vital role in facilitating collaboration and effective communication among different stakeholders throughout the design and construction process. Here are some key aspects of collaboration with other professionals:
Architects: BIM modelers work closely with architects to ensure that the BIM model accurately represents the architectural design. They collaborate on design changes, incorporate architectural elements into the model, and resolve any clashes or conflicts that arise during the coordination process. BIM modelers provide valuable input on constructability, feasibility, and potential design improvements, enhancing the overall quality of the architectural design.
Engineers: Collaboration with engineers is critical for the successful integration of the building’s structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. BIM modelers coordinate with structural engineers to accurately represent the building’s structural elements and ensure their proper integration. They collaborate with mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) engineers to incorporate MEP systems into the BIM model and resolve clashes or conflicts that may arise. Communication and coordination with engineers are essential to optimize system performance, reduce errors, and enhance construction efficiency.
Contractors: BIM modelers collaborate closely with contractors to ensure that the BIM model aligns with construction requirements and sequences. They work with contractors to develop construction schedules, identify potential constructability issues, and optimize construction workflows. BIM modelers provide support to contractors by reviewing shop drawings, coordinating with subcontractors, and assisting in clash detection and resolution on the construction site. Collaboration with contractors helps ensure that the BIM model reflects the reality of the construction process and supports efficient construction operations.
Owners and Facility Managers: Collaboration with owners and facility managers is crucial for the long-term success and maintenance of the building. BIM modelers provide owners and facility managers with accurate as-built BIM models, capturing all modifications made during construction. They collaborate on data management, ensuring that the BIM model contains useful information for facility management, maintenance planning, and future renovations. BIM modelers work closely with owners and facility managers to understand their specific needs and incorporate customized elements into the BIM model.
Other Professionals: BIM modelers collaborate with a wide range of other professionals, including consultants, subcontractors, and suppliers. They coordinate with consultants to integrate specialized elements or systems into the BIM model, such as fire protection or acoustics. They collaborate with subcontractors, such as HVAC or plumbing contractors, to ensure accurate representation of their systems within the BIM model. BIM modelers may also liaise with suppliers to incorporate accurate product information into the model. Effective collaboration with these professionals ensures that the BIM model reflects the expertise and requirements of all stakeholders involved in the project.
Overall, collaboration with other professionals is essential for the success of a BIM modeling project. BIM modelers act as a central point of coordination, facilitating effective communication and collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and other stakeholders. Through collaboration, BIM modelers ensure that the BIM model accurately represents the building’s design, optimizes construction processes, and aligns with the goals and requirements of the entire project team.
Benefits of Hiring a BIM Modeler
Hiring a BIM modeler provides numerous benefits to a construction project, from improved collaboration and communication to enhanced efficiency and accuracy. Here are some key benefits of hiring a BIM modeler:
Streamlined Design and Construction Process: BIM modelers play a crucial role in streamlining the design and construction process. By creating and managing accurate 3D BIM models, BIM modelers facilitate effective collaboration and coordination among stakeholders, helping to identify and resolve clashes or conflicts early on. This reduces the likelihood of errors, rework, and delays, ultimately saving time and costs.
Enhanced Visualization and Communication: BIM models provide a visual representation of the building, allowing stakeholders to better understand the design intent and construction requirements. With their expertise in creating detailed 3D models, BIM modelers enable improved visualization and communication among architects, engineers, contractors, and owners. This leads to a better understanding of the project scope, reduced miscommunication, and increased efficiency in decision-making processes.
Improved Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution: Clash detection is a crucial aspect of BIM modeling, and BIM modelers excel at identifying clashes or interferences among various building elements or systems. By utilizing clash detection software and their knowledge of construction processes, BIM modelers can identify potential conflicts early on, helping to mitigate costly rework and delays. They work collaboratively with the project team to resolve clashes and optimize the design, ensuring a smoother construction process.
Accurate Quantity Takeoffs and Cost Estimation: BIM models contain a wealth of information that can be leveraged for accurate quantity takeoffs and cost estimation. BIM modelers can extract data from the model to generate detailed quantities and reports, enabling more precise cost estimations for materials, labor, and other construction-related expenses. This not only aids in budgeting and cost control but also enhances the overall project planning and procurement processes.
Improved Project Coordination and Management: BIM modelers play a pivotal role in project coordination and management. They collaborate closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to ensure that the project’s digital representation aligns with the intended design and construction plans. BIM models serve as a central source of information, allowing for better coordination of design changes, construction sequencing, and clash resolution. This leads to improved project organization, fewer conflicts, and enhanced overall project management.
Facilitated Facility Management and Maintenance: BIM models are not only valuable during the design and construction phases but also throughout the building’s lifecycle. BIM modelers create accurate as-built models that contain essential information for facility management and maintenance planning. From operating manuals to maintenance schedules and equipment information, BIM models provide facility managers with a comprehensive digital repository of data, enabling more efficient building operations and easier maintenance tasks.
By harnessing the expertise of a BIM modeler, construction projects can benefit from improved collaboration, accurate modeling, efficient clash detection, precise cost estimation, and effective project management. Hiring a BIM modeler helps ensure that projects are delivered on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of all stakeholders involved.
Challenges Faced by BIM Modelers
While working on BIM modeling projects, BIM modelers encounter several challenges that can impact the successful implementation and execution of their tasks. Here are some common challenges faced by BIM modelers:
Software and Technology: BIM modelers need to keep up with the rapid advancements in BIM software and technology. Learning and mastering new software tools or versions, understanding interoperability challenges between different software platforms, and staying updated with the latest industry trends can be demanding and time-consuming.
Coordination and Collaboration: Collaboration is a fundamental aspect of BIM modeling, but it can present challenges. BIM modelers need to coordinate effectively with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders to ensure accurate representation of the building. Communication difficulties, conflicting design visions or priorities, and managing different perspectives and expectations can make collaboration complex and challenging.
Design Changes and Iterations: Construction projects often undergo design changes and iterations, some of which can significantly impact the BIM model. BIM modelers must be adaptable and agile in incorporating these modifications into the model, maintaining accuracy, and ensuring that all stakeholders are updated with the latest revisions. Managing frequent design changes can be time-consuming and may require additional coordination efforts with the project team.
Data Management and Model Updates: Keeping the BIM model up to date with accurate information and as-built data can be demanding. BIM modelers need to manage various data sources, such as architectural drawings, engineering specifications, and construction documentation, to ensure the model reflects the current state of the project. Gathering accurate updates and properly integrating them into the model requires careful attention to detail and effective information management.
Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution: Clash detection is a crucial aspect of BIM modeling, but it can be challenging to identify and resolve clashes among various building elements and systems. BIM modelers need to rely on advanced clash detection software and possess a deep understanding of construction processes to effectively detect conflicts and work with the project team to address them. Resolving clashes may involve compromise, coordination efforts, and design modifications that require careful management and stakeholder communication.
Training and Skill Development: BIM modeling requires a diverse skill set, and continuous training and skill development are essential. BIM modelers need to stay updated with the latest industry standards, software capabilities, and best practices. Investing time and resources in acquiring new skills, pursuing certifications, and attending training programs can be a challenge, especially in fast-paced project environments.
Adoption and Resistance: The adoption of BIM technology and processes can face resistance within the construction industry. Some professionals may be hesitant to shift from traditional 2D workflows to the collaborative nature of BIM modeling. BIM modelers may face challenges in promoting the benefits of BIM, educating stakeholders, and overcoming resistance to change.
Despite these challenges, skilled and experienced BIM modelers can overcome obstacles and deliver successful projects. Their ability to adapt to changing requirements, effectively communicate and collaborate, manage data and models, and keep up with industry advancements is key to mitigating challenges and ensuring the effective implementation of BIM modeling.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the construction industry, revolutionizing the way projects are planned, designed, and constructed. Within the world of BIM, the role of a BIM modeler is pivotal, as they are responsible for creating, managing, and updating the digital models that drive the BIM process. Through their expertise and collaboration with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders, BIM modelers play a critical role in streamlining the design and construction process.
Throughout this article, we have explored the intricacies of BIM modeling, including the definition and benefits of BIM, the responsibilities and required skills of a BIM modeler, the tools and software they must be proficient in, their typical workflow, and the challenges they face in their day-to-day work.
From creating accurate 3D models to facilitating effective coordination and clash detection, BIM modelers bring immense value to construction projects. Their ability to navigate complex software, collaborate with diverse professionals, and manage and update BIM models ensures that projects are completed with accuracy, efficiency, and reduced risk. They not only enhance visualization and communication but also assist in accurate cost estimation, quantity takeoffs, and project coordination.
However, it’s important to recognize that BIM modeling does come with its share of challenges. BIM modelers need to stay updated with evolving technology, effectively manage data and revisions, navigate collaboration hurdles, and address clash detection and conflict resolution. These challenges require adaptability, continual learning, and strong communication and problem-solving skills.
In conclusion, the role of the BIM modeler is indispensable in the modern construction industry. Their expertise in creating, managing, and updating BIM models, along with their ability to collaborate effectively with other professionals, ensures that projects are delivered with improved accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration. By harnessing BIM technology and the skills of a skilled BIM modeler, construction projects can experience enhanced project outcomes, reduced costs, and improved overall project success.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does A BIM Modeler Do?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.







0 thoughts on “What Does A BIM Modeler Do?”