Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To An Existing Network


Smart Home Devices
How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To An Existing Network
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how to seamlessly connect a Wi-Fi router to your existing network for improved connectivity and smart home device integration. Explore step-by-step instructions and tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Read more: How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To A Modem
Understanding the Importance of Wi-Fi Routers
In today's interconnected world, Wi-Fi routers play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless connectivity within homes and workplaces. These devices serve as the gateway to the digital realm, enabling us to access the internet, connect smart home devices, and communicate with others. Understanding the functionality and configuration of a Wi-Fi router is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring a reliable internet connection.
Wi-Fi routers are the cornerstone of modern networking, providing a wireless interface for devices to connect to the internet and communicate with each other. They act as the central hub that distributes internet signals, allowing multiple devices to access the network simultaneously. From smartphones and laptops to smart TVs and IoT devices, Wi-Fi routers facilitate the seamless integration of various technologies into our daily lives.
The significance of Wi-Fi routers becomes even more pronounced in the context of smart homes, where an array of interconnected devices rely on a stable and robust network infrastructure. Whether it's controlling smart lighting, monitoring home security systems, or streaming media content, the reliability and performance of a Wi-Fi router directly impact the user experience and functionality of smart home devices.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity has surged. This has propelled Wi-Fi routers to the forefront of the digital landscape, prompting manufacturers to develop advanced features such as mesh networking, beamforming, and enhanced security protocols. Understanding the intricacies of these features empowers users to harness the full potential of their Wi-Fi routers and create a connected environment that caters to their specific needs.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Wi-Fi routers, exploring the process of connecting a new Wi-Fi router to an existing network and configuring its settings to ensure optimal performance. By gaining a deeper understanding of these fundamental concepts, readers can enhance their networking capabilities and elevate their digital experiences within the smart home ecosystem. Let's embark on this journey to unlock the potential of Wi-Fi routers and transform the way we interact with the digital world.
Key Takeaways:
- Wi-Fi routers are essential for seamless connectivity in smart homes and workplaces, enabling wireless communication, internet access, and integration of smart devices. Understanding their functions and configuration is crucial for optimizing network performance.
- Connecting and configuring a new Wi-Fi router involves physical connection, basic setup, and advanced settings customization. Thorough testing ensures reliable integration into the existing network, validating performance, security, and device interoperability.
Understanding Wi-Fi Routers
Before delving into the process of connecting a Wi-Fi router to an existing network, it is essential to grasp the fundamental principles that underpin the functionality of these ubiquitous devices. A Wi-Fi router serves as a central networking device that enables wireless communication between various devices and the internet. It acts as a bridge, facilitating the transmission of data packets between the local network and the wider internet infrastructure.
At its core, a Wi-Fi router performs several key functions that are integral to the seamless operation of a modern network. These functions include:
-
Wireless Access Point: The router creates a wireless access point, allowing devices equipped with Wi-Fi capabilities to connect to the network without the need for physical cables. This wireless connectivity empowers users to roam freely within the coverage area while staying connected to the internet.
-
Network Switching: In addition to providing wireless connectivity, the router incorporates network switching capabilities, enabling wired devices to communicate with each other and access the internet. This versatility allows for a diverse range of devices to seamlessly integrate into the network.
-
Internet Gateway: As the gateway to the internet, the router manages the exchange of data between the local network and the internet service provider (ISP). It serves as the conduit through which data packets are transmitted and received, facilitating two-way communication between the local network and external servers.
-
Security and Firewall: Wi-Fi routers include built-in security features such as firewalls, encryption protocols, and access control mechanisms to safeguard the network from unauthorized access and malicious activities. These security measures are crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of the network.
Furthermore, modern Wi-Fi routers often incorporate advanced technologies and features designed to optimize network performance and enhance user experience. These may include dual-band or tri-band operation, beamforming for targeted signal transmission, Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, and support for the latest Wi-Fi standards such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax).
By comprehending the multifaceted role of Wi-Fi routers and the diverse array of functions they fulfill, users can gain a deeper appreciation for the pivotal role that these devices play in shaping the modern digital landscape. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can proceed to connect a new Wi-Fi router to an existing network with confidence, knowing that they are embarking on a journey to elevate their network infrastructure and embrace the possibilities of seamless connectivity.
Connecting a Wi-Fi Router to an Existing Network
When integrating a new Wi-Fi router into an existing network, it is crucial to follow a systematic approach to ensure a seamless transition and optimal performance. Whether you are upgrading to a more advanced router or expanding the coverage of your network, the process of connecting a Wi-Fi router to an existing network involves several key steps.
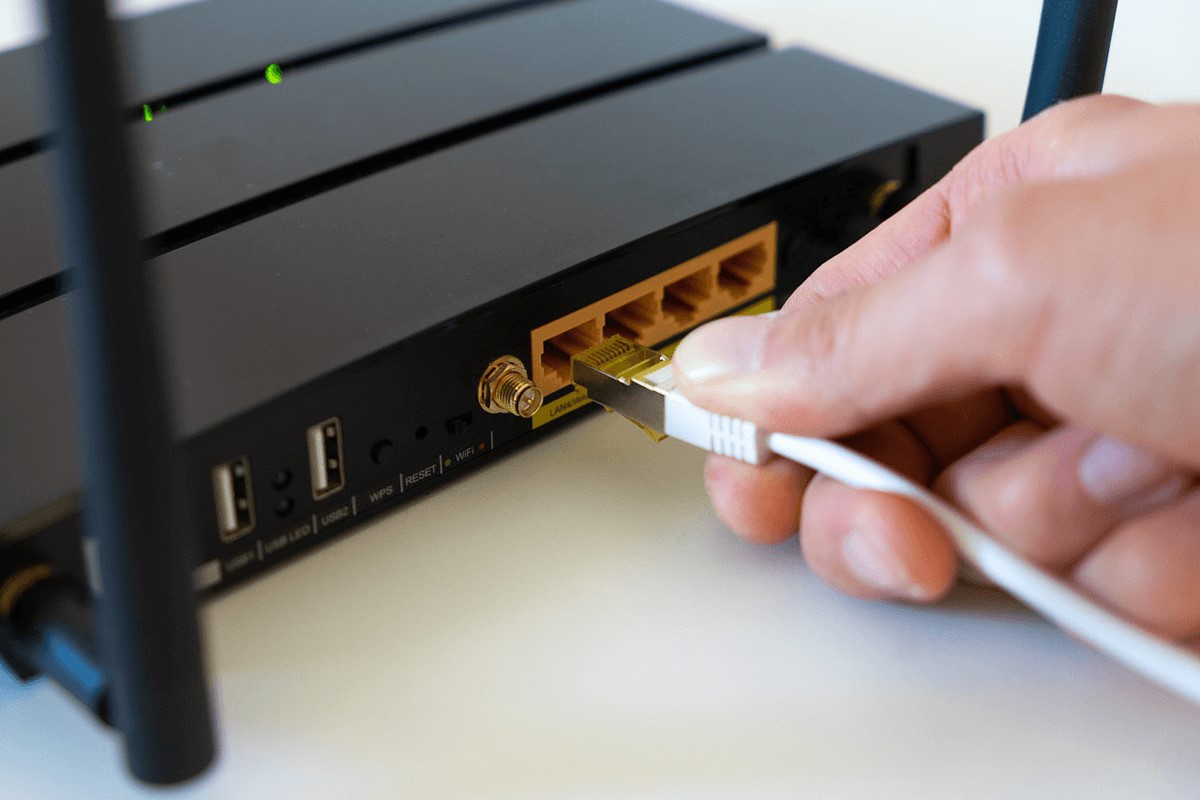
1. Physical Connection: Begin by physically connecting the new Wi-Fi router to a power source and, if applicable, to a modem or the existing router using Ethernet cables. This establishes the initial link between the new router and the network infrastructure, laying the groundwork for the subsequent configuration steps.
2. Accessing the Router Interface: Once the physical connections are in place, access the router’s configuration interface using a web browser on a connected device. This typically involves entering the router’s IP address into the browser’s address bar, which allows you to access the router’s settings and management interface.
3. Configuring Basic Settings: Upon accessing the router’s interface, configure basic settings such as the network name (SSID) and password for the wireless network. This ensures that the new router is identifiable and secure, allowing devices to connect to it without complications.
4. Bridge or Access Point Mode: Depending on the specific requirements of the network, configure the new router to operate in bridge mode or access point mode. Bridge mode allows the new router to function as an extension of the existing network, while access point mode enables it to create a new wireless access point within the network.
5. Network Addressing: Ensure that the new router’s IP address and subnet mask are compatible with the existing network’s addressing scheme. This prevents conflicts and ensures seamless communication between devices connected to the new router and those within the existing network.
6. Testing Connectivity: After completing the configuration steps, test the connectivity by connecting devices to the new router and verifying internet access and network communication. This validation process ensures that the new router is effectively integrated into the existing network and is functioning as intended.
By methodically following these steps, users can successfully connect a new Wi-Fi router to an existing network, expanding the network’s coverage and enhancing its capabilities. This process sets the stage for the subsequent configuration of the router’s settings, enabling users to tailor the network to their specific requirements and create a robust and versatile networking environment.
Configuring the Wi-Fi Router Settings
Once the new Wi-Fi router is physically connected to the existing network and the basic setup is complete, the next crucial step involves configuring the router’s settings to optimize its performance and tailor it to the specific requirements of the network and its users. This process encompasses a range of settings and parameters that influence the functionality and behavior of the router, ultimately shaping the user experience and network performance.
1. Wireless Network Configuration: Access the router’s interface to fine-tune the wireless network settings, including the Wi-Fi channel selection, transmission power, and wireless security protocols. By optimizing these parameters, users can mitigate interference, enhance coverage, and bolster the security of the wireless network.
2. Quality of Service (QoS) Prioritization: Configure QoS settings to prioritize specific types of network traffic, such as video streaming, online gaming, or VoIP calls. This ensures that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth and network resources, resulting in a more consistent and reliable user experience.
3. Guest Network Setup: Many modern routers offer the option to create a separate guest network, allowing visitors to access the internet without compromising the security of the primary network. Configuring the guest network settings, including access restrictions and bandwidth limitations, enhances network security and guest management.
4. Parental Controls and Content Filtering: Utilize the router’s parental control features to manage and restrict the online activities of specific devices or users. This includes setting up content filters, time-based access controls, and website blocking to create a safer and more controlled internet environment for children and other users.
5. Firmware Updates and Security Enhancements: Regularly check for firmware updates for the router and install them to ensure that the device benefits from the latest security patches, performance improvements, and feature enhancements. Additionally, review and configure security settings such as firewall rules, intrusion detection, and device access controls to fortify the network against potential threats.
6. Remote Management and Monitoring: Explore the router’s remote management capabilities, which allow users to monitor and manage the router’s settings and performance from a remote location. Enabling secure remote access provides greater flexibility and control over the network, especially when troubleshooting or making configuration adjustments from afar.
By meticulously configuring these settings and customizing the router’s parameters to align with the specific needs and usage patterns of the network, users can optimize the performance, security, and functionality of their Wi-Fi router. This proactive approach empowers individuals to harness the full potential of their network infrastructure and create a tailored networking environment that caters to their diverse connectivity requirements.
When connecting a Wi-Fi router to an existing network, make sure to disable the DHCP server on the new router to avoid conflicts with the existing network. This will ensure a smooth and seamless connection.
Read more: How To Connect My Wi-Fi Router
Testing the Connection
After connecting and configuring the new Wi-Fi router, it is imperative to conduct comprehensive testing to validate the integrity of the network, assess its performance, and ensure that all connected devices can seamlessly access the internet and communicate with each other. Testing the connection involves a series of checks and evaluations aimed at confirming the successful integration of the new router into the existing network and verifying its adherence to the desired performance benchmarks.
1. Connectivity Verification: Begin by verifying the connectivity of devices connected to the new router. This includes testing the wireless and wired connections to ensure that devices can successfully establish a link with the router and access the network resources, such as shared files and printers.
2. Internet Access: Confirm that the new router is effectively bridging the local network with the internet by testing the internet access from devices connected to the new router. This includes conducting speed tests, accessing websites, and evaluating the responsiveness of online applications to ascertain the quality of the internet connection.
3. Seamless Roaming: If the new router is part of a mesh network or is intended to extend the coverage of an existing wireless network, test the seamless roaming capabilities by moving between different areas of coverage and ensuring that devices maintain a consistent connection without experiencing disruptions or signal degradation.
4. Performance Benchmarks: Evaluate the performance of the network by measuring key metrics such as latency, throughput, and signal strength. This assessment provides insights into the overall quality of the network and helps identify potential areas for optimization or improvement.
5. Device Interoperability: Test the interoperability of various devices within the network, including smart home devices, streaming media players, and IoT gadgets. Verify that these devices can seamlessly communicate with each other and access the network resources without encountering compatibility issues.
6. Security Assessment: Conduct a security assessment to ensure that the new router’s security features are effectively safeguarding the network from unauthorized access and potential threats. This includes verifying the functionality of encryption protocols, access controls, and intrusion detection mechanisms.
By meticulously conducting these tests and evaluations, users can gain confidence in the successful integration of the new Wi-Fi router into the existing network and ascertain its ability to deliver reliable connectivity, robust performance, and enhanced security. This rigorous validation process sets the stage for a seamless and optimized networking experience, empowering users to leverage the full potential of their network infrastructure and smart home ecosystem.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of connecting a Wi-Fi router to an existing network and configuring its settings, it becomes evident that the seamless integration of a new router is a pivotal step in enhancing network performance, expanding coverage, and accommodating the diverse connectivity needs of modern smart homes and workplaces.
Wi-Fi routers, with their multifaceted functionality and advanced features, serve as the linchpin of interconnected environments, facilitating wireless communication, internet access, and the seamless integration of smart home devices. By understanding the intricacies of Wi-Fi routers and following a systematic approach to connecting and configuring them, users can unlock the full potential of their network infrastructure and elevate their digital experiences.
From the initial physical connection and access to the router’s interface to the meticulous configuration of wireless settings, QoS prioritization, and security enhancements, the process of connecting and configuring a Wi-Fi router demands attention to detail and an understanding of networking principles. This proactive approach empowers users to tailor their network to their specific requirements, optimize performance, and create a secure and versatile networking environment that caters to their diverse connectivity needs.
Furthermore, the comprehensive testing of the connection ensures the successful integration of the new router into the existing network, validating its performance, security, and interoperability with a diverse range of devices. This validation process lays the foundation for a reliable and robust network infrastructure that seamlessly supports the demands of modern digital lifestyles and smart home ecosystems.
As technology continues to evolve and the reliance on interconnected devices grows, the role of Wi-Fi routers in shaping the digital landscape becomes increasingly pronounced. By embracing the principles and best practices outlined in this article, users can embark on a journey to harness the full potential of their Wi-Fi routers, creating a connected environment that fosters productivity, entertainment, and innovation.
Ultimately, the process of connecting a Wi-Fi router to an existing network and configuring its settings transcends the realm of networking; it embodies the convergence of technology and lifestyle, empowering individuals to forge seamless connections, unlock new possibilities, and embark on a transformative journey within the digital realm.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To An Existing Network
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To An Existing Network”