Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How Does CAD Software Work


Architecture & Design
How Does CAD Software Work
Modified: January 9, 2024
Explore how CAD software revolutionizes architecture design with its powerful tools and precise measurements. Enhance your workflow and creativity with this essential technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Design plays a crucial role in shaping our world. From the buildings we inhabit to the products we use, every aspect of our lives is influenced by the creative minds behind their creation. In the digital age, the process of designing has been revolutionized by the advent of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. CAD software has become an indispensable tool for architects, engineers, and designers, allowing them to create accurate and detailed models of their ideas.
CAD software, short for Computer-Aided Design, is a type of computer program that enables users to create, modify, and optimize designs in a digital environment. It utilizes advanced algorithms and powerful computing capabilities to facilitate the creation of complex 2D and 3D models. By replacing manual drafting with digital tools, CAD software has streamlined the design process, significantly enhancing productivity and accuracy.
With the introduction of CAD software, designers can now visualize their concepts in a virtual space before they are brought to life. This technology has not only transformed the way we design but has also opened up new possibilities and expanded the boundaries of creativity.
In this article, we will explore the inner workings of CAD software, uncovering its basic principles, techniques, and applications. We will delve into the different types of CAD software, ranging from 2D CAD to advanced 3D modeling tools. Additionally, we will discuss the benefits and limitations of using CAD software, as well as its role in various industries.
Join us on this journey as we demystify CAD software and discover how it has revolutionized the world of design.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD software revolutionizes design by increasing productivity, enhancing visualization, and enabling better collaboration. It empowers professionals to create accurate, detailed models and iterate designs efficiently, saving time and costs.
- While CAD software offers numerous benefits, it also comes with limitations such as a learning curve, hardware requirements, and design constraints. Understanding these limitations and finding creative solutions is crucial for maximizing the potential of CAD software.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Definition of CAD Software
CAD software, or Computer-Aided Design software, is a computer program that enables designers and engineers to create, modify, and optimize 2D and 3D models of objects, buildings, and systems. It provides a digital representation of the design, allowing users to visualize and analyze their ideas before they are realized in the physical world.
CAD software offers a wide range of tools and features that simplify the design process. It allows users to create geometric shapes, apply materials and textures, define dimensions and constraints, and perform simulations and analyses. Additionally, CAD software typically provides tools for collaboration, documentation, and presentation, making it an essential tool for design professionals across various industries.
One of the defining features of CAD software is its ability to automate repetitive tasks and complex calculations. It eliminates the need for manual drafting, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. By automating these tasks, CAD software improves productivity and accuracy, enabling designers to focus on the creative aspects of their work.
Modern CAD software has evolved to include advanced features such as parametric modeling, which allows users to define relationships between various design elements. This means that when a parameter is changed, all related elements are automatically updated, ensuring design consistency and reducing the need for manual adjustments.
Another important aspect of CAD software is its compatibility with other design tools and systems. CAD software integrates with Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, enabling a seamless transition from design to analysis and production.
Overall, CAD software has revolutionized the design process by providing a powerful and efficient way to create and iterate on designs. It has become an indispensable tool for architects, engineers, product designers, and many other professionals involved in the creation of physical objects and systems.
Benefits of Using CAD Software
CAD software has become an essential tool for design professionals due to the numerous benefits it offers. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using CAD software:
- Increased Productivity: CAD software streamlines the design process, allowing designers to create and modify digital models more quickly and efficiently than traditional manual drafting. It eliminates repetitive tasks, automates calculations, and provides a range of tools and features that enhance productivity.
- Improved Accuracy: CAD software provides precise measurement tools and geometric constraints, ensuring accurate and consistent designs. It eliminates human errors and allows for easy adjustments and modifications, reducing the risk of costly mistakes in the final product.
- Enhanced Visualization: CAD software enables designers to visualize their ideas in a realistic and immersive way. They can create 3D models, apply materials and textures, and even simulate real-world conditions. This helps in better understanding and communicating the design concept to clients, stakeholders, and collaborators.
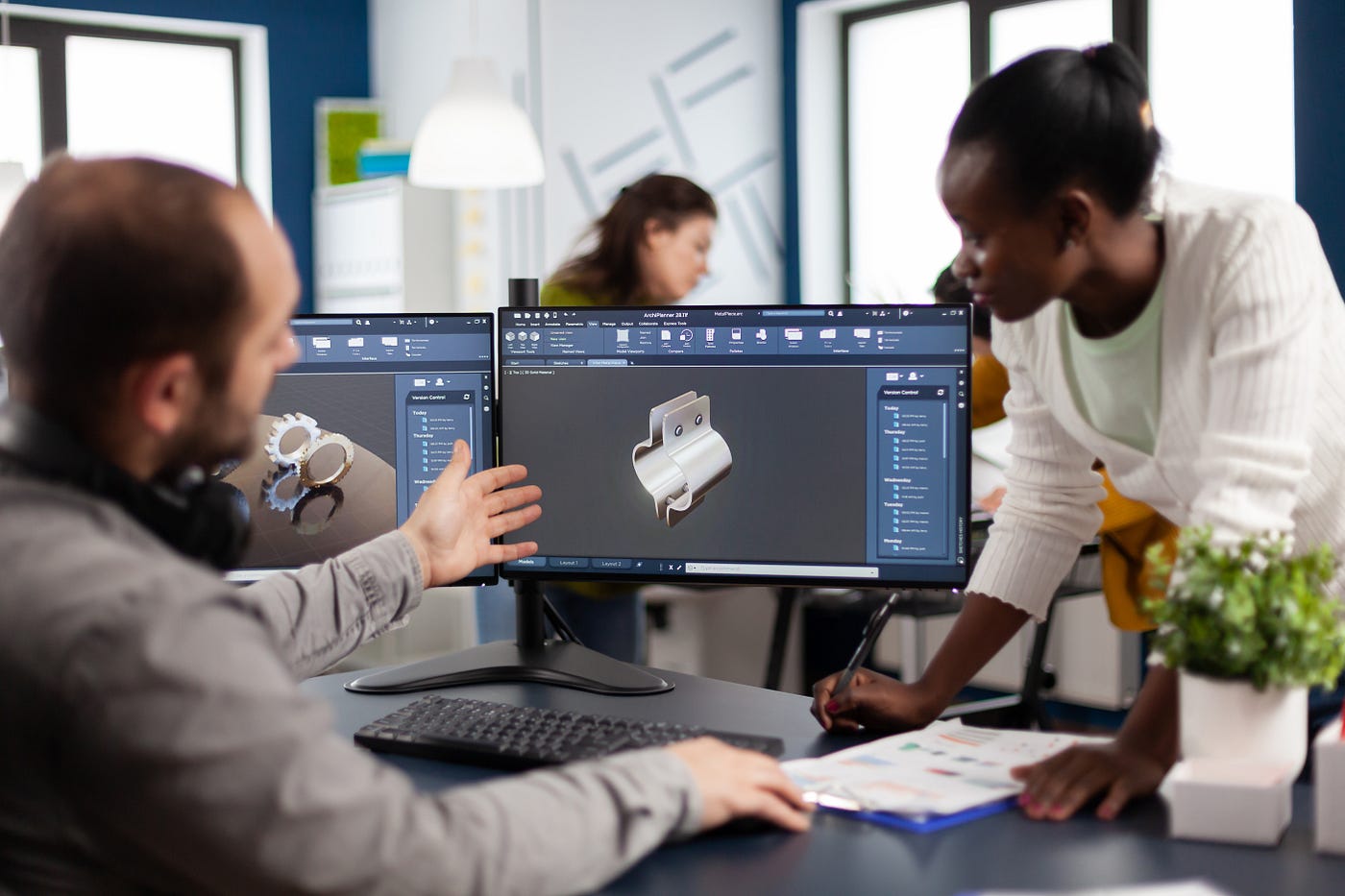
- Better Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. Multiple team members can work on the same project simultaneously, making it easier to share and review design iterations. This leads to better coordination, faster decision-making, and improved teamwork.
- Cost and Time Savings: CAD software reduces the time and cost associated with the design process. It eliminates the need for physical prototypes and allows for virtual simulations and testing, reducing material wastage and expensive reworks. Additionally, CAD models can be easily reused and modified for future projects, further saving time and resources.
- Design Iteration and Optimization: CAD software provides the flexibility to iterate and optimize designs quickly. Designers can experiment with different configurations, materials, and dimensions, and evaluate the impact of changes in real-time. This iterative design approach leads to better results and innovative solutions.
- Easy Documentation: CAD software simplifies the documentation process. It automatically generates accurate drawings, annotations, and bills of materials, reducing the time and effort required for documentation. This ensures that all necessary information is captured and communicated effectively.
Overall, CAD software empowers designers to work more efficiently, deliver higher quality designs, and innovate in their respective fields. It has revolutionized the design process, providing a myriad of benefits for professionals across various industries.
Basic Principles of CAD Software
CAD software operates based on a set of fundamental principles that enable designers to create and manipulate digital models. Understanding these principles is essential for effectively using CAD software. Let’s explore the basic principles of CAD software:
- Geometric Representation: CAD software uses geometric shapes such as points, lines, arcs, curves, and surfaces to represent the objects being designed. These geometric entities are defined by their coordinates, dimensions, and relationships with other elements in the design.
- Parametric Modeling: Parametric modeling is a key principle of CAD software that allows designers to establish relationships between design elements. Parameters, such as dimensions, can be set as variables and linked to other elements. When a parameter is modified, all related elements are automatically updated, ensuring design consistency and reducing manual adjustments.
- Constraints and Dimensions: CAD software provides tools for defining constraints and dimensions. Constraints restrict the movement or behavior of design elements, ensuring they maintain specific relationships. Dimensions define the size and proportions of the objects being designed.
- Layering and Organization: CAD software allows designers to organize their designs using layers. Layers act as virtual sheets of tracing paper, allowing elements to be added or removed independently. This provides greater control over the visibility and organization of design elements.
- Coordinate Systems: CAD software uses coordinate systems to define the position and orientation of design elements. Cartesian coordinate systems, such as X, Y, and Z axes, are commonly used to establish a reference framework for the design.
- Visual Display and Rendering: CAD software provides visual display and rendering capabilities, allowing designers to view and manipulate their designs in 2D or 3D. These tools simulate realistic lighting, shading, and textures, providing a visual representation of the final product.
- Collaboration and File Management: CAD software facilitates collaboration by allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. It provides tools for file management, version control, and sharing, ensuring seamless collaboration and preventing data loss.
- Data Exchange and File Formats: CAD software supports various file formats for importing and exporting design data. Common file formats include DWG, DXF, STL, and IGES. These file formats enable compatibility between different CAD software and other design tools.
By understanding these basic principles, designers can leverage the full capabilities of CAD software and create accurate, efficient, and visually compelling designs. It’s important to familiarize oneself with the specific features and workflows of the chosen CAD software to fully utilize these principles in practice.
2D CAD Software
2D CAD software, as the name suggests, focuses on creating and manipulating two-dimensional designs. It is widely used in various industries, including architecture, engineering, graphic design, and manufacturing. Unlike traditional manual drafting, 2D CAD software offers a range of tools and features that enhance productivity, accuracy, and flexibility in creating technical drawings and plans.
One of the primary advantages of 2D CAD software is its ability to create precise and scalable drawings. Designers can easily define dimensions, angles, and shapes using CAD software, ensuring accuracy and consistency in the design. Additionally, 2D CAD software allows for efficient modification and revision, as changes can be made easily without having to redraw the entire drawing.
2D CAD software provides a wide array of drawing tools and features, such as lines, arcs, circles, polygons, and text, which enable designers to create complex and detailed drawings. These tools often include snap and alignment functionalities, making it easier to create symmetrical and precise drawings. Layers and colors can also be utilized to organize and differentiate different elements within the design.
Another crucial feature of 2D CAD software is the ability to generate accurate and consistent documentation. Designers can automatically generate bills of materials, annotations, dimensions, and other necessary documentation from the 2D CAD model. This ensures that the design information is captured and communicated effectively.
Collaboration is made easier with 2D CAD software, as multiple designers can work on the same project simultaneously. Design files can be easily shared, reviewed, and updated in real-time. This enables better coordination and cooperation among team members, leading to faster and more efficient design processes.
Furthermore, 2D CAD software serves as a foundation for more advanced design processes. It provides a starting point for creating 3D models and performing simulations and analyses. The 2D drawings can be used as blueprints for developing more complex models or as reference material for fabrication and construction.
In summary, 2D CAD software offers a range of tools and features that streamline the creation of accurate and detailed technical drawings. It enhances productivity, accuracy, and collaboration, making it an indispensable tool for designers in various industries.
Read more: How To Use CAD Software
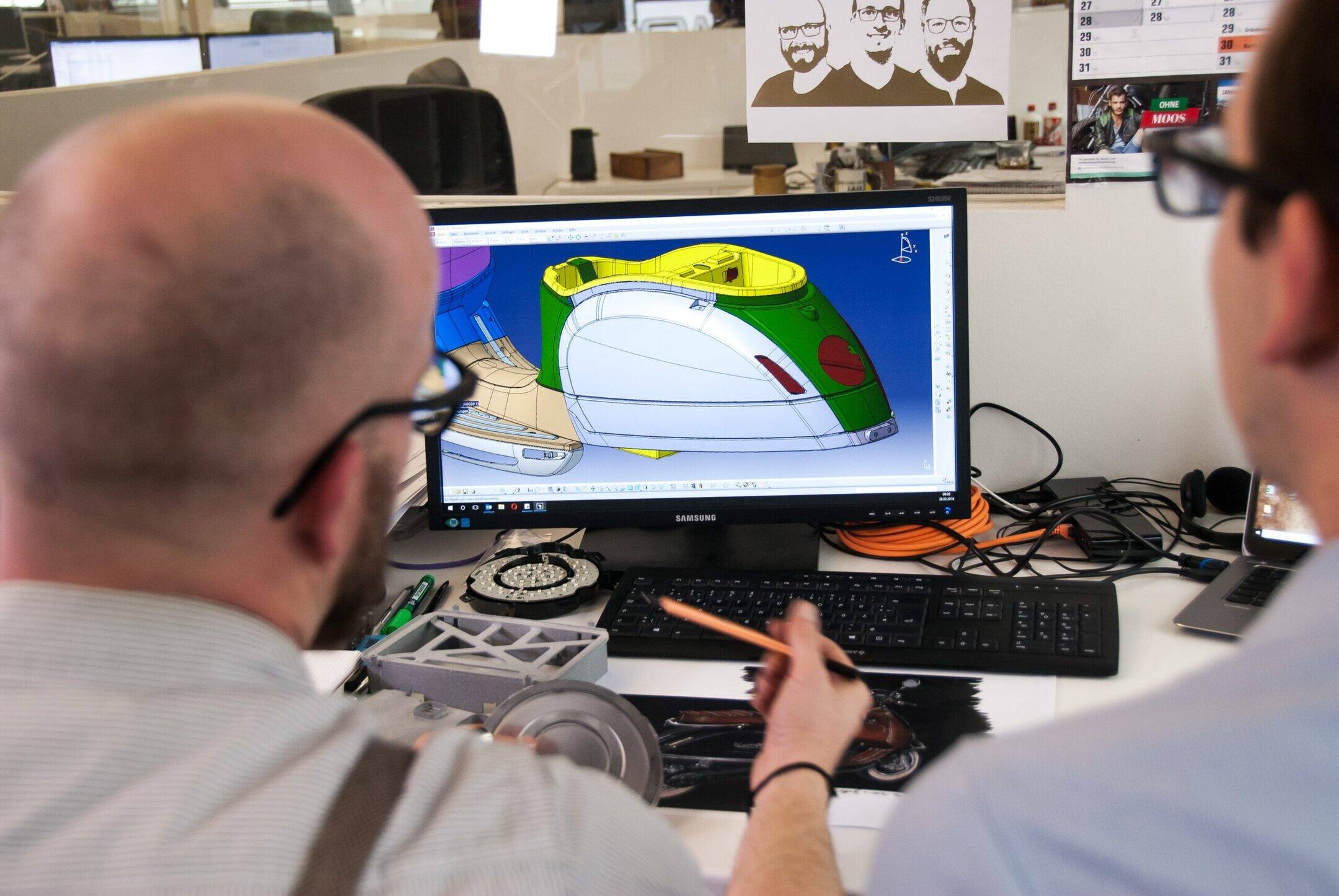
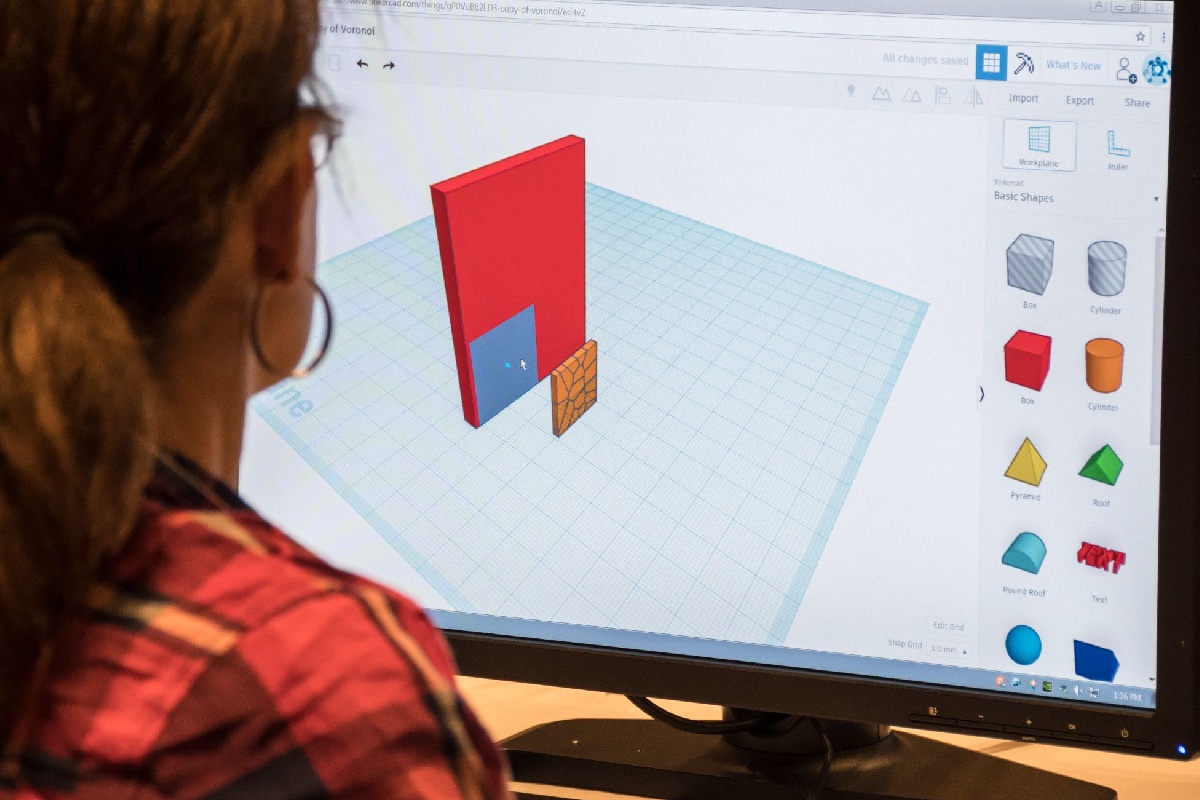
3D CAD Software
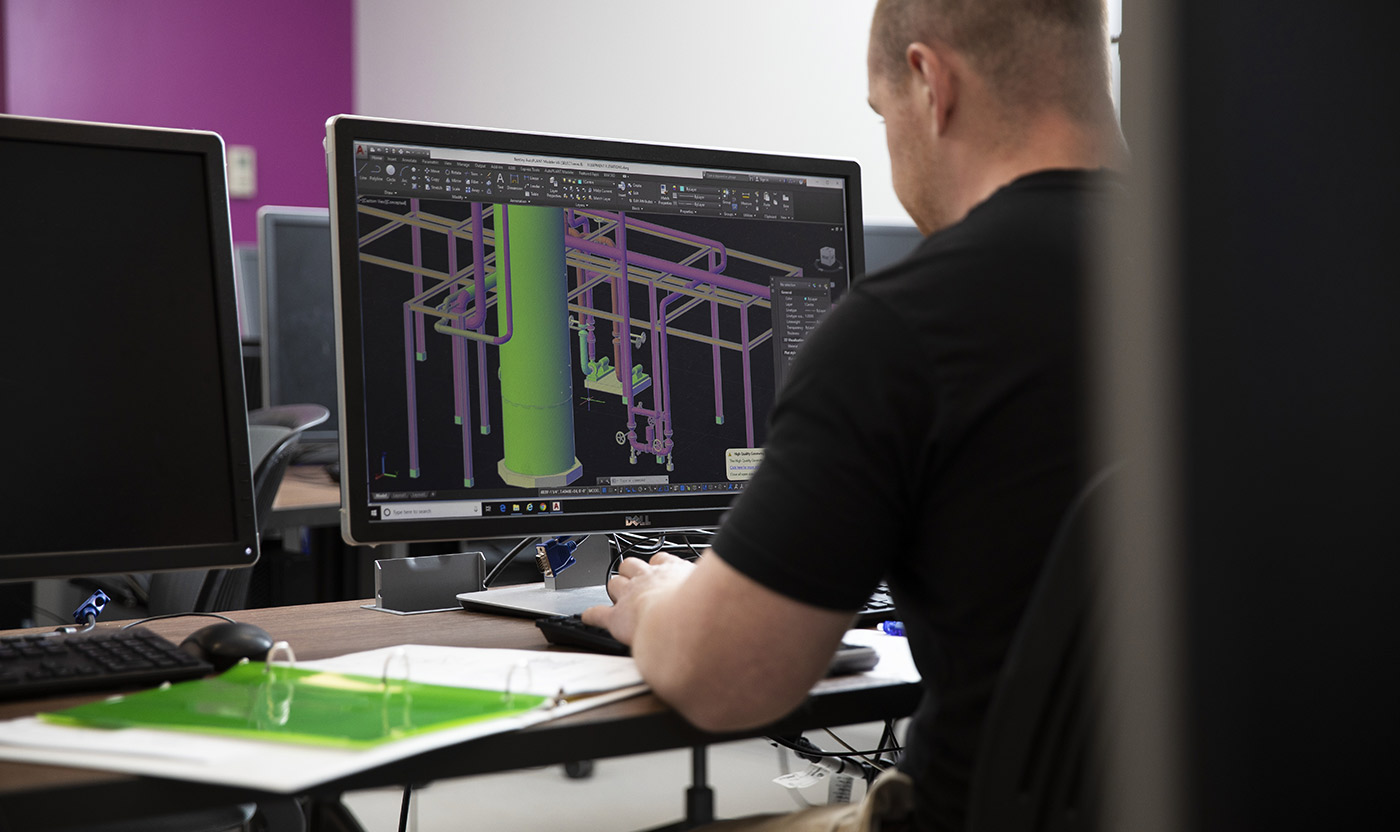
3D CAD software has revolutionized the design and engineering industries by enabling designers to create and manipulate three-dimensional models with precision and detail. Unlike 2D CAD software, which focuses on two-dimensional drawings, 3D CAD software provides a virtual environment where designers can bring their ideas to life in a three-dimensional space.
One of the primary advantages of 3D CAD software is its ability to create realistic and immersive representations of objects and structures. By working in a three-dimensional space, designers can visualize and manipulate their designs from all angles, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the final product.
With 3D CAD software, designers can model complex shapes and surfaces with greater accuracy and efficiency. The software offers a wide range of tools and techniques for creating organic and geometric forms, such as solids, surfaces, curves, and meshes. These tools enable designers to represent intricate details and configurations that may not be easily achievable in traditional manual methods.
Another significant advantage of 3D CAD software is its ability to simulate real-world conditions and perform virtual testing. Designers can apply materials, textures, and physical properties to their models, and then analyze how the design behaves under different conditions. This includes evaluating structural integrity, checking for interference, and simulating mechanical movements. By conducting virtual tests, designers can identify and address potential issues early in the design process, saving time and resources on iterations and physical prototypes.
3D CAD software also enhances collaboration among teams and stakeholders. With the ability to share 3D models electronically, designers can easily collaborate, review, and provide feedback in real-time. This streamlines communication and ensures that all parties involved in the design process are on the same page.
Furthermore, 3D CAD software allows for seamless integration with other computer-aided tools, such as computer-aided engineering (CAE) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). Designs created in 3D CAD software can be transferred seamlessly to these tools for further analysis, simulations, and production planning. This integration promotes a more efficient and interconnected design workflow.
Overall, 3D CAD software has revolutionized the way designers conceptualize and develop their ideas. It provides a powerful platform for designing, analyzing, and visualizing 3D models, leading to enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and innovation in various industries.
CAD software works by allowing users to create and modify 2D or 3D designs using a computer. It uses mathematical algorithms to generate precise shapes and dimensions, and can also simulate real-world conditions for testing.
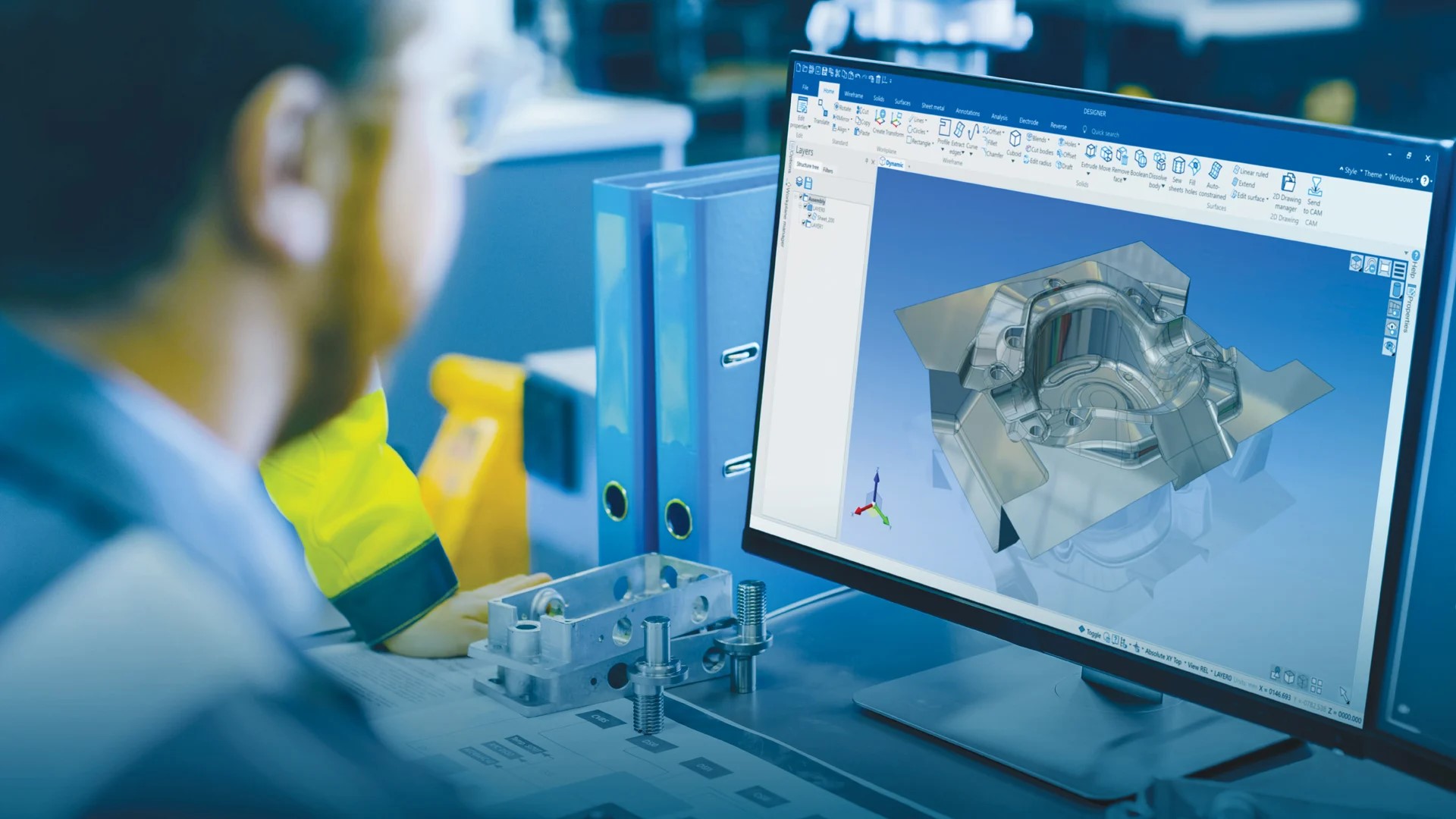
CAD Modeling Techniques
CAD modeling techniques are essential for creating detailed and accurate designs using CAD software. These techniques enable designers to effectively represent objects and structures in a digital environment. Let’s explore some of the commonly used CAD modeling techniques:
- Wireframe Modeling: Wireframe modeling is the simplest form of CAD modeling, representing the basic structure of an object using lines and curves. It provides a skeletal framework to define the size and shape of the design.
- Surface Modeling: Surface modeling focuses on creating the outer skin or surface of an object. It involves defining the contours, curves, and edges that form the visible part of the design, without considering the interior structure.
- Solid Modeling: Solid modeling is a technique used to represent objects as a coherent, three-dimensional shape. It creates a complete and watertight representation of the design, including both exterior and interior geometry. Solid models allow for accurate volume calculations, interference checking, and more.
- Parametric Modeling: Parametric modeling is a powerful CAD technique where changes made to one part of the design automatically update related elements. It involves defining parameters, such as dimensions or constraints, and establishing relationships between them. This allows for easy modifications and design iterations.
- Assembly Modeling: Assembly modeling involves the creation of complex designs consisting of multiple components or parts. Each component is individually modeled and then assembled together to create the final design. It allows designers to analyze fit and functionality, identify interferences, and simulate movements.
- Generative Design: Generative design is an emerging technique that uses algorithms and artificial intelligence to optimize designs based on specified parameters and constraints. It explores a wide range of design possibilities and generates optimized solutions, often using complex shapes and structures that may be unconventional.
- Parametric Curves and Surfaces: This technique allows designers to create complex shapes and surfaces using mathematical equations. Parametric curves and surfaces provide greater control over the design, allowing for precise manipulation and the ability to create intricate details.
- Simulations and Analyses: CAD software provides the capability to perform simulations and analyses on the design. This includes structural analysis, fluid flow analysis, heat transfer analysis, and more. These simulations help identify potential issues, validate the design’s performance, and optimize it for real-world conditions.
These CAD modeling techniques provide designers with a range of tools and approaches to create detailed and accurate models. By leveraging these techniques, designers can efficiently bring their ideas to life, iterate on designs, and optimize their creations for various requirements.
CAD Drawing Tools
CAD software provides a wide range of drawing tools that enable designers to create precise and detailed drawings. These tools enhance productivity, accuracy, and flexibility in the design process. Let’s explore some of the common CAD drawing tools:
- Lines and Polylines: Lines and polylines are the basic drawing tools in CAD software. They allow designers to create straight or curved lines, defining the shape and geometry of the design.
- Shapes: CAD software provides various shape tools, such as rectangles, circles, ellipses, and polygons. These tools allow designers to quickly create predefined shapes, which can be modified and scaled as needed.
- Freehand Drawing: Freehand drawing tools simulate drawing by hand, allowing designers to create organic and irregular shapes. These tools provide more artistic freedom and enable designers to add personal touches to their designs.
- Hatch and Fill: Hatch and fill tools are used to apply patterns or colors to enclosed areas of a drawing. They can be used to denote materials, differentiate regions, or add visual interest to the design.
- Text and Annotations: CAD software offers various text tools for adding annotations, labels, and dimensions to the drawing. These tools enable designers to convey important information and provide clarity to the design.
- Layers: Layers help organize and manage different elements within the drawing. They allow designers to separate and control the visibility of different parts of the design, making it easier to work on complex projects and manage different design components.
- Dimensioning Tools: Dimensioning tools play a crucial role in CAD drawings. They allow designers to define accurate measurements, angles, and distances between different elements, ensuring precision and clarity in the design.
- Spline and Curve Tools: Spline and curve tools are used to create smooth and flowing lines. They allow designers to create complex, free-form shapes or simulate natural curves and contours.
- Modify and Edit Tools: CAD software provides a range of modify and edit tools for making changes to the design. These tools allow designers to move, resize, rotate, mirror, and trim elements, making it easy to refine and adjust the design as needed.
- Measuring and Probing Tools: CAD software includes measuring and probing tools that allow designers to accurately analyze and verify dimensions, angles, and distances in the design. These tools help ensure that the design complies with the required specifications.
These CAD drawing tools are essential for creating precise, detailed, and visually appealing drawings. Designers can leverage these tools to bring their ideas to life, communicate design intent effectively, and produce accurate documentation for manufacturing and construction purposes.
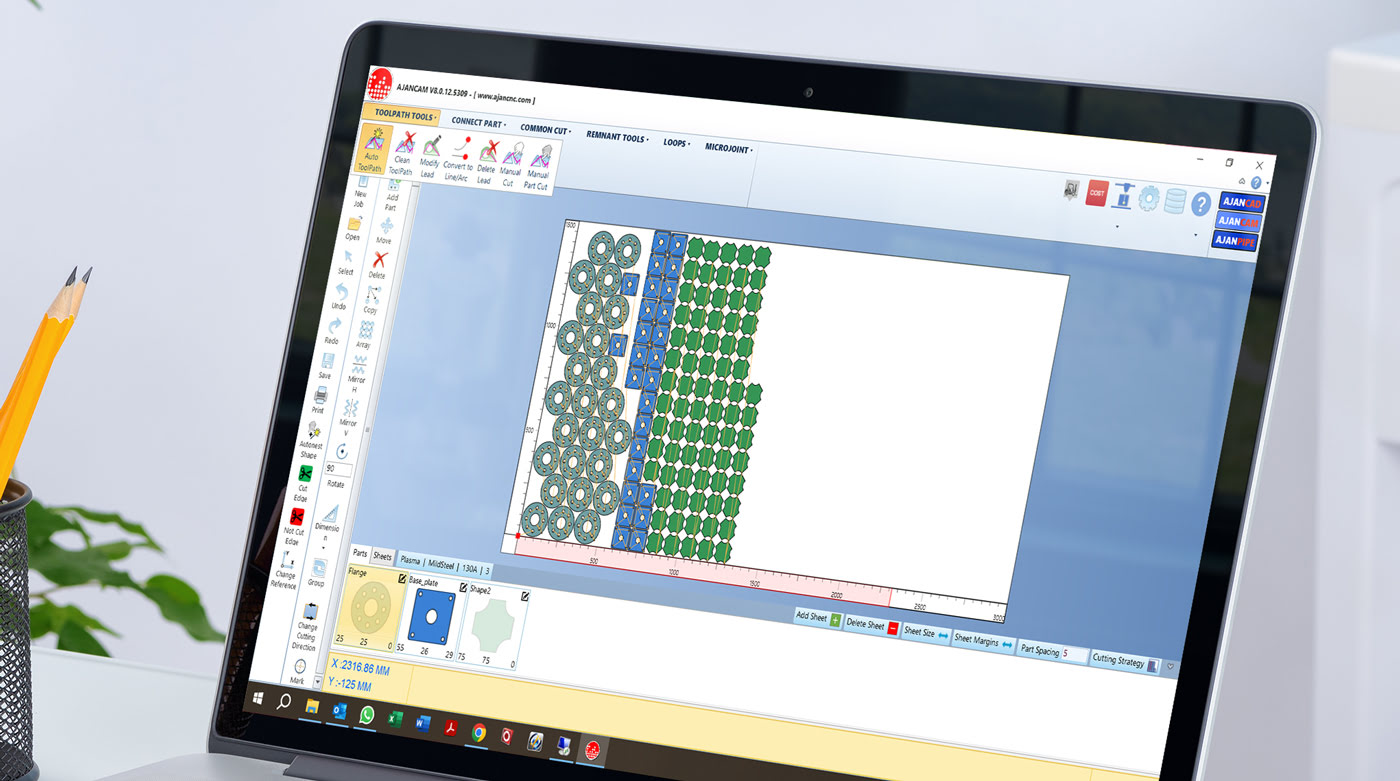
File Formats in CAD Software
CAD software supports various file formats that are used to store and exchange design data. These file formats enable compatibility between different CAD software and other design tools. Understanding the different file formats is essential for efficient collaboration and data exchange. Let’s explore some common file formats in CAD software:
- DWG (Drawing): DWG is one of the most widely used file formats in CAD software. It was originally developed by Autodesk for its AutoCAD software. DWG files contain 2D and 3D design data, including geometry, layers, dimensions, and annotations. Many CAD software applications, both proprietary and open-source, support the DWG format.
- DXF (Drawing Exchange Format): DXF is another file format developed by Autodesk. It is a universal format for exchanging CAD data between different software applications. DXF files contain 2D and 3D design data, similar to DWG files, but in a more simplified and ASCII-based format. DXF files are highly compatible and can be easily imported or exported by various CAD software.
- STL (Stereolithography): STL is a file format commonly used for 3D printing and rapid prototyping. It represents the surface geometry of a 3D model as a collection of triangles. STL files do not contain color or texture information, focusing solely on the geometry. Many CAD software applications support exporting to the STL format, allowing for seamless integration with 3D printing software.
- IGES (Initial Graphics Exchange Specification): IGES is a neutral file format used for exchanging 2D and 3D CAD data between different software applications. IGES files encapsulate geometry, topology, and attributes of the design. They provide a common language for interoperability between various CAD software, making it easier to collaborate across different platforms.
- STEP (Standard for the Exchange of Product Data): STEP is an ISO standard that facilitates the exchange of product data across different CAD software applications. STEP files contain detailed information about the design, including geometry, topology, assembly structures, and metadata. This format supports the complete transfer of design information and enables seamless collaboration between different software systems.
- PDF (Portable Document Format): Although not a CAD-specific file format, PDF is commonly used for sharing and distributing CAD drawings and documents. PDF files preserve the visual integrity and formatting of the design, making it easy to view and print drawings across different platforms and devices. Many CAD software applications support exporting to PDF format.
- OBJ (Wavefront Object): OBJ is a widely supported file format used for 3D model data exchange. It stores information about the geometry, surface normals, texture coordinates, and material properties of the design. OBJ files are often used in 3D rendering, animation, and game development applications.
These file formats play a crucial role in CAD software, enabling seamless data exchange between different platforms and software applications. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each format is essential for efficient collaboration, sharing, and archiving of CAD files.
Read more: What Is NX CAD Software
Limitations of CAD Software
CAD software has revolutionized the design process and greatly enhanced the capabilities of designers and engineers. However, like any tool, CAD software has certain limitations that designers should be aware of. Understanding these limitations is crucial for effectively using CAD software and mitigating potential challenges. Let’s explore some common limitations of CAD software:
- Learning Curve: CAD software can have a steep learning curve, especially for beginners. Mastering the various tools and features requires time and practice. Designers may need to invest in training and education to fully harness the potential of CAD software.
- Hardware Requirements: CAD software can be resource-intensive, requiring powerful computers or workstations to handle complex models and perform simulations. Designers may need to upgrade their hardware to ensure smooth performance and efficient workflow.
- Complexity of Models: While CAD software offers powerful tools for creating complex models, extremely intricate designs may pose challenges. Processing and rendering large and detailed models can strain computer resources and cause performance issues.
- Limitations in Accuracy: CAD software relies on the precision of the input provided by designers. Small errors or inaccuracies in measurements or design intent can lead to issues in the final output. It is important for designers to double-check and validate their work to ensure accuracy.
- Design Constraints: CAD software is constrained by the limitations of the physical materials and manufacturing processes. Certain design features may not be achievable in practice due to manufacturing limitations, cost constraints, or material properties. Designers need to consider these limitations during the design process.
- Interoperability and Compatibility: Although efforts have been made to establish standard file formats, interoperability between different CAD software can still be a challenge. Incompatibilities in file formats, versions, and software features may cause issues when exchanging data between different systems.
- Creativity and Aesthetics: While CAD software offers powerful tools for precise modeling, it may not fully capture the nuances of artistic or aesthetic design. The human touch and creativity may be limited by the constraints of the software’s tools and algorithms.
- Dependency on Software Providers: CAD software typically requires licenses and ongoing support from software providers. Designers rely on these providers for updates, bug fixes, and customer support. Changes in licensing models, discontinued software, or lack of support can impact the availability and accessibility of CAD software.
Despite these limitations, it’s important to note that CAD software has revolutionized the design process and greatly expanded the possibilities for designers and engineers. By understanding and working around these limitations, designers can leverage the benefits of CAD software while finding creative solutions to address any constraints that may arise.
Applications of CAD Software
CAD software finds applications in a wide range of industries and professions. It has revolutionized the design and engineering process, enhancing productivity, accuracy, and innovation. Let’s explore some common applications of CAD software:
- Architecture and Construction: CAD software is extensively used in architecture and construction industries. Architects use CAD software to create detailed 2D and 3D models of buildings, enabling them to visualize and refine designs, produce construction documents, and generate accurate measurements. Construction professionals benefit from CAD software by facilitating project coordination and improving communication between teams.
- Product Design and Manufacturing: CAD software plays a crucial role in product design and manufacturing processes. Designers use CAD software to create detailed 3D models of products, test for functionality and ergonomics, and generate manufacturing specifications. The software enables seamless collaboration between design and manufacturing teams, resulting in faster prototyping and reduced time to market.
- Automotive and Aerospace Engineering: CAD software is widely used in automotive and aerospace industries to design and develop vehicles and aircraft. From creating complex engine components to designing aerodynamic surfaces, CAD software allows engineers to optimize performance, conduct structural analysis, and simulate fluid flow. This improves safety, efficiency, and overall design quality.
- Mechanical Engineering: CAD software is a fundamental tool for mechanical engineers. It aids in designing and analyzing machinery, equipment, and mechanical systems. It enables engineers to simulate and optimize mechanisms, perform stress analysis, and test for dynamic behavior, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable designs.
- Electronics and Electrical Engineering: CAD software is valuable for electronics and electrical engineering applications. It facilitates the design and layout of complex circuit boards, the routing of electrical wiring, and the integration of electronic components. CAD software allows engineers to analyze circuits, verify signal integrity, and optimize energy efficiency.
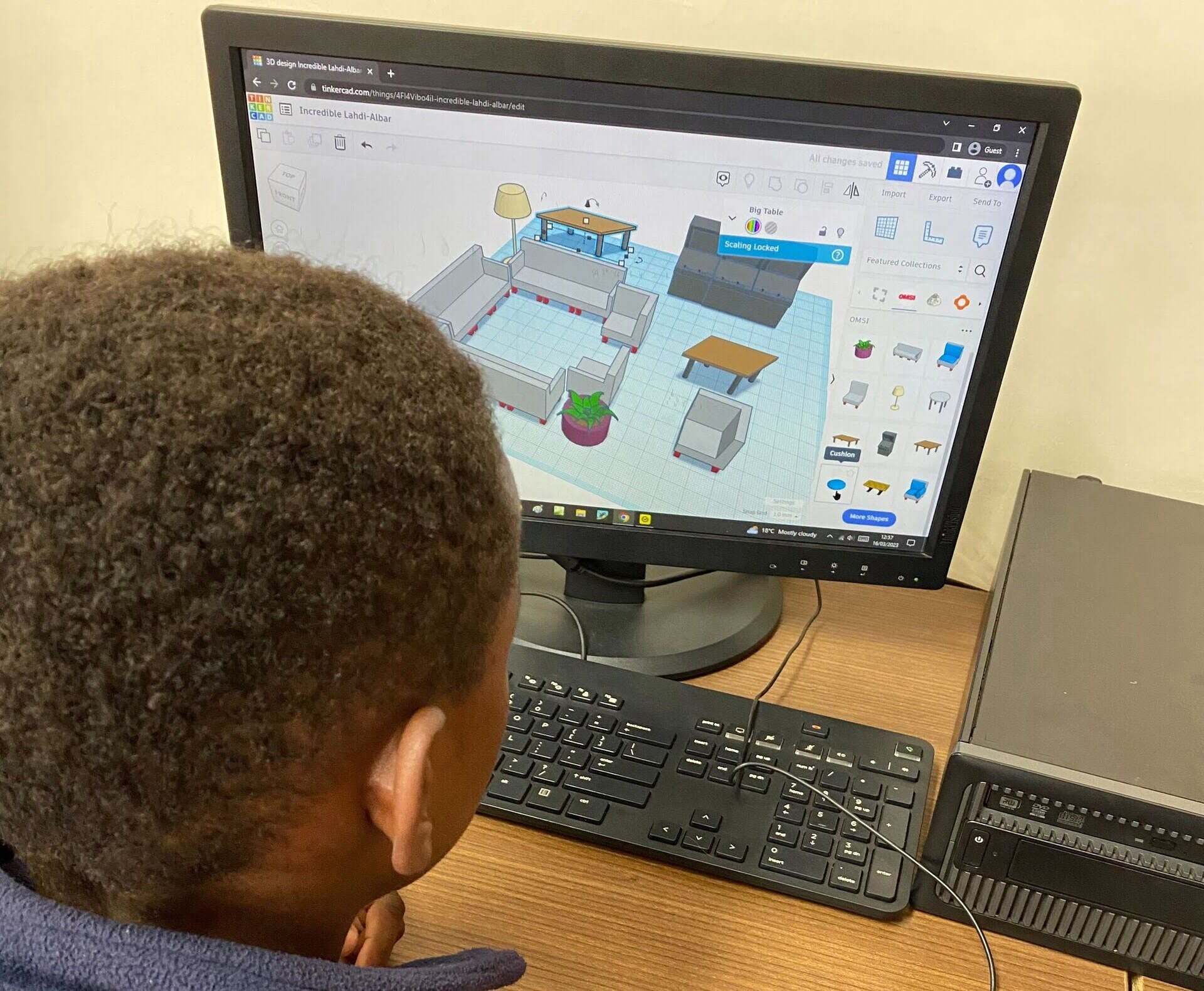
- Interior Design and Furniture: CAD software is widely used in interior design for creating detailed room layouts, furniture designs, and 3D visualizations. Designers can experiment with different color schemes, furniture arrangements, and materials, leading to more accurate representations of the final space.
- Urban Planning and Landscape Architecture: CAD software aids in urban planning and landscape architecture by allowing designers to create detailed site plans, master plans, and 3D visualizations. It helps in analyzing land use, optimizing traffic flow, and creating sustainable and aesthetically pleasing environments.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering: CAD software plays a key role in industrial and manufacturing engineering. It enables the design of production layouts, assembly lines, and manufacturing processes. CAD software helps optimize material flow, improve efficiency, and minimize errors in the manufacturing and production environment.
- Medical and Healthcare: CAD software is utilized in medical and healthcare industries for various purposes, such as designing medical devices, prosthetics, and implants. It aids in creating 3D models from medical imaging data, allowing for personalized and precise treatments.
- Education and Research: CAD software is widely used in educational institutions and research labs for teaching, training, and conducting studies. It helps students and researchers explore design concepts, simulate experiments, and gain practical skills in various disciplines.
These are just a few examples of the vast applications of CAD software. Its versatility and powerful capabilities make it an indispensible tool for design professionals across industries. The continuous advancements in CAD technology will continue to expand its application landscape, enabling even more innovative and efficient design solutions.
Conclusion
CAD software has transformed the world of design and engineering, revolutionizing the way we create, visualize, and communicate ideas. Its advanced tools and features have made design processes faster, more accurate, and more efficient than ever before. From architecture to product design, CAD software has found applications in various industries, enabling professionals to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Throughout this article, we have explored the fundamental principles, benefits, limitations, and applications of CAD software. We have delved into the world of 2D and 3D CAD software, uncovering the power and versatility they offer to designers and engineers. We have also discussed the importance of CAD modeling techniques, drawing tools, and file formats in facilitating effective design processes and collaboration.
The benefits of CAD software are vast and varied. It has increased productivity, improved accuracy, enhanced visualization, and enabled better collaboration among team members. CAD software has also helped save time and costs by eliminating the need for physical prototypes and allowing for virtual simulations. Its use of parametric modeling and automation has revolutionized design iteration and optimization.
However, CAD software does have its limitations. Learning curves, hardware requirements, design constraints, and interoperability issues are among the challenges designers may face. It’s crucial for designers to understand these limitations and work around them to reap the full benefits of CAD software while finding creative solutions to any constraints that may arise.
The applications of CAD software are vast and diverse, spanning industries such as architecture, product design, automotive engineering, and many more. CAD software has become an indispensable tool for professionals in their quest to create efficient, visually appealing, and functional designs.
In conclusion, CAD software has played a pivotal role in transforming the way we design and create in the digital age. It has empowered designers, architects, engineers, and other professionals to bring their ideas to life, enhance collaboration, and push the boundaries of innovation. As technology continues to advance, CAD software will continue to evolve, enabling even greater possibilities in the world of design.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does CAD Software Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “How Does CAD Software Work”