Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How To Connect Antenna To Wi-Fi Router


Smart Home Devices
How To Connect Antenna To Wi-Fi Router
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn how to easily connect your antenna to your Wi-Fi router for seamless integration with your smart home devices. Enhance your home network setup today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of smart home devices, the seamless integration of various technologies is pivotal to ensure optimal performance. When it comes to enhancing the wireless connectivity of a Wi-Fi router, the strategic use of antennas can play a crucial role. Understanding how to connect an antenna to a Wi-Fi router not only empowers users to expand the range and stability of their wireless network but also provides insights into the intricate workings of these essential devices.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process of connecting an antenna to a Wi-Fi router, catering to both novices seeking fundamental knowledge and tech enthusiasts looking to optimize their home network. By exploring the types of antennas and Wi-Fi routers, elucidating the connection process, and offering insights into positioning, adjusting, and troubleshooting, this article aims to equip readers with the expertise to harness the full potential of their wireless connectivity.
With the proliferation of smart home devices and the increasing demand for seamless connectivity, the significance of maximizing the performance of Wi-Fi routers cannot be overstated. By delving into the realm of antennas and their integration with Wi-Fi routers, users can unlock a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that underpin their home network's efficiency. Whether it's eliminating dead zones, bolstering signal strength, or simply fine-tuning the wireless setup, the amalgamation of antennas and Wi-Fi routers holds the key to a robust and reliable wireless network.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we delve into the intricacies of connecting antennas to Wi-Fi routers, unraveling the nuances of wireless connectivity and empowering individuals to harness the full potential of their home networks. Let's embark on this illuminating exploration, where the fusion of technology and practical insights paves the way for an enriched wireless experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Connecting antennas to Wi-Fi routers enhances wireless coverage and performance. Understanding antenna types, positioning, and troubleshooting empowers users to optimize their home network for a seamless wireless experience.
- Different types of antennas and Wi-Fi routers cater to specific networking needs. Integrating antennas strategically and testing the connection ensures reliable and consistent wireless connectivity.
Read more: How To Connect Verizon Wi-Fi Router
Understanding Antennas and Wi-Fi Routers
Before delving into the process of connecting an antenna to a Wi-Fi router, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental roles of antennas and Wi-Fi routers in establishing and maintaining wireless connectivity. Antennas, in the context of wireless communication, serve as conduits for transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals. They play a pivotal role in propagating electromagnetic waves, thereby facilitating the wireless exchange of data between devices and the Wi-Fi router.
Wi-Fi routers, on the other hand, are the central hubs that orchestrate the distribution of wireless signals within a network. These devices receive data from the internet via a wired connection and transmit it wirelessly to connected devices through the utilization of antennas. Wi-Fi routers are equipped with one or more antennas, each contributing to the propagation and reception of wireless signals across varying distances.
When it comes to antennas, it’s crucial to understand that their design and configuration significantly influence the range, coverage, and signal strength of a Wi-Fi network. Different types of antennas, such as omnidirectional and directional antennas, cater to distinct networking requirements. Omnidirectional antennas emit signals in all directions, making them suitable for providing 360-degree coverage in homes or small offices. On the other hand, directional antennas focus their signal in a specific direction, ideal for targeting distant devices or extending coverage to specific areas.
Wi-Fi routers also come in diverse configurations, offering varying speeds, frequency bands, and signal propagation capabilities. Understanding the specifications and capabilities of a Wi-Fi router is essential for optimizing its performance through the strategic integration of antennas. Whether it’s a standard router for home use or a high-performance router for demanding applications, the synergy between antennas and Wi-Fi routers is instrumental in achieving a reliable and efficient wireless network.
By comprehending the symbiotic relationship between antennas and Wi-Fi routers, users can gain insights into the nuanced interplay of these components in establishing robust wireless connectivity. The next sections will delve into the types of antennas and Wi-Fi routers, providing a deeper understanding of their functionalities and applications in diverse networking scenarios.
Types of Antennas
Antennas are integral components of wireless communication systems, and their diverse designs cater to specific networking requirements, offering versatility in coverage, range, and signal propagation. Understanding the types of antennas available for Wi-Fi routers is essential for optimizing wireless connectivity based on the unique demands of different environments.
1. Omnidirectional Antennas:
Omnidirectional antennas emit signals in all directions, providing 360-degree coverage. This design is ideal for establishing a pervasive wireless network within homes, small offices, or public spaces where uniform signal distribution is paramount. Omnidirectional antennas are commonly used in standard Wi-Fi routers to ensure seamless connectivity across varying distances and orientations.
2. Directional Antennas:
Unlike omnidirectional antennas, directional antennas concentrate their signal in a specific direction, offering extended reach and focused coverage. These antennas are beneficial for targeting distant devices or extending wireless connectivity to specific areas, making them suitable for point-to-point communication or scenarios where signal precision is crucial.
3. Yagi Antennas:
Yagi antennas, a type of directional antenna, feature a highly directional beam and are characterized by their gain and narrow radiation pattern. These antennas are adept at providing long-range connectivity and are often utilized in outdoor settings to establish robust wireless links over extended distances, making them suitable for bridging networks between buildings or connecting remote locations.
4. Panel Antennas:
Panel antennas, also known as flat panel antennas, offer a compact and unobtrusive design while providing directional signal propagation. Their streamlined form factor and focused beamwidth make them suitable for indoor and outdoor applications where targeted coverage and aesthetic considerations are paramount. Panel antennas are commonly deployed in environments requiring precise coverage, such as warehouses, campuses, and outdoor venues.
5. Parabolic Grid Antennas:
Parabolic grid antennas feature a grid reflector and a parabolic dish, offering high gain and narrow beamwidth for long-range connectivity. These antennas excel in point-to-point communication, serving as reliable solutions for establishing wireless links between distant locations or connecting network segments across expansive areas.
Understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of these antennas empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting and integrating antennas with Wi-Fi routers. Whether it’s optimizing coverage within a residence, extending connectivity to outdoor spaces, or establishing long-range wireless links, the diverse array of antennas caters to a myriad of networking requirements, ensuring a tailored approach to wireless connectivity.
Types of Wi-Fi Routers
Wi-Fi routers are available in various configurations, each catering to specific networking demands based on factors such as coverage area, data transfer speeds, and the number of connected devices. Understanding the diverse types of Wi-Fi routers empowers users to make informed choices when selecting a router that aligns with their unique requirements, ensuring optimal wireless connectivity within their environment.
1. Single-Band Routers:
Single-band routers operate on the 2.4GHz frequency band and are suitable for basic wireless connectivity in small residences or environments with minimal interference. While these routers offer standard Wi-Fi capabilities, they may be susceptible to congestion in densely populated areas where multiple devices operate on the 2.4GHz band, potentially leading to reduced network performance.
2. Dual-Band Routers:
Dual-band routers operate on both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, offering increased flexibility and reduced interference compared to single-band routers. The 5GHz band provides faster data transfer speeds and is less prone to congestion, making dual-band routers ideal for supporting a larger number of devices and delivering enhanced performance in environments with high wireless activity.
3. Tri-Band Routers:
Tri-band routers feature an additional 5GHz band, effectively tripling the available wireless spectrum compared to dual-band routers. This configuration is advantageous for environments with a multitude of connected devices and high-bandwidth activities such as 4K streaming, online gaming, and simultaneous data transfers. Tri-band routers excel in managing network congestion and optimizing performance across a diverse range of wireless applications.
4. Mesh Routers:
Mesh routers comprise a system of interconnected nodes that work in unison to create a seamless and expansive wireless network. This distributed architecture eliminates dead zones and ensures consistent connectivity throughout a residence or commercial space. Mesh routers are designed to deliver robust coverage, adapt to changing network demands, and provide hassle-free roaming for connected devices, making them an ideal solution for large homes, multi-story buildings, and complex networking environments.
5. Gaming Routers:
Gaming routers are engineered to prioritize low latency, high-speed data transfer, and optimized connectivity for online gaming and streaming. These routers often feature advanced Quality of Service (QoS) capabilities, traffic prioritization, and customizable settings to enhance the gaming experience and minimize network lag. Gaming routers are tailored to meet the stringent demands of gaming enthusiasts and ensure a responsive and stable network for competitive online gaming.
By acquainting themselves with the diverse categories of Wi-Fi routers, users can discern the distinctive features and performance attributes that define each type. Whether it’s catering to the wireless needs of a small household, supporting a multitude of connected devices, or optimizing network performance for specific applications, the range of Wi-Fi routers offers tailored solutions to accommodate a spectrum of networking requirements.
Connecting Antenna to Wi-Fi Router
Connecting an antenna to a Wi-Fi router is a straightforward process that involves identifying the antenna ports on the router and securely attaching the antenna to optimize wireless signal propagation. Before commencing the connection, it’s essential to ensure that the Wi-Fi router is powered off to prevent any potential electrical hazards during the installation process.
1. Identify Antenna Ports:
Wi-Fi routers are equipped with antenna ports, typically located at the rear or sides of the device. These ports are labeled to indicate the number of antennas the router supports, such as “Antenna 1” and “Antenna 2” for dual-antenna routers. Identifying the specific ports designated for antenna connection is the initial step in preparing the router for antenna integration.
2. Select Compatible Antennas:
When selecting antennas for integration with a Wi-Fi router, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with the router’s specifications. Antennas come with varying connector types, such as RP-SMA or N-type connectors, and selecting antennas that align with the router’s connector interface is imperative to facilitate a seamless and secure connection.
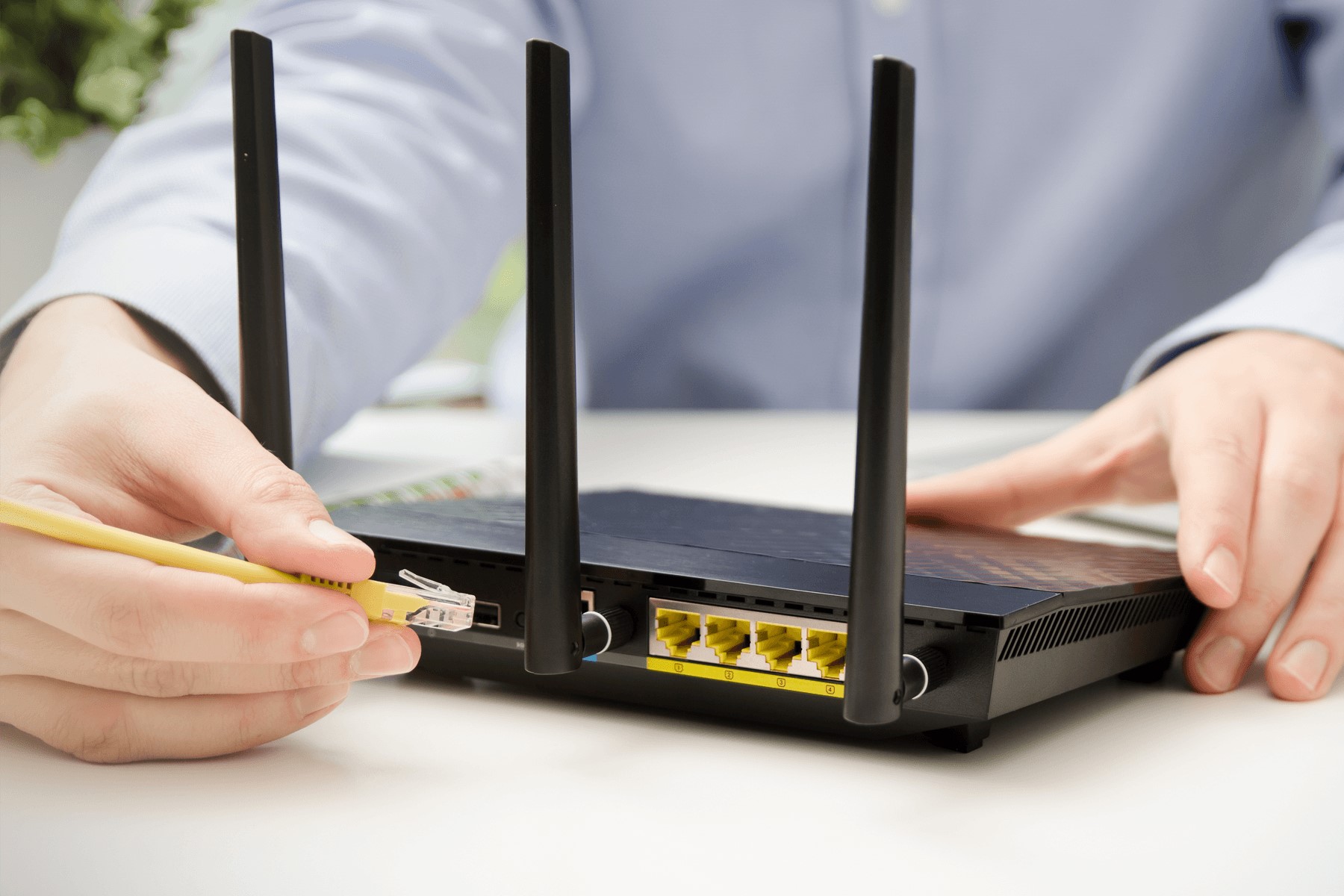
3. Attach the Antennas:
Once the antenna ports are identified and compatible antennas are selected, the next step involves attaching the antennas to the designated ports on the Wi-Fi router. Carefully align the connectors of the antennas with the corresponding ports on the router, ensuring a snug and secure fit to optimize signal transmission and reception.
4. Secure the Antennas:
After attaching the antennas to the router, it’s essential to secure them in place to prevent accidental disconnection or misalignment. Gently tighten the antennas to the router’s ports, taking care not to exert excessive force that may damage the connectors or the router itself. The secure attachment of antennas ensures reliable signal propagation and minimizes the risk of signal degradation due to loose connections.
5. Power On the Router:
Once the antennas are securely connected to the Wi-Fi router, power on the router to initiate the integration of the antennas into the wireless network. The router will detect the newly connected antennas and optimize its signal transmission based on the integrated antenna configuration, enhancing the overall wireless coverage and performance.
By following these simple steps, users can seamlessly integrate antennas with their Wi-Fi routers, harnessing the potential of these components to bolster wireless connectivity and optimize the performance of their home network. The strategic integration of antennas with Wi-Fi routers lays the foundation for enhanced signal propagation, expanded coverage, and a more robust wireless experience.
When connecting an antenna to a Wi-Fi router, make sure to screw the antenna onto the designated port on the back of the router. Ensure it is securely attached to improve the router’s signal strength and range.
Read more: How To Connect My Wi-Fi Router
Positioning and Adjusting the Antenna
Once the antennas are connected to the Wi-Fi router, positioning and adjusting the antennas play a pivotal role in optimizing wireless signal coverage and strength. By strategically orienting the antennas and fine-tuning their positions, users can maximize the effectiveness of their wireless network, mitigate signal interference, and ensure consistent connectivity across their environment.
1. Understanding Antenna Orientation:
Depending on the type of antennas integrated with the Wi-Fi router, understanding their optimal orientation is crucial for achieving the desired signal coverage. Omnidirectional antennas emit signals in all directions, making their orientation less critical, while directional antennas, such as Yagi or panel antennas, require precise alignment to target specific areas or distant devices.
2. Minimizing Signal Interference:
Positioning the antennas away from potential sources of signal interference, such as large metal objects, electronic appliances, or physical obstructions, is essential for optimizing wireless signal propagation. By minimizing signal interference, users can enhance the stability and reliability of their wireless network, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation or connectivity issues.
3. Fine-Tuning Antenna Positions:
Experimenting with different antenna positions and orientations can help users identify the optimal configuration that maximizes signal coverage and minimizes dead zones within their environment. Incremental adjustments to the antenna positions, both vertically and horizontally, enable users to gauge the impact on signal strength and coverage, facilitating the fine-tuning of the wireless network.
4. Consider External Factors:
External factors, such as building materials, layout, and the presence of neighboring wireless networks, can influence the effectiveness of antenna positioning. Users should consider these factors when adjusting the antennas to account for the unique characteristics of their environment, ensuring that the wireless network is tailored to address specific challenges and maximize performance.
5. Utilize Signal Strength Indicators:
Many Wi-Fi routers are equipped with signal strength indicators or mobile apps that provide real-time feedback on signal strength and coverage. Leveraging these indicators while adjusting the antenna positions allows users to make informed decisions based on empirical data, enabling precise optimization of the wireless network’s coverage and performance.
By meticulously positioning and adjusting the antennas in accordance with the aforementioned considerations, users can harness the full potential of their Wi-Fi router and antennas, creating a robust and reliable wireless network tailored to their specific environment. The strategic optimization of antenna positions not only enhances signal coverage and strength but also ensures a seamless and consistent wireless experience across diverse networking scenarios.
Testing the Connection
After connecting and adjusting the antennas on the Wi-Fi router, testing the wireless connection is essential to validate the effectiveness of the integrated antennas and ensure optimal signal propagation and coverage. By conducting comprehensive tests, users can identify potential areas for improvement, gauge the impact of antenna integration on wireless performance, and address any connectivity issues that may arise.
1. Signal Strength Assessment:
Utilize a Wi-Fi-enabled device, such as a smartphone, laptop, or tablet, to assess the signal strength and coverage across different areas within the environment. By moving throughout the space and monitoring the signal strength indicator on the device, users can ascertain the extent of wireless coverage and identify potential dead zones or areas with diminished signal strength.
2. Speed and Stability Testing:
Conduct speed and stability tests using online tools or dedicated applications to measure the data transfer speeds and the consistency of the wireless connection. These tests provide insights into the performance of the wireless network, allowing users to evaluate the impact of antenna integration on data transfer rates, latency, and overall network stability.
3. Coverage Validation:
Verify the coverage of the wireless network by ensuring that all intended areas within the environment receive consistent and reliable connectivity. By testing the connection in various rooms, outdoor spaces, or remote areas, users can confirm that the integrated antennas effectively extend the wireless coverage and mitigate potential connectivity issues across the entire environment.
4. Roaming and Handoff Tests:
If utilizing a mesh Wi-Fi system, conduct roaming and handoff tests to assess the seamless transition of connected devices between different access points. Verify that devices maintain uninterrupted connectivity as they move between areas covered by distinct nodes, ensuring a seamless and uninterrupted wireless experience throughout the environment.
5. Interference and Congestion Evaluation:
Assess the impact of potential signal interference and network congestion on the wireless connection by monitoring the performance during peak usage hours or in proximity to electronic devices that may introduce interference. Identifying and addressing potential sources of interference or congestion ensures sustained network performance and stability.
By meticulously testing the wireless connection post-antenna integration, users can gauge the effectiveness of the antennas in optimizing signal strength, coverage, and network performance. The insights gleaned from these tests empower users to fine-tune their wireless network, address any connectivity challenges, and ensure a reliable and seamless wireless experience across their environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While integrating antennas with a Wi-Fi router can significantly enhance wireless connectivity, users may encounter common issues that impact the performance and stability of their network. By familiarizing themselves with potential challenges and employing effective troubleshooting techniques, users can address these issues proactively, ensuring a seamless and reliable wireless experience.
1. Signal Interference:
Issue: Signal interference from electronic devices, neighboring networks, or physical obstructions can degrade wireless performance and coverage.
Troubleshooting: Identify and mitigate sources of signal interference by repositioning the router and antennas, utilizing the 5GHz band to reduce congestion, or employing shielding materials to minimize external interference.
2. Dead Zones:
Issue: Certain areas within the environment exhibit poor or no wireless connectivity, leading to dead zones that impede seamless network access.
Troubleshooting: Adjust the antenna positions and orientations to extend coverage to dead zones, consider the deployment of additional access points or mesh nodes, and evaluate the impact of building materials on signal propagation within the dead zones.
3. Inconsistent Roaming:
Issue: Devices experience connectivity disruptions or delays when transitioning between different access points within a mesh Wi-Fi system.
Troubleshooting: Optimize access point placement, update firmware to leverage seamless roaming protocols, and ensure that devices support the seamless handoff between access points within the mesh network.
4. Performance Degradation:
Issue: The wireless network experiences diminished data transfer speeds, increased latency, or intermittent connectivity despite antenna integration.
Troubleshooting: Evaluate the impact of network congestion, update router firmware to address performance issues, and consider the utilization of Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical network traffic and applications.
5. Compatibility Challenges:
Issue: Antennas may exhibit compatibility issues with the Wi-Fi router, leading to suboptimal performance or connectivity irregularities.
Troubleshooting: Ensure that the antennas are compatible with the router’s specifications, verify the integrity of the antenna connectors, and consider consulting the router’s documentation or support resources for guidance on antenna integration.
6. Firmware and Software Updates:
Issue: Outdated router firmware or device drivers can impact the overall performance and stability of the wireless network post-antenna integration.
Troubleshooting: Regularly update the router’s firmware and device drivers to leverage performance enhancements, bug fixes, and compatibility improvements that address potential issues affecting the wireless network.
By identifying and addressing these common issues through targeted troubleshooting strategies, users can optimize the performance, coverage, and stability of their wireless network following the integration of antennas with their Wi-Fi router. Proactive troubleshooting not only mitigates potential challenges but also ensures a resilient and efficient wireless experience tailored to the unique demands of the user’s environment.
Conclusion
As we conclude this insightful exploration into the integration of antennas with Wi-Fi routers, it becomes evident that the strategic utilization of antennas plays a pivotal role in optimizing wireless connectivity and enhancing the performance of home networks. By comprehending the nuances of antenna types, Wi-Fi router configurations, and the process of connecting, positioning, and troubleshooting antennas, users are empowered to cultivate a robust and reliable wireless experience tailored to their unique environment.
The seamless integration of antennas with a Wi-Fi router transcends the mere augmentation of wireless coverage; it represents a harmonious fusion of technology and practical insights, culminating in an enriched wireless experience that caters to the diverse networking requirements of modern households and businesses. From mitigating dead zones to addressing signal interference and optimizing roaming capabilities, the integration of antennas with Wi-Fi routers serves as a catalyst for elevating the wireless connectivity paradigm.
As smart home devices proliferate and the demand for seamless connectivity intensifies, the significance of understanding and harnessing the potential of antennas within the context of Wi-Fi routers becomes increasingly pronounced. This knowledge equips users with the expertise to navigate the intricacies of wireless networking, fostering an environment where connectivity is not just a utility but a seamless and integral part of daily life.
By embracing the insights and recommendations presented in this comprehensive guide, users can embark on a journey towards a wireless network that transcends conventional boundaries, delivering unparalleled coverage, stability, and performance. The integration of antennas with Wi-Fi routers represents a testament to the transformative power of technology, where the synergy between components and practical wisdom converges to redefine the wireless experience.
As we look towards the future of wireless connectivity, the integration of antennas with Wi-Fi routers stands as a cornerstone of innovation, adaptability, and personalized networking solutions. Through a nuanced understanding of antennas and their integration with Wi-Fi routers, users are poised to embark on a wireless journey that transcends limitations, embraces seamless connectivity, and fosters a digital landscape where the potential of wireless networking knows no bounds.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Connect Antenna To Wi-Fi Router
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Connect Antenna To Wi-Fi Router”